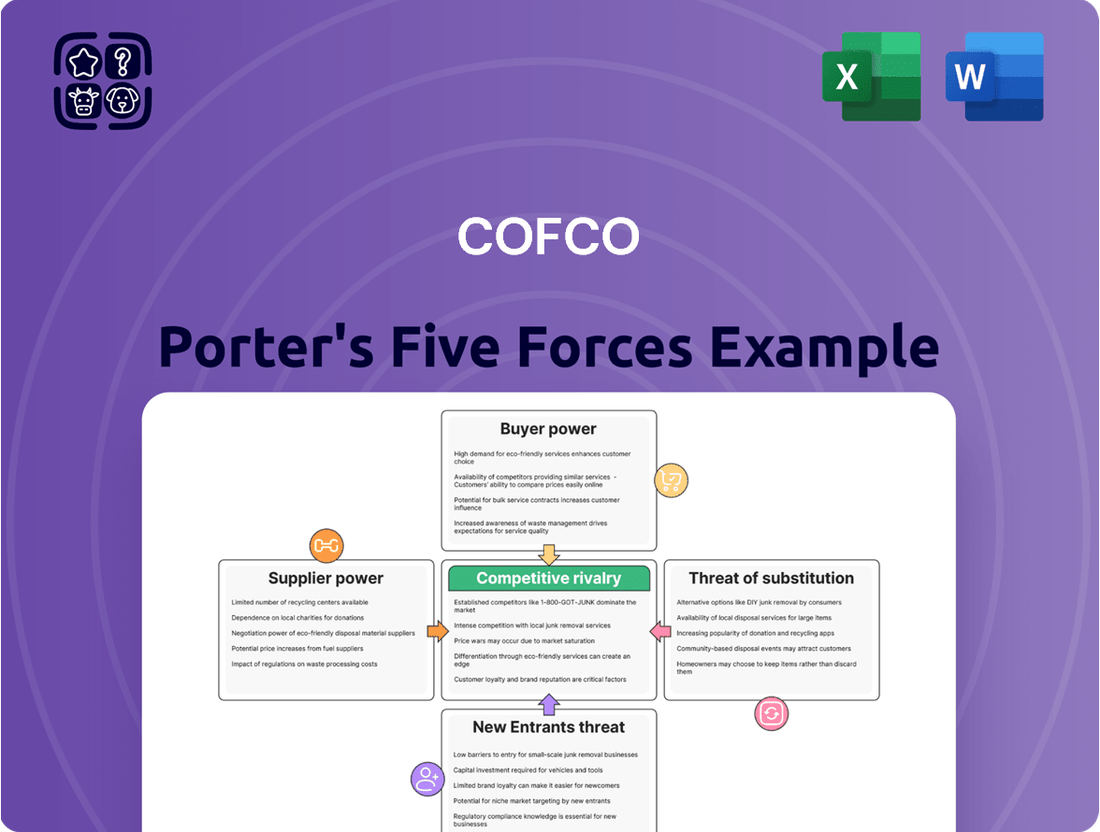
Cofco Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Cofco Bundle
Cofco operates within a dynamic agricultural landscape, where understanding the interplay of competitive forces is paramount for strategic success. This analysis highlights key pressures like intense rivalry and the significant bargaining power of buyers.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Cofco’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
COFCO, a giant in China's food industry, depends on many agricultural suppliers for essential ingredients. The power these suppliers hold hinges on how concentrated they are, how unique their products are, and if COFCO can easily find other sources. For example, if a specific type of grain is cultivated by only a few farms, those farmers gain more leverage.
The costs associated with switching suppliers significantly impact their bargaining power. For COFCO, a major player in the food and agriculture industry, transitioning between large-scale agricultural suppliers can involve considerable logistical hurdles, stringent quality assurance protocols, and complex contractual obligations. These switching costs can empower established suppliers, granting them greater leverage during price and contract negotiations.
While individual farmers typically lack the scale for forward integration, large agricultural cooperatives or consolidated farming operations might consider initial processing or storage. For instance, a major grain cooperative could invest in basic milling facilities, directly competing with COFCO's own processing arms. This move would significantly bolster their leverage by capturing more value and potentially offering finished goods directly to consumers or other food manufacturers.
