Charles River Laboratories International Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Charles River Laboratories International Bundle
Charles River Laboratories International navigates a complex landscape shaped by intense rivalry and significant buyer power, particularly from large pharmaceutical clients. Understanding these forces is crucial for anticipating market shifts and identifying strategic opportunities.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Charles River Laboratories International’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers significantly impacts Charles River Laboratories' bargaining power. For highly specialized research models or unique biological reagents, a small number of providers can dictate terms and pricing, potentially increasing costs for Charles River. For instance, in 2023, Charles River reported that its cost of goods sold increased by 6.8% year-over-year, partly attributable to input costs.
The uniqueness of inputs significantly influences the bargaining power of suppliers for Charles River Laboratories International. When inputs like specialized research models or proprietary testing reagents have few, if any, viable substitutes, suppliers gain considerable leverage. This scarcity can lead to higher prices and more stringent supply terms, directly impacting Charles River's cost structure and operational flexibility.
A prime example of this dynamic is the supply of non-human primates (NHPs), a crucial component for certain preclinical research studies. Disruptions or limitations in the NHP supply chain, as experienced in recent years, directly affect Charles River's ability to fulfill client demands. In 2023, the global NHP market continued to face supply constraints, with prices for some species seeing double-digit percentage increases year-over-year, underscoring the suppliers' strong bargaining position due to the specialized and regulated nature of these inputs.
High switching costs for Charles River Laboratories International can significantly bolster supplier bargaining power. If transitioning from one supplier to another necessitates costly requalification processes, revalidation of critical research protocols, or risks disrupting ongoing vital studies, suppliers can command higher prices and more favorable terms. This complexity in switching is a key factor in supplier leverage.
Charles River does maintain a database to identify and onboard new suppliers, a process that aims to mitigate these switching costs. However, for highly specialized or established suppliers, the practicalities of switching remain a considerable hurdle. The investment in time, resources, and potential scientific disruption can make changing suppliers a complex and expensive undertaking.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into Charles River Laboratories' core drug discovery and development services is generally low. This is primarily due to the immense complexity and broad spectrum of services Charles River provides, which are difficult for a single specialized supplier to replicate comprehensively.
While most suppliers are unlikely to pose a direct threat, a few niche providers with highly specialized, proprietary technologies could potentially offer more integrated solutions. If such a supplier were to expand their offerings further up the value chain, it could marginally reduce Charles River's market scope in those specific areas, though this remains a limited concern.
- Low Likelihood of Full-Scale Forward Integration: Suppliers typically focus on specific components or services, not the entire drug discovery and development continuum.
- Potential for Niche Service Integration: Highly specialized suppliers might offer more bundled services, impacting Charles River's scope in limited segments.
- Complexity Barrier: Replicating Charles River's diverse service portfolio requires significant investment and expertise, deterring most suppliers.
Impact of Tariffs and Regulations
Tariffs and evolving trade policies can significantly influence the bargaining power of suppliers for Charles River Laboratories. For instance, increased tariffs on essential research materials imported from key sourcing regions like China or Vietnam, which are significant global suppliers, directly escalate procurement costs. In 2023, global trade tensions and specific tariffs imposed on various goods could have impacted the cost of raw materials and components Charles River relies on, thereby strengthening supplier leverage.
Regulatory shifts also play a crucial role. Changes in regulations concerning the ethical sourcing of research materials, animal welfare standards, or the import/export of biological substances can limit the pool of available suppliers or impose additional compliance burdens. This constraint inherently enhances the bargaining power of those suppliers who can meet these stringent requirements, potentially leading to higher prices or more restrictive terms for Charles River.
- Increased import tariffs on research materials from countries like China could raise procurement costs for Charles River.
- Trade policies that restrict the flow of goods can empower suppliers who can navigate or are unaffected by these regulations.
- Stricter regulations on ethical sourcing of research animals or materials empower compliant suppliers.
- Compliance with evolving international regulations can limit Charles River's supplier options, increasing supplier bargaining power.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Charles River Laboratories is influenced by supplier concentration and input uniqueness. When few suppliers provide critical, non-substitutable inputs, like specialized research models or proprietary reagents, their leverage increases, potentially driving up costs. For example, the NHP market in 2023 saw double-digit price increases for certain species due to supply constraints, highlighting supplier strength.
