Bright Horizons Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bright Horizons Bundle
Bright Horizons operates in a dynamic market, facing pressures from intense rivalry and the constant threat of new entrants disrupting established players. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the competitive landscape effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Bright Horizons’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Bright Horizons' primary suppliers are its employees, especially qualified early childhood educators and caregivers. The childcare sector consistently grapples with staff shortages and high turnover, directly influencing wage demands and the availability of skilled professionals.
This persistent shortage significantly bolsters the bargaining power of employees. For instance, in 2024, the average hourly wage for childcare workers in the US saw an increase, reflecting the competitive landscape for talent. This trend can lead to escalating operational expenses for Bright Horizons as they compete to attract and retain qualified staff.
Bright Horizons' reliance on real estate and facility providers for its numerous childcare centers positions these entities as significant suppliers. The cost and availability of prime locations, particularly in competitive urban markets, grant landlords considerable leverage. For instance, the company's strategic plan to open and close centers in 2025 highlights the sensitivity of its operations to real estate costs and accessibility.
Suppliers of educational materials, toys, and childcare management software hold significant sway. As technology becomes more central to childcare, companies offering digital platforms, AI-powered content, and interactive learning tools are gaining importance.
The bargaining power of these educational and technology providers is amplified by the uniqueness or proprietary nature of their offerings. For instance, specialized curricula or advanced software solutions can give suppliers considerable leverage, especially if alternatives are limited or less effective for Bright Horizons.
In 2024, the edtech market saw continued growth, with investments in AI and personalized learning solutions increasing. This trend suggests that providers of innovative digital tools could command higher prices or more favorable terms, influencing Bright Horizons' operational costs and strategic choices.
Food and Catering Services
For Bright Horizons centers that offer meals, the bargaining power of food and catering suppliers is a key consideration. While the broader food supply market is often fragmented, specialized providers, especially those meeting stringent nutritional or dietary standards required for childcare, can exert more influence.
Bright Horizons' significant operational scale likely provides leverage, enabling them to achieve economies of scale in their food procurement. This scale can mitigate some of the suppliers' potential bargaining power.
- Fragmented Market: The general food supply market is typically characterized by numerous small and medium-sized suppliers, which typically limits the power of any single supplier.
- Specialized Needs: However, suppliers catering to specific dietary requirements (e.g., allergen-free, organic) or adhering to strict childcare nutritional guidelines may possess greater bargaining power due to limited alternatives.
- Economies of Scale: Bright Horizons' large network of centers allows for bulk purchasing, which strengthens their negotiating position with suppliers, potentially securing more favorable pricing and terms.
- Procurement Strategy: The company's procurement strategy, including supplier diversification and long-term contracts, also plays a crucial role in managing supplier bargaining power.
Regulatory Compliance and Training Providers
Suppliers of regulatory compliance and training services wield significant influence over Bright Horizons. The childcare industry is heavily regulated, and staying current with these rules is paramount. Providers offering specialized training programs, credentialing, and consulting services essential for compliance can therefore charge premium rates.
The critical nature of maintaining compliance means that childcare providers like Bright Horizons are often willing to pay higher fees for reliable and up-to-date expertise. This reliance on specialized knowledge grants these suppliers considerable bargaining power.
- Specialized Knowledge: Providers offering niche training for specific childcare regulations possess unique expertise.
- Critical Need: Non-compliance can lead to severe penalties, making these services indispensable.
- Limited Alternatives: Few in-house resources can match the specialized knowledge of external compliance trainers.
Bright Horizons faces significant bargaining power from its employee suppliers, particularly qualified educators, due to persistent staff shortages and high turnover in the childcare sector. This dynamic drives wage demands and impacts talent availability, as seen with the 2024 increase in childcare worker wages across the US. Real estate providers also hold leverage, especially for prime locations in competitive urban markets, influencing facility costs and accessibility, a factor highlighted by Bright Horizons' 2025 center expansion plans.
