COFORGE Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
COFORGE Bundle
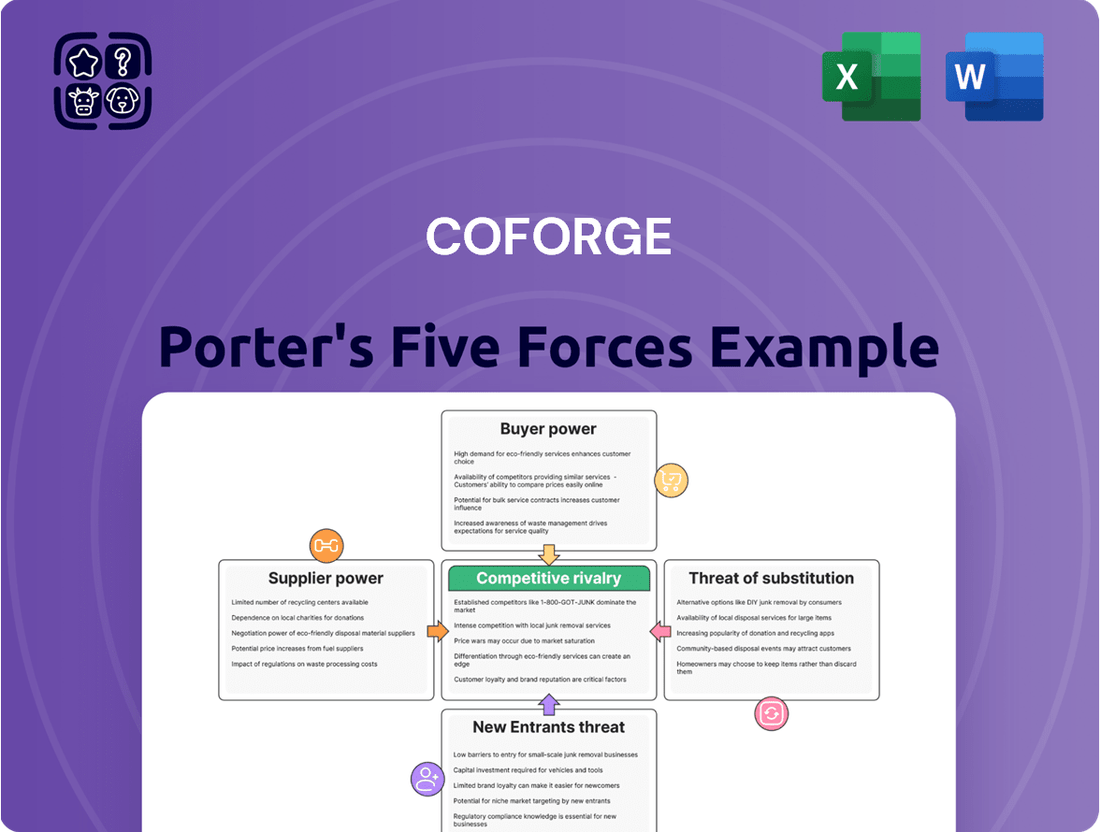
COFORGE navigates a dynamic IT services landscape, where understanding competitive pressures is paramount. Our analysis reveals the intricate interplay of buyer power, threat of new entrants, and substitute products that shape its market position.
The complete report unlocks a comprehensive view of COFORGE's industry, detailing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces. Gain actionable intelligence to refine your strategy and identify growth opportunities.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of Coforge's suppliers, primarily its skilled IT professionals, is a significant factor. The intense demand for specialized digital transformation expertise, including areas like artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and data analytics, means that top talent can command higher salaries and better benefits. This elevated demand directly translates into a moderate to high level of bargaining power for these skilled workers.
Coforge's reliance on technology vendors, including cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, along with enterprise software suppliers, presents a dynamic. The bargaining power of these suppliers can lean towards moderate to high, particularly when Coforge utilizes proprietary or specialized technologies where the cost and complexity of switching are substantial.
For instance, in 2024, the global cloud computing market continued its robust growth, with major providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) holding significant sway due to their extensive infrastructure and service portfolios. Similarly, specialized software vendors for areas like AI or data analytics can command higher prices if their offerings are critical and unique to Coforge's service delivery.
