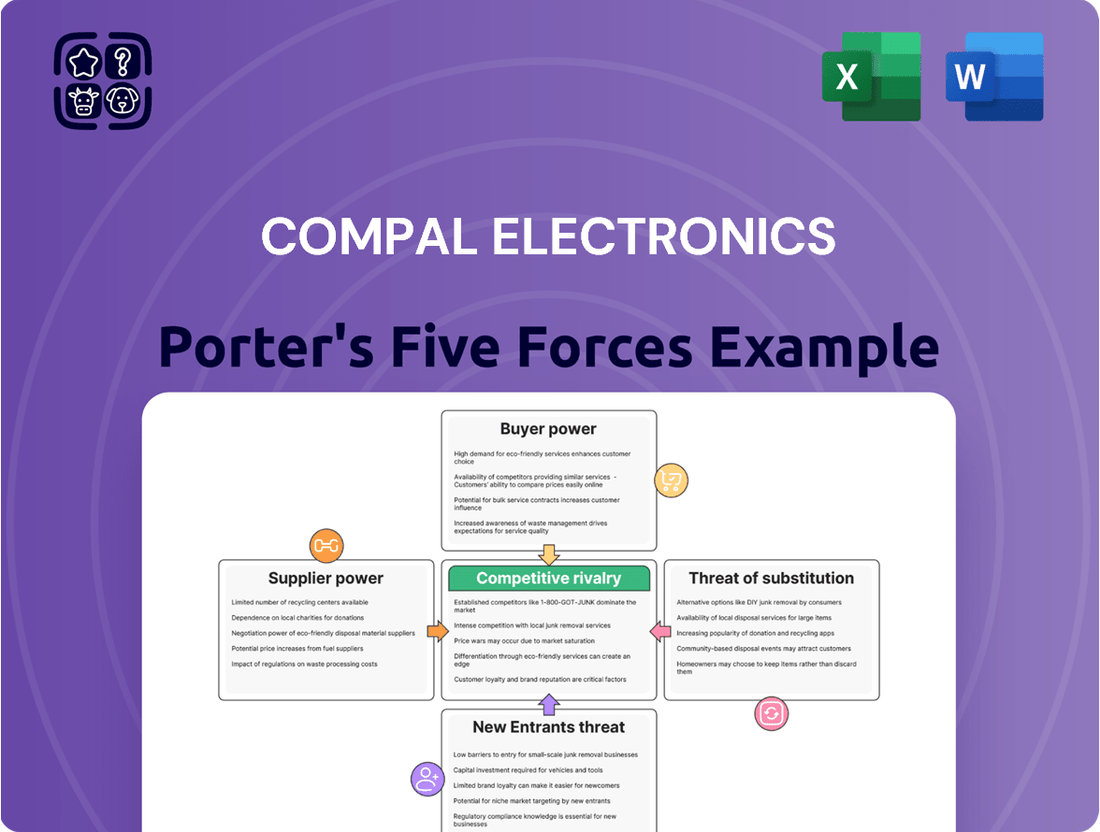
Compal Electronics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Compal Electronics Bundle
Compal Electronics navigates a landscape shaped by intense rivalry and the constant threat of substitutes, while also managing significant buyer power. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Compal Electronics’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Compal Electronics, like many in the electronics manufacturing sector, faces challenges from the concentration of key component suppliers. The semiconductor, display, and memory markets, for instance, are often dominated by a handful of major players. This limited supplier base means these companies can wield considerable influence over pricing and availability, directly affecting Compal's operational costs and production schedules.
The sheer scale of the global electronic components market, which is anticipated to reach approximately USD 1,180.28 billion by 2034, underscores the importance of these suppliers. However, within this vast market, the concentration in critical segments presents a significant factor in the bargaining power of suppliers, potentially forcing ODMs like Compal to accept less favorable terms due to a lack of readily available or cost-effective alternatives.
