Centre Testing International Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Centre Testing International Group Bundle
Centre Testing International Group operates in a dynamic market shaped by intense rivalry and significant buyer power. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its competitive landscape effectively. The threat of new entrants and the bargaining power of suppliers also play pivotal roles in its strategic positioning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Centre Testing International Group’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Centre Testing International Group (CTI) depends heavily on specialized equipment and advanced software for its testing services. If the number of providers for these critical technologies is limited, these suppliers gain significant bargaining power. This can translate into higher costs for CTI, especially for sophisticated, cutting-edge systems like those employing AI for inspection.
For instance, the market for advanced material testing equipment, particularly those integrating novel sensor technologies or complex data analytics platforms, often features a concentrated supplier base. In 2024, the global market for testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) equipment saw continued demand for specialized solutions, with a significant portion of innovation driven by a few key technology developers. This concentration means suppliers of these essential tools can command premium pricing, directly impacting CTI's operational expenses and profitability.
The Testing, Inspection, and Certification (TIC) industry, including Centre Testing International Group (CTI), heavily relies on a workforce possessing specialized skills. This includes engineers, scientists, and accredited inspectors who are crucial for delivering accurate and reliable services. The demand for these experts is high, and a scarcity of such talent can significantly shift the balance of power toward the employees.
When there's a limited pool of highly skilled personnel, their ability to negotiate for better compensation and benefits increases. This directly translates into higher labor costs for companies like CTI. For instance, in 2024, the global shortage of skilled labor in technical fields remained a persistent challenge, with some reports indicating that specialized engineering roles faced recruitment difficulties lasting several months.
As the TIC sector continues to embrace technological advancements, the need for professionals with expertise in areas like AI, data analytics, and advanced materials science will only grow. This evolving landscape means that the bargaining power of highly skilled personnel is likely to remain a significant factor influencing operational costs and competitive strategy for CTI.
While not direct suppliers in the traditional sense, accreditation bodies and regulatory authorities wield significant power over Centre Testing International Group (CTI). These entities set the operational standards and certification requirements CTI must meet. Their influence is substantial because failure to comply can lead to a complete cessation of business activities, making CTI highly reliant on their ever-changing mandates and rigorous auditing procedures.
IT and Digital Solution Providers
The bargaining power of IT and digital solution providers for Centre Testing International Group (CTI) is on the rise due to the increasing digitalization of Testing, Inspection, and Certification (TIC) services. CTI's integration of technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain necessitates deeper reliance on these specialized IT partners.
If these providers offer unique or patented solutions, their leverage increases significantly. For instance, a provider with a proprietary AI algorithm for anomaly detection in testing could command higher prices or more favorable terms. The global market for IT services in the TIC sector is expected to grow substantially. In 2024, the digital transformation within the TIC industry is a key driver, with investments in cloud computing and data analytics solutions projected to accelerate.
- Growing Dependence: CTI's strategic push into advanced digital services amplifies its need for specialized IT and digital solutions.
- Differentiated Offerings: Providers with unique, proprietary technologies, such as advanced AI analytics or secure blockchain platforms, hold stronger bargaining positions.
- Market Dynamics: The increasing demand for digital transformation in the TIC sector, with global IT spending in this area seeing robust growth in 2024, empowers these suppliers.
- Switching Costs: High costs associated with integrating and migrating from specialized IT systems can further strengthen supplier power.
Raw Materials for Laboratory Consumables
Centre Testing International Group (CTI) relies on various laboratory consumables and reagents for its physical and chemical testing services. While the market for these materials is generally fragmented, the bargaining power of suppliers can become moderate if they offer specialized or rare materials. This is particularly true when supply chain disruptions occur or when alternative sources are scarce.
The availability of specialized chemicals and high-purity reagents can significantly influence supplier power. For instance, if CTI requires a unique chemical compound for a niche testing application, the supplier of that specific compound might command higher prices or dictate terms due to limited competition. In 2024, the global laboratory consumables market was valued at approximately $75 billion, with growth driven by increased R&D spending and demand for advanced testing methodologies.
- Supplier Concentration: The bargaining power of suppliers is higher when the market for specific consumables is concentrated among a few key players.
- Input Differentiation: Suppliers of unique or proprietary reagents have greater power compared to those providing standard, commoditized items.
- Switching Costs: If CTI faces significant costs or delays in switching to a different supplier for critical consumables, existing suppliers gain leverage.