Coforge actively manages this by fostering strategic partnerships with leading technology firms. These alliances not only help in securing favorable terms but also enable Coforge to enhance its service capabilities and explore new market opportunities, thereby mitigating some of the supplier's inherent bargaining power.
Infrastructure and connectivity providers, including data centers and network services, exert moderate bargaining power over Coforge. The essential nature of these services for seamless operations means Coforge is reliant on them, making significant price hikes or service disruptions a notable concern. For instance, the global IT infrastructure market was valued at approximately $450 billion in 2023, with growth projected to continue, indicating a robust supplier landscape but also highlighting the critical dependency.
Subcontractors and Freelancers
Coforge, like many IT services firms, leverages subcontractors and freelancers to manage project demands and access specialized expertise. The bargaining power of these external resources is a key consideration. When specific, in-demand skills are scarce, or when projects have tight deadlines, these suppliers can command higher rates, directly affecting Coforge's profitability.
For instance, the global IT talent shortage, particularly in areas like cloud computing and cybersecurity, has been a persistent challenge throughout 2024. This scarcity increases the leverage of skilled freelancers and niche subcontracting firms. If Coforge faces a surge in demand for highly specialized skills that are not readily available internally, the cost of acquiring these external resources can escalate, potentially squeezing operating margins.
- Talent Scarcity Impact: Shortages in specialized IT skills in 2024 empower subcontractors and freelancers, allowing them to negotiate higher fees.
- Cost Pressures: Increased subcontracting costs directly translate to reduced operating margins for Coforge if not effectively managed.
- Project Urgency: Urgent project timelines further amplify the bargaining power of available external talent, forcing Coforge to potentially pay premium rates.
- Strategic Sourcing: Coforge's ability to diversify its subcontractor base and foster long-term relationships can mitigate some of this supplier power.
Industry-Specific Solution Providers
For its focused verticals such as banking, insurance, and travel, Coforge may collaborate with providers offering specialized industry software or data. The distinctiveness and the intricate integration requirements of these solutions can grant these niche suppliers a moderate to significant level of bargaining power.
These specialized providers, often possessing proprietary technology or deep domain expertise, can command higher prices or dictate terms due to the critical nature of their offerings. For instance, a unique core banking platform or a highly specialized travel booking engine integrated into Coforge’s services could represent a significant dependency.
- Supplier Concentration: The number of providers for highly specialized industry solutions is often limited, increasing their leverage.
- Switching Costs: The effort and expense involved in replacing deeply integrated industry-specific software can be substantial, locking Coforge into existing relationships.
- Differentiation: Unique features or capabilities of these solutions make them difficult to substitute with generic alternatives.
The bargaining power of Coforge's suppliers, particularly its skilled IT professionals, is a significant factor. The intense demand for specialized digital transformation expertise in areas like AI and cloud computing means top talent can command higher salaries, granting them moderate to high bargaining power. Similarly, technology vendors for cloud services and enterprise software can wield moderate to high influence, especially when their proprietary technologies involve substantial switching costs.
Infrastructure providers and niche software vendors for specific industries also exert moderate to significant bargaining power. The critical nature of these services and the complexity of integration can lead to higher prices and dictated terms. For example, the global cloud computing market's continued growth in 2024, dominated by major players, underscores the leverage these providers hold.
Coforge's reliance on subcontractors and freelancers, especially during periods of talent scarcity in 2024, further amplifies supplier power. Urgent project needs and a shortage of specialized skills allow these external resources to negotiate higher fees, potentially impacting Coforge's operating margins.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Level | Key Factors | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| Skilled IT Professionals | Moderate to High | Demand for specialized skills (AI, Cloud), talent scarcity | Global IT talent shortage persists, driving up compensation. |
| Technology Vendors (Cloud, Software) | Moderate to High | Proprietary technology, switching costs, market concentration | AWS, Azure, GCP dominate cloud market; specialized AI/data analytics software is critical. |
| Infrastructure & Connectivity Providers | Moderate | Essential services, reliance for operations | Global IT infrastructure market valued around $450 billion in 2023, with continued growth. |
| Subcontractors & Freelancers | Moderate to High (skill-dependent) | Project urgency, niche skill availability, talent shortages | Increased demand for niche skills like cybersecurity and cloud engineering. |
| Niche Industry Software Providers | Moderate to Significant | Specialized solutions, integration complexity, limited providers | Core banking or specialized travel software integration creates dependencies. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to COFORGE's IT services and consulting business.
