Ciena Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ciena Bundle
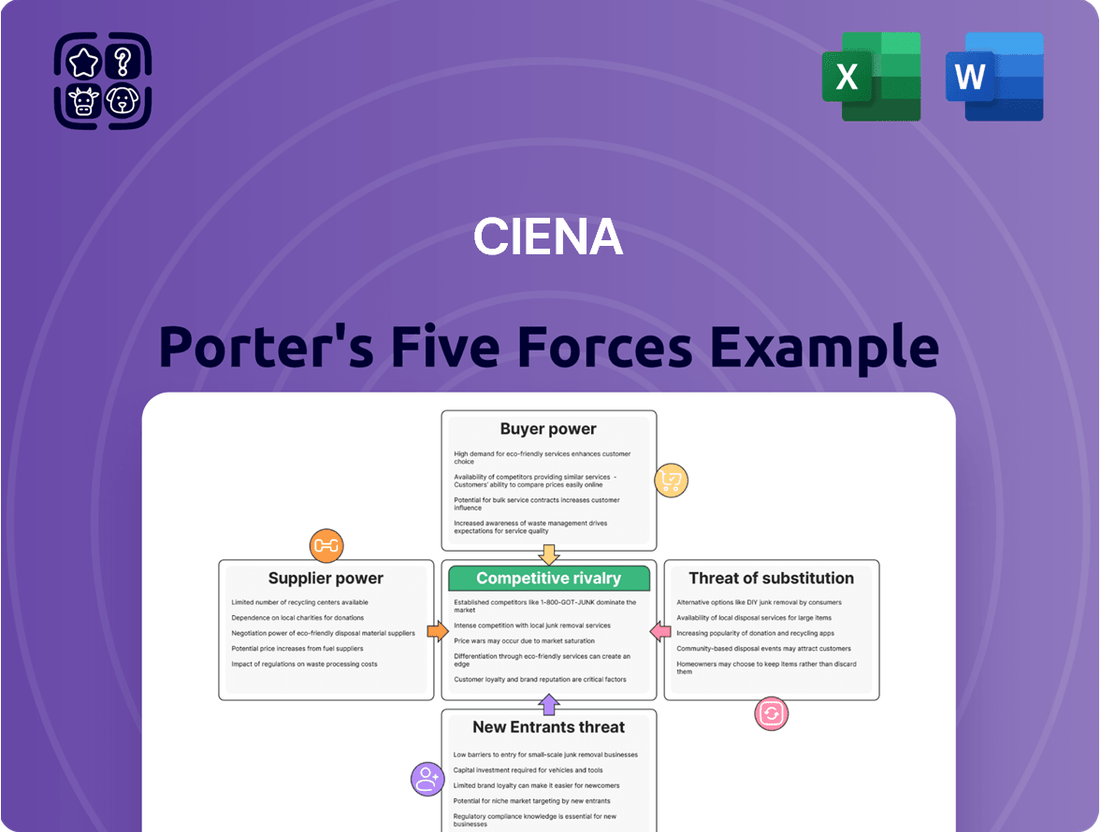
Ciena operates in a dynamic telecommunications infrastructure market, facing significant competitive pressures. Understanding the interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, and the threat of substitutes is crucial for navigating this landscape.
Our full Porter's Five Forces Analysis delves into the intricate details of Ciena's competitive environment, providing a comprehensive framework to assess its market position. Unlock actionable insights to drive smarter strategic decisions and gain a competitive edge.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers in the telecommunications networking equipment sector, especially for specialized optical networking components, significantly impacts bargaining power. If Ciena depends on a small number of manufacturers for critical parts like advanced coherent optical transceivers, these suppliers gain leverage. For instance, in 2024, the market for high-speed optical components remained relatively consolidated, with a few key players dominating innovation and production, potentially increasing their pricing power over equipment manufacturers like Ciena.
