Brady Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Brady Bundle
Brady's Five Forces Analysis reveals the intricate web of competitive pressures shaping its market landscape. Understanding the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threats of substitutes and new entrants is crucial for strategic success. This framework highlights where Brady can build sustainable advantages.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Brady’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Brady Corporation's reliance on specialized materials, such as pressure-sensitive adhesives and unique plastics, positions certain suppliers with significant bargaining power. These suppliers may offer components that are critical and difficult to substitute, giving them leverage in price negotiations and supply terms.
The concentration of Brady's sourcing, with approximately 37% of its raw materials originating from Asia, further amplifies this supplier power. If a limited number of Asian suppliers control the production of key components, they can dictate terms more effectively, potentially impacting Brady's cost of goods sold and production schedules.
Brady faces significant switching costs for critical components, such as specialized printing materials or unique safety device parts. For instance, in 2024, the cost to retool production lines for new materials could range from tens of thousands to over a million dollars, depending on the complexity. This includes expenses for re-qualifying new suppliers and the potential for production disruptions, which can halt output for weeks. These high barriers empower existing suppliers with greater leverage over pricing and contract terms, impacting Brady's operational costs and flexibility.
The availability of substitute raw materials or components significantly impacts the bargaining power of Brady's suppliers. For instance, if alternative plastics for labels or different metals for safety devices are readily available and perform comparably, Brady gains leverage.
In 2024, the global chemical industry, a key supplier segment for Brady, saw prices for certain petrochemical derivatives fluctuate, influenced by crude oil prices and geopolitical events. However, the development of bio-based plastics and recycled material options offered alternative sourcing avenues for label manufacturers, slightly mitigating the power of traditional plastic resin suppliers.
Should a high degree of substitutability exist, Brady can more effectively negotiate pricing and terms with its current suppliers, as the threat of switching to an alternative source is credible and easily executable.
This substitutability directly translates to a reduced reliance on any single supplier, thereby lowering their overall bargaining power and enhancing Brady's procurement flexibility.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into manufacturing identification solutions or workplace safety products can significantly bolster their bargaining power. This means suppliers might decide to produce and sell these end products themselves, directly competing with companies like Brady. For instance, a supplier of specialized RFID chips for asset tracking might possess the technical know-how to develop and market their own tracking solutions.
This particular threat is typically less pronounced for suppliers of highly specialized raw materials, as they often lack the broader market understanding and distribution networks to effectively compete in finished goods. However, for manufacturers of more standardized components, the incentive to move up the value chain can be substantial. Consider a producer of generic safety signage materials; they might see an opportunity to offer pre-made signs directly to end-users.
Brady Corporation's robust and diversified product portfolio, encompassing a wide array of safety and identification solutions, along with its well-established global distribution channels and strong customer relationships, can serve as a crucial buffer against this threat. Their ability to offer integrated solutions and maintain direct customer engagement reduces the likelihood of suppliers finding a viable path to forward integration that bypasses Brady. For example, in 2023, Brady reported net sales of $1.39 billion, demonstrating significant market penetration that makes it challenging for component suppliers to replicate their reach.
The bargaining power of suppliers is influenced by several factors, including the threat of forward integration:
- Supplier's Capacity for Forward Integration: Suppliers with the technical expertise and financial resources to enter Brady's markets directly gain leverage.
- Incentive to Integrate: Higher profit margins in Brady's product segments can motivate suppliers to consider forward integration.
- Nature of Supplier's Product: The threat is greater for suppliers of standardized components than for those providing highly specialized inputs.
- Brady's Market Position: Brady's strong brand, diverse offerings, and extensive distribution network can deter suppliers from attempting forward integration.
Impact of Raw Material and Labor Costs
Brady Corporation is navigating inflationary pressures, particularly concerning raw material and labor costs. The company anticipates these pressures will continue to ease into fiscal year 2025. This suggests that suppliers' ability to dictate higher prices due to these cost inputs may diminish over the coming period.
Despite ongoing cost considerations, Brady's proactive strategies are designed to lessen the impact of supplier power. Through targeted pricing adjustments and a focus on operational efficiency, the company aims to absorb or pass on increased costs, thereby reducing its vulnerability to supplier price hikes.
- Managing Inflation: Brady is actively addressing inflationary impacts on raw materials and labor.
