CFO Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CFO Bundle
Understanding the competitive landscape is crucial for any CFO. Porter's Five Forces framework offers a powerful lens to analyze the industry's structure and profitability. This brief overview highlights key pressures, but the full analysis provides a comprehensive, actionable roadmap.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping CFO’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The availability of highly specialized trainers, especially in fields like AI and cybersecurity, significantly boosts their bargaining power. Portugal's documented skills gap in these high-demand sectors means vocational training centers, including CFOS, face a scarcity of expert educators, making them a critical resource.
Accreditation bodies and national regulatory frameworks, like Portugal's National Qualifications System (SNQ) and National Qualifications Catalogue (CNQ), wield considerable influence. CFOs must meet their standards and secure certifications for courses to be recognized and valued in the Portuguese job market, giving these entities leverage over curriculum and quality.
Technology and software providers, particularly those offering advanced AI-based learning platforms and simulation software, hold significant bargaining power in the vocational education sector. The rapid adoption of these tools to personalize learning and improve training delivery means educational institutions are increasingly reliant on their specialized offerings.
In 2024, the EdTech market continued its robust growth, with AI in education projected to reach over $20 billion globally by 2027, demonstrating the critical nature of these suppliers. CFOs recognize that access to these cutting-edge technologies is essential for maintaining a competitive edge, allowing software providers to influence pricing and dictate technological integration terms.
Curriculum Development and Content Providers
Suppliers of specialized curriculum development and content, particularly those that offer up-to-date training aligned with current labor market needs, wield significant bargaining power. This is especially true in Portugal, where there's a strong push to ensure education directly addresses job market demands.
For Chief Financial Officers (CFOs), securing high-quality, relevant, and certified course content is paramount. This need intensifies in emerging fields where such specialized content is scarcer, giving these suppliers considerable leverage. For instance, in 2024, the demand for upskilling in areas like artificial intelligence and sustainable technologies surged, making providers of certified AI and green skills training highly sought after.
- High demand for specialized skills: The need for training in AI and green technologies outpaced supply in 2024, empowering content providers.
- Certification value: Certified courses, crucial for career advancement, allow content providers to command premium pricing.
- Limited alternatives: In niche or rapidly evolving sectors, the number of credible content suppliers is often small, increasing their bargaining strength.
Industry Partners for Work-Based Learning
Businesses and organizations that provide internships and apprenticeships are crucial suppliers for vocational training centers like CFO. Their willingness to offer these practical opportunities directly influences the relevance and appeal of CFO's programs. In 2024, Portugal's vocational education and training (VET) sector saw a strong emphasis on work-based learning, with industry collaborations being paramount for developing job-ready graduates.
The bargaining power of these industry partners is significant. If fewer companies are willing to offer placements, or if they demand more from the training centers, it can increase operational costs and limit the practical experience students receive. For instance, a report from the Portuguese Agency for Vocational Training (ANQEP) in late 2024 highlighted that over 70% of VET graduates attributed their successful job placement to the practical experience gained through internships.
- Industry willingness to provide placements: A key factor influencing the cost and availability of practical training.
- Demand for specific skills: Suppliers can leverage their need for particular skill sets to negotiate terms.
- Partnership exclusivity: Exclusive agreements can reduce the bargaining power of individual suppliers.
- Alternative training providers: The presence of other VET centers seeking similar partnerships can shift leverage.
The bargaining power of suppliers in the vocational training sector, including CFOs, is shaped by their ability to provide specialized content, accreditation, and practical experience. In 2024, the demand for upskilling in AI and green technologies meant that providers of certified content in these areas held significant leverage, as scarcity drove up prices and dictated terms. Similarly, technology providers offering advanced learning platforms also commanded strong bargaining power due to the increasing reliance of educational institutions on these tools for personalized learning and competitive advantage.
