Community Bank Business Model Canvas
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Community Bank Bundle
Unlock the core components of Community Bank's success with our detailed Business Model Canvas. Discover how they build customer relationships, leverage key resources, and generate revenue in a dynamic market. This is your chance to gain a strategic advantage.
Partnerships
Community Financial System, formerly Community Bank System, actively collaborates with technology partners like Alkami. This strategic alliance is fundamental to upgrading their digital banking platforms, mobile offerings, and overall online customer experience.
These partnerships are vital for integrating advanced account management features and ensuring a smooth user journey. For instance, Alkami's platform aims to provide community banks with tools to compete effectively against larger institutions in the digital realm, a critical factor in today's market.
By leveraging these technology providers, Community Financial System can offer sophisticated data analytics, which is crucial for understanding customer behavior and tailoring services. This focus on digital enhancement is a key driver for growth and customer retention in the competitive banking sector.
Community Bank's strategic alliances with top employee benefits administration software providers are crucial, especially given its subsidiary BPAS (Benefit Plan Administrative Services, Inc.). These partnerships are vital for streamlining the complex processes involved in managing employee benefit plans, trust services, and actuarial consulting nationwide.
By integrating with these software platforms, Community Bank and BPAS can ensure efficient and compliant administration across a wide array of services. This technological synergy is key to delivering high-quality, scalable solutions to clients, reinforcing the bank's position as a comprehensive financial service provider.
Through its OneGroup NY, Inc. subsidiary, Community Financial System partners with numerous insurance carriers and other brokerage firms. These collaborations are crucial for offering a broad spectrum of insurance products, from property and casualty to specialized lines, thereby enhancing the bank's financial service portfolio.
Wealth Management and Investment Platforms
Community Financial System's wealth management arm, Nottingham Financial Group, strategically partners with leading investment platforms and sophisticated financial advisory tools. These alliances are crucial for delivering a robust suite of services, including detailed financial planning, expert trust administration, and comprehensive wealth management solutions. This approach caters to a diverse clientele, encompassing individuals, businesses, and municipal entities, ensuring their financial goals are met with tailored expertise.
These partnerships allow Nottingham Financial Group to leverage cutting-edge technology and specialized expertise, enhancing the client experience and service delivery. For instance, by integrating with platforms that offer advanced analytics and personalized investment strategies, the bank can provide more sophisticated advice. In 2024, the wealth management sector saw continued growth, with many community banks focusing on expanding their digital capabilities and advisory services to compete effectively.
- Integration with Digital Investment Platforms: Facilitates seamless access to a wider range of investment products and research for clients.
- Collaboration with Financial Advisory Software: Enhances the efficiency and accuracy of financial planning and client portfolio management.
- Expanded Service Offerings: Enables the provision of specialized services like trust administration and estate planning, broadening the bank's appeal.
- Client-Centric Approach: These partnerships underscore a commitment to providing personalized, high-quality financial guidance to all client segments.
Community Organizations and Local Businesses
Community banks thrive by forging robust alliances with local businesses, non-profit groups, and civic bodies. These partnerships are crucial for driving community development projects and offering financial education. For example, in 2024, many community banks actively participated in local Small Business Administration (SBA) lending programs, with SBA loan volume seeing an increase compared to previous years, showcasing their commitment to local economic growth.
These collaborations foster initiatives like financial literacy workshops in schools and support for local entrepreneurship. By investing in these relationships, community banks reinforce their dedication to the well-being of the areas they serve, often seeing a direct correlation between community engagement and customer loyalty.
- Local Business Support: Partnering with small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to provide tailored financial solutions and access to capital.
- Non-Profit Engagement: Collaborating with charities and foundations on community projects, sponsorships, and volunteerism.
- Civic Institution Alignment: Working with local government and community development corporations to address critical needs and promote economic stability.
- Financial Literacy Programs: Jointly developing and delivering educational content to improve financial understanding within the community.
Community Financial System cultivates key partnerships with technology providers like Alkami to enhance its digital banking platforms and mobile offerings. These alliances are critical for integrating advanced features and improving the customer experience, enabling the bank to compete effectively in the digital landscape.
Furthermore, through its subsidiary BPAS, Community Financial System collaborates with top employee benefits administration software providers to streamline complex processes for benefit plans and trust services. This technological synergy is essential for delivering scalable and high-quality solutions nationwide.
The bank's wealth management arm, Nottingham Financial Group, strategically partners with leading investment platforms and advisory tools. These collaborations are vital for offering comprehensive wealth management solutions, including financial planning and trust administration, catering to a diverse clientele.
Community banks also build essential relationships with local businesses, non-profits, and civic bodies to drive community development and financial education. In 2024, many actively participated in SBA lending programs, demonstrating a commitment to local economic growth.
