CellaVision Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
CellaVision Bundle
Understanding the competitive landscape for CellaVision is crucial for strategic planning. Our analysis reveals the intricate interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, the threat of new entrants, and the intensity of rivalry within its market. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface.
Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore CellaVision’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate its industry effectively.
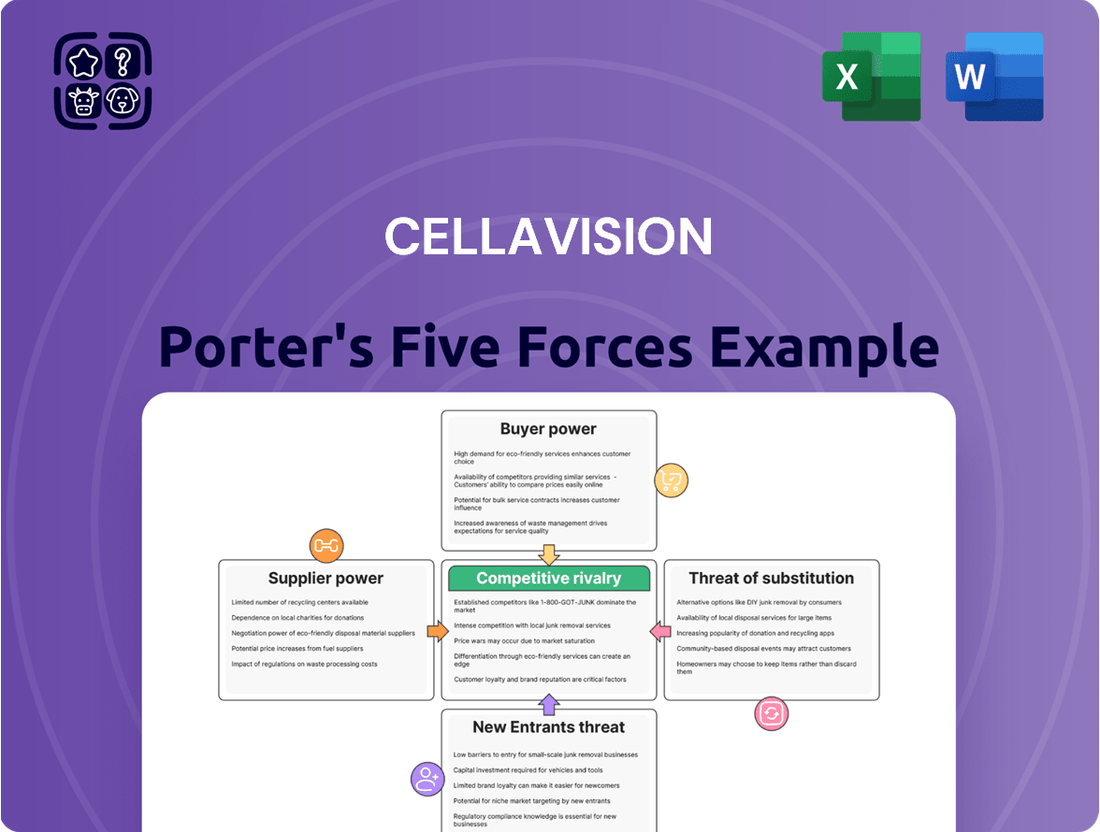
Suppliers Bargaining Power
CellaVision's reliance on specialized components like optics, imaging sensors, and precision robotics means that a concentrated supplier market can significantly impact its bargaining power. If only a handful of companies can provide these highly technical parts, those suppliers gain considerable leverage over CellaVision regarding pricing, quality control, and delivery timelines.
For instance, in the advanced optics market, which is crucial for CellaVision's microscopy systems, a few dominant global players often dictate terms. This limited competition among suppliers means CellaVision has fewer alternatives, potentially leading to higher input costs and less flexibility in its supply chain, a common challenge for technology firms in 2024.
CellaVision faces significant supplier bargaining power due to high switching costs. Changing suppliers for critical components like specialized imaging sensors or proprietary software modules can involve substantial re-engineering of product designs and extensive system re-validation processes. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for a company in the medical device sector to qualify a new critical component supplier ranged from $100,000 to $500,000, encompassing R&D and testing expenses.
