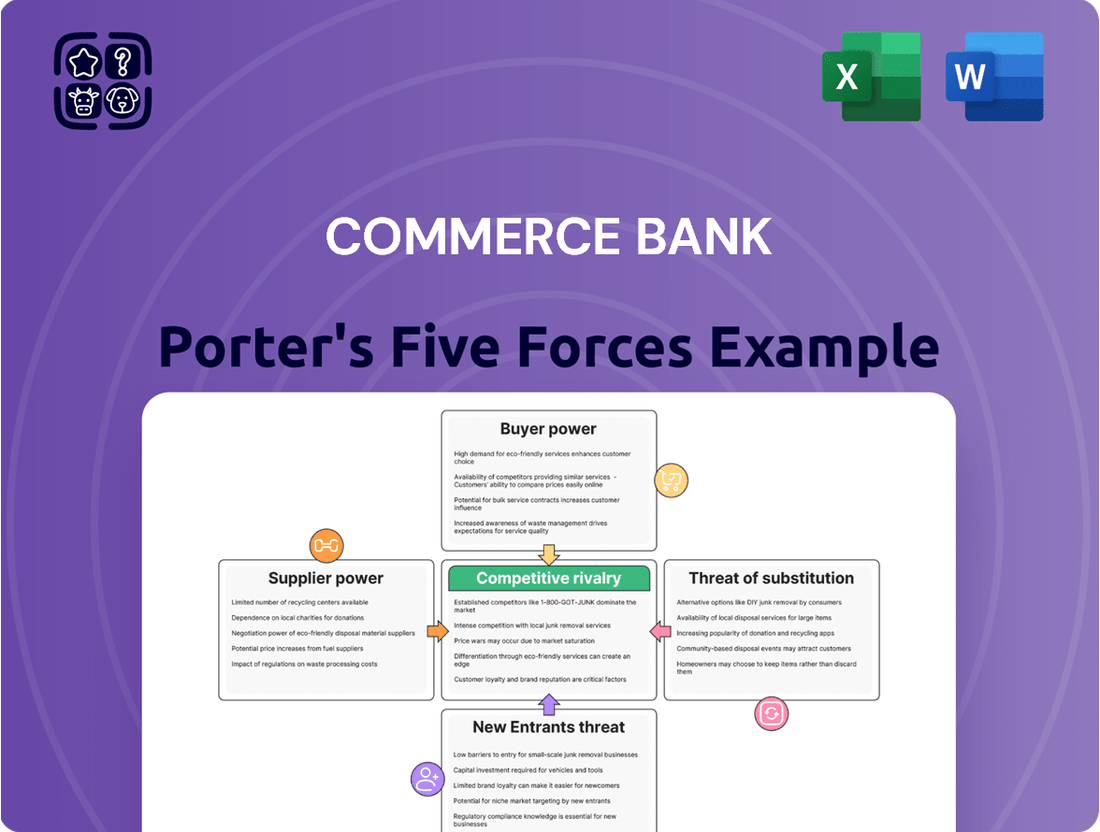
Commerce Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Commerce Bank Bundle
Commerce Bank navigates a competitive landscape shaped by powerful buyer bargaining, intense rivalry, and the ever-present threat of substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for any stakeholder looking to grasp the bank's strategic position.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Commerce Bank’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Technology providers hold considerable sway in the banking sector because financial institutions depend on them for everything from core banking software to cutting-edge cybersecurity and AI-driven analytics. The specialized nature of these solutions, coupled with the intricate integration required, means banks often have limited alternatives, especially for advanced capabilities. For instance, in 2024, banks continued to pour billions into digital transformation, with a significant portion allocated to upgrading core systems and adopting AI, highlighting their reliance on these tech vendors.
Suppliers of financial data, market intelligence, and advanced analytics are increasingly vital for banks like Commerce Bank. These services enable informed decision-making, risk management, and personalized customer offerings. The growing reliance on data means these suppliers hold significant sway.
The uniqueness and proprietary nature of specific data sets can amplify supplier bargaining power. For instance, specialized market sentiment data or exclusive economic forecasts are not easily replicated, giving their providers an advantage. As the financial industry leans more heavily into data-driven strategies, this leverage is only expected to grow.
