Consolidated Edison Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Consolidated Edison Bundle
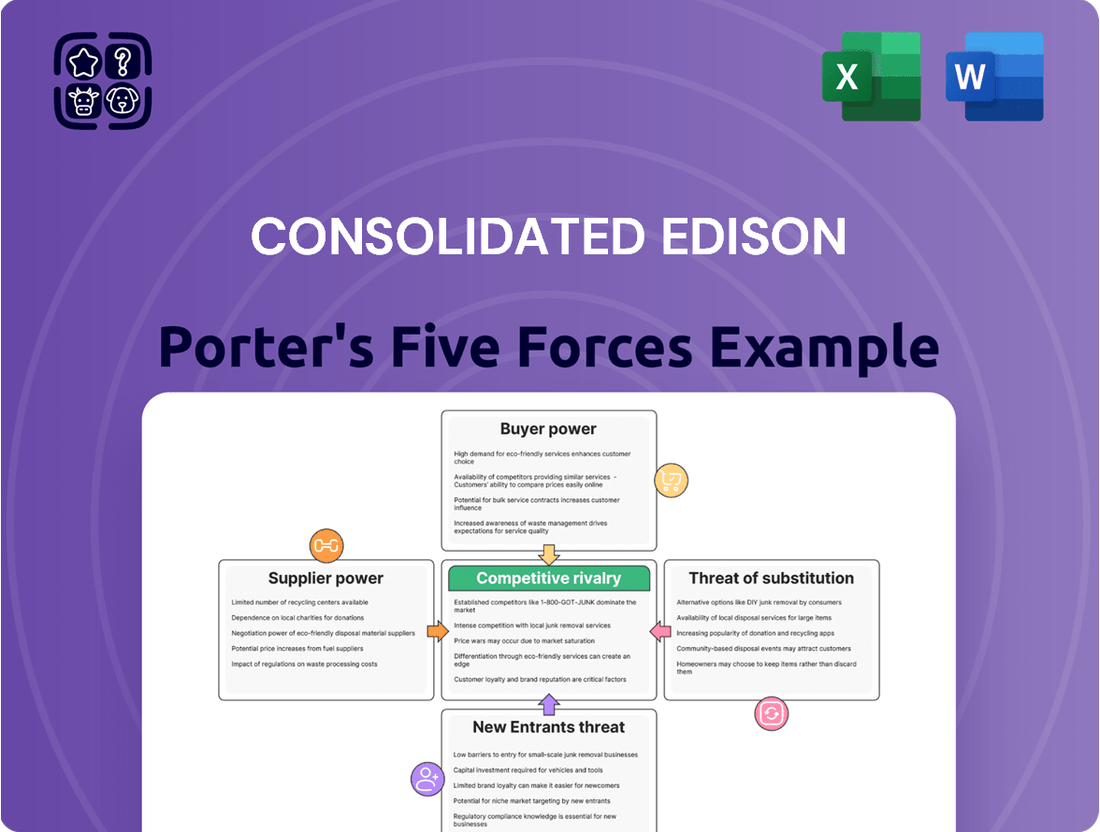
Consolidated Edison operates in a highly regulated utility sector, facing moderate bargaining power from suppliers due to essential infrastructure needs. The threat of new entrants is significantly low due to immense capital requirements and regulatory hurdles, creating a stable competitive landscape.
However, the threat of substitutes, while not immediate, exists through advancements in renewable energy and distributed generation, potentially impacting traditional utility models. Buyer power is somewhat limited by the essential nature of electricity and gas services, though customer choice and energy efficiency initiatives offer some leverage.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Consolidated Edison’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Consolidated Edison sources a wide array of essential inputs, from natural gas and electricity generation components to infrastructure materials. While Con Edison strives to foster competition and maintain a broad supplier network, including significant engagement with small businesses, certain specialized equipment or unique fuel sources may originate from a restricted number of suppliers.
This concentration can empower suppliers of critical or bespoke components, particularly those needed for grid modernization and the transition to clean energy. For instance, in 2023, Con Edison reported capital expenditures exceeding $5 billion, much of which would necessitate specialized equipment from a select group of manufacturers.
