Caledonia Mining Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Caledonia Mining Bundle
Caledonia Mining operates within a dynamic gold mining sector, facing significant pressures from powerful suppliers of essential equipment and consumables. The threat of new entrants, while potentially high in theory, is tempered by substantial capital requirements and regulatory hurdles. Buyer power, though present, is often diffused across various buyers of refined gold, influenced by global market prices.
The intensity of rivalry among existing gold producers is a key consideration, impacting pricing and operational efficiency. Furthermore, the constant availability of substitute materials for industrial applications and the ongoing search for alternative energy sources can indirectly affect gold demand. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface.
Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Caledonia Mining’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Caledonia Mining's reliance on highly specialized underground mining equipment, often sourced from a select group of global manufacturers, grants these suppliers significant bargaining power. The unique demands of operations like those at Blanket Mine mean that custom or specific machinery is frequently required, limiting Caledonia's ability to switch suppliers easily. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of Caledonia's capital expenditure was directed towards acquiring advanced drilling and hoisting equipment, highlighting its dependence on these specialized providers.
Furthermore, the proprietary nature of maintenance services and spare parts for this sophisticated technology further entrenches supplier leverage. Without access to original manufacturer parts and expertise, operational continuity could be severely compromised. This situation means Caledonia may face higher costs for both initial equipment purchases and ongoing upkeep, directly impacting its profitability and operational efficiency.
Energy, especially electricity and fuel, represents a substantial operational expense for Caledonia Mining's operations. The availability and pricing of these critical consumables, particularly within Zimbabwe, can be significantly impacted by a concentrated supplier base or government-controlled utility providers. This situation can grant suppliers considerable leverage over Caledonia's ongoing operational costs.
In 2023, electricity costs were a major factor, and while specific figures for Caledonia's energy expenditure aren't publicly detailed for the entire year, the mining sector globally often sees energy as one of its largest variable costs, sometimes exceeding 30% of total operating expenses. Fluctuations in global energy prices, even if passed through to local markets, directly affect Caledonia's profitability. The reliance on national grid power in Zimbabwe, which has faced reliability challenges in the past, further amplifies the bargaining power of energy suppliers and creates potential for cost volatility.
The bargaining power of labor within Caledonia Mining's operations is significantly influenced by the availability of a skilled mining workforce. Access to specialized talent, such as experienced engineers, geologists, and seasoned miners, is paramount for efficient and safe extraction. If this talent pool is limited in the regions where Caledonia operates, it directly empowers unions or individual skilled workers to negotiate for higher wages and more favorable employment terms, thus increasing their leverage over the company.
Training and retaining these essential personnel also represent a considerable cost and effort for Caledonia Mining, further bolstering the bargaining power of the skilled workforce. For instance, in 2024, the global mining sector has seen a notable increase in demand for skilled labor, with some regions experiencing persistent shortages. This imbalance, coupled with the specialized nature of mining roles, means that Caledonia must carefully manage its compensation and benefits to attract and keep the necessary expertise.
Regulatory & Environmental Services
The bargaining power of suppliers in regulatory and environmental services for Caledonia Mining is considerable. Compliance with mining regulations, environmental standards, and safety protocols necessitates specialized consulting and monitoring services.
A limited pool of accredited firms offering these critical services, coupled with the severe financial and reputational risks of non-compliance, amplifies their leverage over Caledonia. For instance, in 2024, the global mining sector faced increased scrutiny on ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) factors, leading to higher demand for specialized compliance services.
- Limited Number of Accredited Providers: The scarcity of highly qualified and certified environmental and regulatory consultants in key operating regions for Caledonia can concentrate power in the hands of a few firms.
- Criticality of Services: Failure to meet stringent regulatory and environmental standards can result in operational shutdowns, significant fines, and reputational damage, making these services indispensable.
- Increasing Regulatory Complexity: Evolving environmental laws and safety mandates, particularly those related to carbon emissions and water management, require continuous adaptation and specialized expertise, increasing reliance on these suppliers.
