Box Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Box Bundle
Porter's Five Forces reveals the intense competitive landscape Box operates within, highlighting the significant power of buyers and the constant threat of substitutes. Understanding these pressures is crucial for any business looking to navigate the cloud content management space effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Box’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Box's reliance on a few dominant cloud infrastructure providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure, significantly impacts its bargaining power as a supplier. These providers operate at a massive scale, offering specialized services that are critical to Box's operations.
The concentrated nature of the cloud infrastructure market means these providers hold considerable sway. For Box, the potential costs and complexities associated with migrating its deep integrations to a different provider can be substantial, limiting its ability to negotiate favorable terms.
In 2024, the global cloud computing market continued its robust growth, with AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud holding a combined market share exceeding 60% of the public cloud infrastructure market. This consolidation underscores the leverage these providers possess over their clients, including Box.
Suppliers providing highly specialized software components, like cutting-edge security protocols or proprietary AI algorithms, can wield significant bargaining power. This is particularly true if these components are patented or have few viable alternatives. For Box, a platform whose differentiation often hinges on unique functionalities, reliance on such suppliers can create a dependency.
The availability of skilled software engineers, cybersecurity experts, and cloud architects is paramount for Box. In 2024, the tech labor market remained competitive, with demand for these specialized roles often outstripping supply, particularly in areas like AI and machine learning integration, which are key to Box's product development.
A tight labor market, characterized by low unemployment rates for tech professionals, directly amplifies the bargaining power of these human capital suppliers. This can lead to increased salary expectations and benefit demands, directly impacting Box's operational costs and potentially affecting its ability to scale its engineering teams efficiently.
Hardware and Network Equipment Vendors
While Box largely relies on cloud infrastructure, it may still engage with hardware and network equipment vendors for its own data centers or specialized appliances. The bargaining power of these suppliers hinges on factors like product standardization, availability, and the stability of the broader supply chain. For instance, in 2024, the global semiconductor shortage continued to impact the availability and pricing of certain networking components, potentially increasing supplier leverage.
The concentration of suppliers in specific niches can also amplify their power. If only a few vendors offer critical, proprietary hardware or network solutions that Box requires, those suppliers gain significant leverage. Conversely, if Box can source components from multiple standardized providers, its own bargaining position strengthens. The overall market for IT hardware and networking equipment in 2024 saw continued consolidation in some areas, while innovation in others offered more choices.
- Supplier Concentration: The market for specialized network hardware can be concentrated, giving a few key vendors more influence.
- Product Differentiation: Highly differentiated or proprietary hardware solutions increase supplier power compared to commoditized components.
- Switching Costs: High costs associated with switching to a different hardware vendor can lock in customers and empower suppliers.
- Supply Chain Stability: Disruptions in the supply chain, as seen with semiconductor shortages in 2024, can significantly boost supplier leverage.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
Major cloud infrastructure providers, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure, possess significant bargaining power due to the threat of forward integration. These giants could easily leverage their existing infrastructure and customer base to launch competing content management and collaboration services, directly challenging Box. For instance, AWS already offers a suite of productivity tools that could be expanded to directly compete with Box's core offerings.
This potential for direct competition grants these infrastructure providers considerable leverage over Box. Box's dependence on their underlying cloud services means that any move by these providers to offer similar functionalities could disrupt Box's market position and pricing power. In 2023, the cloud computing market was valued at over $600 billion, highlighting the immense resources and reach these providers command, making their potential entry into Box's specific market segment a serious concern.
- Cloud Infrastructure Providers' Market Dominance: In 2023, AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud collectively held over 65% of the global cloud infrastructure market share, giving them substantial influence.
- Potential for Service Expansion: These providers already offer a wide array of complementary services, making the expansion into content management and collaboration a logical, lower-barrier-to-entry move.
- Leverage in Negotiations: Box's reliance on these providers for essential infrastructure services means they are vulnerable to pricing changes or the introduction of competing services that could erode Box's competitive advantage.
