Charter Communications Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Charter Communications Bundle
Charter Communications operates in a dynamic telecom landscape where intense competition and evolving technology significantly impact its market position. Understanding the interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, and the threat of substitutes is crucial for strategic planning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Charter Communications’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Charter Communications, like many in the broadband industry, faces a significant bargaining power from its suppliers due to a limited number of key equipment and content providers. Companies like Cisco Systems, Arris International, and Nokia Networks are crucial for Charter's network infrastructure, and their market dominance allows them to exert considerable influence over pricing and contract terms.
The high switching costs associated with specialized network technology and complex integration mean Charter cannot easily change suppliers. This reliance on a few dominant players in the telecom infrastructure sector, which has experienced notable consolidation, can translate into higher operational expenses for Charter as competitive pressures among suppliers lessen.
Charter Communications faces significant bargaining power from content providers, with a substantial portion of its operating expenses tied to licensing fees from major media companies such as Disney, Warner Bros. Discovery, and Paramount Global. In 2023, Charter's programming and copyright costs represented a considerable outlay, directly reflecting the leverage these content owners wield. The exclusivity and popularity of content from these providers are critical for Charter to attract and retain its video subscriber base, making it difficult to push back on rising programming expenses.
Charter Communications faces significant supplier bargaining power due to its continuous need for substantial capital investments in network infrastructure. This includes the ongoing expansion of fiber optic networks and the development of 5G capabilities, requiring specialized and often proprietary technology.
Suppliers of these advanced components and services are in a strong position to command higher prices. Their products are critical for Charter's network modernization efforts and its ability to maintain a competitive edge in the telecommunications market.
For instance, in 2023, Charter invested approximately $7.6 billion in capital expenditures, a significant portion of which was allocated to network expansion and upgrades. This consistent, high-level investment cycle ensures that suppliers of cutting-edge technology maintain considerable bargaining power.
Concentrated Technology Supply Chain
The telecommunications sector, including Charter Communications, faces a highly concentrated supply chain for essential technology like cable modems and broadband routers. A limited number of global manufacturers control a significant portion of this market, restricting Charter's options for sourcing these critical components. This scarcity of alternatives inherently strengthens the bargaining power of these dominant suppliers, allowing them to influence pricing and contract terms more effectively.
The dominance of a few key players in the broadband equipment market means Charter has fewer negotiating partners. For instance, companies like Arris (now CommScope) and Technicolor have historically been major suppliers, and their market share limits competitive pressure on pricing. This concentration is further amplified by the need for specialized, high-quality equipment that meets stringent industry standards.
- Concentrated Market: A few global manufacturers dominate the cable modem and broadband router supply, limiting Charter's sourcing options.
- Pricing Power: This concentration grants suppliers leverage to dictate prices and terms for critical network infrastructure components.
- Quality and Certification: Established suppliers with proven reliability and industry certifications can command premium pricing, further enhancing their bargaining power.
Suppliers' Ability to Negotiate Prices Based on Demand Fluctuations
Suppliers in the telecommunications sector, especially those providing essential components like fiber optic cables, possess significant leverage. This power is amplified when demand surges, allowing them to dictate terms and prices more effectively. For instance, the ongoing global expansion of 5G networks and the push for enhanced broadband infrastructure in 2024 have created a robust demand for these materials.
Companies like Charter Communications are directly affected by these demand-driven price adjustments. As more communities require faster internet, the cost of deploying these networks increases. This puts pressure on Charter's capital expenditures and operational budgets, as they must secure these vital supplies amidst heightened competition.
The bargaining power of suppliers is a critical factor to monitor for Charter. Consider these points:
- Increased Demand for Broadband: Global internet traffic is projected to grow significantly, with estimates suggesting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of around 25% for the next few years, driving demand for network infrastructure components.
- Supply Chain Constraints: Specific raw materials used in fiber optic cable production, like silica, can experience price volatility due to geopolitical factors or limited production capacity, further strengthening supplier pricing power.
- Project Dependencies: Charter's ambitious network upgrade projects, such as expanding fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) services, rely heavily on timely and cost-effective access to these supplier materials, making them vulnerable to supplier negotiation tactics.
