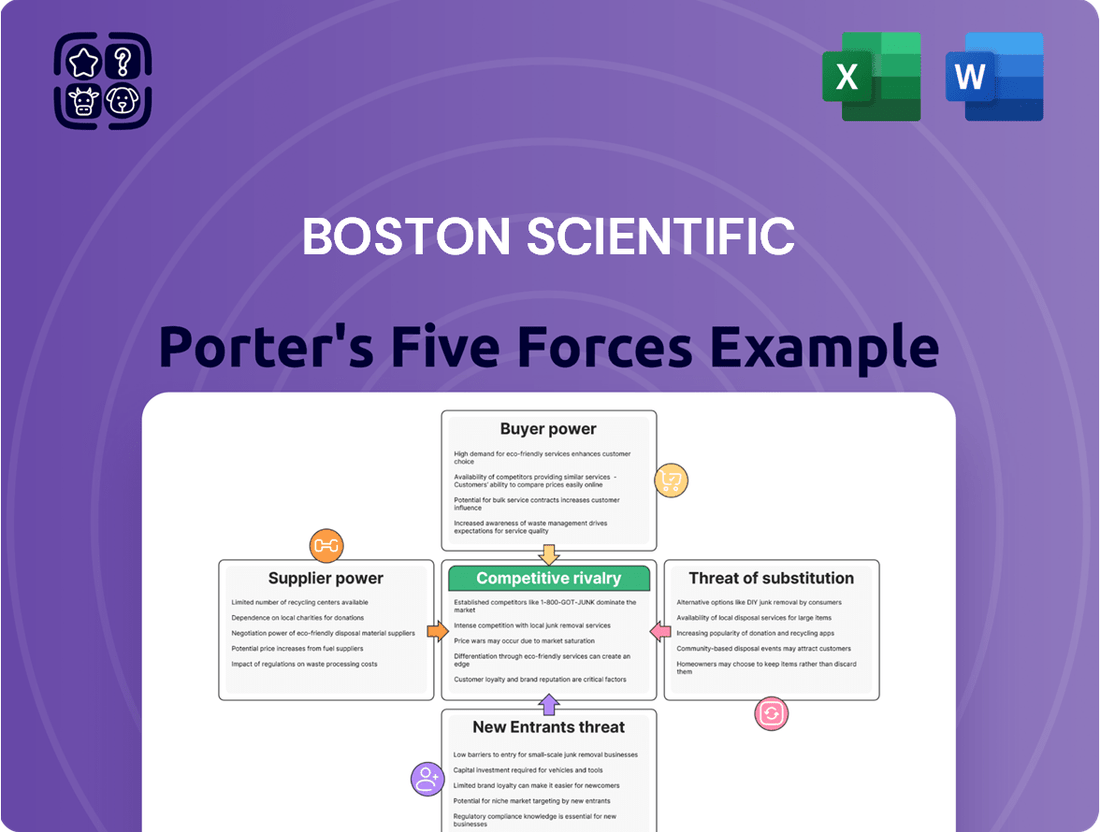
Boston Scientific Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Boston Scientific Bundle
Boston Scientific navigates a complex medical device landscape, facing intense rivalry and significant buyer power from healthcare providers. Understanding the threat of substitutes and new entrants is crucial for their strategic positioning.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Boston Scientific’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Boston Scientific's reliance on highly specialized components for its advanced medical devices significantly influences supplier bargaining power. For instance, suppliers of unique alloys or proprietary polymers, critical for devices like pacemakers or stents, often hold considerable leverage. The limited availability of these specialized inputs means Boston Scientific has few viable alternatives, increasing the supplier's negotiating strength.
Suppliers of materials or services essential for regulatory compliance, like specialized testing or sterile packaging, hold significant sway. Boston Scientific, operating in the highly regulated medical device sector, must ensure its suppliers meet rigorous quality and safety benchmarks, making compliance-critical suppliers non-negotiable. In 2023, the global medical device market was valued at approximately $590 billion, underscoring the immense pressure to maintain compliance across this vast industry.
Intellectual property holders can wield considerable power over companies like Boston Scientific. If a supplier possesses unique patents or proprietary technology essential for Boston Scientific's medical devices, they gain significant leverage. This exclusivity makes it difficult and costly for Boston Scientific to find alternative suppliers or develop the technology in-house. For instance, in 2023, the medical device industry saw continued investment in R&D, with companies filing numerous patents for innovative technologies, underscoring the importance of IP.
Limited Number of Suppliers
For highly specialized medical components, Boston Scientific often faces a limited pool of qualified suppliers. This scarcity, particularly for advanced materials or patented technologies, significantly diminishes the company's bargaining power. For instance, in 2024, the medical device industry continued to grapple with supply chain constraints for critical semiconductors and specialized polymers, where only a handful of global manufacturers possess the necessary certifications and production capacity.
This restricted supplier landscape means that competition among these few providers is often minimal, tipping the scales in favor of the suppliers. Boston Scientific must therefore focus on cultivating strong, long-term relationships and strategic partnerships. These collaborations are essential to ensure reliable supply, favorable pricing, and access to innovation, thereby mitigating the inherent power imbalance posed by a concentrated supplier base.