Importance of Supplier's Input to COFCO's Product Quality
The quality of COFCO's agricultural inputs is paramount, directly influencing the final taste, nutritional value, and safety of its processed foods. Suppliers of critical, high-quality, or unique raw materials, such as specific varieties of grains or specialty fruits, can wield significant bargaining power. For instance, if COFCO relies on a limited number of suppliers for certified organic produce or rare flavor profiles essential for its premium product lines, these suppliers gain leverage.
This dependence on specialized inputs means suppliers can command higher prices or dictate terms. In 2024, COFCO's commitment to premium and healthy food segments, which often require traceable and high-standard ingredients, amplifies the bargaining power of those suppliers meeting these stringent criteria. This is evident in the growing market for sustainably sourced and organic ingredients, where premium pricing is common.
- Critical Inputs: Suppliers of unique or essential agricultural products for COFCO's premium food lines hold greater sway.
- Quality Dependence: COFCO's reputation for quality is directly tied to the consistency and excellence of its raw material suppliers.
- Market Trends: The increasing demand for organic and sustainably sourced ingredients in 2024 strengthens the bargaining position of suppliers meeting these standards.
Availability of Substitute Inputs
The availability of substitute inputs significantly weakens supplier bargaining power. If COFCO can easily switch to alternative agricultural products or source from different geographical regions, suppliers have less leverage. COFCO's extensive global procurement network, which covers a wide array of agricultural commodities and diverse sourcing locations, is a key factor in diminishing the power of individual suppliers or specific regions.
For instance, if there are supply disruptions for a particular grain in one country, COFCO's ability to tap into other markets for that same grain, or even substitute it with a similar commodity, limits the impact of any single supplier's pricing demands. This diversification is crucial for maintaining competitive input costs. In 2023, COFCO International reported sourcing agricultural products from over 100 countries, highlighting its broad reach and ability to navigate supply chain variations.
- Reduced Reliance: COFCO's access to multiple sourcing regions and product alternatives means it is not overly dependent on any single supplier.
- Competitive Sourcing: The presence of substitutes allows COFCO to foster competition among suppliers, driving down prices and improving terms.
- Supply Chain Resilience: A diverse supplier base and product options enhance COFCO's ability to maintain operations even when faced with localized supply shocks.
- Market Flexibility: COFCO can adapt to changing market conditions by shifting sourcing strategies based on availability and price of substitute inputs.
The bargaining power of COFCO's suppliers is influenced by their concentration and the uniqueness of their offerings. For example, if a particular type of high-quality soybean is only grown by a few large farms, those suppliers gain significant leverage in negotiations with COFCO.
Switching costs also play a crucial role; if it's expensive or logistically complex for COFCO to change its suppliers, existing suppliers can demand better terms. COFCO's global sourcing in 2023, spanning over 100 countries, helps mitigate this by providing alternatives, but reliance on specific, high-standard inputs can still empower certain suppliers.
The increasing demand for organic and traceable ingredients in 2024, a key focus for COFCO, further strengthens the position of suppliers who can meet these stringent quality and sustainability requirements, allowing them to command premium prices.
| Factor | Impact on COFCO's Suppliers | Example/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High if few suppliers dominate a key input. | A few large cooperatives controlling a specific grain variety. |
| Switching Costs | High if changing suppliers involves significant logistical/quality hurdles. | COFCO's complex quality assurance for premium ingredients. |
| Input Uniqueness/Quality | High for suppliers of critical, high-standard, or rare ingredients. | Demand for organic produce in 2024 strengthens suppliers meeting these criteria. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Lowers supplier power if COFCO has many alternatives. | COFCO's global sourcing from over 100 countries in 2023. |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Cofco, examining supplier and buyer power, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the agribusiness sector.
Gain immediate insight into competitive pressures with a visually intuitive framework, simplifying complex market dynamics for decisive action.
Customers Bargaining Power
COFCO's customer base is broad, encompassing domestic and international markets, from bulk commodity purchasers to food manufacturers and individual consumers. However, the bargaining power varies significantly. Large entities like major retailers or international trading houses, due to their substantial purchase volumes, wield considerable influence, often negotiating for preferential pricing and customized product specifications.
Customer switching costs play a crucial role in shaping COFCO's bargaining power with its business-to-business clients. If it's easy and inexpensive for a customer to switch to another supplier, they have more leverage. For instance, a food manufacturer needing a specific ingredient might find it costly to re-qualify a new supplier, involving extensive testing and potential product reformulation.