- Threat of Forward Integration: While less common for raw material suppliers in this sector, a supplier's ability to potentially offer testing services themselves could alter the power dynamic.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Centre Testing International Group (CTI) is influenced by the availability and specialization of critical inputs, ranging from advanced equipment to skilled labor. Limited competition among providers of specialized testing technology or unique IT solutions can lead to higher costs for CTI, as seen in the concentrated market for AI-driven inspection systems. Similarly, a scarcity of highly skilled engineers and scientists in 2024, a persistent global challenge, allows these professionals to negotiate better compensation, increasing CTI's labor expenses.
The reliance on specialized laboratory consumables also presents a dynamic where suppliers of unique or rare materials can exert greater influence, particularly during supply chain disruptions. For instance, the global laboratory consumables market, valued at approximately $75 billion in 2024, sees suppliers of niche, high-purity reagents commanding higher prices due to limited alternatives. This concentration of power among key technology developers and specialized talent pools directly impacts CTI's operational costs and strategic flexibility.
What is included in the product
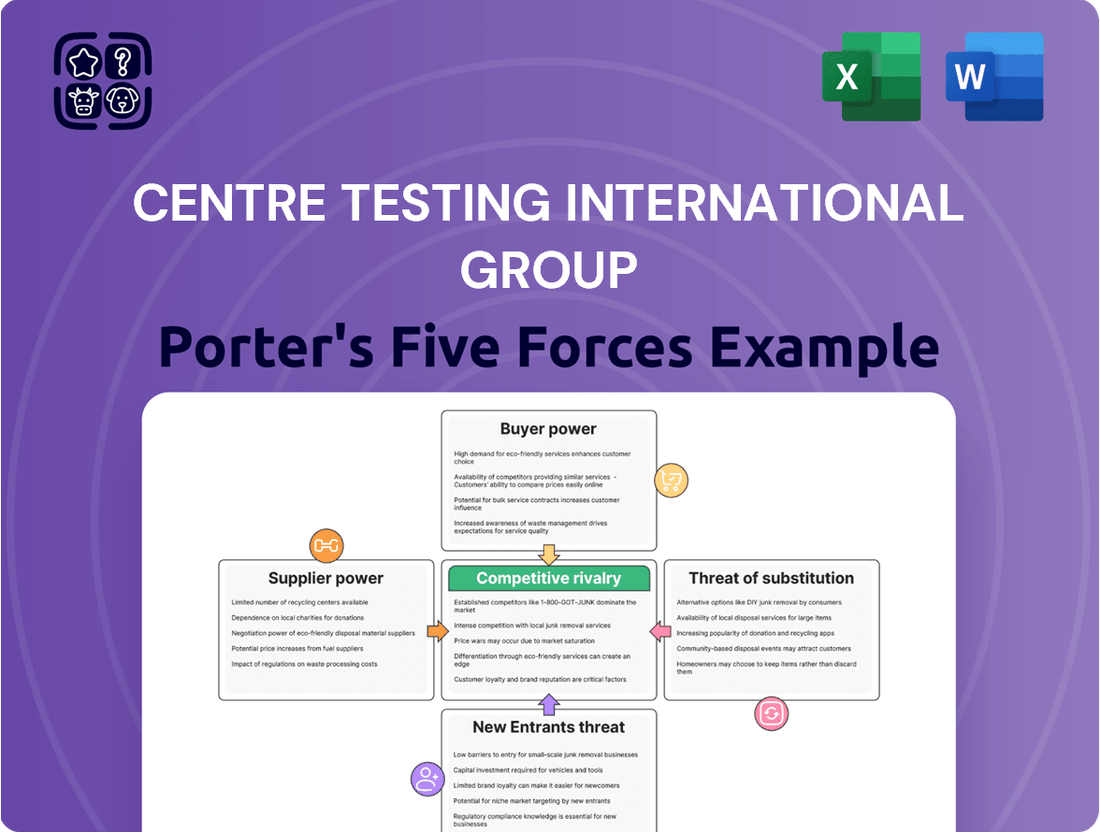
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Centre Testing International Group, evaluating the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry, and the threat of substitutes.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a comprehensive, yet easily digestible, Porter's Five Forces analysis for Centre Testing International Group.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers in sectors like automotive and electronics, which Centre Testing International Group (CTI) serves, often grapple with complex and evolving regulatory landscapes. For instance, the European Union's REACH regulations for chemicals, or the stringent safety standards for medical devices, necessitate rigorous testing and certification. This regulatory burden means customers cannot easily bypass essential compliance services, thereby reducing their leverage.