Suppliers of highly specialized components, like advanced coherent optics, hold considerable sway. Ciena's reliance on these cutting-edge technologies means it often depends on suppliers possessing unique intellectual property or advanced manufacturing expertise, which are not easily replicated.
The cost and complexity for Ciena to switch from one supplier to another for critical components are substantial. This involves significant investment in redesigning products, re-qualifying new parts, and managing potential production delays. For instance, in the telecommunications sector, the integration of new optical components can require extensive testing and validation, often taking months. This high switching cost effectively strengthens the bargaining power of Ciena's existing suppliers.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
If suppliers possess the capability and the motivation to move into Ciena's business and compete directly, their leverage increases significantly. This scenario, while less frequent in the highly specialized telecom equipment component sector, represents a potential long-term risk that Ciena must monitor.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers is a key factor in assessing their bargaining power. Should a major supplier decide to bypass Ciena and sell directly to Ciena's customers, it would fundamentally alter the competitive landscape.
- Supplier Capability: Suppliers need the financial resources, market knowledge, and customer relationships to effectively compete in Ciena's market.
- Incentive to Integrate: If suppliers see greater profit margins or market share by selling finished products, the incentive to integrate forward grows.
- Industry Specialization: The highly technical nature of Ciena's components can act as a barrier to entry for suppliers looking to integrate forward, limiting this threat.
- Market Dynamics: Ciena's strong customer relationships and brand loyalty can also deter suppliers from attempting direct competition.
Supplier Importance to Ciena's Product Quality and Innovation
Ciena's reliance on specialized components means suppliers who provide critical, differentiating elements wield significant bargaining power. The quality and innovation embedded in Ciena's optical networking equipment are directly tied to the advanced materials and technologies these suppliers offer. For instance, a supplier of cutting-edge optical transceivers or specialized silicon chips can command higher prices if Ciena cannot easily source equivalent alternatives, impacting Ciena's cost structure and competitive edge.
The bargaining power of suppliers to Ciena is a key consideration in its competitive landscape. This power is amplified when suppliers provide unique or proprietary components essential for Ciena's product differentiation and technological advancement. If a supplier's technology is a significant driver of Ciena's market leadership, that supplier gains leverage.
- Supplier Dependence: Ciena's product performance and innovation are intrinsically linked to the quality and technological sophistication of components supplied by third parties.
- Differentiation Impact: Suppliers offering unique or patented technologies that enable Ciena's product differentiation and market leadership possess greater bargaining power.
- Cost Implications: Strong supplier power can translate into higher input costs for Ciena, potentially affecting profit margins and pricing strategies.
- Innovation Conduit: Key suppliers can act as crucial partners in Ciena's R&D efforts, making their collaboration and component availability vital for maintaining a competitive technological edge.
The bargaining power of Ciena's suppliers is considerable, especially for specialized optical networking components. This leverage stems from the concentration of suppliers in niche markets and the high cost for Ciena to switch to alternatives. For example, in 2024, the market for advanced coherent optical transceivers, a critical component for Ciena's high-speed networking solutions, remained dominated by a few key innovators, giving them significant pricing influence.
Suppliers of proprietary or highly differentiated components, such as advanced silicon for signal processing or unique optical materials, possess strong bargaining power. Ciena's reliance on these specific technologies, which are difficult to replicate, means these suppliers can command premium pricing. The integration of these specialized parts into Ciena's complex systems represents a substantial switching cost, further solidifying supplier leverage.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers, while currently limited by industry specialization, remains a factor. If suppliers develop the capabilities and motivation to compete directly with Ciena, their bargaining power would increase significantly. Ciena's strong customer relationships and brand loyalty, however, act as a partial deterrent against such moves by its component providers.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on Ciena | Example (2024 Data Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increased leverage, potential for higher prices | Few dominant suppliers for advanced coherent optics |
| Component Uniqueness/IP | High reliance, limited substitution options | Proprietary silicon for advanced signal processing |
| Switching Costs for Ciena | High investment in redesign and re-qualification | Months of testing for new optical component integration |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Potential long-term competitive risk | Suppliers may seek direct customer sales if profitable |
What is included in the product
This analysis examines the competitive forces impacting Ciena, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the optical networking industry.