Suppliers providing highly specialized or unique components, particularly for rapidly advancing fields like AI, 5G, and automotive electronics, hold significant bargaining power. If Compal Electronics relies on these critical, hard-to-substitute parts for its cutting-edge products, these suppliers can dictate higher prices or more demanding contract conditions. For instance, the increasing demand for advanced semiconductor materials like gallium nitride (GaN) in 2024 highlights the growing leverage of suppliers in these niche markets.
The costs Compal faces when switching suppliers are significant. These include expenses for re-tooling manufacturing lines, redesigning products to accommodate new components, and the lengthy process of re-qualifying new suppliers and their parts. For example, the integration of new chipsets or display technologies can require substantial capital investment and time.
These high switching costs directly empower Compal's suppliers. It makes it harder and more expensive for Compal to simply move to another supplier, even if current terms become unfavorable. This lack of easy flexibility strengthens the supplier's position in negotiations.
To counter this, Compal has been actively diversifying its supply chain. In 2023, the company continued its strategy of sourcing components from regions beyond traditional Asian hubs, including exploring options in Europe and North America. This geographical diversification aims to reduce reliance on any single supplier or region, thereby mitigating risks and building greater resilience against supply chain disruptions.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers poses a significant challenge to Compal Electronics. If key suppliers, particularly those providing critical components, possess the capability and motivation to move into the Original Design Manufacturer (ODM) space, they could directly compete with Compal. This scenario would not only diminish Compal's market share but also fundamentally alter the competitive landscape.
While specialized component manufacturers may find this less common, the incentive to capture greater value within the supply chain is a persistent driver. Suppliers integrating forward would inherently increase their bargaining power over remaining ODMs. The electronics manufacturing services (EMS) sector, which encompasses ODMs like Compal, is characterized by a high degree of concentration, meaning a limited number of large suppliers hold substantial market influence, amplifying this threat.
- Supplier Integration Risk: Key suppliers could leverage their expertise and resources to enter the ODM market, becoming direct competitors to Compal.
- Value Chain Capture: Suppliers may integrate forward to capture a larger portion of the value chain, increasing their profitability and leverage.
- Market Concentration: The EMS market's concentration means a few dominant suppliers have the potential to disrupt the industry through forward integration.
Importance of Compal to Supplier's Business
Compal's significant role as a customer directly impacts its suppliers' bargaining power. When Compal constitutes a substantial percentage of a supplier's overall sales, that supplier's leverage is naturally reduced. This is because the supplier has more to lose if they alienate such a key client. For instance, if Compal accounts for 15% of a component manufacturer's revenue, that manufacturer will likely be more accommodating to Compal's demands regarding pricing or terms.
Conversely, if Compal is just one of many clients for a dominant supplier, the supplier's position strengthens considerably. In such scenarios, the supplier can more easily dictate terms, knowing that Compal's business, while important, is not singularly critical. Compal's extensive client list, which includes major brands like Dell, HP, Lenovo, Acer, and ASUS, means that many of its suppliers serve multiple large customers, diffusing Compal's individual purchasing power.
- Compal's Customer Significance: If Compal represents a large portion of a supplier's revenue, the supplier's bargaining power diminishes.
- Supplier Dominance: If Compal is a smaller customer for a dominant supplier, the supplier's bargaining power increases.
- Key Customer Relationships: Compal's partnerships with major brands like Dell, HP, Lenovo, Acer, and ASUS influence the bargaining dynamics with its suppliers.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Compal Electronics is moderately high, primarily due to the concentration in key component markets like semiconductors and displays. This concentration allows a few dominant players to influence pricing and availability, impacting Compal's cost structure and production timelines.
Suppliers of specialized or advanced components, especially those critical for emerging technologies such as AI and 5G, hold significant leverage. The high costs associated with switching suppliers, including re-tooling and re-qualification, further strengthen their position. For example, the increasing demand for advanced semiconductor materials in 2024 underscores this trend.