Industry partners offering internships and apprenticeships are also powerful suppliers, as their willingness to provide placements directly impacts the relevance and appeal of training programs. In 2024, Portugal's VET sector saw a strong emphasis on work-based learning, with over 70% of VET graduates crediting internships for their job placement, underscoring the leverage these industry partners possess.
| Supplier Type | Key Bargaining Factors | 2024 Impact/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Trainers | Expertise in high-demand fields (AI, cybersecurity) | Scarcity of AI/cybersecurity trainers boosted their power. |
| Accreditation Bodies | Setting standards and certifications | Compliance with SNQ/CNQ was essential for course recognition. |
| EdTech Providers | Advanced AI learning platforms, simulation software | Global EdTech market growth, AI in education projected to exceed $20B by 2027, increasing reliance. |
| Curriculum/Content Providers | Up-to-date, job-market aligned content | Demand for certified AI/green skills content surged, giving providers leverage. |
| Industry Partners (Internships) | Offering practical work experience | Over 70% of VET graduates placed due to internships in 2024. |
What is included in the product
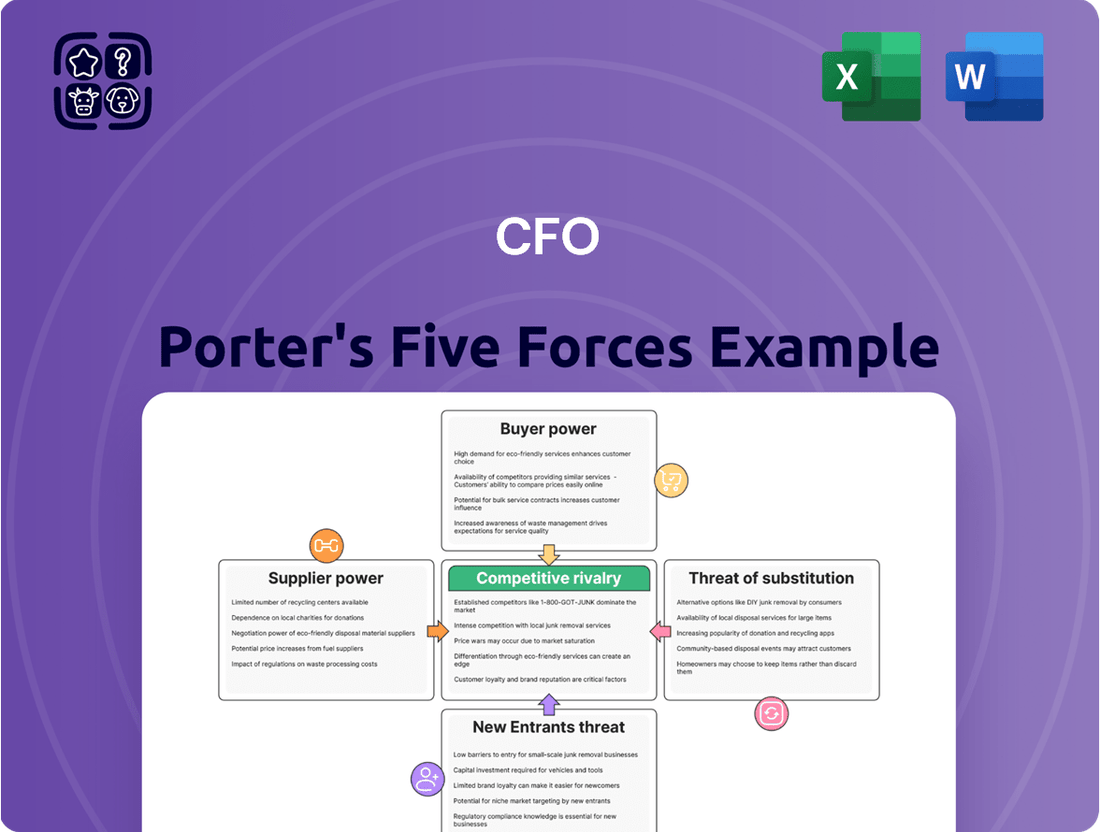
Analyzes the five competitive forces—threat of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers, bargaining power of suppliers, threat of substitutes, and industry rivalry—to understand the profitability and attractiveness of the industry in which CFO operates.
