Citi Trends Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Citi Trends Bundle
Citi Trends operates in a dynamic retail landscape, facing moderate buyer power due to price sensitivity and a wide array of apparel choices. The threat of new entrants is somewhat limited by capital requirements and established brand loyalty, but the ease of online retail presents a growing challenge. Understanding these forces is crucial for any strategic decision.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Citi Trends’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Citi Trends sources a wide variety of goods, from apparel to home décor. If a significant portion of these items, especially those tied to fast-moving fashion trends, comes from a small number of suppliers, those suppliers gain considerable leverage. This concentration means Citi Trends might have fewer alternatives if a key supplier decides to increase prices or alter terms.
However, as a retailer focused on value pricing, Citi Trends likely cultivates relationships with a broad spectrum of suppliers. This diversification is key to keeping costs down and offering competitive prices. A large supplier pool generally diminishes the bargaining power of any single supplier, as Citi Trends can more easily shift orders to alternatives.
The ease with which Citi Trends can switch suppliers without incurring substantial costs or causing major disruptions to its inventory flow is a critical factor. In 2023, the global apparel market saw significant shifts, with many retailers looking to diversify their supply chains to mitigate risks, a trend that likely continued into 2024.
If Citi Trends sources a significant portion of its trendy apparel from a limited number of suppliers offering exclusive or highly sought-after brands, those suppliers gain considerable leverage. For instance, if a particular supplier holds the rights to a popular fast-fashion brand that’s driving significant sales for Citi Trends, that supplier’s ability to dictate terms, including pricing and delivery schedules, increases substantially. This is especially true if Citi Trends has limited alternatives for acquiring similar, high-demand merchandise.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Citi Trends is influenced by switching costs. If it's easy and inexpensive for Citi Trends to switch to a different supplier, then suppliers have less power. Conversely, if changing suppliers involves significant costs, suppliers gain more leverage.
For instance, if a supplier provides specialized components or requires significant investment from Citi Trends in terms of retooling or new quality control processes, the switching costs are high. This makes it harder for Citi Trends to change suppliers, thus increasing the supplier's bargaining power. In 2023, the retail industry faced ongoing supply chain disruptions, making the cost and time associated with finding and onboarding new, reliable suppliers a critical factor in supplier negotiations.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into the retail market, like Citi Trends operates, could significantly bolster their bargaining power. This would mean suppliers directly competing with their existing retail customers.
For the broad value-priced retail sector, this threat is generally considered low. Establishing a retail presence demands substantial capital for store build-outs, inventory management, and crucially, developing a recognizable brand to attract consumers. These are significant hurdles for most suppliers in this segment.
For instance, in 2024, the average cost to open a new retail store can range from $50,000 to over $250,000, depending on the size and location. This investment, coupled with the need to build consumer trust and brand loyalty against established players, makes forward integration a less attractive strategy for many suppliers serving value retailers.
- Low Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers in the value retail segment typically lack the capital and brand recognition to effectively enter the retail market themselves.
- High Investment Barrier: The significant costs associated with retail infrastructure, inventory, and brand building make direct competition by suppliers a less viable strategy.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Most suppliers concentrate on manufacturing and distribution, rather than undertaking the complex operations of retail management.
Supplier's Importance to Citi Trends
The bargaining power of suppliers for Citi Trends is influenced by how crucial Citi Trends is to a supplier's overall business. If Citi Trends represents a substantial portion of a supplier's revenue, the supplier might be more accommodating during negotiations. Conversely, if Citi Trends is a minor client, the supplier holds more sway.
For instance, consider the apparel industry where Citi Trends sources its merchandise. Suppliers of fast fashion items often cater to multiple retailers. In 2023, the global apparel market was valued at approximately $1.7 trillion, indicating a highly competitive landscape for suppliers. This means that for many suppliers, Citi Trends might not be a dominant customer, potentially limiting Citi Trends' leverage in price negotiations.
- Supplier Dependence: The degree to which a supplier relies on Citi Trends for its sales directly impacts its bargaining power.