Identify and neutralize competitive threats before they impact your market share, providing a proactive strategy for sustained profitability.
Customers Bargaining Power
Ciena's customer base is largely concentrated among major service providers, large enterprises, and government entities. This concentration means that a few key clients can wield significant influence.
Indeed, in Ciena's fiscal year 2024, two specific customers alone accounted for more than 25% of the company's total revenue. Such a substantial reliance on a small number of clients grants these customers considerable bargaining power.
While switching to a new networking infrastructure can be a significant undertaking for Ciena's customers, involving high initial deployment and integration expenses, the long-term commitment inherent in these contracts can actually lower switching costs once a system is fully operational. This creates a degree of customer stickiness, making it less likely for them to jump to a competitor without substantial justification.
In the highly competitive telecommunications sector, customers like large service providers often exhibit significant price sensitivity. This is driven by their own need to manage costs and the readily available alternatives from numerous vendors. For Ciena, this translates into direct pressure on its pricing strategies and, consequently, its profit margins.
For instance, major telecom operators, a key customer segment for Ciena, are continuously under pressure to reduce their capital expenditures. In 2024, many of these operators were still navigating the financial implications of their 5G network build-outs, making them particularly watchful of vendor pricing. This environment directly impacts Ciena's ability to command premium pricing for its optical networking equipment.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers poses a significant challenge for Ciena. Large telecommunications service providers and hyperscale cloud companies possess substantial financial and technical resources. These entities could potentially develop certain networking solutions internally, thereby diminishing their dependence on suppliers like Ciena.
This risk is amplified by the ongoing trend of major cloud and artificial intelligence firms heavily investing in their proprietary network infrastructure. For instance, in 2024, companies like Google, Amazon, and Microsoft continued to expand their private network capabilities, aiming for greater control and cost efficiency. This strategic shift directly impacts Ciena's customer base, as these giants represent a considerable portion of its revenue.
- Customer Resources: Major telecom and cloud players have the capital to invest in R&D and manufacturing for network components.
- In-house Development: The capability to design and produce certain networking technologies internally reduces reliance on external vendors.
- Industry Trends: Increased cloud and AI company investment in private network infrastructure highlights a growing trend towards vertical integration.
- Market Impact: Successful backward integration by key customers could lead to reduced demand for Ciena's products and services.
Customer's Access to Information
Customers today have unprecedented access to information, significantly shifting the balance of power. With a few clicks, they can research product features, compare pricing across multiple vendors, and read reviews from other users. This readily available data empowers them to negotiate more effectively, often demanding better prices or more favorable terms.
The transparency fostered by this easy access means customers can quickly identify the best value propositions. For instance, in the telecommunications equipment market, where Ciena operates, buyers can easily compare technical specifications and price points for optical networking solutions. This market intelligence puts them in a stronger position to challenge suppliers on price and service quality.
- In 2024, the global e-commerce market saw a significant increase in customer research, with over 80% of consumers reportedly comparing prices before making a purchase.
- Online review platforms and comparison websites have become primary tools for customers, influencing purchasing decisions for an estimated 70% of online shoppers.
- The availability of detailed product specifications online allows customers to become more informed about technical capabilities, reducing reliance on vendor-provided information.
Ciena's customers, particularly large service providers and hyperscale cloud companies, wield considerable bargaining power. This stems from their significant purchasing volume, the potential for backward integration, and the increasing availability of market information. In fiscal year 2024, two major clients represented over 25% of Ciena's revenue, underscoring their influence.
The ability of these large customers to potentially develop networking solutions internally, coupled with their price sensitivity driven by their own cost management needs, puts direct pressure on Ciena's pricing and margins. For example, telecom operators in 2024 were focused on managing 5G build-out costs, making them keen on competitive pricing for optical equipment.