Uncover hidden competitive advantages and threats with a dynamic, interactive model that visually maps and quantifies each of Porter's Five Forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Coforge's large enterprise clients, often seeking complex digital transformation services, wield considerable bargaining power. The sheer value of these contracts, which can run into millions of dollars, gives them leverage. For instance, in fiscal year 2024, Coforge secured multiple large deals, underscoring the significance of these clients and their ability to negotiate favorable terms.
These major clients also demand highly customized solutions tailored to their specific business needs. This customization requirement, coupled with the presence of numerous alternative IT service providers in the market, further amplifies their bargaining strength. Coforge’s strategic focus on winning these substantial engagements highlights the critical importance of managing these powerful customer relationships effectively.
While customers hold some sway, the bargaining power they exert is often tempered by significant switching costs in the IT services sector, particularly for intricate digital transformation initiatives. These costs can involve data migration, system integration, retraining staff, and potential disruption to ongoing operations, effectively creating vendor lock-in.
Coforge's business model benefits from this dynamic. For instance, their substantial 13-year agreement with Sabre, a major travel technology company, highlights how long-term contracts can lock in clients, thereby diminishing their immediate bargaining power. This long-term commitment signifies a significant investment by the client, making a switch to a competitor less feasible and more costly.
Coforge's strategic focus on key verticals such as Banking and Financial Services (BFS), Insurance, and Travel & Hospitality, while fostering deep domain expertise, also presents a potential vulnerability. A significant portion of its revenue is derived from a concentrated base of large clients within these sectors. For instance, as of the fiscal year ending March 31, 2024, Coforge reported that its top 10 clients contributed approximately 40% of its revenue, highlighting the substantial reliance on a limited number of customers.
This customer concentration directly impacts the bargaining power of these clients. Large clients, especially those representing a substantial percentage of Coforge's overall revenue, can leverage their spending power to negotiate more favorable terms, including pricing, service level agreements, and contract durations. The ability of these key customers to switch to competitors, or even bring services in-house, increases their leverage in any negotiation, potentially impacting Coforge's profitability and margins.
Demand for Cost Optimization and ROI
Customers are increasingly focused on getting the most bang for their buck when it comes to IT services. They’re carefully examining every dollar spent on digital transformation, demanding to see a clear return on investment (ROI). This means companies like Coforge must prove that their solutions are not only effective but also cost-efficient, delivering measurable business results.
The drive for cost optimization means clients are more willing to switch providers if they can find better value elsewhere. They want to see tangible benefits, such as reduced operational costs or increased revenue, directly tied to the services they purchase. This pressure pushes IT vendors to innovate and deliver more impactful outcomes.
- Increased Scrutiny of IT Budgets: Many enterprises are reviewing their IT expenditures, seeking to consolidate vendors and negotiate better terms, especially in light of economic uncertainties.
- Demand for Demonstrable ROI: Clients expect clear metrics and case studies showing how digital initiatives have improved efficiency or profitability. For instance, a recent survey indicated that over 60% of IT decision-makers prioritize vendors who can clearly articulate and prove ROI.
- Shift Towards Outcome-Based Pricing: Some customers are exploring pricing models tied to performance or achieved business outcomes rather than just hours worked, directly impacting how service providers are compensated.
- Competitive Landscape Intensifies: With many IT service providers vying for business, customers have a wider array of choices, strengthening their bargaining position to demand lower prices and higher value.
Access to In-house Capabilities
Large clients of Coforge, particularly those undertaking significant digital transformation, may possess sophisticated in-house IT capabilities. This internal expertise allows them to potentially handle aspects of their projects themselves, reducing their reliance on external vendors.
When clients can insource certain services, it directly enhances their bargaining power. They can leverage this option to negotiate more favorable terms, pricing, and service level agreements with providers like Coforge, as they have a credible alternative.
