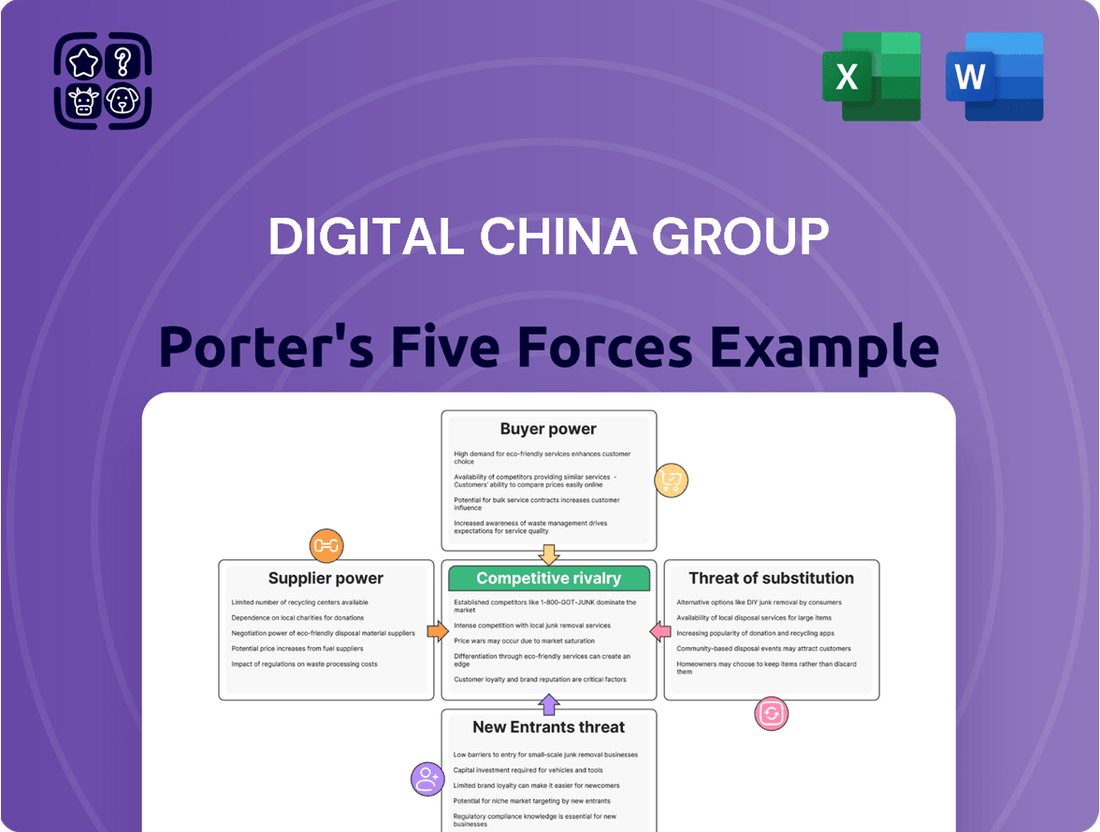
Digital China Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Digital China Group Bundle
Digital China Group navigates a complex landscape shaped by intense rivalry and the growing bargaining power of its customers. Understanding these forces is crucial for any strategic decision. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Digital China Group’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Digital China Group, a major IT services player, depends on numerous hardware and software vendors, including prominent global technology firms. When these suppliers are few, particularly for essential items like advanced AI chips, their ability to influence pricing and terms increases significantly.
The concentration of suppliers is a key factor in their bargaining power. For instance, the market for high-end AI chips is dominated by a limited number of leading companies. This scarcity of choice for buyers like Digital China Group naturally tips the scales in favor of the sellers.
Recent geopolitical developments, such as US export restrictions on advanced semiconductor technology to China, have exacerbated this concentration. This situation may force Chinese companies to source critical components from an even smaller pool of compliant suppliers, thereby amplifying the suppliers' leverage and potentially impacting Digital China Group's procurement costs and operational flexibility.