The bargaining power of suppliers in the regulatory compliance solutions sector for banks is significant. As regulatory demands intensify, specialized RegTech providers offering solutions for AML, KYC, and other compliance needs become indispensable. For instance, in 2024, the global RegTech market was projected to reach over $12 billion, reflecting the critical demand for these specialized services.
Talent and Human Capital
The availability of highly skilled professionals, especially in critical fields like cybersecurity and artificial intelligence, significantly influences a bank's competitive edge and its capacity for innovation. A scarcity of such talent directly amplifies the bargaining power of these human capital ‘suppliers’ – the employees themselves.
This dynamic is particularly pronounced in niche areas such as wealth management and advanced financial technology. For instance, in 2024, the demand for cybersecurity professionals in the financial sector continued to outstrip supply, leading to increased salary expectations and retention challenges for institutions like Commerce Bank.
- Talent Shortages: In 2024, the financial services industry faced persistent shortages in specialized roles, particularly in AI and cybersecurity.
- Increased Labor Costs: This scarcity drove up compensation packages, with average salaries for senior cybersecurity analysts in financial institutions seeing a 10-15% increase year-over-year.
- Impact on Innovation: Banks struggling to attract and retain top tech talent may find their ability to develop and deploy new digital products and services hampered.
Payment Network Providers
Payment network providers like Visa and Mastercard hold substantial bargaining power over banks. Their extensive global networks and brand recognition are essential for facilitating card transactions, making them indispensable partners for banks seeking to offer robust payment services.
Banks rely heavily on these networks for their core retail and corporate banking operations, which often include significant transaction volumes. For instance, in 2023, Visa reported processing over 247 billion transactions globally, highlighting the sheer scale of their network's importance to financial institutions.
- Dominant Market Share: Visa and Mastercard collectively control a vast majority of the global card payment market, limiting banks' alternatives.
- Network Effects: The value of these networks increases with every new user and merchant, creating a strong barrier to entry for potential competitors.
- Interchange Fees: These providers dictate interchange fees, which are a significant revenue stream for banks, giving them leverage in negotiations.
- Infrastructure Investment: The immense investment required to build and maintain such payment infrastructure further solidifies their position.
Suppliers of specialized financial software, particularly in areas like core banking systems and regulatory compliance, wield significant power. Banks' dependence on these often proprietary solutions, coupled with the high costs and complexity of switching, grants these vendors considerable leverage. For example, the global RegTech market was projected to exceed $12 billion in 2024, underscoring the critical demand and reliance on these specialized providers.
The bargaining power of talent suppliers, especially in high-demand fields like cybersecurity and artificial intelligence, is substantial. A shortage of skilled professionals in 2024 led to increased salary expectations, with senior cybersecurity analyst salaries in finance seeing a 10-15% year-over-year rise, impacting banks' ability to innovate and retain talent.
Payment network giants like Visa and Mastercard possess immense bargaining power due to their dominant market share and the network effects inherent in their operations. Their control over essential transaction infrastructure and the interchange fees they set are critical to banks, limiting alternatives and providing significant leverage.
| Supplier Type | Key Dependence | Supplier Leverage Factor | 2024 Data Point/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Technology Providers (Core Banking, AI) | Digital transformation, advanced analytics | Specialized solutions, integration complexity | Billions invested in digital transformation, AI adoption |
| Data & Analytics Providers | Informed decision-making, risk management | Uniqueness of data, proprietary nature | Growing reliance on data-driven strategies |
| RegTech Providers | Regulatory compliance (AML, KYC) | Intensifying regulatory demands, indispensability | RegTech market projected over $12 billion |
| Skilled Professionals (Cybersecurity, AI) | Innovation, operational security | Talent scarcity, specialized skills | 10-15% salary increase for senior cybersecurity analysts |
| Payment Networks (Visa, Mastercard) | Transaction processing, retail banking | Dominant market share, network effects | Visa processed over 247 billion transactions in 2023 |
What is included in the product
This analysis delves into the competitive forces impacting Commerce Bank, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the banking sector.