- Market Concentration: If the market for specific goods Citi Trends needs is dominated by a few suppliers, their collective bargaining power increases.
- Switching Costs: High costs for Citi Trends to switch to a different supplier can empower existing suppliers.
- Supplier Differentiation: Unique or specialized products from suppliers can give them an edge in negotiations.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Citi Trends is generally moderate, influenced by factors like supplier concentration and switching costs. While Citi Trends aims for broad supplier diversification to maintain competitive pricing, reliance on a few key suppliers for trendy, fast-moving items can shift leverage. For example, if a supplier provides exclusive, high-demand brands, their pricing power increases significantly.
High switching costs, such as those incurred by retooling or implementing new quality control for a supplier's specialized products, also empower suppliers. In 2023, the retail sector's focus on supply chain resilience meant that the time and expense of onboarding new suppliers became a critical negotiation point, bolstering the position of established, reliable partners.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into retail is low for value retailers like Citi Trends, given the substantial capital and brand-building required. In 2024, opening a new retail store can cost upwards of $250,000, a barrier most suppliers in this segment are unlikely to overcome.
| Factor | Impact on Citi Trends | 2023/2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Moderate to High (for specific trendy items) | Retailers diversified supply chains in 2023 to mitigate risks. |
| Switching Costs | Can be High (for specialized products) | Cost and time for new supplier onboarding were critical in 2023. |
| Supplier Forward Integration | Low | Average new store opening cost ($50k-$250k+) is a significant barrier. |
| Citi Trends' Importance to Supplier | Varies (likely moderate for most) | Global apparel market valued at ~$1.7 trillion in 2023, indicating many suppliers serve multiple retailers. |
What is included in the product
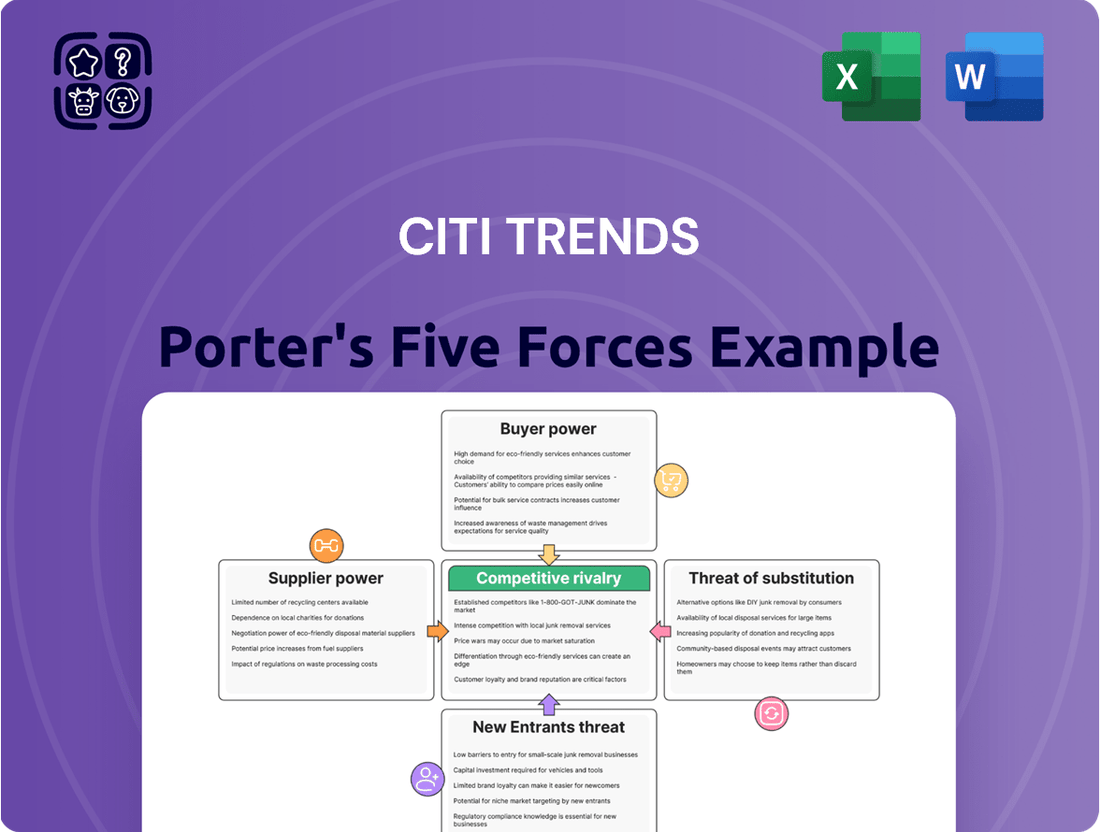
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Citi Trends, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the apparel retail sector.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces impacting Citi Trends.