Furthermore, the ease with which customers can access product information and compare vendors online empowers them to negotiate more effectively. This transparency in pricing and technical capabilities, evident in the broader e-commerce trends where over 80% of consumers compare prices, allows customers to demand better terms from suppliers like Ciena.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | Impact on Ciena |
|---|---|---|
| Major Service Providers | High volume purchasing, price sensitivity, potential backward integration | Price pressure, margin impact |
| Hyperscale Cloud Companies | Significant R&D/financial resources, investment in private networks | Threat of reduced demand through in-house solutions |
| All Customers (Information Access) | Easy access to pricing, features, and reviews | Enhanced negotiation leverage, demand for better terms |
Same Document Delivered
Ciena Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Ciena Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering an in-depth examination of competitive forces within the telecommunications equipment industry. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and ready-to-use analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and value.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The telecommunications networking equipment market is intensely competitive, featuring global giants such as Huawei, Cisco Systems Inc., Broadcom Inc., Ericsson, Nokia Corporation, and Juniper Networks. These companies, along with Ciena, vie for market share across a broad spectrum of networking solutions, from optical transport to routing and switching. This diverse competitive landscape means Ciena must constantly innovate and differentiate its offerings to maintain its position.
The optical communication and networking market is experiencing robust expansion, fueled by the escalating need for faster internet, robust data center infrastructure, and the widespread adoption of 5G technology. This dynamic growth, however, also acts as a magnet for fierce competition.
Projections indicate the optical communication and networking market will reach $35.45 billion by 2029, exhibiting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.5%. This substantial growth rate intensifies rivalry as more companies vie for market share in this expanding sector.
Ciena carves out a competitive edge through its specialization in advanced technologies such as coherent optics, intelligent automation, and software-defined networking. This focus allows for a degree of product differentiation, offering customers sophisticated solutions tailored to complex network needs.
However, the landscape is intensely competitive, with rivals like Nokia and Cisco also making substantial investments in research and development. These companies are actively pursuing and often achieving similar or alternative advanced technological capabilities, narrowing the gap in differentiation.
For instance, Ciena reported revenue of $3.9 billion for its fiscal second quarter ended May 4, 2024, showcasing the scale of operations in this technology-driven market. Competitors are similarly investing in next-generation technologies, ensuring that differentiation is a continuous battle rather than a static advantage.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
The telecommunications equipment sector is characterized by substantial fixed costs. Companies invest heavily in research and development, advanced manufacturing facilities, and extensive global sales and support networks. For example, major players like Ciena often report billions in annual R&D and capital expenditures to stay competitive.
These significant upfront investments create a high barrier to entry and also influence competitive dynamics. To recoup their investments and achieve economies of scale, companies may engage in aggressive pricing strategies to maximize capacity utilization. This can lead to intense price wars, especially when demand fluctuates.
- High R&D Investment: Ciena's R&D spending in fiscal year 2023 was approximately $1.3 billion, highlighting the significant investment required to innovate in optical and routing technologies.
- Capital Intensive Operations: Manufacturing advanced network equipment demands sophisticated machinery and facilities, contributing to high fixed operational costs.
- Aggressive Pricing: The need to cover high fixed costs can pressure companies to offer competitive pricing to secure market share and maintain production levels.
- Exit Barriers: The specialized nature of assets and sunk costs in this industry make it difficult for companies to exit, potentially keeping less profitable firms competing.
Strategic Stakes
The high-capacity networking solutions market is a battleground for strategic dominance. Companies are pouring resources into this sector because it's the backbone for cloud computing and the rapidly expanding world of Artificial Intelligence (AI). This makes gaining market share incredibly important for future growth.
Ciena's performance underscores this strategic significance. For fiscal year 2024, the company reported record revenue specifically from Cloud Providers. This demonstrates a clear trend: securing business with major cloud players is a key objective and a strong indicator of competitive positioning in the networking industry.