For COFCO, these switching costs can be significant, especially when they offer integrated supply chain solutions or have long-standing, deeply embedded relationships. In 2024, the global food and beverage industry saw continued consolidation, meaning fewer, larger buyers might have increased negotiation power if COFCO's offerings are easily replicated. However, COFCO's scale and diversified product portfolio can also create barriers to switching for many of its clients.
Customers armed with detailed market intelligence, including commodity price trends and competitor pricing, wield significant leverage. This information allows them to negotiate more favorable terms with suppliers like COFCO.
In 2024, the Chinese consumer landscape continued its shift towards health and quality. While price sensitivity remains for staple goods, there's a growing willingness to pay a premium for products perceived as healthier, higher quality, or sustainably sourced, impacting COFCO's pricing strategies for different product segments.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers poses a significant concern for COFCO. Large food manufacturers or major retailers, if finding it economically advantageous, could potentially move into food processing or even direct agricultural sourcing. This capability grants them considerable leverage in negotiations with suppliers like COFCO.
While a full backward integration is a complex and capital-intensive endeavor, the mere credible threat can influence pricing and contract terms. For instance, in 2024, major global food retailers continued to explore vertical integration strategies to control supply chains and costs, a trend that could impact COFCO’s margins.
- Customer Leverage: The potential for customers to produce their own inputs increases their bargaining power.
- Economic Viability: Backward integration becomes a real threat when it offers cost savings or supply chain control.
- Industry Trends: In 2024, several large retail chains expanded their private-label manufacturing capabilities, signaling a growing interest in controlling more of the value chain.
Availability of Substitute Products for Customers
Customers, particularly end consumers, face a vast selection of food products, significantly influencing COFCO's bargaining power. The presence of numerous domestic and international brands offering comparable processed foods allows consumers to readily switch if COFCO's pricing or quality is perceived as unfavorable. For instance, in 2024, the global processed food market was valued at approximately USD 1.1 trillion, with a significant portion accessible to Chinese consumers, highlighting the competitive landscape.
This ease of substitution intensifies customer leverage. If COFCO raises prices, consumers can easily opt for offerings from competitors like Yili Group or Mengniu Dairy, both major players in China's dairy and food sectors, which reported substantial revenue growth in 2023. This readily available alternative limits COFCO's ability to dictate terms.
- Abundant Choices: Consumers have access to a wide variety of food items, reducing reliance on any single supplier.
- Price Sensitivity: High availability of substitutes makes customers more sensitive to price increases by COFCO.
- Quality Expectations: If COFCO fails to meet quality standards, customers can easily find alternatives from competitors.
- Emerging Substitutes: The growing market for plant-based and alternative protein products in 2024 presents a new and evolving threat, further diversifying customer options. Global investment in alternative proteins saw continued growth in early 2024, indicating a sustained trend.
COFCO faces significant customer bargaining power due to the sheer volume of purchases by large clients like major retailers and international trading houses, who can negotiate for better prices and tailored product specifications. The ease with which business customers can switch suppliers, especially if COFCO's offerings are not highly differentiated, also amplifies their leverage.
In 2024, the trend of customer consolidation meant fewer, larger buyers held more sway, particularly if COFCO's products were easily substitutable. Conversely, COFCO's scale and diversified portfolio can act as a deterrent to switching. The threat of customers integrating backward into food processing or sourcing also grants them considerable negotiation power.
| Customer Type | Leverage Factors | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|
| Large Retailers/Traders | High purchase volume, negotiation for preferential pricing | Continued consolidation leading to fewer, larger buyers |
| Food Manufacturers | Switching costs (re-qualification, reformulation) | Potential for increased negotiation power if COFCO's offerings are easily replicated |
| End Consumers | Abundant product choices, price sensitivity | USD 1.1 trillion global processed food market, easy access to alternatives |
| All Customer Segments | Market intelligence, threat of backward integration | Retailers exploring vertical integration; growing consumer demand for quality/health |
What You See Is What You Get
Cofco Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Cofco Porter's Five Forces Analysis, providing a comprehensive examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive instantly after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information. You can confidently download and utilize this professionally formatted analysis immediately, empowering your strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The food processing, manufacturing, and trading industries, particularly in China and on a global scale, are characterized by a significant number of both domestic and international competitors. COFCO contends with rivals that include other state-owned enterprises, substantial private firms, and multinational corporations operating across its varied business segments.