- Fiscal Year 2025 Outlook: The company expects these cost pressures to ease into fiscal year 2025.
- Strategic Mitigation: Brady employs targeted pricing and efficiency improvements to counter cost increases.
- Reduced Supplier Leverage: These actions indicate a degree of control over supplier-driven cost escalation.
The bargaining power of suppliers affects Brady Corporation's profitability when they can dictate higher prices or reduce the quality of essential inputs. This power is amplified by factors like limited supplier options, high switching costs for Brady, and a supplier's ability to integrate forward into Brady's business.
For example, in 2024, Brady's reliance on specialized plastics for its durable labeling solutions means that suppliers of these niche materials hold considerable sway. If these suppliers face increased production costs, they are more likely to pass them on to Brady, impacting the cost of goods sold.
Brady's sourcing strategy, with a significant portion of materials from Asia, also concentrates supplier power. In 2024, if geopolitical tensions or logistical disruptions affect a few key Asian suppliers, Brady could face supply shortages or price hikes.
The threat of suppliers integrating forward is a critical consideration. If a supplier of, say, RFID components were to develop and market their own asset tracking solutions, they would bypass Brady's value chain, directly challenging their market position.
| Factor | Impact on Brady | 2024/2025 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | Increased ability to set prices | Approx. 37% of raw materials from Asia |
| Switching Costs | Higher costs to change suppliers | Retooling can cost over $1 million |
| Forward Integration Threat | Potential for direct competition | Less for specialized materials, more for standardized components |
| Substitutability of Inputs | Reduced supplier leverage | Emergence of bio-based plastics offers alternatives |
What is included in the product
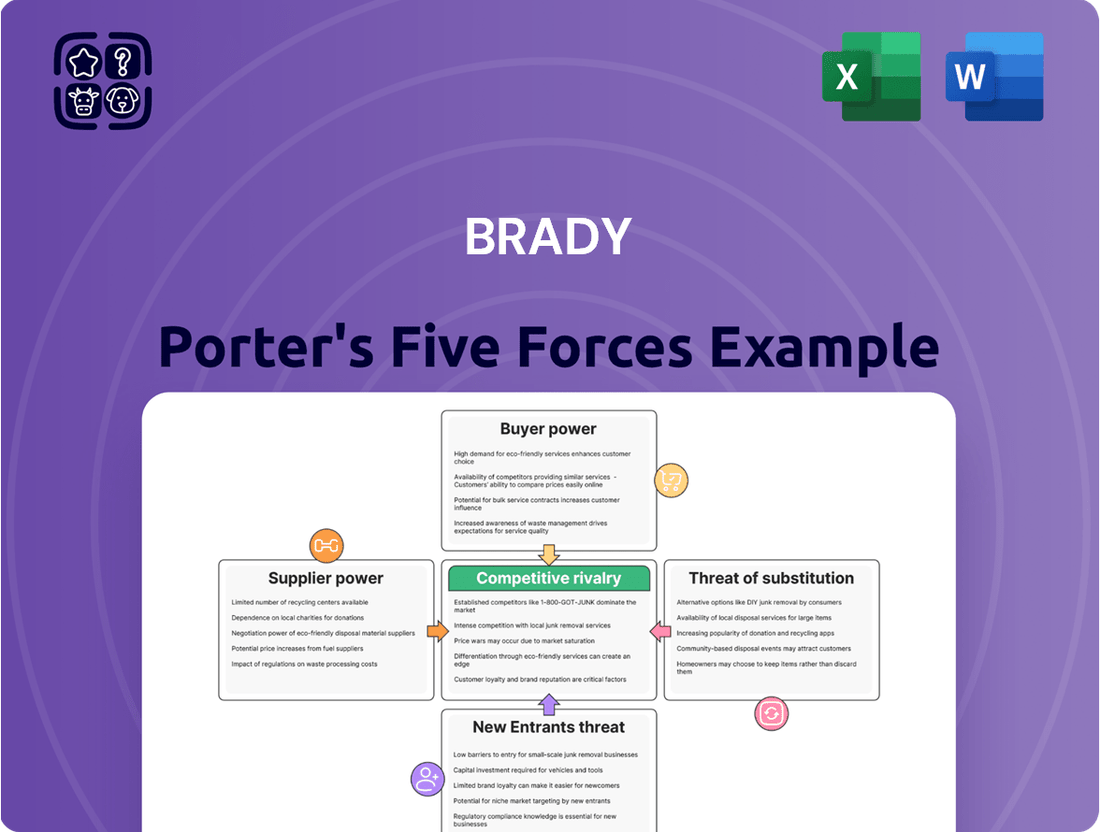
Brady Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a comprehensive framework to understand the competitive intensity and profitability of Brady's operating environment. It meticulously examines the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors.
