Coterra Energy Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Coterra Energy Bundle
Coterra Energy faces a dynamic energy landscape, where the bargaining power of buyers and the threat of substitutes significantly shape its profitability. Understanding these pressures is crucial for navigating the competitive environment.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Coterra Energy’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The oil and gas sector, which includes companies like Coterra Energy, depends on specialized equipment and services from a limited number of oilfield service providers. Major players such as Schlumberger, Baker Hughes, and Halliburton represent this concentration.
This limited supplier base grants these companies moderate bargaining power because their services are essential for critical operations like exploration, drilling, and production. In 2024, the significant capital expenditure required for advanced drilling technologies and specialized services reinforces the suppliers' leverage.
Switching between major oilfield service providers presents substantial hurdles for Coterra. These include the expense of re-tooling equipment, retraining personnel, and the potential for operational downtime, all of which bolster the suppliers' leverage. For instance, the specialized nature of advanced drilling rigs and completion technologies means that Coterra faces high costs if it decides to change service partners.
Suppliers providing highly specialized technologies or proprietary equipment for unconventional resource plays, like those Coterra Energy operates in (Marcellus Shale, Permian Basin, Anadarko Basin), possess increased leverage. This leverage stems from the unique nature of their offerings, which are critical for efficient extraction. For instance, in 2024, the cost of specialized hydraulic fracturing equipment and services saw an upward trend due to high demand and limited availability of advanced units.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers engaging in forward integration, essentially moving into Coterra Energy's core business of exploration and production, is a theoretical concern that could bolster supplier power. However, this scenario is highly improbable within the energy sector.
The immense capital requirements and intricate regulatory landscape inherent in exploration and production activities present significant barriers to entry. These factors typically dissuade even large service providers from attempting such a vertical integration.
For instance, in 2024, the average upfront capital expenditure for a new oil and gas exploration project can easily run into hundreds of millions, if not billions, of dollars, making it an unattractive proposition for most service companies whose business models are built on providing specialized equipment and labor.
- High Capital Intensity: Exploration and production demand substantial upfront investment, far exceeding typical service provider capabilities.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Navigating complex environmental and operational regulations is a significant deterrent for potential integrators.
- Industry Specialization: The energy sector is highly specialized, with distinct skill sets and infrastructure required for E&P versus service provision.
Impact of Commodity Prices on Suppliers
Fluctuations in oil and natural gas prices significantly impact Coterra Energy's profitability and its ability to invest, directly affecting supplier demand and service pricing. When commodity prices surge, suppliers often have greater leverage to negotiate higher rates, whereas depressed prices tend to weaken their bargaining power. This creates a cyclical dynamic where supplier influence ebbs and flows with the energy market.
For instance, in 2024, the volatility in natural gas prices, which saw benchmarks like Henry Hub fluctuate significantly throughout the year, directly translated into shifts in demand for drilling and completion services. This means that during periods of high natural gas prices, the suppliers of specialized equipment and labor could command premium pricing, enhancing their bargaining power.
- 2024 Natural Gas Price Volatility: Henry Hub prices experienced notable swings in 2024, impacting the cost of services for exploration and production companies like Coterra.
- Supplier Cost Pass-Through: Periods of high commodity prices in 2024 allowed suppliers to pass increased operational costs onto their clients, strengthening their negotiating position.
- Investment Capacity Impact: Coterra's investment decisions, influenced by commodity prices, directly shape the volume of work available for suppliers, thereby affecting their bargaining leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Coterra Energy leans towards moderate, primarily due to the specialized nature of oilfield services and equipment required for exploration and production. In 2024, the continued demand for advanced drilling technologies and completion services from a concentrated group of major service providers like Schlumberger and Halliburton meant these suppliers held considerable sway.