Instantly understand competitive pressures with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces analysis, allowing Commerce Bank to proactively address threats and capitalize on opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers of Commerce Bank, whether individuals or businesses, face a landscape brimming with financial service providers. This includes not only other established banks and credit unions but also a dynamic and expanding sector of fintech companies. This abundance of choices significantly amplifies customer bargaining power.
The ease with which customers can switch to a competitor offering better terms or a more suitable service means Commerce Bank must remain highly competitive. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. banking sector saw continued growth in digital-only banks and neobanks, many of which offer competitive interest rates and lower fees, directly challenging traditional institutions like Commerce Bank.
For fundamental banking services such as checking accounts and personal loans, customers are highly attuned to pricing. They actively compare interest rates and fees across different institutions, making them price sensitive. This means Commerce Bancshares, like its competitors, must offer competitive rates to attract and retain these customers, limiting its power to set terms unilaterally.
Today's consumers, especially younger demographics, demand effortless, always-on digital interactions. This includes sophisticated mobile banking apps, intuitive online portals for managing accounts, and the ability to conduct transactions instantly. For instance, by the end of 2023, mobile banking adoption rates continued to climb, with many banks reporting over 70% of their customer base actively using mobile platforms for daily transactions.
The rise of fintech innovators has significantly raised the bar for digital convenience. These agile companies often offer streamlined user interfaces and faster service delivery, compelling traditional institutions like Commerce Bank to accelerate their technological investments. This competitive pressure means banks must continuously upgrade their digital offerings to retain and attract customers who are accustomed to best-in-class digital experiences.
Access to Information and Comparison Tools
Customers today have unprecedented access to information, making it easier than ever to compare financial products and services. Online platforms, comparison websites, and financial news outlets provide a wealth of data, allowing consumers to scrutinize offerings from various institutions. This transparency directly fuels their bargaining power.
The ability to easily compare interest rates, fees, and features empowers customers to seek out the best deals. For instance, in 2024, online comparison sites are actively highlighting differences in mortgage rates, with variations of 0.5% or more being common across lenders for similar loan amounts. This encourages customers to switch providers for better terms.
- Increased Transparency: Online tools allow for side-by-side comparisons of bank accounts, loans, and investment products.
- Informed Decision-Making: Customers can research product features, customer reviews, and fee structures before committing.
- Demand for Competitive Pricing: Easy access to competitor information pushes financial institutions to offer more attractive rates and lower fees.
- Shift in Power Dynamic: The ease of information gathering shifts some control from the bank to the consumer.
Large Corporate and Wealth Management Clients
Large corporate and wealth management clients wield considerable bargaining power with Commerce Bank. These sophisticated clients, often managing substantial assets or engaging in complex financial transactions, can demand highly customized services and competitive pricing. Their ability to move significant volumes of business means Commerce Bank must actively cater to their specific needs to retain them.
For instance, in 2024, large institutional clients often negotiate preferential rates on loans and deposits, directly impacting the bank's net interest margin. Wealth management clients, particularly those with multi-million dollar portfolios, can also exert pressure for premium service levels and exclusive investment opportunities. This concentrated power among a smaller client base necessitates a strategic focus on relationship management and value-added offerings.
- Concentrated Client Base: A smaller number of large corporate and wealth management clients represent a significant portion of Commerce Bank's revenue.
- Demand for Customization: These clients require tailored financial solutions, from complex lending structures to bespoke investment strategies.
- Price Sensitivity: Despite the sophisticated nature of their needs, these clients are often price-sensitive and can leverage competitive offers from other financial institutions.
- Relationship Value: Commerce Bank's profitability is heavily reliant on maintaining strong relationships with these key clients, making their bargaining power substantial.