Instantly visualize competitive intensity and identify your most impactful strategic pressures with a dynamic, interactive spider chart.
Customers Bargaining Power
Brady's diverse customer base across sectors such as electronics, telecommunications, manufacturing, healthcare, and construction helps dilute individual customer bargaining power. This broad reach means no single customer typically represents an overwhelming portion of Brady's revenue, limiting their ability to dictate terms.
However, the impact of customer concentration can shift if a few large enterprise clients or key distributors account for a substantial percentage of Brady's sales volume. These major clients, by virtue of their significant purchasing power, can indeed exert considerable pressure on pricing and contract conditions, potentially impacting Brady's profit margins.
For instance, if a top 10 customer accounted for 15% of Brady's revenue in 2024, their ability to negotiate favorable pricing or extended payment terms would be significantly higher than that of a smaller client representing less than 1% of sales.
Product differentiation significantly impacts the bargaining power of customers. When Brady offers unique, specialized identification and safety solutions, like proprietary label materials or advanced printing technologies, customers have fewer alternatives. This uniqueness, especially when tied to critical safety compliance or operational efficiency, naturally lessens a customer's leverage to demand lower prices or more favorable terms. For instance, Brady's commitment to developing solutions that meet evolving global safety standards can create a competitive moat, making it harder for customers to switch to less specialized providers without compromising on quality or regulatory adherence.
Customers investing in Brady's specialized printing systems and software for identification and safety needs often encounter substantial switching costs. These can include the expense and time required for retraining staff on new equipment and software, integrating the new systems with existing infrastructure, and the potential for operational disruptions during the transition period. For instance, a company relying on Brady's robust asset tracking software might face months of data migration and system testing if they were to consider a competitor, impacting productivity.
These significant switching costs effectively reduce the bargaining power of customers. When it becomes costly and complex to change providers, customers are less likely to seek out alternatives or demand lower prices. This sticky customer base provides Brady with a degree of pricing power and stability, as customers are more inclined to remain with the current solution despite minor price increases or feature differences compared to the hassle of switching.
Availability of Substitute Products for Customers
While direct substitutes for highly specialized, high-performance labels or critical safety devices might be scarce, customers do have options. They can explore alternative identification methods or opt for less specialized, more generic safety products that may meet basic requirements. For instance, in industrial settings, while Brady might offer advanced RFID-enabled asset tags, a customer might consider simpler barcoding solutions if the advanced features aren't strictly necessary.
Brady's strategy focuses on mitigating this threat by highlighting the perceived value and unique features of its integrated solutions. By offering comprehensive systems that combine labeling, software, and hardware, Brady differentiates itself from more commoditized alternatives. This approach aims to make customers see Brady's offerings as superior to generic products, thus reducing the perceived substitutability from the customer's viewpoint.
The availability of substitutes is a key factor in customer bargaining power. If customers can easily switch to a comparable product from a competitor with little cost or effort, their power increases. For example, if a company needs basic safety signage and many suppliers offer similar quality and pricing, customers can effectively play suppliers against each other.
- Limited direct substitutes for specialized safety and identification solutions.
- Customers may consider alternative, less specialized identification methods or safety products.
- Brady differentiates through perceived value and unique features of integrated solutions.
- The ease of switching to alternatives directly impacts customer bargaining power.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Customer price sensitivity is a significant factor in the identification and safety solutions market. Industries such as manufacturing and construction frequently contend with narrow profit margins, making them particularly attuned to the costs associated with essential supplies like safety signage and identification labels.
While Brady Corporation's offerings are recognized for enhancing safety and operational efficiency, a core customer behavior remains the pursuit of value. This is especially true for products purchased in large quantities or those that are more standardized, where minor price differences can accumulate substantially.
