Converge Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Converge Bundle
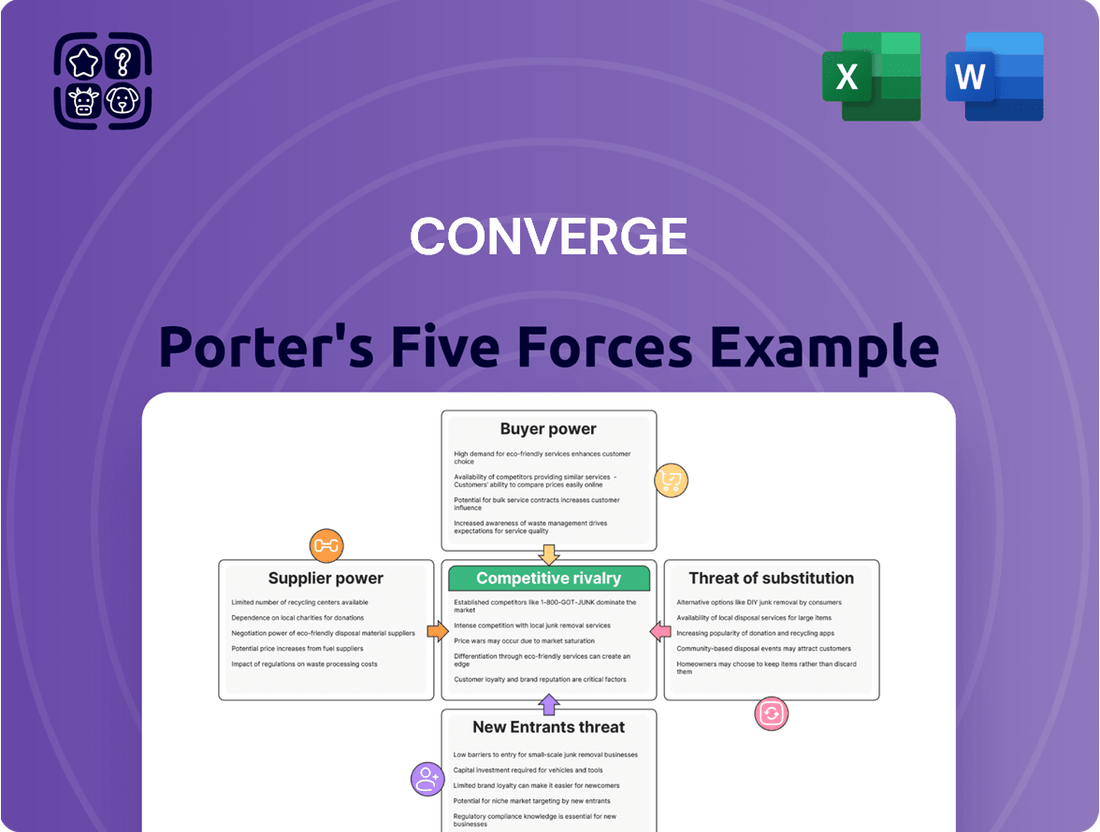
Converge's competitive landscape is shaped by the bargaining power of buyers, the threat of new entrants, and the intensity of rivalry. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its market effectively.
The full Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals the real forces shaping Converge’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The market for specialized fiber optic equipment, particularly for end-to-end fiber networks, is often dominated by a select group of global manufacturers. This concentration means that companies like Converge ICT, which require advanced technology and critical components, face suppliers with considerable leverage. For example, Converge has historically relied on partnerships with leading technology providers such as Infinera Corp. for essential equipment like submarine line terminal equipment, underscoring the dependence on these niche vendors.
Converge ICT's substantial investment in a supplier's core fiber optic technology creates significant switching costs. Once integrated, altering this foundational infrastructure is both complex and expensive, effectively locking Converge into existing relationships.
This lock-in effect grants suppliers considerable bargaining power. They can leverage Converge's reliance for more favorable pricing and terms, especially as the company continues its network expansion. For instance, Converge's 2024 capital expenditure, projected to be substantial for ongoing network build-out and international cable systems, underscores the magnitude of these embedded costs.