The bargaining power of suppliers for educational materials and technology is growing, particularly for those offering unique or proprietary digital solutions and AI-powered learning tools. The edtech market's 2024 growth, with increased investment in AI, indicates these providers can command higher prices. Suppliers of regulatory compliance and training services also exert considerable influence due to the childcare industry's stringent regulations and the critical need for specialized, up-to-date expertise to avoid penalties.
| Supplier Category | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on Bright Horizons | 2024/2025 Data/Trends |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employees (Educators/Caregivers) | Staff shortages, high turnover, demand for competitive wages | Increased labor costs, challenges in recruitment and retention | US childcare worker wages saw an increase in 2024. |
| Real Estate Providers | Availability and cost of prime locations, market competition | Higher facility operating expenses, strategic site selection constraints | Sensitivity to real estate costs noted in 2025 expansion plans. |
| Educational & Technology Providers | Uniqueness of offerings, proprietary software, AI integration | Potential for higher costs for advanced solutions, influence on curriculum delivery | Edtech market growth and AI investment in 2024. |
| Regulatory Compliance & Training Services | Specialized knowledge, critical need for compliance, limited alternatives | Premium pricing for essential services, reliance on external expertise | High demand for up-to-date compliance training. |
What is included in the product
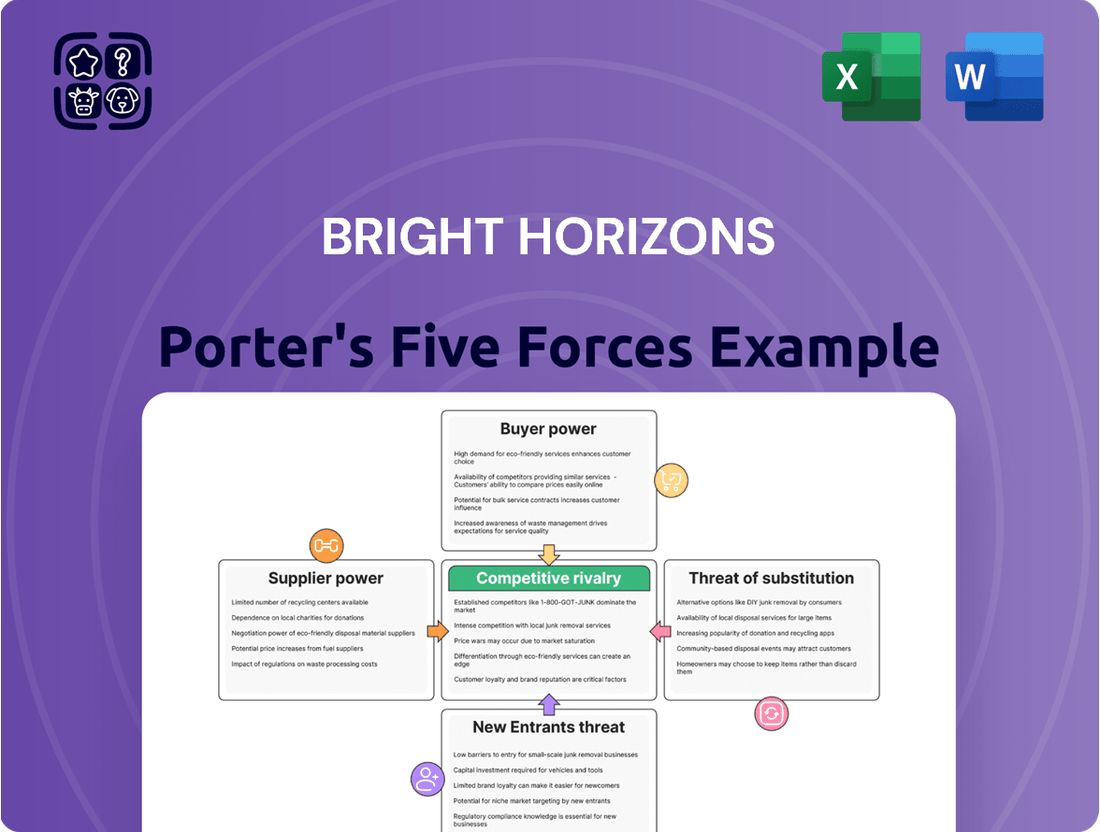
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Bright Horizons, evaluating the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the early childhood education and care industry.
