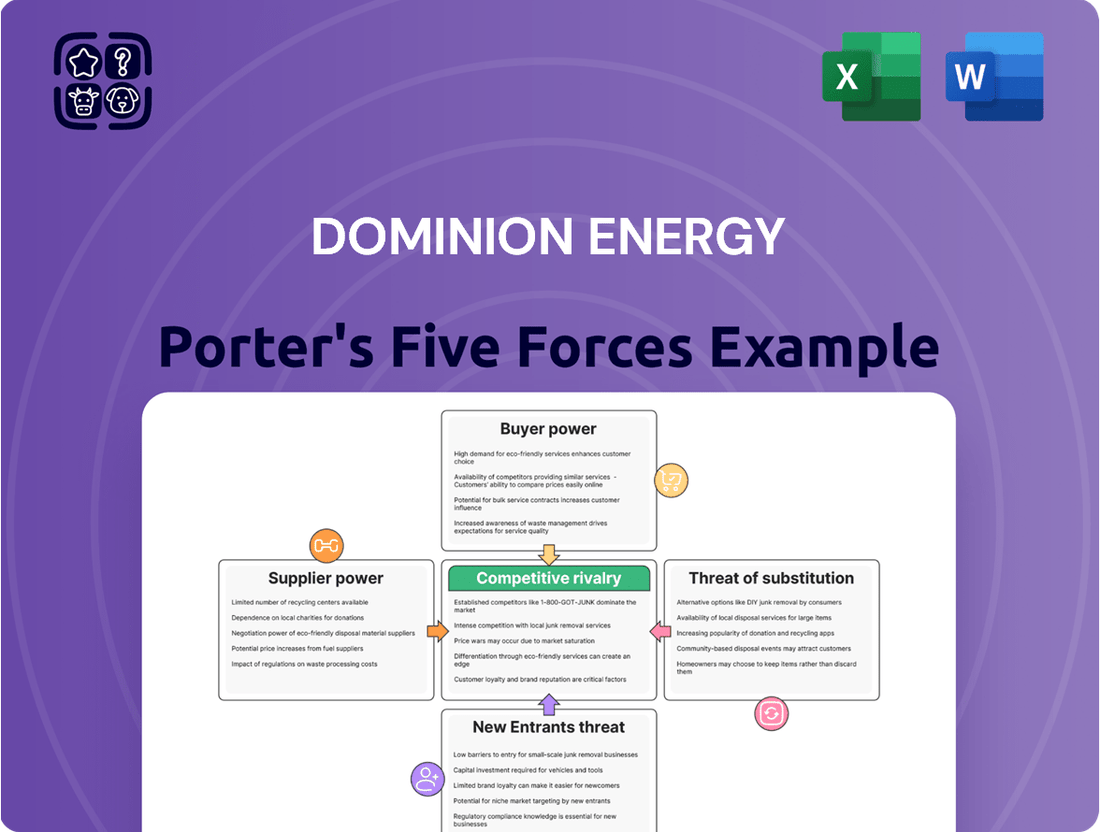
Dominion Energy Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Dominion Energy Bundle
Dominion Energy operates within a complex utility landscape, where the threat of new entrants is generally low due to high capital requirements and regulatory hurdles. However, the bargaining power of buyers, primarily residential and commercial customers, can be significant, influencing pricing and service demands.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Dominion Energy’s industry—from supplier influence to the threat of substitutes like renewable energy sources. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Dominion Energy faces a significant bargaining power from its suppliers due to a limited number of key providers for critical components. This includes specialized items like nuclear fuel, advanced power generation machinery, and intricate grid technology.
The scarcity of viable alternatives and the high costs associated with switching suppliers mean these entities hold considerable influence. For instance, Dominion's substantial capital investment plans, projected to be in the tens of billions of dollars for 2025-2029, underscore its dependence on these specialized suppliers for crucial infrastructure upgrades and new energy projects.
Dominion Energy faces significant supplier power when critical inputs have high switching costs. For example, specialized equipment for its nuclear or offshore wind facilities, or long-term contracts for specific fuel sources like natural gas, lock the company into existing supplier relationships. In 2024, the energy sector continued to see robust demand for specialized components, particularly for renewable energy projects, which can extend lead times and increase the leverage of suppliers providing these essential items.