Suppliers possessing proprietary technology or patents for essential fiber optic components or network management software can wield significant influence over Converge ICT. This means Converge might need to secure licenses or purchase these advanced technologies, potentially incurring higher expenses, or risk facing limitations in its network capabilities. For instance, if a key supplier holds exclusive patents on next-generation fiber splicing equipment, Converge’s ability to deploy faster speeds could be directly impacted by their pricing and terms.
Importance of Supplier's Reputation and Reliability
For a leading fiber internet provider like Converge ICT, the reputation and reliability of its suppliers are critical. Companies known for delivering high-quality components and providing consistent, timely service significantly reduce operational risks. This means Converge ICT is more likely to stick with these trusted vendors, even if newer suppliers offer slightly lower prices, which in turn strengthens the bargaining power of these reputable suppliers.
Converge ICT's commitment to network uptime and performance directly translates to a heightened reliance on suppliers who can guarantee quality and dependability. For instance, in 2024, the telecommunications industry continued to see increased demand for robust network infrastructure. Suppliers who have a proven track record in delivering fiber optic cables, network equipment, and other essential components that meet stringent performance standards are in a strong position. Their established credibility means they can command better terms, as switching to a less reliable supplier could lead to significant service disruptions and customer dissatisfaction.
- Supplier Reputation: Suppliers with a history of delivering high-quality, reliable network components are highly valued.
- Network Performance: Converge ICT's focus on network stability makes it hesitant to engage with unproven suppliers.
- Cost vs. Risk: The potential cost savings from a cheaper, less reliable supplier are often outweighed by the risk of network downtime.
- Supplier Power: Established vendors with strong reputations and proven reliability possess significant bargaining power.
Potential for Forward Integration by Suppliers
While not a frequent occurrence, major equipment suppliers in the telecommunications sector could potentially integrate forward into offering internet services themselves. This is particularly plausible in specialized or underserved market segments. For instance, a large provider of fiber optic cable or network hardware might consider establishing its own ISP operations, especially if regulatory barriers were to decrease.
This theoretical possibility, even if unlikely for established players like Converge ICT's suppliers, could grant them a degree of leverage. It allows them to potentially influence pricing structures and negotiate more favorable terms for their equipment sales by hinting at future competition. Imagine a scenario where a key component supplier, holding significant market share for essential network gear, could leverage this potential to negotiate better deals.
However, the Philippine telecommunications landscape presents substantial obstacles to such forward integration. The immense capital investment required for network build-out, coupled with the stringent regulatory approvals necessary to operate as an internet service provider, creates a high barrier to entry. For example, securing spectrum licenses and navigating the complex permitting processes in the Philippines can take years and significant financial commitment, making this a remote threat for most suppliers.
- Potential for Forward Integration: Large, diversified equipment manufacturers could theoretically enter the ISP market.
- Leverage for Suppliers: This potential gives them bargaining power over existing ISPs like Converge ICT.
- High Barriers in the Philippines: Significant capital and regulatory hurdles make this a difficult strategy to execute.
Suppliers of specialized fiber optic equipment hold significant bargaining power over Converge ICT due to the concentrated nature of the market and high switching costs. Converge's reliance on proprietary technology and the critical need for reliable, high-quality components mean that established vendors can dictate more favorable terms. For instance, Converge's substantial 2024 capital expenditures for network expansion highlight the ongoing need for these specialized inputs, reinforcing supplier leverage.
| Factor | Impact on Converge ICT | Supplier Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|
| Market Concentration | Limited choice of specialized equipment providers. | High |
| Switching Costs | High expenses and complexity in replacing integrated technology. | High |
| Proprietary Technology | Dependence on unique components or software for network capabilities. | High |
| Supplier Reputation & Reliability | Need for consistent performance to avoid service disruptions. | High |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Converge's unique position in the telecommunications and IT services market.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of industry power dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
The Philippine broadband market is a hotbed of competition, with established giants like PLDT and Globe Telecom, alongside newer entrants like DITO Telecommunity, all aggressively pursuing subscribers. This intense rivalry directly translates to increased bargaining power for customers, both residential and enterprise.