These considerable expenses, coupled with the potential for supply chain disruptions and delays in product launches, make it challenging for CellaVision to switch suppliers. The need to re-establish new logistics and ensure compatibility further entrenches existing supplier relationships, amplifying their leverage in negotiations. This situation is common in industries where specialized, high-performance components are integral to product functionality.
CellaVision's advanced digital pathology solutions, which heavily rely on AI and sophisticated image analysis, likely depend on specialized and potentially proprietary components. If suppliers offer unique technologies or patented materials that are fundamental to CellaVision's product differentiation and performance, they gain significant bargaining power. For instance, a supplier providing a crucial AI algorithm or a unique scanner component that CellaVision cannot easily replicate elsewhere would have considerable leverage.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by CellaVision's suppliers is a critical consideration. If suppliers, such as those providing specialized optical components or advanced imaging sensors, possess the capability and the motivation to enter the digital microscopy market themselves, they could become direct competitors. This scenario would significantly shift the balance of power, potentially disrupting CellaVision's supply chain and market position.
This potential shift is particularly relevant given the increasing commoditization of certain technology components. For example, if a supplier of high-resolution CMOS sensors, a key component in digital microscopy, were to develop its own integrated microscopy solutions, it could leverage its existing manufacturing scale and component control to challenge CellaVision. Such a move could limit CellaVision's access to critical inputs and force it to compete on price with entities that also control its primary material costs.
- Supplier Capability: Suppliers need the technical expertise, manufacturing infrastructure, and R&D capacity to develop and produce digital microscopy systems comparable to CellaVision's offerings.
- Supplier Incentive: A supplier might be incentivized to integrate forward if they perceive higher profit margins in the end-product market or if they face declining margins in their component supply business.
- Market Dynamics: The growth rate and profitability of the digital microscopy market, as well as the competitive intensity, will influence a supplier's decision to integrate forward. For instance, a growing market with strong profitability could attract suppliers looking for new revenue streams.
- Impact on CellaVision: Forward integration by suppliers would directly increase competition, potentially reduce CellaVision's profit margins, and create uncertainty regarding the availability and cost of essential components.
Importance of CellaVision to Supplier Revenue
CellaVision's standing as a customer significantly shapes its suppliers' bargaining power. When CellaVision accounts for a minor slice of a supplier's overall sales, that supplier has less incentive to negotiate favorable terms or give CellaVision preferential treatment. This dynamic means suppliers might feel less pressure to accommodate CellaVision's specific demands.
Conversely, if CellaVision represents a substantial portion of a supplier's revenue, CellaVision's own bargaining power is amplified. A supplier heavily reliant on CellaVision's business would likely be more accommodating, offering better pricing, prioritizing CellaVision's orders, and being more responsive to its needs to maintain that crucial relationship. For instance, if a key component supplier, such as a specialized optics manufacturer, derives over 25% of its annual revenue from CellaVision, their ability to dictate terms to CellaVision would be considerably reduced.
- Supplier Dependence: The degree to which suppliers depend on CellaVision for their revenue directly impacts their bargaining power.
- Revenue Contribution: If CellaVision constitutes a small percentage of a supplier's total income, the supplier's leverage is higher.
- Customer Significance: Conversely, when CellaVision is a major client, its purchasing volume grants it greater influence over suppliers.
- Negotiating Leverage: A large customer like CellaVision can negotiate better pricing and terms due to its significant contribution to a supplier's sales figures.
CellaVision's bargaining power with its suppliers is significantly influenced by the concentration of the supplier market. When few companies can provide critical components like specialized optics or imaging sensors, these suppliers gain substantial leverage. For example, in 2024, the market for high-resolution microscopy sensors was dominated by a handful of global manufacturers, allowing them to command higher prices and dictate terms to buyers like CellaVision.
High switching costs further empower suppliers. Re-engineering products and re-validating systems for new components can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars, making it difficult for CellaVision to change suppliers. This inertia benefits existing suppliers, solidifying their negotiating position and potentially increasing CellaVision's input costs.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers also plays a role. If suppliers can leverage their expertise to enter the digital microscopy market, they could become direct competitors, impacting CellaVision's supply chain and market share. This is a growing concern as component technology advances.
