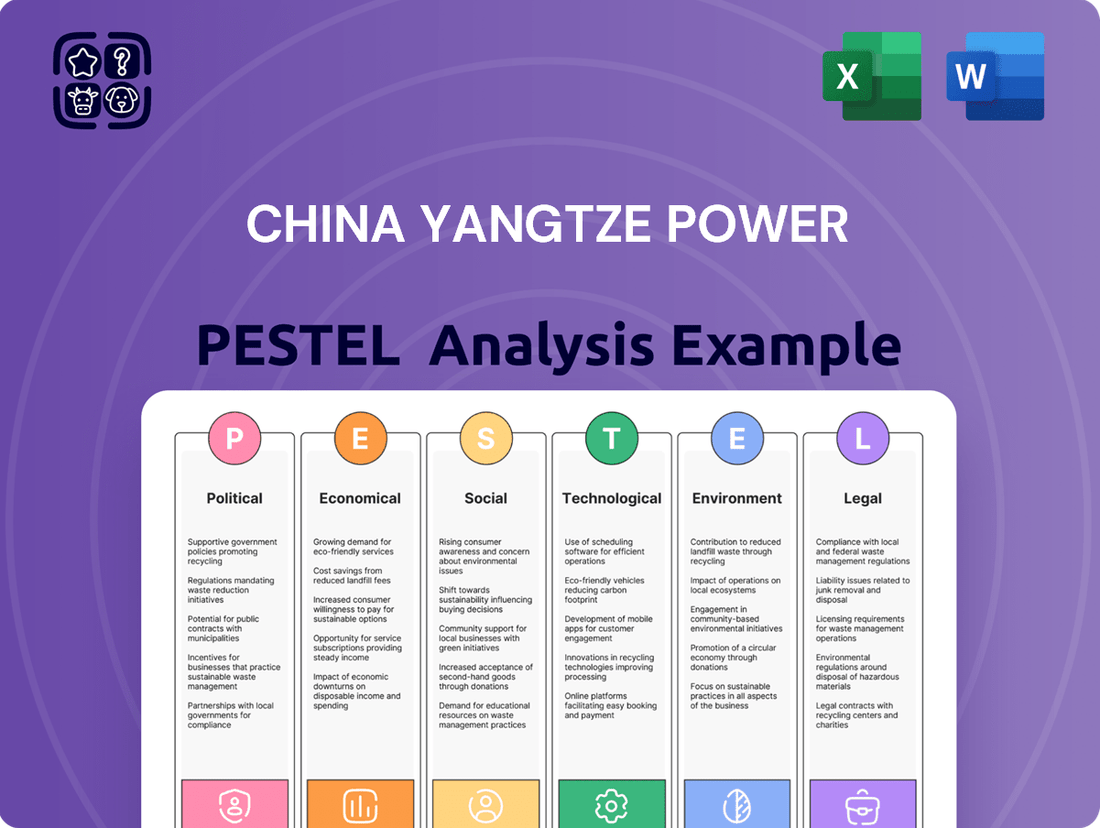
China Yangtze Power PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
China Yangtze Power Bundle
Uncover the critical political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors shaping China Yangtze Power's trajectory. This PESTLE analysis provides a strategic roadmap, highlighting opportunities and potential challenges. Gain a competitive advantage by understanding these external forces. Download the full, actionable report now to inform your investment decisions and strategic planning.
Political factors
The Chinese government's robust commitment to clean energy is a significant political factor. Ambitious targets aim for non-fossil fuel energy consumption to reach 18.9% in 2024 and 20% by 2025, underscoring a strong push for decarbonization and energy security.
This strategic focus directly benefits China Yangtze Power, as hydropower is a cornerstone of the nation's clean energy transition. The overarching '1+N' policy framework further solidifies this direction, guiding decarbonization efforts across all economic sectors, including energy production.
Hydropower is a cornerstone of China's national energy strategy, viewed as critical infrastructure for energy security and diversifying the country's power sources. This focus is evident in the continued expansion of hydropower capacity, with China adding an impressive 14.4 GW in 2024 alone, underscoring its commitment to this renewable sector.
Massive projects, such as the Three Gorges Dam operated by China Yangtze Power, exemplify this strategic imperative. These facilities are instrumental in generating substantial amounts of clean electricity, thereby decreasing dependence on fossil fuels and contributing to China's environmental goals.