With multiple providers vying for their business, customers can readily compare pricing, speeds, and service packages. For instance, as of early 2024, the average broadband speed in the Philippines was around 24.4 Mbps, a figure that providers are constantly pressured to improve to attract and retain customers.
This customer leverage forces companies like Converge ICT to offer more attractive deals and consistently enhance their service quality to remain competitive. Failure to do so risks losing market share to rivals who can better meet customer demands for value and performance.
The rise of prepaid fiber and flexible internet plans, like those offered by Converge, Surf2Sawa, and BIDA Fiber, has significantly boosted customer bargaining power. These options make it easier for consumers to switch providers if they find better deals or service quality, directly impacting price and contract negotiations.
The bargaining power of customers in the internet provider industry is significantly amplified by low switching costs. For many residential and even some enterprise users, the financial and logistical hurdles to change providers are minimal. This ease of transition allows customers to readily seek better deals or services elsewhere if they encounter issues with pricing, quality, or reliability.
In 2024, the competitive landscape continues to favor customers due to this low switching friction. For instance, many providers offer introductory pricing that expires after a year, encouraging customers to re-evaluate their options. The ability to compare plans online and the relative simplicity of installation for new services mean that a dissatisfied customer can often switch providers within a few weeks, putting pressure on existing companies to maintain competitive offerings.
Customer Sensitivity to Price and Performance
Philippine internet users exhibit significant sensitivity to both the price and the performance of their broadband services. This means that as a provider like Converge, keeping costs reasonable while ensuring fast and reliable connections is paramount.
The increasing reliance on digital activities, from remote work to online entertainment, fuels a strong demand for high-speed internet. Customers are actively comparing different providers to find the best value, putting pressure on Converge to maintain competitive pricing and service quality to retain and attract subscribers.
- Price Sensitivity: In 2024, average monthly broadband costs in the Philippines can range significantly, but consumers are often looking for plans under PHP 1,000 for decent speeds, indicating a strong price-consciousness.
- Performance Demands: With the average internet speed in the Philippines improving, users expect a minimum of 20-30 Mbps for a satisfactory experience, making speed and reliability key differentiators.
- Competitive Landscape: The presence of multiple providers means customers have choices, and a slight edge in price or a noticeable improvement in speed can sway user loyalty.
Information Transparency and Online Reviews
The sheer volume of readily accessible information online significantly amplifies customer bargaining power. For instance, in the telecommunications sector, customers can easily compare broadband speeds and pricing plans from various providers. In 2024, platforms like RootMetrics and Ookla continued to provide detailed, independent network performance data, allowing consumers to make highly informed choices. This transparency directly challenges providers who might otherwise rely on information asymmetry to maintain premium pricing.
Customer reviews and online feedback further level the playing field. A study in late 2023 indicated that over 90% of consumers read online reviews before making a purchase decision. This collective voice allows customers to identify and penalize underperforming companies, pushing them to improve service or lower prices. The ease with which customers can switch providers based on this readily available data, such as comparing average monthly costs for similar data plans, puts considerable pressure on businesses to remain competitive.
- Information Transparency: Online platforms offer speed test results, customer reviews, and pricing comparisons, enabling informed consumer choices.
- Reduced Information Asymmetry: Customers can easily identify and switch to better-performing or more affordable alternatives.
- Increased Collective Bargaining Power: The ease of comparison and switching empowers customers to demand better value.
- Impact on Pricing and Service: Businesses face pressure to improve offerings and pricing to retain customers in a transparent market.