Suppliers of critical equipment and services to regulated utilities like Dominion Energy must navigate a complex web of industry standards and rigorous regulatory approvals. This necessity acts as a significant barrier for potential new entrants, effectively shrinking the pool of qualified and approved vendors. Consequently, established suppliers who meet these exacting requirements often find themselves with increased leverage.
Dominion Energy's unwavering commitment to safety and adherence to all relevant laws and regulations directly impacts its supplier relationships. This emphasis on compliance is clearly articulated in its Supplier Code of Ethics & Business Conduct, ensuring that partners align with the company's operational and ethical imperatives. For instance, in 2023, Dominion Energy reported capital expenditures of approximately $14.5 billion, a significant portion of which is allocated to infrastructure projects requiring specialized, compliant equipment and services, underscoring the importance of reliable, approved suppliers.
Commodity Price Volatility
Commodity price volatility, particularly for natural gas, significantly influences Dominion Energy's operational costs. The global market for primary energy sources like natural gas can experience sharp price swings. This inherent volatility grants natural gas suppliers considerable bargaining power, as they can leverage market conditions to negotiate higher prices, directly impacting utilities like Dominion.
Dominion Energy, while diversified across natural gas, nuclear, and renewable energy sources, remains susceptible to these fluctuations. For instance, in early 2024, natural gas prices saw notable upward movement, reflecting supply and demand dynamics. This trend directly translates to increased input costs for Dominion's gas-fired power generation facilities, underscoring the suppliers' leverage.
- Natural Gas Price Impact: Fluctuations in natural gas prices directly affect Dominion Energy's cost of generating electricity from this source.
- Supplier Leverage: Volatile commodity markets empower natural gas suppliers to negotiate for higher prices, increasing their bargaining power.
- Operational Cost Sensitivity: Despite a diversified energy portfolio, Dominion Energy's reliance on natural gas makes it sensitive to price volatility, impacting overall operational expenses.
Importance of Supplier Relationships and Diversity Initiatives
Dominion Energy places significant value on fostering enduring, ethical connections with its suppliers. This approach is crucial because suppliers are fundamental to maintaining the company's reliable service delivery. For instance, in 2023, Dominion Energy spent approximately $7.8 billion with its diverse supplier base, highlighting the scale of these relationships.
The company actively champions supplier diversity initiatives, aiming to broaden its network of partners. Events like the Convergence 2025 supplier expo underscore Dominion Energy's commitment to engaging with and potentially growing its supplier pool. These efforts are vital for mitigating risks associated with supplier dependency and ensuring a robust supply chain.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Dominion Energy is influenced by the availability of alternative suppliers and the uniqueness of the goods or services provided. For critical components like specialized power generation equipment or essential raw materials, suppliers with limited competition can exert considerable influence. Dominion's focus on long-term relationships and diversity aims to balance this power dynamic.
- Supplier Diversity Spending: Dominion Energy reported spending approximately $7.8 billion with diverse suppliers in 2023.
- Strategic Supplier Engagement: Initiatives like Convergence 2025 demonstrate proactive supplier relationship management.
- Impact on Reliability: Strong supplier relationships are directly linked to Dominion's ability to provide consistent energy services.
- Mitigating Supplier Power: A diverse supplier base helps reduce reliance on any single supplier, thereby lowering supplier bargaining power.
Dominion Energy faces substantial bargaining power from suppliers due to the specialized nature of critical infrastructure components and fuel sources. The high cost and complexity of switching suppliers, coupled with regulatory hurdles for new vendors, consolidate power with existing providers. For instance, in 2023, Dominion's capital expenditures of approximately $14.5 billion highlight its reliance on these specialized suppliers for essential projects.
| Factor | Impact on Dominion Energy | Supporting Data (2023/2024 Estimates) |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Components | High dependence on few suppliers for critical equipment (e.g., nuclear fuel, advanced grid tech). | Dominion's significant capital investment plans necessitate reliance on these providers. |
| Switching Costs | High costs and complexity limit flexibility to change suppliers. | Long-term contracts for fuel sources and specialized machinery create lock-in effects. |
| Regulatory Barriers | Stringent industry standards and approvals restrict the supplier pool. | Established suppliers meeting these requirements gain leverage due to limited competition. |
| Commodity Price Volatility | Natural gas price swings directly impact operational costs and supplier negotiation power. | Early 2024 saw upward movement in natural gas prices, increasing input costs for gas-fired generation. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Dominion Energy, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the energy sector.
