Cathay Pacific Airways Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Cathay Pacific Airways Bundle
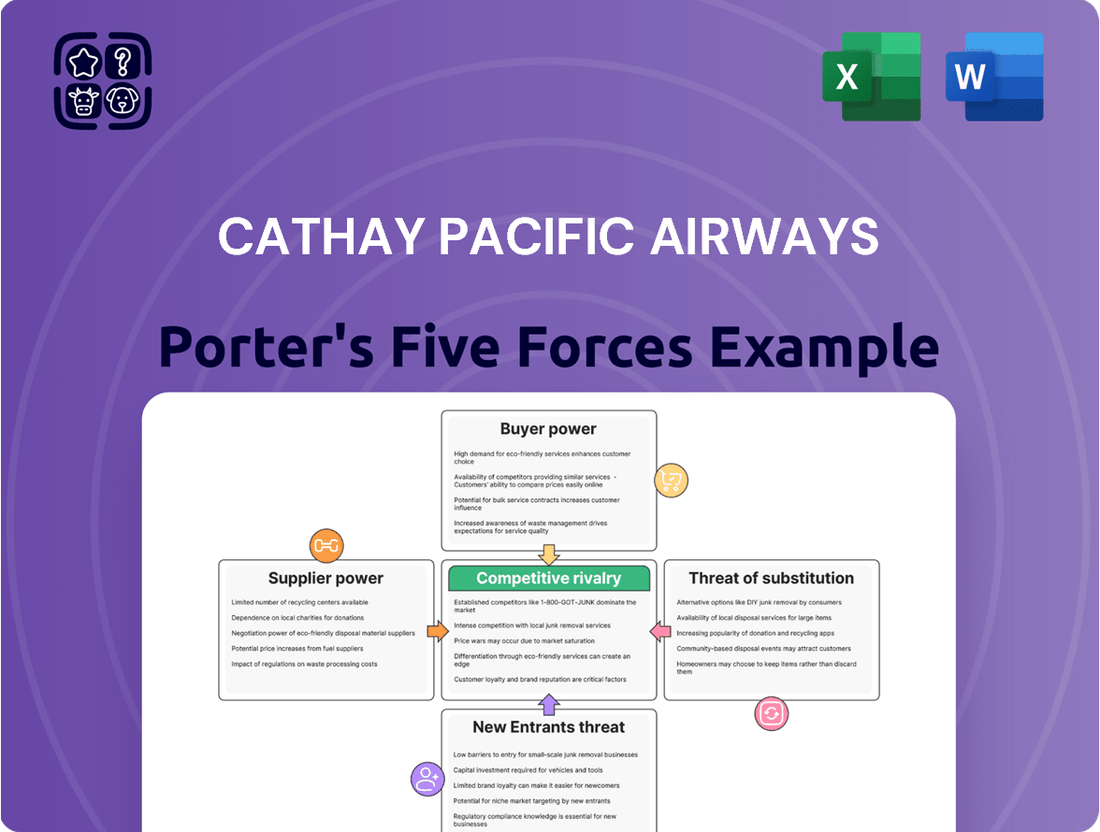
Cathay Pacific Airways navigates a complex competitive landscape, facing intense rivalry from established carriers and the ever-present threat of new entrants. Understanding the bargaining power of buyers, the influence of suppliers, and the looming specter of substitute services is crucial for strategic success in the airline industry.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Cathay Pacific Airways’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The aviation sector faces a reality where a handful of companies dominate the supply of essential aircraft and engines. Manufacturers like Boeing, Airbus, GE, Rolls-Royce, and Pratt & Whitney are the primary sources for these critical components, creating a highly concentrated market. This limited competition grants these suppliers considerable leverage over airlines, including Cathay Pacific.
This supplier power can manifest in significant ways, impacting airline operations and growth. For instance, delays in aircraft deliveries, such as those experienced with Boeing 777-9 models, directly hinder an airline's ability to expand its fleet and routes. Similarly, engine performance issues, like those grounding HK Express aircraft, can disrupt schedules and reduce operational capacity, directly affecting Cathay Pacific's strategic planning and financial performance.