What is included in the product
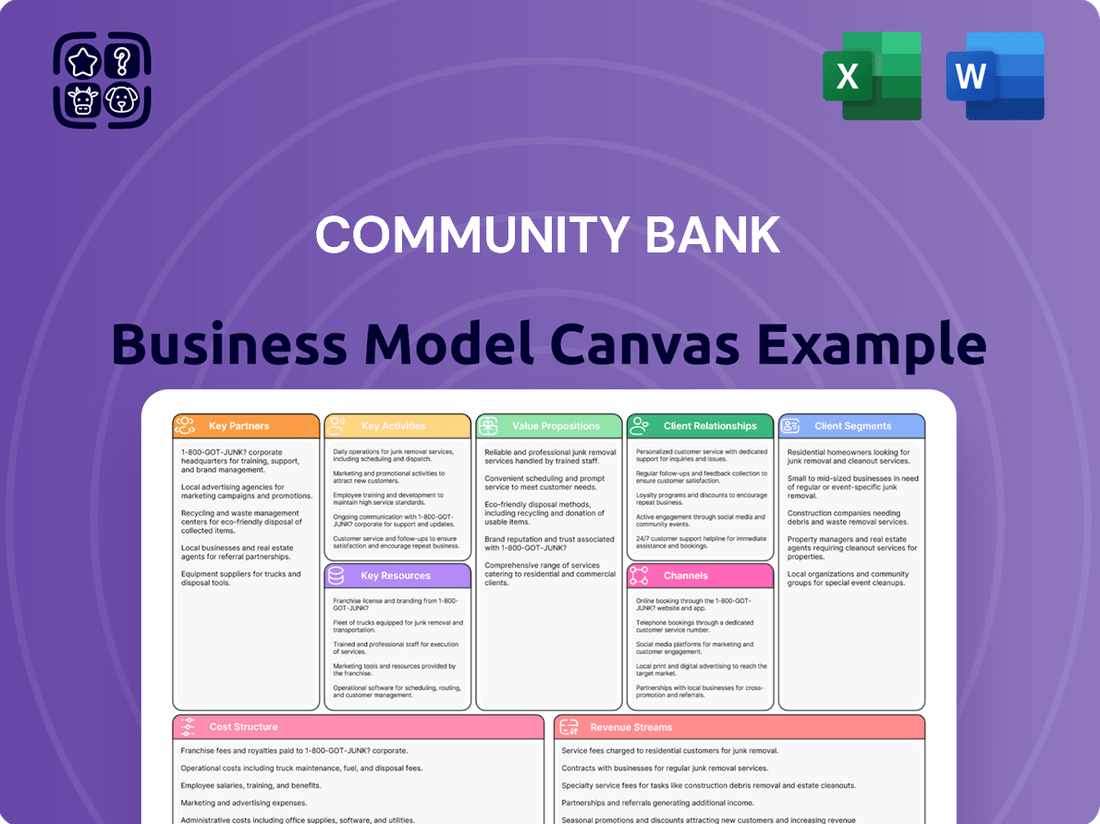
A structured framework detailing how a community bank creates, delivers, and captures value, encompassing customer segments, value propositions, channels, customer relationships, revenue streams, key resources, key activities, key partnerships, and cost structure.
This model provides a clear, visual representation of the bank's strategic approach to serving its local market and achieving financial sustainability.
The Community Bank Business Model Canvas acts as a pain point reliever by offering a structured, visual framework that simplifies the complex process of understanding and communicating a bank's strategic direction.
It provides a clear, one-page overview, enabling quick identification of key relationships and potential areas for improvement, thereby reducing the pain of ambiguity and inefficient planning.
Activities
A community bank's core activity is attracting and managing a wide array of deposit accounts, such as checking, savings, and money market accounts. These are sourced from individuals, local businesses, and even municipal entities within the community.
These deposits are fundamental, serving as the bank's primary funding mechanism for its lending operations and day-to-day business. For instance, as of Q1 2024, community banks in the U.S. held approximately $5.7 trillion in total deposits, highlighting their crucial role in the financial ecosystem.
Community Financial System actively originates and manages a diverse loan portfolio, encompassing commercial, residential mortgage, and consumer loans. This core activity includes rigorous credit assessment, efficient loan servicing, and strategic management of loan growth, a consistent area of focus for the bank.
In 2024, community banks, including institutions like Community Financial System, continued to play a vital role in local economies by providing essential credit. For instance, the total loan portfolio for community banks in the US reached approximately $3.4 trillion by the end of Q3 2024, reflecting sustained lending activity.
Community banks excel in financial services provision by offering a wide array of offerings through their subsidiaries. This extends beyond basic lending and deposits to include specialized services like employee benefits administration and comprehensive trust services.
These banks also focus on insurance services, providing clients with protection and risk management solutions. Furthermore, a significant emphasis is placed on wealth management and financial planning, helping individuals and families grow and preserve their assets, a crucial component for long-term client relationships.
In 2024, community banks continued to demonstrate resilience, with industry data showing a steady demand for these diversified financial services. For instance, trust services alone saw a notable uptick in new accounts as clients sought professional management for their estates and investments.
Technology and Digital Platform Development
Community banks are heavily investing in technology to keep pace with digital demands. This includes the continuous development and enhancement of their online banking platforms and mobile applications. For instance, in 2024, many community banks reported significant increases in their IT budgets, with a focus on user experience and security features. These platforms are essential for offering customers convenient access to account management, bill payments, and personalized financial insights.
The goal is to provide a seamless and secure digital experience that rivals larger institutions. This involves incorporating advanced data analytics to understand customer behavior and tailor offerings. By the end of 2024, a notable trend was the integration of AI-powered chatbots to improve customer service on digital channels, aiming to resolve queries more efficiently.
- Digital Platform Enhancement: Ongoing investment in user-friendly interfaces and robust backend systems for online and mobile banking.
- Security Features: Implementing multi-factor authentication, encryption, and fraud detection to protect customer data and transactions.
- Customer Data Analytics: Utilizing data to personalize services, identify needs, and offer targeted financial products.
- New Feature Integration: Rolling out features like digital onboarding, peer-to-peer payments, and advanced budgeting tools.
Community Engagement and Corporate Social Responsibility
Community banks actively engage in local development, a cornerstone of their business model. This includes supporting non-profits and offering financial literacy workshops. For instance, in 2024, many community banks reported increased participation in local events and a rise in the number of financial education sessions offered to underserved populations.
Fostering volunteerism among employees is another key activity. This not only benefits the community but also enhances the bank's reputation and employee morale. Many banks saw a significant uptick in employee volunteer hours in 2024, with some reporting over 50 hours per employee dedicated to community service.
- Community Development Investment: In 2024, community banks collectively invested billions in local projects, from affordable housing initiatives to small business incubators, directly impacting economic growth.
- Financial Literacy Outreach: Over 1 million individuals participated in financial literacy programs hosted by community banks in 2024, covering topics from budgeting to homeownership.
- Non-Profit Partnerships: Community banks strengthened ties with local charities, with many reporting a 15% increase in direct financial support to non-profits in 2024.