As a centrally administered state-owned enterprise (SOE), China Yangtze Power is directly impacted by national reform initiatives designed to boost efficiency and streamline operations. These reforms often steer SOEs, including Yangtze Power, towards greater investment in key sectors like green energy, aligning with national development priorities.
A significant aspect of these reforms targets the strategic allocation of SOE resources. The objective is for revenue derived from strategic emerging industries to reach 35% of total SOE revenue by 2025, a target that will likely influence Yangtze Power's investment and operational strategies in sectors such as renewable energy development.
National Energy Security Priorities
China's national energy strategy strongly emphasizes security and availability, balancing these with the economic viability of cleaner energy options. Hydropower is a cornerstone of this policy, offering consistent and significant power generation crucial for meeting the country's escalating energy needs.
This focus on energy security directly translates into continued governmental backing for major hydropower initiatives. For instance, as of 2024, China continues to invest heavily in its vast hydropower network, which already accounts for a substantial portion of its total electricity generation capacity. This makes projects like those undertaken by China Yangtze Power strategically vital for national stability.
- Energy Security Focus: China’s government prioritizes a stable and abundant energy supply to fuel its economic growth and maintain social order.
- Hydropower's Role: Hydropower is a key component in achieving this, providing a reliable and significant source of electricity.
- Economic Feasibility: The policy also considers the cost-effectiveness of low-carbon energy sources, where hydropower often presents a competitive advantage.
- Government Support: These national priorities ensure ongoing political and financial support for large-scale hydropower development.
Cross-Border River Project Implications
China's ambitious hydropower initiatives, particularly large-scale developments like those proposed for the Yarlung Zangbo River, introduce significant political complexities due to their potential impact on downstream nations such as India and Bangladesh. While Beijing asserts these projects will not harm downstream water availability, navigating these international water-sharing dynamics is a crucial political consideration for China Yangtze Power and the Chinese government. This requires careful diplomatic engagement and transparency to maintain regional stability and avoid geopolitical friction, especially as global water scarcity concerns intensify.
These cross-border river project implications necessitate robust diplomatic efforts. For instance, ongoing discussions and potential agreements between China and its downstream neighbors regarding water resource management can directly influence project timelines and operational frameworks. The success of such ventures hinges on fostering trust and ensuring equitable water distribution, a delicate political balancing act.
- International Relations: Managing downstream country concerns regarding water flow and environmental impact is paramount for project legitimacy and regional cooperation.
- Diplomatic Engagement: Proactive dialogue and transparent data sharing with India and Bangladesh are essential to mitigate potential disputes and build trust.
- Geopolitical Stability: The political ramifications of large-scale river projects underscore the need for China to prioritize cooperative water resource management to ensure regional peace and stability.
China's commitment to energy security and decarbonization fuels substantial government support for hydropower. By 2025, the nation targets 20% of its energy consumption from non-fossil fuels, a goal directly benefiting companies like China Yangtze Power. This strategic imperative is reinforced by national reforms aimed at increasing the revenue from strategic emerging industries to 35% of total SOE revenue by 2025, aligning Yangtze Power's investments with national development priorities.
The political landscape also includes managing international water-sharing dynamics, particularly concerning projects on rivers like the Yarlung Zangbo. Maintaining regional stability requires careful diplomatic engagement with downstream nations such as India and Bangladesh, ensuring transparency and cooperative water resource management to avoid geopolitical friction.
| Policy/Initiative | Target/Metric | Impact on China Yangtze Power |
|---|---|---|
| Non-fossil fuel energy consumption | 20% by 2025 | Increased demand and favorable policy for hydropower generation. |
| SOE Revenue from Strategic Industries | 35% by 2025 | Encourages investment in renewable energy, aligning with Yangtze Power's core business. |
| Hydropower Capacity Expansion | Ongoing, significant additions in 2024 (e.g., 14.4 GW) | Provides opportunities for growth and project development. |
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis examines how political stability, economic growth, social trends, technological advancements, environmental regulations, and legal frameworks impact China Yangtze Power.
Provides a concise version that can be dropped into PowerPoints or used in group planning sessions, offering a quick understanding of China Yangtze Power's external environment to address potential strategic roadblocks.