- Strategic Importance: The demand for high-capacity networking is directly tied to the growth of cloud computing and AI, making it a critical sector.
- Aggressive Competition: Players are heavily investing to capture market share in this vital area.
- Ciena's Performance: Ciena achieved record revenue from Cloud Providers in fiscal year 2024, validating the strategic value of this customer segment.
The competitive rivalry within the telecommunications networking equipment market is exceptionally intense, driven by a handful of global players like Huawei, Cisco, Nokia, and Juniper Networks, all vying for market share. Ciena's ability to differentiate through advanced technologies like coherent optics and software-defined networking is crucial, but rivals are also investing heavily in R&D, narrowing the competitive gap.
The market's substantial growth, projected to reach $35.45 billion by 2029 with a 7.5% CAGR, fuels this rivalry as companies seek to capitalize on demand from 5G and data centers. High fixed costs associated with R&D and manufacturing also pressure companies towards aggressive pricing to achieve economies of scale, further intensifying competition.
Ciena's fiscal year 2024 performance, including record revenue from Cloud Providers, highlights the strategic importance of securing key customer segments in this high-capacity networking battleground, where AI and cloud growth are paramount.
SSubstitutes Threaten
While fiber optics are currently dominant, alternative technologies like Li-Fi (light fidelity) present a potential threat. Li-Fi uses light waves for data transmission, offering high-speed internet access and could become a viable alternative to Wi-Fi in certain settings. This could reduce the demand for traditional fiber optic infrastructure in localized applications.
The rise of cloud-based networking and virtualization presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional networking hardware. As more network functions are converted into cloud-native network functions (CNFs) and managed through software-defined networking (SDN), the need for specialized, physical network equipment diminishes. This shift allows companies to achieve greater flexibility and potentially lower costs by leveraging software solutions over dedicated hardware, thereby substituting established infrastructure.
The threat of substitutes is growing as integrated solutions challenge standalone networking equipment. Companies are increasingly exploring co-packaged optics (CPO), which embed optical engines directly into logic chips. This integration aims to decrease reliance on external transceivers, a key component in Ciena's current offerings.
This shift could significantly impact the demand for discrete networking hardware. For instance, advancements in silicon photonics are paving the way for more powerful, single-chip solutions that perform functions traditionally requiring multiple devices. This trend is driven by the pursuit of lower power consumption and higher bandwidth density, critical factors in modern data centers and telecommunications networks.
Customer Self-Provisioning or Open Source Alternatives
The threat of substitutes, particularly through customer self-provisioning or open-source alternatives, is a significant concern for companies like Ciena. Large enterprises and cloud providers are increasingly capable of building their own networking infrastructure or adopting open-source solutions, which can bypass the need for Ciena's specialized, proprietary products.
This trend represents a form of backward integration where customers take on functions previously outsourced to vendors. For instance, hyperscale cloud providers have been instrumental in driving the development and adoption of open networking hardware and software, such as the Open Compute Project. This allows them to customize solutions to their exact needs and potentially reduce costs compared to purchasing off-the-shelf equipment.
- Customer Self-Provisioning: Large enterprises can develop in-house expertise to design, build, and manage their own networks, reducing reliance on external vendors.
- Open Source Hardware and Software: Initiatives like the Open Compute Project provide blueprints and software for networking equipment, enabling lower-cost, customizable alternatives.
- Reduced Vendor Lock-in: Adopting open solutions allows companies to avoid proprietary ecosystems, offering greater flexibility and potentially lower total cost of ownership.
- Hyperscaler Influence: Major cloud providers are significant drivers of open networking, setting standards and creating demand for alternative solutions that can impact traditional suppliers.
Lower Bandwidth Alternatives for Specific Use Cases
While Ciena focuses on high-capacity networking, some less demanding applications can still be served by older, simpler technologies. These can act as substitutes, particularly in niche markets or for organizations with less stringent bandwidth needs. For instance, businesses with primarily voice or basic data transmission requirements might not need Ciena's cutting-edge fiber optic solutions.