Switching suppliers for a utility giant like Con Edison involves substantial costs. These can range from the expense of reconfiguring integrated systems to the financial implications of breaking long-term fuel contracts or replacing specialized infrastructure. For instance, in 2024, the energy sector saw continued investment in grid modernization, highlighting the deeply embedded nature of existing supplier relationships and the associated costs of change.
The intricate operations of a utility mean that shifting a key supplier isn't a simple transaction. It often necessitates significant re-engineering of processes, extensive retraining of staff, and carries the risk of temporary operational disruptions, impacting service reliability. These complexities inherently raise the barriers to switching.
Despite these challenges, Con Edison actively works to reduce its suppliers' bargaining power by broadening its vendor base. By cultivating a more diverse pool of suppliers, the company aims to create a competitive landscape where vendors are incentivized to offer better terms, thereby mitigating the impact of high switching costs.
The threat of forward integration by Consolidated Edison's suppliers is generally low. This is primarily because the electric, gas, and steam distribution sectors in New York City and Westchester County are heavily regulated. Operating as a utility requires immense capital, navigating complex regulatory frameworks, and possessing established infrastructure, all of which present significant barriers for most suppliers looking to enter Con Edison's core business.
While direct entry into utility operations is unlikely for most suppliers, some energy producers or technology firms might explore forward integration into related areas. This could involve offering distributed generation solutions or advanced energy management services. Such moves could indirectly compete with certain aspects of Con Edison's existing service portfolio, creating a nuanced competitive pressure.
Importance of Supplier Inputs to Con Edison
Suppliers provide Con Edison with essential resources like natural gas and electricity, crucial for its distribution operations. The company's ability to maintain reliable service hinges on the consistent quality and availability of these vital inputs.
Con Edison's substantial capital expenditure plans, projecting around $38 billion between 2025 and 2029 for grid modernization and clean energy initiatives, underscore a significant reliance on a robust and dependable supply chain for new infrastructure components and technologies.
- Critical Inputs: Natural gas, electricity, materials, and technologies for infrastructure maintenance and upgrades.
- Service Reliability: Directly linked to the quality and consistency of supplier inputs.
- Future Investments: Approximately $38 billion planned from 2025-2029 for grid modernization and clean energy transition, heavily dependent on supply chain stability.
Supplier Power in Renewable Energy Sector
As Consolidated Edison (Con Edison) expands its renewable energy portfolio, including solar and wind projects, the bargaining power of suppliers in these evolving markets is a key consideration. While the overall trend shows decreasing technology costs, specialized components for large-scale renewable installations and advanced grid solutions can still be concentrated among a few global manufacturers, granting them some leverage.
For instance, the market for high-efficiency solar panels or advanced battery storage systems, crucial for grid stability and renewable integration, might be dominated by a limited number of suppliers. This concentration can lead to price pressures or supply chain vulnerabilities for Con Edison if these suppliers have significant market share. In 2023, global solar panel prices saw fluctuations, though generally trending downwards, but the cost of specialized components for large-scale projects can still be a significant factor in project economics.
- Supplier Concentration: Certain specialized components for solar, wind, and battery storage may be sourced from a limited number of global suppliers, potentially increasing their bargaining power.
- Technological Advancements: Suppliers of cutting-edge grid modernization technologies or highly efficient renewable energy components may command higher prices due to their unique offerings.
- Market Dynamics: While overall renewable costs are decreasing, the specific supply chain for critical, specialized equipment can still present challenges and opportunities for supplier negotiation.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Consolidated Edison (Con Edison) is moderate, influenced by the essential nature of their products and the high switching costs involved. While Con Edison aims to diversify its supplier base, specialized components for grid modernization and the renewable energy transition, such as advanced battery storage systems, can be concentrated among a few global manufacturers, granting them some leverage. For example, Con Edison's planned capital expenditures of approximately $38 billion between 2025 and 2029 for grid modernization and clean energy initiatives highlight a significant reliance on these specialized suppliers.
| Factor | Impact on Con Edison | Mitigation Strategies |
| Supplier Concentration for Specialized Components | Can lead to price pressures and supply chain vulnerabilities, particularly for advanced grid technologies and renewable energy equipment. | Diversifying vendor base, long-term contracts, fostering competition among suppliers. |
| High Switching Costs | Significant financial and operational implications for changing suppliers of critical inputs like natural gas or specialized infrastructure materials. | Building strong supplier relationships, standardization of components where possible, thorough due diligence. |
| Dependence on Essential Inputs | Reliability of service is directly tied to the consistent quality and availability of supplies from vendors. | Maintaining strategic inventory levels, ensuring supplier financial stability, exploring alternative sourcing. |
What is included in the product
This analysis uncovers the competitive landscape for Consolidated Edison, examining the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the utility sector.