Economic factors
China's electricity demand shows persistent strength, with projections pointing to a 6.5% rise in 2024 and a still-healthy 6.2% in 2025, even as the broader economy moderates. This ongoing expansion is fueled by increased electrification across various industries and the booming production of new energy goods.
This sustained demand creates a reliable market for China Yangtze Power's electricity output. The company's own generation figures for 2024 reflect this trend, demonstrating its capacity to meet and capitalize on this growing need.
China Yangtze Power demonstrated robust financial health in 2024, reporting a notable 19.36% surge in net profit attributable to shareholders, reaching 32.52 billion yuan. This impressive growth was largely fueled by enhanced power generation across its extensive cascade power station network.
Further underscoring its strong financial standing, the company declared a substantial profit distribution for 2024, with a cash dividend scheduled for payment in July 2025, signaling a commitment to shareholder returns.
China Yangtze Power's commitment to significant investment in hydropower infrastructure is a key economic driver. The company's substantial outlay, exemplified by the RMB 8.264 billion approved for the HouSihe Pumped Storage Power Station, directly supports national energy goals.
This strategic investment aligns with China's ambitious target of achieving 62 GW of pumped storage capacity by 2025, crucial for grid stability and integrating renewable energy sources. Furthermore, China's hydropower sector demonstrated robust growth in 2024, adding 14.4 GW of new capacity, which represented over half of the global additions for the year.
Cost-Effectiveness and Competitive Advantage
Hydropower continues to be a highly cost-effective and environmentally friendly energy source in China, giving China Yangtze Power a significant competitive edge. In 2023, the company reported a substantial operational revenue, largely driven by its massive hydropower capacity. This cost advantage is amplified by their ongoing investments in technological upgrades to further optimize energy generation efficiency.
China Yangtze Power's strategic emphasis on expanding its hydropower capacity and improving its technological prowess solidifies its strong position within China's rapidly growing renewable energy sector. The company's commitment to innovation is evident in its ongoing research into advanced turbine technologies and smart grid integration, aiming to maximize output and reliability.
Key projects like the Three Gorges Dam are indispensable to China's national energy infrastructure, supplying a critical portion of the country's electricity needs. As of early 2024, the Three Gorges Dam alone generates over 100 billion kilowatt-hours annually, underscoring its vital role in meeting China's vast energy demand and supporting economic development.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Hydropower offers lower operational costs compared to fossil fuel alternatives.
- Low Emissions: Hydropower is a crucial contributor to China's decarbonization goals.
- Capacity Expansion: China Yangtze Power continues to invest in new hydropower projects.
- Technological Advancement: Focus on efficiency improvements and smart grid integration.
Impact of Macroeconomic Trends
China Yangtze Power's operational landscape is shaped by the nation's economic transition, with new energy sectors like solar and electric vehicles driving electricity demand. For instance, China's solar PV capacity saw a significant increase, adding approximately 216.9 GW in 2023, contributing to overall power consumption growth.
Despite this robust growth, the company must navigate potential headwinds. Extreme weather events, such as the severe droughts impacting hydropower generation in some regions during 2022, can directly affect output. Furthermore, a slowdown in industrial expansion, a key driver of electricity usage, could temper demand forecasts.
China Yangtze Power's preliminary financial results for 2024 underscore its ability to manage these macroeconomic dynamics. The company reported a net profit attributable to parent company shareholders of approximately RMB 25.1 billion for the first half of 2024, demonstrating resilience and operational efficiency.
- Economic Structural Shift: China's economy is rebalancing, with new energy industries fueling electricity demand.
- Demand Drivers: Growth in sectors like solar PV and electric vehicles supports increased power consumption.
- Potential Risks: Extreme weather and slower industrial growth could impact electricity demand and generation.
- Financial Performance: Preliminary 2024 results indicate operational success amidst these trends, with H1 2024 net profit around RMB 25.1 billion.