High switching costs for Charles River also empower suppliers. The expense and complexity of requalifying research protocols or risking study disruptions when changing suppliers can lead to suppliers commanding higher prices and more favorable terms. This is a significant factor in their leverage, even with Charles River’s efforts to onboard new suppliers.
| Factor | Impact on Charles River | Supporting Data/Example (2023/2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increased costs and reduced flexibility if few suppliers exist for critical inputs. | Cost of goods sold increased 6.8% year-over-year in 2023, partly due to input costs. |
| Uniqueness of Inputs | Suppliers with unique or proprietary inputs have significant pricing power. | Double-digit percentage increases in NHP prices in 2023 due to supply constraints. |
| Switching Costs | High costs to switch suppliers empower existing suppliers with better terms. | Requalification and protocol revalidation are time-consuming and costly processes. |
What is included in the product
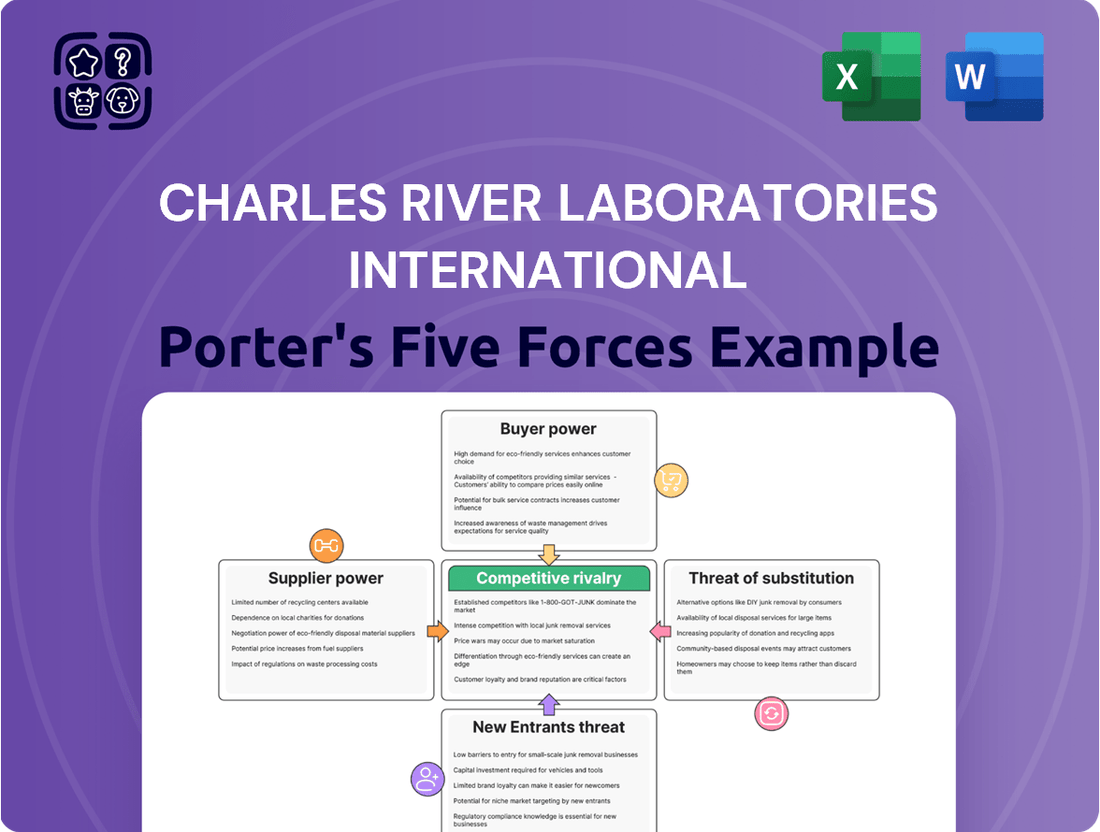
Analyzes the competitive intensity and profitability potential for Charles River Laboratories International by examining supplier power, buyer power, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and existing industry rivalry.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces impacting Charles River Laboratories.
Customers Bargaining Power
Charles River Laboratories (CRL) serves a wide array of clients, from major global pharmaceutical giants and agile biotech startups to government bodies and academic research centers. This diverse customer mix is a key factor in understanding their bargaining power.