The high switching costs for Coterra, involving retraining and equipment adaptation, further solidify supplier leverage. This is particularly true for proprietary technologies crucial in basins like the Permian, where specialized hydraulic fracturing equipment saw increased demand and pricing in 2024, amplifying supplier influence.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on Coterra Energy | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Concentrated Supplier Base | Moderate to High Leverage | Key players dominate specialized services. |
| High Switching Costs | Increased Supplier Power | Expensive to change service providers. |
| Proprietary Technology Demand | Elevated Supplier Leverage | Essential for efficient extraction in key plays. |
| Commodity Price Sensitivity | Cyclical Supplier Influence | High prices in 2024 boosted supplier pricing power. |
What is included in the product
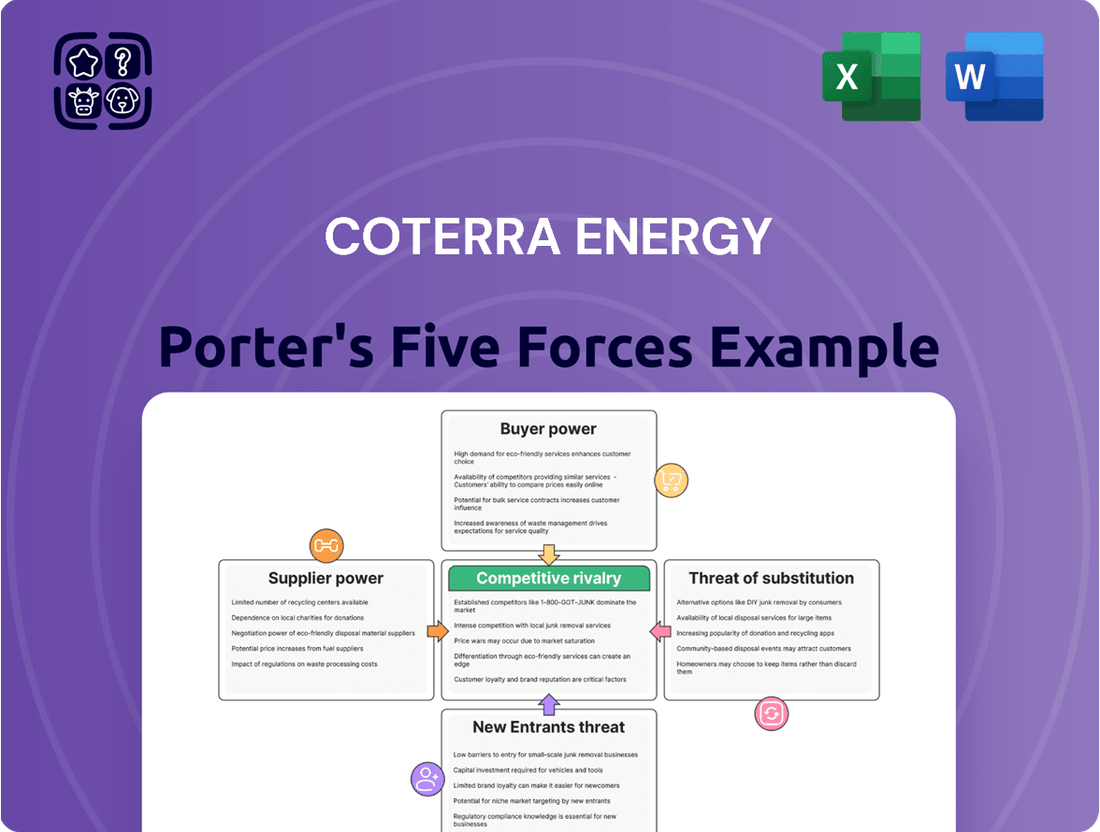
Tailored exclusively for Coterra Energy, analyzing its position within its competitive landscape by examining the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes.
Visualize the competitive landscape with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces analysis, highlighting Coterra Energy's strategic positioning and potential vulnerabilities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Coterra Energy serves a wide array of customers, including refineries, industrial facilities, local gas distributors, and power plants. This diversity means no single buyer typically holds significant sway over Coterra's pricing or terms.
In 2024, the energy market's dynamics, characterized by fluctuating global demand and supply, further dilute the bargaining power of individual customers. Coterra's broad customer reach, spanning multiple sectors, means that even large industrial users represent a small fraction of its overall sales volume.