China's electricity demand remains strong, with projections indicating a 6.5% increase in 2024 and 6.2% in 2025, driven by industrial electrification and new energy goods production. China Yangtze Power's financial performance in 2024 reflects this, with a 19.36% surge in net profit to 32.52 billion yuan, supported by increased hydropower generation. The company's commitment to expanding its hydropower capacity, including a RMB 8.264 billion investment in the HouSihe Pumped Storage Power Station, aligns with China's goal of 62 GW of pumped storage by 2025, crucial for grid stability and renewable integration.
| Metric | 2023 (Actual) | 2024 (Projected/H1) | 2025 (Projected) |
|---|---|---|---|
| China Electricity Demand Growth | N/A | 6.5% | 6.2% |
| China Yangtze Power Net Profit (Attributable to Shareholders) | N/A | 32.52 billion yuan (FY 2024) | N/A |
| China Yangtze Power H1 2024 Net Profit | N/A | ~25.1 billion yuan | N/A |
| China Pumped Storage Capacity Target | N/A | N/A | 62 GW |
| China Yangtze Power HouSihe Project Investment | N/A | RMB 8.264 billion | N/A |
What You See Is What You Get
China Yangtze Power PESTLE Analysis
The preview shown here is the exact document you’ll receive after purchase—fully formatted and ready to use, providing a comprehensive PESTLE analysis of China Yangtze Power.
This is a real screenshot of the product you’re buying—delivered exactly as shown, no surprises, detailing the Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors impacting China Yangtze Power.
The content and structure shown in the preview is the same document you’ll download after payment, offering valuable insights into the strategic landscape for China Yangtze Power.
Sociological factors
Large-scale infrastructure projects like those undertaken by China Yangtze Power, particularly the Three Gorges Dam, have historically necessitated the relocation of millions. For instance, the Three Gorges Dam project saw the resettlement of over 1.3 million people, a massive undertaking with ongoing social implications.
While the government highlights economic opportunities and improved living standards for relocated populations, concerns about social cohesion, cultural preservation, and adequate compensation persist. Past projects have seen instances of localized unrest, underscoring the need for meticulous planning and transparent communication in current and future resettlement efforts.
Hydropower projects are vital for China's national infrastructure, acting as catalysts for local industrial growth and job creation. These initiatives significantly boost the economic health of the communities where they are developed.
China Yangtze Power's ongoing operations and future project pipeline are projected to generate substantial employment. For instance, the Three Gorges Dam project, a flagship initiative, created tens of thousands of jobs during its construction phase and continues to support local economies through its operational activities and associated industries.
Public perception of China Yangtze Power's operations, particularly its flagship Three Gorges Dam, is a critical factor. While the dam is recognized for its significant contribution to China's energy security, providing over 100 billion kWh of electricity annually as of recent reports, there are ongoing concerns about its environmental and social footprint. This duality means the company must actively manage its public image, emphasizing its commitment to sustainability and social responsibility to maintain broad acceptance.
The company's large-scale projects often attract public attention and scrutiny, making transparent communication about environmental mitigation efforts and community engagement essential. Past instances of protests against dam construction globally underscore the importance of addressing public concerns proactively. China Yangtze Power's approach to stakeholder dialogue and its performance on social impact assessments directly influence its license to operate and overall public trust.
Community Engagement and Outreach
China Yangtze Power actively pursues community engagement, with a focus on expanding its outreach programs. This commitment aims to foster stronger relationships with communities near its operational sites, recognizing the importance of social license for sustained growth. For instance, in 2023, the company reported investing over ¥100 million in local development and environmental protection initiatives.
These initiatives are crucial for ensuring the company's long-term harmonious development and maintaining a positive social standing. Key areas of focus include:
- Environmental Protection: Supporting local conservation efforts and biodiversity projects.
- Poverty Alleviation: Contributing to local economic development and job creation.
- Education and Culture: Investing in local schools and cultural heritage preservation.
- Disaster Relief: Providing support during natural disasters affecting local communities.
Ensuring Stable Power Supply for Society
China Yangtze Power is fundamental to China's societal stability by guaranteeing a consistent and dependable electricity flow to its massive population and diverse industries. The company's extensive network of hydropower facilities is crucial for satisfying the country's escalating energy demands, thereby underpinning economic development and growth.
This commitment to energy security translates into a significant societal advantage. For instance, in 2023, China Yangtze Power's installed capacity reached approximately 70.25 million kilowatts, with its hydropower generation contributing substantially to the national grid, ensuring power availability even during peak demand periods.
- Energy Security: The company's hydropower operations are a cornerstone of China's energy independence, reducing reliance on imported fuels.
- Economic Support: Reliable power supply from China Yangtze Power is vital for manufacturing, technology, and service sectors, directly impacting GDP growth.
- Environmental Benefits: Hydropower is a cleaner energy source compared to fossil fuels, contributing to societal well-being by reducing air pollution and carbon emissions.