- High Switching Costs: The process of changing environmental service providers can be lengthy and complex, involving new certifications and operational integration, which can lock Caledonia into existing supplier relationships.
Geopolitical Factors & Local Content
Operating in Zimbabwe, Caledonia Mining Corporation faces unique challenges due to local content requirements and prevailing geopolitical factors, which directly impact the bargaining power of its suppliers. These government mandates, designed to foster domestic economic growth, can restrict Caledonia’s sourcing options. This limitation can inadvertently strengthen local suppliers, particularly if they are the primary or sole providers of essential goods and services, allowing them to command higher prices or dictate terms, thereby increasing their leverage.
The stability and reliability of supply chains within Zimbabwe are also intrinsically linked to these geopolitical dynamics. When local suppliers are essential due to these regulations, any disruption, whether economic or political, amplifies their bargaining power. For instance, if a key local supplier faces production issues or increased operational costs due to the regional environment, Caledonia’s reliance on them intensifies, giving that supplier more influence over pricing and delivery schedules.
- Local Content Requirements: Zimbabwe’s policies often necessitate sourcing a certain percentage of goods and services locally, concentrating demand on fewer domestic suppliers.
- Geopolitical Stability: Regional political and economic stability directly affects the operational capacity and cost structures of local suppliers, influencing their pricing power.
- Limited Supplier Pool: When specialized inputs are only available from a few local providers due to regulations or market structure, their bargaining power is significantly enhanced.
- Supply Chain Vulnerability: Dependence on local suppliers for critical components, especially in an evolving geopolitical landscape, makes Caledonia susceptible to supplier-driven cost increases.
Caledonia Mining's reliance on specialized underground mining equipment from a limited number of global manufacturers gives these suppliers considerable leverage. The need for custom machinery at operations like Blanket Mine makes switching suppliers difficult. In 2024, significant capital expenditure was allocated to advanced drilling and hoisting gear, underscoring this dependence.
Proprietary maintenance services and spare parts for this sophisticated technology further enhance supplier power. Access to original manufacturer parts is crucial for operational continuity. This situation can lead to higher acquisition and upkeep costs for Caledonia, impacting profitability.
Energy, particularly electricity and fuel, is a substantial operational cost. The pricing and availability of these consumables in Zimbabwe, influenced by a concentrated supplier base or state-controlled utilities, grant energy suppliers significant leverage over Caledonia's ongoing expenses.