For instance, a major financial institution might have a dedicated digital innovation team capable of developing custom solutions, thereby limiting the scope of services they need to outsource and strengthening their negotiation position with IT service providers.
- Client In-sourcing Capability: Large enterprise clients often have the financial and human resources to build out internal IT and digital transformation teams.
- Negotiating Leverage: The ability to insource gives clients the power to push for lower prices and better terms from external providers.
- Reduced Dependence: Clients with strong in-house skills are less dependent on vendors, making them more selective and demanding.
Coforge's large enterprise clients, particularly those in sectors like Banking and Financial Services, wield significant bargaining power due to the substantial value of their contracts and the demand for highly customized solutions. This power is amplified by the competitive IT services market, where numerous providers offer alternatives, allowing clients to negotiate favorable terms and pricing.
However, this leverage is often counterbalanced by high switching costs associated with complex digital transformation projects, creating a degree of vendor lock-in. For example, Coforge's long-term agreement with Sabre illustrates how client commitment can mitigate immediate bargaining power.
The concentration of Coforge's revenue among its top clients, with the top 10 contributing approximately 40% in fiscal year 2024, means these key customers can leverage their spending power to secure better pricing and service level agreements.
Clients are increasingly scrutinizing IT budgets and demanding demonstrable ROI, pushing vendors to prove cost-efficiency and tangible business results. This focus on value and the potential for clients to insource services further strengthens their negotiating position.
Preview Before You Purchase
COFORGE Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete COFORGE Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the IT services industry. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive, fully formatted and ready for immediate use upon purchase, ensuring no surprises or missing sections.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The IT services and digital transformation landscape is densely populated with a multitude of competitors, ranging from established global giants like Wipro, TCS, and Infosys to a significant number of agile mid-tier firms such as Persistent Systems, Hexaware Technologies, and Mphasis. This broad spectrum of players creates a highly fragmented market where differentiation and specialization are key to success.
Coforge itself stands as a testament to this competitive intensity, currently ranking as India's seventh-largest software services outsourcer by revenue. This position highlights the fierce competition within the mid-cap segment, where companies must constantly innovate and deliver value to maintain and grow their market share amidst a dynamic environment.
Coforge actively combats intense industry rivalry by cultivating specialized knowledge within specific sectors, allowing them to offer tailored solutions. This deep domain expertise, coupled with a focus on integrating cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and advanced data analytics, provides a distinct competitive edge.
Innovation is a cornerstone of Coforge's strategy to stand out. Their significant investments in areas like Generative AI and automation are not just about keeping pace but about leading the charge, creating unique value propositions that differentiate them from competitors who may offer more generalized services.
Competitive rivalry within the IT services sector, including companies like Coforge, is intense, frequently translating into significant pricing pressure. This pressure directly impacts profit margins as clients, particularly in 2024, continue to scrutinize IT spending, seeking cost efficiencies.
Coforge, like its peers, must navigate this environment by balancing competitive pricing strategies with the imperative to maintain healthy profitability. The ongoing demand for digital transformation services, while robust, is met by a large pool of global providers, intensifying the competition for market share and client contracts.
Acquisition Strategy for Growth and Diversification
Coforge actively pursues inorganic growth to bolster its competitive standing, exemplified by its strategic acquisition of a 54% stake in Cigniti Technologies in May 2024. This move is designed to diversify its service verticals, expand its geographical market presence, and significantly enhance its technological capabilities. Such acquisitions are a prevalent strategy within the IT services sector for accelerating growth and achieving diversification.
This acquisition strategy directly impacts competitive rivalry by enabling Coforge to:
- Expand Service Offerings: Integrating Cigniti's expertise, particularly in digital assurance and digital engineering, allows Coforge to offer a more comprehensive suite of services, directly competing with rivals who already possess these capabilities.
- Strengthen Market Position: The combined entity gains a larger market share and a broader client base, increasing its competitive leverage against other major IT service providers.
- Enhance Talent Pool: Acquiring Cigniti brings in specialized talent and intellectual property, crucial for innovation and delivering advanced solutions, thereby intensifying the war for skilled professionals in the industry.