The bargaining power of suppliers is a critical element in Porter's Five Forces, assessing how much leverage suppliers have over a company. For Box, this power is significantly influenced by the concentration of its key suppliers, particularly in cloud infrastructure and specialized software. When few suppliers dominate a market or offer unique, indispensable components, their ability to dictate terms increases, potentially impacting Box's costs and operational flexibility.
Box's reliance on major cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud, which held over 60% of the public cloud infrastructure market in 2024, illustrates this dynamic. The high switching costs and the potential for these providers to expand into competing services amplify their leverage. Similarly, suppliers of specialized software or skilled tech talent, in a competitive 2024 labor market, can command higher prices and better terms, directly affecting Box's cost structure and strategic options.
The concentration of suppliers in niche areas, whether for proprietary hardware or critical software modules, further empowers them. If Box depends on a limited number of vendors for essential, differentiated components, these suppliers gain considerable influence. This situation is exacerbated by supply chain instabilities, such as the ongoing semiconductor shortages impacting hardware availability in 2024, which can significantly increase supplier leverage and impact pricing.
| Supplier Type | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Impact on Box | Example Data (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cloud Infrastructure Providers (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) | Market concentration, high switching costs, potential for forward integration | Increased operational costs, limited negotiation flexibility | Combined market share > 60% of public cloud infrastructure |
| Specialized Software/AI Algorithm Providers | Proprietary nature, patents, few viable alternatives | Dependency on unique functionalities, potential for higher licensing fees | High demand for AI/ML integration specialists |
| Skilled Tech Talent (Engineers, Architects) | Tight labor market, demand vs. supply | Increased salary and benefit costs, challenges in scaling teams | Competitive tech labor market with high demand for specialized roles |
| Hardware/Network Equipment Vendors | Product standardization, supply chain stability, supplier concentration | Potential price increases and availability issues for critical components | Semiconductor shortages impacting networking component availability |
What is included in the product
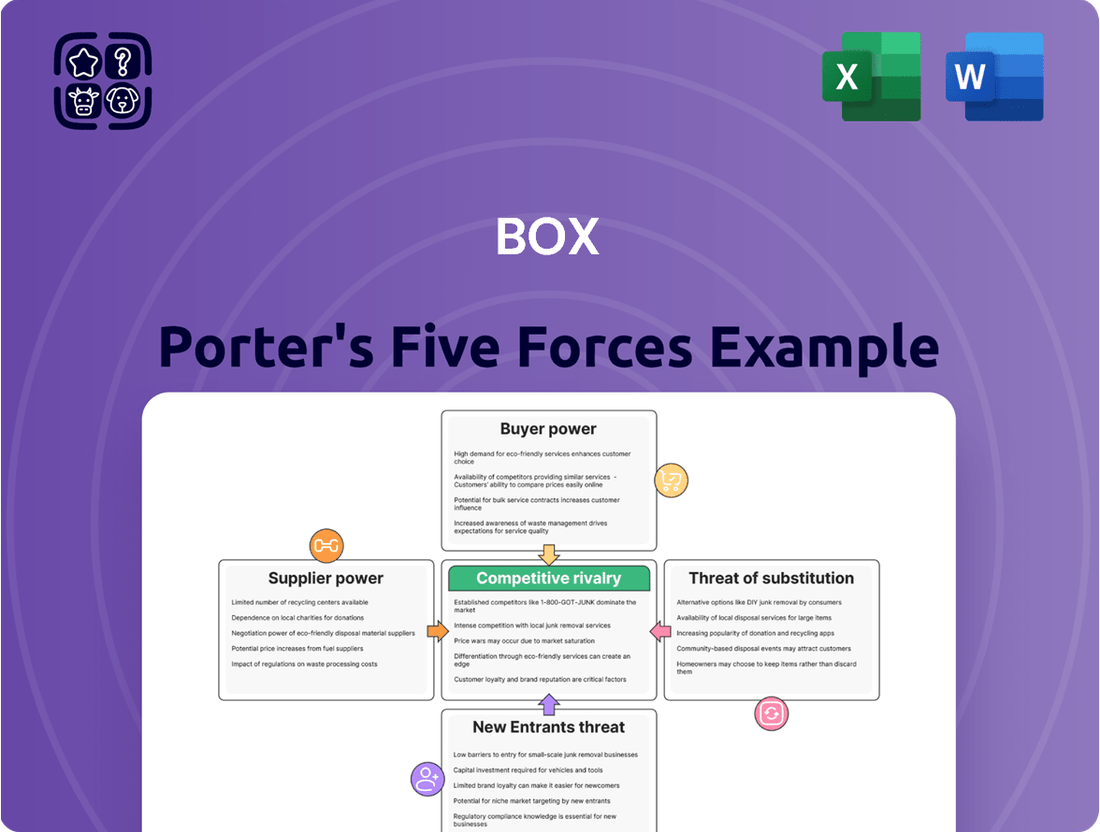
Uncovers the five key competitive forces shaping Box's market, including the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors.
