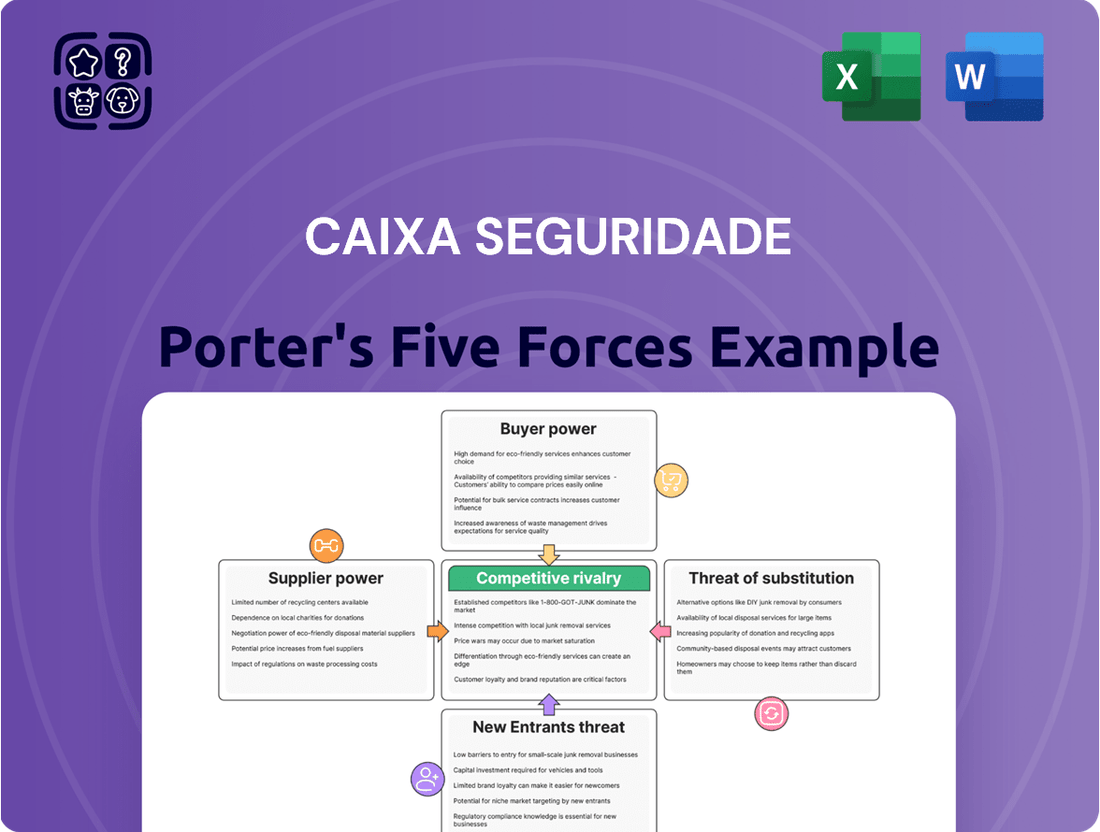
Caixa Seguridade Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Caixa Seguridade Bundle
Caixa Seguridade operates within a dynamic insurance landscape, where understanding the interplay of competitive forces is paramount. Our Porter's Five Forces analysis delves into the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threats posed by new entrants and substitutes, offering a comprehensive view of the sector's profitability potential.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Caixa Seguridade’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Caixa Seguridade's bargaining power of suppliers is influenced by limited supplier concentration, particularly with reinsurers. While the global reinsurance market has major players, Caixa Seguridade's substantial size and its affiliation with Caixa Econômica Federal provide significant leverage in negotiations. This scale allows them to command favorable terms, reducing the impact of any single reinsurer.
Technology providers are another key supplier group, and while crucial for digital transformation, this sector is characterized by increasing competition. The availability of multiple vendors offering advanced platforms for insurance operations means Caixa Seguridade can choose from a competitive landscape, further diminishing the bargaining power of individual technology suppliers. This competitive environment allows Caixa Seguridade to secure advantageous contracts for its technological infrastructure.