However, the reality is that a significant portion of CRL's revenue comes from a smaller number of very large pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies. These major players, due to their immense size and the sheer volume of services they procure, wield considerable bargaining power. For instance, in 2023, CRL reported that its largest customer accounted for approximately 9% of its total revenue, highlighting the concentration within its client base.
Customers often face moderate to high switching costs when looking to change Contract Research Organizations (CROs). This is due to the significant effort involved in transferring ongoing projects, the need to re-establish specific research protocols, and the potential for delays in critical drug development timelines. These factors create a strong incentive for clients to remain with their current CRO.
Charles River Laboratories International (CRL) enhances this customer stickiness through its extensive and integrated service offerings. By providing comprehensive support across various stages, from research models and discovery services to safety assessment and manufacturing, CRL creates a seamless experience. This integrated approach makes it more complex and costly for clients to move their entire research and development pipeline to a competitor.
Pharmaceutical and biotechnology firms, Charles River Laboratories' primary clients, are highly sensitive to the cost of drug discovery and development services. This sensitivity stems from intense pressure to control research and development expenditures.
Looking ahead to 2025, industry analysts project a more moderate growth in R&D spending among major pharmaceutical companies. This environment is likely to empower clients to engage in more aggressive price negotiations for the services Charles River provides.
Availability of In-house Alternatives
Customers, particularly pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, always retain the option to conduct their research and development activities internally. This inherent choice represents a significant aspect of their bargaining power.
However, the substantial financial investment, intricate processes, and specialized scientific knowledge necessary for in-house drug discovery and development often make outsourcing to Contract Research Organizations (CROs) like Charles River Laboratories a more economically viable and efficient strategy. For instance, the global CRO market was valued at approximately $50 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong preference for outsourcing.
- In-house R&D: Companies can choose to build their own labs and hire specialized personnel, but this requires significant capital expenditure and long-term commitment.
- Outsourcing Benefits: CROs offer access to advanced technologies, experienced scientists, and established workflows, reducing upfront costs and time-to-market for clients.
- Cost Efficiency: For many drug development programs, outsourcing is demonstrably more cost-effective than establishing and maintaining equivalent in-house capabilities.
- Focus on Core Competencies: By outsourcing non-core R&D functions, pharmaceutical companies can concentrate their resources on drug discovery, clinical trials, and commercialization.
Customers' Ability to Consolidate Vendors
Charles River Laboratories' customers, particularly large pharmaceutical sponsors, are actively consolidating their vendor relationships. This strategic shift aims to streamline operations and enhance efficiency, leading them to favor CROs offering comprehensive, end-to-end services. For instance, in 2024, many major pharmaceutical companies announced plans to reduce their supplier numbers by 20-30% to centralize procurement and gain better oversight.
This consolidation trend directly impacts the bargaining power of these larger clients. By concentrating a significant portion of their research and development spending with fewer providers, these sponsors gain leverage to negotiate more favorable pricing and contract terms. This is particularly true for integrated service providers that can meet a wider range of client needs, making them more valuable partners but also more susceptible to demands from these consolidated accounts.
The ability of customers to consolidate vendors presents a key challenge for Charles River Laboratories:
- Increased Negotiating Power: Large clients can leverage their consolidated spend to demand lower prices or better service level agreements.
- Shift Towards End-to-End Solutions: Sponsors prefer fewer, more integrated partners, potentially disadvantaging specialized service providers.
- Focus on Efficiency Gains: Vendor consolidation is driven by a desire for operational improvements, putting pressure on CROs to demonstrate value beyond just scientific expertise.
- Potential for Reduced Client Diversification: Over-reliance on a few large, consolidated clients could increase risk if those clients shift their business.
The bargaining power of customers for Charles River Laboratories (CRL) is significant, driven by the concentration of revenue among large pharmaceutical and biotech firms. These clients, such as the largest customer representing 9% of CRL's revenue in 2023, can exert considerable pressure on pricing and contract terms due to their substantial spending. Furthermore, the ongoing trend of vendor consolidation among these major players in 2024, with many aiming to reduce suppliers by 20-30%, amplifies their negotiating leverage by concentrating their procurement power with fewer, integrated providers.
| Factor | Impact on CRL | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Increased leverage for large clients | Largest customer accounted for ~9% of total revenue (2023) |
| Vendor Consolidation Trend | Clients demand more integrated services and better pricing | Major pharma clients planned 20-30% supplier reduction (2024) |
| Cost Sensitivity | Clients push for cost efficiency in R&D | Global CRO market valued at ~$50 billion (2023) indicates outsourcing preference |
| In-house R&D Option | Clients can choose to insource, limiting CRO pricing power | High capital and expertise needed for in-house R&D |
What You See Is What You Get
Charles River Laboratories International Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete Charles River Laboratories International Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering an in-depth examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and immediate value.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The contract research organization (CRO) and drug discovery services sector is quite crowded, featuring major, broad-ranging companies such as Charles River Laboratories, ICON, IQVIA, and Eurofins. These giants compete directly with a multitude of smaller, highly specialized firms that focus on specific areas of research or development.