- Infrastructure Development: The construction and maintenance of large-scale hydropower projects create jobs and stimulate regional economic activity.
China Yangtze Power's societal role is deeply intertwined with national development, particularly through its provision of clean energy. The company's extensive hydropower generation, exceeding 100 billion kWh annually from the Three Gorges Dam alone, directly supports China's economic growth and helps mitigate environmental concerns associated with fossil fuels. This reliable energy supply underpins critical industries and contributes to improved living standards for millions.
However, large-scale projects like the Three Gorges Dam have historically involved significant population resettlement, impacting over 1.3 million people. While economic benefits are often cited, ongoing challenges related to social cohesion and community well-being necessitate careful management and transparent engagement. The company's investment of over ¥100 million in local development and environmental initiatives in 2023 highlights its efforts to address these social considerations.
Public perception remains a key factor, with a need to balance the benefits of energy security against environmental and social impacts. Proactive community engagement and clear communication on mitigation efforts are crucial for maintaining public trust and a social license to operate. The company's commitment to poverty alleviation, education, and disaster relief further shapes its societal contribution.
| Societal Aspect | Key Data/Initiative (2023/2024 Projections) | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Provision | Installed Capacity: ~70.25 million kW | Supports national energy security and economic development. |
| Resettlement Impact | Three Gorges Dam: >1.3 million relocated | Ongoing social implications requiring careful management. |
| Community Investment | Local Development & Environment: >¥100 million invested | Aims to foster positive community relations and address social concerns. |
| Job Creation | Three Gorges Dam construction phase | Tens of thousands of jobs created; ongoing economic support. |
Technological factors
Technological advancements are significantly reshaping China's hydropower sector. The nation is actively pursuing smart hydropower systems, leveraging AI, big data analytics, and real-time monitoring to boost efficiency and performance, particularly in large cascade power stations.
China Yangtze Power, managing some of the globe's most substantial dams like the Three Gorges Dam, is both a beneficiary and a driver of these technological leaps. For instance, in 2023, the company reported that its smart hydropower units achieved an average utilization rate of 90%, a notable increase attributed to these integrated technologies.
Pumped storage hydropower (PSH) development is a significant technological factor for China Yangtze Power. In 2024 alone, China added a substantial 7.75 GW of new PSH capacity, highlighting a strong national commitment to this technology.
China Yangtze Power is actively participating in this trend, approving and developing new PSH projects like the HouSihe station. These projects are crucial for improving grid stability and facilitating the integration of intermittent renewable energy sources such as wind and solar power.
The nation's investment in PSH is robust, with projections indicating China will surpass its 2030 target of 120 GW of PSH capacity. This expansion directly benefits companies like China Yangtze Power by providing opportunities for growth and infrastructure development.
China Yangtze Power is actively championing the integration of multi-energy systems, particularly its 'water-wind-electricity integration' strategy. This approach aims to create more robust and adaptable power grids by synergistically combining hydropower with wind, solar, and energy storage solutions.
This multi-energy complementarity is vital for China's energy transition, facilitating greater utilization of renewable resources and supporting ambitious carbon reduction targets. For instance, by 2023, China's installed capacity of renewable energy sources, including wind and solar, surpassed 1.4 billion kilowatts, underscoring the growing importance of integrating these variable sources with stable hydropower.
AI-Powered Operations and Dispatch
China Yangtze Power is leveraging AI-powered dispatch systems and advanced monitoring to boost operational efficiency. These technologies enable precise control over power output, crucial for managing peak demand and grid stability, especially with the rise of renewable energy sources. For instance, by mid-2024, the company reported that its intelligent dispatch systems contributed to a more than 5% improvement in hydropower generation efficiency across its key facilities.
The integration of AI allows for more sophisticated peak shaving and frequency regulation capabilities. This is vital as China's grid increasingly incorporates variable sources like solar and wind power, requiring flexible and responsive hydropower to maintain balance. China Yangtze Power's strategic investments in these smart grid technologies are designed to enhance grid reliability and optimize the utilization of its vast hydropower assets.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: AI-driven dispatch systems are improving hydropower plant operations by over 5% in efficiency as of mid-2024.
- Grid Stability Support: Advanced monitoring and AI allow for precise control of power output, aiding peak shaving and frequency regulation.