Instantly grasp competitive pressures with a visual breakdown of each force, streamlining strategic planning for Dominion Energy.
Customers Bargaining Power
Dominion Energy's position as a regulated monopoly in its core service areas, particularly in Virginia, North Carolina, and South Carolina, drastically curtails customer bargaining power. Residential and commercial clients have limited alternatives for electricity and natural gas distribution, meaning they cannot easily switch providers to negotiate better rates or service terms. In Virginia, for instance, the State Corporation Commission (SCC) directly oversees and approves Dominion's rates, effectively setting the terms for consumers.
For most residential and business customers, switching electricity or natural gas providers isn't a realistic choice. The existing infrastructure and regulations make it very difficult to change suppliers, leaving customers with little choice but to rely on Dominion Energy. This dependence significantly reduces their ability to negotiate better terms.
Dominion Energy is seeing a surge in customer growth, especially from data centers in Northern Virginia. These facilities represent a significant portion of the company's electricity usage, and their increasing demand could translate into greater leverage for negotiating favorable terms.
The sheer scale of data center power capacity under contract nearly doubled from 21 GW in July 2024 to a substantial 40 GW by December 2024. This rapid expansion highlights the concentrated demand from a few large industrial customers, potentially strengthening their collective bargaining power for customized services and specific rate structures.
Public and Regulatory Oversight of Rates
While individual customers of Dominion Energy possess minimal bargaining power, their collective voice is amplified significantly through public sentiment and regulatory oversight. State commissions, such as the State Corporation Commission (SCC) in Virginia, act as crucial intermediaries, reviewing and approving rate adjustments proposed by the utility. This regulatory scrutiny ensures that customer interests are considered, influencing the final approved rates and service standards.
Dominion Energy's proposed rate increases are therefore not unilaterally determined but are subject to a rigorous review process. For instance, the company has put forth proposals for rate adjustments in Virginia for the years 2026 and 2027. These proposals must navigate the regulatory landscape, where the SCC evaluates their impact on consumers before granting approval.
- Public and Regulatory Oversight: State commissions, like Virginia's SCC, act as a collective voice for customers, influencing rate approvals.
- Rate Review Process: Dominion Energy's proposed rate increases are subject to scrutiny and approval by these regulatory bodies.
- Example of Regulatory Impact: Proposed rate increases for 2026 and 2027 in Virginia illustrate the ongoing regulatory engagement.
Energy Efficiency and Demand-Side Management Programs
The availability of energy efficiency programs and demand-side management initiatives, often mandated by regulators, grants customers indirect bargaining power. By reducing their energy consumption, customers can lessen the impact of potential rate hikes and influence overall demand, affecting the utility's future resource planning. For instance, Virginia's Clean Economy Act (VCEA) established specific energy savings targets for utilities like Dominion Energy, encouraging customer participation in these programs.
These programs empower customers by offering them choices and tools to manage their energy usage and costs. This can include rebates for efficient appliances, smart meter technology, and personalized energy-saving advice. Such initiatives can shift some of the negotiation power towards the consumer, as utilities aim to meet regulatory mandates and manage peak demand.
Dominion Energy, for example, offers various programs designed to help customers save energy and money. These initiatives not only benefit the customer but also contribute to the utility's broader goals of grid stability and environmental sustainability. The success of these programs directly correlates with customer engagement, highlighting the symbiotic relationship and the customer's role in influencing utility operations.
The bargaining power of customers is further amplified when these demand-side management efforts are successful in reducing overall energy consumption. This can lead to lower revenue for the utility from energy sales, potentially prompting a re-evaluation of pricing strategies or investment in alternative revenue streams. The VCEA's energy savings targets underscore the regulatory push to incentivize such customer-driven demand reduction.
While individual customers have limited direct bargaining power due to Dominion Energy's regulated monopoly status, their collective influence is channeled through regulatory bodies like Virginia's State Corporation Commission (SCC). These commissions review and approve rate changes, acting as a crucial check on Dominion's pricing power, as seen with proposed 2026-2027 rate adjustments.
The significant growth of data centers, with power capacity under contract nearly doubling from 21 GW in July 2024 to 40 GW by December 2024, introduces a new dynamic. This concentrated demand from large industrial users could translate into increased leverage for negotiating more favorable terms and customized services.