While Compal's diversification efforts in 2023 aimed to mitigate reliance on single suppliers, the threat of forward integration by these suppliers remains a concern, potentially turning them into direct competitors.
Compal's position as a major customer for many suppliers does temper their power, but this is counterbalanced by the fact that many suppliers also serve Compal's large brand clients, diffusing Compal's individual purchasing influence.
| Factor | Impact on Compal | Supporting Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Moderate to High | Dominance in semiconductor and display markets by a few key players. |
| Switching Costs | High | Expenses for re-tooling, redesign, and re-qualification of components. |
| Supplier Specialization | High | Leverage for suppliers of advanced components for AI, 5G, automotive. |
| Compal's Customer Significance | Moderate | Compal's revenue share with some suppliers is significant, but many suppliers serve multiple large clients. |
What is included in the product
This analysis reveals the intensity of competition in the electronics manufacturing sector, Compal's bargaining power with suppliers and buyers, and the barriers to entry for new players.
Easily identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing Compal's bargaining power with suppliers and buyers.
Customers Bargaining Power
Compal Electronics' customer base is heavily concentrated among major global brand-name companies. Clients like Dell, HP, and Lenovo represent a significant portion of Compal's revenue, granting them substantial bargaining power. This concentration means these key customers can effectively negotiate pricing, delivery schedules, and even product specifications, directly impacting Compal's profitability and operational flexibility.
Major brand customers, possessing significant financial clout and technical know-how, could potentially bring some design and manufacturing processes in-house or opt to partner with multiple Original Design Manufacturers (ODMs). This potential for backward integration or multi-sourcing significantly amplifies customer leverage, compelling Compal to maintain competitive pricing and cutting-edge solutions to secure their loyalty.
Customers in the electronics sector, particularly for common items like laptops and tablets, are frequently very sensitive to price. This means they'll readily seek out cheaper alternatives if available.
If Compal’s offerings don't stand out from what rivals provide, customers have the freedom to switch to other original design manufacturers (ODMs) that offer lower prices. This ability to switch easily significantly boosts customer bargaining power.
The market for tablet and notebook PC ODMs and electronic manufacturing services (EMS) is substantial, estimated to be around USD 150 billion in 2024. This large market size amplifies the impact of customer price sensitivity.
Customer's Access to Information
Customers today have unprecedented access to information. They can easily compare pricing across various Compal competitors, research alternative suppliers, and understand industry pricing benchmarks. This knowledge directly translates into stronger negotiation power.
This transparency empowers customers to demand better terms, potentially squeezing Compal's profit margins. For instance, in 2024, Compal reported an impressive overall customer satisfaction score of 90.2, indicating a strong customer base, but this also means customers are likely well-informed about market offerings.
- Increased Information Access: Customers can readily find pricing, supplier alternatives, and industry standards.
- Enhanced Negotiation Power: This information allows customers to negotiate more effectively with Compal.
- Margin Pressure: Demands for better terms can put pressure on Compal's profitability.
- Customer Satisfaction Metric: Compal's 90.2 customer satisfaction score in 2024 suggests a well-informed and engaged customer base.
Volume of Orders
The sheer volume of orders placed by Compal Electronics' major clients significantly amplifies their bargaining power. As an Original Design Manufacturer (ODM), Compal depends on these large-scale orders to achieve crucial economies of scale and maintain high capacity utilization. For instance, a customer placing a substantial order can effectively negotiate for more favorable pricing or terms, leveraging the significant business volume they represent.
The industry is highly sensitive to order volume, directly impacting Compal's operational efficiency and profitability. This dynamic is underscored by market projections; notebook shipments are anticipated to see a 4.9% increase, reaching 183 million units by 2025, highlighting the importance of securing and retaining these high-volume contracts.
- Customer Leverage: Large order volumes grant customers considerable sway in negotiations.
- Economies of Scale: Compal's reliance on big orders is key to optimizing production costs.