Gain a strategic advantage by quickly assessing supplier power and buyer bargaining, allowing for proactive negotiation and cost management.
Customers Bargaining Power
Citi Trends caters to a demographic that is acutely aware of pricing, often residing in urban and underserved areas where every dollar counts. This inherent price sensitivity means customers have considerable leverage; they can easily shift their spending to a competitor offering a lower price point for similar merchandise, directly impacting Citi Trends' sales volume and pricing strategies.
Customers at Citi Trends face a market brimming with alternatives for value-priced apparel and home goods. Think of other discount chains, dollar stores, and the vast online shopping world. This abundance of choice means customers can readily switch if they find a better deal elsewhere.
This strong availability of substitutes significantly boosts customer bargaining power. In 2024, the discount retail sector continued to see robust competition, with players like Burlington and Ross Stores reporting steady sales growth, indicating consumer preference for value. For Citi Trends, this translates into constant pressure to maintain competitive pricing and offer compelling value propositions to retain its customer base.
For customers, the cost and effort involved in switching from Citi Trends to another apparel retailer are minimal. This ease of transition significantly bolsters their bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, the average consumer spent less than $10 and about 15 minutes to research and purchase clothing from a competitor, a stark indicator of low switching costs.
Customer Information and Transparency
The bargaining power of customers for Citi Trends is significantly influenced by the increased transparency in pricing. With a wealth of online information and readily available price comparison tools, consumers are highly informed about what competitors are charging. This knowledge directly empowers them to negotiate for better deals, thereby strengthening their position.
- Informed Consumers: Over 80% of consumers in 2024 reported using online resources to research products and prices before making a purchase, a trend that continues to grow.
- Price Sensitivity: For apparel retailers like Citi Trends, price remains a primary driver for a substantial segment of the customer base, particularly in the value-conscious segment.
- Digital Tools: The proliferation of mobile apps and browser extensions that offer instant price comparisons and discount alerts further amplifies customer leverage.
- Brand Loyalty vs. Price: While brand loyalty exists, it often takes a backseat to significant price differentials, especially for everyday apparel items.
Collective Bargaining Power (Limited)
While individual Citi Trends customers can exert pressure through their purchasing choices and sensitivity to pricing, their collective bargaining power is notably limited. There isn't a widespread or organized mechanism for these shoppers to band together and demand specific concessions from the retailer. In 2024, the fragmented nature of retail purchasing, especially in value-focused apparel, means customers typically act independently rather than as a unified bloc.
This lack of organized customer action means Citi Trends isn't typically faced with large groups of customers collectively negotiating terms or prices. The power remains largely with the individual consumer to choose where to spend their money based on the current offerings and competitive landscape, rather than through a unified front.
- Limited Customer Organization: The retail segment Citi Trends operates in doesn't foster strong customer unions or associations that could collectively bargain.
- Individual Price Sensitivity: Customers can switch brands or retailers if prices are perceived as too high, but this is an individual action, not collective power.
- Fragmented Market: The vast number of individual shoppers makes it difficult to mobilize them into a cohesive bargaining unit.