Instantly visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic, interactive dashboard that simplifies complex strategic pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
Bright Horizons' primary customers are employers who sponsor childcare and work-life solutions for their employees. These corporate clients, especially large corporations, possess significant bargaining power due to the volume of services they purchase and their ability to negotiate contracts, which can impact pricing and service terms.
Employers are increasingly prioritizing childcare benefits to attract and retain talent, a trend that amplifies their demand for high-quality and flexible solutions from providers like Bright Horizons. This focus on employee well-being, particularly in the competitive 2024 labor market, empowers clients to seek favorable terms and tailored offerings.
While employers are the primary customers for Bright Horizons, individual families are the ultimate beneficiaries of their services. These families, seeking high-quality childcare and educational programs, exert indirect influence through their expectations for excellent care, engaging educational content, and adaptable scheduling. In 2024, the demand for early childhood education remained robust, with many parents prioritizing personalized learning, giving them a degree of choice in the market.
Customers, both employers and families, are increasingly demanding adaptable and personalized childcare solutions. This includes options like part-time care, drop-in services, and extended hours to accommodate diverse and evolving work schedules. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that 65% of parents found flexible scheduling to be a top priority when selecting childcare.
This growing need for flexibility directly enhances customer bargaining power. It compels providers like Bright Horizons to adjust their service models, making them more responsive to individual client requirements. When customers can easily find alternatives that better fit their unique situations, their ability to negotiate terms and pricing increases significantly.
Focus on Employee Retention and Productivity
Employers increasingly see childcare benefits, like those offered by Bright Horizons, as a critical tool for boosting employee productivity and reducing turnover. This perspective elevates the bargaining power of customers, as they demand demonstrable returns on their investment in these services. For instance, companies are increasingly tracking metrics like reduced absenteeism and higher employee retention rates directly linked to robust childcare programs.
Bright Horizons faces pressure to consistently deliver measurable outcomes that justify the cost of their services. This means proving tangible benefits such as improved employee engagement and lower recruitment costs for their clients. In 2024, many organizations reported that enhanced employee benefits, including childcare, contributed to a significant reduction in voluntary turnover, with some seeing decreases of up to 15%.
- Customer Demand for ROI: Clients expect clear evidence of improved retention and productivity from childcare benefits.
- Data-Driven Value Proposition: Bright Horizons must quantify the impact of its services on key HR metrics.
- Competitive Pressure: The growing recognition of childcare benefits as a retention tool intensifies client expectations.
- Focus on Measurable Outcomes: Success is increasingly tied to demonstrable improvements in employee engagement and reduced absenteeism.
Price Sensitivity and Budget Constraints
Employers, the primary customers for Bright Horizons, often operate with defined budgets. This means their price sensitivity is a significant factor, directly influencing how much they are willing to spend on childcare and employee benefits. For instance, in 2024, many companies are reviewing their benefits packages to manage costs effectively, potentially leading them to seek more cost-effective solutions if Bright Horizons' pricing is perceived as too high relative to the value delivered.
The ability of these corporate clients to negotiate or switch providers based on price creates downward pressure on Bright Horizons' fees. If competitors offer comparable services at a lower cost, employers have a strong incentive to explore those alternatives, impacting Bright Horizons' pricing power and profitability.
Bright Horizons must therefore strike a delicate balance. Offering high-quality, comprehensive services is essential for attracting and retaining clients, but this must be weighed against the need to maintain competitive pricing. This dynamic is particularly relevant in 2024 as businesses navigate economic uncertainties and prioritize return on investment for their benefit expenditures.
- Price Sensitivity: Employers' budget constraints directly impact their willingness to pay for childcare services.