- Renewable Integration: These technologies are critical for managing a grid with high penetration of intermittent renewable energy sources.
Global Technological Leadership and Export
China's technological leadership in hydropower is a significant factor, with companies like PowerChina, a major player in the sector where China Yangtze Power operates, extending this expertise globally. This technological advancement, honed through extensive domestic projects, positions Chinese firms as key contractors and operators in international hydropower development.
The advanced technologies and operational experiences accumulated within China serve as valuable benchmarks for global renewable energy initiatives. For instance, China's installed hydropower capacity reached over 419 GW by the end of 2023, showcasing the scale and sophistication of its domestic sector.
- Global Hydropower Exports: Chinese firms are increasingly exporting their hydropower technology and services, contributing to renewable energy infrastructure worldwide.
- Technological Benchmarking: Domestic advancements in turbine efficiency and dam construction techniques provide crucial references for international projects.
- Capacity Growth: China's continuous expansion in hydropower capacity, exceeding 419 GW by late 2023, underscores its technological and engineering capabilities.
Technological advancements are central to China Yangtze Power's strategy, focusing on smart hydropower and pumped storage. By mid-2024, AI-driven dispatch systems boosted efficiency by over 5% in key facilities, enhancing grid stability and renewable integration. China's significant investment in pumped storage, adding 7.75 GW in 2024 alone, provides growth avenues for the company.
| Technology Focus | Impact on China Yangtze Power | Key Data Point (2023/2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Hydropower Systems | Improved operational efficiency, real-time monitoring | 90% average utilization rate for smart units (2023) |
| Pumped Storage Hydropower (PSH) | Grid stability, renewable integration, growth opportunities | 7.75 GW new PSH capacity added nationally (2024) |
| AI & Data Analytics | Optimized power output, peak shaving, frequency regulation | >5% improvement in generation efficiency from AI dispatch (mid-2024) |
Legal factors
China's Energy Law, effective January 1, 2025, is a significant development for the energy sector. It mandates a minimum of 30% renewable energy in total consumption by 2030, a target that directly influences companies like China Yangtze Power.
This legislation also introduces a robust green electricity certificate system, incentivizing the generation and trading of renewable energy. This framework is designed to accelerate the nation's progress towards its dual-carbon goals, aiming for peak emissions before 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060.
China Yangtze Power is subject to stringent environmental protection laws and regulations, reflecting a national focus on ecological preservation and sustainable development. The company actively engages in initiatives aimed at minimizing its ecological footprint, such as reforestation programs and adherence to comprehensive ecological governance plans.
Demonstrating its commitment to environmental stewardship, China Yangtze Power reported zero environmental pollution incidents or penalties during the first half of 2024. This performance underscores the company's dedication to operational integrity and compliance within China's evolving environmental regulatory landscape.
China's commitment to energy efficiency is highlighted by its 2024-2025 action plan, which targets a 13.5% reduction in energy consumption per unit of GDP by 2025, using 2020 as a baseline. This national push directly impacts energy producers like China Yangtze Power.
China Yangtze Power plays a crucial role in meeting these ambitious energy saving and carbon reduction goals. The company's focus on efficient power generation and the expansion of its clean energy portfolio directly supports the nation's drive towards sustainability.
A key component of this national strategy is the goal to increase non-fossil energy consumption to 20% by 2025. China Yangtze Power's investments in renewable energy sources are vital for achieving this significant shift in the country's energy mix.
Dam Safety and Operational Regulations
China Yangtze Power operates under a rigorous legal framework governing dam safety and operational procedures, a critical aspect given the immense scale of its hydropower facilities. These regulations are designed to guarantee the structural integrity and safe operation of key assets, including the monumental Three Gorges Dam and its associated cascade stations.
Compliance with these stringent legal requirements is paramount for ensuring the long-term reliability and safety of China's vital hydropower infrastructure. The government actively monitors adherence to these standards to mitigate the risk of operational failures or accidents. For instance, regulations often mandate detailed inspection schedules and maintenance protocols, with penalties for non-compliance. In 2023, the Ministry of Water Resources continued to emphasize enhanced safety checks across major dams, reflecting an ongoing commitment to regulatory oversight.
- Dam Safety Standards: Adherence to national standards for structural integrity, seismic resistance, and flood control capacity is mandatory for all major hydropower installations.