Instantly assess Consolidated Edison's competitive landscape with a clear, one-sheet summary of all five forces, perfect for quick strategic decision-making.
Customers Bargaining Power
Consolidated Edison's customers encounter exceptionally high switching costs due to its status as a regulated monopoly for electricity, gas, and steam distribution in New York City and Westchester County. This lack of alternative providers for essential utility services makes it virtually impossible for customers to change their primary service provider, thereby diminishing their bargaining power.
While Consolidated Edison (Con Edison) faces high customer switching costs, the bargaining power of its customers is significantly shaped by regulatory oversight and advocacy. The New York State Public Service Commission (PSC) plays a crucial role by approving rate increases, meaning customer concerns and public outcry can directly influence Con Edison's pricing strategies.
For instance, recent proposals for rate increases in 2025-2026 have already generated public discussion, indicating the PSC's responsiveness to customer sentiment. Furthermore, Con Edison's extensive energy affordability programs and incentives for energy efficiency serve as direct channels to address customer concerns and manage the impact of pricing on consumers.
Customers increasingly adopting distributed energy resources (DERs) like rooftop solar and battery storage exert indirect bargaining power. In 2024, Con Edison saw 100 megawatts of solar and 44 megawatts of battery storage installed by customers, with 54,000 solar customers achieving zero electric bills.
This growing self-sufficiency, while not leading to complete grid disconnection, allows customers to reduce their reliance on utility-provided electricity. This trend directly impacts Con Edison's sales volumes and compels the company to adapt its business model to accommodate and facilitate the integration of these customer-owned energy resources.
Customer Price Sensitivity and Affordability Programs
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor for Consolidated Edison, particularly among residential and low-income households who are increasingly feeling the pinch of rising energy costs. Recent rate adjustments have amplified this concern, making affordability a major consideration for a large segment of their customer base.
Con Edison actively addresses this by offering robust assistance programs. For instance, their Energy Affordability Program provided over $300 million in bill discounts during 2024 alone. This level of support highlights the company's awareness of and response to customer affordability challenges.
- Customer Price Sensitivity: Residential and low-income customers are highly sensitive to utility rate increases.
- Affordability Programs: Con Edison's Energy Affordability Program offered over $300 million in bill discounts in 2024.
- Regulatory Impact: Price sensitivity and affordability concerns can limit Con Edison's ability to implement substantial rate increases due to public and political scrutiny.
Limited Customer Differentiation
For Consolidated Edison's core regulated services, customers generally exhibit limited differentiation. They primarily consume essential utilities like electricity, gas, and steam based on their fundamental needs, with minimal leverage to demand highly customized service beyond reliability and competitive pricing. This is particularly true in their monopoly service territories where switching is not an option.
While Con Edison does offer various programs aimed at promoting clean energy adoption and improving energy efficiency, the fundamental delivery of its core utility services remains largely standardized. The company's strategic focus in these areas is on ensuring dependable service delivery and meeting stringent state-mandated clean energy targets, rather than catering to highly segmented customer demands within its regulated operational footprint.
In 2023, Consolidated Edison reported that approximately 90% of its revenue was derived from regulated utility operations, highlighting the significant portion of its business where customer differentiation is inherently low. This underscores the power of customers in these segments being primarily tied to their need for basic, reliable utility provision.
- Limited Customer Differentiation: Customers in Con Edison's regulated utility segments primarily seek reliable and affordable access to electricity, gas, and steam, with little ability to demand bespoke services.
- Standardized Service Delivery: Despite programs for clean energy and efficiency, the core utility services provided by Con Edison remain standardized, limiting customer bargaining power based on unique service needs.