Pinpoint and neutralize competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces, transforming complex market dynamics into actionable insights.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customer switching costs for cloud storage and collaboration platforms like Box can be substantial. For instance, migrating terabytes of sensitive data and ensuring its integrity during a move is a complex and time-consuming process. This complexity, coupled with the need to reconfigure integrated workflows and retrain staff on new systems, creates a significant barrier for many organizations, thereby diminishing their immediate power to switch providers.
Box's customer base spans from small and medium-sized businesses to large enterprises. This diversity means bargaining power varies significantly by customer segment.
Larger enterprise clients, who often represent a substantial portion of Box's revenue, wield considerable influence. Their ability to commit to high-volume purchases, negotiate custom solutions, and potentially switch to competitors gives them leverage in pricing and product roadmap discussions.
For instance, in 2023, Box reported that its largest customers contributed significantly to its annual recurring revenue, highlighting the concentrated impact these clients can have on the company's financial performance and strategic direction.
Customers wield significant power when a multitude of alternative solutions exist. For instance, in the cloud storage market, users can readily switch between major providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, or opt for more specialized or on-premise solutions. This abundance of choice, even if some alternatives require initial setup, directly enhances their bargaining leverage.
Price Sensitivity and Budget Constraints
Customer price sensitivity significantly impacts Box's bargaining power. Businesses, especially smaller ones or those in competitive, cost-focused sectors, are keenly aware of pricing. This means Box often faces pressure to offer attractive pricing structures, including discounts or flexible service tiers, to win and keep customers.
For instance, in 2024, the average annual IT spend for small businesses (1-50 employees) was approximately $15,000, highlighting budget constraints that make them more receptive to competitive pricing. This forces companies like Box to continuously evaluate their pricing strategies to remain competitive in a market where cost is a major deciding factor.
- Price Sensitivity: Many businesses, particularly SMBs, are highly sensitive to the cost of cloud storage and collaboration tools.
- Budget Constraints: Limited IT budgets in 2024 for smaller organizations necessitate cost-effective solutions.
- Competitive Pressure: High price sensitivity empowers customers to negotiate better terms or switch to lower-cost alternatives.
- Impact on Box: Box must offer competitive pricing and value-added services to mitigate the bargaining power of price-sensitive customers.
Customer Demand for Integration and Customization
Enterprise customers frequently require extensive integrations with their current IT infrastructures and specific customization features. This need allows them to exert significant influence over product development and pricing. For instance, in 2024, a survey of IT decision-makers revealed that over 60% consider seamless integration with existing systems a primary factor when selecting new software solutions.
Their capacity to articulate these detailed requirements, combined with the option to explore alternative vendors offering a more tailored fit, substantially bolsters their bargaining power. If a vendor cannot meet these integration and customization demands, customers can easily switch, potentially impacting the vendor's market share and revenue streams.