- Competitive Pressure: The availability of alternative providers with lower pricing can force fee reductions.
- Value Proposition: Bright Horizons must demonstrate superior value to justify its pricing amidst budget-conscious clients.
- Negotiation Power: Large corporate clients can leverage their purchasing power to negotiate more favorable terms.
The bargaining power of customers, primarily employers, is a significant factor for Bright Horizons. Large corporate clients can leverage their substantial purchasing volume to negotiate favorable pricing and service terms. In 2024, the emphasis on employee retention and productivity means employers view childcare benefits as a strategic investment, further enhancing their ability to demand value and tailored solutions.
Customers, both businesses and families, increasingly seek flexibility and demonstrable return on investment. This demand for adaptable services, such as part-time care and data-backed improvements in employee engagement, strengthens their negotiating position. Bright Horizons must balance premium service delivery with competitive pricing to meet these evolving client expectations.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Driver | Impact on Bright Horizons | 2024 Trend Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Employers (Sponsors) | Volume Purchasing Power | Downward pressure on pricing, negotiation of contract terms | Large corporations negotiate customized benefit packages. |
| Employers (Strategic Need) | Talent Attraction/Retention | Demand for high-quality, flexible, and outcome-driven solutions | Companies track reduced turnover linked to childcare benefits. |
| Families (Beneficiaries) | Demand for Quality & Flexibility | Indirect influence on service standards and offerings | 65% of parents prioritize flexible scheduling in 2024. |
| Employers (Cost Sensitivity) | Budget Constraints | Price sensitivity, potential shift to lower-cost alternatives | Businesses review benefits for cost-effectiveness. |
Full Version Awaits
Bright Horizons Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Bright Horizons Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase. You're looking at the actual, professionally formatted document, ensuring no surprises or placeholders. Once you complete your transaction, you'll gain instant access to this exact, ready-to-use analysis.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The childcare and early education sector is notably fragmented, presenting a diverse competitive landscape for Bright Horizons. This fragmentation stems from a wide array of providers, including large national chains, smaller independent centers, in-home care services, and employer-sponsored programs.
Key competitors like KinderCare Education LLC and Learning Care Group operate significant networks of centers, directly vying for market share. These major players, alongside numerous smaller regional and local providers, contribute to the intense rivalry, forcing established companies to continually innovate and maintain service quality.
Bright Horizons differentiates itself through a strong emphasis on quality early education and care, coupled with a robust brand reputation. This focus on educational excellence and a diverse client base is crucial in a market where trust and perceived quality heavily influence the selection of childcare providers by both families and corporate partners.
In 2024, Bright Horizons continued to leverage its established brand, recognized for high standards in child development and education. This reputation directly impacts its competitive standing, making it a preferred choice for parents and employers seeking reliable and high-quality childcare solutions.
Competitive rivalry within the early childhood education sector is significantly fueled by innovation in service offerings. Bright Horizons, for instance, competes by integrating technology, offering personalized learning journeys, and providing holistic work-life solutions for families. Companies that adeptly use technology to streamline operations and boost parent interaction are likely to secure a stronger market position.
Geographic and Segment-Specific Competition
Competitive rivalry for Bright Horizons is not uniform; it shifts significantly based on geographic location and specific service offerings. While the company operates internationally, the intensity of competition is often dictated by local market conditions and the strength of regional players. This means that what constitutes fierce rivalry in one area might be more moderate in another.
The backup care segment, a key growth area for Bright Horizons, faces competition across all its service lines. This underscores the pervasive nature of rivalry, as competitors vie for market share not just in core childcare but also in supplementary services like backup care. This competitive pressure necessitates continuous innovation and service differentiation.
- Regional Competitors: In 2023, the childcare market saw continued fragmentation with numerous local and regional providers, particularly impacting Bright Horizons' ability to achieve uniform pricing and service delivery across all its operating regions.