The specialized nature of inputs like jet fuel, crucial maintenance services, and advanced aviation technology significantly strengthens supplier bargaining power for Cathay Pacific. These are not easily substitutable; switching providers often means higher costs and potential compromises on safety and operational efficiency.
For instance, while jet fuel prices saw some moderation for Cathay Pacific in 2024 compared to previous years, it remains a substantial and volatile cost. The airline's reliance on specific fuel types and the limited number of global suppliers for high-grade aviation fuel give these suppliers considerable leverage.
The aviation industry, including Cathay Pacific, grapples with a significant global shortage of skilled labor, especially pilots and maintenance technicians. This scarcity directly translates into increased bargaining power for labor unions and individual skilled workers.
These unions can leverage the tight labor market to negotiate for higher compensation and improved benefits. For instance, in 2024, reports indicated substantial wage increases for pilots in several major airlines due to these pressures.
Cathay Pacific's announced plans to recruit thousands of new staff in 2025 underscore this ongoing challenge, suggesting continued cost pressures from this critical supplier group as they seek to attract and retain essential talent.
High Switching Costs for Airlines
Airlines like Cathay Pacific face significant hurdles when considering a switch in major suppliers, particularly for aircraft and maintenance services. These switching costs are substantial, encompassing fleet standardization, specialized pilot training programs, the need for new spare parts inventories, and existing long-term contractual agreements. For instance, a major aircraft manufacturer's order can represent billions of dollars and years of commitment.
This inherent lock-in effect means that once an airline establishes relationships with specific suppliers, it becomes exceedingly difficult and costly to transition to new ones. This dynamic significantly enhances the bargaining power of these established suppliers, limiting Cathay Pacific's ability to negotiate favorable terms or easily switch to alternative providers. The complexity and expense involved in changing aircraft types alone can deter airlines from exploring new partnerships.
- Substantial Investment: Airlines commit billions to aircraft orders, creating long-term dependency.
- Operational Disruption: Switching maintenance providers necessitates new certifications and training, impacting flight schedules.
- Inventory Costs: Maintaining diverse spare parts inventories for different aircraft types is inefficient and expensive.
- Contractual Obligations: Existing long-term contracts with suppliers can impose penalties for early termination.
Airport Operators and Infrastructure Control
Airport operators, particularly at Cathay Pacific's primary hub, Hong Kong International Airport (HKIA), hold considerable sway. Their control over essential assets such as runways, terminals, and gate allocations grants them substantial bargaining power. This is evident even with the recent expansion of HKIA's capacity, as its strategic location and finite space continue to empower the operator in dictating terms to airlines.
The commissioning of HKIA's Three-Runway System in November 2024, designed to enhance capacity, has not fundamentally altered the leverage of airport operators. While increased capacity might theoretically dilute some of this power, the ongoing demand and the critical nature of airport infrastructure mean operators can still exert influence over airline operations and associated costs.
- HKIA's Three-Runway System commenced operations in November 2024, aiming to increase passenger and cargo capacity.
- Airport operators control vital infrastructure, including gate slots, which are a scarce resource for airlines.
- The strategic importance and limited physical space of major hubs like HKIA reinforce the operator's bargaining position.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Cathay Pacific is significant, primarily due to the concentrated nature of aircraft and engine manufacturers. Companies like Boeing and Airbus, along with engine makers such as GE and Rolls-Royce, hold considerable sway. This is exacerbated by the specialized nature of aviation components and the high costs associated with switching suppliers, creating a lock-in effect that limits Cathay Pacific's negotiation flexibility.
The reliance on a few key suppliers for critical components like aircraft and engines, coupled with the substantial switching costs, grants these suppliers considerable leverage. For instance, the delivery of new aircraft, such as the Boeing 777-9, can be delayed, directly impacting Cathay Pacific's fleet expansion plans. This dependency means airlines often have limited options when negotiating pricing or terms.