The bargaining power of customers for Commerce Bank is substantial, driven by market saturation and ease of switching. In 2024, the proliferation of digital banking options and fintech solutions means customers have more choices than ever, forcing banks to offer competitive rates and superior service to retain their business. This environment directly limits Commerce Bank's ability to dictate terms, as customers can readily find better deals elsewhere.
| Factor | Impact on Commerce Bank | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Alternatives | High | Continued growth in neobanks and digital-only banks offering competitive rates and lower fees. |
| Customer Information Access | High | Online comparison sites readily highlight rate differences, encouraging switching for better terms. |
| Switching Costs | Low | Minimal barriers to opening new accounts or transferring funds digitally. |
| Price Sensitivity (Retail) | High | Customers actively compare interest rates on savings accounts and loan products. |
| Price Sensitivity (Corporate/Wealth) | High | Large clients negotiate preferential rates and customized services. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Commerce Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Commerce Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for the bank. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted analysis you will receive instantly after purchase, ensuring no surprises and immediate usability for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The banking sector, particularly in areas like the Midwest where Commerce Bancshares has a strong presence, is quite fragmented. You'll find a mix of big national banks, regional players, and smaller community banks all vying for customers. This means there's a lot of competition across different services, from basic checking accounts to more complex corporate lending and wealth management.
This intense rivalry is evident in the market share dynamics. For instance, as of late 2023 and early 2024, while large national banks often hold significant portions of the overall market, regional banks like Commerce Bancshares have successfully carved out substantial niches by focusing on customer service and local market understanding. The sheer number of financial institutions, with thousands of banks operating in the US, underscores this competitive intensity.
Fintech companies are significantly intensifying competitive rivalry in the banking sector. These digital-first entities, often unburdened by legacy systems, are introducing innovative, customer-centric solutions that challenge traditional banks. For instance, by mid-2024, platforms like PayPal and Square (now Block) continued to expand their merchant services and payment processing capabilities, offering competitive rates that pressure established players.
This surge in fintech innovation compels traditional banks, including Commerce Bank, to accelerate their own digital transformation efforts. To remain competitive, banks must invest heavily in technology, improve user experience, and potentially lower fees to match the agility and cost-effectiveness of fintech disruptors. The ongoing digital arms race means banks are constantly evaluating their service offerings and operational efficiencies.
Fluctuations in interest rates directly affect a bank's net interest income, which is a core revenue stream. For instance, the Federal Reserve's aggressive rate hikes in 2022 and 2023, while initially boosting margins for some, created a more volatile environment. As of early 2024, the prospect of rate cuts or prolonged high rates continues to shape how banks manage their balance sheets.
A declining interest rate environment, or even the anticipation of it, often compresses net interest margins. This forces banks like Commerce Bank to compete more fiercely for both deposits and loans. In 2023, many banks saw their net interest margins narrow as funding costs rose faster than asset yields, intensifying the pressure to attract and retain customers.
Focus on Non-Interest Income and Diversification
Commerce Bank faces heightened competition as financial institutions, including itself, actively seek to grow non-interest income. This strategic shift diversifies revenue beyond traditional lending margins, pushing competition into areas like wealth management, payment processing, and investment banking. For instance, in 2024, many banks reported significant growth in fee-based income, with some seeing non-interest income comprise over 50% of their total revenue, a trend expected to continue.
This focus on diversification means that rivalry extends beyond mere interest rate competition. Banks are now vying for market share in advisory services, transaction fees, and capital markets activities. This intensifies the competitive landscape as firms must excel in multiple service areas to remain competitive and capture a larger share of customer wallet.
- Diversification into Fee-Based Services: Banks are increasingly generating revenue from wealth management, payment processing, and investment banking, moving beyond traditional lending.
- Intensified Rivalry in New Arenas: Competition is no longer limited to deposit and loan rates but extends to the quality and breadth of non-interest services offered.
- Revenue Stream Growth: In 2024, many banks saw non-interest income contribute a substantial portion of their total revenue, highlighting its growing importance and competitive focus.
Geographic Expansion and M&A Activity
Regional banks, including Commerce Bancshares, are actively pursuing geographic expansion and engaging in mergers and acquisitions (M&A). This strategy aims to achieve greater scale, broaden service portfolios, and strengthen their competitive standing. For instance, in 2024, the banking sector saw a notable uptick in M&A discussions as institutions looked to consolidate and gain market share.
These consolidation efforts are directly influencing the competitive intensity. As larger entities emerge through M&A, smaller or less diversified banks may find it harder to compete on price or service breadth. This dynamic reshapes the landscape, potentially leading to fewer, but larger, players in key markets.