- Regulatory Focus: Con Edison's strategy in regulated areas prioritizes reliable service and compliance with clean energy mandates over catering to highly specific or segmented customer demands.
- Revenue Concentration: In 2023, around 90% of Con Edison's revenue stemmed from regulated operations, reinforcing the low differentiation of its customer base in these essential service areas.
Customers of Consolidated Edison possess limited bargaining power primarily due to the high switching costs associated with their regulated monopoly for essential utilities. While price sensitivity is a factor, especially for residential and low-income households, Con Edison's extensive affordability programs, such as the over $300 million in bill discounts provided in 2024, help mitigate this. The growing adoption of distributed energy resources by customers is beginning to exert indirect pressure, impacting sales volumes and necessitating adaptation from Con Edison.
| Factor | Impact on Con Edison | Customer Action/Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | Very High (Regulated Monopoly) | Customers cannot easily switch utility providers. |
| Price Sensitivity | High (Residential/Low-Income) | Customers are affected by rising energy costs. |
| Affordability Programs | Mitigates Price Sensitivity | Con Edison provided >$300M in bill discounts (2024). |
| Distributed Energy Resources (DERs) | Indirect Bargaining Power | Customer solar/battery adoption (100MW solar, 44MW battery in 2024) reduces reliance on utility. |
What You See Is What You Get
Consolidated Edison Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete Consolidated Edison Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within the utility sector. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive instantly after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information. You can confidently expect this professionally formatted analysis to be ready for immediate use, providing valuable strategic insights.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Consolidated Edison's regulated monopoly status in New York City and Westchester County significantly dampens competitive rivalry for its core electricity, natural gas, and steam distribution services. This structure means there isn't direct competition from other utility providers vying for the same customers within its service territory. For instance, in 2023, Con Edison's regulated utility segment generated a substantial portion of its revenue, highlighting its dominant position in providing essential services.
While Con Edison's direct competition is geographically constrained, it faces indirect rivalry from other major utility players. Companies such as NextEra Energy, Ameren, National Grid, DTE Energy, and Southern Company serve as benchmarks for investors and analysts evaluating industry performance and strategic direction. For instance, as of early 2024, NextEra Energy reported a market capitalization significantly larger than Con Edison's, highlighting differing scales of operation and investor sentiment within the utility sector.
Consolidated Edison's direct competition in renewable energy development significantly shifted in 2022 when it divested its Clean Energy Businesses. This sale included approximately 3,300 megawatts of renewable projects, a substantial portion of its prior competitive footprint in this sector.
The primary competitors in the renewable energy space are other developers and independent power producers. While Con Edison is currently restricted from owning large-scale generation within New York, it actively participates in policy discussions, advocating for regulatory changes that could re-open opportunities for direct involvement in renewable generation development.
Market Growth and Regulatory Targets
The competitive landscape for Consolidated Edison (Con Edison) in New York is shaped less by traditional market share battles and more by ambitious state-mandated clean energy targets. New York aims for 70% renewable electricity by 2030 and 100% carbon-free power by 2040. This regulatory push necessitates substantial investment in infrastructure modernization and clean energy integration, defining Con Edison's growth trajectory.
Con Edison is actively investing billions of dollars to meet these stringent environmental mandates and upgrade its aging grid infrastructure. This regulated approach to growth means the company's efforts are focused on fulfilling state requirements and enhancing grid reliability rather than engaging in direct competitive expansion against other utilities for customer acquisition in the traditional sense.
- New York's Renewable Energy Mandates: 70% renewable electricity by 2030, 100% carbon-free by 2040.
- Investment Focus: Billions allocated for grid modernization and clean energy integration.
- Growth Driver: State mandates, not traditional market share competition.
Reputation and Reliability as Competitive Factors
In the highly regulated utility sector, a company's reputation and its ability to deliver reliable service are paramount competitive advantages. Con Edison's commitment to operational excellence is clearly demonstrated by its consistent high reliability figures.
In 2024, Con Edison achieved an impressive overall reliability rate of 99.997%. This performance significantly surpasses both national averages and New York State benchmarks for utility service.
- Reputation as a Differentiator: A strong reputation for safety and reliability builds trust with customers and regulators, a critical factor in a monopolistic or regulated market.