However, it's crucial to note that the overwhelming industry trend is a relentless demand for higher bandwidth. Ciena's own financial performance reflects this, with continued growth in its high-capacity optical networking segments. In 2023, Ciena reported revenue of $4.3 billion, a significant portion of which is driven by demand for advanced, high-speed solutions.
- Limited Impact: The threat from lower bandwidth alternatives is generally low for Ciena's core business, which targets high-demand sectors like telecommunications and cloud providers.
- Niche Applications: Substitutes are more relevant for specific, less bandwidth-intensive use cases where cost savings might outweigh the need for advanced features.
- Industry Trend: The broader market is moving towards increased bandwidth consumption, diminishing the long-term viability of lower-capacity substitutes for most Ciena customers.
- Ciena's Focus: Ciena strategically positions itself at the forefront of this bandwidth expansion, making its solutions increasingly indispensable for modern networks.
The threat of substitutes for Ciena's high-capacity optical networking solutions is evolving. While direct replacements for core fiber optic functionality are limited, integrated solutions like co-packaged optics (CPO) are emerging. These embed optical components into chips, potentially reducing the need for Ciena's discrete transceiver modules. For instance, advancements in silicon photonics are enabling single-chip solutions that perform functions previously requiring multiple devices, driven by the need for lower power and higher bandwidth density.
Furthermore, the rise of cloud-native network functions (CNFs) and software-defined networking (SDN) offers substitutes by virtualizing network operations. This shift allows more network functions to be managed through software, potentially decreasing reliance on specialized, physical network hardware. This trend is amplified by large enterprises and cloud providers increasingly adopting open-source solutions and developing in-house networking capabilities, a form of backward integration that bypasses traditional vendor offerings.
For example, hyperscale cloud providers are key drivers of open networking initiatives like the Open Compute Project, enabling customized and potentially lower-cost network solutions. While less demanding applications might still use simpler technologies, the overwhelming industry trend favors higher bandwidth, reinforcing Ciena's market position. Ciena's 2023 revenue of $4.3 billion highlights the continued demand for its advanced, high-speed solutions.
| Emerging Substitute Technology | Potential Impact on Ciena | Key Drivers | Example/Initiative |
| Co-Packaged Optics (CPO) | Reduces demand for discrete transceivers | Lower power consumption, higher bandwidth density | Silicon photonics integration |
| Cloud-Native Network Functions (CNFs) & SDN | Diminishes need for specialized hardware | Flexibility, cost efficiency through software | Network function virtualization (NFV) |
| Customer Self-Provisioning & Open Source | Bypasses traditional vendor solutions | Customization, cost reduction, reduced vendor lock-in | Open Compute Project |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the telecommunications networking equipment market, particularly in sophisticated segments like optical and packet networking, demands immense capital. Companies like Ciena must invest heavily in research and development to stay competitive, alongside building advanced manufacturing capabilities and establishing a worldwide sales and support network. For instance, in 2023, major players in the industry reported R&D expenditures in the hundreds of millions of dollars, highlighting the significant financial commitment required.
The threat of new entrants in the telecommunications networking sector, particularly concerning intellectual property and patents, is significantly mitigated by the substantial R&D investments already made by established players like Ciena. Ciena, for instance, holds a robust portfolio of patents covering critical areas such as optical networking, software-defined networking, and network automation. For a new company to enter this space and directly challenge Ciena's technological leadership would necessitate either a massive upfront investment in developing novel, patentable technologies or securing costly licensing agreements for existing intellectual property. This high barrier to entry, rooted in accumulated knowledge and protected innovations, effectively deters many potential new competitors.
Ciena, like many established players in the telecommunications equipment sector, benefits significantly from economies of scale. This means that as Ciena produces more network equipment, its per-unit cost of production decreases, making it harder for newcomers to compete on price. For instance, in 2023, Ciena reported revenue of $4.2 billion, a testament to its large-scale operations and established market presence.