Furthermore, the global shortage of skilled aviation labor, particularly pilots and maintenance technicians, has amplified the bargaining power of these workers and their unions. In 2024, reports indicated significant wage increases for pilots across the industry. Cathay Pacific’s own recruitment drive for thousands of new staff in 2025 highlights the ongoing pressure to attract and retain essential talent, further strengthening the position of these labor suppliers.
| Supplier Category | Key Players | Impact on Cathay Pacific | 2024/2025 Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aircraft Manufacturers | Boeing, Airbus | Limited choice, delivery schedules, pricing | Ongoing delivery challenges for new models impact fleet planning. |
| Engine Manufacturers | GE, Rolls-Royce, Pratt & Whitney | Performance, maintenance costs, technological upgrades | Engine reliability is crucial for operational efficiency and cost management. |
| Skilled Labor (Pilots, Technicians) | Labor Unions, Individual Specialists | Wage demands, working conditions, availability | Labor shortages in 2024 led to increased compensation negotiations. Cathay Pacific's 2025 hiring plans reflect this pressure. |
| Jet Fuel Suppliers | Global Oil Companies | Price volatility, supply availability | While prices moderated in 2024, fuel remains a significant and volatile cost. |
What is included in the product
Tailored exclusively for Cathay Pacific Airways, this analysis dissects the competitive forces shaping its industry, from buyer and supplier power to the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
Easily identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces impacting Cathay Pacific Airways.
Customers Bargaining Power
Leisure travelers, a key demographic for Cathay Pacific, exhibit significant price sensitivity, particularly given the rise of budget airlines and more direct flight options. This can put pressure on airlines to keep fares competitive.
In 2024, this price sensitivity played a role in the normalization of passenger yields for Cathay Pacific and its subsidiary HK Express. This trend highlights the impact of increased competition on regional routes, where growing supply aimed to match recovering demand.
Passengers can easily switch between airlines, a key factor in the bargaining power of customers for Cathay Pacific. Online travel agencies and direct booking sites simplify price and service comparisons, giving travelers ample choice. This accessibility means Cathay Pacific must consistently offer competitive fares and a high standard of service to keep passengers loyal.
Cathay Pacific's customers wield significant bargaining power due to the widespread availability of flight information. Websites like Skyscanner and Google Flights allow passengers to easily compare fares across numerous airlines, including Cathay Pacific, making price a key decision factor. In 2023, over 70% of air travelers reported using online travel agencies or comparison sites to book their flights, underscoring this trend.
Furthermore, customer reviews on platforms such as TripAdvisor and airline-specific forums provide detailed insights into service quality, punctuality, and overall passenger experience. This transparency empowers passengers to make informed choices, putting pressure on Cathay Pacific to maintain competitive pricing and high service standards to attract and retain their business. For instance, a significant portion of travelers consider online reviews as a primary influence when selecting an airline.
Influence of Corporate Travel Policies
Large corporate clients wield significant bargaining power over Cathay Pacific. Their substantial travel volume allows them to negotiate favorable rates and customized service packages, directly impacting Cathay's revenue per passenger. For instance, in 2024, major corporations continued to leverage their booking volume to secure discounts, a trend that intensified as airlines focused on rebuilding corporate travel segments.
The evolving landscape of corporate travel, influenced by factors like the increasing adoption of virtual meetings, further amplifies customer bargaining power. This shift can lead to reduced demand for traditional business trips, forcing airlines to compete more aggressively on price and service to retain these clients. The economic climate of 2024 saw many companies scrutinizing travel expenditures more closely, demanding greater value from their airline partners.
- Corporate Volume Discounts: Large corporations can negotiate substantial discounts based on their annual travel spend, reducing Cathay Pacific's average fare realization.
- Demand Elasticity: Increased reliance on virtual alternatives makes corporate travel demand more price-sensitive, giving customers leverage to switch providers if pricing is not competitive.
- Contractual Terms: Favorable payment terms, flexible booking options, and loyalty program benefits are often negotiated by powerful corporate clients, influencing Cathay's operational flexibility and costs.
Impact of Loyalty Programs and Premium Experience
Cathay Pacific's efforts to build customer loyalty through premium experiences and programs like its Marco Polo Club face a significant challenge from competitors employing aggressive pricing strategies. While the airline invests heavily in enhancing its offerings, such as the new Aria Suite business class, the bargaining power of customers remains a key consideration.
In 2024, the airline industry continued to see intense competition, with many carriers offering competitive fares, particularly in economy and premium economy classes. This environment means that even a superior product can be undermined if price becomes the dominant factor for a large segment of travelers.