In 2023, electricity costs were a major factor for the mining sector. While specific figures for Caledonia are not fully detailed, global mining operations often see energy as one of their largest variable costs. Reliance on Zimbabwe's national grid, which has experienced reliability issues, amplifies the bargaining power of energy providers and introduces cost volatility.
What is included in the product
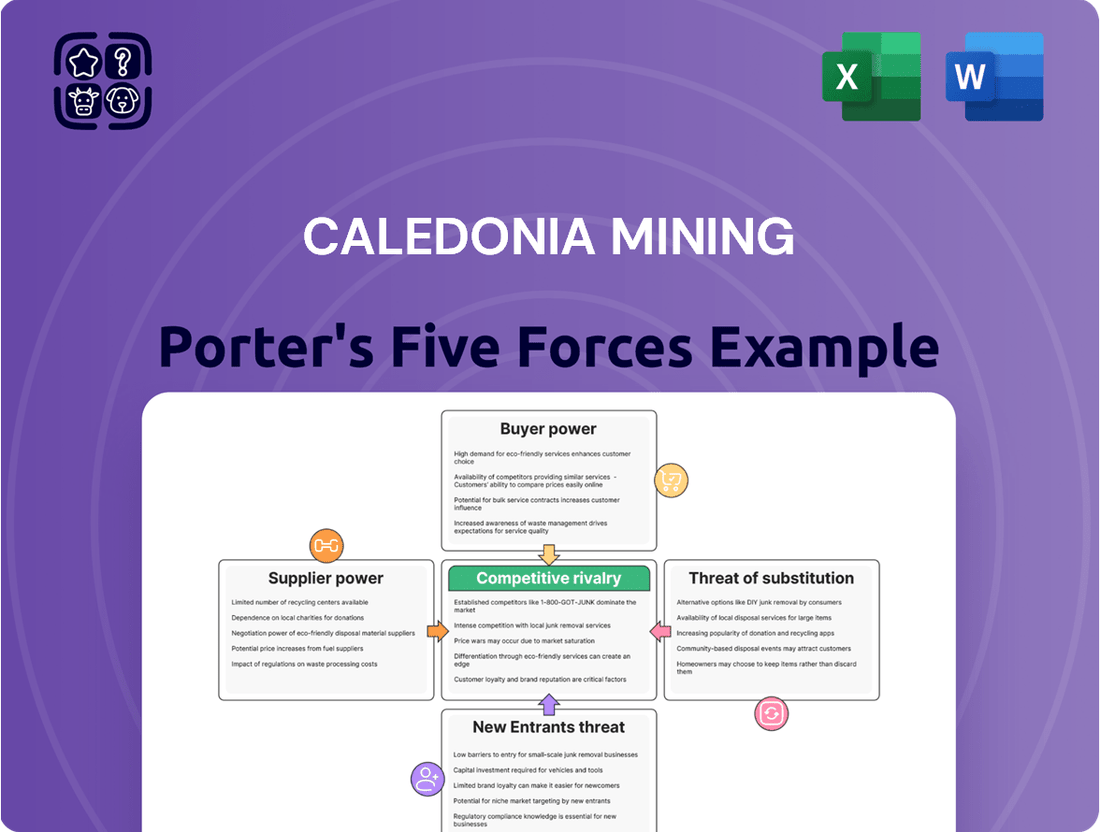
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Caledonia Mining dissects the industry's competitive landscape, examining the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of Caledonia Mining's market landscape.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of customers in the context of commodity pricing for gold, Caledonia Mining's primary product, is inherently low. Gold is a globally traded commodity where prices are dictated by broad international supply and demand, macroeconomic trends, and investor sentiment, not by individual customer actions. This positions Caledonia Mining as a price-taker, with very little ability to influence the market price of the gold it produces, thus diminishing any single buyer's leverage.
The fundamental nature of mined gold, often in the form of doré bars, presents a significant challenge regarding customer bargaining power. Once refined, gold from Caledonia Mining is virtually indistinguishable from gold produced by other mining operations worldwide.
This inherent lack of differentiation means that buyers, such as refiners or bullion dealers, face a vast global market with readily available alternatives. Consequently, individual customers hold very little sway in dictating prices or terms for Caledonia's output. The global spot price of gold, which averaged around $2,069 per ounce in early 2024, effectively dictates the value.
The global gold market is exceptionally robust and liquid, with demand stemming from a wide array of sectors. These include jewelry, technological and industrial uses, investment vehicles like exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and physical bullion, and significant purchases by central banks worldwide. This broad market access means Caledonia Mining isn't reliant on any single buyer, effectively limiting customer leverage.
In 2023, global gold demand reached 4,899 tonnes, according to the World Gold Council, showcasing the market's depth. This consistent and widespread demand provides Caledonia with numerous avenues to sell its production, diminishing the bargaining power of any individual customer.
Refinery Relationships
Caledonia Mining's relationships with gold refiners are a key aspect of its customer bargaining power. The company typically sells its doré, a semi-pure gold alloy, to a select group of specialized refiners. These refiners are crucial as they transform the doré into the high-purity gold bullion that is traded on global markets.
However, the bargaining power of these refiners is somewhat limited. The refining industry, while specialized, is competitive, and the consistent global demand for gold ensures that refiners are keen to secure supply from reliable miners like Caledonia. This dynamic prevents refiners from dictating unfavorable terms to Caledonia. Their influence leans more towards operational efficiency and logistical capabilities rather than significant price leverage over the miner.