This broad and fragmented competitive environment inherently escalates the intensity of rivalry. For instance, in the global agribusiness sector, companies like Cargill and ADM are major players, directly competing with COFCO in areas such as grain trading and oilseed processing. In 2024, the global food and beverage market was valued at over $8.9 trillion, underscoring the vastness and the multitude of entities vying for market share.
China's food and beverage market is a significant growth area, with an anticipated annual growth rate of 7.38% between 2024 and 2029. This robust expansion generally tempers intense rivalry as companies can grow without directly stealing market share. However, within this overall growth, specific segments might experience slower expansion, leading to heightened competition among players vying for a larger piece of a more stagnant pie.
For COFCO, navigating this dynamic is key. The company's diverse operations, spanning commodity trading, which can be more mature, and food manufacturing, a segment with higher growth potential, mean the intensity of rivalry isn't uniform. In segments where growth is slower, COFCO likely faces more aggressive competition as companies fight harder for existing customers and market share.
In the commodity trading segment, COFCO faces intense rivalry as products like raw grains and oilseeds are largely undifferentiated, making competition primarily driven by price. This commodity nature means buyers see little distinction between suppliers, putting pressure on margins.
However, COFCO's food manufacturing division offers a significant avenue for product differentiation. By investing in strong branding, ensuring superior product quality, and focusing on innovation, such as developing healthy or functional food options, COFCO can carve out distinct market positions. Sustainability claims are also becoming a key differentiator, appealing to increasingly conscious consumers and business partners.
For instance, COFCO's efforts in premium branding for its Mengniu dairy products or its focus on organic certifications for its agricultural produce exemplify successful differentiation strategies. In 2024, the global food and beverage market saw continued growth in demand for products with perceived health benefits and ethical sourcing, areas where COFCO is actively investing.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers for companies in the agricultural and food sectors, including COFCO, can significantly intensify competitive rivalry. These barriers might include specialized, illiquid assets, such as large-scale processing plants or extensive distribution networks, which are difficult to sell or repurpose. Long-term supply contracts with farmers or retailers also lock companies into operations, making a swift exit impractical even during periods of low profitability. For a state-owned enterprise like COFCO, these barriers are amplified by strategic considerations.
COFCO's mandated role in ensuring China's food security acts as a substantial exit barrier. This strategic imperative means the company is expected to maintain operations and supply chains, even if market conditions are unfavorable. For instance, during periods of global commodity price volatility, COFCO might be directed to stabilize domestic prices or ensure availability of key foodstuffs, effectively preventing it from withdrawing from certain market segments. This commitment to national objectives can keep COFCO and its competitors engaged in the market longer than purely economic factors would dictate, thereby sustaining competitive pressure.
The implications for competitive rivalry are direct: companies facing high exit barriers are less likely to leave the market, even when facing declining profits or market share. This can lead to prolonged periods of intense competition, as firms fight to maintain their position rather than seeking an exit. In 2023, for example, global agricultural commodity prices experienced significant fluctuations, impacting margins across the industry. Companies like COFCO, bound by their strategic mandates, would have been less able to adjust their operational scale or exit unprofitable ventures compared to more agile, privately held firms without such obligations.
- Specialized Assets: Difficulty in divesting or repurposing sector-specific infrastructure.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to suppliers and customers that restrict operational flexibility.
- Social/Strategic Considerations: Government mandates or national importance that discourage market withdrawal.
- Impact on Rivalry: Sustained competitive intensity as firms are compelled to remain active, even in challenging economic environments.
Strategic Stakes and Government Influence
As a state-owned enterprise, COFCO's commitment to China's food security significantly shapes its competitive approach. This strategic mandate can translate into behaviors that diverge from purely profit-driven entities, potentially including preferential government backing or state-directed capital infusions. Such backing can alter the intensity of rivalry within the agricultural and food sectors.
For instance, in 2024, China's agricultural sector received substantial state support, with the government prioritizing modernization and self-sufficiency. COFCO, as a key player, benefits from policies aimed at bolstering domestic production and supply chains. This can create an uneven playing field, as COFCO might access resources or operate under different economic pressures than private competitors.