- Operational Protocols: Strict guidelines govern water release, power generation, and emergency response procedures to ensure safe and efficient operation.
- Environmental Impact Assessments: Legal frameworks require thorough environmental assessments and mitigation plans for new projects and ongoing operations to minimize ecological disruption.
- Regulatory Oversight: Government bodies conduct regular inspections and audits to verify compliance with safety and operational regulations, with enforcement mechanisms in place for violations.
Water Resource Management and International Accords
China Yangtze Power's operations, particularly concerning large dams on transboundary rivers, are influenced by international water resource management principles. While specific legal frameworks are not always explicit, adherence to potential international agreements or diplomatic understandings regarding water sharing is crucial for smooth operations and maintaining regional stability.
Downstream nations' concerns, such as India's discussions regarding projects on the Yarlung Zangbo river, underscore the importance of careful legal and diplomatic engagement. This highlights the potential for international legal scrutiny and the need for proactive water diplomacy to mitigate disputes and ensure equitable resource utilization.
- International Water Law: Adherence to principles of international water law, though often customary, guides the management of transboundary water resources.
- Diplomatic Engagements: China participates in bilateral and multilateral discussions on water resource management, impacting projects on shared river basins.
- Downstream Concerns: India's expressed concerns in 2023-2024 regarding water flow from upstream projects emphasize the legal and diplomatic sensitivity of transboundary water management.
The legal landscape for China Yangtze Power is shaped by national energy policies and environmental regulations, including the new Energy Law effective January 1, 2025, which mandates a 30% renewable energy share by 2030. Stringent dam safety standards and operational protocols are critical, with the Ministry of Water Resources emphasizing enhanced safety checks in 2023. Furthermore, international water law principles and diplomatic engagements are increasingly important for managing transboundary rivers, with downstream nations like India raising concerns about water flow.
| Legal Area | Key Regulation/Principle | Impact on China Yangtze Power | Data Point/Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Policy | China Energy Law (effective Jan 1, 2025) | Mandates 30% renewable energy by 2030. | Company must increase renewable generation capacity. |
| Environmental Regulation | Ecological Preservation Laws | Requires minimizing ecological footprint. | Reported zero environmental pollution incidents/penalties in H1 2024. |
| Dam Safety | National Dam Safety Standards | Ensures structural integrity and safe operation. | Ministry of Water Resources emphasized enhanced safety checks in 2023. |
| International Water Law | Transboundary Water Management Principles | Influences operations on shared rivers. | India's concerns in 2023-2024 regarding Yarlung Zangbo river projects. |
Environmental factors
China Yangtze Power's extensive hydropower operations are a cornerstone in China's ambitious carbon reduction strategy. By harnessing the power of water, the company directly supports the nation's commitment to peaking carbon emissions before 2030 and reaching carbon neutrality by 2060.
These clean energy projects are crucial in diminishing the country's dependence on coal and other fossil fuels. In 2023 alone, China Yangtze Power's generation is estimated to have avoided the emission of over 100 million tons of CO2 equivalent compared to if that electricity had been produced from thermal power plants.
While China Yangtze Power's hydroelectric projects, like the Three Gorges Dam, offer significant clean energy, their ecological footprint is a major concern. These massive structures alter river flow, impacting aquatic life and disrupting natural sediment transport. For instance, the Three Gorges Dam, completed in 2012, has been linked to changes in downstream water temperatures and increased erosion along its banks.
Environmental groups frequently highlight the dam's effect on fish migration patterns, particularly for endangered species like the Chinese sturgeon, whose breeding grounds have been affected. Furthermore, concerns persist regarding the geological stability of the reservoir region and the potential for increased seismic activity, a factor closely monitored by authorities and the company.
China Yangtze Power acknowledges these challenges and invests in mitigation strategies. This includes ongoing research into fish passage technologies and habitat restoration efforts. The company also reports extensive geological monitoring around its dams, aiming to preemptively address any stability issues, though specific financial outlays for these environmental programs are often integrated within broader operational budgets.
Hydropower generation, a cornerstone of China Yangtze Power's operations, is intrinsically linked to water inflow, which is increasingly susceptible to seasonal shifts and the unpredictable impacts of climate change. These environmental factors directly influence the reliability and volume of electricity produced.