- Limited Number of Refiners: Caledonia works with a concentrated group of specialized gold refiners, creating a degree of dependence for both parties.
- Competitive Refining Market: The presence of multiple refiners eager for supply mitigates their individual power to impose unfavorable pricing on Caledonia.
- Global Gold Demand: Strong international demand for gold bullion supports miners by ensuring a ready market for refined products, indirectly limiting refiner pricing power.
- Focus on Processing: Refiners' leverage is primarily derived from their processing capacity and efficiency, not their ability to significantly alter the price of gold doré.
Long-Term Contracts
Long-term contracts generally strengthen a supplier's position, but for Caledonia Mining, the dynamics of gold sales often limit customer bargaining power. While some long-term off-take agreements might exist, the prevailing nature of commodity markets leans towards spot prices or short-term contracts with standardized terms. This structure inherently caps an individual customer's ability to demand significantly preferential pricing or terms that diverge from global benchmarks.
Caledonia's revenue streams are therefore likely closely tied to prevailing market rates for gold. For instance, in 2023, the average gold price was approximately $1,978 per ounce, a figure that dictates the baseline for most transactions. The limited ability for customers to negotiate unique terms means their bargaining power is constrained by these market realities rather than individual contractual leverage.
- Limited Price Negotiation: Customers typically buy at prevailing market rates, reducing their power to negotiate discounts.
- Standardized Terms: Contracts often adhere to industry standards, preventing customers from dictating unique terms.
- Market Volatility: Fluctuations in gold prices (e.g., averaging $1,978/oz in 2023) create a baseline that limits significant deviations.
- Commodity Nature: Gold's fungible nature means individual customer relationships have less impact on pricing compared to bespoke products.
Customers, primarily gold refiners and bullion dealers, possess very low bargaining power against Caledonia Mining. This is due to gold's status as a globally standardized commodity where prices are set by international supply and demand, not by individual buyers.
The company's output, once refined, is indistinguishable from that of other producers. This fungibility means buyers have numerous alternatives, limiting their ability to dictate terms or prices to Caledonia. The average gold price in early 2024 was around $2,069 per ounce, setting a strong market benchmark.
The broad and diverse global demand for gold, from jewelry and investment to central bank reserves, ensures Caledonia has many sales channels. For example, global gold demand in 2023 was 4,899 tonnes, underscoring this market depth and reducing reliance on any single customer.
While Caledonia sells to a select group of refiners, their bargaining power is constrained by the competitive refining market and consistent global demand for gold. Refiners' influence is more operational than price-setting.
| Aspect | Caledonia Mining Context | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|
| Commodity Nature | Gold is a standardized, globally traded asset. | Customers cannot negotiate unique terms or prices for differentiated features. |
| Market Price Influence | Prices dictated by global supply/demand, macroeconomic factors, investor sentiment. (e.g., Avg. 2023 price: $1,978/oz) | Caledonia is a price-taker; customers buy at prevailing market rates, limiting negotiation leverage. |
| Customer Base Diversity | Wide range of buyers including refiners, bullion dealers, investors, central banks. (Global demand: 4,899 tonnes in 2023) | Caledonia's reliance on any single customer is low, weakening individual buyer power. |
| Refiner Relationships | Sales typically to specialized refiners for processing into bullion. | Refiners are competitive for supply, and their leverage is primarily in processing efficiency, not price negotiation. |
Full Version Awaits
Caledonia Mining Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Caledonia Mining Corporation, offering a detailed examination of its competitive landscape. The exact document you see here is what you will receive immediately upon purchase, ensuring transparency and no hidden surprises. This analysis delves into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the gold mining industry, providing actionable insights. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Caledonia Mining Corporation PLC operates within a highly competitive global gold market. It faces rivalry from established major international gold producers with significant economies of scale, as well as numerous smaller, agile junior mining companies. This diverse range of competitors actively contests for market share, exploration rights, and access to essential resources.