For many manufacturers, Centre Testing International Group's (CTI) testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) services are not just beneficial, they are essential for accessing key global markets. Without CTI's approvals, products might be barred from sale, creating a significant dependency.
This criticality directly translates into substantial bargaining power for CTI's customers, as they often face stringent regulatory hurdles. For instance, in 2024, the global TIC market was valued at approximately $230 billion, highlighting the immense scale of these essential services and the critical role CTI plays within it.
Centre Testing International Group's (CTI) customers, particularly large enterprises or those with substantial testing and certification needs, wield significant bargaining power. These clients, by virtue of their scale, can often negotiate more favorable pricing or customized service agreements. For instance, in 2023, CTI reported revenue of approximately RMB 1.4 billion, indicating a diverse client base where larger accounts likely represent a considerable portion of this figure, thus amplifying their negotiation leverage.
Availability of Alternative TIC Providers
While Centre Testing International Group (CTI) benefits from specialized expertise, the broader Testing, Inspection, and Certification (TIC) market is characterized by a significant number of alternative providers. This competitive landscape, featuring both large global players and numerous smaller, niche firms, directly impacts customer bargaining power. Customers can indeed switch providers if they are dissatisfied with CTI's services or pricing, granting them a degree of leverage.
The availability of these alternatives means that customers are not entirely dependent on CTI. For instance, in 2024, the global TIC market was valued at over $200 billion, with many companies offering a wide array of services. This sheer volume of choice allows customers to shop around for the best combination of price, quality, and responsiveness, thereby increasing their ability to negotiate favorable terms or seek out competitors if their needs are not met.
- High Market Saturation: The TIC industry is populated by many established global firms and a growing number of regional and specialized players, offering customers a wide selection.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers can leverage the presence of competitors to negotiate better pricing for TIC services, especially for standardized testing or inspection requirements.
- Service Differentiation: While CTI may have specialized expertise, customers can still find providers offering similar core services, making switching a viable option for those prioritizing specific aspects like speed or cost.
- Global Reach of Competitors: Major international TIC companies operate across numerous geographies, providing customers with readily available alternatives to local or regional providers like CTI.
Customer's Internal Testing Capabilities
Centre Testing International Group (CTI) may encounter customers possessing their own internal testing facilities. This capability, particularly among larger clients, can act as a counter-balance, reducing their reliance on external providers like CTI. While these in-house labs might not carry the same weight of accreditation as third-party specialists, their existence still grants customers a degree of leverage in negotiations.
The existence of internal testing capabilities can influence pricing and service demands. For instance, if a significant client operates its own testing infrastructure, it might negotiate for lower rates from CTI, citing the cost savings it achieves by handling some testing internally. This can be particularly true in sectors where standardized testing protocols are well-established and can be replicated with readily available equipment.
- Customer Leverage: In-house testing facilities provide customers with a credible alternative, even if less accredited, which can be used to negotiate terms with third-party testing providers.
- Cost Influence: Clients with internal testing may seek reduced service fees from CTI, reflecting their own cost efficiencies in performing certain tests.
- Market Dynamics: The prevalence of internal testing capabilities within a customer base can shape the competitive landscape for testing service providers, potentially impacting market share and profitability.
Centre Testing International Group's (CTI) customers possess considerable bargaining power due to the critical nature of TIC services for market access. This dependency, however, is tempered by the sheer scale of the global TIC market, valued at over $200 billion in 2024, and the presence of numerous alternative providers. Customers can leverage this competitive environment to negotiate better pricing and terms.