- Integration Demands: Businesses often need software to connect with ERP, CRM, and other critical systems.
- Customization Needs: Tailoring features to unique workflows is crucial for operational efficiency.
- Vendor Switching Costs: High integration costs can sometimes deter switching, but unmet needs can override this.
- Market Alternatives: The availability of multiple solutions with varying degrees of customization increases customer leverage.
The bargaining power of customers for cloud storage and collaboration platforms like Box is influenced by several factors, including the availability of alternatives and the cost of switching. When numerous providers offer similar services, customers gain leverage to negotiate better terms. For instance, the cloud storage market in 2024 is highly competitive, with major players like Microsoft OneDrive, Google Drive, and Dropbox offering robust features, increasing customer options.
Customer price sensitivity remains a critical element. Businesses, especially smaller ones, often operate with tight IT budgets, making them acutely aware of costs. This sensitivity pressures companies like Box to offer competitive pricing and flexible plans to retain clients. In 2024, many SMBs reported that cost was a primary driver in software selection, with average IT budgets for businesses under 50 employees often remaining constrained.
The need for deep integration with existing enterprise systems and specific customization requirements also amplifies customer bargaining power. When a provider cannot adequately meet these technical demands, customers can leverage this gap to negotiate or seek alternatives. A 2024 IT trends report indicated that over 65% of enterprises prioritize seamless integration when choosing new cloud solutions, underscoring the importance of this factor.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Example/Data Point (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Availability of Alternatives | High | Numerous competitors like Google Workspace and Microsoft 365 offer comparable cloud storage and collaboration features. |
| Switching Costs | Moderate to High | Migrating large datasets and reconfiguring integrated workflows can be complex and costly for enterprises. |
| Price Sensitivity | High | SMBs, with average IT budgets around $15,000 in 2024, are highly responsive to pricing and discounts. |
| Integration & Customization Needs | High | Over 65% of enterprises in a 2024 survey prioritized seamless integration with existing systems. |
What You See Is What You Get
Box Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive intensity and industry attractiveness. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no surprises. You can confidently download and utilize this comprehensive tool to understand your industry's landscape and strategic positioning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Box faces formidable competition from tech titans like Microsoft, Google, and Amazon. These giants leverage their extensive resources and vast customer bases to offer integrated cloud storage and collaboration tools, often bundled with their broader enterprise software suites. For instance, Microsoft's OneDrive and SharePoint are deeply embedded within the Microsoft 365 ecosystem, a significant advantage for many businesses already reliant on Microsoft products.
The sheer scale and financial might of these major tech players present a substantial challenge. In 2024, Microsoft reported its cloud services revenue, including Azure and Microsoft 365, reached hundreds of billions of dollars annually, demonstrating the immense resources available to bolster their content collaboration offerings. Google Workspace and Amazon WorkDocs also benefit from the vast cloud infrastructure and existing enterprise relationships of their parent companies.
Beyond the major cloud storage providers, Box faces intense competition from a multitude of niche players. These specialized competitors often focus on specific industries, such as healthcare with its stringent data privacy needs, or the legal sector requiring advanced document management and e-discovery capabilities. For instance, companies like Veeva Systems cater specifically to the life sciences industry, offering tailored content management solutions.
These specialized offerings allow niche competitors to capture significant market share within their target segments by providing highly customized features and compliance expertise that broader platforms may not match. This fragmentation means Box must continually innovate to address the unique demands of diverse vertical markets, even as it competes with giants like Microsoft SharePoint and Google Workspace.
The cloud content management landscape is a hotbed of innovation, with major players like Microsoft SharePoint, Google Workspace, and Dropbox constantly pushing the envelope. This intense competition means that features once considered cutting-edge, such as AI-driven content analysis and sophisticated workflow automation, quickly become standard offerings. For Box, this translates into a perpetual need to invest heavily in research and development to stay ahead, as failing to match competitors' feature sets can lead to market share erosion.