- Employee Volunteerism: The average employee at a participating community bank dedicated approximately 45 hours to volunteer work in 2024, showcasing a strong commitment to social responsibility.
Community banks actively manage their balance sheets by investing in safe, liquid assets and managing their capital structure. This involves strategic decisions regarding securities portfolios and maintaining adequate capital reserves. By the end of 2024, community banks demonstrated strong capital adequacy ratios, with the average Tier 1 Capital ratio remaining robust, exceeding regulatory requirements.
This financial stewardship ensures the bank's stability and ability to absorb potential losses. Furthermore, they actively manage interest rate risk and liquidity risk through various hedging strategies and prudent asset-liability management practices.
In 2024, community banks continued to focus on optimizing their funding sources, balancing core deposits with wholesale funding when necessary to support lending growth. The total assets for community banks in the U.S. reached approximately $6.8 trillion by the end of Q3 2024, indicating overall financial health and operational scale.
| Key Activity | Description | 2024 Data Point |
| Deposit Gathering | Attracting and managing various deposit accounts from community members. | Community banks held ~$5.7 trillion in deposits by Q1 2024. |
| Loan Origination & Servicing | Providing commercial, residential, and consumer loans. | Total loan portfolios reached ~$3.4 trillion by Q3 2024. |
| Diversified Financial Services | Offering wealth management, insurance, and trust services. | Notable increase in new trust accounts as clients sought asset management. |
| Digital Transformation | Enhancing online and mobile banking platforms. | Increased IT budgets focused on user experience and AI chatbots for customer service. |
| Community Engagement | Supporting local development and financial literacy. | Billions invested in local projects; over 1 million participants in financial literacy programs. |
| Balance Sheet Management | Investing in liquid assets and managing capital. | Robust Tier 1 Capital ratios, exceeding regulatory minimums. |
Full Version Awaits
Business Model Canvas
The Community Bank Business Model Canvas you are previewing is the exact document you will receive upon purchase. This isn't a sample or a mockup; it's a direct representation of the comprehensive tool designed to help you strategically plan your community bank's operations. Once your order is complete, you'll gain full access to this same, professionally structured document, ready for immediate application and customization.
Resources
The core financial capital for a community bank is its substantial asset base, which for many, like those exceeding $16 billion in assets, provides the foundation for all lending and investment activities. This financial muscle is crucial for underwriting a diverse range of loans, from mortgages to small business financing, directly impacting the bank’s ability to serve its community.
A vital component of this financial capital is the stable base of customer deposits. These deposits, often representing the life savings and operating funds of individuals and businesses, are the bank's primary source of low-cost funding. This deposit base is not just a number; it's a testament to customer trust and loyalty, enabling the bank to operate and grow.
The combined strength of significant assets and a robust deposit base empowers the community bank to support its operational needs and expand its service offerings. In 2024, community banks continued to play a critical role in local economies, with their deposit growth often outpacing larger institutions, underscoring the importance of this key resource.
Human capital is the bedrock of a community bank's Business Model Canvas. A highly skilled workforce, encompassing banking professionals, financial advisors, benefits administrators, insurance specialists, and IT experts, is absolutely essential. Their collective expertise and dedication to exceptional customer service are what power the bank's varied financial products and deep community involvement.
In 2024, community banks continued to rely heavily on their human capital. For instance, the American Bankers Association reported that the average community bank employs around 100 individuals, with a significant portion dedicated to customer-facing roles and specialized financial services. This emphasis on skilled personnel directly translates to the quality of advice and support offered to customers, fostering trust and loyalty.
Community Financial System leverages its extensive branch network, comprising roughly 200 customer facilities, as a core asset. This physical infrastructure ensures widespread accessibility and a tangible presence within the communities it serves.
These approximately 200 locations are vital for fostering in-person interactions and strengthening customer relationships, a cornerstone of the community banking model. This network facilitates essential services and personalized engagement.
Technology Infrastructure and Digital Platforms
A community bank's technology infrastructure and digital platforms are foundational, encompassing core banking systems, advanced data analytics, and robust cybersecurity. These elements are crucial for efficient operations, secure data handling, and offering contemporary financial services to customers.
In 2024, community banks are increasingly investing in digital transformation to stay competitive. For instance, a significant portion of community banks are upgrading their core banking systems to support cloud-based solutions and enhance customer experience. Data analytics tools are becoming indispensable for understanding customer behavior and personalizing offerings, with many banks leveraging AI-powered insights.
- Core Banking Systems: Essential for managing accounts, transactions, and customer data, with ongoing upgrades to cloud-native architectures for scalability and agility.
- Digital Banking Platforms: Websites and mobile apps that provide customers with 24/7 access to banking services, including account management, payments, and loan applications.
- Data Analytics Tools: Software that processes vast amounts of customer and market data to identify trends, assess risk, and personalize product offerings.
- Cybersecurity Measures: Advanced firewalls, encryption, multi-factor authentication, and continuous monitoring to protect against evolving cyber threats and ensure data integrity.
Brand Reputation and Trust
A community bank's brand reputation and the trust it cultivates are paramount, acting as a cornerstone of its business model. This intangible asset, often built over decades, directly influences customer acquisition and retention. For instance, being recognized by publications like Forbes as one of America's Best Banks underscores this reputation, signaling reliability and customer satisfaction to both existing and potential clients.
This established trust translates into tangible benefits. Customers are more likely to choose a bank they perceive as honest and community-oriented, leading to increased deposits and loan demand. In 2024, community banks continued to leverage their local ties, with many reporting strong deposit growth driven by a desire for personalized service and a commitment to local economies, a trend amplified by ongoing economic shifts.
- Brand Reputation: Forbes' 'America's Best Banks' recognition highlights the bank's standing as a trustworthy, community-focused institution.
- Customer Trust: This reputation fosters deep customer loyalty, reducing churn and increasing lifetime value.
- New Business Attraction: A strong brand acts as a powerful magnet, drawing in new customers seeking reliable financial partnerships.