- Service Segment Focus: While Bright Horizons is a leader in full-time childcare, the backup care segment, which grew significantly in 2023, faces a different competitive set, including smaller, niche providers and employer-sponsored internal programs.
- Market Penetration: The degree of local market saturation by established providers directly influences the intensity of rivalry. For example, in densely populated urban areas with many childcare options, competition for Bright Horizons is heightened compared to less developed regions.
Talent Acquisition and Retention
The intense competition for qualified early childhood educators significantly fuels rivalry within the childcare sector. Bright Horizons, like its peers, faces the challenge of attracting and keeping skilled staff, a critical factor that directly influences service delivery and the ability to scale operations. This talent scarcity means companies are not just vying for families but also for the educators who form the backbone of their services.
The ongoing shortage of early childhood educators is a persistent issue. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projected employment of preschool and kindergarten teachers to grow 4 percent from 2022 to 2032, slower than the average for all occupations. This limited supply of qualified professionals intensifies the competition, as providers must offer competitive compensation and benefits to secure and retain their workforce.
- Talent Scarcity: A persistent shortage of early childhood educators creates a highly competitive labor market.
- Impact on Operations: Difficulty in attracting and retaining staff can limit a childcare provider's capacity and affect the consistency of service quality.
- Competitive Pressure: Companies must invest in competitive compensation, benefits, and professional development to stand out in the recruitment and retention of qualified educators.
- Industry-Wide Challenge: This talent acquisition and retention issue is not unique to Bright Horizons but is a fundamental competitive dynamic across the entire childcare industry.
The competitive rivalry in the childcare sector is intense, driven by a fragmented market with numerous providers, from large chains to small local centers. Bright Horizons differentiates itself through its commitment to quality education and a strong brand reputation, which is vital in attracting both families and corporate clients. This rivalry is further amplified by the ongoing shortage of qualified early childhood educators, forcing providers to compete fiercely for talent through competitive compensation and benefits.
| Competitor Type | Key Competitors | Competitive Factor |
|---|---|---|
| National Chains | KinderCare Education LLC, Learning Care Group | Scale of operations, brand recognition |
| Regional/Local Providers | Numerous independent centers | Local market knowledge, community ties |
| In-Home Care | Nannies, home-based care providers | Flexibility, personalized attention |
| Employer-Sponsored Programs | Internal corporate childcare solutions | Convenience for employees, tailored benefits |
SSubstitutes Threaten
In-home childcare, such as nannies, au pairs, and care provided by family members, presents a significant substitute for Bright Horizons' center-based services. These options cater to families prioritizing personalized attention and greater scheduling flexibility, directly competing with the structured environment of a childcare center.
While Bright Horizons does offer backup care that can incorporate in-home solutions, the direct, long-term provision of in-home care by families themselves or through hired help represents a distinct alternative. This substitution is particularly relevant for parents seeking a more tailored approach to their child's daily care and development.
The demand for in-home care can fluctuate based on economic conditions and parental preferences. For instance, in 2024, reports indicated a continued strong demand for nannies, with average salaries for experienced nannies in major metropolitan areas often exceeding $25 per hour, underscoring the cost consideration for families opting for this substitute.
Families facing the cost of formal childcare, such as Bright Horizons' services, may turn to informal care arrangements. These can include relying on relatives, friends, or neighbors to provide supervision and care for children. This trend is particularly pronounced when budgets are tight, as informal care is often free or significantly less expensive.
The prevalence of informal care is a notable threat. For instance, in 2024, the average annual cost of center-based infant care in the US was estimated to be over $15,000, a figure that can be prohibitive for many. This makes the availability of free or low-cost informal care a compelling alternative, directly impacting demand for paid services.
The rise of extended parental leave policies, with some companies offering up to 12 weeks of paid leave, and the widespread adoption of flexible work arrangements, such as hybrid models, can lessen the reliance on external childcare. This shift allows parents more opportunity to manage childcare responsibilities directly.
However, this evolving landscape also creates a demand for adaptable and personalized childcare options. For instance, a significant portion of parents, around 60% in a 2024 survey, expressed a preference for childcare services that could accommodate non-traditional work schedules.