CellaVision's importance to its suppliers also shapes this dynamic. If CellaVision represents a small fraction of a supplier's business, the supplier has less incentive to offer favorable terms. Conversely, if CellaVision is a major client, its purchasing volume grants it greater influence and negotiating power.
| Factor | Impact on CellaVision's Bargaining Power | Example/Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Market Concentration | Weakens CellaVision's power | Limited number of high-end optics providers |
| Switching Costs | Weakens CellaVision's power | Average $100k-$500k to qualify new critical component supplier |
| Supplier Forward Integration Threat | Weakens CellaVision's power | Potential for sensor manufacturers to enter microscopy market |
| CellaVision's Customer Significance | Strengthens CellaVision's power (if significant) | If CellaVision accounts for >25% of a supplier's revenue |
What is included in the product
This analysis evaluates the five competitive forces impacting CellaVision, assessing the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, to understand CellaVision's strategic position.
Effortlessly assess competitive intensity by visualizing the five forces, allowing for swift identification of strategic opportunities and threats.
Customers Bargaining Power
CellaVision's customer base is primarily composed of large hospital laboratories and commercial laboratories worldwide. This consolidation means that if these major clients band together or are already highly concentrated, they possess considerable power to negotiate pricing and contract terms. For instance, a few very large laboratory networks could collectively demand better deals, impacting CellaVision's profitability.
If the core digital cell morphology technology becomes widely standardized, customers might see less unique value in CellaVision's offerings. This standardization can increase price sensitivity, as buyers can more easily compare and switch between providers based on cost alone.
For instance, in 2024, the global laboratory diagnostics market, which includes hematology, was valued at approximately $100 billion, indicating a substantial market where standardization could significantly impact competitive dynamics. A highly commoditized segment within this market would empower customers to negotiate harder on price.
Healthcare providers, often operating under tight budgetary constraints, exhibit significant price sensitivity when evaluating new laboratory solutions. This means that the cost of CellaVision's automated systems, including both the initial purchase price and the recurring expenses for consumables like reagents, directly impacts purchasing decisions.
For instance, in 2024, many hospital laboratory budgets faced increased pressure due to rising operational costs and staffing shortages, making the total cost of ownership a paramount concern for potential CellaVision customers. The perceived value proposition, which centers on improved efficiency and accuracy, must demonstrably outweigh these financial considerations.
Availability of Alternative Solutions
Customers can choose between CellaVision's automated digital microscopy solutions and traditional manual microscopy. This choice is significant because manual microscopy, while less efficient, represents a baseline alternative. In 2024, the global digital pathology market, which includes solutions like CellaVision's, was valued at approximately USD 1.8 billion, indicating a growing but still competitive landscape where manual methods persist.
The existence of these alternatives, including other vendors offering digital or automated solutions, empowers customers. They can leverage this availability to negotiate pricing or seek better terms from CellaVision. If CellaVision's value proposition, considering both cost and benefits, doesn't align with customer expectations, the ability to switch to a competitor or even stick with manual methods provides considerable bargaining power.
- Alternative Options: Customers can opt for manual microscopy or other digital pathology vendors.
- Customer Leverage: Availability of alternatives allows customers to negotiate better pricing and terms.
- Competitive Landscape: The digital pathology market's growth to USD 1.8 billion in 2024 highlights competitive pressures.
- Switching Costs: While digital solutions offer benefits, the inertia of manual processes or switching to a different digital vendor can influence customer decisions.
Low Switching Costs for Customers (Potentially)
While integrating new laboratory equipment can incur costs like training and LIS integration, CellaVision's focus on digital pathology might see these diminish. Advancements in interoperability and standardized data formats are key here. For instance, if the process of switching between different digital microscopy systems becomes more streamlined, customers gain more leverage due to fewer switching barriers.