- Drive Revenue Growth: The acquisition is projected to contribute to Coforge's revenue, allowing for reinvestment in R&D and sales, further fueling its competitive efforts.
Talent Acquisition and Retention
The intense competition for skilled IT professionals significantly fuels competitive rivalry within the industry. Companies like Coforge face a constant challenge in attracting and keeping top talent, as their expertise directly impacts the quality and innovation of their service offerings.
Human capital is a critical differentiator, and the ongoing demand for specialized skills means that retaining experienced employees is as crucial as acquiring new ones. This talent war necessitates substantial investment in recruitment, competitive compensation, and employee development programs.
- Talent Acquisition Costs: In 2024, the average cost to hire a tech employee in India, a key market for IT services, continued to be a significant expense, often ranging from several thousand dollars upwards depending on the seniority and specialization.
- Employee Retention Rates: For leading IT service firms, maintaining employee retention rates above 80% is a key performance indicator, reflecting the success of their strategies against the backdrop of aggressive poaching by competitors.
- Impact on Service Delivery: A high turnover rate can disrupt project timelines and impact client satisfaction, underscoring the direct link between talent retention and Coforge's ability to deliver on its promises.
Competitive rivalry is a defining characteristic of the IT services sector, with Coforge operating within a crowded marketplace. The presence of numerous global and domestic players, including giants like TCS and Wipro, alongside specialized firms, intensifies competition for clients and talent. This dynamic environment necessitates continuous innovation and strategic differentiation to maintain market share.
Coforge's strategy to counter this rivalry involves deep domain expertise and technological specialization, particularly in areas like Generative AI and cloud. The company's acquisition of a majority stake in Cigniti Technologies in May 2024 for approximately $260 million is a clear move to bolster its service offerings in digital assurance and engineering, directly enhancing its competitive edge.
The intense competition also translates into pricing pressures, requiring companies like Coforge to balance cost-effectiveness for clients with maintaining healthy profit margins. In 2024, the ongoing demand for digital transformation services is met by a vast supply of providers, leading to a constant battle for contracts and client retention.
The war for talent further exacerbates competitive rivalry, as attracting and retaining skilled IT professionals is crucial for service delivery and innovation. Companies invest heavily in recruitment and retention, with average hiring costs for specialized tech roles in India often exceeding several thousand dollars, underscoring the value of human capital.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of in-house IT capabilities as a substitute for external providers like Coforge is a significant consideration. Large enterprises, especially those with substantial financial resources, may choose to build or enhance their internal IT departments to manage digital transformation projects directly. This can reduce their reliance on third-party service providers.
For instance, in 2024, many large corporations continued to invest heavily in upskilling their existing IT workforce and hiring new talent to bring critical digital transformation competencies in-house. This trend is driven by a desire for greater control, data security, and potentially lower long-term costs for ongoing digital initiatives, directly impacting the market share available for external IT service companies.
The growing accessibility of powerful off-the-shelf software and SaaS platforms presents a significant threat to companies like Coforge. These readily available solutions can automate many business processes, diminishing the demand for custom development and ongoing maintenance services that form a core part of Coforge's offerings. For instance, the global SaaS market was projected to reach over $200 billion in 2024, indicating a substantial and expanding alternative for businesses seeking digital solutions.
Traditional management consulting firms, though not direct IT service providers, pose a threat by offering strategic guidance on digital transformation. This advice might steer clients toward implementing solutions with alternative vendors or internal resources, bypassing comprehensive IT service providers like Coforge.
For instance, a firm like McKinsey or BCG might advise a client on a new cloud strategy, which could then be executed by the client's internal IT department or a specialized cloud provider, rather than engaging a full-service IT partner for the entire journey.
Low-code/No-code Platforms
The increasing accessibility of low-code and no-code development platforms presents a significant threat of substitution for traditional custom software development services. These platforms allow businesses to create applications with significantly less reliance on skilled programmers, potentially bypassing the need for external IT partners for many projects. This trend is accelerating as businesses seek faster, more cost-effective ways to digitize operations.