The ability for customers to switch providers, driven by market saturation and the availability of similar core services, significantly enhances their negotiation leverage. For instance, the vastness of the TIC sector means clients can readily find other firms offering comparable testing and certification, especially for standardized needs. This dynamic allows customers to effectively shop around, ensuring they secure the most advantageous service agreements.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Market Saturation & Alternatives | Increases bargaining power | Global TIC market > $200 billion (2024); numerous competitors offer similar services. |
| Switching Costs | Low for standardized services | Customers can readily find alternative providers if dissatisfied with CTI's pricing or quality. |
| Customer Scale & Needs | Increases bargaining power for large clients | Large enterprises with substantial testing needs can negotiate favorable pricing and customized agreements. CTI's 2023 revenue was ~RMB 1.4 billion, indicating potential for large account influence. |
| Internal Testing Capabilities | Increases bargaining power | Customers with in-house labs can use this as leverage to negotiate lower fees with third-party providers like CTI. |
Same Document Delivered
Centre Testing International Group Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the detailed Porter's Five Forces analysis for Centre Testing International Group, providing a comprehensive examination of competitive forces within its industry. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring transparency and immediate usability. You'll gain insights into the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products, all presented in this ready-to-use analysis.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) market is incredibly crowded, featuring big global names like SGS, Bureau Veritas, and Intertek, alongside many smaller local and regional companies. This means Centre Testing International Group faces competition from all sides, making it tough to stand out.
This intense rivalry forces companies to focus on what they do best: offering top-notch service, demonstrating deep technical knowledge, and delivering results quickly. For Centre Testing International Group, excelling in these areas is crucial to winning and keeping clients in such a competitive landscape.
Centre Testing International Group (CTI) and its rivals operate in a landscape where diversification is key, leading to intense competition across numerous sectors. Companies like CTI offer services spanning consumer products, industrial goods, food safety, environmental testing, and automotive assessments. This wide reach means that competition isn't confined to a single market but unfolds on multiple fronts, requiring continuous innovation and adaptation to stay ahead.
In 2024, the testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) market, which CTI actively participates in, continued its robust growth. For instance, the global TIC market was projected to reach over $250 billion by 2024, highlighting the significant opportunities but also the crowded nature of the industry. Competitors are actively expanding their service portfolios and geographical footprints to capture market share in these diverse segments, intensifying the rivalry for CTI.
The competitive landscape for Centre Testing International Group (CTI) is significantly shaped by rapid technological advancements and the ongoing digitalization of testing and inspection services. Companies are fiercely competing to integrate cutting-edge technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and advanced automation into their core operations. This drive for innovation is crucial for enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and the overall value proposition offered to clients.
CTI, like its rivals, faces the imperative to continuously invest in these evolving technologies to remain competitive. For instance, the adoption of AI in data analysis and predictive maintenance can streamline processes, while IoT sensors can provide real-time monitoring and data collection, offering more comprehensive insights. Failure to keep pace with these technological shifts could lead to a loss of market share as competitors offering more advanced, digitally-enabled solutions gain traction.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance Expertise
The ability to successfully navigate a complex and constantly changing regulatory environment is a significant driver of competition within the testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) industry. Companies that demonstrate robust expertise in both international standards and specific local compliance requirements often secure a distinct advantage. For instance, in 2024, the European Union continued to emphasize stringent regulations around product safety and sustainability, impacting sectors like electronics and textiles. Companies adept at managing these evolving mandates, such as those providing CE marking certification, found themselves in higher demand.
This regulatory expertise translates directly into a competitive edge, as clients increasingly seek partners who can ensure their products meet all necessary legal and safety obligations across diverse markets. A strong track record in compliance can reduce client risk and streamline market access. For example, adherence to updated cybersecurity standards in the automotive sector, a growing concern in 2024, became a critical differentiator for TIC providers.
- Regulatory complexity is a key competitive factor in the TIC sector.
- Expertise in international and local compliance offers a significant advantage.
- Companies demonstrating strong regulatory navigation skills attract more clients seeking to mitigate risk.
- Evolving standards in areas like product safety and cybersecurity in 2024 highlighted the importance of compliance proficiency.
Mergers, Acquisitions, and Strategic Partnerships
Mergers, acquisitions, and strategic partnerships are significant drivers of competitive rivalry within the Testing, Inspection, and Certification (TIC) sector, including for entities like Centre Testing International Group. Companies actively pursue these strategies to broaden their service offerings, extend their geographical presence, and solidify their market standing. This consolidation trend naturally intensifies competition as larger, more integrated players emerge.
For instance, in 2024, the TIC industry continued to witness substantial M&A activity. Bureau Veritas, a major player, announced several acquisitions aimed at strengthening its position in key growth areas like digital services and sustainability testing. Similarly, SGS continued its strategic expansion through targeted acquisitions, enhancing its capabilities in specialized sectors. These moves often lead to a more concentrated market, increasing the pressure on remaining independent or smaller firms.