- Customer Price Sensitivity: Despite investments in premium products, a substantial portion of Cathay Pacific's customer base may still prioritize lower fares, especially for non-business travel.
- Competitor Pricing Power: Airlines with lower operating costs or different business models can exert downward pressure on prices, directly impacting Cathay Pacific's ability to command premium pricing solely on experience.
- Loyalty Program Effectiveness: While loyalty programs encourage repeat business, their ultimate effectiveness in mitigating customer bargaining power is contingent on the perceived value proposition relative to competitor offerings and pricing.
Customers, both individual travelers and large corporate entities, exert considerable bargaining power over Cathay Pacific. This is driven by easy access to price comparisons, the availability of numerous alternatives, and a growing sensitivity to cost, especially in the post-pandemic travel recovery. In 2024, the airline faced this pressure as demand rebounded, forcing a delicate balance between service quality and competitive pricing.
The ease with which passengers can compare fares online significantly enhances their bargaining power. In 2023, a survey indicated that over 70% of air travelers utilized online travel agencies or comparison sites to book flights, a trend that continued into 2024. This transparency compels Cathay Pacific to maintain competitive pricing to attract and retain its customer base.
| Factor | Impact on Cathay Pacific | 2024 Trend/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Price Comparison Ease | Empowers customers to find lower fares, pressuring Cathay Pacific on pricing. | Over 70% of travelers used comparison sites in 2023, a trend sustained in 2024. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Increases customer choice and willingness to switch airlines. | Growth in budget carriers and direct routes intensified competition in 2024. |
| Corporate Volume | Large clients negotiate discounts, reducing revenue per passenger. | Corporate travel recovery in 2024 saw continued leverage of booking volume for rate negotiation. |
| Demand Elasticity | Virtual alternatives make corporate travel more price-sensitive. | Companies scrutinized travel spend in 2024, demanding greater value. |
What You See Is What You Get
Cathay Pacific Airways Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Cathay Pacific Airways Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the airline industry. You are looking at the actual document; once your purchase is complete, you’ll receive instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Cathay Pacific navigates a fiercely competitive landscape within the Asia-Pacific aviation sector. Rivalry is not only from established full-service airlines but also from an increasing presence of low-cost carriers, a segment that includes Cathay Pacific's own subsidiary, HK Express.
This intense rivalry, especially on popular regional routes, has put downward pressure on passenger yields for Cathay Pacific. For instance, HK Express reported a financial loss in 2024, underscoring the challenging pricing environment and the impact of competition on profitability within the group.
Cathay Pacific operates in an industry with substantial fixed costs, including aircraft purchases, maintenance, and staffing, which demand high utilization rates for profitability. The perishable nature of airline seats means unsold inventory is lost revenue, intensifying pressure to fill every flight.
This dynamic fuels aggressive pricing and capacity management, as airlines strive to maximize load factors. In 2024, global airline load factors hit an impressive 83.5%, underscoring the intense competition to capture passengers and mitigate the impact of these inherent cost structures.
The global aviation sector is seeing a significant surge in capacity as airlines rebound from recent disruptions. Cathay Pacific, for instance, is aiming for a substantial 30% annual capacity increase in 2025, alongside introducing new flight paths. This expansionist approach, mirrored by many other carriers, directly fuels more intense competition for passengers and market dominance.
Strategic Importance of Hong Kong Hub
Hong Kong International Airport (HKIA) is undeniably a cornerstone of Cathay Pacific's operations, with substantial investments solidifying its position. This deep integration offers a significant competitive edge. However, HKIA is also a battleground, with other major carriers leveraging their extensive networks and services from the same hub, leading to fierce competition for critical airport resources and desirable flight paths.
The rivalry at HKIA is intense, as multiple airlines vie for dominance. In 2023, HKIA handled approximately 30.3 million passengers, a substantial increase from 5.4 million in 2022, signaling a robust recovery and heightened activity. This surge in traffic intensifies the competition for prime gate assignments and valuable takeoff and landing slots, directly impacting operational efficiency and route planning for all airlines, including Cathay Pacific.