In its primary operational region of Southern Africa, Caledonia Mining also contends with regional players. These competitors are similarly seeking out promising exploration targets, securing valuable mining concessions, and attracting specialized geological and operational talent. The presence of both global giants and local contenders intensifies the competitive pressure on Caledonia.
For context, the global gold mining industry saw significant activity in 2024. Major producers continued to optimize operations, while exploration budgets remained a key factor in identifying future growth. The price of gold itself, which fluctuated throughout 2024, also directly influences the intensity of competition as companies strive for profitability.
Caledonia Mining operates in an environment where competition for essential resources is fierce. Securing capital for exploration and development projects is a constant challenge, with companies vying for investor attention and financing. This intense competition for funding directly impacts the ability to acquire and develop new gold deposits.
The scarcity of high-quality gold deposits further intensifies rivalry. Companies are actively seeking out and bidding on promising exploration targets, driving up acquisition costs. For instance, in 2024, global exploration budgets for gold remained robust, reflecting the ongoing demand for new discoveries, which naturally increases the cost of securing attractive mineral rights.
This competition for both capital and quality assets can lead to more aggressive strategies among mining companies. Players may engage in higher bids for mineral rights or offer more attractive terms to secure funding, ultimately intensifying the competitive landscape for Caledonia Mining.
Competitive rivalry in gold mining is intensely focused on cost structures and production efficiency. Companies that can achieve lower all-in sustaining costs (AISC) gain a significant edge, particularly when gold prices are volatile. For example, in early 2024, while specific industry-wide AISC figures fluctuate, producers with efficient operations and lower energy costs are better positioned to weather price downturns.
Caledonia Mining, through its Blanket Mine, must relentlessly pursue operational optimization to stay competitive. This means focusing on improving extraction rates, managing energy consumption, and minimizing waste to lower its AISC. Against larger, more established miners with economies of scale, Caledonia's ability to control its cost base is paramount for sustained profitability and market standing.
Mergers & Acquisitions Activity
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are a constant feature in the gold mining sector, with companies frequently consolidating to bolster their asset portfolios, enhance operational efficiencies through economies of scale, and secure access to new, promising gold reserves. This dynamic M&A landscape directly impacts the intensity of competitive rivalry by altering the structure of the industry, potentially leading to the emergence of larger, more dominant players or the consolidation of smaller entities. Caledonia Mining itself actively explores and pursues expansion opportunities, often through strategic acquisitions or partnerships, to strengthen its market position and growth trajectory.
The M&A trend in gold mining can significantly reshape the competitive environment. For instance, in 2023, the total value of announced gold M&A deals reached approximately $17 billion, indicating robust activity and a clear strategy for many companies to grow through consolidation. Major transactions, such as Barrick Gold's acquisition of a controlling stake in RTX, underscore the strategic importance of M&A in gaining market share and operational synergies.
- Consolidation Drive: The gold mining industry’s M&A activity is driven by the pursuit of economies of scale and access to new reserves, directly impacting competitive intensity.
- Market Reshaping: M&A deals can create larger, more formidable competitors or eliminate smaller players, altering the overall competitive landscape.
- Caledonia's Strategy: Caledonia Mining actively engages in expansion opportunities, often through M&A, to enhance its market standing and growth prospects.
- 2023 M&A Value: The gold mining sector saw around $17 billion in announced M&A deals in 2023, highlighting the strategic importance of consolidation.
Regulatory & Geopolitical Landscape
Operating in specific jurisdictions, such as Zimbabwe for Caledonia Mining, significantly intensifies competitive rivalry. Beyond operational efficiency, companies must excel at navigating intricate regulatory frameworks, managing geopolitical uncertainties, and securing their social license to operate. This multifaceted competition means that firms adept at managing these external factors gain a substantial advantage, impacting their long-term sustainability and market position. For instance, in 2024, the mining sector in Zimbabwe continued to face evolving fiscal policies and a strong emphasis on local beneficiation, requiring significant strategic adaptation from all players.