- Reliability Metrics: Con Edison's 2024 reliability of 99.997% showcases its operational efficiency and resilience.
- Regulatory Standing: Consistent reliability is key to maintaining favorable relationships with regulatory bodies, influencing future rate decisions and operational flexibility.
- Competitive Benchmarking: While direct competition within specific service territories is limited, this high reliability serves as a benchmark against other utilities nationwide, influencing investor perception and overall market standing.
Consolidated Edison's competitive rivalry is significantly muted within its core service territories due to its regulated monopoly status, meaning direct competition for essential services like electricity and gas distribution is virtually non-existent. However, the company faces indirect competition and benchmarking against larger utility peers, such as NextEra Energy, which had a considerably higher market capitalization as of early 2024. Con Edison's strategic shift away from renewable energy development in 2022, divesting approximately 3,300 megawatts of projects, further altered its competitive landscape in that specific sector.
The primary competitive driver for Con Edison is now meeting New York's ambitious clean energy mandates, such as achieving 70% renewable electricity by 2030. This regulatory environment dictates substantial infrastructure investments, estimated in the billions, rather than traditional market share battles. Con Edison's operational excellence, evidenced by a 99.997% reliability rate in 2024, serves as a key differentiator and a benchmark for its performance against other utilities nationwide.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant threat of substitutes for Consolidated Edison stems from customer-owned distributed generation, particularly rooftop solar panels paired with battery storage. This allows customers to generate their own power, lessening their dependence on the utility's grid and potentially lowering their energy expenses.
In 2024 alone, Con Edison customers added 100 megawatts of solar capacity and 44 megawatts of battery storage. This surge brings the total solar capacity installed by Con Edison customers to over 679 megawatts across 75,200 separate installations. These technologies are becoming more attractive due to falling prices and available incentives, enabling some consumers to drastically cut or even eliminate their electricity bills.
Energy efficiency and conservation measures represent a significant threat of substitutes for Consolidated Edison's core business of supplying electricity and gas. Customers adopting these practices directly reduce their demand for utility-provided energy, impacting sales volumes.
Con Edison itself is a major proponent of these substitutions, investing over $1.5 billion by 2025 in customer energy efficiency programs. These initiatives aim to lower overall energy consumption and encourage electrification, which, while beneficial for emissions, inherently diminishes the need for traditional utility services.
The increasing adoption of alternative heating and cooling technologies, especially heat pumps, presents a significant threat to Con Edison's established gas and steam businesses. New York State's ambitious decarbonization targets, coupled with Con Edison's own Clean Heat initiative, are actively encouraging customers to move away from fossil fuel-based HVAC systems.
This shift is already evident, with nearly 14,000 heat pumps installed through Con Edison's program in 2024 alone. The surge in applications for these programs underscores a clear customer preference for electric alternatives in heating, directly impacting the demand for traditional energy sources.
Community Energy Projects and Microgrids
The growing popularity of community energy projects and microgrids presents a significant threat of substitution for Consolidated Edison. These localized energy solutions allow consumers to access renewable power without the need for individual rooftop installations, thereby diversifying energy sources away from the traditional utility model. While still developing, these options empower communities to generate and manage their own electricity.
These community-based initiatives are gaining traction, offering an alternative to relying solely on large, centralized utility providers. For instance, as of early 2024, the U.S. Department of Energy reported a steady increase in microgrid development, with over 150 operational microgrids and many more in planning stages across the nation. This trend indicates a growing customer appetite for more resilient and potentially cost-effective energy solutions that bypass traditional grid infrastructure.
- Community Solar Growth: Community solar projects allow multiple customers to benefit from a shared solar installation, reducing the need for individual rooftop solar.
- Microgrid Development: Microgrids offer localized energy generation and distribution, potentially allowing communities to disconnect from the main grid during outages and manage their own power supply.
- Diversification of Supply: These alternatives empower customers to source energy from sources other than Con Edison, weakening the utility's traditional market dominance.
- Customer Empowerment: By providing greater control over energy generation and consumption, these projects can shift customer loyalty away from established utility providers.