This price consciousness directly translates into increased bargaining power for these customers. For instance, in 2023, the industrial safety equipment market saw growth, but competitive pricing remained a key differentiator for suppliers.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers in sectors like construction and manufacturing often have tight margins, influencing their purchasing decisions.
- Volume Purchases: For high-volume, less specialized items, customers are more likely to seek out the lowest cost options.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Even with safety benefits, customers will actively compare prices to find the most economical solutions.
- Bargaining Leverage: This focus on cost gives customers more power to negotiate prices with suppliers like Brady.
The bargaining power of customers is shaped by several factors, including the availability of substitutes and the ease with which they can switch to alternative suppliers. For Brady, while highly specialized safety and identification solutions may have limited direct substitutes, customers might explore less specialized alternatives or different identification methods if Brady's premium features are not strictly essential for their needs.
Price sensitivity remains a key driver, especially in industries with tighter profit margins. Customers in sectors like manufacturing and construction are keenly aware of costs and actively seek value, particularly for high-volume or standardized items. This focus on cost-effectiveness grants them leverage to negotiate prices, making it crucial for Brady to demonstrate the superior value and efficiency of its integrated solutions.
In 2023, the global industrial safety equipment market experienced growth, but competitive pricing was a significant factor for suppliers. This highlights how customers, even when prioritizing safety, will compare options to secure the most economical solutions, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
| Factor | Impact on Brady's Customers | Brady's Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Substitutes | Customers may opt for less specialized or alternative identification methods if Brady's advanced features are not critical. | Emphasize perceived value and unique features of integrated solutions to reduce substitutability. |
| Switching Costs | High switching costs (training, integration, disruption) limit customers' ability to change providers easily. | Build customer loyalty through specialized systems and comprehensive support, increasing stickiness. |
| Price Sensitivity | Industries with tight margins (e.g., construction, manufacturing) are highly cost-conscious, especially for high-volume items. | Highlight the total cost of ownership and return on investment, focusing on safety and operational efficiency benefits. |
| Customer Concentration | Large enterprise clients or key distributors with significant purchasing power can exert considerable pressure on pricing and terms. | Diversify customer base to reduce reliance on any single large customer. |
What You See Is What You Get
Brady Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Brady Porter's Five Forces Analysis, reflecting the identical, professionally formatted document you will receive instantly upon purchase. You are viewing the exact deliverable, meticulously prepared to provide a comprehensive understanding of competitive forces within an industry. No placeholders or sample content are present; what you see is precisely what you get, ready for immediate application in your strategic planning. This ensures transparency and immediate value, allowing you to leverage this crucial analysis without delay.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The markets for identification solutions and workplace safety are quite fragmented, meaning there are many companies operating within them. This includes big, diversified corporations as well as smaller, specialized firms. For Brady Corporation, this translates into facing competition from a broad spectrum of players.
Key competitors include established names like Allegion, which offers a wide range of security and safety products, and Acuity Brands, a leader in lighting and building management solutions that often intersect with safety requirements. Generac, traditionally known for backup power, has also expanded into home and personal safety devices.
The diversity of these competitors highlights the varied nature of the markets Brady operates in. Some rivals focus on specific areas like access control or emergency lighting, while others, like large industrial conglomerates, may offer a more comprehensive suite of products that include identification and safety equipment, creating a complex competitive environment.
The rapid expansion of key markets directly influences competitive rivalry. For instance, the global workplace safety market is anticipated to experience robust growth, with a projected compound annual growth rate of 11% between 2025 and 2030. This upward trend attracts more players, naturally intensifying competition as businesses strive to capture a larger piece of this expanding pie.
Even more dynamic is the digital identity solutions market, which is forecast to surge at an impressive CAGR of 19.9% from 2025 to 2032. Such accelerated growth creates fertile ground for new entrants and encourages existing companies to innovate and aggressively pursue market share, thereby heightening the competitive landscape.
Brady's strategy heavily relies on product differentiation through significant investment in research and development. The company focuses on creating new printing systems, advanced materials, and integrated industrial track and trace solutions to set its products apart.
Continuous innovation is key to maintaining a competitive edge. This includes developing high-performance labels, incorporating smart technologies such as RFID, and building comprehensive software solutions that meet the dynamic needs of its customer base.