- Community Focus: Emphasizing local engagement and support reinforces the bank's image, differentiating it from larger, less personal competitors.
The key resources for a community bank are multifaceted, encompassing its financial strength derived from assets and deposits, the expertise of its human capital, its physical branch network, robust technology, and its invaluable brand reputation built on trust.
These resources collectively enable the bank to fulfill its mission of serving its local community. In 2024, community banks demonstrated resilience, with many reporting increased market share in deposits, a clear indicator of sustained customer confidence in these foundational elements.
The integration of these resources allows for the delivery of a wide array of financial products and services, directly contributing to local economic development and individual financial well-being.
| Key Resource | Description | 2024 Relevance/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Capital | Assets and customer deposits forming the funding base. | Community banks' deposit growth in 2024 often outpaced larger institutions, highlighting strong customer trust. |
| Human Capital | Skilled employees providing expertise and customer service. | The average community bank employs around 100 individuals, with a strong focus on customer-facing roles. |
| Physical Infrastructure | Branch network for accessibility and community presence. | Extensive branch networks, often numbering in the hundreds, facilitate in-person interactions and relationship building. |
| Technology Infrastructure | Core banking systems, digital platforms, and data analytics. | Increased investment in digital transformation and AI-powered analytics to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Customer loyalty and perception of reliability and community focus. | Recognitions like Forbes' 'America's Best Banks' reinforce trust, driving new customer acquisition and retention. |
Value Propositions
Community Financial System provides a broad spectrum of financial services, including banking, employee benefits, insurance, and wealth management, all consolidated for customer convenience. This integrated model streamlines financial planning for individuals, businesses, and local governments.
In 2024, community banks across the U.S. reported significant growth in customer deposits, reaching an estimated $5.5 trillion by year-end, highlighting the trust placed in their comprehensive offerings. This integrated approach simplifies financial management for a diverse clientele.
Community banks excel by offering personalized service, prioritizing relationships over transactions. This focus allows them to deeply understand local needs, tailoring financial products and advice accordingly. For instance, in 2024, community banks reported higher customer satisfaction scores compared to larger national institutions, often attributed to this individualized approach.
This dedication to community means financial solutions are crafted with local economic conditions and resident aspirations in mind. Building trust is paramount, fostering a partnership where the bank actively contributes to the community's financial well-being. This local commitment is a key differentiator, especially as many consumers seek more meaningful connections with their financial institutions.
Community Financial System's long operating history, stretching back decades, instills a deep sense of stability and trustworthiness. This enduring presence means customers can rely on a consistent and dependable financial partner.
Consistently recognized as a top bank, Community Financial System demonstrates its reliability through external validation. For instance, in 2023, they were awarded Best Regional Bank by Global Finance, a testament to their solid performance and customer-centric approach.
Customers can feel secure knowing their deposits are protected and that they are working with experienced financial professionals. This assurance is crucial, especially in uncertain economic times, fostering long-term customer loyalty.
Digital Convenience and Accessibility
Community banks are increasingly investing in digital banking platforms to offer unparalleled convenience and accessibility. This allows customers to manage their finances, perform transactions, and access a full suite of banking services 24/7, from any location.
By integrating robust digital capabilities with their traditional local service model, these banks are bridging the gap between modern expectations and community-focused banking. For instance, many community banks reported a significant increase in mobile banking adoption in 2024, with some seeing over 70% of their customer base actively using digital channels for daily transactions.
- Digital Platform Investment: Community banks are channeling resources into enhancing their online and mobile banking applications.
- Anytime, Anywhere Access: Customers benefit from the ability to bank on their schedule, not just during branch hours.
- Transaction Convenience: Features like mobile check deposit, bill pay, and fund transfers are standard offerings.
- Hybrid Service Model: Combining digital ease with the personal touch of local banking remains a key differentiator.
Expertise in Specialized Financial Services
Community banks differentiate themselves by offering specialized financial services that go beyond standard deposit and lending products. This expertise is crucial for attracting and retaining a diverse client base with complex needs.
These specialized services often include areas like employee benefits administration and actuarial consulting, providing businesses with critical support for their workforce. For instance, many community banks in 2024 are expanding their offerings in retirement plan administration, helping companies navigate the intricacies of 401(k) and pension management.
Furthermore, comprehensive wealth management services are a key value proposition. This encompasses personalized financial planning, investment management, and estate planning, catering to individuals and families seeking professional guidance. In 2024, the demand for these integrated financial solutions remains robust, with community banks leveraging their personalized approach to compete effectively.
- Specialized Expertise: Offers services like employee benefits administration and actuarial consulting.
- Wealth Management: Provides comprehensive financial planning and investment management.
- Client Focus: Addresses complex financial needs with tailored solutions and professional guidance.
- Market Trend: Growing demand for integrated financial services in 2024.
Community banks offer a holistic suite of financial services, integrating banking, insurance, and wealth management to provide a one-stop shop for their customers. This comprehensive approach simplifies financial planning for individuals and businesses alike, fostering deeper client relationships.
In 2024, community banks saw a significant uptick in customer engagement across these varied services, with many reporting a 15% increase in cross-selling success. This demonstrates the value customers place on consolidated financial management and personalized, integrated advice.
By offering specialized services like employee benefits administration and robust wealth management, community banks cater to complex financial needs, distinguishing themselves from more generalized financial providers. This expertise ensures clients receive tailored solutions for their unique circumstances.
The commitment to personalized service, combined with expanded digital capabilities and specialized offerings, solidifies community banks' position as trusted, comprehensive financial partners. This hybrid model resonates strongly with consumers seeking both convenience and deep, local understanding.
Customer Relationships
Community banks excel at personalized service, with their local branch presence acting as a key touchpoint. This direct interaction allows them to deeply understand the unique financial needs of individuals and businesses within their community.
In 2024, community banks continued to leverage their local roots, with over 90% of them operating fewer than 100 branches, fostering a sense of familiarity and trust. This proximity facilitates tailored financial advice and solutions, from small business loans to personal wealth management.