- HKIA's Passenger Traffic Growth: HKIA saw a significant rebound in passenger traffic in 2023, reaching 30.3 million, a stark contrast to the 5.4 million recorded in 2022, indicating a highly active and competitive environment.
- Intensified Slot Competition: Increased passenger numbers translate to greater demand for limited airport resources like gates and flight slots, directly intensifying rivalry among airlines operating at HKIA.
- Cathay Pacific's Strategic Position: Cathay Pacific's deep-rooted presence and investments at HKIA provide a foundational advantage, yet this must be constantly defended against aggressive competition from other major carriers.
Brand Differentiation and Service Quality
Cathay Pacific actively cultivates a premium brand image, underscored by its expansive global route network and a steadfast commitment to superior in-flight service quality. This strategic focus on differentiation aims to capture a segment of travelers who prioritize experience over mere cost.
The airline demonstrably invests in product innovation. For instance, recent upgrades include the introduction of new First and Business Class cabin designs, alongside enhancements to the Economy Class experience. These investments are crucial for standing out in a highly competitive aviation market where price sensitivity remains a significant factor for many consumers.
- Brand Positioning: Cathay Pacific targets discerning travelers by emphasizing luxury and extensive connectivity.
- Product Innovation: Ongoing investment in cabin upgrades, including new First and Business Class seating, aims to enhance passenger experience.
- Market Strategy: Differentiation through service quality and brand image is key to competing with price-focused rivals.
The competitive rivalry for Cathay Pacific is exceptionally high, driven by both legacy carriers and a growing number of low-cost airlines. This pressure is particularly acute on popular regional routes, impacting passenger yields. For example, Cathay Pacific's subsidiary, HK Express, faced profitability challenges in 2024 due to this intense pricing environment.
Airlines operate with substantial fixed costs, making high load factors critical for profitability. The perishable nature of airline seats means unsold inventory represents lost revenue, intensifying the need to fill every flight. In 2024, global airline load factors averaged 83.5%, reflecting this constant drive for passenger capture.
Cathay Pacific's strategic positioning at Hong Kong International Airport (HKIA) provides an advantage, but HKIA itself is a highly competitive hub. In 2023, HKIA handled 30.3 million passengers, a significant increase from 5.4 million in 2022, intensifying competition for valuable airport resources like gates and slots.
Cathay Pacific differentiates itself through a premium brand image, extensive global routes, and superior service, investing in product innovation like new cabin designs. This strategy aims to attract travelers prioritizing experience, even as price-sensitive competition remains a significant factor.
| Metric | 2023 Value | 2024 Outlook/Trend | Impact on Rivalry |
|---|---|---|---|
| HKIA Passenger Traffic | 30.3 million | Continued growth expected | Increased competition for slots/gates |
| Global Load Factor (Avg) | 83.5% (2024 est.) | Stable to increasing | Intensified competition for passengers |
| HK Express Profitability | Loss reported in 2024 | Challenging pricing environment | Downward pressure on yields |
| Cathay Pacific Capacity Increase | Targeting 30% in 2025 | Expansionist strategy | Increased direct competition |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The increasing sophistication and widespread adoption of virtual communication platforms present a significant threat of substitutes for traditional business travel. Companies are increasingly leveraging tools like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, and Google Meet for internal and external meetings, reducing the perceived need for physical presence. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that 65% of businesses now regularly conduct client meetings virtually, a trend that directly impacts demand for air travel, especially for shorter, routine business trips.
For shorter and medium-haul routes, especially within densely connected regions like mainland China, high-speed rail presents a growing and convenient alternative to air travel. By 2024, China's high-speed rail network had surpassed 45,000 kilometers, making it the longest in the world and a formidable competitor for regional journeys.
While Cathay Pacific primarily targets international and long-haul markets, the increasing efficiency and accessibility of high-speed rail can still affect the flow of passengers who might otherwise connect through its Hong Kong hub. This impact on feeder traffic is a crucial consideration for network planning and route profitability.
For certain types of goods, sea and land freight offer significantly cheaper, though slower, alternatives to air cargo. For instance, in 2024, the average cost per kilogram for ocean freight remained substantially lower than air freight, making it an attractive option for less time-sensitive shipments.