In 2024, the emphasis on AI integration within content management systems is particularly pronounced. Companies are increasingly seeking solutions that can automatically tag, categorize, and even summarize vast amounts of data, improving searchability and user productivity. Box's ability to deliver these advanced AI capabilities at a competitive pace is crucial for maintaining its market position against rivals who are also heavily investing in this area.
Pricing Pressure and Value Proposition
Intense competition in the cloud content management space, particularly from giants like Microsoft OneDrive and Google Drive, forces Box to engage in frequent pricing adjustments and offer attractive subscription bundles. This dynamic directly impacts Box's ability to maintain premium pricing without a clear differentiator.
Box's strategy hinges on showcasing its advanced security features, robust workflow automation, and seamless integration with other business applications. These elements are crucial for justifying its subscription costs and preventing its services from being perceived as a mere commodity, especially as competitors often bundle similar functionalities into broader productivity suites.
- Pricing Pressure: Competitors often use aggressive pricing strategies, with many offering substantial free tiers or bundled cloud storage with other software subscriptions. For example, Microsoft 365 subscriptions include OneDrive storage, creating a significant competitive hurdle.
- Value Proposition: Box differentiates by emphasizing enterprise-grade security, compliance certifications (like FedRAMP High and HIPAA), and advanced content collaboration tools. These specialized features are critical for businesses with stringent data governance requirements.
- Market Dynamics: As of late 2024, the cloud storage market continues to consolidate, with major players leveraging their existing customer bases to upsell cloud services. Box's success depends on its ability to maintain customer loyalty and attract new enterprise clients by consistently delivering superior value beyond basic storage.
High Switching Costs for Customers
High switching costs for customers, a significant factor in competitive rivalry, mean that once a customer is with Box, it's difficult and expensive for them to move to a competitor. This dynamic, while beneficial for Box in retaining existing business, simultaneously makes it a challenging endeavor to attract new clients away from rivals. For instance, in the cloud storage sector, where Box operates, integration with existing IT infrastructure and data migration can represent substantial costs and operational disruptions for businesses, often running into thousands or even tens of thousands of dollars depending on the scale of data and complexity of systems.
This situation intensifies the competition for acquiring new customers. Companies like Box must invest heavily in sales and marketing to convince potential clients that the benefits of switching outweigh the immediate costs. The battle for market share becomes a strategic game of acquisition and retention, as losing even a single large client can translate into a significant long-term revenue deficit, impacting future growth projections.
- Customer Retention Focus: High switching costs encourage companies to prioritize customer satisfaction and loyalty to minimize churn.
- Acquisition Challenges: Competitors face hurdles in luring customers away due to the financial and operational burdens of switching.
- Strategic Importance: Understanding these costs is crucial for Box's strategy in pricing, service offerings, and customer support.
- Market Stalemate: In mature markets with high switching costs, market share shifts can be slow and costly.
The competitive rivalry for Box is fierce, primarily driven by tech giants like Microsoft, Google, and Amazon, who leverage their vast ecosystems and resources to offer integrated cloud storage and collaboration tools. These giants often bundle their services, making it challenging for standalone players like Box to compete on price alone.
Box also contends with numerous niche competitors specializing in specific industries, such as healthcare or legal, offering tailored solutions that address unique compliance and feature requirements. This fragmentation necessitates continuous innovation from Box to meet diverse vertical market demands.
The market is characterized by rapid feature development, especially in AI integration for content analysis and automation, forcing Box into substantial R&D investments to remain competitive. Pricing pressure is also a major factor, as rivals frequently use aggressive pricing or bundle services, compelling Box to highlight its advanced security and workflow capabilities as key differentiators.