Furthermore, Ciena has accumulated substantial experience over years in designing, manufacturing, and deploying complex optical and routing systems. This experience curve translates into improved efficiency, product quality, and a deeper understanding of customer needs, advantages that are difficult and time-consuming for new entrants to replicate quickly.
Customer Relationships and Brand Loyalty
Ciena benefits from deeply entrenched customer relationships with major service providers, enterprises, and government entities. These long-standing partnerships, built on trust and a proven track record, make it difficult for newcomers to penetrate the market. Securing large-scale, multi-year contracts is a significant hurdle, requiring substantial time and resources to establish credibility and demonstrate reliability.
The company's fiscal 2024 annual report highlighted the strength of these customer bonds, underscoring the loyalty Ciena has cultivated. This loyalty translates into a considerable barrier to entry for potential competitors, as new entrants would need to overcome Ciena's established reputation and existing contractual obligations.
- Established Trust: Ciena's history with key clients fosters significant trust, a difficult asset for new entrants to replicate.
- Long Sales Cycles: The lengthy process of securing large contracts in the telecommunications infrastructure sector deters new companies.
- Customer Retention: Strong existing relationships contribute to high customer retention rates, limiting opportunities for new players.
- Brand Reputation: Ciena's established brand loyalty acts as a protective shield against emerging competitors.
Regulatory Hurdles and Standards
The telecommunications sector, where Ciena operates, faces significant regulatory scrutiny. New companies entering this space must contend with a complex web of national and international regulations governing spectrum allocation, data privacy, and service provision. For instance, in 2024, many countries continued to refine their 5G deployment policies, often involving intricate licensing processes and local content requirements.
Beyond regulatory frameworks, adherence to stringent technical standards is paramount. Ciena's products, like optical networking equipment, must meet specific interoperability and performance benchmarks to be integrated into existing carrier networks. This necessitates substantial investment in research and development to ensure compliance, acting as a considerable barrier to entry for potential competitors who may lack the necessary capital or expertise.
These combined regulatory and technical challenges significantly increase the cost and complexity of launching a new venture in the telecommunications infrastructure market. For example, the ongoing development and adoption of standards like those set by the O-RAN Alliance, while promoting openness, also require new entrants to invest heavily in R&D to ensure their solutions are compatible and competitive.
- Regulatory Complexity: Navigating diverse global telecom regulations (e.g., spectrum licensing, data sovereignty) presents a significant barrier.
- Technical Standards: Meeting industry-wide interoperability and performance standards requires substantial R&D investment.
- Interoperability Demands: New entrants must ensure their equipment seamlessly integrates with existing carrier infrastructure, a costly undertaking.
The threat of new entrants for Ciena is relatively low due to substantial capital requirements for R&D, manufacturing, and global sales networks. For instance, in 2023, industry R&D spending reached hundreds of millions of dollars, a significant hurdle for newcomers.
Existing intellectual property and patents held by Ciena further deter new entrants, as developing or licensing competing technologies demands massive investment. Ciena's established economies of scale, evidenced by its $4.2 billion revenue in 2023, also make it difficult for smaller, newer companies to compete on price.
Deeply entrenched customer relationships and long sales cycles also act as barriers, requiring new companies to invest considerable time and resources to build credibility and secure contracts. Regulatory complexity and the need to adhere to stringent technical standards, such as O-RAN Alliance specifications, add further cost and difficulty for potential entrants.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Ciena's Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Very High | Established financial strength and scale |
| Intellectual Property | High Barrier | Extensive patent portfolio |
| Economies of Scale | Significant Disadvantage | Lower per-unit costs due to high volume |
| Customer Relationships | Difficult to Replicate | Long-standing trust and contracts |
| Regulatory & Technical Standards | High Compliance Costs | Expertise and resources for adherence |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Ciena Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including Ciena's annual reports, investor presentations, and filings with the SEC. We also incorporate insights from leading industry analyst reports and market research firms specializing in the telecommunications and networking sectors.