This potential for lower switching costs directly impacts CellaVision's customer bargaining power. If customers can easily move to a competitor's digital pathology solution with minimal disruption or additional expense, they are more likely to demand better pricing or terms. In 2023, the global digital pathology market was valued at approximately USD 1.5 billion, and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a competitive landscape where customer loyalty can be influenced by ease of transition.
- Reduced Integration Complexity: As digital pathology solutions become more standardized, the effort required to integrate them with existing Laboratory Information Systems (LIS) decreases, lowering switching costs for customers.
- Interoperability Standards: The adoption of industry-wide interoperability standards in digital pathology can make it easier for customers to adopt new systems without costly data migration or system overhauls.
- Customer Choice Amplification: When switching costs are low, customers have a wider array of choices and are empowered to negotiate more effectively with providers like CellaVision.
CellaVision's customers, often large hospital and commercial laboratories, possess significant bargaining power due to market concentration and price sensitivity. The availability of alternatives, from manual microscopy to competing digital solutions, allows them to negotiate favorable terms. In 2024, the global laboratory diagnostics market was valued at around $100 billion, a substantial arena where customer negotiation power can impact vendors.
The value proposition of CellaVision's digital cell morphology technology must clearly outweigh the total cost of ownership, especially given the budget constraints faced by healthcare providers in 2024. The global digital pathology market, valued at approximately USD 1.8 billion in 2024, signifies a competitive environment where customers can leverage alternative options.
Furthermore, decreasing switching costs, driven by advancements in interoperability and standardized data formats within digital pathology, amplifies customer leverage. As of 2023, the digital pathology market was valued at USD 1.5 billion, with projections for significant growth, indicating that ease of transition between systems will continue to empower customers to negotiate more effectively.
| Factor | Description | Impact on CellaVision |
| Customer Concentration | Large hospital and commercial labs form CellaVision's core base. | High concentration among buyers increases their collective bargaining power. |
| Price Sensitivity | Budgetary constraints drive demand for cost-effective solutions. | Customers can negotiate harder on pricing, impacting CellaVision's margins. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Manual microscopy and other digital pathology vendors exist. | Customers can switch or choose alternatives, giving them leverage. |
| Switching Costs | Integration complexity and data migration can be barriers. | Lowering these costs enhances customer ability to negotiate for better terms. |
What You See Is What You Get
CellaVision Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the exact CellaVision Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises or placeholders. You are viewing the complete, professionally formatted document, ready for immediate download and use. What you see here is precisely the deliverable you will get, offering a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape for CellaVision.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The digital medical microscopy market, especially in hematology, is a hotbed of innovation. CellaVision itself is pouring substantial resources into research and development, focusing on areas like artificial intelligence and expanding into new applications such as bone marrow analysis. This drive for technological superiority naturally fuels fierce competition as companies race to develop and market the most advanced solutions.
CellaVision competes in a global arena against numerous medical technology firms specializing in digital pathology and hematology. The landscape features both well-established companies with significant market share and nimble startups introducing novel solutions, intensifying the rivalry.
For instance, in 2023, the digital pathology market was valued at approximately USD 1.5 billion and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a dynamic and competitive environment. Companies like Leica Biosystems and Philips are major players, but CellaVision also contends with newer entrants leveraging AI and advanced imaging, creating a crowded field.
CellaVision stands out by offering patented technology and sophisticated software designed for classifying and analyzing cells, creating an integrated digital environment. This strong product differentiation, rooted in its features, precision, and workflow enhancements, effectively reduces direct price wars.
The company’s commitment to continuous innovation is crucial for sustaining this competitive edge. For instance, CellaVision's advanced AI algorithms, which achieved over 95% accuracy in recent internal benchmarks for specific cell types, directly address the need for reliable and efficient diagnostic tools in laboratories worldwide.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers, like CellaVision's significant investment in specialized technology and ongoing research and development, can trap companies in an industry. This means firms might continue operating even when not highly profitable, as the cost of leaving is too high. For example, in 2023, CellaVision reported R&D expenses of approximately SEK 100 million, highlighting a substantial commitment to its technological infrastructure.
These substantial investments create a situation where exiting the market would mean forfeiting these assets and potentially incurring further financial penalties. Consequently, companies are incentivized to compete fiercely to retain market share and recover their investments, even in challenging economic conditions. This can lead to intensified price competition and a prolonged period of lower returns for all players involved.