The commodity nature of oil and natural gas significantly shapes customer bargaining power. Because these resources are largely undifferentiated, buyers tend to focus heavily on price. This fungibility allows customers to readily switch between suppliers if a better price is offered, particularly when the market is well-supplied.
Coterra Energy's customers, particularly those using its natural gas and oil as essential inputs, exhibit a high degree of price sensitivity. This is because any increase in Coterra's product costs directly impacts their own operational expenses and profit margins, making them keenly aware of price fluctuations.
For instance, in 2024, the natural gas market has experienced significant price volatility, with spot prices at Henry Hub fluctuating considerably. This volatility means that if Coterra were to implement substantial price hikes, its customers would be strongly incentivized to explore alternative suppliers or even curtail their own production, especially if those alternatives offer more stable or lower pricing.
Availability of Alternatives for Customers
The availability of alternatives significantly impacts Coterra Energy's customer bargaining power. Customers can choose from numerous oil and gas producers, creating a competitive landscape. For instance, in 2024, the global natural gas market saw continued diversification of supply sources, with increased LNG exports from various regions, offering buyers more options beyond traditional pipeline gas.
While direct, immediate substitutes for all of Coterra's products might be scarce in certain applications, the growing adoption of renewable energy sources presents a long-term challenge. By the end of 2023, renewable energy sources accounted for over 30% of new electricity generation capacity additions globally, signaling a gradual shift in the energy mix that can empower customers to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels over time.
- Customer Choice: Coterra's customers have access to a wide array of oil and gas suppliers, intensifying competition.
- Substitution Threat: The long-term trend towards renewable energy sources like solar and wind provides customers with an increasing alternative to fossil fuels.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, the global natural gas market's diversification, particularly through LNG, offered buyers more leverage.
- Energy Transition: Renewable energy's growing share in new capacity additions (over 30% by end of 2023) indicates a potential long-term reduction in demand for traditional energy sources.
Customer Switching Costs
Customer switching costs for Coterra Energy are generally low for its buyers, particularly large industrial clients and power plants. While there are some logistical and contractual considerations when changing natural gas or oil suppliers, these are typically less burdensome than the costs Coterra incurs when switching its own service providers. This asymmetry in switching costs gives customers a degree of leverage.
The existing infrastructure for transporting and distributing natural gas and oil also contributes to lower customer switching costs. Buyers can often access multiple suppliers through established pipelines and distribution networks without needing significant new investments. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. natural gas pipeline network continued to expand, facilitating easier access to various supply sources for end-users.
- Low Switching Costs: Industrial customers and power plants face minimal financial or operational hurdles when changing their natural gas or oil supplier.
- Infrastructure Advantage: Established transportation and distribution networks allow customers to readily access alternative suppliers.
- Supplier Leverage: The ease with which customers can switch suppliers enhances their bargaining power against Coterra.
Coterra Energy's customers, particularly large industrial users and power plants, possess moderate bargaining power. This is primarily due to the commodity nature of oil and gas, which allows for easy price comparisons and supplier switching, especially given the robust pipeline infrastructure available in 2024. While the energy transition presents a long-term substitution threat, in the immediate term, the availability of multiple suppliers and relatively low switching costs empower buyers.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | 2024 Context/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | Low; Coterra serves many diverse buyers. | No single buyer dominates Coterra's sales volume. |
| Product Differentiation | Low; Oil and gas are largely fungible. | Buyers focus on price due to undifferentiated products. |
| Switching Costs | Low; Minimal logistical or contractual barriers. | Established pipeline networks facilitate easy supplier changes. |
| Substitution Threat | Moderate (Long-term); Growing renewable energy adoption. | Renewables accounted for over 30% of new capacity additions by end of 2023. |
| Price Sensitivity | High; Energy costs directly impact customer margins. | Volatility in 2024 natural gas prices (e.g., Henry Hub) heightens sensitivity. |
What You See Is What You Get
Coterra Energy Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Coterra Energy Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of the competitive landscape within the energy sector. The document you see here is the exact, fully formatted analysis you will receive immediately upon purchase, providing actionable insights without any hidden placeholders or samples. You can confidently acquire this professionally written report, knowing that the preview accurately represents the complete and ready-to-use deliverable that will be yours instantly after payment.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Coterra Energy operates within a U.S. oil and gas exploration and production sector characterized by significant fragmentation and a high number of participants. This intense competition spans Coterra's primary operational areas, including the Marcellus Shale, Permian Basin, and Anadarko Basin. Companies of varying scales, from major integrated oil corporations to smaller, specialized independent exploration and production firms, vie for market share and resources.