Charter Communications faces considerable supplier bargaining power, particularly from providers of essential network infrastructure and content. The limited number of key equipment manufacturers, such as those producing advanced routers and fiber optic components, allows these suppliers to influence pricing and contract terms. This is further exacerbated by high switching costs and the specialized nature of the technology involved.
Content providers also hold significant leverage over Charter, as licensing fees for popular programming represent a substantial portion of operational expenses. The exclusivity and demand for content from major media conglomerates make it challenging for Charter to negotiate lower rates, directly impacting profitability and subscriber retention strategies.
The ongoing need for network upgrades, including fiber expansion and 5G deployment, means Charter must continuously invest in new technologies. Suppliers of these cutting-edge components are well-positioned to command higher prices due to the critical nature of their products for Charter's competitive standing and network modernization efforts.
| Key Supplier Areas | Impact on Charter | Supplier Bargaining Power Factors |
| Network Infrastructure Equipment (e.g., routers, modems) | High costs for essential hardware, limited alternative suppliers | Market concentration, high R&D investment, proprietary technology |
| Content Licensing (e.g., premium channels, sports) | Significant programming expenses, subscriber retention dependence | Content exclusivity, brand recognition, audience demand |
| Fiber Optic and 5G Technology | Increased capital expenditure for network upgrades, reliance on specialized components | Demand surge from 5G rollout, supply chain constraints, technological innovation |
What is included in the product
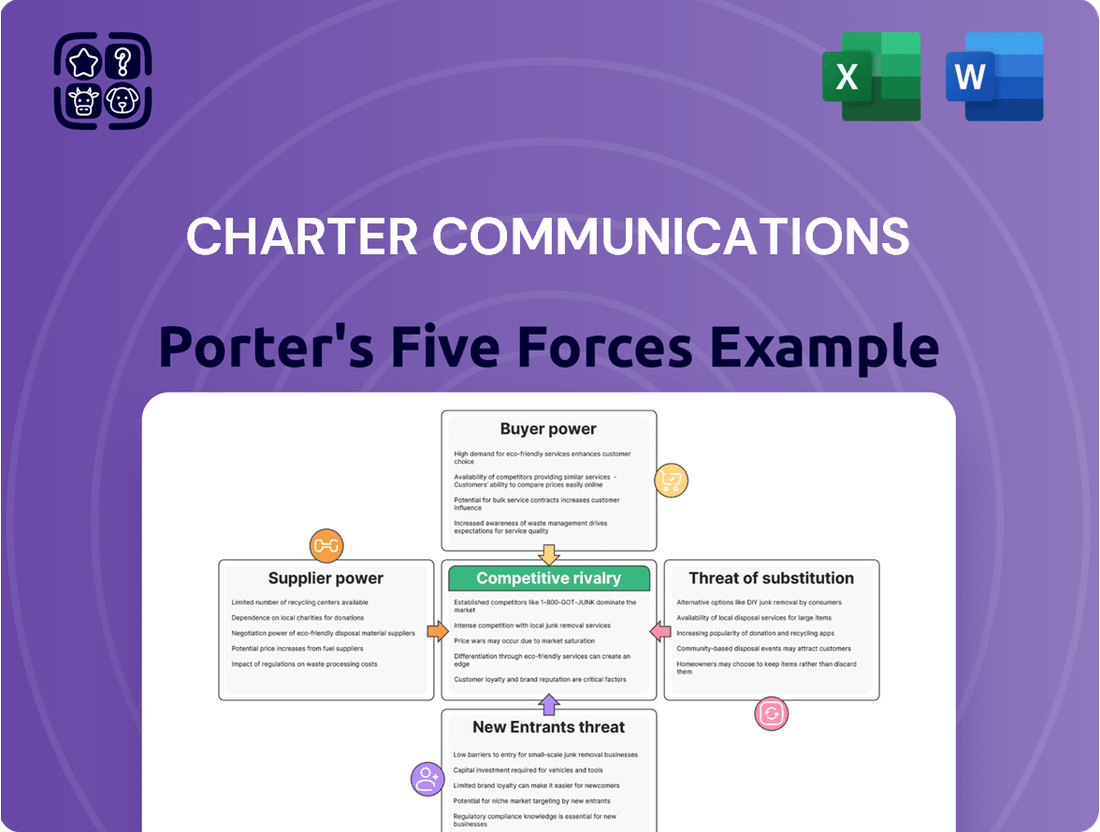
This analysis details Charter Communications' competitive environment, examining the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threats from new entrants and substitutes.