- Strategic Expansion: Commerce Bancshares, like many regional peers, is evaluating opportunities in high-growth areas to capture new customer bases.
- M&A Drivers: Key motivations for M&A include achieving economies of scale, diversifying revenue streams, and enhancing technological capabilities.
- Competitive Impact: Successful M&A can significantly alter market share and pricing power, intensifying rivalry for remaining independent institutions.
- 2024 Trends: The first half of 2024 indicated continued interest in bank mergers, driven by regulatory considerations and the pursuit of efficiency gains.
The banking sector is highly competitive, with Commerce Bank facing rivals ranging from large national institutions to nimble fintech startups. This intense rivalry is evident in the ongoing battle for market share across various financial services, from basic deposit accounts to sophisticated wealth management solutions. By mid-2024, fintech platforms continued to pressure traditional banks with innovative, customer-centric offerings, forcing established players to accelerate digital transformation and potentially adjust pricing.
| Competitor Type | Key Competitive Actions | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|
| Large National Banks | Broad service offerings, extensive branch networks, aggressive marketing | Significant market share, price competition on core products |
| Regional Banks (e.g., Commerce Bank) | Customer service focus, local market expertise, digital investment | Carving out niches, competing on relationship banking and tailored solutions |
| Fintech Companies | Digital-first approach, innovative products, lower overhead | Disrupting traditional models, driving digital adoption, fee pressure |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Fintech and digital payment platforms present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional banks like Commerce Bank. Companies offering digital wallets, peer-to-peer payments, and online lending are increasingly capturing market share by providing convenient and often cheaper alternatives to established banking services. For instance, the global digital payments market was valued at over $8.7 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong shift towards these substitute solutions.
Non-bank lenders and the growing private credit market present a significant threat of substitution for traditional banks like Commerce Bank. These alternative financing channels, which include private equity firms, hedge funds, and specialized debt funds, increasingly offer tailored solutions for businesses and individuals, particularly for complex or larger-scale transactions. This trend diversifies funding options, lessening the dependence on conventional bank lending.
The private credit market has seen substantial growth, with global private debt assets projected to reach $2.7 trillion by 2028, up from an estimated $1.3 trillion in 2023. This expansion means more capital is available outside the traditional banking system, directly competing with banks for lending opportunities and potentially capturing market share, especially from clients seeking speed and flexibility.
The rise of online brokerage platforms and robo-advisors presents a significant threat to traditional banks like Commerce Bank in wealth management. These digital alternatives offer lower fees and greater accessibility, attracting a wide array of investors, including those with smaller account balances who might not meet the minimums for traditional advisory services.
By 2024, the digital wealth management sector has seen substantial growth, with many platforms boasting billions in assets under management. For instance, major robo-advisors have expanded their offerings to include more sophisticated investment strategies, directly competing with the personalized advice previously exclusive to brick-and-mortar institutions.
Cryptocurrencies and Blockchain-based Solutions
Cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology present a growing threat of substitution for traditional banking services, particularly in payments and remittances. While their adoption is still in development, these digital assets offer decentralized alternatives to established financial intermediaries, potentially bypassing traditional channels. For instance, the global remittance market, a significant area for banks, saw approximately $831 billion in flows in 2022, according to the World Bank, and cryptocurrencies offer a faster and potentially cheaper method for cross-border transactions.
These evolving solutions could impact Commerce Bank by offering alternative payment rails and investment vehicles. The increasing regulatory clarity and institutional interest in digital assets, evidenced by the approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs in the US in early 2024, signal a maturing market. This could lead to a gradual shift in consumer and business preference towards blockchain-based financial tools if they prove more efficient or cost-effective.
- Decentralized Payment Alternatives: Cryptocurrencies offer peer-to-peer transaction capabilities, reducing reliance on traditional banking networks for everyday payments and international transfers.
- Potential for Disintermediation: Blockchain's distributed ledger technology can facilitate secure and transparent transactions without the need for central authorities, potentially impacting services like trade finance and escrow.