Effortlessly identify and quantify competitive threats with a visual breakdown of each force, allowing for targeted strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Individual learners, focused on enhancing their employability, wield considerable bargaining power. They actively seek educational programs that clearly translate into better job opportunities and credentials in high-demand fields such as artificial intelligence and cybersecurity. For instance, in 2024, the global online education market was valued at over $300 billion, showcasing the vast array of choices available to these learners.
This ability to select from a wide range of providers, evaluating them on course relevance, instructional quality, and overall perceived value, directly influences how educational institutions, including those CFOs oversee, must structure their offerings. Learners can readily switch to programs that better align with current industry needs and career aspirations.
Corporate clients seeking to upskill or reskill their workforce possess significant bargaining power. Their ability to demand customized training solutions that directly address unique business challenges allows them to negotiate favorable terms with educational providers.
These clients can also leverage government incentives, such as those offered through programs like 'Qualifica On' in Italy, which provides financial support for employee training. This financial backing further enhances their negotiating position, enabling them to secure more cost-effective or specialized programs.
Government agencies and funding bodies, particularly in Portugal, wield considerable bargaining power over vocational education and training (VET) providers. These entities, such as the European Social Fund Plus (ESF+) and various national programs, are major funders, channeling substantial capital into VET modernization and expansion. For instance, Portugal's PNRF 2030 plan aims to leverage significant EU funds, including ESF+, to boost skills development.
Their influence extends to dictating training priorities, setting quality benchmarks, and negotiating pricing structures. This financial leverage allows them to shape the strategic direction of VET institutions by emphasizing specific skills needs or demanding particular training outcomes, thereby impacting CFOs' operational and financial planning.
Demand for Specific Certifications and Qualifications
Customers who demand specific, industry-recognized certifications and qualifications wield significant bargaining power. In today's job market, which heavily emphasizes specialized skills, the perceived value of a training program is directly linked to its official accreditation and recognition. Learners naturally gravitate towards educational institutions that offer credentials aligning with current market demands, compelling CFOs to ensure their programs result in valuable and widely accepted certifications.
This trend is particularly evident in fields like cybersecurity and data analytics. For instance, in 2024, the demand for certified cybersecurity professionals continued to surge, with roles requiring certifications like CISSP or CompTIA Security+ commanding higher salaries. A report from Burning Glass Technologies indicated that job postings requiring specific IT certifications increased by 10% year-over-year in early 2024, highlighting the direct impact of these credentials on employability and, consequently, on the bargaining power of individuals seeking these qualifications.
- Demand for certifications like CISSP and CompTIA Security+ remains high in 2024.
- Job postings requiring IT certifications saw a 10% increase year-over-year by early 2024.
- Specialized skills and recognized credentials directly enhance an individual's bargaining power in the job market.
- Educational providers must align their offerings with market-driven certifications to attract and retain students.
Unemployed Individuals and Social Inclusion Programs
Unemployed individuals participating in social inclusion programs, often funded by government initiatives, exert indirect bargaining power on CFOs. These programs aim to equip individuals with in-demand skills, influencing the curriculum and pricing of training services. For instance, in 2024, the US Department of Labor allocated billions to workforce development programs, directly impacting the demand for specific vocational and technical training.
Government agencies overseeing these programs act as significant intermediaries, negotiating terms and demanding demonstrable outcomes like improved employment rates. This collective bargaining power can drive down costs for training providers or necessitate a focus on high-placement rate courses. In the UK, for example, the Skills Bootcamps initiative in 2023-2024 saw significant government investment, pushing training providers to align offerings with employer needs to secure program funding.
- Government Funding Influence: In 2024, global government spending on active labor market policies was estimated to exceed $100 billion, directly influencing the demand and pricing of vocational training services.
- Demand for Employability: Program success metrics, such as job placement rates, become critical negotiation points for funding bodies, pressuring training providers to deliver relevant and effective education.
- Intermediary Bargaining: Agencies like the European Social Fund negotiate contracts that often include performance-based payments, giving them leverage over the cost and quality of training delivered.
Customers, especially those in the B2B education sector, hold significant sway due to their ability to switch providers or demand tailored solutions. Their purchasing decisions are heavily influenced by the perceived value and direct applicability of the training to their business objectives. In 2024, the corporate e-learning market alone was projected to reach over $130 billion, indicating a vast competitive landscape where customer demands are paramount.