Switching costs for Digital China Group can be substantial, particularly when dealing with integrated IT systems and comprehensive digital transformation projects. These costs encompass not just direct financial expenditures but also the potential for project disruptions, the need for new staff training, and the complexities of integrating with different vendor platforms. For instance, a significant migration of a company-wide ERP system from one provider to another could involve millions in licensing, implementation, and data migration fees, alongside weeks or months of operational downtime.
Suppliers offering highly specialized or proprietary technologies, like unique AI algorithms or niche cloud infrastructure components, possess significant bargaining power. Digital China Group's strategic focus on data and cloud integration necessitates reliance on specific vendors for advanced solutions in these areas. This dependence allows these suppliers to potentially dictate higher prices or impose more stringent contractual terms, influencing Digital China Group's operational costs and flexibility.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Digital China Group's business, offering IT services directly to end-users, is a significant factor influencing their bargaining power. This capability allows suppliers to capture more value by moving up the supply chain, potentially disintermediating companies like Digital China.
While hardware suppliers typically lack the incentive or capability for such a move, major software and cloud platform providers represent a more potent threat. For instance, a large cloud provider could choose to offer its managed IT services directly, bypassing its existing channel partners. This risk is particularly relevant for standardized service offerings where Digital China's unique value proposition might be less pronounced.
- Increased Supplier Leverage: If suppliers can effectively integrate forward, they gain leverage by controlling the direct customer relationship, potentially dictating terms and pricing to intermediaries.
- Cloud Provider Strategy: In 2024, major cloud providers continued to strengthen their direct sales and support channels for enterprise clients, indicating a trend towards disintermediation in certain service segments.
- Digital China's Mitigation: Digital China's deep understanding of the Chinese market, its localized service delivery capabilities, and its expertise in integrating complex IT solutions act as crucial defenses against direct competition from global platform providers.
Importance of Digital China Group to Suppliers
Digital China Group's importance to its suppliers hinges on the scale of their business relationship and any strategic alliances. For smaller, niche suppliers, Digital China Group can be a substantial customer, granting the Group a degree of leverage in negotiations.
However, when dealing with major global technology providers, Digital China Group often represents just one client among many. This dilutes the Group's individual bargaining power with these dominant suppliers.
For example, in 2024, Digital China Group's procurement from leading cloud service providers, which are often global giants, means their individual purchasing volume might not significantly sway pricing or terms for those providers. Conversely, their purchases from specialized software developers or hardware manufacturers could represent a much larger percentage of those smaller firms' revenue, thereby increasing Digital China Group's influence.
- Customer Dependence: Digital China Group's impact on suppliers varies. For specialized firms, it can be a primary revenue source, increasing the Group's bargaining power.
- Market Dominance of Suppliers: For globally dominant tech suppliers, Digital China Group is one of many clients, reducing the Group's individual leverage.
- Strategic Partnerships: The presence of strategic partnerships can elevate Digital China Group's importance to suppliers, potentially fostering more favorable terms.
- Volume-Based Negotiation: The sheer volume of Digital China Group's purchases directly correlates with its ability to negotiate better terms and pricing from its supplier base.
The bargaining power of Digital China Group's suppliers is a significant factor, especially given the concentration in critical technology markets like AI chips.
Suppliers of specialized or proprietary technologies, such as advanced AI algorithms or unique cloud components, hold considerable sway, potentially leading to higher prices for Digital China Group.
The threat of major software and cloud providers integrating forward to offer services directly to end-users could disintermediate Digital China Group, particularly for standardized offerings.
Digital China Group's leverage with suppliers is diminished when dealing with global tech giants, as they represent a smaller portion of these large firms' overall business compared to niche suppliers.
| Factor | Impact on Digital China Group | Example/Data (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High | Dominance of a few firms in AI chip market increases supplier leverage. |
| Switching Costs | High | Migrating enterprise ERP systems can cost millions and cause operational downtime. |
| Supplier Differentiation | High | Proprietary AI algorithms or cloud solutions allow suppliers to dictate terms. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Moderate to High | Major cloud providers expanding direct enterprise services. |
| Customer Importance | Varies (Low for giants, High for niche) | Digital China's volume with global cloud providers may not sway pricing; it can significantly impact smaller tech firms. |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive landscape for Digital China Group, detailing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the Digital China Group's Porter's Five Forces, allowing for proactive strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Digital China Group's customer base spans vital sectors like government, finance, manufacturing, and retail. This diversification inherently lowers the risk associated with any single customer segment. However, the presence of large enterprise and government clients introduces a significant element of customer bargaining power. These major clients, due to the sheer volume and complexity of their projects, can exert considerable influence on pricing and demand highly tailored solutions, impacting Digital China Group's margins.