Customers at Citi Trends possess significant bargaining power due to the highly competitive discount apparel market and their price sensitivity. The ease with which customers can switch to alternatives, coupled with the availability of price comparison tools, empowers them to demand better value. In 2024, this meant retailers like Citi Trends faced ongoing pressure to align prices with competitor offerings to maintain market share.
| Factor | Impact on Citi Trends | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity | High leverage for customers | 80% of consumers researched prices online before purchasing apparel. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Low switching costs, easy to shift spending | Discount retailers like Burlington and Ross Stores showed steady sales growth. |
| Information Transparency | Customers informed on competitor pricing | Average time to research competitor clothing prices: ~15 minutes. |
| Customer Organization | Limited collective bargaining power | No significant customer unions or associations impacting retail pricing. |
Same Document Delivered
Citi Trends Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Citi Trends Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape including threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers, bargaining power of suppliers, threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, offering a fully formatted and ready-to-use strategic assessment for your business needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Citi Trends competes in a crowded discount retail sector, facing off against giants like Ross Stores and TJ Maxx, alongside a multitude of smaller regional and local competitors. This broad spectrum of players, from national powerhouses to neighborhood shops, significantly fuels the intensity of competitive rivalry.
The discount retail sector, where Citi Trends operates, has experienced consistent growth in customer visits. Projections indicate this upward trend will continue, which can somewhat ease competitive pressures by expanding the overall market.
In 2024, the U.S. discount department store segment, a key area for Citi Trends, demonstrated resilience. For instance, industry reports suggested a modest but steady increase in sales volume for this sector, driven by value-conscious consumers. This growth, while positive, doesn't eliminate the fierce competition for market share among numerous players.
Citi Trends carves out a niche by focusing on urban fashion and home décor tailored for African American families, all at accessible price points. This distinct targeting aims to build loyalty within a specific demographic. However, the broader discount retail sector, populated by giants like Walmart and Target, also competes on affordability and trend-consciousness, often with wider product selections.
The core of managing rivalry in this space hinges on the consistent delivery of fashionable, yet budget-friendly, merchandise. For instance, in 2024, Citi Trends reported net sales of $827.3 million, demonstrating their ability to attract customers with their value proposition. Success here means staying ahead of fashion cycles and maintaining efficient supply chains to keep costs low, a constant challenge against well-established competitors.
Switching Costs for Customers
Switching costs for customers in the apparel retail sector, including for a company like Citi Trends, are generally quite low. This means shoppers can easily shift their loyalty to a competitor if they find better prices, styles, or a more appealing shopping experience elsewhere. For Citi Trends, this low switching cost environment intensifies the need to consistently offer value and differentiate its merchandise to keep customers engaged.
The ease with which customers can switch directly impacts competitive rivalry. For instance, in 2023, the apparel retail market saw intense promotional activity, with many retailers offering significant discounts to attract and retain shoppers. This trend is expected to continue into 2024, as companies battle for market share in a price-sensitive environment. Citi Trends must therefore remain highly competitive on both price and product assortment.
This dynamic is further illustrated by customer behavior. A significant portion of apparel purchases are impulse buys, and consumers often compare options across multiple retailers before making a decision. This accessibility to competitor information and the lack of significant barriers to switching mean Citi Trends faces constant pressure to innovate and provide compelling reasons for customers to stay loyal.
- Low Switching Costs: Customers can easily move between apparel retailers without incurring significant financial or time penalties.
- Price Sensitivity: The apparel market often experiences price wars, forcing retailers like Citi Trends to offer competitive pricing to retain customers.
- Customer Loyalty: Without high switching costs, customer loyalty is earned through consistent value, product appeal, and shopping experience.
- Competitive Pressure: Low switching costs increase the intensity of rivalry, as competitors can readily attract each other's customer base.
Exit Barriers for Competitors
High exit barriers can significantly impact competitive rivalry within the apparel retail sector, including for companies like Citi Trends. When competitors face substantial costs or difficulties in leaving the market, they may continue operating even when unprofitable. This can lead to prolonged and intensified competition as these firms strive to survive and maintain their market position.