Effortlessly visualize Charter Communications' competitive landscape with a dynamic spider chart, instantly highlighting the intensity of each Porter's Five Force to pinpoint strategic pain points.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customers in the telecommunications sector generally face low costs when switching providers. These costs, often associated with early termination fees, typically fall between $50 and $200, making it financially feasible for consumers to explore alternatives. This low barrier to switching directly enhances customer bargaining power, allowing them to easily move to competitors offering more attractive pricing, faster speeds, or superior service. Charter's reported internet subscriber churn rate of 4.2% in the fourth quarter of 2023 underscores this dynamic of customer mobility.
Customers' expectations for faster internet and better streaming are definitely growing, and this gives them more say. In 2024, a significant 74% of Charter's internet customers were looking for speeds over 200 Mbps. This means if a provider can't keep up with these demands for high bandwidth and smooth streaming, customers will likely look elsewhere.
Charter is aware of this and is actively working to meet these rising expectations. They are investing in offering multi-gigabit speeds and bundling streaming benefits, which is a direct reaction to customers having more power to choose the best service for their needs.
Charter Communications offers bundled services, combining internet, cable, voice, and mobile, a strategy embraced by 68% of its customers in 2024. This bundling can increase customer loyalty, but it also empowers customers. They can now easily compare comprehensive packages from various providers, giving them more leverage in their choices.
The attractiveness of these bundled offerings directly influences customer decisions. If competitors can match or even surpass the value Charter provides through its bundles, it directly amplifies the bargaining power of Charter's customers, making it easier for them to switch providers.
Impact of Cord-Cutting and Alternative Video Services
The increasing prevalence of cord-cutting, fueled by a surge in streaming services, directly weakens Charter's bargaining power with its customers. In the first half of 2025, Charter experienced noticeable declines in its traditional video subscriber numbers, a clear indicator of this shift. Customers now have greater leverage, able to choose more affordable and adaptable entertainment solutions, thereby decreasing their dependence on legacy cable packages.
This evolving landscape forces Charter to adapt its offerings. For instance, the company's strategy to integrate popular streaming applications into its expanded basic cable packages demonstrates a direct acknowledgment of customer demand for flexibility and value.
- Cord-Cutting Impact: Charter's video subscriber base saw declines in Q1 and Q2 2025 due to the rise of streaming services.
- Customer Empowerment: Consumers are gaining power by opting for cheaper, more flexible entertainment alternatives to traditional cable.
- Strategic Response: Charter is incorporating streaming apps into its expanded basic packages to retain subscribers.
Increased Competition from Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) and Fiber Providers
The increasing availability of Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) from major carriers like T-Mobile and Verizon, coupled with aggressive fiber optic network expansion by companies such as AT&T, significantly enhances customer bargaining power. These expanding broadband alternatives provide consumers with more choices, directly pressuring Charter Communications. For instance, T-Mobile reported over 4.7 million home internet customers by the end of Q1 2024, a substantial increase that offers a viable alternative for many of Charter's subscribers.
This intensified competition compels Charter to remain highly competitive on pricing and service quality to retain its existing internet customer base. Customers can now more readily leverage these emerging options to negotiate better deals or switch providers if Charter's offerings become less attractive. The ability for customers to easily switch or demand better terms directly weakens Charter's pricing power.
- Increased Broadband Choices: FWA and fiber expansion by T-Mobile, Verizon, and AT&T provide consumers with viable alternatives to traditional cable internet.
- Pricing Pressure: The enhanced competition forces Charter to offer more competitive pricing to retain customers.
- Service Quality Demands: Customers expect higher service quality and reliability, leveraging competitive offerings as leverage.
- Customer Retention Challenges: Charter faces a greater challenge in retaining its internet subscriber base due to the growing number of attractive alternatives.
Customers' ability to switch providers remains a significant factor, with early termination fees typically ranging from $50 to $200, making it easy for consumers to explore better deals. Charter's Q4 2023 internet subscriber churn rate of 4.2% highlights this ease of switching.
The demand for faster speeds, with 74% of Charter's internet customers seeking over 200 Mbps in 2024, empowers customers to pressure providers like Charter to upgrade their services. Bundled services, used by 68% of Charter's customers in 2024, also give customers leverage as they can compare complete packages from competitors.