- Growing Institutional Adoption: The increasing acceptance and integration of digital assets by financial institutions and regulators, as seen with the 2024 spot Bitcoin ETF approvals, indicate a growing legitimacy and competitive threat.
Embedded Finance
The threat of substitutes for traditional banking services, like those offered by Commerce Bank, is significantly amplified by the rise of embedded finance. This trend sees financial functionalities seamlessly integrated into non-financial platforms. For instance, e-commerce sites now commonly offer point-of-sale financing, allowing customers to secure loans directly at checkout without ever needing to engage with a bank. This innovation bypasses traditional banking channels, presenting a powerful substitute for services like personal loans or credit card offerings.
Embedded finance blurs industry lines, creating new competitive landscapes. Consider that by the end of 2023, the global embedded finance market was projected to reach over $2.6 trillion, with significant growth expected. This indicates a substantial shift in how consumers access financial products. For example, buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) services, often embedded within retail platforms, are rapidly gaining traction, directly competing with traditional credit products. In 2024, BNPL transaction volumes are anticipated to continue their upward trajectory, further challenging incumbent banks.
- Increased Convenience: Embedded finance offers unparalleled ease of use by bringing financial services directly to the point of need, such as within a shopping cart.
- Reduced Friction: Consumers can access credit or payment solutions without the traditional application processes associated with banks, lowering barriers to entry.
- New Entrants: Technology companies and non-financial businesses can now offer financial products, expanding the competitive set beyond traditional financial institutions.
- Data Utilization: Embedded finance platforms leverage user data from their primary services to offer more tailored and potentially risk-adjusted financial products, a capability banks are also developing.
The threat of substitutes for Commerce Bank is substantial, driven by evolving financial technologies and consumer preferences. Digital payment platforms, non-bank lenders, and online wealth management tools are increasingly offering competitive alternatives, often with lower costs and greater convenience.
The rise of embedded finance, where financial services are integrated into non-financial platforms, further intensifies this threat. By 2024, the global embedded finance market is projected to exceed $2.6 trillion, highlighting a significant shift in how consumers access financial products, directly challenging traditional banking models.
| Substitute Category | Key Offerings | Market Size/Growth Indicator (2023/2024 Projections) | Impact on Commerce Bank |
| Fintech & Digital Payments | Digital wallets, P2P payments, online lending | Global digital payments market valued over $8.7 trillion in 2023 | Reduced transaction fees, customer attrition |
| Non-Bank Lenders & Private Credit | Tailored business loans, alternative financing | Global private debt assets projected to reach $2.7 trillion by 2028 | Loss of lending market share, particularly for complex deals |
| Online Brokerages & Robo-Advisors | Low-fee investment management, accessible advice | Digital wealth management sector with billions in AUM by 2024 | Erosion of wealth management revenue |
| Cryptocurrencies & Blockchain | Decentralized payments, remittances | Global remittance market: $831 billion in 2022 | Potential disintermediation in payments and cross-border transactions |
| Embedded Finance | Point-of-sale financing, BNPL services | Global embedded finance market projected over $2.6 trillion by end of 2023 | Bypassing traditional banking for credit and payment needs |
Entrants Threaten
The banking sector is a minefield of regulatory complexities. New entrants must secure numerous licenses and adhere to strict capital adequacy ratios, such as the Basel III framework, which mandates higher liquidity and solvency standards. For instance, in 2023, the Federal Reserve continued to emphasize robust capital planning for large banks, a significant hurdle for any newcomer aiming to compete with established players like Commerce Bank.
Commerce Bancshares, like many established financial institutions, enjoys a significant advantage due to its deeply ingrained brand recognition and the trust it has cultivated over years of operation. This is a formidable barrier for any new bank attempting to enter the market, as building that level of customer confidence takes considerable time and consistent performance.
In the financial services sector, trust is not just a marketing buzzword; it's the bedrock of customer loyalty and a critical differentiator. New entrants face the daunting task of convincing consumers to entrust their money and financial well-being to an unfamiliar entity, a hurdle that often requires substantial investment in marketing and a proven track record.