CellaVision’s specialized nature, with its focus on digital pathology solutions, also implies that its assets are not easily transferable to other industries. This lack of fungibility further increases the difficulty and cost associated with exiting the market, reinforcing the impact of high exit barriers on competitive rivalry.
- High R&D Investment: CellaVision's commitment to innovation, evidenced by substantial R&D spending, creates a barrier to exit.
- Specialized Assets: The company's technology is specific to digital pathology, limiting its resale value or alternative use.
- Intensified Rivalry: High exit barriers compel companies to compete aggressively, potentially impacting profitability.
- Market Entrapment: Firms may remain in the market despite low profitability due to the high costs associated with leaving.
Strategic Alliances and Partnerships
CellaVision actively cultivates strategic alliances, notably with Sysmex, to bolster its sales and distribution networks. These collaborations are crucial as they expand market penetration and facilitate deeper integration with complementary laboratory systems, thereby intensifying competition for rivals lacking comparable partnerships.
These strategic alliances can significantly alter the competitive dynamics by creating more robust market presences and offering more comprehensive solutions. For instance, a partnership that integrates CellaVision's imaging technology with a broader diagnostic workflow can present a more compelling value proposition than standalone offerings.
- Strategic Alliances Enhance Market Reach: CellaVision's partnerships, like the one with Sysmex, directly expand its global sales and distribution capabilities, allowing it to access a wider customer base.
- Integration Creates Competitive Advantage: By integrating with other lab systems, these alliances offer a more seamless workflow, increasing the switching costs for customers and making it harder for competitors to offer equivalent solutions.
- Rivalry Intensifies for Non-Partnered Firms: Companies without similar strategic alliances may struggle to match the market reach and integrated offerings, potentially facing increased pressure and diminished market share.
The competitive rivalry in CellaVision's market is intense, driven by innovation and the presence of both established players and agile newcomers. Companies are investing heavily in R&D, particularly in AI for hematology and digital pathology, to gain a technological edge. This race for advanced solutions means firms must constantly differentiate themselves.
CellaVision's focus on patented technology and sophisticated software for cell analysis provides a strong basis for differentiation, reducing the likelihood of direct price wars. For example, their AI algorithms have demonstrated over 95% accuracy for specific cell types in internal testing, a critical factor for diagnostic reliability.
High exit barriers, stemming from significant investments in specialized technology and ongoing R&D, mean companies are likely to stay and compete aggressively. CellaVision's 2023 R&D expenditure of approximately SEK 100 million underscores this commitment. This can lead to sustained competition even in less profitable periods.
Strategic alliances, such as CellaVision's partnership with Sysmex, enhance market reach and offer integrated solutions, creating a competitive advantage. This makes it harder for rivals without similar collaborations to compete effectively on a global scale.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant threat of substitutes for CellaVision's digital microscopy solutions comes from traditional manual microscopy. While CellaVision offers automation and enhanced efficiency, some smaller laboratories or those operating with tighter budgets may continue to favor manual methods due to their lower upfront investment costs. For instance, in 2023, the global laboratory automation market, which includes digital microscopy, was valued at approximately USD 5.5 billion, indicating a significant ongoing investment in advanced solutions.
While CellaVision excels in digital morphology, alternative diagnostic methods like flow cytometry and molecular diagnostics present a threat of substitutes. These technologies can offer valuable cellular and genetic information, sometimes bypassing the need for detailed visual assessment. For instance, flow cytometry can rapidly identify cell populations based on surface markers, and molecular diagnostics can detect specific genetic mutations or pathogens, potentially reducing reliance on traditional morphology in certain clinical scenarios.
Large hospital networks or research institutions might develop their own in-house digital imaging and analysis solutions. This is a resource-intensive path, but it can serve as a substitute if commercial offerings don't meet very specific, niche needs. For example, a major academic medical center with a dedicated bioinformatics department might invest in custom software development, potentially diverting resources from purchasing CellaVision's platform.