The rise of streaming services and cord-cutting, evidenced by Charter's video subscriber declines in early 2025, further strengthens customer bargaining power by offering cheaper, more flexible entertainment options. Additionally, the expansion of Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) and fiber networks, with T-Mobile reporting over 4.7 million home internet customers by Q1 2024, creates more broadband choices, forcing Charter to compete on price and service.
| Factor | Impact on Charter | Data/Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | Low, enhancing customer power | Early termination fees: $50-$200; Q4 2023 churn: 4.2% |
| Demand for Speed | High, driving service upgrades | 74% of customers sought >200 Mbps (2024) |
| Bundling Strategy | Can increase loyalty but also comparison power | 68% of customers used bundles (2024) |
| Cord-Cutting | Weakens video subscriber base | Video subscriber declines (early 2025) |
| Broadband Alternatives | Increases competition and customer options | T-Mobile FWA: >4.7M customers (Q1 2024) |
What You See Is What You Get
Charter Communications Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. The comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Charter Communications meticulously details the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the telecommunications industry.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Charter Communications faces fierce competition in the broadband market, particularly from fiber optic providers like AT&T Fiber and Verizon Fios. These competitors offer symmetrical multi-gigabit speeds, often exceeding the capabilities of traditional cable networks, directly challenging Charter's market position.
The superior upload speeds and enhanced reliability of fiber technology present a significant threat to Charter's broadband customer base, especially in densely populated urban and suburban areas where fiber deployment is rapidly increasing. This competitive pressure necessitates substantial investment from Charter in upgrading its network infrastructure to maintain its competitive edge.
Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) from major mobile carriers like T-Mobile and Verizon is becoming a significant competitive force, directly challenging cable providers such as Charter. These FWA services are attracting a growing number of broadband subscribers, offering a simpler and often cheaper alternative to traditional cable internet. For instance, T-Mobile reported adding 550,000 FWA net additions in the first quarter of 2024, underscoring the rapid adoption of this technology.
Charter's Spectrum brand excels by bundling high-speed broadband, video, voice, and mobile services, creating a compelling value proposition. This integrated approach is crucial in a market where customers increasingly seek consolidated solutions. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, Charter reported over 32 million total customer relationships, highlighting the success of its bundled offerings.
However, this bundling strategy intensifies rivalry, as major competitors like Comcast and AT&T also leverage similar converged product strategies. This means Charter faces significant pressure to retain and attract customers who have a wide array of bundled options available from other providers.
Charter's deliberate expansion into mobile services is a direct response to this competitive landscape. By offering mobile as part of its Spectrum bundle, Charter aims to deepen customer loyalty and provide a more comprehensive service package, directly challenging competitors who have historically dominated the mobile market.
Cord-Cutting and Streaming Service Proliferation
The ongoing trend of cord-cutting, where consumers ditch traditional cable for over-the-top (OTT) streaming services, significantly heats up competition in the video content arena. This forces companies like Charter to rethink their video strategies, often by integrating streaming benefits and more flexible packages to keep their existing customer base. The sheer volume of streaming platforms available directly challenges and diminishes the established revenue models for cable and satellite providers.
This intensified rivalry is evident in the market's evolution. For instance, by the end of 2023, the number of U.S. households subscribing to at least one streaming service reached an estimated 90 million, highlighting the shift away from traditional pay-TV. Charter itself has been actively responding to this by introducing new products and partnerships aimed at capturing a share of the streaming market and retaining video subscribers.
- Consumer Shift: An increasing number of households are opting for streaming services over traditional cable packages, fundamentally altering the media consumption landscape.
- Charter's Adaptation: Charter Communications is actively adapting by enhancing its video offerings, often by bundling streaming services or creating more flexible, à la carte options to combat subscriber loss.
- Revenue Erosion: The proliferation of standalone streaming platforms directly competes with and erodes the traditional subscription revenue streams that cable providers have historically relied upon.
- Market Dynamics: By Q4 2023, the U.S. pay-TV market saw a continued decline in subscribers, with many households now subscribing to multiple streaming services, underscoring the competitive pressure.