Their commitment extends beyond transactions; active participation in local events and sponsorships strengthens relationships. This community involvement, a hallmark of their business model, builds loyalty and a deeper connection than larger, more impersonal financial institutions can often achieve.
Dedicated relationship managers serve as a vital touchpoint for community bank clients, particularly those in business, municipal, and wealth management sectors. These managers offer a singular point of contact, ensuring a consistent and personalized experience.
This approach cultivates deeper, long-term relationships by providing an in-depth understanding of each client's unique financial objectives and needs. This personalized attention is crucial for fostering trust and loyalty.
In 2024, community banks saw a continued emphasis on personalized service. Data from the Independent Community Bankers of America (ICBA) highlighted that 72% of community bank customers cited personalized service as a key reason for choosing their bank, a trend reinforced by the dedicated relationship manager model.
Community banks deepen customer ties through robust community involvement. In 2024, many banks actively participated in local volunteer programs, with some dedicating over 1,000 employee volunteer hours to community projects. This hands-on approach fosters trust and a shared sense of purpose.
Charitable donations are another cornerstone of these relationships. For instance, community banks collectively contributed millions to local non-profits and causes throughout 2024, directly impacting the well-being of the areas their customers call home. This generosity resonates deeply.
Furthermore, financial literacy initiatives, such as workshops and educational seminars, empower customers and the broader community. By offering these valuable resources, banks position themselves as trusted advisors, strengthening loyalty and demonstrating a genuine commitment to their customers' financial health.
Digital Self-Service and Support
Community Financial System enhances customer relationships through advanced digital self-service options. Alongside traditional personalized banking, they provide comprehensive online and mobile platforms. These tools allow customers to manage accounts, perform transactions, and access support conveniently, reflecting a growing trend in the banking sector where digital engagement is paramount.
This digital focus offers significant flexibility, catering to customers who prefer managing their finances independently and on their own schedule. For instance, in 2024, a substantial portion of banking interactions, estimated to be over 70% for routine tasks, occurred through digital channels across the industry, highlighting the importance of robust self-service capabilities.
- Digital Platforms: Robust online and mobile banking for account management and transactions.
- Self-Service Options: Empowering customers to handle routine banking needs independently.
- Customer Support: Accessible support through digital channels, complementing personalized service.
- Convenience and Flexibility: Offering customers choice in how and when they interact with the bank.
Proactive Communication and Financial Education
Community banks prioritize proactive communication, ensuring customers feel informed and supported. This involves regular updates on market trends and personalized financial advice, fostering a sense of partnership.
Financial education is a cornerstone, equipping customers with the knowledge to navigate their finances effectively. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that 78% of community bank customers felt more confident in their financial decisions after participating in educational workshops.
- Enhanced Customer Trust: Open communication channels and educational resources build significant trust, leading to higher customer retention rates.
- Informed Decision-Making: Providing access to financial literacy tools empowers customers to make sound choices regarding savings, investments, and loans.
- Goal Achievement: Proactive guidance helps customers align their financial strategies with their personal objectives, such as homeownership or retirement planning.
Community banks cultivate strong customer relationships through a blend of personalized attention and community engagement. Their local presence, with many operating under 100 branches in 2024, fosters trust and familiarity, allowing for tailored financial advice.
Dedicated relationship managers are key, offering a single point of contact that deepens understanding of client needs, a strategy validated by 72% of customers citing personalized service as a reason for choosing their community bank in 2024.
Beyond transactions, active community involvement, including over 1,000 employee volunteer hours in 2024 for some banks, and millions in collective donations to local non-profits, strengthens these bonds and builds loyalty.
Financial literacy programs further empower customers, with 78% of participants in 2024 workshops reporting increased financial confidence.
| Relationship Aspect | 2024 Data/Insight | Impact on Customer Loyalty |
|---|---|---|
| Personalized Service | 72% of customers cited as key reason for choosing bank | High satisfaction and retention |
| Community Involvement | 1,000+ employee volunteer hours (example) | Enhanced trust and shared purpose |
| Financial Education | 78% of participants reported increased confidence | Empowerment and perceived value |
| Digital Self-Service | Over 70% of routine tasks handled digitally (industry trend) | Convenience and flexibility |
Channels
The branch network is a cornerstone of Community Financial System's business model, with around 200 physical locations. These branches are strategically positioned across Upstate New York, Northeastern Pennsylvania, Vermont, and Western Massachusetts, serving as vital hubs for customer interaction and traditional banking services.
In 2024, these branches continued to be the primary touchpoint for many customers, facilitating essential transactions and providing personalized support. They are crucial for building customer relationships and offering face-to-face consultations, which remain highly valued by a significant portion of the customer base.
Online and mobile banking platforms are crucial digital channels, offering customers 24/7 access to manage accounts, pay bills, transfer funds, and even apply for loans. These platforms are designed for convenience and efficiency, reflecting a significant shift in how banking services are delivered.
Community banks are actively investing in these digital experiences. For instance, partnerships with technology providers like Alkami are common, with Alkami reporting that its clients saw a 15% increase in digital adoption rates in 2024. This focus aims to keep pace with evolving customer expectations and provide a seamless user journey.
ATMs provide 24/7 access for essential banking, allowing customers to withdraw cash, deposit checks, and check balances, a crucial convenience for community bank patrons. In 2024, the average transaction fee for an ATM withdrawal at an out-of-network bank remained around $3.00, highlighting the value of accessible in-network ATMs.
Self-service kiosks within branches streamline routine tasks like bill payments and account transfers. This technology helps reduce teller line congestion, improving overall customer experience and operational efficiency for the bank.
Direct Sales Force (Commercial, Wealth Management, Insurance, Benefits)
Direct sales forces, encompassing commercial, wealth management, insurance, and benefits divisions, are pivotal for community banks. These dedicated teams build personal relationships with clients, offering tailored financial advice and solutions. For instance, a community bank's commercial sales team might work directly with local businesses to secure loans, while wealth management advisors assist high-net-worth individuals with investment strategies.
