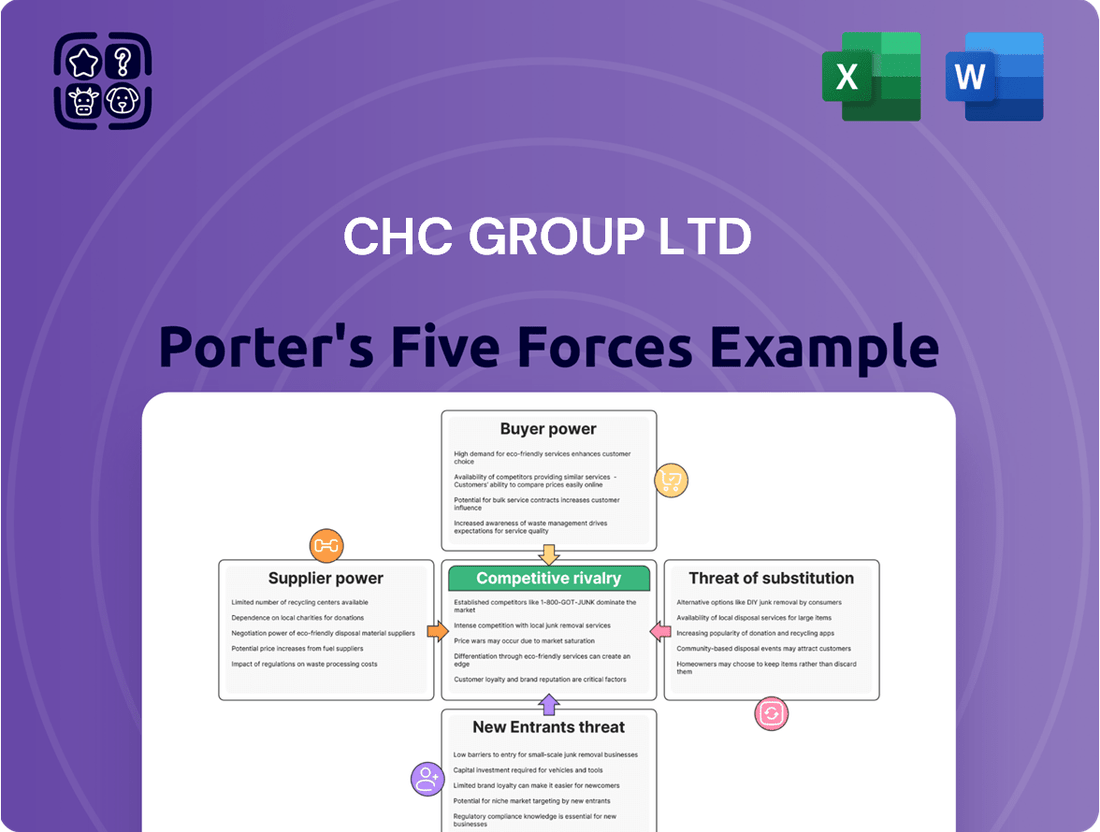
CHC Group Ltd Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CHC Group Ltd Bundle
CHC Group Ltd operates in a dynamic market shaped by several key competitive forces. Understanding the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors is crucial, as is the bargaining power of both suppliers and buyers, which can significantly impact CHC's profitability.
The threat of new entrants and the availability of substitute products also present distinct challenges that require strategic consideration. These forces collectively define the landscape in which CHC Group Ltd must navigate to maintain and grow its market position.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore CHC Group Ltd’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers for critical helicopter components significantly impacts CHC Group Ltd's bargaining power. If there are only a handful of manufacturers producing essential items like airframes, advanced engines, or specialized avionic systems, these suppliers gain considerable leverage. For instance, as of early 2024, the global market for heavy-lift helicopter engines is dominated by a few key players such as Rolls-Royce and Pratt & Whitney Canada. This limited supplier base means CHC has fewer alternatives, giving these suppliers the ability to dictate terms and potentially increase prices, thereby reducing CHC's profitability.