High switching costs for enterprise clients, while aiding retention, create significant hurdles for customer acquisition, making it a strategic battle for market share. Box's success hinges on demonstrating superior value beyond basic storage to justify its subscription costs against bundled offerings.
| Competitor | Key Offerings | 2024 Market Position/Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Microsoft (OneDrive/SharePoint) | Integrated with Microsoft 365, extensive enterprise adoption | Dominant player, leveraging bundled subscriptions and deep ecosystem integration. Reported hundreds of billions in annual cloud services revenue in 2024. |
| Google (Workspace/Drive) | Cloud-native productivity suite, strong collaboration features | Significant market share, benefits from Google's vast infrastructure and AI capabilities. Continually enhancing Workspace with AI-driven features. |
| Amazon (WorkDocs) | Leverages AWS infrastructure, enterprise-focused | Growing presence, capitalizing on AWS client relationships and scalable cloud solutions. |
| Niche Players (e.g., Veeva Systems) | Industry-specific solutions (e.g., life sciences) | Capturing specific verticals with tailored features and compliance expertise, posing localized competitive threats. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Generic cloud storage services like Dropbox, Google Drive, and iCloud present a significant threat to specialized enterprise solutions. For many small businesses and individual users, these consumer-grade platforms adequately fulfill basic file storage and sharing requirements. Their widespread adoption and user-friendly interfaces make them an accessible alternative, even if they lack the advanced security and management features of enterprise-focused providers.
The cost-effectiveness of these generic services is a primary driver of their substitutability. For instance, many offer substantial free storage tiers, with paid plans being considerably cheaper than enterprise-grade solutions. This low barrier to entry makes them particularly attractive for organizations with budget constraints or those whose data management needs are not highly complex. In 2024, the continued growth in the consumer cloud storage market, with billions of active users globally, underscores the accessibility and perceived value of these alternatives.
On-premise document management systems represent a significant threat of substitutes for cloud-based solutions like Box. Businesses with stringent regulatory compliance needs or those prioritizing absolute data control often opt for these on-premise solutions. While they demand substantial initial capital expenditure and ongoing maintenance, they provide unparalleled data sovereignty, making them a compelling alternative for certain market segments.
The market for on-premise solutions remains relevant, particularly in sectors like finance and healthcare where data security and compliance are paramount. For instance, a significant portion of financial institutions, perhaps over 60% as of recent surveys, still maintain substantial on-premise IT infrastructure, including document management, due to regulatory mandates and historical investment. This demonstrates a continued preference for direct control over data, even with the rise of cloud alternatives.
For straightforward file sharing and team discussions, email attachments and basic chat platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams can act as substitutes. These tools, while not offering the robust content management of dedicated platforms, effectively meet immediate needs for sending documents and quick communication.
In 2024, the reliance on email for document exchange remains significant, with billions of emails sent daily, highlighting its persistent role as a basic substitute. Similarly, collaboration platforms like Slack reported over 12 million daily active users in early 2024, demonstrating their widespread adoption for essential communication, even if they lack advanced content features.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) or CRM Systems
The threat of substitutes for content management platforms like Box is amplified by the increasing integration of document management features into enterprise resource planning (ERP) and customer relationship management (CRM) systems. Many of these core business applications now offer built-in capabilities for storing, organizing, and managing content, directly addressing many of the functional needs previously met by standalone solutions.
This trend means businesses can potentially consolidate their software stack, reducing the need for a separate content platform. For instance, a company using Salesforce for CRM might find its document sharing and collaboration needs adequately met within the platform itself, lessening the appeal of a service like Box. In 2024, the market for integrated business software continues to grow, with vendors actively enhancing their platforms to offer end-to-end solutions.
- Growing Integration: ERP and CRM systems increasingly incorporate document management, reducing reliance on dedicated platforms.
- Cost Efficiency: Consolidating software can lead to significant cost savings for businesses by eliminating redundant subscriptions.
- Streamlined Workflows: Keeping content within core business applications simplifies processes and improves data accessibility.
- Market Trends: The demand for comprehensive, integrated business solutions is a key driver in software development and adoption.