For Digital China Group's clientele, transitioning to a different IT service provider often entails significant expenses and operational hurdles. This is especially true for intricate projects like digital transformation, cloud adoption, and system integration, where the complexity itself acts as a deterrent.
The deeply integrated nature of Digital China Group's offerings, woven into the very fabric of their clients' daily operations, establishes formidable switching barriers. This deep embedding effectively diminishes the bargaining power of customers, as the cost and effort to disentangle and re-establish services elsewhere are substantial.
Customers, particularly large enterprise clients, are becoming much savvier about IT market prices and available solutions. This heightened awareness, driven by increased transparency in the IT services sector, empowers them to negotiate more effectively.
This trend directly impacts Digital China Group by intensifying price pressure, especially on their more standardized IT products and services. For instance, in 2024, the average IT service contract negotiation saw a 5-7% reduction in initial quoted prices due to customer-driven information gathering.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
Customers, particularly large enterprises and government bodies, may explore building their own IT infrastructure to decrease dependence on Digital China Group. This threat is amplified by the increasing availability of advanced IT talent and the potential for cost savings. For instance, in 2024, many large Chinese enterprises were investing heavily in private cloud solutions, aiming for greater control over their data and operations.
However, the steep learning curve and substantial investment required for cutting-edge technologies like AI and big data analytics present significant barriers to full backward integration for most customers. The rapid pace of technological change means that maintaining state-of-the-art capabilities in-house is a continuous and costly challenge.
- High Cost of Entry: Implementing and maintaining advanced IT infrastructure, including cloud and AI capabilities, demands significant capital expenditure.
- Technological Complexity: The rapid evolution of digital technologies requires specialized expertise that is difficult and expensive to acquire and retain internally.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Many customers prefer to concentrate on their primary business operations rather than diverting resources to complex IT development.
- Scalability and Flexibility: External providers like Digital China Group often offer greater scalability and flexibility, which can be difficult to replicate in-house.
Availability of Substitute Services for Customers
The bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by the availability of substitute IT services. Digital China Group faces competition not only from other local and international IT service providers but also from open-source alternatives and readily available off-the-shelf software. This broad spectrum of choices empowers customers, allowing them to switch providers if Digital China Group's offerings do not meet their expectations or pricing. For instance, the global IT services market, valued at approximately $1.3 trillion in 2023, demonstrates the sheer scale of competition, with numerous players vying for market share.
To counter this, Digital China Group must prioritize continuous innovation and differentiation. By developing unique solutions and demonstrating superior value, the company can solidify customer loyalty. In 2024, companies across the IT sector are investing heavily in areas like artificial intelligence and cloud computing to create distinct competitive advantages. Digital China Group's ability to stay ahead in these technological advancements will be crucial for retaining its customer base amidst the readily available alternatives.
- Customer Choice: The presence of numerous IT service providers, including global giants and specialized local firms, alongside accessible open-source and packaged software, grants customers substantial leverage.
- Competitive Landscape: The IT services market is highly fragmented, with many alternatives available, putting pressure on pricing and service quality.
- Innovation Imperative: Digital China Group must consistently enhance its service portfolio and technological capabilities to stand out and prevent customer attrition.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, the demand for specialized IT solutions, such as AI-driven analytics and robust cybersecurity, is high, offering opportunities for differentiation but also highlighting the availability of specialized substitutes.
Digital China Group's bargaining power with customers is moderated by the increasing savviness of its large enterprise and government clients. These sophisticated buyers, armed with market knowledge, are actively negotiating for better terms, leading to an average 5-7% reduction in initial IT service contract prices in 2024 due to their informed approach.