Policy-Driven Electrification
New York State's ambitious climate agenda, targeting 100% carbon-free electricity by 2040 and the phase-out of natural gas power plants, significantly increases the threat of substitutes for Con Edison's traditional gas and steam services. This policy directly encourages the adoption of electric alternatives for heating, cooling, and transportation, impacting demand for fossil fuels. For instance, the state aims for 1 million electric vehicles (EVs) on the road by 2030, a clear substitute for gasoline-powered vehicles, which in turn increases electricity demand but reduces demand for other energy sources.
Con Edison is actively investing billions to facilitate this transition, including grid modernization and EV charging infrastructure, acknowledging the structural shift away from gas. By 2024, the company had already committed significant capital to its clean energy transition initiatives. This strategic pivot, while necessary, highlights how regulatory mandates and evolving consumer preferences driven by environmental concerns create potent substitutes for established energy delivery methods.
- Policy Mandates: New York's Climate Leadership and Community Protection Act (CLCPA) sets aggressive decarbonization targets.
- Electrification Push: Encouragement of electric vehicles and heat pumps directly substitutes for natural gas and oil.
- Investment Shift: Con Edison's capital expenditures are increasingly directed towards electric infrastructure and renewable energy integration.
- Market Disruption: The shift to cleaner energy sources presents a long-term threat to revenue streams tied to fossil fuel distribution.
The threat of substitutes for Consolidated Edison is substantial, driven by advancements in distributed generation and energy efficiency. Rooftop solar panels combined with battery storage allow customers to generate their own power, reducing reliance on the utility. In 2024, Con Edison customers added 100 megawatts of solar and 44 megawatts of battery storage, increasing total solar capacity to over 679 megawatts.
Energy efficiency measures also directly reduce demand for Con Edison's services. The company itself is investing heavily in these programs, with over $1.5 billion allocated by 2025 to promote energy efficiency, which inherently lessens the need for traditional utility-supplied energy.
Alternative heating and cooling technologies, particularly heat pumps, pose a significant threat to Con Edison's gas and steam businesses. New York State's decarbonization goals and Con Edison's Clean Heat initiative are encouraging a shift away from fossil fuels. In 2024 alone, nearly 14,000 heat pumps were installed through Con Edison's program, indicating a clear customer preference for electric heating solutions.
Community energy projects and microgrids offer further substitution opportunities by providing localized, renewable power sources. As of early 2024, the U.S. Department of Energy noted over 150 operational microgrids nationwide, demonstrating a growing trend towards energy solutions that bypass traditional utility infrastructure.
| Substitute Technology | 2024 Impact/Trend | Con Edison Response/Investment |
| Rooftop Solar & Battery Storage | 100 MW solar added; 44 MW battery added | Investing in grid modernization to integrate distributed energy resources |
| Energy Efficiency Programs | Customer adoption reduces demand | Over $1.5 billion invested by 2025 |
| Heat Pumps | 14,000 installed via Con Edison program in 2024 | Clean Heat initiative promotes electrification |
| Community Solar & Microgrids | Over 150 operational microgrids in the US (early 2024) | Acknowledging and exploring integration of these solutions |
Entrants Threaten
The utility sector, especially in bustling urban centers like New York City, demands substantial capital for building, maintaining, and upgrading infrastructure. This means new players face an uphill battle from the start.
Consolidated Edison itself is projecting a massive investment of around $38 billion between 2025 and 2029. These funds are earmarked for crucial upgrades to its electric, gas, and steam systems, with a strong focus on enhancing grid resilience and advancing clean energy projects. Such significant financial commitments create an exceptionally high barrier to entry, effectively deterring potential new utility providers from even attempting to compete.
The extensive regulatory framework and licensing requirements in New York present a significant barrier to entry for new utility companies. Operating as a regulated utility means adhering to a complex web of rules established by the Public Service Commission (PSC). For instance, in 2024, the PSC continued to emphasize stringent compliance across all utility operations, from infrastructure maintenance to customer service standards.
New entrants must obtain numerous licenses, permits, and approvals, a process that is both time-consuming and costly. These requirements cover critical areas like safety, environmental protection, and service quality, ensuring that any new player meets high operational benchmarks. This regulatory hurdle, coupled with the lengthy approval timelines, effectively discourages new companies from attempting to enter Consolidated Edison's core utility distribution market.