Manual Processes and Physical Storage
Manual processes and physical storage represent a significant, albeit inefficient, substitute for cloud-based content management systems like Box, particularly in smaller or less digitized organizations. These legacy methods, including shared network drives and paper filing systems, serve as the baseline alternative that Box seeks to displace by offering enhanced efficiency, accessibility, and security.
While these manual methods are often perceived as cheaper upfront, their long-term costs in terms of lost productivity, storage space, and risk of data loss or corruption are substantial. For instance, studies in 2024 continue to highlight the inefficiencies inherent in paper-based workflows, with businesses still spending significant resources on printing, filing, and retrieving physical documents.
- Inefficiency: Manual document handling and retrieval can consume hours of employee time weekly.
- Storage Costs: Physical storage requires dedicated space, which incurs rental or opportunity costs.
- Risk of Loss: Paper documents are susceptible to damage from fire, water, or simply misplacement.
- Limited Collaboration: Sharing physical documents or files on local drives hinders real-time collaboration.
The threat of substitutes for cloud content management platforms like Box is multifaceted, stemming from both readily available digital alternatives and traditional methods. Generic cloud storage, integrated business software, and even basic communication tools can fulfill some of Box's core functions, often at a lower cost or with greater familiarity for users.
These substitutes, ranging from consumer-grade cloud storage to on-premise solutions and collaboration platforms, present a constant challenge by offering varying degrees of functionality and cost-effectiveness. The market's dynamic nature, with new integrations and enhanced features appearing regularly, ensures that businesses have numerous options to consider beyond specialized content management systems.
The continued prevalence of email for document sharing, with billions of emails sent daily in 2024, and the substantial user base of collaboration tools like Slack, highlight how these simpler solutions can meet basic needs. Furthermore, the significant on-premise IT infrastructure maintained by sectors like finance, potentially over 60% of their IT, underscores the enduring appeal of direct data control.
The increasing integration of document management into ERP and CRM systems also poses a threat, as businesses can consolidate their software needs. This trend, coupled with the cost-efficiency and streamlined workflows offered by consolidated solutions, makes them attractive alternatives to standalone platforms.
| Substitute Type | Key Characteristics | Threat Level to Box | 2024 Market Relevance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Generic Cloud Storage (e.g., Google Drive) | Low cost, user-friendly, basic file sharing | High for individuals/SMBs | Billions of global users, continued growth |
| On-Premise Solutions | High security, data sovereignty, regulatory compliance | Moderate to High for specific industries | Significant infrastructure in finance/healthcare |
| Collaboration Platforms (e.g., Slack) | Real-time communication, basic file sharing | Moderate for simple needs | Over 12 million daily active users (early 2024) |
| Integrated ERP/CRM Systems | Consolidated workflows, built-in document features | Growing threat | Vendors enhancing end-to-end capabilities |
| Manual/Physical Storage | Low upfront cost, inefficient, high long-term cost | Low for digitized businesses | Still prevalent in less digitized organizations |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants is significantly dampened by the substantial capital requirements and extensive infrastructure costs inherent in establishing a robust cloud content management platform. Companies need to invest heavily in secure, scalable, and globally accessible data centers, sophisticated network capabilities, and advanced security protocols. For instance, major cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure have invested billions of dollars in their global infrastructure, creating a high barrier to entry for smaller players.
The technical complexity involved in building a competitive platform is a significant barrier to entry. Developing a robust system with advanced security, seamless integration, and an intuitive user experience requires specialized skills that are both scarce and expensive. For instance, in 2024, the average salary for a senior software engineer with cybersecurity expertise could easily exceed $150,000 annually, making it a substantial upfront investment for any new entrant.
Furthermore, navigating stringent regulatory compliance, such as GDPR or CCPA for data privacy, adds another layer of technical and legal intricacy. New companies must invest heavily in legal counsel and specialized compliance software, often costing tens of thousands of dollars, to ensure they meet industry standards. This expertise is not easily acquired and represents a considerable hurdle for potential new competitors aiming to enter established markets.