The bargaining power of suppliers for CHC Group Ltd is influenced by the uniqueness of the inputs they provide. If suppliers offer highly specialized or proprietary components and services that are critical for CHC's helicopter operations and cannot be readily substituted, their leverage increases significantly. For instance, if a particular engine manufacturer holds patents on advanced, fuel-efficient engine technology essential for CHC's fleet modernization plans, that supplier would possess considerable power.
For CHC Group Ltd, the bargaining power of suppliers is significantly influenced by switching costs. These costs encompass not only direct financial outlays but also the operational disruptions and time investments required to transition to a new supplier. For instance, if CHC relies on specialized helicopter components or advanced maintenance services that demand extensive re-certification of its fleet or retraining of its engineering staff, the associated switching costs would be substantial. This financial and operational inertia makes it difficult and expensive for CHC to change suppliers, thereby granting existing suppliers greater leverage in negotiations.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers is a significant consideration for CHC Group Ltd in the helicopter services market. If key suppliers, such as helicopter manufacturers or component providers, were to enter the service provision space themselves, they would become direct competitors. This prospect inherently strengthens their bargaining position, allowing them to dictate terms more forcefully.
For instance, a major helicopter manufacturer could leverage its existing product base and technical expertise to offer its own maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) services, or even direct charter operations. This would directly challenge CHC’s market share and profitability. The potential for such a move is amplified if suppliers possess proprietary technology or unique manufacturing capabilities that are difficult for CHC to replicate independently.
- Suppliers entering the helicopter services market directly increases their leverage over CHC.
- This threat is more pronounced with helicopter manufacturers or critical component suppliers.
- A strong possibility of forward integration by suppliers would likely lead to increased costs for CHC.
- CHC's reliance on specialized parts or technology from certain suppliers makes this threat more acute.
Importance of CHC to Suppliers
The significance of CHC Group Ltd as a customer to its suppliers is a critical factor in assessing the bargaining power of those suppliers. If CHC represents a substantial portion of a supplier's overall sales, CHC would likely wield more influence in negotiations, potentially securing better pricing and terms. Conversely, if CHC is a minor client for a supplier, that supplier would possess greater leverage.
For instance, in 2024, the aviation services sector, which CHC operates within, saw significant demand for specialized helicopters and related parts. Suppliers catering to this niche market might find CHC to be a key client. Information regarding CHC's procurement spend as a percentage of its key suppliers' total revenue would be crucial here. Without specific data on CHC's customer share for its critical component suppliers, it's difficult to definitively quantify this power dynamic.
- CHC's dependence on suppliers for critical components like advanced rotor systems and specialized avionics highlights potential supplier leverage.
- The number of alternative suppliers available for these specialized components directly impacts CHC's ability to switch, thus influencing supplier bargaining power.
- If CHC accounts for a substantial percentage of a supplier's revenue, its bargaining power increases, potentially leading to more favorable pricing.
- Conversely, if CHC is a small customer to a supplier, that supplier holds greater power to dictate terms and prices.
The bargaining power of suppliers for CHC Group Ltd is heightened by the limited number of providers for essential helicopter parts, such as engines and airframes. As of early 2024, a few key players like Rolls-Royce and Pratt & Whitney Canada dominate the heavy-lift helicopter engine market, giving them significant leverage over CHC due to fewer alternatives. This concentration of suppliers can lead to price increases, impacting CHC's profitability.
| Factor | Impact on CHC Group Ltd | Example (Early 2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High leverage for suppliers, potential for price increases. | Dominance of Rolls-Royce and Pratt & Whitney Canada in heavy-lift helicopter engines. |
| Uniqueness of Inputs | Suppliers with proprietary technology gain significant power. | Patented advanced engine technology essential for fleet modernization. |
| Switching Costs | High costs for CHC to change suppliers, strengthening supplier leverage. | Re-certification of fleet and retraining of staff for new components. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Suppliers entering service provision directly increases their power. | Major helicopter manufacturers offering MRO services. |
| CHC's Customer Significance | CHC's influence depends on its share of supplier revenue. | CHC's procurement spend as a percentage of key suppliers' total revenue is crucial. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to CHC Group Ltd's helicopter services industry, highlighting the impact of regulatory bodies and technological advancements.