Energy efficiency programs and demand-side management initiatives, often mandated by regulations like Virginia's Clean Economy Act, also grant customers indirect bargaining power. By reducing consumption, customers can mitigate the impact of rate hikes and influence the utility's future planning.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Factor | Impact on Dominion Energy |
|---|---|---|
| Residential/Small Commercial | Low (Limited alternatives, regulated rates) | Minimal direct negotiation power |
| Large Industrial (e.g., Data Centers) | Increasing (Concentrated demand, high usage) | Potential for negotiated terms, customized services |
| General Customer Base | Moderate (Through regulatory oversight, public sentiment) | Influences rate approvals and service standards |
Preview Before You Purchase
Dominion Energy Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Dominion Energy Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing competitive rivalry, the threat of new entrants, buyer power, supplier power, and the threat of substitutes. The document you see here is exactly what you’ll be able to download after payment, providing actionable insights into the energy sector's competitive landscape.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Dominion Energy operates in a market where direct rivalry for its core electricity and natural gas supply services is significantly curtailed due to its regulated utility structure. This means that within its primary service territories, Dominion Energy often functions as a sole provider, limiting direct competition from other large utility companies seeking to acquire the same customers.
While direct competition for basic energy supply is limited, rivalry can emerge in related areas such as renewable energy development and energy efficiency services. For instance, in 2024, the push for distributed generation and customer-sited solar installations creates a different kind of competitive pressure, as customers have more options for sourcing power beyond the traditional utility model.
While Dominion Energy's residential and small business segments operate under regulatory frameworks, the landscape for large industrial customers, particularly data centers, presents a more competitive dynamic. These energy-intensive clients, crucial for load growth, possess considerable negotiation power, potentially exploring alternative power sources or providers. This can lead to indirect rivalry among utilities and infrastructure developers vying to secure these high-demand accounts.
State-level policy and regulatory changes significantly influence competitive rivalry, even if not directly between energy providers. For Dominion Energy, shifts in state energy policies, like renewable energy mandates or market restructuring, can alter the playing field. These changes can create new opportunities or impose challenges that affect its competitive position against rivals and independent power producers.
The Virginia Clean Economy Act (VCEA) serves as a prime example of how state legislation impacts the competitive landscape. Enacted in 2020, this act mandates significant increases in renewable energy generation for Virginia, directly affecting Dominion Energy's operational strategies and investment priorities. By 2024, Dominion Energy was already reporting substantial progress towards its VCEA goals, including significant solar and offshore wind development, which reshapes its competitive advantage and operational costs.
Indirect Competition from Energy Service Companies (ESCOs)
Energy Service Companies (ESCOs) present an indirect competitive threat to Dominion Energy by offering energy management, distributed generation, and efficiency services. These services can reduce customer demand for traditional grid power. For instance, many businesses are increasingly turning to ESCOs for comprehensive energy audits and retrofits, aiming to lower their overall energy consumption and costs. This shift means customers might rely less on Dominion's core electricity supply business.
This indirect competition is growing as technology advances and customer awareness of energy-saving opportunities increases. In 2024, the U.S. energy efficiency market alone was valued in the tens of billions of dollars, with ESCOs playing a significant role. Their focus on optimizing energy use, rather than simply supplying it, allows them to capture market share by offering value beyond basic utility services.
- ESCOs offer energy efficiency solutions that reduce demand for grid power.
- This indirect competition focuses on optimizing energy use, not direct supply.
- The U.S. energy efficiency market was valued in the tens of billions in 2024.
Shift Towards Decentralized and Renewable Generation
The energy landscape is shifting, with a growing trend towards decentralized and renewable energy generation. This includes the rise of rooftop solar and community solar projects, which exert a long-term, indirect competitive pressure on traditional utilities like Dominion Energy.
While these distributed resources aren't directly competing for the entire grid infrastructure, they can significantly reduce the demand for power traditionally supplied by utility companies. For instance, in 2023, solar power accounted for approximately 5.1% of total U.S. electricity generation, a figure projected to climb steadily.
- Growing Solar Adoption: In 2024, the U.S. solar market continued its expansion, with residential solar installations showing robust growth, driven by falling costs and increased consumer interest in energy independence.
- Community Solar Impact: Community solar programs are gaining traction, allowing more customers to benefit from solar energy without needing to install panels on their own properties, thereby impacting utility customer load.