Lower-Cost, Less Sophisticated Digital Solutions
Emerging competitors are introducing simpler, more affordable digital microscopy solutions. While these may lack the advanced features of CellaVision's offerings, they could meet the basic needs of some laboratories.
These less sophisticated alternatives might attract price-sensitive customers or those with lower testing volumes, presenting a viable substitute for CellaVision's higher-end products. For instance, in 2024, the global digital pathology market, which includes these types of solutions, was valued at approximately $1.7 billion, with a significant portion driven by more accessible technologies.
- Emerging Competitors: Introduction of simpler, lower-cost digital microscopy solutions.
- Customer Appeal: Attracts price-sensitive customers or those with lower volume needs.
- Market Impact: Offers a viable substitute for premium offerings in specific laboratory segments.
- Market Context: The digital pathology market, a related sector, was valued around $1.7 billion in 2024, indicating a competitive landscape with varying price points.
Evolving Healthcare Technologies
The threat of substitutes for CellaVision's digital cell morphology systems is growing as other healthcare technologies advance rapidly. For instance, highly automated hematology analyzers with integrated screening capabilities are emerging, potentially reducing the need for manual review and, consequently, dedicated digital cell morphology systems in certain laboratory workflows.
These advancements represent a significant substitute threat. Consider that in 2024, the global in-vitro diagnostics market, which includes hematology analyzers, was valued at approximately $110 billion, with a significant portion driven by automation. As these automated systems become more sophisticated, they may absorb some of the functions currently performed by CellaVision's products.
- Emerging Automation: Highly automated hematology analyzers with integrated screening reduce reliance on manual microscopic review.
- Market Growth: The IVD market, including hematology, is expanding, fostering innovation in competing technologies.
- Workflow Integration: Advancements aim to streamline laboratory processes, potentially bypassing the need for separate digital morphology solutions.
- CellaVision's Response: Continuous R&D is crucial for CellaVision to maintain its competitive edge against these evolving substitutes.
The threat of substitutes for CellaVision's digital cell morphology solutions is multifaceted, encompassing both traditional methods and emerging technologies. While manual microscopy remains a lower-cost alternative for some, advancements in flow cytometry and molecular diagnostics offer alternative pathways for cellular analysis, potentially reducing reliance on visual morphology in specific applications. Furthermore, the development of in-house solutions by large institutions and the rise of simpler, more affordable digital microscopy alternatives present ongoing competitive pressures.
| Substitute Category | Description | Potential Impact on CellaVision | Market Context (2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Manual Microscopy | Lower upfront cost, familiar workflow | Attracts budget-constrained or low-volume labs | Global laboratory automation market valued at approx. USD 5.5 billion (2023) |
| Alternative Diagnostic Technologies | Flow cytometry, molecular diagnostics | Bypass visual morphology in certain analyses | Flow cytometry market projected to reach USD 4.4 billion by 2027 |
| In-house Developed Solutions | Customized for specific niche needs | Resource-intensive, but a substitute for unmet needs | N/A (highly specific to institutional capabilities) |
| Simpler Digital Microscopy | Lower cost, fewer advanced features | Appeals to price-sensitive segments | Digital pathology market valued at approx. USD 1.7 billion (2024) |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the advanced medical microscopy market, particularly in areas like digital cell analysis pioneered by companies such as CellaVision, demands significant upfront capital. Developing sophisticated software, high-resolution imaging hardware, and robust data management systems requires substantial investment in research and development. For instance, in 2024, companies in the medical device sector often allocate hundreds of millions of dollars to R&D annually.
Beyond R&D, establishing manufacturing facilities capable of producing precision optical and electronic components, along with building a global distribution and support network, necessitates further massive capital outlays. This creates a formidable barrier, making it difficult for smaller or less-funded entities to compete effectively with established players like CellaVision, thereby limiting the threat of new entrants.
CellaVision's robust intellectual property portfolio, particularly its patents in digital image analysis, AI, and automated microscopy, presents a formidable barrier to entry. New companies would need substantial investment in research and development to create comparable proprietary technology without infringing on CellaVision's existing patents, a process that typically takes years and significant capital. For instance, the significant R&D expenditure in the digital pathology market, which CellaVision operates within, underscores the cost and time involved in developing such advanced technologies.