The ability to effectively manage these non-market factors can be a key differentiator. Competitors who can proactively engage with government bodies, anticipate policy shifts, and foster positive community relations are better positioned to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities. This often translates into more stable operations and a stronger competitive footing.
- Navigating Zimbabwe's evolving mining legislation, including indigenization laws and royalty rates, presents a direct competitive challenge.
- Geopolitical stability and the potential for policy changes directly influence investment decisions and operational continuity, creating an uneven playing field.
- Companies with strong government relations and community engagement programs in 2024 demonstrated greater resilience against potential operational disruptions.
- The comparative success in securing permits and licenses, influenced by regulatory expertise, directly impacts a company's ability to expand or maintain production levels.
Competitive rivalry is intense in the global gold market, with Caledonia Mining facing pressure from large established miners and agile junior companies. This rivalry extends to securing exploration rights and essential resources. In 2024, the gold market saw active exploration and operational optimization by major producers, with gold price volatility directly influencing competitive efforts to maintain profitability.
The competition for capital and quality gold deposits significantly drives up acquisition costs. For instance, robust global gold exploration budgets in 2024 reflected a strong demand for new discoveries. This scarcity of prime assets compels companies to pursue more aggressive strategies, such as higher bids for mineral rights and attractive financing terms, thus intensifying the overall competitive landscape for Caledonia Mining.
Operational efficiency and cost structures are critical differentiators in gold mining. Companies with lower all-in sustaining costs (AISC), often benefiting from efficient operations and favorable energy costs, are better positioned during price downturns. Caledonia Mining must continuously enhance its operational optimization to lower AISC and remain competitive against larger players with economies of scale.
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) are a significant factor reshaping the competitive environment. The gold mining sector saw approximately $17 billion in announced M&A deals in 2023, underscoring a trend towards consolidation. These transactions aim to bolster asset portfolios and operational efficiencies, potentially creating larger, more dominant competitors and impacting Caledonia's market position.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for physical gold, Caledonia Mining's core product, is remarkably low. For its primary roles as a monetary asset, a store of value, and in key industrial applications like electronics and dentistry, there simply isn't a direct, perfect replacement. This is due to gold's unique chemical properties, its inherent rarity, and its long-standing global acceptance as a currency, making it difficult to replicate its function. In 2024, gold’s price volatility, while present, did not diminish its appeal as a hedge against inflation, with prices often reacting to geopolitical tensions and economic uncertainty.
While gold itself, Caledonia Mining's core product, doesn't have a direct substitute in its physical form, investors looking for similar investment characteristics face a range of alternatives. These include government bonds, considered safe-haven assets, and certain fiat currencies that might act as inflation hedges.
Real estate and other precious metals like silver and platinum also present investment options for those seeking portfolio diversification or a hedge against economic uncertainty. For instance, as of early 2024, U.S. Treasury yields offered competitive returns, making them an attractive alternative to physical commodities for some investors.
The decision to invest in these alternatives over gold is heavily influenced by individual investor objectives, prevailing market conditions, and personal risk tolerance. These are considered investment alternatives that cater to similar financial goals rather than direct product substitutes for gold.
The emergence of digital currencies like Bitcoin presents an evolving threat of substitutes for traditional stores of value. While some investors view cryptocurrencies as a form of 'digital gold,' offering decentralization and a capped supply, their significant price volatility and ongoing regulatory ambiguity limit their current ability to fully replace gold. However, this digital asset class is increasingly attracting specific investor segments seeking alternative investment avenues, representing an indirect but growing competitive pressure.
Industrial Application Substitutes
While engineers constantly seek cost-effective alternatives, the threat of substitutes for gold in specific industrial applications remains generally low, particularly for high-tech uses. Gold's unparalleled conductivity, exceptional corrosion resistance, and inherent malleability make it difficult to replace in critical components. For instance, in aerospace and advanced electronics, where reliability is paramount, the performance benefits of gold often outweigh its cost. The average price of gold in 2024 hovered around $2,300 per ounce, a significant increase that could incentivize some substitution, but not where gold's unique properties are indispensable.