Customers in the Philippine broadband market hold significant sway due to intense competition and low switching costs. This allows them to readily compare providers based on price, speed, and service, as evidenced by the average broadband speed in the Philippines hovering around 24.4 Mbps in early 2024, a metric providers are pressured to enhance.
| Key Customer Bargaining Factors (Philippines Broadband, 2024) | Description | Impact on Providers |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | Customers actively seek plans under PHP 1,000 for adequate speeds. | Forces competitive pricing strategies. |
| Performance Demands | Expectations for minimum 20-30 Mbps for satisfactory use. | Drives investment in network upgrades and reliability. |
| Information Transparency | Easy access to speed tests, reviews, and pricing comparisons. | Reduces information asymmetry, empowers informed choices. |
| Low Switching Costs | Minimal financial or logistical hurdles to change providers. | Increases customer churn risk, necessitates customer retention efforts. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Converge Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Converge Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You're looking at the actual, comprehensive document detailing the competitive landscape for Converge, ready for your strategic planning. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Philippine telecommunications landscape is characterized by intense competition, largely driven by the presence of major established players like PLDT and Globe Telecom, alongside Converge ICT. This oligopolistic structure fuels aggressive rivalry as these giants vie for dominance in both the consumer and business sectors. For instance, in 2023, PLDT reported a net income of PHP 23.7 billion, while Globe Telecom announced a net income of PHP 24.4 billion for the same period, highlighting their significant market positions and competitive drive.
The fiber internet sector demands massive initial outlays for network infrastructure, creating a high-cost barrier. Converge ICT, for example, incurs significant fixed costs in establishing and maintaining its pure fiber optic network, which necessitates high capacity utilization to be economically viable.
This financial reality drives intense competition as providers like Converge strive to onboard and keep customers. The imperative to spread these substantial fixed costs over a larger subscriber base fuels aggressive strategies to gain market share and ensure efficient network usage.
Converge, alongside rivals like Globe and PLDT, is heavily invested in aggressive network expansion. In 2023, Converge announced plans to deploy an additional 1.8 million fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) ports, significantly increasing its capacity and reach. This relentless infrastructure build-out, including new data centers, fuels intense competition as each player vies for market share by connecting more households and businesses.
Product and Service Differentiation Attempts
Converge ICT, while offering core internet connectivity, actively differentiates through value-added services. This includes bundling popular streaming platforms like Netflix and Disney+ with their plans, enhancing the appeal beyond basic internet access.
The company also targets specific market segments with specialized offerings, such as prepaid fiber plans for greater flexibility and tailored enterprise solutions for businesses. This strategic segmentation intensifies rivalry by catering to diverse customer needs.
- Bundled Services: Partnerships with streaming providers like Netflix aim to increase customer stickiness and perceived value.
- Segmented Plans: Converge offers prepaid fiber options and enterprise-grade solutions, broadening their market reach.
- Innovation Focus: Continuous introduction of new plans and services keeps the competitive landscape dynamic.
Price Wars and Promotional Activities
The telecommunications sector, particularly in the Philippines, is characterized by intense rivalry, often manifesting as aggressive price wars and widespread promotional campaigns. Converge ICT's strategic move to introduce more affordable prepaid plans in 2023 and early 2024 directly triggered competitive responses from rivals like Globe and PLDT, who subsequently adjusted their own pricing and bundled offerings to retain and attract subscribers. This dynamic highlights a market where customer acquisition and retention are heavily influenced by price sensitivity and the constant lure of promotional deals.
These promotional activities are not limited to price reductions; they often include bundled services, faster speeds for a limited time, or loyalty rewards. For instance, in late 2023, major players were observed offering significant discounts on installation fees and introductory monthly rates. This constant promotional churn forces companies like Converge to continuously innovate their value propositions to stand out in a saturated market.
- Price Wars: Converge's entry with competitive prepaid pricing in 2023 led to immediate price adjustments from major competitors.
- Promotional Activities: The market sees frequent promotions, including discounts, bundled services, and speed upgrades, to capture market share.
- Customer Switching: High promotional activity encourages subscribers to switch providers based on the best available deals.
- Market Sensitivity: The Philippine broadband market demonstrates a high degree of price sensitivity among consumers.