The extensive banking network of Caixa Econômica Federal serves as a critical distribution channel for Caixa Seguridade, effectively acting as a powerful supplier. This deep integration means Caixa Seguridade has privileged access to a vast customer base across Brazil, significantly diminishing the bargaining power of other potential distribution partners.
In 2023, Caixa Econômica Federal reported over 26,000 service points nationwide, providing Caixa Seguridade with unparalleled reach. This captive distribution network is a substantial competitive advantage, as it allows for cost-effective customer acquisition and service delivery, thereby limiting the leverage of external distribution suppliers.
Suppliers of regulatory compliance services, including legal and consulting firms focused on Brazil's insurance market, possess considerable leverage. The intricate and ever-changing regulatory environment, highlighted by the upcoming Brazilian Insurance Act (Law No. 15,040/2024) effective December 2025, creates a significant need for specialized legal and compliance expertise. This increased demand for these niche services naturally enhances the bargaining power of these essential suppliers.
Underwriting and Actuarial Services
Specialized underwriting and actuarial service providers are crucial for Caixa Seguridade's risk assessment and product development, granting them a degree of bargaining power. The insurance sector's reliance on accurate risk modeling and competitive pricing means that firms with unique expertise in these areas can command influence.
For instance, the demand for sophisticated actuarial modeling, especially in areas like climate risk or advanced mortality studies, can empower niche providers. In 2024, the global actuarial services market was valued at approximately USD 25 billion, with a projected compound annual growth rate of over 5%, indicating sustained demand for specialized skills.
- High Demand for Niche Expertise: Providers with specialized skills in areas like AI-driven underwriting or complex catastrophe modeling hold stronger negotiating positions.
- Switching Costs: The integration of actuarial and underwriting systems can create significant switching costs for Caixa Seguridade, deterring easy transitions to new providers.
- Concentration of Providers: If the market for a specific actuarial service is dominated by a few key players, their collective bargaining power increases.
- Regulatory Compliance: Suppliers who are adept at navigating evolving regulatory landscapes in insurance can be indispensable, enhancing their leverage.
Financial Market Conditions
Broader financial market conditions, particularly interest rate movements, directly impact Caixa Seguridade's cost of capital and its capacity to effectively manage its substantial insurance reserves. For instance, in 2024, persistently high interest rates, while potentially boosting investment income on reserves, also increase the cost of borrowing if the company needs external financing. This dynamic can alter the profitability of long-term insurance products and the appeal of private pension plans, indirectly influencing the perceived cost of these financial inputs.
Fluctuations in investment opportunities also play a critical role. A challenging investment landscape in 2024, characterized by market volatility, could limit Caixa Seguridade's ability to generate attractive returns on its invested assets, thereby increasing the effective cost of providing insurance coverage and pension benefits. This necessitates a careful balancing act between risk and reward to maintain competitive pricing and profitability.
- Interest Rate Impact: Rising interest rates in 2024 can increase investment income on reserves but also raise borrowing costs for Caixa Seguridade.
- Investment Opportunity Shifts: Market volatility in 2024 affects the returns Caixa Seguridade can achieve on its invested assets, influencing product profitability.
- Cost of Capital: Overall financial market health dictates the cost of capital, directly impacting Caixa Seguridade's operational expenses and strategic investment capacity.
Caixa Seguridade's bargaining power with suppliers is generally moderate, influenced by its scale and strategic partnerships. While the company benefits from limited supplier concentration in reinsurance and a competitive technology vendor market, it faces higher supplier leverage from specialized regulatory and actuarial service providers due to the complexity of Brazil's insurance landscape. The intrinsic link with Caixa Econômica Federal's vast distribution network significantly reduces reliance on external distribution channels, thereby limiting supplier power in that domain.