Instantly identify and address competitive pressures with a dynamic, five-force analysis, simplifying strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
CHC Group Ltd's customer concentration is a key factor in assessing customer bargaining power. If a significant portion of CHC's revenue comes from a small number of major clients, particularly in sectors like oil and gas which are known for large-scale contracts, these customers gain considerable leverage. For instance, if the top five clients represent over 60% of CHC's revenue, they can more effectively negotiate for lower service fees or more favorable contract terms, impacting CHC's profitability.
The bargaining power of CHC Group Ltd's customers is significantly influenced by switching costs. If customers can easily move to another helicopter service provider with minimal effort or expense, their leverage increases. For instance, if a customer can switch operators without incurring substantial fees, retraining personnel, or reconfiguring equipment, they hold more power in negotiations.
For CHC, low switching costs mean customers can readily explore alternatives, putting pressure on CHC to maintain competitive pricing and service quality. In the oil and gas sector, a major client might have the option to contract with multiple providers, or even bring services in-house if feasible, thereby amplifying their bargaining position. The accessibility of numerous alternative helicopter operators in key markets directly correlates with higher customer bargaining power.
CHC Group Ltd's customer price sensitivity is a key factor influencing their bargaining power. In the helicopter services industry, particularly for standard offshore transport, customers can become quite sensitive to price fluctuations, especially when the oil and gas sector experiences economic downturns. For instance, in 2023, the average day rate for offshore helicopter transport can vary significantly based on contract length and specific service requirements, and customers with multiple supplier options will naturally gravitate towards the most cost-effective solutions.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers poses a significant challenge to CHC Group Ltd. This occurs when major clients, such as oil and gas companies or emergency medical services, consider developing their own in-house helicopter fleets and operational capabilities. Such a move would allow them to bypass CHC's services entirely, thereby increasing their leverage over CHC.
A credible threat of backward integration directly enhances customer bargaining power. For instance, if a large energy producer, which represents a substantial portion of CHC's revenue, were to explore acquiring its own helicopters and maintenance infrastructure, it would gain considerable negotiating strength. This is particularly relevant given the high capital expenditure required for fleet acquisition and maintenance, which might be a barrier for some customers but not for the largest, most financially robust ones.
The potential for customers to integrate backward is influenced by factors such as the cost-effectiveness of owning versus outsourcing helicopter services, the availability of skilled personnel, and regulatory hurdles. If these factors become more favorable for customers, the threat intensifies.
Consider the global aviation services market, where the trend of vertical integration is observed in various sectors. For example, in 2023, several large logistics firms explored bringing their air cargo operations in-house to control costs and improve delivery reliability, demonstrating a precedent for this type of strategic shift.
- Customer Control: Customers might seek to integrate backward to gain greater control over operational costs, scheduling, and service quality.
- Cost Savings Potential: If customers believe they can operate helicopter services more efficiently and at a lower cost than CHC, the incentive for backward integration increases.
- Market Dynamics: The overall financial health and strategic objectives of CHC's major clients will dictate their appetite and capacity for undertaking such a significant operational change.
Availability of Substitutes for Customers
The availability of substitutes significantly influences customer bargaining power for helicopter services. If customers can easily switch to alternative transport methods, their ability to negotiate better terms with CHC Group Ltd increases. For instance, in offshore oil and gas operations, marine vessels can serve as substitutes for helicopter transport, especially for personnel or cargo where time sensitivity is less critical. Similarly, for medical evacuations, fixed-wing aircraft might be a viable alternative for longer distances, reducing reliance on helicopters.
The presence of readily available and cost-effective substitutes directly enhances customer leverage. This means customers can demand lower prices or better service levels, knowing that CHC Group Ltd faces competition not just from other helicopter operators but also from entirely different modes of transport. For 2024, the ongoing advancements in maritime technology and the continued efficiency gains in regional fixed-wing aircraft operations further bolster these substitution possibilities.