The competitive rivalry in the Philippine telecommunications sector is fierce, driven by a few dominant players like PLDT, Globe, and Converge ICT. This intense competition leads to aggressive pricing strategies and frequent promotions as companies battle for subscribers. For example, in 2023, Converge's introduction of more affordable prepaid plans prompted rivals to adjust their own pricing and bundles, underscoring the market's price sensitivity.
| Provider | 2023 Net Income (PHP Billions) | 2023 Subscriber Growth (%) | 2023 Network Expansion (Ports) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLDT | 23.7 | N/A | N/A |
| Globe Telecom | 24.4 | N/A | N/A |
| Converge ICT | N/A | N/A | 1.8 million FTTH |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Mobile broadband, particularly with the widespread adoption of 5G, presents a growing threat to traditional fixed-line internet services. As of early 2024, 5G networks are increasingly offering speeds that rival or even surpass some fiber optic connections, making 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) a viable alternative for many consumers and businesses.
For users prioritizing flexibility or located in areas where fiber deployment is costly or slow, 5G FWA provides a compelling substitute. This is especially true for those who can leverage the mobility aspect of wireless technology, reducing their reliance on a physical connection. The convenience factor, coupled with competitive pricing strategies from mobile carriers, further amplifies this threat.
Satellite internet services, exemplified by Starlink, represent a growing threat of substitutes for traditional broadband providers like Converge. These services are particularly compelling in remote or underserved regions where laying fiber optic cable is prohibitively expensive. For instance, Starlink's expansion efforts are targeting areas with limited terrestrial broadband options, potentially capturing a segment of the market that Converge currently serves or could serve.
While satellite internet has historically been associated with higher costs and latency, technological advancements are rapidly improving performance and affordability. This trend could make it a more competitive alternative for a wider range of consumers, including those in urban or suburban areas if cost parity is achieved. Converge's own strategic move to partner with and resell Starlink services underscores the recognition of this evolving competitive landscape and the potential for satellite technology to disrupt traditional markets.
Public Wi-Fi and community networks present a notable threat of substitutes for traditional fixed broadband. For many, especially in urban areas, readily available free or low-cost Wi-Fi in cafes, libraries, or public squares can fulfill basic internet needs, reducing the perceived necessity of a dedicated home or business subscription. This is particularly true for casual browsing or mobile device usage.
The availability of these alternative networks directly impacts the demand for broadband services. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of mobile data usage, particularly in developed nations, occurs over Wi-Fi, often in public spaces, thereby siphoning off potential revenue from fixed broadband providers. This trend is expected to continue as 5G deployment makes mobile hotspots more robust and accessible.
Traditional DSL and Cable Internet (though declining)
While fiber optic internet is clearly the leading technology, older options like DSL and traditional cable internet still serve as substitutes. These are particularly relevant in areas where fiber deployment hasn't reached yet. Even with their slower speeds, the established infrastructure and potentially more attractive pricing can appeal to a portion of consumers.
For instance, in 2024, while fiber adoption continued to grow, a significant number of households still relied on cable or DSL. This reliance is often driven by cost consciousness or the simple fact that fiber is not yet universally available. The threat lies in their ability to capture and retain customers who prioritize budget over the absolute highest speeds.
- Existing Infrastructure: DSL and cable networks are already in place, reducing the need for new installations for many users.
- Cost Sensitivity: Lower monthly fees for DSL and cable can be a significant draw for price-sensitive consumers.
- Geographic Limitations: In areas where fiber is not yet available, these older technologies are the only viable options, diminishing their substitutability threat in those specific locations but highlighting their continued presence elsewhere.
- Declining but Persistent Market Share: While their overall market share is shrinking, they still represent a meaningful segment of the internet service provider market in 2024, especially in less developed or rural areas.
Self-Contained Enterprise Networks and Private Connectivity Solutions
Large enterprises requiring ultra-secure and high-performance connectivity may choose to build their own self-contained private networks or utilize direct leased lines. These solutions bypass public internet infrastructure entirely, offering unparalleled control over data flow and bandwidth, which can be a significant threat to Converge's enterprise offerings.