Network Upgrades and Rural Expansion Initiatives
Charter Communications is heavily investing in network upgrades, notably deploying DOCSIS 4.0 and expanding its fiber optic footprint. These efforts are designed to offer multi-gigabit speeds, a crucial differentiator in the increasingly competitive broadband market. For instance, Charter announced plans to invest billions in its network, aiming to bring faster speeds to more homes.
Simultaneously, Charter is actively pursuing rural expansion, often leveraging government subsidies. This strategy targets new customer segments in previously underserved areas, directly confronting a key competitive pressure. These rural build-outs are vital for Charter to gain market share against established providers and emerging competitors.
- Network Modernization: Charter's deployment of DOCSIS 4.0 and fiber optics aims to provide multi-gigabit speeds, enhancing its service offering.
- Rural Market Penetration: Government-supported rural expansion initiatives allow Charter to compete in new, often less-served, geographic areas.
- Competitive Imperative: These investments are essential for Charter to maintain and improve its position against both legacy and new broadband providers.
Competitive rivalry is intense for Charter Communications, primarily driven by advancements in fiber optic technology and the rise of Fixed Wireless Access (FWA). Competitors like AT&T Fiber and Verizon Fios offer superior upload speeds, directly challenging Charter's cable network capabilities. T-Mobile and Verizon's FWA services are also gaining traction, presenting a more affordable alternative. In Q1 2024, T-Mobile alone added 550,000 FWA subscribers, demonstrating the growing threat.
Charter counters by bundling broadband, video, voice, and mobile services, a strategy also employed by rivals like Comcast and AT&T. This converged approach aims to retain customers amidst the ongoing cord-cutting trend, where consumers increasingly favor streaming services. By Q4 2023, an estimated 90 million U.S. households subscribed to at least one streaming service, highlighting the shift away from traditional pay-TV.
| Competitor Type | Key Offerings | Impact on Charter | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber Providers | Symmetrical multi-gigabit speeds | Directly challenges cable network speeds | AT&T Fiber and Verizon Fios expanding |
| FWA Providers | Wireless broadband access | Offers simpler, cheaper alternative | T-Mobile added 550K FWA subs in Q1 2024 |
| Bundled Service Providers | Integrated broadband, video, mobile | Intensifies competition for customer relationships | Comcast and AT&T also pursue converged strategies |
| Streaming Services | Over-the-top content delivery | Drives cord-cutting, erodes video revenue | 90M U.S. households subscribed to streaming by Q4 2023 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) from mobile carriers like T-Mobile and Verizon poses a growing threat to Charter's broadband business. These services utilize 5G technology to offer high-speed internet without physical cables, making them attractive alternatives for consumers. By the end of 2023, T-Mobile reported over 2.7 million FWA customers, demonstrating significant market penetration.
The rise of Over-the-Top (OTT) streaming services like Netflix, Disney+, and Max presents a significant threat of substitutes for Charter Communications' traditional cable video services. These platforms offer consumers greater flexibility and on-demand access to a vast library of content, often at a competitive price point, directly challenging cable's bundled approach.
This shift is evident in the ongoing cord-cutting trend, where consumers are ditching traditional pay-TV subscriptions. In the first quarter of 2024, Charter reported a net loss of 207,000 video customers, underscoring the impact of these substitutes on its core business.
Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) services, offered by competitors like AT&T and Verizon Fios, present a significant threat of substitution for Charter Communications' cable broadband. These fiber connections boast symmetrical multi-gigabit speeds and superior reliability, directly challenging cable's performance. As fiber networks continue their expansion, especially in densely populated areas, they directly compete with Charter's existing infrastructure.
Satellite Broadband Services (e.g., Starlink)
Satellite broadband services, like SpaceX's Starlink, present a growing threat of substitutes for Charter Communications, particularly in areas where wired broadband infrastructure is lacking. These services offer an alternative for customers in rural and underserved regions, providing internet access where traditional cable or fiber may not be available. While often characterized by higher latency compared to wired connections, satellite broadband is becoming a more competitive option, especially for those prioritizing availability over speed.
Charter's strategic response includes expanding its own network into these rural markets, directly addressing the demand that satellite services aim to fill. This expansion is crucial to retaining customers and capturing new ones who might otherwise turn to satellite providers.