The increasing demand for specialized skills in actuarial services, evidenced by a global market valued at approximately USD 25 billion in 2024, grants these niche providers considerable influence. Similarly, the evolving regulatory environment, with new legislation like Law No. 15,040/2024 set to take effect in December 2025, amplifies the bargaining power of legal and compliance consultants. These factors necessitate careful supplier relationship management to maintain favorable terms and operational efficiency.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Factors | Caixa Seguridade's Position |
|---|---|---|
| Reinsurers | Supplier concentration, Caixa Seguridade's scale | Moderate to Low (due to scale) |
| Technology Providers | Competition among vendors | Low (due to competitive landscape) |
| Distribution (Caixa Econômica Federal) | Integration, network size | Very Low (captive channel) |
| Regulatory/Legal Services | Complexity of regulations, niche expertise | High (due to specialized needs) |
| Actuarial/Underwriting Services | Specialized skills, switching costs | Moderate to High (due to demand for expertise) |
What is included in the product
Explores market dynamics that deter new entrants and protect incumbents like Caixa Seguridade, while assessing the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers within the Brazilian insurance sector.
Understand the competitive landscape for Caixa Seguridade's insurance products with a clear, one-sheet summary of all five forces—perfect for quick decision-making.
Customers Bargaining Power
Caixa Seguridade leverages Caixa Econômica Federal's extensive customer base, estimated in the tens of millions, significantly diminishing the bargaining power of individual customers. This broad reach means that the sheer volume of clients limits the ability of any single customer to negotiate terms.
The bancassurance model, where insurance and financial products are offered directly through banking channels, fosters strong customer loyalty. This integration makes it less likely for customers to seek alternative providers, further consolidating Caixa Seguridade's market position and reducing customer leverage.
While Caixa Seguridade benefits from a large customer base, specific segments like auto and basic personal insurance exhibit notable price sensitivity. This means customers in these areas have more power to compare offerings and seek out the best deals, influencing pricing strategies.
The Brazilian insurance market experienced growth in 2024, yet increased competition within these price-sensitive segments allows customers to exert leverage. They can more easily switch providers if prices are perceived as too high, forcing insurers to remain competitive on cost.
Customers in Brazil's insurance sector are increasingly empowered by readily available information and digital platforms. This allows them to easily compare products and prices from various providers. For instance, by mid-2024, a significant portion of Brazilian consumers were actively using online comparison tools for financial services, a trend that directly impacts insurers like Caixa Seguridade.
While Caixa Seguridade leverages its own digital offering, Youse, the broader digital transformation across the Brazilian insurance market amplifies customer bargaining power. This digital shift means consumers have more avenues to research, negotiate, and switch providers, forcing companies to offer competitive pricing and superior service to retain business.
Switching Costs
Switching costs for Caixa Seguridade's customers can vary. For standalone products like some private pension plans, customers might find it relatively easy to transfer their assets if they discover better terms or investment options with competitors. This low friction encourages price sensitivity.
However, when Caixa Seguridade's offerings are bundled or deeply integrated with the broader services of Caixa Econômica Federal, the effort required to switch increases. This integration can create higher switching costs, as customers might need to untangle multiple financial relationships, potentially impacting convenience and incurring administrative hurdles.
For instance, a customer with a pension plan linked to a specific Caixa checking account might face more complexity in moving their savings compared to someone with only an insurance policy. This difference in integration directly influences the bargaining power of these customer segments.
- Low Switching Costs: Customers with standalone products can easily move their funds if better offers arise.
- High Switching Costs: Bundled products or those tied to Caixa Econômica Federal's banking infrastructure present greater friction for switching.
- Impact on Bargaining Power: Higher switching costs generally reduce customer bargaining power by increasing the inconvenience of changing providers.
Regulatory Protections for Consumers
Regulatory developments, such as the Brazilian Insurance Act, are increasingly emphasizing consumer protection, which can indirectly bolster customer bargaining power. These regulations aim to create a fairer playing field, giving consumers more leverage when choosing insurance products.
Regulations that enhance transparency and simplify insurance processes empower customers by providing them with clearer information and more straightforward options. This increased confidence and understanding can lead to greater price sensitivity and a willingness to switch providers, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
- Consumer Protection Focus: Laws like the Brazilian Insurance Act mandate greater transparency and fairness in insurance contracts.
- Informed Decisions: Simplified processes and accessible information allow consumers to compare offerings more effectively.
- Increased Competition: Enhanced consumer confidence can drive competition among insurers, benefiting customers.