For instance, financial institutions or government agencies with stringent security mandates might find these private solutions more appealing, even at a higher cost, as they can offer dedicated, unshared resources. This is particularly relevant as companies increasingly handle sensitive data and demand guaranteed uptime for critical business functions.
- Dedicated Leased Lines: Offer guaranteed bandwidth and lower latency compared to shared internet services.
- Private Network Infrastructure: Allows for complete control over network architecture, security protocols, and data routing.
- Enhanced Security: Minimizes exposure to public internet threats and provides greater data privacy.
- Customization: Enables tailored network configurations to meet very specific operational needs.
The threat of substitutes for broadband providers like Converge is multifaceted, encompassing wireless technologies, satellite internet, public Wi-Fi, and even older fixed-line alternatives. Each of these offers a different value proposition, from mobility and cost savings to enhanced security and dedicated bandwidth, directly challenging the traditional market for fixed broadband services.
Mobile broadband, especially with 5G, is increasingly competitive. As of early 2024, 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) offers speeds comparable to some fiber connections, making it a viable substitute for users prioritizing flexibility or in areas with slow fiber deployment. This trend is further fueled by competitive pricing from mobile carriers.
Satellite internet, notably Starlink, is a growing substitute, particularly for remote areas where fiber is uneconomical. While historically more expensive and with higher latency, technological advancements are improving its performance and affordability, making it a potential competitor even in urban settings if cost parity is reached.
Public Wi-Fi and community networks offer a substitute for basic internet needs, reducing the perceived necessity of dedicated broadband subscriptions for casual use. In 2024, a significant portion of mobile data usage occurred over Wi-Fi, often in public spaces, impacting revenue for fixed broadband providers.
Older technologies like DSL and cable remain substitutes where fiber is unavailable, appealing to cost-conscious consumers. Despite declining market share, they still hold a meaningful segment of the market in 2024, especially in less developed areas.
Enterprises may opt for private networks or leased lines for enhanced security and dedicated bandwidth, bypassing public infrastructure. Financial institutions, for example, may choose these solutions for their stringent security mandates and guaranteed uptime.
| Substitute Technology | Key Advantage | Market Segment Impacted | 2024 Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) | Mobility, competitive speeds | Residential, small business | Growing rapidly, challenging fiber |
| Satellite Internet (e.g., Starlink) | Remote area access, improving performance | Underserved, rural areas | Expanding reach, becoming more competitive |
| Public Wi-Fi | Free or low-cost access | Casual users, mobile device users | Reduces demand for dedicated home broadband |
| DSL/Cable Internet | Established infrastructure, lower cost | Cost-sensitive consumers, areas without fiber | Persistent market share, especially in non-fiber areas |
| Private Networks/Leased Lines | High security, dedicated bandwidth | Enterprises with strict requirements | Critical for high-security sectors |
Entrants Threaten
The fiber internet provider market demands substantial upfront investment for constructing extensive fiber optic networks, a significant hurdle for new players. Converge, for instance, has committed to considerable capital expenditures for its ongoing network expansion and data center development, underscoring the high barrier to entry.
The telecommunications sector in the Philippines faces significant barriers to entry due to its intricate regulatory landscape. New companies must navigate a complex web of licensing and permit requirements, including obtaining a legislative franchise, a process known for its time-consuming and demanding nature. For instance, as of early 2024, the National Telecommunications Commission (NTC) continues to emphasize stringent compliance for all telecom operators, impacting the ease with which new players can establish operations.
Established players like Converge ICT, PLDT, and Globe Telecom have invested heavily in building extensive fiber optic networks across the Philippines. This infrastructure advantage, coupled with years of brand building, has fostered significant customer loyalty. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, Converge reported over 2 million broadband subscribers, indicating a substantial existing customer base that new entrants would need to attract.