- Starlink's User Growth: As of early 2024, Starlink reported over 2.7 million active users globally, indicating a significant and growing customer base that could represent potential churn for traditional providers like Charter.
- Rural Availability Gap: In 2023, approximately 14% of US households, largely concentrated in rural areas, lacked access to broadband speeds of at least 25 Mbps download and 3 Mbps upload, a segment Starlink actively targets.
- Charter's Rural Investment: Charter committed to investing billions in expanding its network to underserved rural areas, aiming to connect millions of new homes, directly competing with the reach of satellite internet.
Public Wi-Fi and Mobile Hotspots
Public Wi-Fi and mobile hotspots present a threat of substitutes for Charter Communications, particularly for light internet users. These alternatives offer basic connectivity, potentially diminishing the perceived necessity of a dedicated home broadband subscription. For instance, in 2023, the global public Wi-Fi market was valued at approximately $2.3 billion, indicating significant adoption.
While these substitutes may not fully replicate the speed and reliability of Charter's offerings, they can satisfy the needs of users who primarily browse the web or check emails. This can lead to a reduction in demand for higher-tier broadband packages. The increasing prevalence of 5G mobile technology further strengthens this substitute threat, with speeds capable of supporting more data-intensive tasks.
However, it's crucial to note that for bandwidth-intensive activities like streaming high-definition video, online gaming, or large file downloads, dedicated broadband remains largely indispensable. Charter's continued investment in network infrastructure and speed upgrades is key to maintaining its competitive edge against these evolving substitutes.
Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) from mobile carriers like T-Mobile and Verizon is a significant substitute, leveraging 5G for high-speed internet without cables. T-Mobile reported over 2.7 million FWA customers by the end of 2023, showing substantial market penetration.
Over-the-Top (OTT) streaming services are directly substituting Charter's traditional video services, with consumers increasingly cutting the cord. Charter lost 207,000 video customers in Q1 2024 alone, highlighting the impact of these flexible, on-demand alternatives.
Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) from competitors like AT&T offers superior symmetrical multi-gigabit speeds and reliability, directly challenging Charter's cable broadband performance as fiber networks expand.
Satellite broadband, particularly SpaceX's Starlink, is a growing substitute, especially in rural areas lacking wired infrastructure. As of early 2024, Starlink had over 2.7 million users globally, targeting the 14% of US households in 2023 without adequate broadband access.
| Substitute Type | Key Competitors | Impact on Charter | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) | T-Mobile, Verizon | Direct broadband competition | T-Mobile had >2.7M FWA customers by end of 2023 |
| Over-the-Top (OTT) Streaming | Netflix, Disney+, Max | Video subscriber loss (cord-cutting) | Charter lost 207K video customers in Q1 2024 |
| Fiber-to-the-Home (FTTH) | AT&T, Verizon Fios | Broadband performance challenge | Fiber expansion in densely populated areas |
| Satellite Broadband | Starlink (SpaceX) | Rural market alternative | Starlink had >2.7M global users by early 2024 |
| Public Wi-Fi/Mobile Hotspots | Various providers | Reduces need for dedicated broadband for light users | Global public Wi-Fi market valued at ~$2.3B in 2023 |
Entrants Threaten
The telecommunications industry, especially for incumbents like Charter, demands colossal upfront capital for network infrastructure. This includes the expensive process of laying fiber optic cables and installing sophisticated equipment, creating a substantial financial hurdle for potential competitors.
These infrastructure requirements, often running into billions of dollars, serve as a significant deterrent. For instance, the cost to deploy a new broadband network can easily exceed $1,000 per premise passed, making it prohibitively expensive for newcomers to match Charter's existing reach and capabilities.
Entering the telecommunications sector, especially for broadband and cable services, is fraught with extensive regulatory hurdles and licensing requirements. Potential new entrants must contend with a labyrinth of local, state, and federal regulations governing everything from infrastructure deployment to service provision. For instance, securing rights-of-way for laying fiber optic cables can involve lengthy negotiations and approvals from numerous municipalities, a process that can take years and incur substantial legal and administrative costs.
These significant legal and bureaucratic barriers create a formidable entry barrier. The sheer complexity and cost of achieving compliance mean that only well-capitalized and experienced entities can realistically consider entering the market. Charter Communications, having operated for decades, has already navigated these challenges, establishing a significant advantage through its existing licenses and familiarity with regulatory processes. As of 2024, the ongoing evolution of telecommunications policy, including net neutrality debates and spectrum allocation, continues to add layers of complexity for any prospective player.