For example, in fiscal year 2023, Brady reported that its innovation pipeline contributed significantly to sales growth, highlighting the direct impact of R&D on market position and customer acquisition in a competitive landscape.
Exit Barriers
Companies in the industrial identification and safety products sector often face substantial exit barriers due to the significant capital required for manufacturing facilities, specialized machinery, and the development of proprietary intellectual property. These considerable upfront and ongoing investments make it economically challenging for firms to simply shut down operations when profitability wanes.
For instance, a typical advanced industrial printing press can cost upwards of $100,000, and many companies operate multiple such units. Furthermore, the research and development into new, compliant safety materials and identification technologies can run into millions annually. These high fixed costs effectively lock companies into the market.
Consequently, firms may choose to continue competing, even in less profitable times, rather than incur substantial losses from ceasing operations or selling assets at a steep discount. This dynamic can lead to intensified competitive rivalry as businesses strive to maintain market share and cover their substantial exit costs.
- High Capital Investment: Significant outlays for specialized manufacturing equipment and R&D in compliance and technology.
- Asset Specificity: Equipment and intellectual property are often highly specialized, limiting resale value and increasing exit costs.
- Continued Competition: Companies may operate at lower profit margins to avoid substantial losses associated with exiting the market.
- Intensified Rivalry: The reluctance to exit due to high barriers can prolong periods of intense competition among existing players.
Competitive Strategies and Acquisitions
Brady Corporation's competitive landscape is marked by a dynamic interplay of strategic moves and consolidation. The company actively pursues digital enhancements and superior customer service, initiatives mirrored by its rivals aiming to capture market share. Acquisitions like Gravotech and Funai are key to Brady's strategy, broadening its product and service portfolio to compete more effectively.
This environment fosters a climate where competitors also leverage mergers and acquisitions to bolster their capabilities and market reach. For instance, the industrial identification and traceability sector, where Brady operates, saw significant M&A activity in 2023 and early 2024 as companies sought to expand their offerings and geographical presence. Companies like Zebra Technologies and Honeywell are frequently cited as major competitors, often engaging in similar strategic acquisitions to stay ahead.
- Digital Transformation: Competitors are investing heavily in digital platforms and solutions to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency.
- Acquisition-Led Growth: The industry is characterized by strategic acquisitions aimed at consolidating market share and expanding product lines, a trend observed throughout 2023 and into 2024.
- Customer Centricity: A strong focus on customer service and support is a critical differentiator, with companies enhancing their service networks and digital support channels.
- Product Innovation: Continuous investment in research and development to introduce new technologies and improve existing product offerings remains a key competitive driver.
Competitive rivalry within Brady Corporation's markets is intense due to a fragmented industry structure and significant growth potential. Competitors like Allegion, Acuity Brands, and Generac actively vie for market share, with many focusing on niche areas while others offer broader safety and identification solutions. This dynamic is fueled by expanding markets, such as the global workplace safety market projected to grow at an 11% CAGR from 2025-2030, and the digital identity solutions market, expected to surge at a 19.9% CAGR from 2025-2032.
SSubstitutes Threaten
While Brady Corporation's core business relies on traditional labels and signs, the rise of digital identity solutions and advanced tracking technologies like RFID presents a significant threat of substitutes. The global digital identity solutions market is experiencing robust growth, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 15% through 2027. This trend highlights a move towards non-physical or digitally integrated identification methods that could potentially replace or reduce the need for some of Brady's conventional products.
The adoption of substitute solutions, like advanced software for asset tracking or digital safety protocols, hinges on their cost-effectiveness and performance compared to Brady's physical products. For instance, as of early 2024, the market for digital asset management software is projected to grow significantly, with some segments expecting CAGR of over 15% through 2028, indicating increasing investor interest and potential adoption.
If these digital alternatives provide demonstrably superior efficiency or long-term cost savings, even with a higher initial investment, they represent a considerable threat. Companies are increasingly willing to invest in digital transformation, and if the ROI for digital safety and tracking solutions becomes clearer and more compelling than that of traditional physical products, Brady could see market share erosion.
Technological advancements are a significant threat of substitutes in workplace safety and identification. Rapid progress in areas like the Internet of Things (IoT), Artificial Intelligence (AI), and robotics is creating entirely new solutions that can replace traditional physical products. For instance, IoT-enabled wearables can monitor worker health and location in real-time, offering a digital substitute for basic ID badges or manual check-ins.