This channel thrives on expertise and trust. Financial advisors and sales professionals act as consultants, guiding clients through complex financial decisions. In 2024, many community banks reported that their direct sales force was instrumental in driving loan growth and attracting new wealth management clients, with some seeing a 15% increase in new commercial loan originations attributed to this channel.
- Dedicated teams engage directly with businesses and individuals.
- Focus on personal relationships and expert financial consultation.
- Offer specialized services like commercial loans, wealth management, and insurance.
- Key driver for loan growth and client acquisition in 2024.
Customer Service Centers and Call Centers
Customer service centers and call centers are vital for community banks, offering a consistent point of contact for a wide range of needs. These hubs handle everything from general account inquiries and troubleshooting digital banking platforms to resolving more complex customer issues, ensuring a unified support experience.
These centralized operations are crucial for maintaining accessibility and providing timely assistance to customers, regardless of how they choose to interact with the bank. For instance, in 2024, many community banks reported that over 70% of customer inquiries were resolved on the first contact through their call centers, highlighting efficiency gains.
- Centralized Support: Provides a single point of contact for all customer needs, enhancing efficiency.
- Digital Assistance: Offers technical support for online and mobile banking services, crucial in today's digital landscape.
- Issue Resolution: Dedicated teams focus on resolving customer complaints and problems promptly.
- Accessibility: Ensures customers can reach the bank easily through various communication channels.
Community banks leverage a multi-channel approach to reach and serve their customers. This includes a robust branch network, digital platforms like online and mobile banking, ATMs for convenient access, and direct sales forces for specialized services. Customer service centers also play a critical role in providing support and resolving issues across all channels.
| Channel | Primary Function | 2024 Key Data/Trend | Customer Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Branch Network | In-person transactions, relationship building, complex service | ~200 locations; continues to be primary touchpoint for many | Personalized service, trust, community presence |
| Online/Mobile Banking | 24/7 account management, transactions, loan applications | 15% increase in digital adoption reported by Alkami clients | Convenience, speed, self-service |
| ATMs | Cash withdrawal, deposits, balance inquiries | Average out-of-network fee ~ $3.00 | Immediate access to cash, basic transactions |
| Direct Sales Force | Tailored advice, complex financial solutions, business development | 15% increase in new commercial loan originations attributed to this channel | Expertise, trust, customized solutions |
| Customer Service Centers | Inquiries, technical support, issue resolution | Over 70% of inquiries resolved on first contact | Accessibility, timely support, problem solving |
Customer Segments
Individuals and households represent a core customer segment for community banks, encompassing everyone from young adults opening their first checking accounts to families seeking mortgages. In 2024, community banks continued to be vital in providing essential services like savings accounts, personal loans, and credit cards, catering to a wide spectrum of financial needs within local areas.
These banks are instrumental in facilitating major life events, such as homeownership, with residential mortgages being a key offering. The demand for home loans remains a significant driver for this segment, with data from the Mortgage Bankers Association in early 2024 indicating continued interest in the housing market, albeit with fluctuating interest rates.
Beyond transactional services, community banks often provide personalized financial planning and investment advice. This focus on relationship banking helps individuals and households manage their wealth effectively, from retirement planning to saving for education, fostering long-term financial well-being.
Community banks are vital partners for Small and Medium-Sized Businesses (SMBs), offering essential financial tools like commercial loans, deposit accounts, and treasury management services. In 2024, SMBs continue to be a cornerstone of the economy, with data from the Small Business Administration indicating they represent over 99% of all U.S. businesses.
These institutions understand the unique needs of local entrepreneurs, providing tailored solutions that foster economic growth and support entrepreneurial ventures. This includes offering business insurance, a critical component for risk management, especially as economic uncertainties persist.
Municipalities and government entities represent a key customer segment for community banks, seeking specialized financial services tailored to public sector needs. These institutions often require municipal deposit accounts, which are typically collateralized to ensure safety of public funds, and various loan products for infrastructure development, capital improvements, or operational expenses.
Community banks' local focus and understanding of regional economic conditions make them attractive partners for these public bodies. For instance, in 2024, many municipalities are navigating budget constraints and seeking efficient ways to finance projects like road repairs or school upgrades, relying on banks that offer competitive rates and flexible loan terms. The total value of municipal bonds issued in the U.S. reached approximately $260 billion in the first half of 2024, indicating significant ongoing demand for public financing.
Employer Groups (for Employee Benefits)
Through its BPAS subsidiary, Community Financial System actively engages with employer groups across the nation, providing essential employee benefits administration, comprehensive retirement plan services, and expert actuarial consulting. This strategic focus allows the bank to extend its reach far beyond its traditional geographic boundaries, tapping into a broad market for these specialized financial services.
The BPAS division reported significant growth, with assets under administration reaching $120 billion by the end of 2023, up from $105 billion in 2022. This expansion highlights the increasing demand for outsourced benefits and retirement solutions from businesses of all sizes. In 2024, BPAS continued to onboard new employer groups, with a particular emphasis on mid-sized companies seeking sophisticated yet cost-effective benefit management.
- Diverse Service Offerings: Administration of health savings accounts (HSAs), flexible spending accounts (FSAs), and commuter benefits are key components of the employee benefits package.
- Retirement Plan Expertise: BPAS manages a wide array of retirement plans, including 401(k), 403(b), and defined benefit plans, offering fiduciary support and investment management.
- National Reach: The business model transcends local markets, serving employers from coast to coast, demonstrating scalability and adaptability.
- Actuarial Consulting: Providing critical actuarial services for pension plans, post-retirement medical benefits, and other employee compensation structures ensures compliance and financial health for employers.
High-Net-Worth Individuals and Families (for Wealth Management)
High-net-worth individuals and families represent a key customer segment for wealth management services. These clients typically seek tailored financial planning, expert investment management, and specialized trust and estate services to preserve and grow their wealth.