The U.S. oil and gas sector is largely mature, meaning growth isn't explosive. This maturity, combined with recent price swings and a strong emphasis on efficient operations over rapid expansion, makes competition for existing market share quite fierce among established companies like Coterra Energy.
The oil and natural gas industry, where Coterra Energy operates, is largely characterized by undifferentiated commodities. This means competition often boils down to who can extract and deliver these resources most cost-effectively. For instance, in 2024, benchmark crude oil prices fluctuated, making operational efficiency a critical differentiator for companies like Coterra.
Coterra's strategy centers on achieving operational excellence and a commitment to responsible resource development. This approach aims to build value and a competitive edge even within a market driven by commodity prices. Their focus on efficient drilling and production techniques, coupled with environmental stewardship, helps them stand out.
Exit Barriers
The oil and gas sector, including companies like Coterra Energy, faces substantial exit barriers. The immense capital investment required for exploration, drilling, and establishing production infrastructure means that once a company is in, it's very difficult to get out without incurring massive losses. These high fixed costs are a constant pressure, compelling firms to continue production even when market prices are low, simply to try and recoup some of their sunk investments.
This situation directly fuels competitive rivalry. When companies are reluctant to exit due to these significant sunk costs, they tend to stay in the market and compete fiercely for market share, even if it means operating at reduced profitability. This can lead to prolonged periods of intense competition as players fight for survival in a capital-intensive industry.
For example, in 2023, the average cost to drill and complete a new oil well in the Permian Basin, a key operational area for many US producers, could range from $6 million to $10 million, highlighting the substantial upfront investment. These figures underscore the difficulty of simply walking away from such operations, reinforcing the exit barriers and the subsequent competitive pressures.
- High Capital Intensity: Exploration and production require massive upfront investment in specialized equipment, seismic surveys, and well development.
- Specialized Assets: Infrastructure like pipelines, refineries, and processing facilities are highly specialized and have limited alternative uses, making them difficult to repurpose or sell.
- Long-Term Contracts: Many companies are bound by long-term supply or transportation contracts, which can be costly to break and obligate continued operation.
- Regulatory and Environmental Obligations: Decommissioning wells and restoring sites involves significant costs and regulatory compliance, adding to the financial burden of exiting.
Strategic Objectives of Competitors
Competitors in the energy sector often pursue divergent strategic goals. Some may focus on aggressively increasing production volumes to capture market share, while others prioritize generating substantial free cash flow to strengthen their balance sheets or fund expansion. These differing objectives directly shape how companies interact within the industry, influencing pricing, investment decisions, and overall market dynamics.
Coterra Energy's strategic approach centers on delivering robust financial returns and maintaining disciplined capital allocation. This means the company aims to generate strong cash flow while carefully managing its investments, often prioritizing shareholder value through dividends and buybacks. For instance, in 2024, Coterra continued to emphasize capital discipline, with its capital expenditures focused on high-return projects, contributing to its ability to return capital to shareholders.
- Maximizing Production vs. Free Cash Flow: Competitors may choose to boost output, potentially at lower margins, or focus on efficient production to maximize cash generation.
- Shareholder Returns: Some rivals might prioritize immediate returns to shareholders through dividends and buybacks, influencing their investment and operational strategies.
- Coterra's Focus: Coterra Energy's strategy emphasizes financial discipline and shareholder returns, aiming for efficient operations that generate consistent cash flow.
- Impact on Rivalry: These varied objectives create a complex competitive landscape where companies react differently to market conditions and opportunities.