Strategic partnerships also play a crucial role in shaping the competitive landscape. Companies collaborate to share resources, develop new technologies, and gain access to new markets, thereby improving operational efficiency and creating mutual benefits. These alliances can create formidable competitive advantages, forcing other market participants to either join similar collaborations or face increased competitive pressure.
- Increased Market Consolidation: M&A activity in the TIC sector, particularly in 2024, has led to a more consolidated market, raising the stakes for competitive positioning.
- Service Portfolio Expansion: Companies are acquiring or partnering to gain access to new service lines, such as advanced material testing or cybersecurity certification, to meet evolving client demands.
- Geographical Reach Enhancement: Acquisitions often serve to expand a company's footprint into new regions, allowing them to serve a broader international client base and intensifying competition in those new markets.
- Technological Advancement: Partnerships are frequently formed to co-develop or integrate new technologies, like AI-driven inspection tools, providing a competitive edge through innovation.
The testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) market is highly competitive, with numerous global and regional players vying for market share. Centre Testing International Group (CTI) faces intense rivalry from established giants like SGS, Bureau Veritas, and Intertek, as well as a multitude of smaller, specialized firms. This crowded field necessitates a strong focus on service quality, technical expertise, and rapid delivery to retain and attract clients.
In 2024, the global TIC market was estimated to be worth over $250 billion, underscoring the significant opportunities but also the fierce competition. Companies are actively expanding their service offerings and geographical reach to capture a larger portion of this growing market, intensifying the challenge for CTI. This competitive pressure drives innovation, particularly in adopting new technologies like AI and IoT to enhance efficiency and value.
The ability to navigate complex and evolving regulatory landscapes is a critical differentiator. Companies with deep expertise in international standards and local compliance, such as those adept at CE marking or automotive cybersecurity standards in 2024, gain a distinct advantage. This regulatory proficiency is essential for clients aiming to minimize risk and ensure smooth market access, making it a key battleground for TIC providers.
Mergers, acquisitions, and strategic partnerships are reshaping the competitive dynamics within the TIC sector. In 2024, significant M&A activity saw major players like Bureau Veritas and SGS expanding their capabilities and market presence. These consolidation efforts increase pressure on independent firms like CTI, necessitating strategic alliances or acquisitions to maintain competitiveness and expand service portfolios.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The primary substitute for Centre Testing International Group's (CTI) third-party testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) services is a client's own in-house testing capabilities or the practice of self-certification. Many companies maintain their own laboratories and quality control departments to perform necessary checks. For example, in 2023, a significant portion of manufacturing firms continued to rely on internal quality assurance processes, especially for routine product checks.
However, these in-house efforts often fall short when compared to the independent credibility, rigorous regulatory recognition, and specialized accreditations that external TIC providers like CTI possess. Self-certification, while cost-effective for basic compliance, may not satisfy international standards or gain the trust of global markets. CTI's accreditations, such as ISO 17025 for testing and calibration laboratories, are crucial for market access and consumer confidence, a level of assurance difficult and expensive to replicate internally.
The threat from substitutes is mitigated by the increasing complexity of global regulations and the demand for universally recognized certifications. For instance, the expansion of standards in sectors like renewable energy and advanced materials in 2024 necessitates specialized expertise and equipment that many companies find uneconomical to develop in-house. CTI's ability to offer a broad range of accredited services across diverse industries positions it favorably against the limitations of in-house testing and self-certification.
For many regulated sectors, the threat of substitutes is minimal because certified compliance is often non-negotiable. Products lacking proper testing and certification simply cannot legally enter these markets or fulfill essential requirements, effectively eliminating direct substitutes for crucial services.
In 2024, industries like aerospace, medical devices, and food safety continue to demonstrate this reliance on certification. For instance, the medical device market, valued at over $600 billion globally in 2024, requires stringent FDA or CE marking, making uncertified alternatives non-viable for patient care.
Emerging technologies in quality assurance, such as advanced sensors and real-time monitoring systems, could potentially reduce the reliance on certain traditional inspection services offered by companies like Centre Testing International Group (CTI). For instance, the widespread adoption of IoT devices capable of continuous, automated data collection might lessen the demand for periodic, on-site physical inspections in some sectors.
Predictive analytics, powered by AI and machine learning, can also offer a substitute by identifying potential quality issues before they manifest, thereby decreasing the need for reactive testing. While CTI's 2023 revenue was approximately €1.5 billion, indicating a strong market position, the growing capability of these technological substitutes poses a long-term threat to specific service lines within the TIC industry.