Existing banks like Commerce Bank leverage significant economies of scale, particularly in their extensive branch networks and advanced technology infrastructure. This allows them to spread fixed costs over a larger customer base, leading to lower per-unit operating expenses. For instance, in 2024, major banks continued to invest billions in digital transformation, a cost that is more manageable for established players than for startups.
These economies of scale translate into competitive advantages, enabling incumbents to offer a wider array of products and services, from basic checking accounts to complex wealth management solutions. New entrants often struggle to match this breadth and depth of offerings without substantial upfront investment, making it harder for them to attract a diverse customer base and achieve profitability quickly.
Technological Investment and Infrastructure
The sheer scale of technological investment and the intricate infrastructure required to offer a full suite of banking services present a formidable barrier for new entrants. While nimble fintech startups can innovate quickly in niche areas, establishing a robust platform for retail, corporate, and wealth management, alongside secure payment processing, demands immense capital and specialized expertise. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for a traditional bank to upgrade its core banking system could range from tens of millions to hundreds of millions of dollars, a sum that is often prohibitive for newcomers aiming for broad market penetration.
Building this foundational technology stack is not a one-time expense; it requires continuous investment to maintain security, compliance, and competitiveness. New entrants must contend with the ongoing costs associated with data management, cybersecurity, regulatory technology (RegTech), and the integration of emerging technologies like AI and blockchain. This ongoing financial commitment, coupled with the need for highly skilled IT professionals, creates a significant hurdle that limits the number of entities capable of challenging established players like Commerce Bank across its diverse service lines.
Consider the following factors contributing to this threat:
- High Capital Outlay: Establishing the necessary IT infrastructure, including core banking systems, cybersecurity measures, and compliance platforms, requires billions of dollars in investment.
- Regulatory Compliance Burden: New entrants must navigate complex and costly regulatory frameworks, such as those for data privacy (e.g., GDPR, CCPA) and anti-money laundering (AML), which necessitate significant technological and operational resources.
- Talent Acquisition and Retention: The demand for specialized IT talent in the financial sector is exceptionally high, making it challenging and expensive for new companies to attract and retain the expertise needed to build and maintain advanced banking technology.
- Economies of Scale in Technology: Existing large banks benefit from economies of scale in their technology spending, spreading the costs of infrastructure and innovation over a larger customer base, which new entrants struggle to match initially.
Talent Acquisition and Retention
New entrants face significant hurdles in attracting and retaining skilled banking professionals. The competition for talent, particularly in specialized fields like credit risk analysis, regulatory compliance, and wealth management, is intense. Established institutions like Commerce Bank benefit from existing, deep talent pools and years of accumulated institutional knowledge, making it difficult for newcomers to match their human capital advantage.
For instance, in 2024, the demand for cybersecurity experts in the financial sector saw a notable increase, with many banks reporting difficulties in filling these critical roles. This talent scarcity is exacerbated for new entrants who lack the established employer brand and robust HR infrastructure of incumbents.
- Talent Scarcity: New entrants struggle to attract experienced banking professionals, especially in specialized areas.
- Established Advantage: Incumbent banks possess deep talent pools and institutional knowledge.
- Competitive Landscape: The financial industry faces high demand for skills like credit risk and compliance, intensifying competition for talent.
The threat of new entrants for Commerce Bank is considerably low due to substantial barriers. High capital requirements for technology and regulatory compliance, coupled with the need to build brand trust and economies of scale, make market entry challenging. For example, in 2024, the cost of upgrading core banking systems for established players like Commerce Bank could run into hundreds of millions of dollars, a sum prohibitive for most startups.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Significant investment needed for technology, infrastructure, and regulatory capital. | Very High - Limits the number of well-funded entrants. |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | Established banks benefit from long-standing customer relationships. | High - New entrants must overcome skepticism and build credibility. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Navigating complex licensing and compliance frameworks. | High - Demands extensive legal and operational resources. |
| Economies of Scale | Incumbents leverage cost advantages from size in technology and operations. | High - Newcomers struggle to match pricing and service breadth. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Commerce Bank is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial statements, investor relations reports, and industry-specific market research from reputable firms. This blend of primary and secondary data allows for a comprehensive understanding of competitive dynamics.