The bargaining power of customers for Caixa Seguridade is moderate, influenced by product type and market dynamics. While the sheer scale of Caixa Econômica Federal's customer base limits individual leverage, increased market transparency and digital comparison tools in 2024 empower price-sensitive segments. Higher switching costs for integrated products can mitigate this power, but regulatory pushes for consumer protection are a counteracting force.
| Customer Segment | Switching Cost Level | Bargaining Power Influence |
|---|---|---|
| Standalone Insurance Products | Low | Higher (due to ease of comparison and switching) |
| Bundled Financial Services (with Caixa Econômica Federal) | High | Lower (due to increased complexity and inconvenience of switching) |
| Price-Sensitive Segments (e.g., auto, basic personal insurance) | Variable | Moderate to High (driven by market competition and information accessibility) |
Same Document Delivered
Caixa Seguridade Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of Caixa Seguridade's competitive landscape through a detailed Porter's Five Forces analysis, covering the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, the threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This in-depth analysis is crucial for strategic decision-making within the insurance sector.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Brazilian insurance market presents a dynamic landscape, characterized by its substantial size and ongoing expansion. Total premiums hit BRL 153.4 billion by September 2024, and the market surpassed R$400 billion for the entire year of 2024, demonstrating robust growth. This increasing market value naturally draws a multitude of participants, ranging from established domestic giants to agile international insurers, intensifying competitive pressures.
Caixa Seguridade benefits immensely from its robust bancassurance model, deeply integrated with Caixa Econômica Federal's vast retail network. This allows them to reach a broad customer base across Brazil, a crucial advantage in a fragmented insurance market.
This distribution power translates into tangible results; in 2023, Caixa Seguridade's insurance premiums reached R$22.2 billion, showcasing the effectiveness of their channel strategy. This extensive reach significantly intensifies competitive rivalry by providing unparalleled access to potential customers.
Caixa Seguridade operates in a highly competitive landscape, featuring robust domestic players such as Bradesco Vida e Previdência, alongside other significant Brazilian financial institutions. This domestic strength is further amplified by the presence of major international insurers vying for market share across diverse insurance segments.
The intense rivalry spans across critical lines of business, including life insurance, property insurance, and auto insurance. For instance, in 2023, the Brazilian insurance market saw significant premium growth, with life and pension segments showing particular dynamism, indicating active competition among all major participants.
Digital Transformation and Insurtech Growth
The competitive rivalry within the insurance sector is significantly amplified by the burgeoning insurtech landscape in Brazil. Early 2025 saw substantial funding rounds for these agile, digitally-native companies, injecting innovation and new competitive pressures. These insurtechs are challenging traditional players by offering streamlined digital-first products and novel business models, forcing established entities to adapt or risk losing market share.
While Caixa Seguridade benefits from its digital subsidiary, Youse, the broader insurtech ecosystem presents a dynamic and increasingly crowded competitive environment. The rapid growth and investment in insurtechs mean that new entrants are constantly emerging, each vying for customer attention with unique value propositions and often more flexible operational structures. This heightened rivalry necessitates continuous investment in digital capabilities and customer experience to remain competitive.
Key indicators of this intensified rivalry include:
- Increased Insurtech Funding: Brazilian insurtechs collectively secured over R$500 million in venture capital funding in the first half of 2025, a notable surge from the previous year.
- Digital-First Product Launches: Over 20 new digital insurance products were introduced by insurtechs in 2024, targeting specific niches and customer segments underserved by traditional insurers.
- Customer Acquisition Costs: The heightened competition has led to an estimated 15% increase in customer acquisition costs for digital channels as companies vie for online visibility and engagement.
Regulatory Changes and Market Adaptation
Ongoing regulatory shifts, like the implementation of the new Brazilian Insurance Act and SUSEP's strategic regulatory agenda for 2025, are poised to significantly alter the competitive dynamics within the insurance sector. These evolving rules create both challenges and opportunities for established players and new entrants alike.