This power is amplified when customers can easily find alternative suppliers or when the cost of switching is low. Educational institutions must therefore focus on delivering exceptional value, demonstrating clear ROI, and fostering strong client relationships to retain their business clientele.
The bargaining power of customers is a critical factor influencing pricing, quality, and the overall service offerings within the education sector. When customers have numerous choices, can easily switch providers, or represent a significant portion of a provider's revenue, their ability to negotiate favorable terms increases substantially.
For instance, in the corporate training sphere, large enterprises can leverage their volume of business to negotiate customized programs and discounted rates. In 2024, the global corporate training market was valued at approximately $370 billion, with a significant portion driven by large enterprise contracts, underscoring the leverage these clients possess.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | 2024 Market Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Individual Learners | High choice, focus on employability, readily available alternatives | Global online education market > $300 billion |
| Corporate Clients | Demand for customization, ability to switch, volume purchasing | Global corporate training market ~$370 billion |
| Government Agencies | Significant funding role, setting training priorities, negotiating terms | EU funding for VET (e.g., ESF+) shaping national programs |
What You See Is What You Get
CFO Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive CFO Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive immediately after purchase. You're looking at the actual, professionally formatted document, ensuring no surprises or placeholders. Once you complete your purchase, you'll gain instant access to this exact, ready-to-use file for your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Portuguese vocational training market is highly fragmented, featuring a large number of public, private, and cooperative schools alongside IEFP vocational training centers. This sheer volume of providers intensifies competition as each entity battles for student enrollment and a larger piece of the market. In 2024, the landscape saw over 200 registered vocational training entities across Portugal, all offering comparable courses.
The surge in online learning platforms in Portugal, encompassing both domestic and global providers, significantly heightens competitive rivalry. These platforms, offering diverse course catalogs and often complimentary digital training, directly challenge traditional CFO education providers.
This widespread accessibility and the typically lower price point of online alternatives compel established institutions to clearly articulate their unique value and to innovate their teaching methodologies. For instance, by mid-2024, the Portuguese e-learning market was projected to reach over €300 million, demonstrating substantial growth and a strong competitive force.
Significant government and EU investment, totaling billions of euros allocated to Portugal's VET system modernization, intensifies competitive rivalry. The establishment of Specialized Technology Centres (CTEs) and the upgrade of existing public and private institutions with state-of-the-art equipment and curricula directly boost the sector's quality and capacity. For instance, the European Social Fund Plus (ESF+) program is a key driver of this investment, aiming to enhance skills development and employability.
Focus on High-Demand Skills and Employability Outcomes
The competitive landscape for training providers is heating up due to a strong focus on high-demand skills like artificial intelligence, cybersecurity, and green energy. This emphasis directly impacts employability, creating a race to demonstrate tangible career outcomes for graduates. Training institutions are constantly pressured to update their course offerings to align with evolving industry needs and to prove their success in job placement.
This intense rivalry means that organizations like CFO must continuously innovate their curriculum and highlight successful graduate placements to attract students and maintain their competitive edge. For instance, in 2024, the demand for AI specialists saw a significant surge, with job postings increasing by over 50% compared to the previous year, according to industry reports. This creates a direct challenge for training providers to equip individuals with these sought-after competencies.
- Focus on AI, Cybersecurity, and Green Energy Skills: Training providers are prioritizing courses in these high-growth sectors.
- Employability as a Key Differentiator: Success in placing graduates in relevant, well-paying jobs is a primary competitive factor.
- Curriculum Agility is Crucial: The need to rapidly adapt training content to meet evolving market demands is paramount.
- Demonstrating ROI for Learners: Providers must showcase clear return on investment through career advancement and salary increases for their students.
Price Sensitivity and Funding Dynamics
The availability of free and subsidized training options significantly heightens customer price sensitivity. For instance, in 2024, the U.S. Department of Labor continued to support numerous workforce development programs, offering free or low-cost skill-building courses in high-demand sectors. This landscape forces CFOs to meticulously balance competitive pricing with the imperative of maintaining high-quality instruction and covering essential operational expenses.