While air cargo is indispensable for high-value, time-sensitive, and the rapidly growing e-commerce sector, the persistent cost advantage of sea and land transport creates a tangible substitution threat for a portion of Cathay Pacific's freight market share.
Shift to Other Forms of Leisure Travel
Consumers are increasingly exploring alternatives to traditional air travel for leisure. This includes a notable rise in domestic road trips and staycations, particularly as fuel prices and airfare costs fluctuate. For instance, in 2024, many travelers sought out experiences closer to home, driven by budget considerations and a desire for more flexible travel plans.
Cruises also present a significant substitute, offering an all-inclusive experience that can be perceived as more predictable in terms of cost compared to flights, accommodation, and local transport. The cruise industry has seen a steady recovery and growth, indicating a sustained consumer interest in this form of vacationing.
- Rising popularity of domestic travel: Many travelers in 2024 prioritized road trips and local explorations over international flights.
- All-inclusive appeal of cruises: Cruises offer a bundled price, making budgeting easier for consumers compared to piecing together airfare and hotel costs.
- Perception of value: When air travel becomes expensive or inconvenient, consumers actively seek out more cost-effective or appealing alternatives like staycations.
- Broader competitive set: The threat of substitutes expands Cathay Pacific's competitive landscape beyond just other airlines to include the entire leisure and tourism sector.
Perceived Value and Convenience of Alternatives
If the perceived value of air travel declines, perhaps due to rising ticket prices or more cumbersome airport procedures, alternatives become more appealing. For instance, in 2024, the average airfare for domestic flights in the US saw an increase, potentially pushing some travelers to consider other options.
Environmental concerns are also a growing factor. As awareness of aviation's carbon footprint increases, travelers might favor lower-emission transport. This could lead to a greater adoption of high-speed rail or even electric vehicles for shorter or medium-haul journeys, especially as infrastructure for these alternatives improves.
The convenience factor plays a crucial role. If train travel or driving offers a more seamless door-to-door experience, especially when factoring in travel to and from airports, these substitutes gain an edge. For example, many European cities boast efficient rail networks that connect city centers directly, bypassing airport transit times.
- Increased Airfares: Rising fuel costs and operational expenses in 2024 contributed to higher ticket prices, making alternatives more attractive.
- Environmental Awareness: Growing public concern over aviation's environmental impact encourages a shift towards more sustainable travel modes.
- Convenience of Alternatives: High-speed rail and improved road networks offer direct city-center to city-center travel, often bypassing airport-related delays.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in electric vehicles and high-speed rail technology are enhancing the viability and appeal of substitute transportation.
The threat of substitutes for Cathay Pacific is multifaceted, impacting both passenger and cargo segments. Virtual communication platforms are increasingly replacing business travel, with a 2024 survey showing 65% of businesses regularly holding virtual client meetings. High-speed rail, particularly in mainland China with over 45,000 km of track by 2024, offers a strong alternative for regional journeys, potentially impacting feeder traffic to Cathay's Hong Kong hub. For leisure travel, staycations and cruises are gaining traction, especially when airfares rise, as seen with domestic flight price increases in the US in 2024.
| Substitute | Impact Area | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Virtual Communication | Business Travel | 65% of businesses regularly conduct virtual client meetings. |
| High-Speed Rail | Regional Travel/Hub Traffic | China's network exceeded 45,000 km, offering a faster alternative for shorter routes. |
| Staycations/Local Travel | Leisure Travel | Increased prioritization due to fluctuating airfare and fuel costs. |
| Cruises | Leisure Travel | Steady recovery and growth indicate sustained consumer interest in bundled vacation experiences. |
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a new airline demands enormous upfront capital for aircraft purchases, navigating stringent regulatory hurdles, and building essential operational infrastructure. This substantial financial barrier significantly limits the number of new players able to enter the market.
Cathay Pacific's commitment to a HK$100 billion investment in its fleet and network expansion underscores the sheer scale of financial resources required. Such significant capital outlays create a formidable entry barrier, effectively deterring most potential competitors from challenging established carriers in this capital-intensive industry.