While high switching costs and deep integration create customer stickiness, the threat of in-house IT development, particularly in private cloud solutions, is a growing concern for Digital China Group. Many large Chinese enterprises are investing in this area in 2024 to gain greater operational control and potentially reduce reliance on external providers.
The availability of numerous IT service providers and open-source alternatives intensifies customer leverage. Digital China Group must continuously innovate, especially in high-demand areas like AI and cloud computing, to differentiate its offerings and retain clients in this competitive 2024 market.
Same Document Delivered
Digital China Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Digital China Group, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for the company. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, providing actionable insights without any placeholders or alterations.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The IT services market in China is intensely competitive, featuring a broad array of both domestic and international companies vying for market share. Digital China Group must contend with formidable rivals, including major cloud providers such as Alibaba Cloud, Huawei Cloud, and Tencent Cloud. These giants collectively commanded a substantial portion of the market in the fourth quarter of 2024, highlighting the concentrated power at the top tier of the industry.
This competitive landscape is further characterized by its diversity. Digital China Group faces competition not only from these large, integrated service providers but also from numerous smaller, specialized firms that focus on specific niche areas within the IT services sector. This spectrum of competitors, from industry behemoths to agile specialists, creates a dynamic and challenging environment for any player, including Digital China Group.
The China IT services market is on a strong growth trajectory, with expectations of a 9% compound annual growth rate between 2025 and 2030. This expansion is largely fueled by the burgeoning cloud computing sector, which is forecast to hit $74.13 billion in 2025.
While robust industry growth typically offers ample room for multiple participants, it doesn't eliminate competitive pressures. In fact, the fight for market share can intensify, particularly within rapidly advancing areas like AI-driven cloud services, where innovation and client acquisition are paramount.
Digital China Group distinguishes itself with a unique 'data and cloud integration' approach, building its core on cloud-native, data-native, and AI-native technologies. This allows them to offer comprehensive, integrated solutions to their clients.
While this strategy offers a strong foundation, the competitive landscape is intense. Many rivals also provide comparable cloud and data services, meaning Digital China Group must consistently innovate and add value to maintain its competitive edge in the market.
Exit Barriers
Digital China Group operates in a market characterized by high exit barriers, particularly within its IT services segment. Significant investments in specialized infrastructure and the development of unique employee skill sets mean that companies find it difficult and costly to withdraw from the market, even when facing low profitability. This reluctance to exit can lead to intensified competition as existing players remain engaged, potentially suppressing returns for all involved.
The IT services industry, where Digital China Group has substantial operations, often involves long-term contracts and substantial capital outlays for hardware, software, and talent. For instance, a typical enterprise IT transformation project can span several years, locking in resources and commitments. This creates a sticky environment where divesting or winding down operations becomes a complex and financially burdensome undertaking.
- High Fixed Asset Investment: Digital China Group's IT infrastructure, including data centers and specialized hardware, represents a considerable fixed asset base. In 2023, the company reported significant capital expenditures in its infrastructure development, a trend likely to continue as it expands cloud and data services.
- Specialized Employee Skills: The demand for highly skilled IT professionals, such as cloud architects and cybersecurity experts, means that talent acquisition and retention are critical. The cost and time involved in training and developing these specialized skills create a barrier to exiting the market, as these assets are not easily transferable.
- Long-Term Contracts: Many of Digital China Group's service agreements are multi-year engagements. These contracts provide revenue stability but also bind the company to ongoing commitments, making a swift exit from specific service lines or the overall market challenging without incurring penalties or reputational damage.
Market Share and Aggressiveness of Competitors
The competitive landscape for Digital China Group is marked by intense rivalry, particularly from leading Chinese technology firms actively expanding their cloud and AI infrastructure. These companies are not just competing; they are investing heavily, signaling a high degree of aggressiveness. For instance, in 2023, Tencent Cloud announced significant investments aimed at bolstering its AI capabilities, mirroring similar moves by Alibaba Cloud. This environment necessitates Digital China Group’s ongoing focus on enhancing profitability and fortifying its core competitive strengths through strategic business expansion to maintain its market position.