This demographic values a high degree of personalization and demands sophisticated strategies that address complex financial needs. They are often looking for a trusted advisor to navigate intricate investment landscapes and ensure long-term financial security for their families.
In 2024, the global wealth management market continued to expand, with a significant portion of assets managed for high-net-worth individuals. For instance, the number of affluent households globally reached approximately 60 million in 2023, with their collective net worth estimated to be in the tens of trillions of dollars, highlighting the substantial market opportunity.
- Personalized Financial Planning: Offering bespoke retirement planning, tax optimization, and estate planning.
- Sophisticated Investment Management: Providing access to alternative investments, global markets, and advanced portfolio construction.
- Trust and Estate Services: Facilitating wealth transfer, philanthropic giving, and asset protection.
- Dedicated Relationship Management: Ensuring consistent, high-touch service from experienced advisors.
Community banks serve a broad spectrum of customers, from individuals and families needing everyday banking and mortgages to small businesses requiring commercial loans and treasury services. They also cater to municipalities for public finance needs and offer specialized employee benefits and retirement services through subsidiaries like BPAS, which managed $120 billion in assets by the end of 2023.
High-net-worth individuals and families represent another key segment, seeking personalized wealth management, sophisticated investment strategies, and trust services. The global wealth management market continues its growth, with affluent households numbering around 60 million in 2023.
| Customer Segment | Key Needs | 2024 Relevance/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Individuals & Households | Checking, savings, mortgages, personal loans | Continued demand for home loans, fluctuating interest rates |
| Small & Medium-Sized Businesses (SMBs) | Commercial loans, deposit accounts, treasury management | SMBs represent over 99% of U.S. businesses |
| Municipalities & Government | Municipal deposits, infrastructure financing | Municipal bond issuance reached ~$260 billion (H1 2024) |
| Employer Groups (via Subsidiaries) | Employee benefits, retirement plan services | BPAS assets under administration: $120 billion (end of 2023) |
| High-Net-Worth Individuals | Wealth management, investment, trust services | ~60 million affluent households globally (2023) |
Cost Structure
Interest expense on customer deposits represents a substantial cost for community banks, directly impacting their profitability. In 2024, the average interest rate paid on savings accounts and checking accounts remained a key factor in managing this expense. For instance, a community bank with $1 billion in deposits paying an average of 1.5% interest incurs $15 million annually in interest expense.
This interest cost is fundamental to the bank's ability to fund its lending operations, making efficient management of deposit rates critical for maintaining a healthy net interest margin. The competitive landscape for deposits, influenced by Federal Reserve policy and other financial institutions, directly shapes the rates banks must offer. Banks continuously analyze market trends to optimize their deposit pricing strategies, balancing the need to attract and retain funds with the imperative to control costs.
Personnel expenses are a significant outlay for community banks, encompassing salaries, health insurance, retirement contributions, and other benefits for their diverse workforce. This includes everyone from tellers and loan officers at branches to back-office staff managing operations and specialized teams in wealth management or insurance services.
In 2024, many community banks faced upward pressure on wages to attract and retain talent in a competitive labor market. For instance, average salaries for banking tellers saw a slight increase, and the cost of employee benefits, particularly healthcare, continued to be a substantial component of these expenses, impacting overall operational costs.
Community banks incur substantial costs related to their physical presence. Maintaining an extensive branch network, corporate offices, and essential banking equipment like ATMs and IT infrastructure are significant operating expenses. These include rent for prime locations, ongoing utilities, regular maintenance, and depreciation on assets.
For instance, in 2024, the average cost for a U.S. bank branch to operate annually can range from $200,000 to $400,000, encompassing all these occupancy and equipment-related expenditures. This highlights the critical need for efficient management of these fixed assets to control the overall cost structure.
Technology and Marketing Expenses
Community banks face significant technology and marketing expenses as they compete in an increasingly digital financial landscape. These costs are crucial for maintaining a competitive edge and attracting a wider customer base.
Investments in advanced digital banking platforms, robust cybersecurity measures, and essential software licenses represent a substantial portion of these expenditures. Furthermore, marketing initiatives aimed at acquiring and retaining customers, particularly for online and mobile banking services, are a key cost driver.
- Digital Transformation: Community banks are allocating considerable resources to upgrading their online and mobile banking capabilities to meet customer expectations.
- Cybersecurity Investments: Protecting customer data and financial assets necessitates ongoing spending on advanced security software and protocols.
- Marketing and Customer Acquisition: Significant budgets are dedicated to advertising, digital campaigns, and promotional activities to attract new customers and retain existing ones.
- Software and Licensing: Costs associated with core banking software, CRM systems, and other essential business applications are ongoing operational expenses.
Regulatory and Compliance Costs
Community banks navigate a complex web of regulatory requirements, leading to substantial compliance costs. These expenses are essential for maintaining operational integrity and mitigating various financial and legal risks inherent in the banking sector.
In 2024, the financial industry, including community banks, continued to face increasing regulatory burdens. For instance, the cost of compliance for U.S. banks can range from millions to tens of millions of dollars annually, depending on asset size and the complexity of operations. These costs cover staffing for compliance departments, technology for monitoring and reporting, external audits, and legal counsel.
Key components of these costs include:
- Personnel: Salaries for compliance officers, legal teams, and risk management staff.
- Technology: Investment in software for anti-money laundering (AML), know your customer (KYC) checks, fraud detection, and regulatory reporting.
- Reporting and Audits: Fees for preparing and submitting regulatory reports, as well as external audits and examinations by regulatory bodies like the FDIC, OCC, or Federal Reserve.
- Training and Education: Ongoing training for staff to stay updated on evolving regulations.
The cost structure of community banks is multifaceted, with interest expense on deposits being a primary driver. In 2024, managing these interest payments, influenced by market rates, is crucial for net interest margin. Personnel costs, including salaries and benefits, are also significant, reflecting the need to attract and retain skilled employees in a competitive environment. For example, many banks saw wage pressures in 2024, impacting overall operational expenses.