Industry-Specific Software and Digital Tools
The rise of industry-specific software and digital tools presents a notable threat of substitutes for Centre Testing International Group (CTI). These platforms can automate certain compliance monitoring and preliminary testing functions that CTI traditionally provides. For instance, in 2024, the global market for regulatory technology (RegTech) was projected to reach over $15 billion, indicating a significant investment in digital solutions that can handle compliance tasks internally.
This trend means that clients might opt for these software solutions to manage aspects of their testing and compliance needs in-house, thereby reducing their reliance on external service providers like CTI. Such internal capabilities can offer cost savings and greater control for businesses, especially smaller ones or those with simpler testing requirements.
- Software as a Substitute: Digital platforms offering automated compliance and testing can perform some of CTI's core functions.
- Market Growth: The RegTech market's expansion, with projections exceeding $15 billion in 2024, highlights the increasing adoption of such digital solutions.
- Client Impact: Businesses might leverage these tools for cost efficiency and internal control, potentially shrinking the market for outsourced testing services.
Alternative Compliance Mechanisms
In sectors with lighter regulation, companies might explore alternative compliance methods, such as industry-led self-regulation. While these can offer flexibility, they generally lack the robust validation provided by independent, third-party certifications. For instance, a sector might adopt voluntary codes of conduct, but these may not carry the same weight or public trust as a certified process. This creates a potential substitute that, while less stringent, could appeal to businesses seeking to reduce the cost and complexity associated with formal accreditation.
These alternative mechanisms can pose a threat by drawing away demand from more rigorous certification services. Consider the case of emerging technology sectors where standards are still evolving. Businesses in these areas might opt for internal quality checks or peer reviews rather than seeking formal certification, especially if the latter is perceived as slow or overly burdensome. This trend could impact the market share of established certification bodies like Centre Testing International Group (CTI).
- Reduced Demand: Alternative compliance methods can siphon off potential clients who find third-party certification too costly or time-consuming.
- Lower Barrier to Entry: Self-regulation or industry codes often have lower entry barriers, making them more accessible to smaller or newer businesses.
- Perceived Equivalence: In some cases, businesses might perceive self-audited compliance as functionally equivalent to third-party certification, especially if the risks are deemed low.
- Evolving Standards: As new industries develop, they may create their own compliance frameworks that bypass traditional certification routes.
The threat of substitutes for Centre Testing International Group (CTI) primarily stems from clients' in-house capabilities and the growing availability of specialized software. While self-certification offers cost savings, it often lacks the independent credibility and regulatory recognition that CTI provides through its accreditations, such as ISO 17025. The increasing complexity of global regulations in sectors like medical devices, which require stringent certifications like FDA or CE marking, reinforces the value of third-party TIC services, making uncertified alternatives non-viable for market access.
Emerging technologies like IoT sensors and AI-powered predictive analytics also present a substitute threat by enabling continuous, automated quality assurance, potentially reducing the need for periodic on-site inspections. Furthermore, the burgeoning Regulatory Technology (RegTech) market, projected to exceed $15 billion in 2024, offers digital platforms that can automate compliance monitoring, allowing businesses to manage more testing functions internally and potentially reducing their reliance on external providers.
Entrants Threaten
The testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) industry, particularly for specialized areas like electronics or advanced materials, demands substantial upfront capital. Newcomers must invest heavily in state-of-the-art laboratories, sophisticated testing equipment, and cutting-edge technology to meet industry standards and client expectations. For instance, setting up a laboratory capable of advanced semiconductor failure analysis can easily run into millions of dollars, creating a significant hurdle for potential competitors.
New entrants into the testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) sector, like Centre Testing International Group (CTI), face significant hurdles in acquiring the deep technical expertise and highly skilled workforce necessary to operate effectively. This is particularly true in specialized fields requiring advanced scientific knowledge and practical experience, creating a substantial barrier to entry.
Furthermore, obtaining the numerous stringent accreditations and certifications from diverse national and international regulatory bodies is a time-consuming and costly process. For instance, in 2024, the global TIC market was valued at approximately $230 billion, with compliance and accreditation forming a core component of market access and credibility.