This diverse mix of competitors, from large, integrated service providers to niche specialists, fuels significant rivalry. For instance, in 2023, the global CRO market was valued at approximately $45.9 billion, indicating a substantial number of entities vying for market share across various service offerings.
The global drug discovery services market is booming, with projections showing a rise from $18.27 billion in 2024 to $20.59 billion in 2025, a robust 12.7% compound annual growth rate.
This rapid expansion within the broader contract research organization (CRO) market, which is set to grow from $69.56 billion in 2025 to a substantial $126.17 billion by 2034, fuels intense competition.
As the industry expands, it naturally draws in more players and significant investment, intensifying the rivalry among existing and new service providers vying for market share.
Charles River Laboratories (CRL) distinguishes itself through an extensive array of offerings, encompassing research models, drug discovery, safety evaluations, and manufacturing assistance. This broad service spectrum, coupled with a significant global presence and profound scientific knowledge, sets them apart.
While competitors also provide wide-ranging services, CRL’s commitment to continuous innovation and niche specialization is crucial for sustaining its competitive advantage. For instance, in 2023, CRL reported revenue of $4.2 billion, showcasing the scale of operations within this competitive landscape.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
Charles River Laboratories operates in an industry characterized by substantial fixed costs. These include maintaining a global network of research facilities, investing in sophisticated laboratory equipment, and retaining a highly specialized scientific workforce. For instance, the capital expenditure for advanced analytical instruments and bio-containment facilities represents a significant upfront investment.
These high fixed costs, coupled with the specialized nature of assets and the difficulty in repurposing them, create significant exit barriers within the Contract Research Organization (CRO) sector. Companies are often compelled to continue operations and compete aggressively, even during periods of reduced demand, to spread these fixed costs over a larger revenue base. This dynamic intensifies competition among existing players.
- High Capital Investment: The CRO industry requires substantial investment in state-of-the-art laboratories and specialized equipment, contributing to high fixed costs.
- Specialized Workforce: Maintaining a team of highly skilled scientists and technicians represents a significant ongoing fixed cost.
- Exit Barriers: The difficulty and cost associated with divesting specialized assets and shutting down operations make it challenging for companies to exit the market, thus prolonging competitive pressure.
- Competitive Intensity: High fixed costs and exit barriers encourage incumbent firms to remain and compete fiercely, even in less favorable market conditions.
Strategic Mergers and Acquisitions
The competitive rivalry within the contract research organization (CRO) sector is intensified by a significant trend of industry consolidation. Large CROs are actively pursuing mergers and acquisitions (M&A) to broaden their service offerings, extend their global presence, and enhance their technological expertise. This strategic move allows them to achieve economies of scale and offer more comprehensive solutions to clients.
Charles River Laboratories International (CRL) itself has a well-established track record of executing strategic acquisitions. For instance, in 2021, CRL acquired Cognate BioServices, a leading cell and gene therapy contract development and manufacturing organization (CDMO), for $860 million to bolster its biologics capabilities. These acquisitions not only strengthen CRL's competitive position but also contribute to the overall consolidation, creating larger, more integrated players in the market.
- Industry Consolidation: The CRO market is seeing significant M&A activity as larger players acquire smaller ones.
- Portfolio Expansion: Acquisitions aim to broaden service portfolios, geographic reach, and technological capabilities.
- CRL's Acquisition Strategy: Charles River Laboratories has a history of strategic acquisitions to enhance its service offerings, such as the 2021 acquisition of Cognate BioServices.
- Increased Competition: These consolidations result in larger, more formidable competitors, intensifying overall rivalry.