Companies demonstrating agility in adapting to these regulatory changes, such as those that can quickly integrate new compliance requirements or capitalize on emerging product allowances, are likely to secure a distinct competitive advantage. For instance, SUSEP's focus on digital transformation and consumer protection, as outlined in its 2025 plan, will reward insurers who invest in compliant technology and transparent customer practices.
- Regulatory Impact: The new Brazilian Insurance Act and SUSEP's 2025 regulatory plan are key drivers of change, influencing product development, capital requirements, and operational procedures.
- Adaptation as a Differentiator: Insurers proactively adjusting to these regulations, perhaps by enhancing digital platforms or strengthening data privacy measures, will be better positioned than slower-moving competitors.
- Market Opportunities: Regulatory adjustments may open avenues for innovative products or distribution channels, rewarding firms that can identify and exploit these new market spaces.
Caixa Seguridade faces intense competition from both established domestic insurers like Bradesco Vida e Previdência and a growing number of agile insurtechs. The market saw over 20 new digital insurance products launched by insurtechs in 2024, and these companies secured over R$500 million in venture capital in the first half of 2025. This rivalry drives up customer acquisition costs by an estimated 15% in digital channels.
| Competitor Type | Key Players | 2024/2025 Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Domestic Insurers | Bradesco Vida e Previdência, Other Brazilian Financial Institutions | Significant market share, established customer bases |
| International Insurers | Various Global Insurance Companies | Expanding presence, diverse product offerings |
| Insurtechs | Youse (Caixa's subsidiary), Numerous Startups | Rapid innovation, digital-first products, increased funding (R$500M+ H1 2025) |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For private pension plans, direct savings vehicles like mutual funds or investment products offered by banks and asset managers represent significant substitutes. These alternatives often provide greater flexibility and potentially higher returns, drawing customers away from traditional insurance-based pension products.
The current economic climate, with rising interest rates in 2024, further enhances the attractiveness of direct savings. As interest rates climb, traditional savings accounts and fixed-income investments become more competitive, potentially offering a more appealing alternative to certain insurance-linked savings products, especially those with lower guaranteed returns.
Brazil's public social security programs, the Regime Geral de Previdência Social (RGPS) and the Regime Próprio de Previdência Social (RPPS), represent a significant substitute for private pension plans. These government-backed schemes offer a foundational level of retirement income, particularly for those primarily concerned with basic coverage.
The existence of these mandatory government programs can diminish the perceived urgency for individuals to seek out private pension solutions. While private plans often offer supplementary benefits and potentially higher returns, the guaranteed, albeit often lower, payout from public sources acts as a powerful substitute, especially for a large segment of the population prioritizing security over enhanced returns.
For instance, in 2023, the RGPS covered over 38 million beneficiaries, highlighting its extensive reach and the reliance many Brazilians place on it for their retirement security. This broad coverage directly competes with the market for private pension products offered by companies like Caixa Seguridade.
Self-insurance, also known as risk retention, presents a viable substitute for traditional insurance products, particularly for larger, financially robust corporations. This strategy involves a company setting aside its own funds to cover potential losses rather than paying premiums to an external insurer. For instance, in 2024, many large enterprises with well-established risk management protocols might find the cost of comprehensive insurance for predictable, lower-severity events to be a greater financial burden than self-insuring for those specific risks.
This approach is most effective for risks that are well-understood, quantifiable, and have a relatively low probability of catastrophic occurrence. Companies can effectively act as their own insurer for certain liabilities, such as minor property damage or employee injury claims, by establishing dedicated reserve funds. The decision to self-insure often hinges on a detailed cost-benefit analysis, comparing the potential cost of retained losses against the expense of insurance premiums and administrative fees. For example, a large manufacturing firm might self-insure its fleet of vehicles for minor fender-benders, saving on insurance overhead, while still insuring against major accidents.
Alternative Financial Products
The threat of substitutes for Caixa Seguridade's traditional insurance products is significant, as consumers increasingly explore alternative avenues for financial security and wealth accumulation. Beyond core insurance offerings, various financial instruments and services can effectively address similar needs, potentially diverting customer interest and capital.
For instance, readily accessible credit lines or robust emergency funds can serve as substitutes for certain short-term protection products, offering immediate liquidity and a safety net without the commitment of insurance premiums. In 2024, the growth of digital lending platforms and the increasing emphasis on personal savings highlight this trend.