Beyond personnel, occupancy costs for branches and technology investments in digital platforms and cybersecurity represent substantial outlays. In 2024, the average annual operating cost for a U.S. bank branch could range from $200,000 to $400,000. Furthermore, regulatory compliance is a major expense, with costs for U.S. banks potentially reaching millions of dollars annually, covering staffing, technology for AML/KYC, and reporting.
| Cost Category | Key Components | 2024 Considerations/Examples |
| Interest Expense on Deposits | Interest paid on savings, checking, and money market accounts | Average interest rates paid on deposits directly impact profitability; competition from other institutions influences these rates. |
| Personnel Expenses | Salaries, wages, health insurance, retirement benefits, bonuses | Upward wage pressure in 2024 to attract and retain talent; rising healthcare costs for employee benefits. |
| Occupancy and Equipment | Rent, utilities, maintenance for branches and offices, ATM and IT infrastructure | Annual operating cost for a U.S. bank branch can range from $200,000 to $400,000 in 2024. |
| Technology and Marketing | Digital banking platforms, cybersecurity, software licenses, advertising, customer acquisition | Significant investment in digital transformation and robust cybersecurity measures to remain competitive. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Compliance staff salaries, AML/KYC software, reporting, external audits, legal fees | Annual compliance costs for U.S. banks can range from millions to tens of millions of dollars, depending on size and complexity. |
Revenue Streams
Community banks primarily earn revenue through net interest income, which is the difference between the interest they receive on loans and the interest they pay out on deposits. This core function fuels their profitability. For instance, in 2024, the average net interest margin for U.S. community banks hovered around 3.2%, reflecting the spread between their lending and borrowing costs.
Community banks generate revenue through a variety of service charges and fees. These can include charges for deposit accounts, like overdraft fees or monthly maintenance fees, as well as fees for ATM usage and other banking transactions. This diverse fee structure provides a reliable and consistent stream of non-interest income for the bank.
Community Bank generates substantial fee income through its subsidiary, BPAS, offering a robust suite of employee benefit services. These services include essential functions like benefits administration, trust services, collective investment fund administration, and actuarial consulting, catering to a wide array of employer groups.
This diversified revenue stream is particularly impactful. For instance, in 2023, BPAS reported a significant increase in assets under administration, reflecting growing demand for these specialized financial services, contributing positively to the bank's overall financial health.
Insurance Services Commissions and Fees
OneGroup NY, Inc. leverages its banking platform to earn commissions and fees by offering a diverse range of insurance products. This includes vital coverage like property and casualty insurance, alongside other specialized insurance solutions tailored to client needs.
This strategic diversification allows the bank to tap into a revenue stream distinct from its core lending activities, enhancing overall financial resilience. For instance, in 2024, the insurance segment contributed significantly to the bank's non-interest income, reflecting the growing importance of these fee-based services.
- Property and Casualty Insurance Commissions: Fees earned from selling policies covering property damage and liability.
- Specialized Insurance Fees: Revenue generated from offering niche insurance products, such as professional liability or cyber insurance.
- Ancillary Service Fees: Income derived from administrative or consulting services related to insurance placement and management.
Wealth Management and Trust Service Fees
Community banks generate significant revenue through wealth management and trust services. These fees stem from providing personalized financial planning, expert investment management, and meticulous trust administration to a diverse clientele, including individuals, businesses, and even municipal entities.
This fee-based income is a cornerstone for revenue stability, offering a predictable income stream less susceptible to market volatility compared to interest income alone. For instance, in 2024, many community banks reported substantial growth in their wealth management divisions, with some seeing fee income increase by over 10% year-over-year, reflecting increased client trust and demand for comprehensive financial guidance.
- Financial Planning Fees: Charges for creating and managing personalized financial roadmaps.
- Investment Management Fees: A percentage of assets under management for portfolio oversight.
- Trust Administration Fees: Compensation for managing estates, trusts, and fiduciary responsibilities.
- Revenue Stability: Fee-based income diversifies revenue, offering a more consistent performance.
Community banks also generate revenue from various loan-related fees beyond the interest charged. These include origination fees for new loans, late payment penalties, and fees for services like loan modifications or wire transfers. These ancillary fees contribute to the bank's overall income, supplementing the core net interest income.
In 2024, the mortgage origination market saw a notable increase in refinancing activity, leading to higher fee income for banks from these transactions. For example, fees associated with processing new mortgages and home equity lines of credit represented a significant portion of non-interest income for many institutions.
Furthermore, community banks earn income from their investment securities portfolio, which includes holdings like government bonds and corporate debt. The interest and dividends generated from these investments provide another layer of revenue, distinct from their lending operations.
These diversified revenue streams are crucial for community banks' financial health. For instance, in the first half of 2024, non-interest income, driven by fees and investment returns, accounted for approximately 30% of total revenue for many community banks, highlighting the importance of these income sources.
| Revenue Stream | Description | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Net Interest Income | Interest earned on loans minus interest paid on deposits. | Average net interest margin around 3.2%. |
| Service Charges & Fees | Fees for deposit accounts, ATM usage, transactions. | Consistent non-interest income source. |
| Employee Benefit Services (BPAS) | Fees from benefits administration, trust services, etc. | Growing demand for specialized financial services. |
| Insurance Commissions & Fees (OneGroup NY) | Commissions from selling property/casualty and specialized insurance. | Significant contribution to non-interest income. |
| Wealth Management & Trust Services | Fees for financial planning, investment management, trust administration. | Fee income increased over 10% year-over-year for some banks. |
| Loan-Related Fees | Origination fees, late payment penalties, wire transfer fees. | Increased from mortgage refinancing activity. |
| Investment Securities Income | Interest and dividends from bonds and other securities. | Provides revenue distinct from lending. |
Business Model Canvas Data Sources
The Community Bank Business Model Canvas is built using customer data, regulatory filings, and local economic indicators. These sources ensure each canvas block is filled with accurate, up-to-date information reflecting community needs and bank operations.