Box has cultivated significant brand recognition and trust, particularly with large enterprise clients who prioritize data security and reliability. This established reputation acts as a formidable barrier for potential new entrants.
New competitors face a substantial hurdle in replicating the deep-seated trust and credibility that Box has earned, which are absolutely essential when dealing with sensitive business information. For instance, in 2024, Box reported a 96% customer retention rate, underscoring the stickiness of its trusted platform.
Network Effects and Ecosystem Integrations
The threat of new entrants for a company like Box is significantly influenced by strong network effects and deep ecosystem integrations. Existing players already benefit from a virtuous cycle: more users attract more developers, leading to more integrated applications, which in turn makes the platform more valuable and sticky for users. This creates a substantial barrier for newcomers. For instance, in 2024, Box reported having over 100,000 business customers, a testament to its established user base and the value derived from its integrated services.
New entrants must overcome the immense challenge of replicating this extensive network. Building out a comparable ecosystem of third-party integrations, crucial for seamless workflow and collaboration, requires significant time, investment, and strategic partnerships. Without this, a new platform may struggle to offer the same utility and convenience that users have come to expect from established players like Box.
- Network Effects: A larger user base enhances the platform's value for all participants.
- Ecosystem Integration: Over 1,500 apps are integrated with Box, creating a robust workflow environment.
- Barrier to Entry: New entrants must invest heavily to build a comparable range of integrations.
- Customer Stickiness: The integrated ecosystem makes it difficult for users to switch to a less connected platform.
Regulatory Compliance and Security Standards
The cloud content management sector faces significant barriers to entry due to the rigorous regulatory compliance and security standards it must adhere to. New players must allocate substantial resources to meet complex mandates such as GDPR and HIPAA, which increases both the initial investment and the time it takes to launch a product.
These compliance requirements act as a formidable deterrent. For instance, the cost of achieving and maintaining certifications like ISO 27001 can run into tens of thousands of dollars annually, not to mention the ongoing legal and audit expenses. This financial and temporal burden makes it challenging for smaller or less capitalized entities to compete effectively with established providers who have already absorbed these costs.
- High Compliance Costs: Meeting standards like GDPR and HIPAA requires significant investment in secure infrastructure, data privacy protocols, and ongoing audits, potentially costing new entrants hundreds of thousands of dollars in the first year.
- Extended Time-to-Market: The process of achieving necessary certifications and ensuring full compliance can add 12-24 months to a new entrant's development cycle, delaying revenue generation.
- Reputational Risk: Failure to comply can lead to severe penalties and irreparable damage to a new company's reputation, making the stakes exceptionally high.
The threat of new entrants into the cloud content management space is considerably low due to the immense capital investment required for infrastructure and technology development. Building secure, scalable data centers and advanced software platforms demands billions of dollars, a barrier that deters most startups. For example, major cloud providers like AWS and Microsoft Azure continue to invest heavily, with AWS alone reporting over $15 billion in capital expenditures in 2024, a figure that highlights the scale of entry costs.
| Barrier | Description | Estimated Cost/Impact (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Building global data centers, network infrastructure, and R&D for secure platforms. | Billions of USD (e.g., AWS capital expenditures exceeding $15 billion in 2024) |
| Technical Expertise | Hiring specialized engineers for security, AI, and platform development. | Senior cloud engineer salaries can exceed $170,000 annually. |
| Brand & Trust | Establishing a reputation for security and reliability with enterprise clients. | Box reported a 96% customer retention rate in 2024, indicating high trust. |
| Ecosystem Integration | Developing integrations with thousands of third-party applications. | Box integrates with over 1,500 apps, requiring significant partnership and development effort. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meeting stringent data privacy laws (GDPR, CCPA) and security certifications (ISO 27001). | Compliance costs can reach tens of thousands of dollars annually, plus potential legal fees. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of publicly available information, including company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and government economic data.