AI-powered video analytics can identify unauthorized access or unsafe behaviors, potentially reducing the need for manual surveillance or physical security barriers. Predictive safety tools, leveraging AI and machine learning, can forecast potential hazards, offering a proactive digital solution rather than relying solely on reactive safety equipment. These tech-driven alternatives are becoming increasingly sophisticated and cost-effective, presenting a compelling case for businesses to adopt them over older, physical methods.
Customer Switching Costs to Substitutes
Switching from traditional identification and safety products to newer technological alternatives, such as moving from physical labels to RFID or from static signs to dynamic smart sensors, often incurs substantial upfront costs. These investments can encompass new hardware, specialized training for personnel, and the necessary overhaul of existing operational processes.
These elevated switching costs act as a significant barrier, effectively moderating the immediate threat posed by these technological substitutes. For instance, a company investing heavily in a legacy barcode system might be hesitant to adopt an RFID solution without a clear and substantial return on investment, given the cost of new readers, tags, and integration.
The financial commitment required can be substantial. For example, implementing a comprehensive RFID system across a large manufacturing facility, including tags for thousands of assets and new scanning infrastructure, could easily run into hundreds of thousands or even millions of dollars. This capital expenditure is a key factor that influences the pace at which substitutes gain market traction.
Consider these factors when evaluating the threat of substitutes:
- Infrastructure Investment: The need to purchase new readers, servers, and network upgrades for technologies like IoT sensors or advanced biometric scanners.
- Training and Skill Development: Equipping employees with the knowledge to operate and maintain new systems, potentially requiring new hires or extensive retraining programs.
- Process Re-engineering: Adapting existing workflows and business processes to seamlessly integrate with new technological solutions.
- Data Migration and Integration: The effort and cost involved in transferring and integrating data from old systems to new ones.
Regulatory and Compliance Requirements
Many of Brady's core products are designed to meet stringent regulatory and compliance mandates across diverse sectors, particularly in workplace safety and identification. For instance, OSHA's Hazard Communication Standard (HCS) necessitates specific labeling practices for chemicals, a crucial area for Brady. Similarly, ANSI Z535 standards guide the design of safety signs and labels.
The nature of these regulations often dictates the form and function of safety and identification solutions. This means that while technological advancements might offer alternative methods for conveying information, direct substitutes for physical signs, labels, and safety devices are frequently not permissible or practical without substantial shifts in regulatory frameworks.
Consequently, the threat of substitutes is somewhat mitigated because compliance is non-negotiable for businesses. Companies cannot simply opt for a less regulated or different method if it doesn't align with established safety and identification standards.
- Regulatory Mandates: Compliance with standards like OSHA HCS and ANSI Z535 creates a demand for specific product types, limiting readily available substitutes.
- Industry Standards: Many industries rely on established physical identification and safety signage, making it difficult for new technologies to fully replace these without regulatory approval.
- Safety Imperative: The critical nature of workplace safety means that solutions must be proven and compliant, reducing the willingness to adopt unproven substitutes.
- Limited Alternatives: Without changes to existing regulations, direct substitutes for essential safety labels and signs often lack the necessary certification or acceptance.
The threat of substitutes for Brady Corporation's products is influenced by the potential for digital alternatives and technological advancements. Markets like digital identity solutions are growing rapidly, with some segments expected to see over 15% CAGR through 2027, indicating a shift towards non-physical identification methods that could reduce demand for traditional labels and signs.
Entrants Threaten
Entering the industrial identification and workplace safety market, especially for high-performance labels and safety devices, demands significant upfront capital. New players need to invest heavily in advanced manufacturing equipment, research and development for innovative products, and robust distribution channels to reach their target customers.
Brady Corporation benefits from substantial economies of scale in its manufacturing processes and raw material procurement. This allows them to produce goods at a lower per-unit cost, creating a significant barrier for new entrants who cannot yet achieve similar production volumes or purchasing power.
For instance, in fiscal year 2023, Brady reported total assets of approximately $2.6 billion, reflecting the considerable investment in its operational infrastructure. This scale makes it challenging for smaller, newly established companies to compete on price and efficiency.