Digital China Group's strategic imperative to strengthen profitability and core competitiveness is a direct response to this aggressive market dynamic. The company’s commitment to strategic business growth is crucial for navigating a sector where major players are making substantial capital expenditures. For example, in the first half of 2024, several major Chinese tech firms reported double-digit percentage increases in their R&D spending, heavily allocated towards cloud and AI development, underscoring the pressure on all participants.
- Intense Investment in Cloud and AI: Leading Chinese tech giants are pouring significant capital into cloud computing and artificial intelligence infrastructure, creating a highly competitive environment.
- Aggressive Market Stance: Competitors are demonstrating a proactive and aggressive approach to market share capture and technological advancement.
- Digital China's Strategic Response: Digital China Group is actively working to improve its profitability and strengthen its core competencies to effectively compete.
- Impact on Growth Strategies: The aggressive rivalry necessitates strategic business growth initiatives to maintain and enhance Digital China Group's market standing.
The competitive rivalry within China's IT services sector is fierce, with Digital China Group facing significant pressure from major domestic cloud providers like Alibaba Cloud, Huawei Cloud, and Tencent Cloud. These dominant players collectively held a substantial market share in late 2024, indicating a concentrated market at the top. The market's rapid growth, projected at a 9% CAGR from 2025 to 2030, with cloud computing alone expected to reach $74.13 billion in 2025, fuels this intense competition.
| Competitor | Key Offerings | 2024 Market Position Indicator |
| Alibaba Cloud | Cloud Computing, AI Services, Big Data | Leading Market Share |
| Huawei Cloud | Cloud Infrastructure, AI Solutions, Enterprise Services | Significant Market Presence |
| Tencent Cloud | Cloud Services, Gaming Infrastructure, AI Development | Major Industry Player |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Traditional on-premise IT infrastructure and legacy software present a potential substitute for Digital China Group's cloud and digital transformation offerings. Many organizations, especially those with substantial existing IT investments or stringent regulatory compliance needs, may continue to rely on these established systems. For instance, in 2023, a significant portion of enterprise IT spending globally remained allocated to maintaining and upgrading on-premise data centers, indicating a persistent demand for these solutions.
While these traditional IT solutions can act as substitutes, the market's clear trajectory favors cloud-native operating models. This shift is driven by the inherent scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency benefits of cloud computing. Consequently, the long-term threat posed by traditional IT substitutes to Digital China Group's business is diminishing as more businesses embrace digital transformation and cloud adoption.
Many large enterprises and government entities possess robust in-house IT departments, capable of handling a significant portion of their technology needs. This internal capacity directly substitutes for external IT service providers, particularly for routine maintenance, basic software development, and data management. For instance, in 2024, a survey by TechTarget revealed that 70% of mid-to-large enterprises planned to increase their internal IT spending to enhance core capabilities, signaling a potential reduction in reliance on outsourcing for certain functions.
The choice between in-house IT and outsourcing hinges on a careful evaluation of cost-effectiveness, stringent security requirements, and the specialized nature of the technology solutions needed. While outsourcing can offer scalability and access to niche expertise, the control and perceived security of managing IT internally remain strong deterrents for some organizations. In 2023, Gartner reported that while IT outsourcing spending was projected to reach $132 billion globally, a significant portion of that was for specialized cloud services, with core IT functions often remaining in-house.
The growing availability and capability of open-source software and platforms, particularly in areas like cloud computing, big data, and artificial intelligence, pose a significant threat of substitution for Digital China Group's proprietary offerings. These open-source alternatives enable businesses to develop and deploy solutions more affordably, reducing their dependence on commercial vendors. For instance, the widespread adoption of Linux in enterprise environments and the increasing use of TensorFlow and PyTorch for AI development demonstrate this trend, allowing companies to build robust systems without the licensing costs associated with commercial software.
Simplified, Off-the-Shelf Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
For less complex digital needs, readily available Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications present a significant threat of substitution. Businesses can often find off-the-shelf SaaS solutions that fulfill basic functionalities, bypassing the need for custom-built or deeply integrated systems. This trend is amplified as the SaaS market continues to mature, offering more specialized and cost-effective alternatives.