CHC Group Ltd must therefore consider the cost and performance characteristics of these substitutes when setting its pricing and service offerings. The ease with which a customer can shift to an alternative transport solution is a direct measure of their bargaining power.
- Marine Vessels: Offer a lower-cost alternative for non-time-sensitive offshore personnel and cargo transport.
- Fixed-Wing Aircraft: Provide a viable substitute for longer-distance medical transfers and certain personnel movements.
- Ground Transportation: For certain onshore or near-shore operations, ground transport can be a substitute for helicopter use.
- Drones and Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs): Emerging technologies for cargo delivery and some inspection tasks present potential future substitutes.
CHC Group Ltd's customers possess significant bargaining power, primarily driven by the concentration of clients and low switching costs. When a few large clients, particularly in the oil and gas sector, account for a substantial portion of revenue, they can leverage this position to negotiate favorable terms. For instance, if the top five clients represent over 60% of CHC's revenue, their ability to influence pricing and contract conditions is considerably amplified.
The ease with which customers can transition to alternative helicopter service providers directly enhances their leverage. Low switching costs mean clients can readily explore other options without incurring significant expenses or operational disruptions. This dynamic pressures CHC to maintain competitive pricing and service quality to retain its customer base, especially as numerous alternative operators exist in key markets.
Customer price sensitivity further bolsters their bargaining power, particularly during economic downturns. Clients in sectors like oil and gas, facing their own cost pressures, will actively seek the most economical solutions. For example, the average day rate for offshore helicopter transport in 2023 varied, and customers with multiple supplier choices naturally gravitated towards the most cost-effective providers, impacting CHC's profit margins.
| Factor Influencing Customer Bargaining Power | Impact on CHC Group Ltd | Supporting Data/Examples (as of 2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High leverage for large clients | If top 5 clients represent >60% of revenue, they can demand lower fees. |
| Switching Costs | Increased power for customers | Minimal fees, retraining, or re-equipment needed to switch operators. |
| Price Sensitivity | Customers seek cost-effective solutions | Oil & gas clients sensitive to price fluctuations; average day rates vary by contract. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Customers may bring services in-house | Large energy producers might acquire their own fleets, increasing negotiating strength. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Customers have alternative transport options | Marine vessels for offshore, fixed-wing aircraft for medical; drone tech emerging. |
Full Version Awaits
CHC Group Ltd Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. Our comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of CHC Group Ltd delves into the competitive landscape, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This detailed report equips you with actionable insights into the strategic positioning and potential challenges faced by CHC Group Ltd within its industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global helicopter services market, a key arena for CHC Group Ltd, is characterized by a moderate number of significant competitors. These players, including Bristow Group and PHI Aviation, often possess substantial financial resources and established operational footprints, particularly in critical segments like offshore oil and gas transportation and search and rescue (SAR) operations. For instance, in 2024, the offshore helicopter market continues to be consolidated, with CHC and Bristow holding substantial combined market share in many regions, though regional players also command significant presence.
The helicopter services market is experiencing moderate growth, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 4% to 5% through 2028. This suggests a relatively stable but not explosive expansion. While not a declining industry, this growth rate means companies are not facing intense pressure from shrinking markets. Instead, competition is more focused on capturing incremental market share and differentiating services.
CHC Group Ltd's competitive rivalry is significantly influenced by its product and service differentiation. Where services are largely undifferentiated, such as basic offshore transport, competition tends to focus heavily on price, intensifying the rivalry among players.
CHC's ability to offer specialized services, like advanced search and rescue capabilities or tailored logistics solutions for complex offshore operations, creates a degree of differentiation. This allows them to move beyond pure price competition, as clients value the unique capabilities and reliability offered.
For instance, during 2024, the demand for specialized helicopter services in challenging environments, such as deepwater exploration or remote site support, remained strong. Companies that could demonstrate superior safety records, advanced technology, and experienced crews, like CHC, often commanded premium pricing and faced less direct price pressure from competitors offering more commoditized services.
The offshore oil and gas industry, a key market for CHC, increasingly demands sophisticated operational support. Competitors struggling to match CHC's investment in modern fleets and specialized training find themselves in a more price-sensitive segment of the market, thereby increasing the overall rivalry for those less differentiated providers.