Competitive rivalry in the contract research organization (CRO) sector is fierce, driven by a large number of diverse players, from global giants to specialized niche firms. The market's rapid growth, with the global CRO market valued at approximately $45.9 billion in 2023 and projected to expand significantly, fuels this intense competition as more entities vie for market share. This dynamic is further amplified by industry consolidation, where major CROs, including Charles River Laboratories, strategically acquire smaller companies to enhance their service offerings and market reach, leading to larger, more formidable competitors and increased pressure on all participants.
| Metric | 2023 Value (USD Billions) | 2024 Projection (USD Billions) | 2025 Projection (USD Billions) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Global CRO Market | 45.9 | 69.56 | N/A |
| Global Drug Discovery Services Market | N/A | 18.27 | 20.59 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Pharmaceutical and biotechnology firms increasingly possess robust in-house research and development capabilities, presenting a direct substitute for Contract Research Organization (CRO) services. This trend allows companies to perform drug discovery and development internally, potentially reducing reliance on external partners.
For instance, in 2024, many large pharmaceutical companies continued to invest heavily in their internal R&D infrastructure, with significant portions of their annual budgets allocated to discovery and early-stage development. This internal capacity can directly compete with CRO offerings, especially for routine or well-established research processes.
The rapid advancement of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in drug discovery presents a significant potential substitute for traditional contract research organizations (CROs). These technologies promise to slash development timelines and boost success rates. For instance, by late 2023, numerous AI-driven drug discovery companies reported accelerating lead identification by months, with some achieving preclinical candidate selection in under a year, a stark contrast to the multi-year averages for conventional methods.
AI platforms can integrate vast datasets, including genomic, proteomic, and chemical information, to accelerate molecule design and predict efficacy and toxicity. This capability could reduce the reliance on outsourced, lab-based services that Charles River Laboratories (CRL) currently provides. Companies like Recursion Pharmaceuticals and Exscientia have demonstrated success in this area, with Exscientia having multiple AI-discovered drugs in clinical trials by early 2024.
Innovations like lab-on-a-chip, digital twin simulations, and organ-on-chip platforms are emerging as potent substitutes in preclinical testing. These advanced technologies offer alternative pathways for early-stage drug assessment, potentially diminishing reliance on traditional animal models and certain in-vivo studies. For instance, organ-on-chip technology, which mimics human organ functions, is gaining traction as a more predictive and ethical alternative to animal testing, with the market for this technology projected to reach billions by the end of the decade.
Drug Repurposing and Repositioning Strategies
The growing trend of drug repurposing and repositioning presents a significant threat of substitutes for Charles River Laboratories' novel drug discovery services. This strategy, which involves identifying new therapeutic uses for already approved or failed drugs, bypasses much of the early-stage research and development inherent in discovering entirely new compounds. By leveraging existing safety and efficacy data, drug repurposing can dramatically reduce timelines and costs.
This shift in the pharmaceutical landscape means companies may opt for repurposing existing drugs rather than investing in de novo discovery, directly impacting demand for Charles River's core offerings. For instance, the market for drug repurposing is expected to grow substantially, with some estimates suggesting it could reach tens of billions of dollars annually by the late 2020s. This growth is fueled by the inherent advantages of reduced risk and faster market entry.
- Reduced R&D Costs: Repurposing can cut discovery and preclinical costs by as much as 70-80% compared to novel drug development.
- Faster Time to Market: Existing drugs already have established safety profiles, potentially shortening clinical trial phases and regulatory review.
- Increased Investment in Repurposing: Venture capital and government funding are increasingly directed towards repurposing initiatives, signaling a growing industry focus.
- Leveraging Existing Data: The vast amount of data available on approved drugs provides a rich foundation for identifying new therapeutic applications.
Growth of 'Drug Discovery as a Service' Platforms
The increasing prevalence of specialized Drug Discovery as a Service (DDaaS) platforms presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional Contract Research Organizations (CROs) like Charles River Laboratories. These platforms, frequently leveraging advanced AI capabilities, offer a more flexible, component-based approach to drug discovery. For example, a company might utilize an AI-driven target identification platform instead of engaging a full-service CRO for early-stage research.
This modularity allows clients to select specific, technologically advanced solutions, bypassing the need for comprehensive, end-to-end CRO partnerships. This could fragment the value chain, with clients assembling their discovery process from various specialized providers. For instance, a biotech firm might use a DDaaS platform for hit identification and then outsource lead optimization to another specialized service, bypassing larger CROs for the entire workflow.