The increasing accessibility and affordability of SaaS platforms mean that companies, especially small and medium-sized enterprises, may choose these subscription-based models over more extensive, bespoke digital development. This shift can directly impact demand for custom integration services and complex platform development, areas where Digital China Group might operate.
- SaaS Market Growth: The global SaaS market was projected to reach over $270 billion in 2024, indicating a substantial and growing pool of readily available alternatives.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Many SaaS solutions offer predictable monthly or annual fees, making them a more attractive option for businesses prioritizing budget control over extensive customization.
- Reduced Implementation Time: Off-the-shelf SaaS applications typically require less setup and integration time compared to bespoke solutions, allowing businesses to deploy digital tools more rapidly.
- Focus on Core Competencies: By outsourcing basic digital functions to SaaS providers, companies can redirect internal resources towards their core business activities rather than complex IT management.
Emerging Technologies and New Paradigms
Rapid technological shifts, like the rise of edge computing for Generative AI and novel data management strategies, present a significant threat of substitutes. These advancements could enable alternative IT service delivery models that circumvent established, integrated providers.
For instance, the increasing modularity of cloud services and the growth of specialized SaaS platforms allow businesses to assemble IT solutions from best-of-breed components, potentially reducing reliance on a single, comprehensive IT service vendor.
Digital China Group's strategic pivot towards AI-accelerated data and cloud integration directly addresses this threat. By actively incorporating these emerging technologies, the company aims to remain competitive and offer value propositions that are difficult to replicate through fragmented or substitute solutions.
- Edge Computing Adoption: Global spending on edge computing is projected to reach $274 billion in 2024, a 11.7% increase from 2023, highlighting its growing importance for new applications like GenAI.
- AI in Data Management: Companies are increasingly leveraging AI for data analytics and management, with the AI in data management market expected to grow significantly, offering new ways to process and derive value from data.
- Cloud Integration Trends: Hybrid and multi-cloud strategies continue to dominate, with many enterprises seeking integrated solutions that can manage diverse cloud environments, a space where Digital China Group is focusing its efforts.
The availability of robust open-source software and platforms, particularly in cloud, big data, and AI, directly substitutes for Digital China Group's proprietary offerings. These alternatives allow businesses to build solutions more affordably, reducing dependence on commercial vendors. For example, the widespread adoption of Linux and frameworks like TensorFlow in enterprise environments illustrates this trend, enabling companies to create powerful systems without the licensing costs of commercial software.
Off-the-shelf Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications also pose a significant threat for less complex digital needs. Businesses can readily deploy these pre-built solutions, bypassing the requirement for custom development or deep integration. The SaaS market's continued maturity offers increasingly specialized and cost-effective alternatives, impacting demand for bespoke services.
Emerging technologies like edge computing for Generative AI and novel data management strategies introduce new IT service delivery models that could bypass established providers. The modularity of cloud services and specialized SaaS platforms enable businesses to assemble IT solutions from best-of-breed components, potentially lessening reliance on a single, comprehensive vendor.
| Substitute Type | Description | Market Trend/Data Point |
| On-Premise IT & Legacy Software | Existing IT investments and regulatory needs drive continued reliance on traditional systems. | Global enterprise IT spending on maintaining on-premise infrastructure remained significant in 2023. |
| In-House IT Departments | Large enterprises and government entities with strong IT capabilities can handle many technology needs internally. | 70% of mid-to-large enterprises planned increased internal IT spending in 2024 to enhance core capabilities (TechTarget survey). |
| Open-Source Software | Affordable and capable alternatives in cloud, big data, and AI reduce reliance on commercial vendors. | Widespread adoption of Linux and AI frameworks like TensorFlow and PyTorch. |
| SaaS Applications | Off-the-shelf solutions for basic digital needs bypass custom development. | Global SaaS market projected to exceed $270 billion in 2024; many offer predictable subscription fees and faster implementation. |
| Emerging Technologies (Edge, GenAI) | New IT delivery models using modular services and specialized platforms. | Edge computing spending projected to reach $274 billion in 2024, a 11.7% increase from 2023. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the integrated IT services sector, particularly in advanced areas like cloud computing and digital transformation, demands significant upfront capital. Companies need to invest heavily in building and maintaining data centers, robust network infrastructure, and cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence. For instance, establishing a hyperscale data center can easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars, creating a formidable financial hurdle for aspiring competitors.