Stringent regulatory hurdles significantly deter new entrants in the aviation sector. The industry is governed by rigorous safety standards, extensive licensing, and complex operational certifications. For instance, in 2024, obtaining an Air Operator Certificate (AOC) from aviation authorities like the FAA or EASA can take years and involve substantial investment in compliance and training, effectively acting as a formidable barrier.
Major international airports, particularly established hubs like Hong Kong International Airport (HKIA), face a significant barrier to entry due to limited available take-off and landing slots. These slots are often already allocated to incumbent airlines, making it difficult for new entrants to secure commercially viable operations. For instance, while HKIA's Three-Runway System, completed in 2024, has aimed to increase capacity, the competition for prime slots remains intense, posing a substantial hurdle for any new airline looking to establish a presence.
Strong Brand Loyalty and Network Economies
Established carriers like Cathay Pacific leverage decades of brand development and extensive global networks, fostering strong customer loyalty. This deep-rooted brand recognition and comprehensive route system present a formidable barrier for newcomers attempting to attract and retain passengers, as replicating such reach is a significant undertaking.
Network economies further solidify this advantage. Cathay Pacific's established partnerships and operational efficiencies across its vast network translate into cost advantages and superior customer convenience that new entrants find challenging to match. For instance, by 2024, Cathay Pacific's loyalty program, Marco Polo Club, boasts millions of members, demonstrating substantial customer stickiness.
- Brand Loyalty: Decades of consistent service and marketing have built significant trust and preference for Cathay Pacific.
- Network Economies: The airline's extensive global route map and partner network offer convenience and integrated travel experiences.
- Switching Costs: Loyalty program benefits and established travel patterns create tangible costs for customers to switch to a new airline.
- Customer Retention: These factors contribute to a high customer retention rate, making it difficult for new entrants to gain market share.
Incumbent Response and Consolidation
Existing airlines, like Cathay Pacific, can deploy significant market power and financial resources to counter new entrants. This often involves aggressive pricing, adjusting flight capacity to saturate routes, or even acquiring promising startups. For instance, during periods of intense competition, major carriers have been known to temporarily slash fares to unsustainable levels for smaller rivals.
The airline sector has a well-documented history of consolidation. Major mergers and acquisitions have concentrated market share among a few dominant players. This trend, evident throughout the 2010s and continuing into the 2020s, makes it exceedingly difficult for new, smaller airlines to establish a sustainable presence against established giants with extensive networks and brand loyalty.
- Market Power: Incumbents like Cathay Pacific can leverage existing customer bases and strong supplier relationships.
- Economies of Scale: Larger airlines benefit from lower per-unit costs in areas like aircraft maintenance and fuel purchasing.
- Consolidation Trends: The industry has seen significant consolidation, with fewer, larger players dominating. For example, the global airline industry's top 10 carriers by revenue in 2023 controlled a substantial portion of the market share.
- Barriers to Entry: High capital requirements for aircraft, regulatory hurdles, and established brand recognition act as significant barriers.
The threat of new entrants in the airline industry, particularly for a carrier like Cathay Pacific, remains relatively low due to exceptionally high barriers. These include the immense capital required for fleet acquisition and operational setup, alongside stringent regulatory approvals that can take years to secure.
Furthermore, established airlines benefit from strong brand loyalty and extensive network economies, making it difficult for newcomers to compete on convenience and customer experience. For instance, Cathay Pacific's Marco Polo Club loyalty program had millions of members by 2024, indicating significant customer stickiness.
Limited access to prime airport slots, such as those at Hong Kong International Airport, presents another significant hurdle, even with capacity expansions like the Three-Runway System completed in 2024. The airline industry's ongoing consolidation also concentrates market power among fewer, larger players, further deterring new entrants.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | Aircraft purchase, infrastructure, operational setup | Extremely High |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Licensing, safety standards, certifications | High, Time-Consuming |
| Brand Loyalty & Network | Customer preference, route density, partnerships | High |
| Airport Slot Availability | Limited prime slots at major hubs | High |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs for incumbents | Significant |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Cathay Pacific Airways is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including the airline's annual reports, industry-specific market research from firms like IATA, and regulatory filings from aviation authorities.
We also leverage data from financial news outlets, competitor financial statements, and macroeconomic indicators to provide a robust assessment of industry rivalry, buyer power, and supplier influence.