The medical technology sector, where CellaVision operates, is characterized by significant regulatory hurdles. New entrants must navigate a labyrinth of stringent clinical trials and secure approvals from bodies like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the European CE Mark. These processes are not only time-consuming but also incredibly costly, acting as a substantial deterrent to new companies looking to enter the market.
Established Distribution Channels and Partnerships
CellaVision's established distribution channels, bolstered by strategic global partnerships such as the one with Sysmex, create a formidable barrier to entry. These collaborations grant CellaVision extensive market reach and deep-rooted relationships with laboratories across the globe, a network that is difficult and time-consuming for new players to replicate.
New entrants would need to invest heavily in building their own sales and distribution infrastructure, a process that not only requires significant capital but also time to cultivate the necessary trust and credibility with potential customers. For instance, Sysmex, a key partner, has a well-established presence in over 170 countries, a testament to the scale of CellaVision's existing network.
The threat of new entrants is therefore significantly mitigated by these entrenched distribution advantages. New companies would struggle to match CellaVision's ability to efficiently deliver its products and services to a broad customer base, making it challenging to compete on reach and accessibility alone.
- Global Reach: CellaVision's partnership with Sysmex provides access to over 170 countries.
- Customer Trust: Established relationships with laboratories worldwide are difficult for new entrants to build.
- Distribution Costs: Replicating CellaVision's extensive network would incur substantial upfront investment for new competitors.
- Market Penetration: Existing channels enable CellaVision to penetrate new markets more effectively than a newcomer.
Brand Reputation and Customer Loyalty
CellaVision's long-standing presence as a pioneer in intelligent microscopy for thirty years has cultivated a robust brand reputation. This is further solidified by an impressive installed base of over 8,000 units globally, a testament to established customer loyalty. New entrants face a significant hurdle in displacing this entrenched market position and must invest heavily to build comparable trust and recognition.
The threat of new entrants is significantly mitigated by CellaVision's established brand equity and deep customer relationships. Building a comparable level of trust and market penetration, especially in a specialized field like medical diagnostics, requires substantial time and resources, often exceeding what new players can readily deploy.
- Established Brand Reputation: CellaVision has been a leader for 30 years.
- Strong Installed Base: Over 8,000 units deployed worldwide.
- Customer Loyalty: Existing customers are likely to continue with a trusted provider.
- High Barrier to Entry: Newcomers need significant investment to build trust and market share.
The threat of new entrants into CellaVision's market is considerably low due to substantial capital requirements for research, development, and manufacturing. For example, in 2024, medical device companies often invest hundreds of millions annually in R&D to stay competitive, a financial hurdle that deters many potential newcomers.
Furthermore, CellaVision's extensive intellectual property portfolio, coupled with stringent regulatory approvals like FDA clearance, creates significant barriers. Navigating these complex processes can cost millions and take years, effectively limiting the appeal for new companies seeking to enter the advanced cell analysis space.
Established distribution networks, exemplified by CellaVision's partnership with Sysmex reaching over 170 countries, and a strong brand reputation built over 30 years with an installed base of over 8,000 units, further solidify CellaVision's market position. These factors make it exceedingly difficult and costly for new entrants to achieve comparable market penetration and customer trust.
| Barrier Category | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example Data/Fact |
| Capital Requirements | High costs for R&D, manufacturing, and global distribution. | Significant financial barrier. | 2024 medical device R&D spending in the hundreds of millions annually. |
| Intellectual Property & Regulation | Patented technology and lengthy, costly regulatory approval processes. | Time-consuming and expensive to overcome. | FDA approval can take years and millions of dollars. |
| Distribution & Brand Loyalty | Established global networks and strong brand reputation with a large installed base. | Difficult to replicate reach and customer trust. | CellaVision's 30-year presence and 8,000+ units installed globally. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our CellaVision Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including CellaVision's annual reports, industry-specific market research from firms like Frost & Sullivan, and publicly available competitor financial filings.
We also incorporate insights from regulatory bodies and economic databases to provide a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape, supplier power, buyer bargaining, threat of new entrants, and substitute products relevant to CellaVision.