- Capacity Utilization: Substantial orders are vital for keeping Compal's manufacturing facilities running efficiently.
- Favorable Terms: Customers with significant order commitments can demand better pricing and conditions.
Compal's customers, primarily large global brands, wield significant bargaining power due to their concentrated purchasing volume and the availability of alternative ODMs. This leverage allows them to negotiate favorable pricing and terms, directly impacting Compal's margins. For example, the tablet and notebook PC ODM market was valued at approximately USD 150 billion in 2024, indicating a competitive landscape where customer choice is paramount.
| Factor | Impact on Compal | Supporting Data (2024/2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High leverage for major clients like Dell, HP, Lenovo. | Significant portion of Compal's revenue tied to a few key accounts. |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers readily seek lower-cost alternatives. | Notebook shipments projected to reach 183 million units by 2025, highlighting market volume. |
| Switching Costs | Low for customers due to multiple ODM options. | The ODM market's size (USD 150 billion in 2024) offers ample alternatives. |
| Information Access | Customers are well-informed on pricing and alternatives. | Compal's 90.2% customer satisfaction in 2024 suggests an engaged, knowledgeable customer base. |
Full Version Awaits
Compal Electronics Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Compal Electronics, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for the company. You're looking at the actual document. Once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, providing an in-depth examination of buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and industry rivalry as they pertain to Compal's operations and market position.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Original Design Manufacturer (ODM) market for electronic devices, especially notebooks and tablets, is incredibly crowded. Compal Electronics operates in an environment with numerous strong competitors, all vying for market share.
Key rivals for Compal include giants like Foxconn (Hon Hai Precision Industry Co., Ltd.), Quanta Computer, Wistron, and Pegatron. This intense rivalry naturally fuels price wars, which can squeeze profit margins for all involved and put constant pressure on companies to innovate faster.
Compal holds a significant position as the world's second-largest notebook ODM, commanding a substantial 16% share of the global notebook shipment market. This scale, however, doesn't diminish the fierce competition it faces from its equally large and capable competitors.
The global electronic components market is projected for growth, but mature areas like traditional notebooks and tablets might see more modest expansion. This slower growth in key segments naturally fuels more intense competition among players vying for market share.
Specifically, the market for Original Design Manufacturers (ODMs) and Electronics Manufacturing Services (EMS) in the tablet and notebook PC sectors is expected to reach approximately USD 220 billion by 2033. This represents a compound annual growth rate of 4.5% between 2025 and 2033, indicating a steady but not explosive growth trajectory.
Compal Electronics, like other Original Design Manufacturers (ODMs), faces intense rivalry driven by the need for cutting-edge design, streamlined production, and novel technological solutions. This competitive landscape necessitates continuous investment in research and development to stay ahead.
To counter this, Compal is actively diversifying beyond its traditional PC manufacturing base. Its strategic expansion into burgeoning sectors like automotive electronics, smart healthcare, and 5G communication technologies aims to create distinct value propositions and mitigate risks associated with market fluctuations in established segments.
Compal's focus on innovation, particularly in leveraging advanced technologies to support AI adoption and enterprise system upgrades, is crucial for its differentiation strategy. For instance, in 2023, Compal reported a significant increase in its R&D expenditure, reflecting its commitment to developing these next-generation solutions.
Switching Costs for Customers (OEMs)
While Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) hold considerable bargaining power, the costs associated with switching Original Design Manufacturers (ODMs) remain a notable factor. These switching costs can be substantial, stemming from deeply integrated supply chains, shared intellectual property, and the need to retool or adapt specific manufacturing processes. For instance, the initial setup and validation phases for a new ODM can represent a significant investment in time and resources for an OEM.
The perception of these switching costs directly influences competitive rivalry. If OEMs view the transition to a different ODM as relatively low-cost and straightforward, the pressure on existing ODMs like Compal to maintain competitive pricing and service levels intensifies. This dynamic encourages a more aggressive competitive landscape within the ODM sector.