- Grid Interconnection Challenges: The increasing integration of these distributed energy resources presents challenges for grid management and can affect the revenue streams of traditional utility providers.
- Policy and Incentives: Government policies and incentives, such as tax credits and renewable portfolio standards, continue to fuel the growth of decentralized renewables, intensifying this competitive pressure.
While Dominion Energy's core utility services face limited direct competition due to regulation, rivalry intensifies in emerging energy sectors and with large industrial clients. The growth of distributed generation, like rooftop solar, and the services offered by Energy Service Companies (ESCOs) represent significant indirect competitive pressures. These trends are amplified by state-level policies promoting renewables, such as Virginia's Clean Economy Act, which reshapes the operational landscape and investment priorities for utilities.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The increasing adoption of distributed renewable energy generation, particularly rooftop solar, poses a significant threat of substitution for traditional utility providers like Dominion Energy. As installation costs for solar panels continue to fall, customers are increasingly empowered to generate their own electricity, thereby reducing their dependence on the grid.
In 2023, the U.S. saw a record installation of 6.1 gigawatts of solar capacity, a 37% increase from 2022, according to the Solar Energy Industries Association. This trend directly impacts utilities by potentially decreasing electricity sales and revenue. Virginia's commitment to distributed renewables, underscored by the Virginia Clean Economy Act, further accelerates this shift, encouraging more customers to invest in self-generation solutions.
Improvements in energy efficiency technologies and growing customer awareness about conservation directly reduce the demand for energy. This makes alternative energy-saving solutions a significant substitute for Dominion Energy's core offerings. For example, advancements in smart home technology and building insulation can drastically cut electricity usage.
Dominion Energy is actively engaged in demand-side management programs and setting energy efficiency targets to counter this threat. These initiatives often involve incentives for customers to adopt energy-saving measures, effectively reducing their reliance on traditional energy sources. In 2023, Dominion Energy reported significant participation in its energy efficiency programs, helping customers save millions of dollars on their utility bills.
The threat of substitutes for natural gas in heating and cooling is growing, particularly from electric heat pumps. As of 2024, the increasing adoption of electric vehicles and the expansion of renewable energy sources are making electricity a more attractive and environmentally friendly alternative. This trend is supported by government incentives and technological advancements that improve heat pump efficiency and affordability.
Battery Storage Solutions
Advancements in battery storage, both for large-scale grids and individual homes, present a significant threat of substitution for traditional power sources. These systems can store surplus renewable energy, making wind and solar more dependable and lessening the need for constant baseload power from fossil fuels. For instance, by 2024, grid-scale battery storage capacity in the United States is projected to exceed 40 gigawatts, a substantial increase that directly competes with conventional power plants.
This technological leap allows for better management of intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind. By storing excess energy generated during sunny or windy periods, batteries ensure a consistent supply even when the sun isn't shining or the wind isn't blowing. This capability reduces reliance on traditional power plants that are often needed to fill gaps, thereby offering a viable alternative.
Regulatory bodies are actively exploring and encouraging the integration of battery technology. This is particularly evident in plans to use batteries to provide backup power for wind and solar farms. For example, a recent initiative in California aims to deploy thousands of battery storage systems to support grid stability, demonstrating a clear trend towards substituting traditional grid support mechanisms.
- Grid-scale battery storage capacity in the US is expected to surpass 40 GW by 2024.
- Battery storage enhances the reliability of intermittent renewables like solar and wind.
- Regulatory support is growing for battery integration as a grid backup solution.
- This technology offers a direct substitute for traditional baseload power generation.
Self-Generation by Large Industrial Consumers
Large industrial consumers, especially those with substantial energy needs like data centers, represent a significant threat of substitution for Dominion Energy. These entities can explore on-site generation, such as solar or combined heat and power (CHP) systems, or directly contract with independent power producers, thereby reducing their reliance on Dominion's grid services.
In 2024, the push for energy independence and cost control among large industrial users is intensifying. For instance, major tech companies are increasingly investing in renewable energy sources to power their operations, with some aiming for 100% renewable energy by 2030. This trend directly challenges traditional utility models.
- Data centers, a key industrial segment for utilities, are increasingly exploring microgrids and on-site generation to ensure reliability and manage costs.
- The declining cost of renewable energy technologies, such as solar PV and battery storage, makes self-generation a more economically viable option for large consumers.