- Strategic Importance: COFCO's role in national food security grants it a unique position, influencing its competitive actions.
- Government Support: State ownership can lead to directed investments and preferential policies, impacting market dynamics.
- Rivalry Influence: This government backing can either temper or intensify competition depending on strategic objectives.
COFCO operates in a highly competitive landscape with numerous domestic and international players, including giants like Cargill and ADM. The global food and beverage market, valued at over $8.9 trillion in 2024, is vast, but specific segments within China's food and beverage market, which is projected to grow at 7.38% annually from 2024-2029, can still see intense rivalry, especially where product differentiation is limited.
In commodity trading, where products are largely undifferentiated, competition is primarily price-driven, squeezing margins. However, COFCO can leverage its food manufacturing division to differentiate through branding, quality, and innovation, such as focusing on health benefits or sustainability, which are growing consumer demands in 2024.
High exit barriers in agriculture and food, such as specialized assets and long-term contracts, compel companies like COFCO to remain in markets even during downturns, sustaining competitive pressure. COFCO's state-owned status and its mandate for China's food security further amplify these barriers, potentially leading to prolonged, intense competition as firms cannot easily exit unprofitable segments.
State backing can also influence rivalry dynamics. China's agricultural sector, a key focus for modernization and self-sufficiency in 2024, sees significant state support, which COFCO, as a major player, benefits from. This can create an uneven competitive field compared to private entities.
| Competitor Type | Examples | Impact on Rivalry |
| State-Owned Enterprises | Other Chinese SOEs | Can lead to coordinated strategies or competition for state resources. |
| Private Domestic Firms | WH Group, New Hope Group | Agile and often price-competitive, especially in specific segments. |
| Multinational Corporations | Cargill, ADM, Nestlé | Bring global scale, advanced technology, and strong brand recognition. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for COFCO's diverse product portfolio hinges on the price-performance ratio of alternatives. For basic commodities like grains and oilseeds, consumers might opt for cheaper, unprocessed versions or even direct sourcing, bypassing COFCO's value-added processing. For instance, in 2024, global grain prices saw fluctuations, making unbranded or locally sourced grains a more attractive substitute for some buyers.
In the processed food sector, private label brands and smaller, niche manufacturers present a significant threat. These competitors often offer similar products at lower price points, directly impacting COFCO's market share. Reports from early 2024 indicated a growing consumer preference for private label goods in several key markets, driven by cost-consciousness.
The threat of substitutes for COFCO's products is significant, particularly in the evolving food industry. Consumers have an increasing array of dietary choices, from plant-based alternatives to novel proteins like lab-grown meat, and the resurgence of home cooking. This broad availability makes switching relatively easy for many customers.
For instance, the plant-based food market has seen substantial growth. In 2024, the global plant-based meat market was projected to reach over $15 billion, indicating a strong consumer shift towards these alternatives. This directly impacts traditional meat and dairy products that COFCO offers.
Furthermore, the accessibility of ingredients for home cooking, coupled with the convenience of meal kits, presents another substitute. Consumers can choose to prepare their own meals, bypassing the need for many pre-packaged or processed food items that are part of COFCO's portfolio.
Consumer trends in China are significantly impacting Cofco's threat of substitutes. A notable shift towards healthier, organic, and plant-based foods is evident, with market research from 2024 indicating a substantial increase in consumer spending on these categories. This growing health consciousness and concern for sustainability make Chinese consumers more receptive to alternative food products, directly challenging traditional offerings.
Relative Price of Substitutes
The relative price of substitutes directly impacts COFCO's market position. If alternative food sources, such as plant-based proteins or lab-grown meats, become significantly more affordable than COFCO's traditional product lines, consumer demand will likely shift. For example, a substantial drop in the price of plant-based burgers could draw consumers away from beef products, a key area for many agricultural companies.
This price sensitivity is a critical factor. Consider the global market for meat alternatives, which was projected to reach over $100 billion by 2025. If the cost of producing these alternatives continues to fall, making them more competitive with conventional animal agriculture, the threat of substitution for COFCO's meat products will intensify.
The affordability of substitutes is not the only driver; perceived value also plays a role. However, when prices become a primary differentiator, COFCO must ensure its pricing strategies remain competitive.