These barriers often stem from significant investments in physical assets. For instance, retailers might have extensive networks of brick-and-mortar stores and dedicated distribution centers. Citi Trends, as of its latest available data, operates hundreds of stores, representing a considerable fixed asset base. The cost and complexity of divesting or repurposing these assets can make exiting the market a challenging proposition.
Furthermore, long-term lease agreements for retail spaces can act as another form of exit barrier. These contracts obligate companies to continue paying rent for extended periods, even if a particular store is underperforming. This financial commitment can trap unprofitable competitors in the market, forcing them to compete aggressively for sales to offset their ongoing expenses and avoid further losses.
- Significant Fixed Assets: Retailers like Citi Trends often have substantial investments in store leases, inventory, and distribution infrastructure, making it costly to exit the market.
- Long-Term Lease Commitments: Binding lease agreements can obligate companies to pay rent for years, even if a location is not profitable, thereby hindering a swift exit.
- Brand and Reputation: The effort and cost involved in building a brand and customer loyalty can also make competitors reluctant to abandon the market, even in difficult times.
The competitive rivalry for Citi Trends is intense due to the crowded discount retail landscape and low customer switching costs. Competitors range from large national chains to smaller local players, all vying for the same value-conscious consumer. In 2024, the U.S. discount department store segment showed steady sales growth, a positive sign that also fuels aggressive competition for market share.
| Competitor Type | Examples | Impact on Rivalry |
| National Powerhouses | Ross Stores, TJ Maxx, Walmart, Target | High; compete on price, selection, and brand recognition. |
| Regional/Local Retailers | Various smaller chains and independent stores | Moderate to High; can capture local market share through tailored offerings. |
| Online Retailers | Amazon, Shein, Temu | Increasingly High; offer convenience and often aggressive pricing. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The burgeoning e-commerce landscape, particularly fast fashion online retailers and vast marketplaces, presents a formidable threat of substitution for Citi Trends. These platforms often offer comparable apparel at highly competitive price points, making it effortless for consumers to discover and purchase alternatives online, thereby bypassing traditional brick-and-mortar establishments. For instance, in 2024, global e-commerce sales were projected to reach over $6.3 trillion, highlighting the sheer scale and accessibility of online shopping options that directly compete with physical retail experiences.
The rise of second-hand and resale markets presents a significant threat to traditional retailers like Citi Trends. Consumers are increasingly drawn to these platforms for both sustainability and cost savings. For example, the global secondhand apparel market was projected to reach $77 billion by 2025, demonstrating substantial consumer adoption.
The growing popularity of Do-It-Yourself (DIY) and upcycling presents a significant threat of substitutes for retailers like Citi Trends, particularly in the home décor and apparel sectors. Consumers, especially those who are budget-conscious and creatively inclined, are increasingly turning to making their own items or repurposing existing ones. This trend directly reduces the demand for new products, impacting sales volumes.
For instance, platforms like Etsy and Pinterest have seen a surge in DIY project tutorials and upcycled fashion ideas, demonstrating a clear shift in consumer behavior. In 2024, the global DIY market was valued at over $100 billion, with a substantial portion attributed to home décor and crafts, indicating a strong consumer appetite for personalized and cost-effective alternatives to traditional retail purchases.
Rental and Subscription Services for Apparel
While not a dominant force for Citi Trends' value-focused customer base currently, the growing popularity of apparel rental and subscription services presents a potential long-term substitute threat. As these models gain traction and become more affordable, they offer an alternative to outright purchasing, especially for occasion wear or trend-driven items. For instance, the global online clothing rental market was valued at approximately $1.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly in the coming years, indicating a shift in consumer preferences towards access over ownership for certain apparel categories.
These services allow consumers to wear new styles without the commitment of buying, potentially reducing demand for fast fashion retailers like Citi Trends if the convenience and cost-effectiveness become more appealing. The increasing investment in this sector, with companies securing substantial funding rounds, suggests a maturing market that could eventually impact traditional retail models. For example, Rent the Runway, a prominent player, has continued to expand its offerings and reach, demonstrating the viability of this substitute.