The cost advantage derived from Brady's established scale means that new entrants would face a steep uphill battle to achieve comparable profitability without matching Brady's operational footprint and market share, a feat that requires immense financial resources.
Brady possesses a vast global distribution network and deep-seated relationships with a wide array of customers spanning numerous industries. This extensive infrastructure presents a formidable barrier for any potential newcomer. For instance, in 2024, the cost of establishing a comparable distribution network for industrial chemicals alone could easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars, encompassing warehousing, logistics, and sales force development.
New entrants would encounter substantial hurdles and considerable expenses in replicating Brady's established distribution channels and securing market access. This is particularly true within specialized industrial sectors where trust and long-standing partnerships are paramount. Building brand recognition and proving reliability to acquire similar market share to Brady, which reported $5.5 billion in revenue in 2023, would be a protracted and capital-intensive undertaking.
Brady Corporation, with its origins tracing back to 1914, has cultivated a strong reputation for quality and integrated solutions within its specialized industrial sectors. This deep-seated brand loyalty, built over a century, makes it exceptionally difficult and costly for newcomers to replicate the trust and recognition Brady commands among its established customer base, thus acting as a considerable deterrent.
Proprietary Technology and Intellectual Property
Brady's significant investment in research and development, particularly in advanced printing systems, specialized materials, and sophisticated software, creates a substantial barrier to entry. This commitment to innovation, evidenced by their continuous product evolution, likely results in a robust portfolio of patents and proprietary technologies. These intellectual property rights are not easily bypassed.
These protected technologies give Brady a competitive edge by making it exceedingly difficult for new players to replicate their product offerings without facing considerable financial hurdles and potential legal disputes. For instance, in 2023, companies in the industrial printing sector often spend upwards of 10-15% of revenue on R&D, a figure Brady likely matches or exceeds.
- High R&D Investment: Brady's commitment to innovation means new entrants must invest heavily to compete.
- Patented Technologies: Existing patents protect Brady's core offerings, preventing easy replication.
- Replication Costs: Developing comparable technology requires significant capital and time, deterring potential competitors.
- Legal Hurdles: Infringing on intellectual property can lead to costly litigation, further discouraging new market entrants.
Regulatory Hurdles and Compliance Expertise
The workplace safety and identification sectors are heavily regulated, requiring new companies to understand and adhere to standards set by bodies like OSHA and ISO. This means significant investment in compliance expertise and product certification processes, which can be costly and time-consuming. For instance, achieving UL certification for safety equipment can take months and cost tens of thousands of dollars. This complexity acts as a substantial barrier, deterring many potential new entrants who lack the necessary resources or knowledge to navigate these requirements effectively.
The threat of new entrants in Brady Corporation's market is significantly mitigated by the substantial capital requirements for establishing advanced manufacturing capabilities and R&D. For instance, in 2024, the cost of setting up a facility with the necessary precision printing technology could easily exceed $50 million. Furthermore, replicating Brady's extensive global distribution network, which serves diverse industrial sectors, would demand hundreds of millions in investment for logistics, warehousing, and sales infrastructure.
Brady's established economies of scale, evidenced by its 2023 total assets of approximately $2.6 billion, allow for lower per-unit production costs, creating a price disadvantage for smaller newcomers. Their strong brand reputation, built over a century, fosters customer loyalty that is difficult and expensive to overcome, while proprietary technologies and patents present significant hurdles, often requiring 10-15% of revenue for R&D investment in this sector.
| Barrier | Description | Estimated Cost/Impact for New Entrants (2024 Estimates) |
| Capital Requirements | Investment in advanced manufacturing and R&D facilities. | $50 million+ for manufacturing; substantial for R&D. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high production volume. | New entrants struggle to match Brady's cost efficiency. |
| Brand Reputation & Loyalty | Established trust and long-term customer relationships. | Costly marketing and sales efforts to build comparable recognition. |
| Intellectual Property | Patented technologies and proprietary product designs. | Significant R&D spending (10-15% of revenue) and potential legal costs. |
| Distribution Network | Extensive global logistics and sales infrastructure. | Hundreds of millions in investment for comparable reach. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to industry standards and certifications. | Tens of thousands of dollars and months for certifications like UL. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages data from investor relations websites, industry-specific market research reports, and government economic statistics to provide a comprehensive view of competitive pressures.