Consolidated Edison benefits from an extensive and deeply embedded infrastructure for delivering electricity, gas, and steam, a network meticulously developed over many years. This established physical presence creates substantial economies of scale, enabling Con Edison to operate at a cost efficiency that new competitors would find exceedingly difficult to match when starting from zero. For instance, in 2023, Con Edison invested $5.3 billion in capital expenditures, largely focused on modernizing and expanding this very infrastructure, demonstrating the ongoing commitment to maintaining this barrier.
Access to Distribution Channels and Customer Base
New entrants would find it incredibly difficult to access the distribution channels and secure customers in Con Edison's service area. Con Edison serves millions of customers across New York City and Westchester. Establishing a new customer base and building parallel infrastructure to serve them would represent an enormous cost and logistical hurdle, severely limiting market entry.
The sheer scale of Con Edison's existing customer relationships, built over decades, creates a significant barrier. Acquiring even a fraction of these millions of residential, commercial, and industrial customers would require substantial investment in marketing and infrastructure development. For instance, Con Edison reported serving approximately 3.4 million customer accounts in its 2023 annual report, highlighting the entrenched nature of its customer base.
- Established Infrastructure: Con Edison's extensive network of pipes, wires, and substations is a massive capital investment that new entrants would need to replicate.
- Customer Loyalty and Switching Costs: Customers are accustomed to Con Edison's services, and switching providers, especially for essential utilities, involves significant effort and potential disruption.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Gaining approval to build and operate competing utility infrastructure is a complex and lengthy process, often favoring incumbent utilities.
- Economies of Scale: Con Edison benefits from significant economies of scale in operations and maintenance, making it difficult for smaller, new entrants to compete on price.
Incumbent Retaliation and Lobbying Power
Consolidated Edison's substantial resources and established lobbying power act as a significant deterrent to new entrants. While direct price wars might be constrained in a regulated environment, Con Edison can leverage its influence to shape regulatory outcomes and policy, making it difficult for newcomers to gain a foothold.
Any aspiring competitor would face considerable hurdles, including potential legal challenges and regulatory opposition orchestrated by Con Edison. The company's active engagement in policy discussions, particularly concerning rate cases and the clean energy transition, demonstrates its commitment to maintaining its market position and discouraging disruptive new players.
- Lobbying and Regulatory Influence: Con Edison actively engages with policymakers, influencing decisions on rate cases and clean energy mandates, which can create barriers for new entrants.
- Resource Advantage: As a large, established utility, Con Edison possesses significant financial and legal resources to counter competitive threats and navigate complex regulatory landscapes.
- Barriers to Entry: The combination of regulatory hurdles and incumbent retaliation significantly raises the risk and cost for potential new entrants seeking to challenge Con Edison's market dominance.
The threat of new entrants for Consolidated Edison is exceptionally low due to immense capital requirements for infrastructure and a complex regulatory environment. Con Edison's planned $38 billion investment between 2025 and 2029 for system upgrades and clean energy projects highlights these high barriers. The stringent licensing and compliance demands from bodies like the Public Service Commission in 2024 further solidify this, making market entry prohibitively expensive and time-consuming for potential competitors.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Con Edison's Position | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Building and maintaining utility infrastructure demands vast sums. | Extremely high cost to replicate existing networks. | Established, extensive physical network. | Con Edison invested $5.3 billion in capital expenditures in 2023. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex licensing, permits, and adherence to PSC standards. | Lengthy, costly, and uncertain approval processes. | Deep familiarity and influence within regulatory bodies. | PSC continued to emphasize stringent compliance in 2024. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to large-scale operations. | New entrants cannot match incumbent cost efficiencies. | Operates at significant scale, reducing average costs. | Serves approx. 3.4 million customer accounts. |
| Customer Entrenchment | Long-standing customer relationships and switching inertia. | Difficult to acquire a substantial customer base. | Millions of loyal residential, commercial, and industrial customers. | ~3.4 million customer accounts reported in 2023. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Consolidated Edison Porter's Five Forces analysis is built on a robust foundation of data, drawing from the company's annual reports, SEC filings, and investor presentations. We also incorporate industry-specific data from reputable sources like the Edison Electric Institute and government regulatory bodies to ensure a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