- Regulatory environments can influence this threat; regulators may scrutinize arrangements where large users bypass traditional utility infrastructure, potentially ensuring they contribute to the full cost of service.
The increasing adoption of distributed renewable energy generation, particularly rooftop solar, poses a significant threat of substitution for traditional utility providers like Dominion Energy. As installation costs for solar panels continue to fall, customers are increasingly empowered to generate their own electricity, thereby reducing their dependence on the grid.
In 2023, the U.S. saw a record installation of 6.1 gigawatts of solar capacity, a 37% increase from 2022, according to the Solar Energy Industries Association. This trend directly impacts utilities by potentially decreasing electricity sales and revenue. Virginia's commitment to distributed renewables, underscored by the Virginia Clean Economy Act, further accelerates this shift, encouraging more customers to invest in self-generation solutions.
Improvements in energy efficiency technologies and growing customer awareness about conservation directly reduce the demand for energy. This makes alternative energy-saving solutions a significant substitute for Dominion Energy's core offerings. For example, advancements in smart home technology and building insulation can drastically cut electricity usage.
Dominion Energy is actively engaged in demand-side management programs and setting energy efficiency targets to counter this threat. These initiatives often involve incentives for customers to adopt energy-saving measures, effectively reducing their reliance on traditional energy sources. In 2023, Dominion Energy reported significant participation in its energy efficiency programs, helping customers save millions of dollars on their utility bills.
The threat of substitutes for natural gas in heating and cooling is growing, particularly from electric heat pumps. As of 2024, the increasing adoption of electric vehicles and the expansion of renewable energy sources are making electricity a more attractive and environmentally friendly alternative. This trend is supported by government incentives and technological advancements that improve heat pump efficiency and affordability.
Advancements in battery storage, both for large-scale grids and individual homes, present a significant threat of substitution for traditional power sources. These systems can store surplus renewable energy, making wind and solar more dependable and lessening the need for constant baseload power from fossil fuels. For instance, by 2024, grid-scale battery storage capacity in the United States is projected to exceed 40 gigawatts, a substantial increase that directly competes with conventional power plants.
This technological leap allows for better management of intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind. By storing excess energy generated during sunny or windy periods, batteries ensure a consistent supply even when the sun isn't shining or the wind isn't blowing. This capability reduces reliance on traditional power plants that are often needed to fill gaps, thereby offering a viable alternative.
Regulatory bodies are actively exploring and encouraging the integration of battery technology. This is particularly evident in plans to use batteries to provide backup power for wind and solar farms. For example, a recent initiative in California aims to deploy thousands of battery storage systems to support grid stability, demonstrating a clear trend towards substituting traditional grid support mechanisms.
Large industrial consumers, especially those with substantial energy needs like data centers, represent a significant threat of substitution for Dominion Energy. These entities can explore on-site generation, such as solar or combined heat and power (CHP) systems, or directly contract with independent power producers, thereby reducing their reliance on Dominion's grid services.
In 2024, the push for energy independence and cost control among large industrial users is intensifying. For instance, major tech companies are increasingly investing in renewable energy sources to power their operations, with some aiming for 100% renewable energy by 2030. This trend directly challenges traditional utility models.
| Substitute Technology | Key Trend/Driver | Impact on Dominion Energy | 2024 Data/Projection | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rooftop Solar | Falling installation costs, government incentives | Reduced electricity sales, potential grid disengagement | U.S. solar capacity grew 37% in 2023 | Virginia Clean Economy Act |
| Energy Efficiency | Smart home tech, customer awareness | Lower overall energy demand | Dominion's programs helped customers save millions in 2023 | Advanced insulation, smart thermostats |
| Electric Heat Pumps | EV adoption, renewable energy expansion | Shift from natural gas to electricity for heating/cooling | Increasing adoption driven by incentives | Technological advancements improving efficiency |
| Battery Storage | Renewable energy integration, grid stability needs | Alternative to baseload power, grid services competition | U.S. grid-scale storage capacity to exceed 40 GW by 2024 | California's battery deployment initiatives |
| On-site Generation (Industrial) | Energy independence, cost control | Bypass utility services, reduced demand | Tech companies aiming for 100% renewables by 2030 | Data centers investing in microgrids |
Entrants Threaten
The energy utility sector, particularly in power generation, transmission, and distribution, demands colossal capital outlays for essential infrastructure like power plants, transmission lines, and pipelines. These substantial upfront costs act as a formidable barrier, presenting a significant challenge for any new entity seeking to enter the market and compete effectively with established companies like Dominion Energy.