Furthermore, direct real estate investments or other alternative asset classes are increasingly viewed as viable substitutes for long-term savings and investment products traditionally offered by insurers. As of early 2025, reports indicate a continued strong interest in real estate as a hedge against inflation and a source of passive income, potentially impacting long-term savings product uptake.
- Alternative Savings Vehicles: The rise of fintech platforms offering high-yield savings accounts and investment apps provides accessible alternatives to life insurance-linked savings plans.
- Credit and Liquidity Solutions: Personal loans and flexible credit facilities can substitute for credit life insurance or short-term income protection.
- Direct Investment Opportunities: Real estate, cryptocurrencies, and peer-to-peer lending present direct investment avenues that compete with traditional annuity and investment-linked insurance products.
- Government Social Programs: In some markets, expanded government social security nets and unemployment benefits can reduce the perceived need for certain private insurance coverage.
Informal Protection Mechanisms
For Caixa Seguridade, informal protection mechanisms can pose a threat, especially in segments of the population with limited access to formal financial services. These community-based or family support networks often act as substitutes for formal insurance products, particularly among lower-income brackets. For instance, in Brazil, a significant portion of the population relies on informal savings groups or familial assistance for unexpected financial needs, potentially reducing demand for formal insurance offerings.
These informal networks can be particularly resilient where formal insurance penetration remains low. In 2024, while Brazil's overall insurance penetration rate is growing, it still lags behind more developed economies. This gap provides fertile ground for informal mechanisms to thrive, offering a perceived lower-cost or more accessible alternative for risk mitigation, thereby impacting Caixa Seguridade's market share in certain segments.
- Informal Protection as Substitute: Family support and community-based safety nets offer alternatives to formal insurance.
- Lower-Income Segment Impact: These informal mechanisms are more prevalent in lower-income demographics with limited access to formal financial services.
- Brazil's Insurance Penetration: While growing, Brazil's 2024 insurance penetration rate still presents opportunities for informal solutions to compete.
The threat of substitutes for Caixa Seguridade's offerings is multifaceted, encompassing both formal financial products and informal support systems. Direct savings vehicles, government social programs, and even self-insurance strategies can siphon demand away from traditional insurance and pension products.
In 2024, rising interest rates made traditional savings accounts more competitive against certain insurance-linked products, while Brazil's extensive public social security system, the RGPS, covers millions, acting as a foundational safety net. Furthermore, informal protection networks remain significant, particularly in lower-income segments where formal insurance penetration is still developing.
| Substitute Type | Description | Impact on Caixa Seguridade | 2024/2025 Relevance |
| Direct Savings Vehicles | Mutual funds, investment apps, high-yield savings accounts | Diverts capital from insurance-linked savings | Increased attractiveness due to rising interest rates |
| Government Social Programs | RGPS, RPPS (Brazil) | Provides basic retirement income, reducing perceived need for private plans | Covers over 38 million beneficiaries (2023 data), highlighting broad reach |
| Self-Insurance | Companies setting aside funds for losses | Viable for large corporations with predictable risks | Cost-benefit analysis favors self-insurance for lower-severity events |
| Informal Protection | Family support, community savings groups | Offers risk mitigation in lower-income segments | Significant where formal insurance penetration is low; Brazil's rate growing but still presents opportunity for informal solutions |
Entrants Threaten
High regulatory barriers significantly deter new entrants in the Brazilian insurance sector. The Superintendence of Private Insurance (SUSEP) enforces stringent capital requirements and complex licensing processes, making it challenging for newcomers to establish a foothold. For instance, the upcoming Brazilian Insurance Act, effective December 2025, is expected to further enhance these regulatory hurdles, demanding even greater compliance and financial robustness from any aspiring insurer.
Setting up an insurance business, particularly one that covers various insurance types like Caixa Seguridade, demands significant upfront capital. This investment is needed for building essential infrastructure, acquiring advanced technology, and recruiting skilled personnel. For instance, the Brazilian insurance market is projected to reach USD 135.7 billion by 2025, highlighting the considerable financial resources new entrants must possess to compete effectively.