Exit Barriers
Exit barriers in the helicopter services industry, like those faced by CHC Group Ltd, can significantly influence competitive rivalry. These barriers represent the difficulties and costs companies encounter when trying to leave the market. High exit barriers mean that even underperforming companies may continue to operate, adding pressure to the competitive landscape.
For instance, the specialized nature of helicopter fleets, including maintenance and pilot training, creates substantial sunk costs. These assets are not easily redeployed to other industries. Additionally, long-term service contracts with government agencies or major corporations can lock companies into operations, making a swift exit impractical or financially detrimental.
Regulatory hurdles also play a role. Obtaining and maintaining certifications for aircraft and operations is a complex and costly process. The prospect of losing these certifications or facing penalties for early contract termination can deter firms from exiting, thus prolonging competition.
- Specialized Assets: Helicopter fleets and related infrastructure require significant capital investment and are difficult to repurpose.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to clients can impose penalties for early termination, hindering a quick exit.
- Regulatory Obligations: Compliance with aviation safety and operational standards can be costly and time-consuming to dismantle.
- Brand Reputation: A strong reputation built over years can be lost if a company exits prematurely, impacting future ventures.
Fixed Costs vs. Variable Costs
The helicopter services industry, including players like CHC Group Ltd., faces significant competitive rivalry, partly due to its cost structure. High fixed costs associated with acquiring and maintaining helicopters, along with operational infrastructure like hangars and specialized maintenance facilities, create pressure to maximize asset utilization.
This means companies are often compelled to seek higher flight hours and contract volumes to spread these substantial fixed expenses over a larger revenue base. For instance, a new helicopter can cost millions, and ongoing maintenance contracts are also considerable. This cost dynamic can lead to aggressive pricing strategies and a greater willingness to compete on price to secure business, intensifying the rivalry among existing players.
- High Capital Investment: The initial purchase price for a new, medium-lift helicopter like the Airbus H175 can range from $15 million to $20 million, representing a substantial fixed cost.
- Ongoing Maintenance Expenses: Scheduled maintenance, parts replacement, and hangarage fees contribute significantly to the fixed cost base, regardless of flight hours.
- Utilization Drive: Companies must achieve high utilization rates, often exceeding 70%, to ensure profitability and cover their fixed cost commitments.
- Operational Leverage: A high proportion of fixed costs means that once break-even is achieved, additional revenue contributes significantly to profit, incentivizing companies to push for more operational activity.
Competitive rivalry within the helicopter services sector, where CHC Group Ltd operates, is characterized by a moderate number of well-resourced competitors like Bristow Group. The market is not overly fragmented, but key players often vie for significant contracts, particularly in specialized areas such as offshore oil and gas support and emergency services. In 2024, pricing strategies remain a key differentiator, especially for less specialized services, as companies seek to maximize the utilization of their substantial fixed assets.
| Competitor | Key Market Segment | 2024 Estimated Market Share (Offshore) |
|---|---|---|
| CHC Group Ltd | Offshore Oil & Gas, SAR | ~20-25% (Global Offshore) |
| Bristow Group | Offshore Oil & Gas, SAR | ~25-30% (Global Offshore) |
| PHI Aviation | Offshore Oil & Gas, Medical Transport | ~10-15% (US Offshore) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for CHC Group Ltd's helicopter services is significant, primarily stemming from alternative transportation methods for offshore personnel. Marine vessels, such as crew boats and supply vessels, offer a direct substitute for reaching offshore platforms.
The viability and cost-effectiveness of these marine alternatives directly impact the substitutability for CHC's core business. For instance, during 2024, fluctuating fuel prices for both helicopters and marine vessels can shift the cost advantage between these modes of transport. A significant portion of offshore personnel movements can be handled by these slower but often more cost-efficient sea-based options, especially for shorter transit distances or when payload capacity is a greater concern than speed.
The threat of substitutes for CHC Group's helicopter services is influenced by the relative price and performance of alternative transportation or service delivery methods. If other options, such as fixed-wing aircraft for certain transport needs or ground-based logistics for cargo, become more cost-effective or offer comparable efficiency, they could siphon demand away from helicopters.