Competitive rivalry within the U.S. oil and gas sector is intense, driven by a large number of players and the commodity nature of the products. Coterra Energy operates in highly competitive basins like the Permian and Marcellus, where efficiency and cost management are paramount. The maturity of the market means companies are fiercely competing for existing market share, making operational excellence a key differentiator.
The high capital intensity and specialized assets in oil and gas create significant exit barriers, compelling companies to remain operational and competitive even during downturns. This persistence among rivals, coupled with divergent strategic goals such as maximizing production versus focusing on free cash flow, further intensifies the competitive landscape.
Coterra Energy's strategy of financial discipline and shareholder returns, as demonstrated by its capital allocation in 2024, positions it to navigate this rivalry. For example, in the first quarter of 2024, Coterra reported strong free cash flow generation, allowing for continued shareholder distributions while investing in high-return projects.
| Key Competitor Metric | Coterra Energy (Q1 2024) | Industry Average (Est. 2024) | Impact on Rivalry |
| Production Cost per BOE (Barrel of Oil Equivalent) | $11.50 | $12.00 - $15.00 | Lower costs provide a competitive advantage. |
| Free Cash Flow Yield | 8.5% | 6.0% - 7.5% | Strong FCF allows for reinvestment and shareholder returns. |
| Capital Efficiency (Drilling & Completions) | High | Varies by operator | Efficient operations reduce breakeven costs. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The primary substitutes for Coterra Energy's oil and natural gas products include a growing array of alternative energy sources like solar, wind, nuclear, and biofuels. These alternatives present a significant long-term threat as their adoption increases.
Global investment in renewable energy reached a record $624 billion in 2023, a 17% increase from 2022, signaling a strong shift towards cleaner alternatives. Technological advancements continue to drive down costs for these substitutes, making them increasingly competitive with traditional fossil fuels.
The threat of substitutes for Coterra Energy's products, primarily oil and natural gas, is significantly shaped by the relative price and performance of alternative energy sources. While hydrocarbons are still indispensable for many industrial and transportation needs, advancements in renewable energy technologies are steadily improving their cost-effectiveness and efficiency.
For instance, the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) for solar photovoltaic (PV) and wind power continued to decline in 2023, making them increasingly competitive with fossil fuels in many regions. Solar PV LCOE averaged around $30-60 per megawatt-hour (MWh), while onshore wind averaged $25-55 per MWh, according to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA). This trend suggests that as renewable technologies mature and scale, they could capture a larger share of the energy market, posing a growing threat to traditional oil and gas demand.
For customers, the transition from fossil fuels to alternative energy sources often involves significant switching costs. These can include the expense of new infrastructure, such as installing charging stations for electric vehicles or upgrading home heating systems to heat pumps. For instance, the average cost to install a home solar panel system in 2024 can range from $15,000 to $25,000, a considerable upfront investment that deters many from immediate adoption.
These substantial upfront investments in new equipment and potential modifications to existing systems currently act as a barrier, thereby mitigating the immediate threat of substitution for Coterra Energy's products. The need for new technology adoption and the associated learning curve also contribute to these switching costs, making it less appealing for consumers to move away from established fossil fuel solutions in the short term.
Government Regulations and Environmental Policies
Increasing government regulations and environmental policies aimed at promoting cleaner energy and reducing carbon emissions significantly bolster the threat of substitutes for companies like Coterra Energy. These policies directly incentivize the adoption of renewable energy sources, making them more competitive and attractive alternatives to traditional fossil fuels. For instance, in 2024, many nations continued to implement stricter emissions standards and offer substantial subsidies for solar and wind power, directly impacting the demand for oil and gas.
The push towards decarbonization is a major factor. Policies such as carbon taxes, renewable portfolio standards, and electric vehicle mandates directly increase the cost or decrease the attractiveness of fossil fuel consumption. This creates a more favorable environment for substitutes to gain market share. By 2024, the global investment in clean energy technologies was projected to surpass traditional energy investments, a trend driven by these regulatory frameworks.