- Price Competitiveness: If the cost of alternative food sources drops, COFCO faces increased substitution risk.
- Plant-Based Meat Example: A significant price decrease in plant-based meats could lead consumers to switch from traditional meat products.
- Market Projections: The rapidly growing meat alternative market, valued in the tens of billions, highlights the potential for price-driven substitution.
- Value Proposition: COFCO needs to balance price with the overall value offered to mitigate the threat of substitutes.
Innovation in Substitute Industries
The threat of substitutes for COFCO is escalating due to rapid innovation in adjacent industries. For instance, advancements in alternative proteins, such as plant-based meats and precision fermentation, are creating compelling alternatives to traditional animal protein sources. Cellular agriculture, which grows meat from cells, also presents a future substitute that could disrupt the conventional meat market. New food technologies, like 3D printed food and novel ingredient sourcing, further expand the range of potential substitutes.
COFCO must actively monitor these evolving sectors. For example, the global plant-based food market was valued at approximately $22.6 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $162 billion by 2030, indicating significant growth and potential for substitution. Similarly, the cultivated meat market, though nascent, received substantial investment in 2023, with companies raising hundreds of millions of dollars for research and development. These trends highlight the need for COFCO to engage with or invest in these emerging areas to preemptively address the long-term threat of substitution across its diverse product portfolio.
- Alternative Proteins: Rapid development in plant-based and cultivated meat technologies offers direct substitutes for COFCO's traditional protein offerings.
- New Food Technologies: Innovations in areas like vertical farming and novel ingredient processing can alter consumer preferences and create new product categories that bypass traditional supply chains.
- Market Growth: The plant-based food market alone is projected for substantial growth, underscoring the increasing viability and consumer acceptance of substitutes.
- Investment Trends: Significant venture capital funding flowing into cellular agriculture and alternative food tech in 2023 signals a strong commitment to developing these substitutes.
The threat of substitutes for COFCO is amplified by the growing consumer interest in healthier and more sustainable food options. For instance, in 2024, the market for plant-based foods continued its upward trajectory, with sales in key regions showing double-digit growth. This directly challenges COFCO's traditional meat and dairy product lines.
Furthermore, the accessibility of ingredients for home cooking and the rise of meal kit services offer alternatives to processed foods. Consumers increasingly value convenience and control over their diets, making it easier to bypass pre-packaged goods.
The affordability of substitutes is a critical factor. As alternative protein sources, like plant-based meats, become more cost-competitive, consumer switching becomes more likely. The global market for meat alternatives is projected to exceed $100 billion by 2025, indicating a substantial shift in consumer preference driven by price and perceived value.
Innovation in food technology, including cellular agriculture and novel ingredients, presents a long-term threat. These advancements could fundamentally alter the food landscape, offering new substitutes that bypass traditional agricultural methods. Significant investment in these sectors in 2023 underscores their growing potential.
| Substitute Category | 2024 Market Insight | Potential Impact on COFCO |
|---|---|---|
| Plant-Based Foods | Continued strong growth, with double-digit sales increases in key markets. | Direct challenge to meat and dairy portfolios. |
| Home Cooking/Meal Kits | Increased consumer preference for convenience and dietary control. | Reduces demand for processed and pre-packaged goods. |
| Alternative Proteins (Price) | Increasing price competitiveness with traditional products. | Drives consumer switching from conventional meat. |
| Cellular Agriculture | Significant investment and R&D in 2023, signaling future disruption. | Potential long-term threat to animal protein supply chains. |
Entrants Threaten
The agricultural value chain, especially large-scale food processing and global trading, requires immense capital for infrastructure, logistics, and processing plants. This high barrier deters many potential new companies from entering the market. COFCO’s vast asset base and worldwide operations exemplify this significant entry hurdle.
Established players like COFCO leverage substantial economies of scale, particularly in bulk purchasing of agricultural commodities and widespread distribution networks. This allows them to secure lower input costs and achieve greater efficiency in their operations. For instance, in 2024, COFCO's vast supply chain likely facilitated significant cost advantages over smaller competitors.
New entrants face a considerable hurdle in matching these cost efficiencies. Building a comparable scale in procurement and processing would require massive upfront investment, making it challenging to compete on price against deeply entrenched, high-volume producers. Without achieving similar operational leverage, new companies would find it difficult to gain market share.