The market for low-code/no-code is experiencing robust growth, indicating a shift in how software is developed. For instance, Gartner projected that the low-code development technology market would reach $26.9 billion in 2023, an increase of 19.6% from 2022. By 2027, it's expected to account for over 70% of new application development. This surge directly impacts companies like Coforge, which offer custom IT services, by offering an alternative route for application creation.
- Reduced Demand for Custom Coding: Businesses can now build internal tools, automate workflows, and even develop customer-facing applications using visual interfaces, diminishing the need for bespoke coding from external vendors for simpler requirements.
- Cost and Time Efficiency: Low-code/no-code solutions offer a faster and often cheaper alternative to traditional development cycles, making them an attractive substitute for budget-conscious organizations or those with urgent digital transformation needs.
- Democratization of Development: Citizen developers within business units can now create functional applications, reducing the bottleneck and reliance on centralized IT departments or external service providers.
- Platform Lock-in Concerns: While offering speed, reliance on specific low-code/no-code platforms can lead to vendor lock-in, which may eventually necessitate migration or integration services, creating a different type of demand for IT expertise.
Process Automation and AI Tools
The rise of process automation and AI tools presents a significant threat of substitutes for Coforge. Clients can increasingly leverage these technologies to perform tasks previously outsourced or requiring manual intervention.
For instance, many companies are investing in Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and AI-powered analytics to streamline operations. In 2024, the global RPA market was valued at approximately $3.5 billion, with projections indicating substantial growth, suggesting a strong client appetite for these self-service solutions.
This trend directly impacts demand for traditional BPO and application maintenance services. Clients may opt for in-house automation to reduce costs and gain greater control, thereby diminishing their reliance on external providers like Coforge for certain functions.
- Increased Adoption of RPA: Clients are implementing RPA for repetitive tasks, reducing the need for manual data entry and processing services.
- AI-Driven Analytics: AI tools can now perform complex data analysis and generate insights, substituting the need for some outsourced analytics services.
- Cost-Efficiency of Automation: Standalone automation solutions often offer a lower long-term cost compared to ongoing outsourcing contracts.
- In-house Capabilities: Companies are building internal expertise in automation and AI, enabling them to manage processes internally rather than outsourcing.
The threat of substitutes for Coforge is multifaceted, stemming from readily available technologies and evolving client strategies. Businesses can opt for off-the-shelf software, low-code/no-code platforms, or even build robust in-house IT capabilities, all of which reduce reliance on external IT service providers for custom solutions and ongoing support. Furthermore, the rise of process automation and AI tools allows clients to handle tasks internally that were previously outsourced, directly impacting demand for services like BPO and application maintenance.
In 2024, the global SaaS market was projected to exceed $200 billion, highlighting the significant availability of alternative software solutions. Similarly, the low-code development market was expected to reach $26.9 billion in 2023, with projections suggesting it would account for over 70% of new application development by 2027. These figures underscore the increasing accessibility and adoption of alternatives that can bypass traditional IT service engagements.
The increasing adoption of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and AI-driven analytics presents a clear substitute. The global RPA market, valued at approximately $3.5 billion in 2024, demonstrates a strong client interest in solutions that automate tasks and provide insights, potentially reducing the need for outsourced BPO and analytics services. This shift towards self-service automation and in-house expertise directly challenges the market share of external IT providers.
| Substitute Category | Impact on Coforge | 2024/2025 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| In-house IT Capabilities | Reduced demand for outsourced IT projects and digital transformation services. | Continued heavy investment by large enterprises in upskilling internal IT teams. |
| Off-the-shelf Software & SaaS | Decreased need for custom development and maintenance services. | Global SaaS market projected to exceed $200 billion. |
| Low-Code/No-Code Platforms | Bypass custom development for many applications. | Low-code market expected to account for over 70% of new app development by 2027. |
| Process Automation & AI | Substitution for BPO and application maintenance services. | Global RPA market valued at approx. $3.5 billion in 2024. |
Entrants Threaten
The digital services and solutions sector, where Coforge operates, demands substantial upfront investment. This includes building robust technology infrastructure, funding continuous research and development, and assembling a large, highly skilled talent pool. For instance, in 2024, the global IT services market was projected to reach over $1.5 trillion, underscoring the scale of capital required.