Caixa Seguridade's strong brand recognition, deeply rooted in its affiliation with Caixa Econômica Federal, presents a substantial barrier to new entrants. This established trust, cultivated over years of reliable service, makes it difficult for newcomers to gain market traction. For instance, in 2023, Caixa Econômica Federal maintained a leading position in customer deposits, underscoring the deep trust consumers place in the brand, which extends to its insurance arm, Caixa Seguridade.
Distribution Network Challenges
The sheer scale and established nature of Caixa Seguridade's distribution network present a formidable barrier to new entrants. Replicating access to Caixa Econômica Federal's vast branch network, its legion of lottery dealers, and its extensive base of banking correspondents would require immense capital investment and time, if it's even feasible.
This proprietary channel is not easily duplicated; it represents a significant competitive advantage that new insurers would struggle to overcome. For instance, in 2024, Caixa Econômica Federal boasted over 3,400 branches and a network of over 13,000 lottery outlets, providing unparalleled reach across Brazil.
- Extensive Reach: Caixa Seguridade leverages Caixa Econômica Federal's over 3,400 branches and more than 13,000 lottery outlets as of 2024.
- High Replication Cost: New entrants face prohibitive costs and significant time investment to build a comparable distribution infrastructure.
- Proprietary Advantage: The deeply embedded and trusted nature of Caixa's network is a difficult-to-replicate proprietary asset.
Rise of Insurtechs and Niche Players
While the insurance industry generally boasts high barriers to entry, the emergence of insurtechs, particularly those adept at digital distribution and catering to specific market niches, presents a growing threat. These agile companies can bypass traditional infrastructure, offering streamlined customer experiences and potentially lower operating costs.
Investment in insurtechs in Latin America, with Brazil as a key market, has shown a notable uptick in early 2025. This surge in funding suggests increased entrepreneurial activity and a greater capacity for new players to challenge established incumbents like Caixa Seguridade.
- Insurtech Funding Growth: Latin American insurtechs secured significant investment rounds in early 2025, signaling growing investor confidence and market potential.
- Digital Distribution Advantage: New entrants often leverage digital-first strategies, enabling them to reach customers more efficiently than traditional, branch-heavy models.
- Niche Market Focus: Insurtechs can successfully target underserved or specialized market segments, creating competitive pressure on broader insurers.
The threat of new entrants for Caixa Seguridade is generally low due to substantial barriers. However, the evolving landscape of insurtechs, fueled by increasing investment and digital capabilities, presents a growing challenge. These agile players can bypass traditional distribution models, offering specialized products and streamlined customer experiences, potentially eroding market share in specific segments.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Caixa Seguridade's Advantage | 2024/2025 Data Point |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regulatory | Stringent capital requirements and licensing by SUSEP. | High barrier, costly compliance. | Established compliance infrastructure. | Upcoming Brazilian Insurance Act (Dec 2025) to increase hurdles. |
| Capital Intensity | Significant upfront investment for infrastructure and technology. | Demands substantial financial resources. | Strong financial backing via Caixa Econômica Federal. | Brazilian insurance market projected at USD 135.7 billion by 2025. |
| Brand Loyalty | Deep trust in Caixa Econômica Federal's brand. | Difficult to gain customer trust and market share. | Leverages strong brand recognition and customer loyalty. | Caixa Econômica Federal led in customer deposits in 2023. |
| Distribution Network | Vast network of branches, lottery dealers, and banking correspondents. | Extremely high replication cost and time. | Proprietary and difficult-to-duplicate distribution channels. | Caixa Econômica Federal had over 3,400 branches and 13,000+ lottery outlets in 2024. |
| Insurtech Innovation | Digital-first strategies, niche market focus. | Potential to disrupt with lower costs and better customer experience. | Requires adaptation to digital channels. | Latin American insurtech funding increased significantly in early 2025. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Caixa Seguridade leverages data from the company's official investor relations website, annual reports, and regulatory filings. We also incorporate insights from reputable financial news outlets and industry-specific market research reports to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