- Rise of AI-powered DDaaS: Platforms offering AI-driven target identification, compound screening, and preclinical modeling are gaining traction.
- Modular vs. Integrated Services: Clients can now cherry-pick discrete services, reducing reliance on full-service CROs for entire drug discovery pipelines.
- Efficiency and Cost Potential: Specialized platforms may offer faster turnaround times and potentially lower costs for specific tasks compared to traditional CRO models.
- Market Fragmentation: The availability of these specialized services could lead to a more fragmented market, where clients assemble their discovery efforts from multiple vendors.
The threat of substitutes for Charles River Laboratories (CRL) is amplified by the growing capabilities of pharmaceutical companies to conduct research internally. Many large pharma firms in 2024 continued to bolster their in-house R&D, allocating substantial budgets to early-stage drug discovery. This internal capacity serves as a direct substitute for outsourcing to CROs, especially for established research processes.
AI and machine learning are rapidly emerging as powerful substitutes, accelerating drug discovery timelines significantly. By late 2023, AI-driven companies reported reducing lead identification periods by months, with some achieving preclinical candidate selection in under a year. These platforms integrate diverse datasets to predict efficacy and toxicity, potentially lessening the need for traditional lab-based services.
Innovations like organ-on-chip technology offer alternative preclinical testing methods, diminishing reliance on animal models and certain in-vivo studies. This market is projected to reach billions by the end of the decade, presenting a more predictive and ethical substitute for traditional outsourced preclinical services.
Drug repurposing also poses a threat, as it bypasses much of the early-stage discovery that CROs typically handle. This strategy leverages existing data on approved drugs, reducing timelines and costs. The drug repurposing market is anticipated to grow substantially, potentially reaching tens of billions annually by the late 2020s.
Specialized Drug Discovery as a Service (DDaaS) platforms, often powered by AI, offer modular solutions that fragment the traditional CRO value chain. Clients can now select specific, advanced services, reducing reliance on full-service CROs for entire discovery pipelines. This shift allows for greater flexibility and potentially lower costs for discrete tasks.
| Substitute Area | Key Technologies/Strategies | Impact on CROs | Example/Data Point (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Internal R&D Expansion | Increased in-house investment in discovery and early development | Reduced outsourcing demand for routine tasks | Large pharma companies continued significant R&D budget allocations in 2024 |
| AI/ML in Drug Discovery | Accelerated lead identification, compound screening, predictive modeling | Potential to shorten outsourced project timelines, increased competition from AI platforms | AI companies achieving preclinical candidate selection in under a year by late 2023 |
| Advanced Preclinical Testing | Organ-on-chip, lab-on-a-chip technologies | Decreased reliance on traditional in-vivo CRO services | Organ-on-chip market projected to reach billions by decade-end |
| Drug Repurposing | Identifying new uses for existing drugs | Bypasses early-stage discovery services offered by CROs | Repurposing market expected to reach tens of billions annually by late 2020s |
| Specialized DDaaS Platforms | AI-driven target ID, modular service offerings | Market fragmentation, clients cherry-picking services | Emergence of platforms offering discrete, technologically advanced solutions |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a comprehensive drug discovery and development service provider, akin to Charles River Laboratories, demands immense capital. This includes significant investment in cutting-edge laboratories, specialized research models, and a robust global infrastructure to support diverse client needs.
The sheer scale of financial commitment required for facilities, advanced equipment, and regulatory compliance acts as a substantial deterrent for potential new entrants. For instance, building and equipping a single, state-of-the-art preclinical research facility can easily run into tens of millions of dollars.
The pharmaceutical and biotechnology sectors, where Charles River Laboratories operates, are heavily regulated. Agencies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) impose rigorous standards for drug development, manufacturing, and testing. For instance, in 2024, the FDA continued to emphasize stringent Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) and Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP) compliance, requiring extensive documentation and validation processes.
Navigating this complex regulatory environment presents a significant barrier for potential new entrants. The costs associated with meeting these compliance requirements are substantial, encompassing everything from facility upgrades to specialized personnel and extensive quality control systems. These upfront investments and ongoing compliance burdens deter many smaller or less-capitalized companies from entering the market.
The drug discovery and development landscape requires a profound depth of scientific knowledge, encompassing biology, chemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology. New companies entering this field face a substantial hurdle in assembling and keeping a team of highly skilled scientists and specialists.