The threat of substitutes is amplified as governments set ambitious net-zero targets. These targets necessitate a rapid transition away from fossil fuels, encouraging innovation and deployment of alternative energy solutions. For example, the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act of 2022, with its provisions extending through 2032, continued to provide significant tax credits for renewable energy projects in 2024, directly challenging the market position of oil and gas producers.
- Regulatory Incentives for Renewables: Government subsidies and tax credits for solar, wind, and other renewable energy sources make these alternatives more cost-effective.
- Carbon Pricing Mechanisms: Carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems increase the operational costs of fossil fuel extraction and consumption, enhancing the competitiveness of substitutes.
- Emissions Standards and Mandates: Stricter regulations on greenhouse gas emissions and mandates for renewable energy adoption directly reduce demand for fossil fuels.
- Net-Zero Commitments: National and international commitments to achieve net-zero emissions by specific dates drive policy decisions that favor the displacement of fossil fuels by cleaner alternatives.
Technological Advancements in Substitutes
Technological advancements are significantly bolstering the threat of substitutes for traditional energy sources like those Coterra Energy operates in. For instance, improvements in battery storage technology are making renewable energy sources more reliable and dispatchable, reducing their intermittency issues. In 2024, global investment in battery storage projects reached an estimated $70 billion, a substantial increase from previous years, signaling growing confidence in this substitute technology.
The efficiency of solar panels continues to climb, with commercially available panels now exceeding 22% efficiency, up from around 15% a decade ago. This increased efficiency means more power can be generated from the same footprint, making solar more competitive. Similarly, wind turbine technology has seen innovations leading to larger, more efficient turbines, capable of capturing more energy even at lower wind speeds. These ongoing improvements make alternative energy sources increasingly viable and cost-effective replacements.
- Enhanced Battery Storage: Global investment in battery storage projects estimated at $70 billion in 2024.
- Solar Panel Efficiency: Commercial solar panels now exceeding 22% efficiency.
- Wind Turbine Innovation: Larger, more efficient turbines improving energy capture.
The threat of substitutes for Coterra Energy's oil and natural gas products is growing, driven by advancements and increasing adoption of alternative energy sources like solar, wind, and electric vehicles. While switching costs, such as the $15,000-$25,000 average cost for home solar installation in 2024, currently mitigate immediate substitution, these barriers are expected to decrease over time.
Government policies, including subsidies for renewables and stricter emissions standards, further accelerate the shift away from fossil fuels. For example, global investment in renewable energy hit a record $624 billion in 2023, a 17% increase from 2022, underscoring this trend. These factors collectively strengthen the long-term threat of substitutes.
| Factor | Impact on Coterra Energy | Supporting Data (2023-2024) |
| Renewable Energy Competitiveness | Increasingly competitive with fossil fuels due to falling costs. | Solar PV LCOE ~$30-60/MWh; Onshore Wind LCOE ~$25-55/MWh (IRENA). |
| Switching Costs | High upfront investment in new technology (e.g., home solar $15k-$25k in 2024) acts as a temporary barrier. | Home solar installation costs remain significant. |
| Government Policy & Investment | Policies incentivize renewables, driving demand away from fossil fuels. | Global renewable energy investment reached $624 billion in 2023. U.S. IRA provisions extend tax credits through 2032. |
Entrants Threaten
The oil and gas exploration and production sector demands massive upfront investment. This includes securing land rights, the complex process of drilling, and building essential infrastructure, all of which create a formidable barrier for any newcomers.
Coterra Energy's own financial activities underscore this point. In 2023, the company reported capital expenditures of approximately $1.7 billion, demonstrating the significant financial commitment required to operate and grow within this industry.
New companies entering the oil and gas sector often find it difficult to gain access to essential distribution channels like pipelines and processing facilities. These critical assets are typically owned or controlled by established companies, creating a significant barrier to entry. For instance, Coterra Energy benefits from its existing infrastructure in key producing regions, giving it a distinct advantage in getting its product to market efficiently.