For instance, the first half of 2025 presented a mixed picture for China Yangtze Power's major reservoirs. The Three Gorges Reservoir recorded a notable 8.39% reduction in water inflow compared to historical averages. Conversely, the Wudongde Reservoir experienced an increase in its water inflow during the same period.
Navigating these fluctuating water levels, driven by evolving weather patterns attributed to climate change, poses a significant environmental and operational hurdle for the company. Adapting to and mitigating the effects of such variability is crucial for sustained output and strategic planning.
Reforestation and Biodiversity Initiatives
China Yangtze Power actively engages in reforestation and biodiversity initiatives, demonstrating a commitment to environmental stewardship. A notable project along the Yangtze River aims to plant 10 million trees by 2025, directly contributing to ecological restoration.
These proactive measures go beyond their core power generation operations, focusing on enhancing biodiversity and mitigating climate change impacts. Such initiatives are crucial for long-term sustainability and align with increasing global environmental awareness and regulatory pressures.
- Reforestation Target: 10 million trees by 2025 along the Yangtze River.
- Biodiversity Enhancement: Efforts to restore and protect local ecosystems.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Contribution to carbon sequestration and environmental resilience.
Commitment to Sustainable Development
China Yangtze Power's commitment to sustainable development is a cornerstone of its operations, emphasizing environmental stewardship. The company actively works to reduce its ecological footprint, aligning with national environmental protection laws and integrating ecological considerations into its business strategy. This commitment is evident in initiatives like the development of 'zero-carbon dam areas', showcasing a forward-thinking approach to energy production.
In 2023, China Yangtze Power continued to invest in green energy, with its renewable energy sources contributing significantly to its power generation mix. The company reported a substantial increase in its hydropower output, underscoring its role in China's transition to cleaner energy. For instance, its hydropower generation capacity reached new heights, supporting the national goal of carbon neutrality.
- Hydropower Dominance: China Yangtze Power operates some of the largest hydropower stations globally, including the Three Gorges Dam, contributing over 100 billion kilowatt-hours annually.
- Green Energy Investments: The company is actively expanding its portfolio to include wind and solar power, aiming to diversify its renewable energy sources.
- Environmental Compliance: Adherence to stringent environmental regulations is a key operational principle, with ongoing efforts to monitor and mitigate the environmental impact of its facilities.
- Zero-Carbon Initiatives: The company is pioneering 'zero-carbon dam areas', integrating advanced technologies to minimize emissions and enhance ecological preservation around its projects.
Climate change significantly impacts China Yangtze Power's operations, affecting water inflow to its hydropower facilities. While the Three Gorges Reservoir saw an 8.39% reduction in water inflow in early 2025 compared to averages, other reservoirs like Wudongde experienced increases, highlighting the variability.
The company's commitment to environmental stewardship is demonstrated through reforestation efforts, with a target of planting 10 million trees by 2025 along the Yangtze River to enhance biodiversity and climate resilience.
China Yangtze Power's extensive hydropower generation, exceeding 100 billion kilowatt-hours annually from facilities like the Three Gorges Dam, directly supports China's carbon reduction goals, having avoided over 100 million tons of CO2 equivalent emissions in 2023 compared to thermal power.
However, large-scale projects like the Three Gorges Dam have ecological consequences, including altered river flows and impacts on aquatic life, prompting ongoing research into mitigation strategies and geological monitoring.
| Environmental Factor | Impact on China Yangtze Power | 2023/2025 Data/Initiatives |
|---|---|---|
| Climate Change/Water Inflow Variability | Affects hydropower generation reliability and volume. | Three Gorges Reservoir inflow down 8.39% in early 2025 vs. average; Wudongde Reservoir inflow increased. |
| Ecological Footprint of Hydropower | Altered river flow, impact on aquatic life, sediment transport. | Ongoing research into fish passage technologies and habitat restoration. |
| Carbon Reduction Strategy Alignment | Supports China's goals of peaking emissions before 2030 and carbon neutrality by 2060. | Estimated over 100 million tons CO2 equivalent avoided in 2023. |
| Biodiversity and Reforestation | Mitigation of environmental impact, ecological restoration. | Target of 10 million trees planted by 2025 along the Yangtze River. |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our China Yangtze Power PESTLE Analysis is meticulously constructed using data from official Chinese government bodies, international financial institutions like the World Bank, and leading industry research firms. This ensures comprehensive coverage of political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting the company.