Compal Electronics is actively addressing potential shifts in these switching costs and competitive pressures. A key strategy involves the diversification of its production facilities. By establishing manufacturing sites in various geopolitical regions, Compal aims to enhance its supply chain resilience and offer greater flexibility to its OEM clients, thereby potentially increasing the perceived switching costs for those clients considering other ODMs.
- Established Relationships: OEMs often have long-standing partnerships with ODMs, involving intricate supply chain integration and trust built over years.
- Intellectual Property & Customization: Sharing proprietary designs or requiring highly customized manufacturing processes creates significant barriers to switching for OEMs.
- Manufacturing Process Adaptation: Replicating or adapting complex manufacturing workflows and quality control measures at a new ODM can be time-consuming and costly.
- Geopolitical Diversification: Compal's strategy to spread production across different regions aims to mitigate risks and offer OEMs more secure and adaptable supply chain options, indirectly influencing switching costs.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers, like substantial fixed assets and specialized labor, can trap companies in an industry, even when unprofitable, thus fueling competitive rivalry. Compal's significant investments in its global manufacturing footprint and advanced R&D for ODM services mean that exiting the market would involve considerable sunk costs.
These high exit barriers, particularly the specialized nature of its integrated supply chain and manufacturing capabilities, mean Compal is committed to its operational scale. For instance, in 2023, Compal reported revenue of approximately NT$970.3 billion (around $31 billion USD), demonstrating the scale of its ongoing operations and the difficulty of divesting such assets.
- Significant Capital Investments: Compal's extensive network of manufacturing facilities requires immense capital, making a quick exit financially prohibitive.
- Specialized Workforce and Technology: The company relies on a highly skilled workforce and proprietary technologies, which are difficult to redeploy or sell off.
- Long-Term Commitments: Existing contracts with clients and suppliers create ongoing obligations that act as a deterrent to immediate withdrawal.
- Strategic Importance of Global Operations: Compal's continued investment in its global operations and agile supply chain management underscores its long-term commitment and the high cost of exiting these integrated systems.
The competitive rivalry within the Original Design Manufacturer (ODM) sector, particularly for notebooks and tablets, is exceptionally fierce. Compal Electronics, as a major player, contends with formidable rivals like Foxconn, Quanta Computer, Wistron, and Pegatron, all of whom are constantly striving to capture market share through aggressive pricing and rapid innovation.
This intense competition is further exacerbated by the relatively mature nature of the notebook and tablet markets, which are projected to grow at a modest CAGR of 4.5% between 2025 and 2033, reaching an estimated USD 220 billion by 2033. In such an environment, companies like Compal must continuously invest in R&D, as evidenced by its increased R&D expenditure in 2023, to maintain a competitive edge and differentiate their offerings.
Compal's position as the world's second-largest notebook ODM, with a 16% market share, highlights its scale but does not insulate it from the pressures of this highly competitive landscape. The company's strategic diversification into areas like automotive electronics and smart healthcare is a direct response to these pressures, aiming to reduce reliance on the highly competitive PC segment.
The ODM market is characterized by significant switching costs for Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs), stemming from integrated supply chains and intellectual property sharing. Compal leverages this by diversifying its production facilities globally, enhancing supply chain resilience and potentially increasing perceived switching costs for its clients, thereby mitigating some competitive pressures.
| Competitor | 2023 Revenue (USD Billions Approx.) | Key Products |
| Foxconn (Hon Hai) | 110.7 | Smartphones, Laptops, Servers, Gaming Consoles |
| Quanta Computer | 39.2 | Notebooks, Servers, Automotive Electronics |
| Wistron | 22.0 | Notebooks, Servers, Consumer Electronics |
| Pegatron | 20.0 | Smartphones, Laptops, Consumer Electronics |
| Compal Electronics | 31.0 | Notebooks, Tablets, Servers, Automotive Electronics |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Compal Electronics, an Original Design Manufacturer (ODM), primarily comes from Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) opting for in-house production or utilizing alternative manufacturing service providers like Electronic Manufacturing Services (EMS) companies. While ODMs provide valuable design and manufacturing expertise, large OEMs may choose vertical integration for greater control over their product lifecycle or strategic advantages.