For instance, while helicopters offer unique access to remote or offshore locations, the rising costs of fuel and maintenance for helicopters in 2024 could make alternative transport methods more appealing for less demanding routes. If the price per flight hour for CHC's services significantly outstrips that of a comparable journey by a chartered turboprop aircraft or even specialized ground transportation for certain onshore operations, the threat intensifies.
Performance metrics are also key; if a substitute can achieve a similar objective, like personnel transfer to a slightly less remote site, with greater speed or reliability, it presents a stronger challenge. For example, advancements in drone technology for cargo delivery or even specialized ground vehicles for certain types of onshore support could reduce the reliance on helicopters for some niche applications.
Customer willingness to substitute for CHC Group Ltd's services is influenced by the critical nature of their operations. For instance, in offshore helicopter transport, safety regulations and the need for reliable, time-sensitive transport significantly reduce the appeal of substitutes. Customers often prioritize proven reliability and adherence to stringent aviation standards, making it difficult for less regulated or unproven alternatives to gain traction. In 2023, the global offshore helicopter market saw continued demand for specialized services, with safety certifications being a key differentiator.
Technological Advancements in Substitutes
Technological advancements in substitute offerings pose a significant threat to CHC Group Ltd. The development of more efficient and cost-effective alternative transport methods could erode demand for helicopter services. For instance, improvements in advanced marine vessels for offshore logistics or the increasing capabilities of drones for specific tasks like inspection or light cargo delivery could directly compete. Furthermore, enhanced fixed-wing aircraft offering greater range or payload for certain routes might also present a viable substitute.
The impact of these emerging technologies is already being observed. By 2024, the global drone services market was projected to reach approximately $40.7 billion, indicating a substantial and growing competitive landscape. This growth is fueled by advancements in battery technology, sensor capabilities, and autonomous flight systems, making drones increasingly viable for applications previously dominated by helicopters.
- Increased drone payload capacity: Drones are increasingly capable of carrying heavier loads, directly challenging helicopters in some delivery and survey applications.
- Advancements in autonomous flight: Enhanced AI and navigation systems reduce the need for human pilots in certain drone operations, lowering operational costs.
- Improved offshore vessel technology: Specialized vessels are becoming more efficient for personnel and equipment transfer in offshore environments, offering an alternative to helicopter transport.
- Growth in electric vertical takeoff and landing (eVTOL) aircraft: While still nascent, eVTOL technology represents a potential long-term disruptor across various aviation sectors, including those served by CHC.
Impact on Core Business Segments
The threat of substitutes for CHC Group Ltd varies significantly across its core business segments. Routine crew change operations, primarily within the offshore segment, face a higher risk from marine-based transportation alternatives. These could include larger vessels or even specialized ferries for shorter routes, potentially offering cost advantages for less time-sensitive transfers.
Conversely, CHC's Search and Rescue (SAR) operations are considerably less vulnerable to substitution. The specialized equipment, highly trained personnel, and rapid response capabilities required for SAR missions are difficult and costly for alternative providers to replicate. Similarly, Emergency Medical Services (EMS) rely on a unique blend of aviation and medical expertise that presents a high barrier to substitution.
The Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) segment also exhibits a moderate to low threat from substitutes. While third-party MRO providers exist, CHC's integrated model and proprietary knowledge of its fleet can offer efficiencies and specialized service that are hard to match. In 2024, the aviation MRO market continued to grow, driven by fleet expansion and the need for specialized maintenance, reinforcing the value of established providers like CHC.
- Offshore Crew Changes: Higher vulnerability to marine transport alternatives due to cost and operational similarities for routine transfers.
- Search and Rescue (SAR): Very low vulnerability due to specialized skills, equipment, and rapid response requirements.
- Emergency Medical Services (EMS): Low vulnerability stemming from the complex integration of aviation and medical expertise.
- Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO): Moderate to low vulnerability, supported by integrated services and proprietary fleet knowledge.