However, in less demanding applications or where price sensitivity is higher, substitutes can emerge. For example, in certain jewelry or decorative uses, less expensive metals or plated alternatives might be considered. Nonetheless, the unique combination of properties gold offers means that direct, equally effective substitutes are scarce and often prohibitively expensive to develop or implement. The challenge lies in finding materials that can replicate gold's performance across all its critical attributes.
- Gold's Unique Properties: Conductivity, corrosion resistance, and malleability are difficult to replicate.
- High-Tech Applications: In sectors like aerospace and electronics, gold's reliability is crucial, limiting substitution.
- Price Sensitivity: Higher gold prices (e.g., around $2,300/ounce in 2024) can drive some substitution in less critical areas.
- Limited Viable Substitutes: Finding materials that match gold's performance across all attributes is challenging and costly.
Jewelry Market Trends
The threat of substitutes in the jewelry market, particularly concerning gold, presents a nuanced challenge for Caledonia Mining. Consumers can indeed turn to other precious metals like platinum, palladium, or silver if gold prices become too high or if fashion preferences lean elsewhere. For instance, silver jewelry demand has shown resilience, with global silver jewelry consumption estimated at around 600 million ounces in 2023, demonstrating an alternative for price-conscious buyers.
However, gold's unique position as a store of value and its deep cultural significance globally limit the extent to which these substitutes can fully replace its demand in the jewelry sector. While fashion trends can shift, the intrinsic appeal and long-standing tradition associated with gold jewelry remain powerful drivers of consumer choice. This means that while some demand may be diverted, a significant portion of the market remains loyal to gold. The World Gold Council reported that jewelry accounted for 40% of total gold demand in 2023, underscoring its enduring importance.
- Alternative Precious Metals: Platinum, palladium, and silver offer direct substitutes for gold in jewelry, particularly when gold prices are elevated.
- Non-Precious Materials: While less direct, fashion trends can sometimes favor non-precious materials, impacting a segment of the jewelry market.
- Gold's Intrinsic Value: The enduring store of value and investment appeal of gold, separate from its use in jewelry, provides a baseline of demand that substitutes struggle to replicate.
- Cultural Significance: Gold's deep-rooted cultural importance in many societies worldwide acts as a significant barrier to widespread substitution in jewelry.
The threat of substitutes for gold, Caledonia Mining's primary product, is generally low due to its unique properties and long-standing global acceptance. While other precious metals like silver and platinum serve as alternatives in jewelry and investment, gold's intrinsic value and cultural significance create a durable demand. Digital currencies like Bitcoin represent an emerging, albeit volatile, substitute for a store of value, but regulatory uncertainty limits their current impact.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the gold mining sector, particularly for underground operations similar to Caledonia Mining's Blanket Mine, requires substantial upfront capital. This includes significant investment in exploration, mine development, building essential infrastructure, and acquiring specialized equipment.
Estimates for establishing a new underground gold mine can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars, with some projects exceeding a billion. For instance, in 2023, several mid-tier gold projects announced development plans with capital expenditures ranging from $200 million to over $600 million.
These immense costs present a formidable barrier to entry, deterring many potential new players from even considering entering the market. The sheer financial commitment needed to reach production stages effectively limits the pool of viable competitors.
The lengthy lead times and complex development cycles inherent in gold mining present a significant barrier to new entrants. Bringing a new mine from initial exploration to full commercial production can easily span over a decade, encompassing rigorous geological assessments, detailed feasibility studies, obtaining numerous permits, and extensive construction phases. This extended timeline, coupled with the inherent uncertainties, discourages companies focused on rapid profitability, thereby acting as a strong deterrent to potential competitors.
New players in the gold mining sector, like Caledonia Mining, face significant regulatory and permitting challenges, especially in jurisdictions such as Zimbabwe. These hurdles encompass strict environmental, social, and governance (ESG) compliance, securing land rights, and obtaining necessary licenses. For instance, in 2024, the Zimbabwean government continued to emphasize local ownership and beneficiation, adding layers to the licensing process that can deter smaller, less experienced entrants.