In 2024, the electronics manufacturing landscape continues to be shaped by outsourcing. OEMs leverage ODMs and EMS providers to achieve cost efficiencies and faster time-to-market, but the option to bring manufacturing in-house remains a viable substitute for those with the scale and resources to manage it effectively.
For Compal Electronics, the threat of substitutes is significant as other devices increasingly overlap in functionality with their core products like notebooks and tablets. More powerful smartphones, the emergence of foldable devices, and sophisticated integrated smart displays can now perform many tasks previously exclusive to traditional laptops and tablets, directly impacting demand for Compal's offerings.
The tablet market, a key segment for Compal, faces a particularly challenging future. Long-term growth potential is largely flat, with more powerful smartphones eating into tablet market share by offering comparable or even superior mobile computing experiences for many users. This trend, evident in recent market analyses, puts pressure on Compal to innovate and differentiate its tablet products.
The rise of cloud computing and software-as-a-service (SaaS) presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional hardware manufacturers like Compal Electronics. As more processing power and storage move to the cloud, the need for high-performance, locally installed devices diminishes. This trend could steer consumers towards less powerful, more affordable devices or even subscription models for accessing computing capabilities, directly substituting the need for Compal's core product offerings.
For instance, the global cloud computing market was valued at approximately $590.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $1,674.7 billion by 2030, demonstrating a strong compound annual growth rate. This expansion indicates a growing preference for cloud-based services over on-premises hardware solutions.
Compal's strategic diversification into cloud servers and AI applications is a direct response to this evolving landscape. By developing solutions for the cloud infrastructure itself, Compal aims to mitigate the threat of substitution by becoming a provider within the very ecosystem that could otherwise undermine its traditional business. This strategic pivot acknowledges the shift in demand and seeks to capture value from these emerging technological trends.
Emergence of New Technologies
The rapid evolution of technology presents a significant threat of substitutes for Compal Electronics. New technological categories, such as immersive augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) devices, or entirely new device form factors, could emerge to replace traditional electronic products by offering enhanced user experiences or novel functionalities. For example, if AR glasses become sophisticated enough to replace smartphones for many tasks, this would directly impact Compal's core business.
Compal is proactively addressing this by investing in and exploring cutting-edge technologies. Their focus on AI-integrated solutions and advanced communication technologies, like 5G and beyond, positions them to adapt to or even lead these technological shifts. This strategic foresight is crucial as the market for consumer electronics and computing devices continues to be disrupted by innovation.
- Technological Disruption: Emerging technologies like advanced AR/VR can offer alternative functionalities to traditional devices, potentially cannibalizing Compal's existing product lines.
- AI Integration: Compal's investment in AI-powered solutions aims to create new product categories or enhance existing ones, mitigating the threat of substitutes by becoming a provider of these new solutions.
- Advanced Communications: Focus on 5G and future communication tech allows Compal to be at the forefront of devices that leverage these new networks, potentially displacing older communication hardware.
- Market Adaptability: The ability to pivot and integrate new technologies quickly is key to Compal's strategy in neutralizing the threat of substitutes.
Cost-Effectiveness of Substitutes
The threat of substitutes for Compal Electronics is significant, particularly when alternative solutions offer comparable or superior functionality at a notably lower price point. As technology rapidly advances, the emergence of more affordable alternatives can exert considerable pressure on Compal. This necessitates continuous innovation and rigorous cost optimization to maintain a competitive edge in the market.
For instance, in the notebook ODM (Original Design Manufacturer) market, Compal faces competition from manufacturers who can leverage lower labor costs or more efficient production processes. In 2024, the global average selling price for laptops continued to be a critical factor for consumers, with many seeking value-for-money options. This trend directly impacts Compal's ability to command premium pricing if substitutes offer similar performance at a reduced cost.