Stay-at-Home Parenting
The decision for one parent to stay home, often driven by economic calculations about childcare costs versus potential earnings, presents a significant substitute threat to childcare providers like Bright Horizons. For instance, in 2024, the average annual cost of center-based infant care in the US was estimated to be around $16,000, a figure that can easily sway a household's decision if one parent's income doesn't substantially outweigh this expense.
Personal preferences also play a crucial role, with some families prioritizing in-home care and parental involvement over external services, regardless of the financial implications. This preference can be amplified during economic downturns or periods of personal reassessment, making stay-at-home parenting a more appealing alternative.
The availability of flexible work arrangements, such as remote work or part-time employment, further bolsters the substitute threat. These options allow parents to manage childcare responsibilities themselves, reducing the reliance on third-party providers.
- Economic Impact: High childcare costs, averaging over $16,000 annually for infant care in 2024, can make stay-at-home parenting a financially viable substitute.
- Personal Preferences: A growing segment of parents prioritize direct involvement in child-rearing, viewing in-home care as a superior alternative.
- Work Flexibility: Increased remote and flexible work opportunities enable parents to balance careers with childcare, reducing the need for external services.
Digital Learning Platforms and At-Home Educational Resources
The threat of substitutes for early education programs, like those offered by Bright Horizons, is evolving. While digital learning platforms and at-home educational resources have become more prevalent, they primarily serve as supplementary tools rather than direct replacements for the comprehensive care and structured learning environments provided by established early education providers. For instance, in 2024, the global EdTech market, which includes digital learning platforms, continued its robust growth, projected to reach over $400 billion. However, parental surveys consistently indicate a strong preference for in-person social interaction and guided development, aspects that digital solutions can only partially replicate.
These digital and at-home resources, while offering flexibility and accessibility, often lack the crucial elements of social-emotional development and peer interaction that are fundamental to early childhood education. Parents are increasingly aware that while apps and online programs can reinforce learning, they do not substitute for the holistic development fostered in a professional childcare setting. Data from 2024 suggests that while screen time for educational purposes has increased, parents still prioritize physical environments that encourage collaborative play and direct teacher-child engagement for their young children's foundational learning.
- Digital platforms offer supplementary learning but not comprehensive childcare.
- Parental preference leans towards in-person social and emotional development.
- The EdTech market's growth doesn't negate the value of structured early education.
The threat of substitutes for Bright Horizons' services is multifaceted, encompassing in-home care, informal arrangements, and even one parent staying home. High childcare costs, with infant care averaging over $16,000 annually in 2024, make these alternatives financially appealing. Furthermore, evolving work flexibility allows parents to manage childcare themselves, reducing reliance on external providers. While digital learning platforms are growing, they are seen as supplementary, not replacements for crucial social-emotional development offered by professional settings.
| Substitute Type | Key Drivers | 2024 Data Point |
| In-Home Care (Nannies/Au Pairs) | Personalization, Flexibility | Nanny salaries often exceeding $25/hour in major cities. |
| Informal Care (Family/Friends) | Cost Savings | Average annual infant care cost ($16,000+) makes free/low-cost options attractive. |
| Stay-at-Home Parenting | Economic Calculation, Personal Preference | Childcare costs can outweigh one parent's income potential. |
| Digital Learning Platforms | Accessibility, Supplementary Learning | Global EdTech market projected over $400 billion, but lacks social-emotional development. |
Entrants Threaten
The significant capital required to establish new, high-quality center-based childcare facilities presents a substantial hurdle for potential entrants. This includes costs for real estate acquisition or leasing, extensive renovations, specialized educational equipment, and obtaining necessary operating licenses and accreditations. For instance, in 2024, the average cost to build a new childcare center could range from $500,000 to over $2 million, depending on size and location, making it a considerable financial commitment.