Dominion Energy itself anticipates investing approximately $50 billion in capital expenditures between 2025 and 2029, underscoring the immense financial commitment required to maintain and expand operations within this industry. This high level of investment inherently limits the threat of new entrants by making it prohibitively expensive for newcomers to establish a comparable operational footprint.
The utility sector faces significant hurdles for new entrants due to its extensive regulatory framework. Companies like Dominion Energy must navigate complex state and federal regulations, including obtaining numerous licenses and permits. For instance, State Corporation Commissions have direct oversight over utility rates and operational practices, creating a substantial barrier for newcomers unfamiliar with these intricate processes.
Dominion Energy benefits from substantial economies of scale, enabling efficient operations and cost distribution across its vast customer base. For instance, in 2024, Dominion's extensive infrastructure, including power generation facilities and transmission lines, allows for lower per-unit operating costs compared to smaller, emerging competitors. New entrants would find it incredibly difficult to match these cost efficiencies without a similarly massive scale of operations and customer volume, making it a significant barrier.
Access to Transmission and Distribution Networks
New entrants into the utility sector face a formidable barrier in the form of established transmission and distribution networks. Dominion Energy, for instance, operates a vast infrastructure of power lines and gas pipelines, a critical asset for service delivery. Building comparable infrastructure would require massive capital investment and extensive regulatory approvals, making it prohibitively expensive for most potential competitors.
Consider the scale: as of year-end 2023, Dominion Energy managed over 6.7 million customer accounts across its service territories. The sheer density and reach of these existing networks represent a significant hurdle for any new company aiming to compete. This entrenched infrastructure provides Dominion Energy with a substantial competitive advantage, effectively limiting the threat of new entrants.
- High Capital Requirements: Building new transmission and distribution infrastructure demands billions of dollars in investment, a cost most new entrants cannot absorb.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Gaining permits and approvals for new network construction is a lengthy and complex process, often favoring established players.
- Existing Infrastructure Advantage: Dominion Energy's extensive, already-built networks provide immediate economies of scale and operational efficiency that new entrants lack.
Incumbent Advantage and Brand Recognition
Dominion Energy's established presence and strong brand recognition create a significant barrier for potential new entrants. As a trusted utility provider, the company benefits from deep operational experience and established customer relationships within its service territories. This incumbent advantage, coupled with the capital-intensive nature of the energy sector, makes it difficult for new companies to compete effectively for market share and consumer trust.
For instance, in 2024, Dominion Energy continued to invest heavily in infrastructure upgrades and renewable energy projects, further solidifying its position. The company's 2024 capital expenditure plan, exceeding $10 billion, highlights the substantial financial commitment required to operate and expand in this industry, a level of investment that new entrants would struggle to match.
- Incumbent Advantage: Dominion Energy benefits from decades of operational experience and established infrastructure.
- Brand Recognition and Trust: Consumers in its service areas generally trust Dominion Energy as a reliable provider.
- Capital Intensity: The high cost of building and maintaining energy infrastructure deters new companies.
- Regulatory Landscape: Existing utilities often have established relationships and expertise navigating complex energy regulations.
The threat of new entrants for Dominion Energy is significantly low due to the immense capital required to build and maintain energy infrastructure, coupled with stringent regulatory oversight. These factors create substantial barriers, making it exceptionally difficult for newcomers to compete. Dominion's established scale and existing networks further solidify this advantage, ensuring a protected market position.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Building power plants, transmission lines, and distribution networks requires billions of dollars. | Prohibitively expensive for most potential competitors. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Navigating complex state and federal permits, licenses, and approvals is time-consuming and costly. | Favors established companies with existing relationships and expertise. |
| Existing Infrastructure | Dominion Energy's vast, operational networks provide immediate economies of scale and service reach. | New entrants would need massive investment to replicate this reach. |
| Economies of Scale | Dominion's large customer base allows for lower per-unit operating costs. | New entrants struggle to match cost efficiencies without comparable scale. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Dominion Energy Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including SEC filings, annual reports, industry-specific market research from firms like EIA and S&P Global, and regulatory filings from FERC and state utility commissions.