Established players like Digital China Group leverage significant economies of scale, particularly in bulk procurement of IT hardware and software, which lowers their per-unit costs. For instance, in 2023, Digital China’s revenue reached approximately RMB 100 billion, indicating the sheer volume of their operations and purchasing power.
Furthermore, economies of scope allow Digital China to offer a comprehensive suite of integrated services, from cloud computing to supply chain solutions. This broad portfolio creates a synergistic effect, making it difficult for new entrants to match the cost-effectiveness and value proposition offered by a single, diversified provider.
The Chinese government's ambitious 'Digital China' initiative, aimed at fostering domestic technological advancement, presents a significant barrier to new entrants. While this policy encourages digital transformation, it also imposes stringent data sovereignty and cybersecurity regulations. For example, the Cybersecurity Law of the People's Republic of China (effective June 1, 2017) mandates strict data localization and security assessments, making compliance a complex hurdle for newcomers, particularly foreign firms, to overcome.
Access to Distribution Channels and Customer Relationships
Digital China Group's deep-rooted customer relationships across critical sectors such as government, finance, and manufacturing present a formidable barrier. For instance, in 2023, the company reported serving over 10,000 government and enterprise clients, a testament to its established trust and integration. This extensive network makes it difficult for new entrants to gain traction and build comparable loyalty.
Furthermore, Digital China Group possesses a robust and widespread distribution network for IT products, honed over years of operation. This infrastructure is not easily replicated, requiring substantial investment and time to establish. New competitors would struggle to match the reach and efficiency of Digital China Group's existing channels, hindering their ability to deliver products and services effectively.
- Established Client Base: Digital China Group's significant presence in government, finance, and manufacturing sectors, evidenced by its 2023 client numbers, creates high switching costs and loyalty for new entrants.
- Distribution Network Advantage: The company's extensive IT product distribution network, built over many years, offers a competitive edge that new players would find challenging and costly to replicate.
- Trust and Credibility: New entrants face the arduous task of building trust and credibility to compete with Digital China Group's long-standing reputation and proven track record in the market.
Brand Identity and Switching Costs for Customers
Digital China Group has cultivated a robust brand identity as a premier integrated IT service provider in China. This strong brand recognition, coupled with the significant switching costs associated with migrating from established IT service relationships, presents a considerable hurdle for potential new entrants aiming to capture market share.
Customers often face substantial expenses and operational disruptions when changing IT service providers. These costs can include data migration, system integration, employee retraining, and potential downtime, making them hesitant to switch. For instance, in 2024, many enterprises reported that the integration of new cloud services alone could take several months and cost upwards of 15% of the initial service contract value.
- Established Brand Loyalty: Digital China Group's long-standing presence and consistent delivery of services have fostered deep customer loyalty.
- High Switching Costs: The financial and operational burdens of transitioning to a new IT service provider act as a powerful deterrent for customers.
- Integrated Service Offerings: The comprehensive nature of Digital China Group's IT solutions makes it more complex and costly for clients to unbundle and replace services piecemeal.
- Market Perception: The company's reputation for reliability and expertise further solidifies its position, making it difficult for new, unproven entities to compete for customer trust.
The threat of new entrants into China's integrated IT services market is significantly mitigated by substantial capital requirements for infrastructure and technology. For example, building hyperscale data centers, a necessity for cloud services, can cost hundreds of millions of dollars, creating a high financial barrier.
Digital China Group benefits from significant economies of scale, evidenced by its RMB 100 billion revenue in 2023, which allows for lower per-unit costs in hardware procurement. This scale makes it difficult for smaller, new entrants to compete on price.
Furthermore, the company's established customer relationships, serving over 10,000 government and enterprise clients in 2023, coupled with high switching costs for clients, create strong customer loyalty. These factors, along with a robust distribution network and brand recognition, present formidable challenges for any new player seeking to enter the market.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Digital China Group Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of diverse data, including official company filings, reputable industry research reports, and government economic data. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