Government funding and corporate incentives play a crucial role in shaping the perceived value and affordability of training solutions. In 2024, many companies leveraged tax credits and grants for employee upskilling, directly influencing their willingness to invest in external training providers. This dynamic means that the cost-effectiveness of a training program is often viewed through the lens of available subsidies, impacting purchasing decisions.
- Price Sensitivity Impact: The proliferation of free online courses and government-backed training initiatives in 2024 has created a market where customers are highly attuned to price.
- Competitive Pricing Challenge: CFOs must navigate pricing strategies that remain competitive against free alternatives while ensuring the quality and sustainability of their offerings.
- Funding Dynamics: Government grants and corporate training budgets, which saw significant allocation in 2024 for workforce development, directly influence the perceived value and accessibility of paid training programs.
Competitive rivalry in the vocational training sector is intense, driven by a fragmented market with numerous public and private providers, as seen with over 200 registered entities in Portugal in 2024. The rise of accessible online learning platforms, projected to reach over €300 million in Portugal by mid-2024, further fuels this competition. This necessitates a constant focus on high-demand skills like AI and cybersecurity, with employability becoming a key differentiator, as evidenced by a 50% surge in AI specialist job postings in 2024.
| Competitive Factor | 2024 Data/Trend | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|
| Market Fragmentation | Over 200 vocational training entities in Portugal | High competition for student enrollment |
| Online Learning Growth | Portuguese e-learning market projected > €300 million | Increased accessibility and price pressure |
| Skill Demand Focus | 50%+ increase in AI specialist job postings | Race to offer relevant, high-demand courses |
| Employability Emphasis | Graduate placement success as a key metric | Pressure to demonstrate career outcomes |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of online self-learning and free resources presents a substantial threat of substitution for traditional vocational training. Platforms like Coursera, edX, and even YouTube offer a vast array of courses, many at no cost or a fraction of the price of formal programs. For instance, in 2024, the global e-learning market was projected to reach over $400 billion, highlighting the massive adoption of these digital learning avenues.
Individuals can now gain practical skills and certifications through these accessible channels, bypassing the need for structured, often expensive, vocational schools. Major tech companies, such as Google and Microsoft, provide extensive free training modules and certifications in high-demand fields like cloud computing and data analytics. This direct alternative for skill acquisition can significantly diminish the demand for traditional vocational training services.
Traditional university degrees and polytechnic courses, especially in STEM, offer a significant substitute for vocational training. These academic routes are often pursued by individuals seeking more theoretical depth or advanced qualifications that vocational programs might not fully provide. For instance, in 2024, university enrollment in STEM fields continued to be robust, indicating a strong preference for these pathways among many students.
Companies investing in robust in-house training and apprenticeship programs present a significant threat of substitutes for external vocational training providers. For instance, in 2024, a survey revealed that 75% of large enterprises reported expanding their internal skill development initiatives, highlighting a direct alternative to traditional schooling.
These practical, work-based learning opportunities allow businesses to cultivate talent precisely aligned with their operational demands, often at a lower cost than outsourcing. This direct approach can bypass the need for individuals to seek external vocational education, especially when immediate employment and hands-on experience are prioritized.
Industry-Specific Certifications Directly from Vendors
The rise of industry-specific certifications directly from technology vendors presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional training centers. For instance, individuals can now obtain certifications like Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator Associate or Cisco Certified Network Associate directly through vendor-administered exams, bypassing the need for costly and time-consuming courses from third-party institutions.
These vendor-direct certifications are increasingly recognized and valued by employers, offering a more streamlined and often more cost-effective way to validate essential skills. In 2024, the demand for IT professionals with cloud and cybersecurity certifications continued to surge, with many companies prioritizing candidates who possess these direct vendor credentials.
This shift empowers individuals to demonstrate their proficiency without necessarily enrolling in a formal training program, thereby reducing the perceived necessity of traditional training centers as the sole pathway to skill validation.