The threat of substitutes for CHC Group Ltd is notably lower for specialized services like Search and Rescue (SAR) and Emergency Medical Services (EMS). This is due to the high degree of technical expertise, specialized equipment, and regulatory compliance required, which are difficult and costly for alternatives to replicate. For instance, the critical nature of SAR missions demands immediate availability and specific aircraft configurations that simpler transport methods cannot provide.
However, for routine offshore crew changes, marine transportation remains a viable and often cost-effective substitute, particularly for shorter transit times or when payload capacity is more important than speed. In 2024, continued volatility in aviation fuel prices could further incentivize the use of crew boats and supply vessels, especially if their operating costs remain more stable or lower than helicopter charters for specific routes.
Emerging technologies, such as advanced drone capabilities for cargo delivery and potentially eVTOL aircraft in the longer term, also represent growing substitute threats across various segments. By 2024, the increasing payload capacity and autonomy of drones are making them competitive for light cargo and inspection tasks, areas that might have previously relied on helicopters.
| Service Segment | Vulnerability to Substitutes | Key Substitute Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Offshore Crew Changes | High | Marine vessels (cost, payload), fuel price fluctuations (2024) |
| Search and Rescue (SAR) | Very Low | Specialized equipment, trained personnel, rapid response needs |
| Emergency Medical Services (EMS) | Low | Integration of aviation and medical expertise, regulatory standards |
| Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) | Moderate to Low | Third-party MRO providers, integrated services, proprietary knowledge |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the helicopter services sector, like that of CHC Group Ltd, demands immense capital. Potential new players must be prepared to invest heavily in acquiring a modern fleet of specialized helicopters, which can easily run into tens or hundreds of millions of dollars. For instance, a single medium-lift helicopter can cost upwards of $10 million, and a significant fleet is necessary for competitive operations.
Beyond aircraft acquisition, establishing robust maintenance facilities equipped with specialized tools and certified technicians is a substantial financial undertaking. These facilities are crucial for ensuring safety and operational readiness, adding another layer of significant upfront cost. The industry also requires obtaining numerous certifications and regulatory approvals, a process that is both time-consuming and expensive.
The helicopter services industry, particularly for specialized operations like offshore transport, search and rescue (SAR), and emergency medical services (EMS), is heavily regulated. New entrants must contend with stringent safety regulations, obtain numerous operational licenses, and secure various certifications that vary significantly by country and region. For example, obtaining an Air Operator Certificate (AOC) from authorities like the FAA in the US or EASA in Europe is a lengthy and costly process, often taking years and millions of dollars.
These complex and evolving regulatory landscapes act as a substantial barrier. Navigating requirements for pilot training and certification, aircraft maintenance standards, and operational procedures demands significant expertise and capital investment. This high barrier to entry effectively deters many potential new competitors from entering the market, especially those without established experience or substantial financial backing.
In 2024, the global helicopter market, valued at approximately $28 billion, continues to be shaped by these regulatory hurdles. Companies like CHC Group Ltd invest heavily in compliance and certification to maintain their competitive edge. The ongoing focus on safety and operational integrity by aviation authorities worldwide reinforces the difficulty for new, unproven entities to establish a foothold in critical sectors like offshore energy support.
New entrants face significant hurdles in accessing established distribution channels and customer bases within the oil and gas sector. CHC Group Ltd, for instance, benefits from deeply entrenched relationships with major oil and gas operators and government entities, often secured through years of reliable service and performance. These long-standing contracts and trusted partnerships are not easily replicated by newcomers, creating a substantial barrier to entry. For example, securing offshore helicopter contracts, a core business for companies like CHC, requires extensive vetting and a proven track record, which new players lack.
Economies of Scale for Incumbents
CHC Group Ltd, as a major player in the helicopter services industry, benefits significantly from economies of scale. This means that as CHC's operations grow, its per-unit costs tend to decrease. For instance, bulk purchasing of fuel, spare parts, and even new aircraft leads to lower prices than what a smaller competitor could secure.
These cost advantages are a substantial barrier for new entrants. Imagine trying to start a helicopter service when you can't get the same favorable rates on essential supplies. This puts new companies at an immediate disadvantage when trying to compete on price with established operators like CHC.