This high barrier to entry effectively deters many new players, particularly those looking to replicate the scale and quality of established providers like Bright Horizons. The sheer financial outlay necessary to meet regulatory standards and provide a comprehensive learning environment means only well-funded organizations or experienced operators can realistically consider entering this market segment.
The childcare sector faces a formidable barrier to entry due to stringent regulatory and licensing requirements. These often encompass detailed health, safety, and educational standards that new businesses must meticulously adhere to. For instance, in 2024, many regions updated their child-to-staff ratios and background check protocols, adding layers of complexity and cost for aspiring operators.
Navigating this intricate web of regulations significantly increases startup expenses and extends the time it takes to become operational. New entrants must invest in compliance, staff training, and facility modifications to meet these evolving benchmarks, making it a substantial hurdle compared to less regulated industries.
Building a strong brand reputation and earning parental trust in the childcare sector is a lengthy and resource-intensive process. New entrants face a significant hurdle in replicating the established credibility and perceived quality that companies like Bright Horizons, with over 35 years of operational history, have cultivated.
In 2024, the childcare industry continues to emphasize safety, educational outcomes, and caregiver qualifications, areas where established providers often have a demonstrable track record. Bright Horizons, for instance, reported a 96% parent satisfaction rate in its 2023 annual survey, a testament to its long-standing commitment to quality and trust.
Difficulty in Attracting and Retaining Qualified Staff
The ongoing shortage of qualified early childhood educators is a major hurdle for new entrants in the childcare sector. This difficulty in finding and keeping experienced staff is a significant barrier, even for established providers. For instance, in 2023, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported a demand for over 200,000 new childcare workers, highlighting the competitive labor market.
New companies face immense challenges in building a capable workforce when even seasoned organizations struggle with recruitment and retention. This scarcity of talent directly impacts the quality of care and operational capacity, making it tough for newcomers to establish a foothold and compete effectively.
- Staffing Shortages: A persistent lack of qualified early childhood educators.
- Recruitment Difficulties: Challenges in attracting experienced personnel.
- Retention Issues: High turnover rates make it hard to maintain a stable workforce.
- Competitive Labor Market: New entrants must compete with established providers for limited talent.
Employer Partnership Network Development
The threat of new entrants into Bright Horizons' employer partnership network is relatively low. Building a strong network of corporate clients requires significant time, resources, and a demonstrated ability to deliver high-quality, integrated childcare and family support solutions.
Bright Horizons' established reputation and extensive sales infrastructure, cultivated over years of operation, present a substantial barrier. For instance, in 2024, the company continued to expand its reach, serving a significant portion of the Fortune 500 companies, a testament to the depth of its existing relationships.
- Significant Sales & Marketing Investment: New entrants would need to invest heavily in sales teams and marketing to even begin replicating Bright Horizons' existing employer relationships.
- Proven Track Record & Credibility: Demonstrating reliability and effectiveness to large corporations takes years, a hurdle new competitors must overcome.
- Integrated Solution Complexity: Offering the comprehensive suite of services that employers expect, from on-site centers to backup care and family resource programs, is a complex operational challenge.
The threat of new entrants for Bright Horizons is mitigated by substantial capital requirements, stringent regulations, and the difficulty of building trust and a qualified workforce. These factors create significant barriers, particularly for those aiming to match the scale and quality of established providers.
| Barrier Type | Description | 2024 Impact/Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High costs for real estate, renovations, and equipment. | New center construction costs: $500,000 - $2 million+. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to health, safety, and educational standards. | Updated child-to-staff ratios and background checks in many regions. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Cultivating parental confidence takes time and consistent quality. | Bright Horizons' 96% parent satisfaction rate (2023). |
| Staffing Shortages | Difficulty in recruiting and retaining qualified educators. | U.S. childcare worker demand: over 200,000 new workers needed (2023). |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Bright Horizons is built upon a robust foundation of industry-specific market research reports, proprietary customer surveys, and financial disclosures from publicly traded competitors. This blend ensures a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape, including threat of new entrants and the bargaining power of both suppliers and buyers.