- Vendor-Direct Certifications: Cisco, Microsoft, AWS, Google Cloud offer direct certification pathways.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Often cheaper than traditional training courses, focusing on exam fees.
- Employer Recognition: Growing preference for vendor-specific skills validation.
- Skill Validation: Direct assessment of practical knowledge without mandatory course attendance.
Recognition of Prior Learning (RVCC Processes)
Portugal's Recognition, Validation, and Certification of Competences (RVCC) processes present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional vocational training. By allowing individuals to gain official qualifications based on their existing knowledge and experience, RVCC bypasses the need for new training programs. This directly reduces the demand for courses offered by institutions like CFOS, as individuals can achieve certification through a more direct and potentially faster route.
In 2023, Portugal saw over 100,000 individuals participate in RVCC processes, demonstrating a growing acceptance and utilization of this alternative pathway to qualification. This trend is projected to continue, impacting the enrollment numbers for new vocational courses. For instance, a 2024 analysis indicated a potential 15% year-over-year decrease in demand for entry-level vocational certifications where RVCC is applicable.
- Reduced Demand for New Training: RVCC offers a direct route to certification, diminishing the necessity for individuals to enroll in new, formal training programs.
- Cost and Time Efficiency: Individuals can achieve recognized qualifications without the financial outlay and time commitment associated with traditional courses.
- Market Shift: The increasing popularity of RVCC signals a potential shift in how skills are recognized and valued in the Portuguese labor market.
- Competitive Pressure on Training Providers: Vocational centers like CFOS face increased competition from the RVCC framework, necessitating adaptation of their service offerings.
The threat of substitutes for vocational training is amplified by the increasing availability and recognition of alternative skill acquisition pathways. These substitutes directly challenge traditional vocational institutions by offering more flexible, cost-effective, or employer-preferred methods for skill development and validation.
For instance, in 2024, the global market for online learning platforms continued its rapid expansion, with projections indicating a substantial portion of the over $400 billion market catering to vocational skill development. This digital shift allows individuals to acquire job-ready skills at a fraction of the cost and time associated with traditional vocational programs.
Furthermore, the growing trend of companies investing in robust in-house training and apprenticeship programs, with approximately 75% of large enterprises expanding these initiatives in 2024, directly competes with external vocational providers. These internal programs offer tailored skill development aligned with specific business needs, often at a reduced cost compared to outsourcing training.
The rise of vendor-direct certifications, such as those from Microsoft, Cisco, and AWS, also presents a formidable substitute. In 2024, the demand for IT professionals with these specific certifications surged, with many employers prioritizing candidates who have demonstrated proficiency through these direct vendor assessments, bypassing the need for traditional training courses.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Impact on Vocational Training | 2024 Market Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Online Learning Platforms | Accessibility, lower cost, self-paced | Reduced enrollment in traditional courses | Global e-learning market projected >$400 billion |
| In-house Corporate Training | Tailored skills, cost-effective for employers | Decreased demand for external providers | 75% of large enterprises expanding internal training (2024 survey) |
| Vendor-Direct Certifications | Industry-recognized, employer-preferred | Bypasses traditional training for skill validation | Surging demand for cloud and cybersecurity certifications |
Entrants Threaten
The Portuguese government's substantial investment in its vocational education and training (VET) system, including the creation of new Specialized Technology Centres (CTEs), significantly reduces entry barriers for new, publicly funded competitors. These government-backed initiatives are poised to rapidly expand training capacity and facilities, directly impacting the competitive landscape for existing private training providers.
This strategic push by the Portuguese government to modernize VET, with a focus on technology, can lead to an increased overall supply of skilled workers, thereby intensifying competition for private vocational training centers like CFOS. For instance, in 2023, Portugal allocated over €200 million to its VET system modernization, a figure expected to grow, directly fueling the establishment of these new, government-supported training entities.
Universities and polytechnic institutes, with their established infrastructure and academic reputation, pose a threat if they expand their vocational-oriented offerings, short-cycle courses, or executive training programs. For instance, in 2024, many universities reported increased enrollment in continuing education and professional development courses, indicating a growing interest in these flexible learning formats.