- Cost Pressure: The availability of lower-priced substitute products, such as those from emerging market manufacturers or alternative device types, directly challenges Compal's pricing power and profit margins.
- Technological Obsolescence: Rapid technological shifts can render existing product designs less attractive, increasing the threat from substitutes that incorporate newer, more cost-effective technologies.
- Market Sensitivity: In segments where price is a primary purchasing driver, Compal must constantly benchmark against cost-effective substitutes to ensure its offerings remain competitive.
The threat of substitutes for Compal Electronics is multifaceted, encompassing both alternative manufacturing models and evolving technological capabilities that can replace traditional devices. For instance, the increasing functionality of smartphones and the advancements in cloud computing reduce the reliance on dedicated devices like tablets and notebooks, which are core to Compal's ODM business.
The market for computing devices is dynamic, with new form factors and integrated solutions constantly emerging. Compal must remain agile, as products like advanced smart displays or even highly capable wearable technology could eventually serve as substitutes for some of its current offerings. The global market for smart home devices, for example, saw significant growth, indicating a trend towards integrated and multi-functional electronics.
Furthermore, the potential for Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEMs) to bring design and production in-house presents a direct substitute for Compal's ODM services. While outsourcing offers cost and efficiency benefits, large-scale OEMs may opt for vertical integration to gain greater control over their supply chains and intellectual property, especially in a competitive 2024 market where margins are often tight.
Here's a look at the evolving landscape of device substitutes:
| Device Category | Substitute Trend | Impact on Compal | 2024 Market Insight |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tablets | Advanced Smartphones, Foldable Devices | Reduced demand for traditional tablets | Smartphone screen sizes are increasing, blurring lines with tablets. |
| Notebooks | Cloud Computing, High-Performance Smartphones | Potential shift towards lighter, less powerful devices or cloud-based solutions | The average selling price for laptops remained a key consideration for consumers in 2024. |
| Manufacturing Services | In-house OEM Production, Alternative EMS Providers | Loss of ODM contracts for large OEMs | OEMs continue to evaluate the cost-benefit of outsourcing vs. vertical integration. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the Original Design Manufacturer (ODM) industry, particularly at the scale Compal operates, demands immense capital. New players need significant investments in state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, cutting-edge research and development, and robust supply chain networks to compete effectively.
These substantial upfront capital requirements serve as a formidable barrier, deterring many potential entrants from challenging established giants like Compal. The global electronics manufacturing services (EMS) market itself was valued at a considerable USD 580.2 billion in 2023, indicating the sheer scale of investment needed to gain even a small foothold.
Established Original Design Manufacturers (ODMs) like Compal Electronics leverage substantial economies of scale, particularly in manufacturing, component procurement, and research and development. For instance, Compal's massive production volumes in 2024 allow for significantly lower per-unit costs compared to any potential new entrant. This cost advantage makes it incredibly difficult for newcomers to compete on price.
Furthermore, the experience curve effect plays a crucial role. Compal's decades of operational experience have honed its processes, leading to greater efficiency and reduced waste. New entrants lack this accumulated knowledge, facing a steep learning curve and higher initial operating costs, which further hinders their ability to achieve cost parity.
Compal's extensive global manufacturing footprint and sophisticated supply chain management, refined over years of operation, provide a level of stability and cost-competitiveness that is challenging for new players to replicate. This integrated approach ensures consistent product quality and timely delivery, reinforcing Compal's market position.
Compal Electronics' established relationships with major global brands like Dell, HP, Lenovo, Acer, and ASUS present a significant barrier for new entrants. These long-standing partnerships are crucial for securing consistent order volumes, a lifeline in the competitive ODM industry where reliability and quality are paramount. New players would struggle immensely to replicate this level of trust and gain access to these vital distribution channels.