Securing effective distribution channels, both within China and on the global stage, is absolutely vital for any player in the food industry. COFCO's existing, well-developed networks and strong relationships give it a significant leg up here.
Newcomers would find it incredibly difficult to replicate COFCO's extensive distribution reach, facing substantial hurdles in securing shelf space and gaining essential market access. For instance, in 2024, the retail landscape in China saw continued consolidation, making it even harder for smaller, unestablished brands to secure prime placement.
Government Policy and Regulation
Government policy and regulation represent a substantial barrier to entry for new players in China's agricultural sector, particularly given COFCO's critical role in national food security. New entrants, especially foreign companies, may encounter more stringent licensing requirements, import/export restrictions, and land use regulations than established entities like COFCO. For instance, China's agricultural policies often prioritize domestic production and can favor state-owned enterprises in areas like grain procurement and distribution, making it challenging for newcomers to gain a foothold.
The Chinese government's commitment to food security, a priority reinforced by recent initiatives aiming to stabilize agricultural supply chains, directly impacts market access for new entrants. COFCO, as a state-backed entity, benefits from this strategic alignment. In 2024, China continued to emphasize self-sufficiency in key agricultural products, with policies designed to support domestic producers and processors, potentially increasing the compliance burden and operational costs for foreign competitors seeking to enter the market.
- Stricter Licensing and Approval Processes: New foreign agricultural companies may face extended timelines and more complex approval procedures compared to domestic or state-affiliated enterprises.
- Preferential Policies for State-Owned Enterprises: Government subsidies, access to credit, and favorable land allocation policies can disproportionately benefit incumbents like COFCO.
- Trade and Import/Export Regulations: Tariffs, quotas, and phytosanitary regulations can be leveraged to manage market entry and protect domestic industries, creating hurdles for new importers.
- Food Security Mandates: Policies prioritizing national food self-sufficiency can lead to preferential treatment for companies aligned with these objectives, such as COFCO.
Brand Loyalty and Switching Costs for Customers
While brand loyalty might not be as intense as in some other consumer sectors, COFCO benefits from significant brand recognition and deeply entrenched customer relationships across both its business-to-business (B2B) and business-to-consumer (B2C) operations. This established presence translates into tangible switching costs for customers, as new entrants would need to invest heavily in building comparable trust and awareness. For instance, in the agricultural inputs sector, farmers often rely on established suppliers for consistent quality and reliable delivery, making a shift to an unknown brand a considerable risk.
COFCO's long-standing history and its critical role in China's food security initiatives have cultivated a high level of implicit trust among consumers and business partners alike. This deep-seated confidence acts as a substantial barrier to entry. New companies entering the market would struggle to replicate this ingrained trust, especially when COFCO's operations are often perceived as stable and essential to the national supply chain. In 2024, COFCO's market share in key agricultural commodities remained robust, underscoring the stickiness of its customer base.
- Brand Recognition: COFCO's extensive portfolio, from grains to packaged foods, ensures high visibility, making it a default choice for many.
- Established Relationships: Long-term contracts and partnerships in the B2B space create inertia against switching.
- Implicit Trust: COFCO's role in national food security fosters a sense of reliability and safety for consumers.
- Switching Costs: The effort and risk involved in vetting and onboarding new suppliers deter many customers from changing.
The threat of new entrants for COFCO is generally low due to significant capital requirements for infrastructure and logistics, which are substantial barriers. Economies of scale achieved by COFCO in procurement and distribution further enhance this deterrent. Additionally, government policies favoring domestic production and food security initiatives, coupled with COFCO's established brand recognition and customer trust, create formidable hurdles for newcomers.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | COFCO's Advantage |
| Capital Requirements | High (infrastructure, logistics) | Vast asset base, established operations |
| Economies of Scale | Difficult to match (procurement, distribution) | Lower input costs, operational efficiency |
| Government Policy | Complex licensing, import/export restrictions | Preferential treatment, alignment with food security |
| Brand Loyalty & Trust | Challenging to build | Deep-seated confidence, established relationships |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Cofco Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of diverse and credible data sources, including Cofco's own annual reports and investor presentations, alongside industry-specific market research reports from firms like Euromonitor and Statista. We also incorporate data from financial databases such as Bloomberg and S&P Capital IQ, as well as relevant government and trade association publications.