Furthermore, attracting and retaining top-tier talent, particularly in cutting-edge fields like artificial intelligence, machine learning, and cloud computing, presents a significant hurdle. Companies like Coforge invest heavily in employee development and competitive compensation packages, creating a high barrier to entry for new players who may struggle to match these resources and expertise.
Established players like Coforge have cultivated robust brand reputations and deep client trust over many years, presenting a substantial hurdle for newcomers. This history translates into a preference among clients for partners with a proven track record, especially when undertaking complex digital transformation initiatives.
For instance, Coforge's consistent delivery and long-standing client relationships, evidenced by their revenue growth of 12.5% year-on-year to reach $1.16 billion in Q3 FY24, underscore the value clients place on reliability and established expertise.
Coforge's deep specialization in sectors like banking and insurance creates a significant barrier. Developing the intricate knowledge and custom solutions required to serve these industries effectively takes years, if not decades. Newcomers would struggle to replicate this level of domain expertise and proprietary technology, making it challenging to gain traction against established players.
Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
Operating within sectors like financial services and healthcare presents significant challenges due to intricate compliance mandates. New entrants must allocate substantial capital to meet these stringent standards, creating a formidable barrier to entry.
For instance, in 2024, the financial services industry continued to grapple with evolving regulations such as the Digital Operational Resilience Act (DORA) in Europe, requiring significant investments in cybersecurity and IT infrastructure from all players, including potential new entrants.
- DORA compliance mandates robust IT security and risk management frameworks.
- Healthcare regulations like HIPAA in the US demand strict patient data protection.
- Capital expenditure for compliance can run into millions for new firms.
- Navigating legal frameworks requires specialized expertise and ongoing monitoring.
Scalability and Global Delivery Capabilities
The threat of new entrants in the IT services sector, particularly concerning scalability and global delivery, is significantly mitigated by the immense capital and time required to establish a comparable infrastructure. New players face a steep uphill battle in replicating the extensive network of delivery centers and the robust technological backbone that established firms like Coforge possess. For instance, building out a global presence with centers in key locations like India, North America, and Europe involves substantial investment in real estate, technology, and skilled personnel, a barrier that deters many potential entrants.
New entrants would find it incredibly difficult to quickly build the necessary scalable global footprint to compete effectively. Establishing a presence in multiple countries requires navigating complex regulatory environments, securing talent, and ensuring seamless service delivery across different time zones and cultures. This complexity makes it challenging for newcomers to match the operational efficiency and reach of incumbents who have spent years refining their global delivery models. By 2024, the demand for hybrid and remote work capabilities further complicates this, requiring significant investment in secure and efficient distributed infrastructure.
- High Capital Investment: New entrants need substantial upfront capital to establish global delivery centers, IT infrastructure, and secure necessary certifications.
- Time to Market: Building a comparable global delivery network and brand reputation takes years, creating a significant time-to-market disadvantage for new players.
- Established Client Relationships: Incumbents benefit from long-standing relationships and trust with major clients, making it hard for new entrants to gain initial traction.
- Talent Acquisition and Retention: Attracting and retaining skilled IT professionals globally is a continuous challenge, requiring significant investment in HR and employee development.
The threat of new entrants for Coforge is relatively low due to the significant capital investment required for infrastructure and talent acquisition. Building a global delivery network and establishing a strong brand reputation takes years, creating a substantial time-to-market disadvantage for newcomers. Furthermore, stringent compliance requirements in sectors like financial services and healthcare demand considerable resources, acting as a further deterrent.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment in technology, infrastructure, and R&D. | Significant financial hurdle, limiting the number of capable new entrants. |
| Talent Acquisition | Need for highly skilled professionals in niche areas like AI and cloud. | Difficulty in attracting and retaining top talent, impacting service quality. |
| Brand Reputation & Client Trust | Established players have proven track records and long-standing relationships. | New entrants struggle to gain initial client trust for critical projects. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meeting complex regulations in finance and healthcare requires substantial investment. | Increased costs and complexity for new firms entering regulated markets. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our COFORGE Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including financial statements, analyst reports, industry-specific market research, and competitor disclosures.