The oil and gas sector faces significant regulatory hurdles, including stringent environmental standards and complex permitting requirements. These processes can be lengthy and expensive, acting as a considerable barrier for potential new entrants aiming to establish operations.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Established players like Coterra Energy leverage significant economies of scale in their operations, from purchasing drilling equipment to managing complex extraction processes. For instance, in 2024, major oil and gas producers continued to benefit from bulk purchasing power, which lowers per-unit costs compared to smaller, emerging companies. This scale advantage extends to their experience curve; years of optimizing production techniques in plays like the Permian Basin mean Coterra can extract more hydrocarbons more efficiently and at a lower cost than a newcomer could replicate quickly.
New entrants face a steep climb to match Coterra's operational efficiencies and cost structures. They would need substantial upfront capital investment not only for exploration and production but also to build the necessary infrastructure and develop the specialized knowledge that Coterra already possesses. This creates a formidable barrier, as achieving comparable cost per barrel or per unit of natural gas would require significant time and learning, making it difficult for them to compete on price or profitability from the outset.
- Economies of Scale: Coterra benefits from lower per-unit costs in procurement, drilling, and logistics due to its large operational footprint.
- Experience Curve: Accumulated knowledge in optimizing production from unconventional resources allows for greater efficiency and lower operating expenses.
- Capital Intensity: New entrants require massive capital investment to achieve comparable scale and efficiency, a significant hurdle.
- Competitive Pricing: Existing players' cost advantages make it challenging for new entrants to compete on price in the market.
Brand Loyalty and Reputation
Brand loyalty and reputation are significant barriers to entry in the oil and gas sector, even though the products are essentially commodities. Coterra Energy, like its peers, benefits from decades of established relationships with key suppliers and a proven track record of operational reliability. For instance, in 2023, Coterra reported a production of 274,000 barrels of oil equivalent per day, underscoring its capacity and consistent output, a level of performance new entrants would find challenging to match immediately.
New companies entering the market must contend with the immense task of building trust and demonstrating a comparable level of dependability. This involves not only securing reliable supply chains but also convincing major industrial customers and downstream partners of their ability to deliver consistently. The capital investment required to achieve this scale and reputation is substantial, often running into billions of dollars, making it a formidable hurdle for nascent competitors.
- Established Relationships: Coterra’s long-standing ties with suppliers and customers provide a competitive edge.
- Reputation for Reliability: A history of consistent operations builds crucial trust in the industry.
- Operational Scale: Achieving Coterra’s production levels, such as its 2023 daily output, requires massive investment and expertise.
- Barriers to Entry: The need to build trust and demonstrate reliability presents a significant challenge for new entrants.
The threat of new entrants for Coterra Energy is generally low due to substantial capital requirements and established infrastructure. New companies face immense upfront costs for land acquisition, drilling, and essential infrastructure development, creating a significant financial barrier. For instance, Coterra’s 2023 capital expenditures were around $1.7 billion, highlighting the scale of investment needed.
Access to critical distribution channels like pipelines is also limited, as these are often controlled by existing players. Coterra’s existing infrastructure provides a distinct advantage in market access. Furthermore, stringent regulatory environments and the need to build a reputation for reliability and consistent output, exemplified by Coterra’s 2023 production of 274,000 barrels of oil equivalent per day, present considerable challenges for newcomers.
| Barrier Type | Description | Coterra Energy Example/Data |
| Capital Intensity | Massive upfront investment for exploration, drilling, and infrastructure. | $1.7 billion in capital expenditures in 2023. |
| Infrastructure Access | Limited access to pipelines and processing facilities controlled by incumbents. | Coterra benefits from existing infrastructure in key producing regions. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex permitting and stringent environmental standards. | Lengthy and expensive processes for new operators. |
| Economies of Scale & Experience | Lower per-unit costs and optimized production techniques from large-scale operations. | Benefit from bulk purchasing power and years of operational optimization. |
| Reputation & Relationships | Established trust with suppliers, customers, and a history of reliability. | 2023 production of 274,000 boe/day demonstrates operational capacity and consistency. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Coterra Energy is built upon a foundation of robust data, including publicly available SEC filings, annual reports, and investor presentations. We also leverage industry-specific market research reports and publications to capture current trends and competitive landscapes.