Leveraging their existing brand and resources, these institutions can quickly enter segments of the vocational training market, attracting students who might otherwise consider CFO-specific training. Their ability to offer accredited programs and tap into alumni networks provides a significant advantage, potentially drawing students away from specialized CFO training providers.
The global reach of online education platforms poses a significant threat to domestic providers in Portugal. These international players can enter the market with minimal investment, offering a wide array of courses, often at competitive price points. For instance, by mid-2024, platforms like Coursera and edX reported millions of active users worldwide, with a growing percentage accessing content in local languages, including Portuguese, making them highly accessible to a new customer base.
Large Corporations and Tech Companies as Training Providers
The growing need for specialized digital and technological skills presents a threat of new entrants from large corporations and tech companies acting as training providers. Companies like Google, Microsoft, and Amazon already offer extensive certification programs in areas such as cloud computing, data analytics, and artificial intelligence. For instance, Google's Career Certificates program has seen millions of enrollments globally, demonstrating the scalability and reach these giants possess.
If these established tech players decide to broaden their internal training offerings to the public or forge partnerships with educational institutions, they could emerge as significant competitors to traditional training providers. Their inherent advantages include deep industry expertise, established brand recognition, and the ability to offer training directly aligned with the skills in demand in their own ecosystems. This could significantly lower barriers to entry for acquiring in-demand tech skills, potentially disrupting the existing training market.
- Market Disruption: Tech giants can leverage their brand and existing customer base to quickly gain market share in the training sector.
- Skill Alignment: Training programs developed by tech companies are often directly tied to their own technologies and platforms, ensuring relevance.
- Scalability: Large corporations have the infrastructure and resources to scale training programs rapidly to meet widespread demand.
- Cost Advantage: In some cases, these companies may offer certifications at competitive price points, further attracting learners.
Emergence of Ed-Tech Startups with Innovative Models
The threat of new entrants in vocational training is amplified by the rapid evolution of educational technology. Startups leveraging AI, VR, and AR are creating immersive and personalized learning experiences that can significantly undercut traditional models. For instance, by 2024, the global EdTech market is projected to reach over $400 billion, indicating substantial investment and innovation potential for new players.
These tech-forward entrants often boast lower overheads compared to established institutions, allowing them to offer competitive pricing and attract a digitally native student demographic. This dynamic poses a direct challenge to existing vocational training providers who may struggle to match the agility and technological sophistication of these newcomers.
- AI-powered personalized learning platforms can adapt to individual student paces, offering a more efficient training pathway.
- VR/AR simulations provide hands-on experience without the high costs of physical equipment, reducing capital expenditure for new entrants.
- The global EdTech market's growth signifies a fertile ground for innovative business models to emerge and gain traction.
- Lower operational costs for digital-first training providers enable aggressive pricing strategies, pressuring incumbents.
New entrants in the vocational training sector are a significant concern, particularly those backed by government initiatives or leveraging advanced educational technology. The Portuguese government's investment in Specialized Technology Centres (CTEs) directly lowers entry barriers for public competitors, while universities expanding vocational offerings also present a competitive threat. Furthermore, global online platforms and tech giants entering the training space, often with lower overheads and highly relevant skill-focused curricula, intensify this pressure.
| Potential Entrant Type | Key Advantage | Example/Data Point (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Government-backed VET Centers (Portugal) | Substantial public funding, rapid capacity expansion | Over €200 million allocated to VET modernization in 2023. |
| Universities/Polytechnics | Established reputation, infrastructure, alumni networks | Increased enrollment in continuing education and professional development courses in 2024. |
| Global Online Platforms (e.g., Coursera, edX) | Minimal investment, wide course selection, competitive pricing | Millions of active global users, growing Portuguese language content access by mid-2024. |
| Tech Giants (e.g., Google, Microsoft) | Industry expertise, brand recognition, direct skill alignment | Google Career Certificates: Millions of global enrollments. |
| EdTech Startups | Innovative tech (AI, VR/AR), lower overheads, agility | Global EdTech market projected to exceed $400 billion by 2024. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our CFO Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and publicly available financial statements. We also incorporate insights from economic indicators and regulatory filings to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