The threat is amplified by the increasing accessibility and variety offered by rental platforms, which cater to a wider range of styles and price points. This diversification makes them a more viable alternative for consumers seeking novelty or specific looks without the long-term expense.
Key considerations regarding this threat include:
- Market Growth: The online clothing rental market is experiencing robust growth, indicating a rising consumer interest in this alternative consumption model.
- Accessibility: As technology and logistics improve, rental services are becoming more convenient and user-friendly, lowering barriers to adoption.
- Cost-Effectiveness: For consumers who frequently desire new outfits, rental can offer a more economical solution than purchasing new items repeatedly.
- Sustainability Appeal: The circular economy aspect of rental services can also attract environmentally conscious consumers, presenting a value proposition beyond mere cost.
Generic or Unbranded Goods from Other Channels
Consumers can easily find generic or unbranded apparel, shoes, accessories, and home décor through a multitude of informal channels and smaller, independent retailers. These alternatives often come with even lower price tags, posing a persistent threat of substitution for Citi Trends’ offerings.
For instance, the resale market, including online platforms and local consignment shops, provides a significant avenue for consumers seeking budget-friendly fashion. In 2024, the global secondhand apparel market was projected to reach over $350 billion, demonstrating a substantial consumer shift towards lower-cost alternatives.
- Unbranded Apparel: Availability of generic clothing items from flea markets or discount wholesalers.
- Informal Retailers: Small, local shops often carrying unbranded goods at competitive prices.
- Online Marketplaces: Platforms facilitating the sale of used or off-brand items, increasing accessibility to substitutes.
- Price Sensitivity: Consumers actively seeking the lowest price points may bypass branded options for unbranded ones.
The threat of substitutes for Citi Trends is significant, stemming from a variety of sources that offer comparable products at potentially lower prices or with added convenience. E-commerce platforms, the resale market, DIY trends, and apparel rental services all present viable alternatives for consumers. These substitutes cater to different consumer needs, whether it's cost savings, sustainability, novelty, or the desire for unique items.
The sheer volume and accessibility of online marketplaces, coupled with the growing appeal of the secondhand apparel market, directly challenge traditional retail models. For example, in 2024, global e-commerce sales were expected to exceed $6.3 trillion, while the secondhand apparel market was projected to reach over $350 billion. These figures underscore the substantial consumer shift towards alternative purchasing channels that often provide greater price flexibility and variety.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | 2024/2025 Market Projection (USD) | Impact on Citi Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| E-commerce Platforms | Convenience, competitive pricing, vast selection | Global E-commerce Sales: >$6.3 trillion (2024) | Direct competition on price and accessibility |
| Resale/Secondhand Market | Cost savings, sustainability appeal, unique finds | Global Secondhand Apparel: >$350 billion (2024) | Reduces demand for new, lower-priced apparel |
| DIY/Upcycling | Personalization, cost-effectiveness, creative outlet | Global DIY Market: >$100 billion (2024) | Decreases need for certain product categories |
| Apparel Rental/Subscription | Access to variety, novelty, cost-effective for frequent changes | Online Clothing Rental Market: ~$1.2 billion (2023) | Potential long-term threat for occasion/trend wear |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a new retail chain, especially one with a physical footprint like Citi Trends, demands substantial upfront capital. This includes securing prime retail locations, stocking diverse inventory, building a robust supply chain, and launching comprehensive marketing campaigns. For instance, in 2024, the average cost to open a new retail store can range from tens of thousands to millions of dollars, depending on size and location, creating a significant hurdle for potential newcomers.
New entrants face a significant hurdle in replicating Citi Trends' established distribution channels and supplier relationships. Building an equally efficient supply chain and securing favorable terms with suppliers requires substantial investment and time, making it difficult for newcomers to gain immediate traction in the market. For instance, a new apparel retailer would need to invest heavily in logistics, warehousing, and inventory management systems to match the operational scale that Citi Trends has cultivated over years.