Established Client Relationships and Reputation
Charles River Laboratories International (CRL) benefits significantly from deeply entrenched client relationships, particularly with major pharmaceutical and biotechnology firms. These long-standing partnerships are built on a foundation of trust and a proven track record of quality and reliability, making it difficult for newcomers to penetrate the market. For instance, CRL’s extensive service offerings and integrated solutions often become embedded within their clients' research and development pipelines, creating substantial switching costs.
The threat of new entrants is considerably mitigated by CRL's strong reputation, which is a critical asset in an industry where scientific rigor and dependable results are paramount. New companies must not only match CRL's scientific capabilities but also invest heavily in building a comparable level of trust and credibility, a process that can take years and significant capital. This relationship-driven nature of the contract research organization (CRO) sector means that simply offering competitive pricing is rarely enough to displace an established player.
- Long-Standing Client Relationships: CRL maintains enduring partnerships with a substantial portion of the top global pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, often serving as a primary or exclusive provider for certain research services.
- Reputation for Quality and Reliability: The company's brand is synonymous with high-quality data and dependable execution, a reputation cultivated over decades of successful project delivery.
- High Switching Costs for Clients: Integrating CRL's services into a client's R&D workflow creates operational dependencies and data management complexities that deter easy switching to a new provider.
- Barriers to Trust Building: New entrants face a significant hurdle in establishing the same level of trust and scientific validation that CRL has earned, a crucial factor in securing and retaining business in this sector.
Intellectual Property and Proprietary Technologies
The threat of new entrants for Charles River Laboratories International (CRL) is significantly influenced by intellectual property and proprietary technologies. Existing players, like CRL, possess substantial intellectual property, encompassing unique research models, specialized testing assays, and sophisticated technological platforms developed over years of operation and significant investment. For instance, in 2023, CRL reported substantial R&D expenses, indicating a continuous effort to enhance and protect its technological edge.
New competitors entering the contract research organization (CRO) space would face considerable hurdles in replicating or developing comparable proprietary assets. The process of creating and validating novel research methodologies or advanced technological systems is both expensive and time-consuming. This necessitates substantial upfront capital and a long development cycle, thereby acting as a significant barrier to entry for potential new players seeking to compete on technological parity.
- Proprietary Research Models: CRL's extensive library of genetically engineered models and specialized disease models represents a significant competitive advantage, difficult for new entrants to replicate quickly.
- Advanced Assay Development: The company's proprietary assays, validated through rigorous scientific processes, offer unique diagnostic and analytical capabilities that require substantial R&D investment to match.
- Technological Platforms: CRL's investment in cutting-edge technologies, such as advanced imaging and high-throughput screening platforms, creates a high technological barrier for newcomers.
The threat of new entrants into the contract research organization (CRO) market, particularly for a company like Charles River Laboratories (CRL), is considerably low due to immense capital requirements and stringent regulatory hurdles. The need for advanced facilities, specialized equipment, and compliance with global standards like Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) demands substantial upfront investment, often in the tens of millions of dollars for a single preclinical research site. For example, in 2024, regulatory bodies like the FDA continued to enforce rigorous compliance, adding to the cost and complexity of market entry.
Furthermore, CRL benefits from deeply entrenched client relationships and a strong reputation for quality and reliability, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. Building the necessary trust and scientific validation can take years, and high switching costs for clients further solidify CRL's market position. Proprietary technologies and unique research models also present significant barriers, requiring substantial R&D investment for competitors to match.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment in labs, equipment, and infrastructure. | Significant financial barrier; building a single state-of-the-art facility can cost tens of millions. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to strict FDA, EMA, GLP, and GMP standards. | Costly and time-consuming; requires extensive documentation, validation, and specialized personnel. |
| Client Relationships & Switching Costs | Long-standing partnerships and integrated R&D pipelines. | Difficult for new entrants to penetrate; clients face operational complexities when switching. |
| Proprietary Technology & IP | Unique research models, assays, and technological platforms. | Requires substantial R&D investment and time to replicate or develop comparable assets. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Charles River Laboratories International leverages data from annual reports, SEC filings, and industry-specific market research reports to understand competitive dynamics.
We incorporate insights from financial databases like Bloomberg and S&P Capital IQ, alongside trade publications and government regulatory data, to assess the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers.