Consider fleet maintenance: CHC likely has its own specialized maintenance facilities and highly trained personnel, allowing them to manage upkeep more efficiently and at a lower cost per hour than a new entrant outsourcing these services. Similarly, their large-scale pilot training programs can reduce the per-pilot training cost.
- Fleet Size and Purchasing Power: CHC's substantial fleet size (e.g., operating over 200 aircraft across various models in previous years) allows for bulk discounts on new aircraft acquisitions and parts, significantly lowering capital expenditure per unit compared to a startup with a few helicopters.
- Operational Efficiency: Centralized maintenance and repair operations, supported by dedicated technical teams, reduce overhead and improve turnaround times for aircraft servicing, translating into lower operational costs per flight hour.
- Fuel Procurement: Large-scale fuel contracts provide CHC with preferential pricing, a critical cost component in aviation, which new, smaller entrants cannot easily replicate.
- Training and Certification: Investing in in-house, type-specific pilot and maintenance training programs ensures a skilled workforce while spreading the substantial training costs over a larger operational base, making it more cost-effective than relying on external, more expensive training providers.
Proprietary Technology or Expertise
CHC Group Ltd benefits significantly from its proprietary technology and deep expertise, acting as a substantial barrier to new entrants. This specialized knowledge encompasses advanced operational techniques, stringent safety protocols crucial in aviation, and sophisticated maintenance, repair, and overhaul (MRO) capabilities. For instance, CHC's investment in advanced helicopter technologies and pilot training programs requires considerable capital and time to replicate.
The development of such specialized expertise from scratch presents a major hurdle for any new company aiming to enter the helicopter services market. This includes not only the technical know-how but also the regulatory compliance and certifications that are time-consuming and expensive to acquire. For example, in 2024, the global aerospace MRO market was valued at over $80 billion, underscoring the significant investment required to establish competitive capabilities.
New entrants would face immense challenges in matching CHC's established operational efficiency and safety track record, which are built upon years of experience and continuous refinement.
- Proprietary Technology: CHC's exclusive access to and development of specialized helicopter systems and operational software.
- Expertise in MRO: Years of accumulated knowledge in maintaining complex aircraft, leading to higher reliability and lower downtime.
- Safety Protocols: Highly refined and industry-leading safety procedures that are difficult and costly for newcomers to develop and implement effectively.
- Specialized Training: Unique training programs for pilots and maintenance crews, ensuring a highly skilled workforce that is a competitive advantage.
The threat of new entrants for CHC Group Ltd is considerably low due to the substantial capital requirements for fleet acquisition and infrastructure. For example, a single medium-lift helicopter can cost over $10 million, and building the necessary maintenance facilities adds millions more. The global helicopter market, valued around $28 billion in 2024, reflects this high entry cost.
Stringent regulatory requirements, including obtaining Air Operator Certificates, present another significant barrier, often taking years and millions of dollars to secure. Navigating complex safety standards and pilot certifications demands extensive expertise and financial commitment, effectively deterring many potential competitors from entering specialized sectors like offshore transport.
CHC's established customer relationships, particularly within the oil and gas sector, are difficult for newcomers to replicate, as securing these contracts requires a proven track record and years of reliable service. Furthermore, economies of scale in purchasing, maintenance, and training provide CHC with cost advantages that new entrants cannot easily match, making price competition challenging.
Proprietary technology, deep operational expertise, and highly refined safety protocols also act as significant barriers. Developing comparable MRO capabilities, which represent a market valued over $80 billion globally in 2024, requires substantial time and investment, making it difficult for new players to achieve CHC's level of efficiency and reliability.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for CHC Group Ltd is built upon a comprehensive review of publicly available financial reports, including annual and quarterly statements, alongside industry-specific market research from leading providers like IBISWorld and Statista.
We also incorporate data from competitor disclosures, regulatory filings, and relevant trade publications to provide a robust understanding of the competitive landscape, supplier power, buyer influence, threat of new entrants, and the intensity of substitutes.