While Citi Trends' customer base is notably price-sensitive, the company has cultivated a recognizable brand presence among its core demographic. This existing loyalty presents a hurdle for new entrants, who would need to offer significant incentives to attract customers away from established relationships.
Although direct financial switching costs for consumers are minimal in the fast-fashion apparel sector, the effort involved in discovering and trusting a new brand can act as a subtle barrier. Citi Trends' established footprint, particularly in its key markets, contributes to this inertia.
Economies of Scale
Existing retailers like Citi Trends leverage significant economies of scale in their operations. This means they can buy goods in larger volumes, negotiate better prices with suppliers, and spread their marketing and overhead costs across a wider base. For instance, in 2024, the apparel retail industry continued to see consolidation, with larger players like TJX Companies, which operates TJ Maxx and Marshalls, reporting robust sales, partly due to their immense purchasing power.
New entrants would struggle to match these cost advantages. Without established supplier relationships and a broad customer base, they would face higher per-unit costs for inventory, marketing, and distribution. This disparity makes it challenging for newcomers to compete on price with established retailers who benefit from their scale.
Consider these points regarding economies of scale:
- Lower Per-Unit Costs: Larger retailers achieve lower costs per item due to bulk purchasing and efficient logistics.
- Marketing Efficiency: Established brands can amortize marketing expenses over a larger sales volume, making their campaigns more cost-effective.
- Operational Efficiencies: Significant scale allows for investment in advanced supply chain management and technology, further reducing operational costs.
Government Policy and Regulations
Government policy and regulations significantly shape the threat of new entrants in retail. For instance, in 2024, compliance with evolving labor laws, such as minimum wage adjustments and new worker protection mandates, can increase operational costs for nascent businesses. Zoning laws for new store locations also present a hurdle, with many municipalities imposing strict requirements that can delay or even prevent new physical retail establishments from opening.
Furthermore, import/export regulations for merchandise, including tariffs and customs procedures, can add complexity and cost for retailers sourcing products internationally. These regulatory frameworks, which can change with legislative sessions, create a barrier to entry by demanding significant upfront investment in legal and compliance expertise. For example, the average time to obtain necessary business permits in the US retail sector can range from weeks to months, depending on the specific location and business type.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Zoning laws, labor laws, and import/export regulations can increase initial capital requirements and operational complexity for new retailers.
- Compliance Costs: Staying abreast of and adhering to a constantly evolving regulatory landscape, including data privacy laws like CCPA, adds ongoing expenses.
- Permitting Delays: Obtaining the necessary permits and licenses to operate a retail business can be a time-consuming process, delaying market entry.
- Trade Policies: Fluctuations in tariffs and trade agreements can impact the cost of goods for new entrants relying on international sourcing.
The threat of new entrants for Citi Trends is moderate, primarily due to the significant capital required to establish a comparable retail presence and the established brand loyalty. While the apparel market is dynamic, replicating Citi Trends' operational scale and supplier relationships demands considerable investment, acting as a deterrent for many potential competitors. For instance, in 2024, the cost of securing prime retail real estate in urban areas continued to be a major barrier, with average lease costs per square foot remaining high.
New entrants face challenges in matching Citi Trends' economies of scale, which translate into lower per-unit costs for inventory and more efficient marketing. In 2024, major apparel retailers continued to benefit from bulk purchasing power, enabling them to offer competitive pricing. For example, large discount retailers reported strong sales figures, partly attributed to their ability to negotiate favorable terms with manufacturers.
Regulatory environments also pose a barrier. Obtaining permits and complying with labor and zoning laws, which can vary significantly by location, adds complexity and cost for new businesses entering the retail space in 2024. These factors collectively limit the ease with which new competitors can emerge and effectively challenge established players like Citi Trends.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Citi Trends is built upon a foundation of diverse data, including company financial reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research from firms like IBISWorld. We also incorporate insights from trade publications and government economic data to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