Proprietary Technology and Intellectual Property
The threat of new entrants in the Original Design Manufacturer (ODM) space, particularly for companies like Compal Electronics, is significantly mitigated by the substantial barriers erected by proprietary technology and intellectual property (IP). Established ODMs, including Compal, have cultivated extensive portfolios of patents, unique design methodologies, and highly optimized manufacturing processes over many years. This accumulated IP represents a critical competitive advantage, making it incredibly difficult and costly for newcomers to replicate the same level of technological sophistication and operational efficiency. The investment in research and development, coupled with the time required to build a robust IP library, acts as a powerful deterrent.
Compal's commitment to innovation is clearly demonstrated by its consistent recognition in prestigious design rankings. For instance, Compal secured a position in the Top 10 of the iF WORLD DESIGN INDEX 2025, a testament to its design excellence and ability to create market-leading products. This strong emphasis on design and technological advancement not only enhances Compal's own market standing but also raises the bar for potential entrants, requiring them to possess comparable innovative capabilities to compete effectively.
The hurdles for new ODMs are substantial:
- Significant R&D Investment: New entrants must commit substantial capital to research and development to acquire or develop comparable technological capabilities.
- Intellectual Property Acquisition: Building a strong IP portfolio, akin to those held by established players like Compal, is a lengthy and expensive process.
- Design Expertise: Replicating Compal's proven design excellence and innovation requires deep expertise and a track record of successful product development.
- Manufacturing Process Optimization: Developing proprietary, efficient manufacturing processes that match the scale and quality of existing ODMs presents a major challenge.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policies and regulations significantly influence the threat of new entrants for companies like Compal Electronics. For instance, stringent environmental standards, such as those implemented by the European Union's RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances) directive, require substantial investment in compliance and product redesign, creating a hurdle for newcomers. Similarly, labor practice regulations, particularly in manufacturing hubs like China, add to operational costs and complexity, making it harder for new players to compete on price.
International trade policies and geopolitical tensions also act as barriers. In 2023, for example, ongoing trade disputes and tariffs impacted global supply chains, increasing the cost and uncertainty for businesses importing or exporting components and finished goods. New entrants must navigate these complex trade landscapes, which can involve significant legal and logistical expenses, further deterring market entry.
- Environmental Regulations: Compliance with standards like RoHS and REACH can cost new entrants millions in testing and product modification.
- Labor Laws: Adhering to diverse international labor practices and minimum wage laws increases operational overhead for new manufacturers.
- Trade Tariffs and Policies: In 2023, escalating trade tensions led to increased costs for key electronic components, impacting new entrants' pricing strategies.
- Geopolitical Instability: Supply chain disruptions due to geopolitical events can pose significant risks and capital requirements for new market participants.
The threat of new entrants for Compal Electronics is low due to substantial capital requirements. Establishing a presence in the ODM sector necessitates massive investments in advanced manufacturing facilities, cutting-edge R&D, and resilient supply chains, a barrier underscored by the global EMS market's USD 580.2 billion valuation in 2023.
Existing players like Compal benefit from significant economies of scale, particularly in procurement and production, which lower per-unit costs. Compal's 2024 production volumes allow it to achieve cost efficiencies that are nearly impossible for newcomers to match, effectively pricing them out of direct competition.
Compal's established brand loyalty and deep-rooted relationships with major clients such as Dell and HP are critical entry barriers. These partnerships ensure consistent order flow and market access, which new entrants would find extremely difficult to secure given the industry's emphasis on reliability and proven performance.
Compal's strong intellectual property portfolio and proprietary technologies, honed through years of R&D, present a significant hurdle. The iF WORLD DESIGN INDEX 2025 recognition highlights Compal's design prowess, demanding comparable innovation from any potential competitor.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Compal Electronics is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial statements, investor relations reports, and industry-specific market research from reputable firms. We also incorporate data from trade publications and news archives to capture current market dynamics and competitive pressures.