Charter Communications, operating as Spectrum, boasts significant brand recognition and a vast customer base exceeding 32 million subscribers across 41 states. This established presence creates a substantial hurdle for new entrants, who would require considerable investment in marketing and aggressive pricing to even begin chipping away at Charter's market share. The existing customer loyalty and brand equity make it inherently difficult for newcomers to quickly gain traction.
Economies of Scale and Scope
Charter Communications benefits significantly from economies of scale, operating a vast network infrastructure that spans millions of homes. This extensive reach allows them to spread fixed costs over a larger customer base, reducing the per-unit cost of delivering services like broadband internet and cable television. For instance, in 2024, Charter continued to invest heavily in its network, aiming to enhance speeds and reliability, which further solidifies its cost advantage.
The company also capitalizes on economies of scope by offering bundled services, including internet, TV, voice, and mobile. This cross-selling strategy increases customer loyalty and reduces churn, while also improving operational efficiency by leveraging existing infrastructure and customer relationships. New entrants would face immense difficulty replicating this breadth of service and the associated cost efficiencies, making it challenging to compete effectively on price or service package attractiveness.
- Economies of Scale: Charter's extensive network infrastructure enables lower per-unit costs for service delivery.
- Economies of Scope: Bundled services (internet, TV, voice, mobile) enhance customer value and operational efficiency.
- Barriers to Entry: New entrants struggle to match Charter's cost efficiencies and service breadth without comparable scale.
- Competitive Disadvantage for Newcomers: Achieving similar cost advantages and offering a comparable range of services requires substantial upfront investment, posing a significant hurdle for potential competitors.
Rapid Technological Evolution and Need for Continuous Innovation
The telecommunications sector, including Charter Communications, is defined by relentless technological progress. Think about the shift to 5G and the constant push for faster broadband. New companies entering this space must pour significant capital into the latest technology to even hope to compete with established players like Charter, which are already investing in multi-gigabit speed networks.
This ongoing requirement for innovation and adaptation acts as a substantial hurdle for new entrants aiming for long-term viability. For instance, Charter's commitment to network upgrades, including expanding its fiber footprint, necessitates substantial upfront investment that can deter potential competitors.
- High Capital Expenditure: Building out advanced network infrastructure, like fiber optic cables, requires billions of dollars in investment, a significant barrier for newcomers.
- Spectrum Acquisition Costs: Wireless communication relies on licensed spectrum, which can be incredibly expensive to acquire, as seen in recent FCC auctions.
- Research and Development: Staying ahead in technology means continuous R&D spending on new services and network enhancements, a costly endeavor.
- Economies of Scale: Larger, established companies benefit from economies of scale in purchasing equipment and operating networks, giving them a cost advantage.
The threat of new entrants for Charter Communications is generally low due to the immense capital required for network infrastructure, estimated in the billions of dollars, and the significant regulatory hurdles and licensing processes involved in telecommunications. Established brand recognition and economies of scale further solidify Charter's position, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on cost or market penetration.
New entrants must also contend with rapid technological advancements, necessitating continuous and substantial investment in R&D and network upgrades to remain competitive. For example, Charter's ongoing investment in multi-gigabit speed networks and fiber expansion presents a formidable challenge for any prospective competitor seeking to match their service capabilities and cost efficiencies.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Building out extensive broadband and cable networks demands billions in upfront investment for infrastructure like fiber optics. | Extremely High: Limits entry to only the most well-funded organizations. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Navigating local, state, and federal regulations, including securing rights-of-way, involves lengthy and costly processes. | High: Creates significant delays and administrative expenses. |
| Economies of Scale | Charter's large customer base and extensive network allow for lower per-unit costs in service delivery and equipment purchasing. | High: New entrants struggle to match cost efficiencies without comparable scale. |
| Technological Obsolescence | The need for continuous investment in new technologies like 5G and faster broadband requires ongoing R&D and capital expenditure. | High: Demands significant and sustained investment to keep pace with incumbents. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Charter Communications is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial reports, including SEC filings and annual reports, supplemented by industry-specific market research and data from reputable financial data providers.