Established players like Centre Testing International Group (CTI) leverage deep-seated client relationships and a robust brand reputation, cultivated over years of reliable service. These existing bonds create significant loyalty, making it difficult for newcomers to penetrate the market. For instance, CTI's consistent performance in delivering testing and inspection services has fostered trust among its diverse clientele, a trust that takes considerable time and investment to replicate.
Economies of Scale and Scope
Established Testing, Inspection, and Certification (TIC) firms, like Centre Testing International Group (CTI), leverage significant economies of scale and scope. This means they can spread their fixed costs over a larger volume of business and offer a wider range of services efficiently. For instance, a large TIC provider can invest in advanced testing equipment and global networks, making it challenging for newcomers to match their cost-effectiveness and comprehensive service offerings.
The breadth of services also creates a barrier. Companies that can provide everything from product safety testing to environmental compliance and supply chain audits across numerous industries and regions have a distinct advantage. New entrants typically start with a narrower focus, making it harder to compete with the all-encompassing solutions offered by incumbents. This integrated approach often translates into better pricing and streamlined processes for clients.
Consider the competitive landscape in 2024. Major players in the TIC sector have demonstrated robust revenue streams, with global leaders reporting billions in annual turnover. This financial muscle allows for continuous investment in technology, talent, and market expansion, further solidifying their dominant positions. For example, Bureau Veritas, a key competitor, reported revenues exceeding €6 billion in 2023, highlighting the scale of operations that new entrants must contend with.
- Economies of Scale: Large TIC companies can reduce per-unit costs through high-volume operations, making it difficult for smaller firms to compete on price.
- Economies of Scope: Offering a diverse portfolio of services across multiple industries allows established players to cross-sell and capture a larger share of client business.
- Capital Investment: Significant upfront investment in specialized equipment, accreditations, and global infrastructure is required, posing a substantial barrier to entry.
- Brand Reputation: Long-standing TIC providers have built trust and recognition, which is a valuable asset that new entrants must work hard to establish.
Evolving Regulatory Landscape
The constantly changing and increasing complexity of global regulatory standards acts as a dynamic barrier to entry for new players in the testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) sector. For instance, in 2024, the European Union continued to refine its AI Act regulations, impacting how AI-driven testing solutions must be developed and deployed, requiring significant upfront investment in compliance for any new entrant.
New entrants must continuously adapt to these evolving requirements, which demands substantial investment in specialized knowledge, legal counsel, and robust compliance systems. Failure to do so can lead to penalties and market exclusion, effectively deterring smaller or less capitalized firms from entering the market.
- Evolving Regulatory Complexity: Global regulations are becoming more intricate, demanding specialized expertise and significant compliance investment.
- Increased Compliance Costs: Adapting to new standards, such as those related to AI or environmental reporting, raises the barrier to entry.
- Need for Specialized Knowledge: Staying abreast of and implementing complex regulatory frameworks requires dedicated resources and expertise.
- Investment in Compliance Systems: New entrants must allocate capital to technology and processes that ensure adherence to diverse and changing rules.
The threat of new entrants for Centre Testing International Group (CTI) is moderate due to substantial capital requirements and the need for specialized expertise. Setting up advanced testing facilities can cost millions, and acquiring highly skilled personnel is a significant challenge. For example, in 2024, the global TIC market, valued at around $230 billion, necessitates considerable investment to meet stringent industry standards and client expectations, creating a high barrier for newcomers.
Established players like CTI benefit from strong brand loyalty and deep client relationships, making it difficult for new companies to gain traction. The time and investment required to build comparable trust and recognition are considerable. Furthermore, the sheer scale of operations and the ability to offer a wide array of services across different sectors provide incumbents with cost advantages and a competitive edge that new entrants struggle to match.
| Barrier to Entry | Impact on New Entrants | Example/Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | High | Setting up advanced labs can cost millions. |
| Technical Expertise | High | Requires specialized scientific knowledge and practical experience. |
| Accreditations & Certifications | High | Time-consuming and costly to obtain diverse regulatory approvals. |
| Brand Reputation & Client Relationships | High | Years of reliable service needed to build trust. |
| Economies of Scale/Scope | High | Established firms offer cost efficiencies and comprehensive services. |
| Regulatory Complexity | Moderate to High | Evolving standards (e.g., AI Act) demand continuous investment in compliance. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Centre Testing International Group Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including CTG's annual reports and investor presentations, alongside industry-specific market research from firms like Statista and IBISWorld. We also incorporate publicly available regulatory filings and macroeconomic data to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