Economies of Scale and Scope
Incumbent providers in many sectors, particularly those with network effects, benefit significantly from economies of scale. This means their per-unit costs decrease as their output or customer base grows. For example, in the telecommunications industry, established players like Verizon and AT&T leverage their vast infrastructure, allowing them to spread fixed costs over millions of subscribers, leading to lower operational expenses per customer compared to a new entrant starting from scratch. This scale advantage extends to customer acquisition and maintenance, where existing brands and established processes reduce the cost of onboarding and supporting new users.
These economies of scale translate directly into pricing power. Larger companies can afford to offer more competitive pricing, potentially even engaging in price wars that new entrants cannot sustain. Consider the ride-sharing market; companies like Uber and Lyft, with their massive driver and rider networks, can offer discounts and promotions that make it difficult for smaller, regional players to gain traction. In 2024, the sheer size of their operations allows them to absorb marketing costs more effectively.
New entrants face a considerable hurdle in achieving similar cost efficiencies. Building out a comparable network, acquiring customers at scale, and establishing brand recognition require substantial upfront investment. This initial disadvantage in cost structure makes it challenging for newcomers to compete on price or even to achieve profitability in the early stages. For instance, a startup in the cloud computing space would need massive capital to match the infrastructure and service offerings of giants like Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure, which have benefited from years of scaling.
- Economies of Scale: Incumbents benefit from lower per-unit costs due to large-scale operations.
- Network Effects: Value increases with more users, a barrier for new entrants.
- Customer Acquisition Costs: Established brands have lower costs to attract new customers.
- Pricing Disadvantage: Newcomers struggle to match competitive pricing due to higher initial costs.
Access to Key Resources and Infrastructure
New entrants in the telecommunications sector often face significant hurdles in securing essential resources. For instance, obtaining rights-of-way for laying fiber optic cables or gaining access to existing utility poles can be a complex and time-consuming process. Established companies frequently hold long-term agreements or possess exclusive rights, making it difficult for newcomers to establish a competitive physical network.
Access to critical infrastructure, such as international submarine cable landing stations, is another major barrier. These facilities are vital for global connectivity, and existing providers often control these gateways. In 2024, the cost and availability of such landing station access remain a significant deterrent, with new entrants needing to negotiate or invest heavily to secure their place in the global digital infrastructure.
- Limited Rights-of-Way: Established telecommunication companies often have pre-existing rights-of-way agreements, making it difficult and costly for new entrants to build their own physical networks.
- Access to Utility Poles: Securing access to existing utility poles, a crucial component for last-mile connectivity, can be challenging due to exclusive contracts or high rental fees charged by incumbent utilities.
- Submarine Cable Landing Stations: Control over international submarine cable landing stations is concentrated among a few major players, creating a significant barrier to entry for companies seeking to offer global internet services.
The threat of new entrants in the fiber internet market is significantly mitigated by the immense capital required for network build-out and regulatory compliance. Established players like Converge have already made substantial investments, creating high barriers. For instance, securing legislative franchises and navigating complex NTC regulations in the Philippines, as emphasized in early 2024, deters many potential newcomers.
Furthermore, existing providers benefit from strong economies of scale and established brand loyalty, making it difficult for new companies to compete on price or customer acquisition. Converge's subscriber base, exceeding 2 million by Q1 2024, illustrates this advantage. New entrants also face challenges in accessing critical infrastructure like submarine cable landing stations, often controlled by incumbents, further limiting their ability to establish a competitive presence.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Extensive investment needed for fiber optic network construction. | High barrier due to significant upfront costs. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex licensing, permits, and legislative franchise requirements. | Time-consuming and costly process, deterring new players. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs for established providers with large customer bases. | New entrants struggle to match competitive pricing and operational efficiency. |
| Infrastructure Access | Control of rights-of-way, utility poles, and submarine cable landing stations by incumbents. | Limited physical network expansion and global connectivity options for newcomers. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a comprehensive mix of data sources, including industry-specific market research reports, financial statements from public companies, and government economic indicators. This robust foundation allows for a thorough evaluation of competitive intensity, supplier and buyer power, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