Navigating these intricate legal and bureaucratic landscapes demands specialized expertise and considerable time, often proving to be a lengthy and unpredictable journey. This complexity acts as a substantial barrier to entry for potential competitors. Obtaining mining leases and environmental impact assessments, critical for operations, can take several years, significantly increasing upfront costs and delaying revenue generation for any new mining venture.
Access to Proven Reserves & Expertise
The difficulty in identifying and acquiring economically viable gold deposits presents a significant barrier for new entrants. Much of the high-grade, easily accessible gold has already been discovered, making the search for new reserves a costly and complex undertaking. This requires specialized geological expertise and substantial capital, which emerging companies often lack.
Existing players, such as Caledonia Mining, benefit from their established geological knowledge and experienced operational teams. These established players have already invested heavily in exploration and development, giving them a distinct advantage in securing and exploiting quality assets. For instance, Caledonia's Blanket Mine in Zimbabwe has a long history of production, demonstrating the value of sustained operational experience.
The threat of new entrants is therefore mitigated by the high upfront investment and specialized knowledge needed to access proven reserves and build operational capacity. Without this, newcomers would find it exceptionally difficult to compete with established mining operations that possess:
- Established geological databases and exploration expertise.
- Significant capital reserves for acquisitions and development.
- Proven track records in navigating complex mining regulations and operations.
- Access to experienced management and skilled workforces.
Operational & Geopolitical Risks
Operating a gold mine, particularly in a jurisdiction like Zimbabwe, presents substantial operational hurdles. These include the technical complexities of extraction, the potential for labor disputes, and the ever-present risk of political instability. These factors create a significant barrier to entry for new players.
Newcomers often lack the deep-seated local knowledge, established relationships with government and local communities, and the robust risk management frameworks that established operators like Caledonia Mining have cultivated over time. For instance, navigating Zimbabwe's regulatory environment, as of 2024, requires intricate understanding and experience to mitigate potential disruptions.
The unique difficulties associated with operating in Zimbabwe amplify the threat of new entrants. These challenges can range from infrastructure limitations to evolving fiscal policies, making it less attractive for potential competitors to commit the substantial capital required for a new mining venture.
Caledonia Mining's Blanket Mine, for example, has demonstrated resilience by managing these operational and geopolitical risks effectively. Their operational expenditure per ounce for 2023 was $977, showing a degree of cost control amidst these challenging conditions. This established operational proficiency serves as a deterrent to new entrants who would need to replicate or surpass such efficiency from day one.
- Operational Risks: Technical challenges in mining and processing, equipment reliability, and the need for specialized geological expertise.
- Geopolitical Risks: Political instability, changes in mining legislation, potential for nationalization, and security concerns.
- Local Knowledge & Relationships: Understanding and navigating local customs, labor laws, community relations, and government bureaucracy.
- Risk Management Experience: Proven ability to manage volatile economic conditions, currency fluctuations, and supply chain disruptions.
The threat of new entrants for Caledonia Mining is considerably low due to the immense capital requirements for establishing an underground gold mine, with development costs often reaching hundreds of millions of dollars, as seen in mid-tier project announcements in 2023. This financial barrier, coupled with the decade-long lead times from exploration to production and complex regulatory landscapes in jurisdictions like Zimbabwe, significantly deters potential competitors.
New entrants also struggle with acquiring economically viable gold deposits, as easily accessible high-grade reserves are scarce, demanding specialized geological expertise and capital that emerging companies often lack. Furthermore, established players like Caledonia benefit from deep operational experience and established relationships, making it difficult for newcomers to match their efficiency and navigate the inherent operational and geopolitical risks, which were evident in Caledonia's 2023 operational expenditure of $977 per ounce.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Caledonia Mining Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data from annual reports, SEC filings, and reputable industry analysis firms. We also incorporate insights from macroeconomic data and market research reports to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