- Limited Supplier Options: In sectors requiring deep technical expertise or strict regulatory compliance, the number of approved suppliers can be extremely low.
- Reduced Negotiation Leverage: A small number of suppliers means less competition, giving them more power in price and term negotiations with Boston Scientific.
- Importance of Partnerships: Building strategic alliances and long-term contracts is vital for Boston Scientific to secure supply and manage costs effectively.
- Industry Trends: The medical device sector in 2024 continued to see consolidation and specialization, further concentrating the supplier market for certain critical components.
Supplier's Forward Integration Threat
While not a frequent occurrence, there's a possibility that highly specialized component suppliers might explore forward integration, moving into manufacturing medical devices themselves. This threat, though carrying significant entry barriers, could empower suppliers during negotiations with Boston Scientific. For instance, if a supplier with unique technology were to partner with a direct competitor, it would immediately shift leverage.
This potential for suppliers to integrate forward, even if just a theoretical risk, necessitates Boston Scientific cultivating robust and collaborative relationships. Maintaining open communication and demonstrating mutual value is key to mitigating this supplier bargaining power. In 2024, the medical device industry continued to see consolidation, making strategic supplier partnerships even more critical for maintaining competitive advantage.
- Supplier Forward Integration: Specialized component suppliers could potentially enter medical device manufacturing.
- Leverage in Negotiations: The threat of integration or partnerships with competitors enhances supplier bargaining power.
- Strategic Importance: Boston Scientific must foster strong supplier relationships to counter this potential leverage.
Suppliers of highly specialized components, critical for Boston Scientific's advanced medical devices, possess significant bargaining power due to limited alternatives and proprietary technology. This concentration in the supplier base, particularly evident in 2024 with ongoing supply chain challenges for semiconductors and specialized polymers, means fewer providers dictate terms. Boston Scientific must therefore prioritize strategic partnerships to ensure reliable supply and favorable pricing.
| Factor | Impact on Boston Scientific | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Specialization | High leverage for suppliers of unique alloys, polymers, or patented technologies. | Continued demand for advanced materials in medical devices. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Suppliers meeting strict safety and quality standards hold considerable power. | Global medical device market valued at approx. $590 billion in 2023, emphasizing compliance needs. |
| Limited Supplier Pool | Scarcity of qualified suppliers diminishes Boston Scientific's negotiation leverage. | Supply chain constraints for critical components persist. |
What is included in the product
This analysis meticulously examines the competitive forces impacting Boston Scientific, detailing the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the pressure from substitute products within the medical device industry.
Instantly assess competitive pressures with a dynamic, interactive Porter's Five Forces model, allowing for swift strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Boston Scientific's key customers, like major hospital systems and Group Purchasing Organizations (GPOs), buy medical devices in large quantities. In 2023, GPOs represented a significant portion of the medical device market, with some estimates suggesting they influence over 90% of hospital purchasing. This consolidation allows these entities to negotiate aggressively for lower prices and better contract terms.
These powerful customer groups can exert considerable bargaining power by threatening to shift their substantial business to competitors. For instance, a large hospital network might negotiate for discounted pricing on a range of Boston Scientific's products, from cardiovascular stents to endoscopy equipment, potentially impacting revenue streams if concessions are too steep.
Healthcare systems are increasingly focused on cost containment, directly influencing pricing for medical devices. For instance, in 2024, many payers continued to emphasize value-based purchasing, pushing manufacturers to demonstrate clear cost-effectiveness for their products. This trend puts significant downward pressure on prices for companies like Boston Scientific.
Changes in reimbursement rates for procedures utilizing Boston Scientific's technologies can significantly impact demand and pricing power. For example, if Medicare reimbursement for a specific surgical procedure declines, hospitals may seek lower prices for the associated devices to maintain their margins. This dynamic was evident in ongoing discussions around bundled payments in 2024.
Customers in the medical device market, including hospitals and physicians, have a significant number of alternative devices available from Boston Scientific's competitors. For instance, in the cardiovascular segment, companies like Medtronic, Abbott, and Edwards Lifesciences offer competing stent, valve, and catheter technologies. This wide selection allows buyers to readily compare features, efficacy, and pricing.
The presence of numerous comparable products directly fuels customer bargaining power. If Boston Scientific's offerings are perceived as too expensive or if their service falls short, a hospital can more easily pivot to a competitor. This ease of switching is a critical factor in negotiating better terms, as demonstrated by the competitive bidding processes common in hospital procurement, where price is often a major determinant.
In 2024, the medical device industry continued to see robust competition, with companies investing heavily in R&D to differentiate their products. Boston Scientific itself reported net sales of $13.0 billion for the full year 2023, a 5.4% increase over 2022, indicating growth amidst this competitive landscape. The ability for customers to access similar technologies from multiple vendors means they are less reliant on any single supplier, thereby strengthening their negotiating position.
Clinical Outcomes and Evidence
Healthcare providers, the primary customers for medical device companies like Boston Scientific, are increasingly scrutinizing clinical outcomes and evidence when making purchasing decisions. This focus on demonstrated superior patient results, cost-effectiveness, and long-term value significantly influences their choices. For instance, a 2024 study highlighted that over 70% of hospital procurement managers consider clinical trial data a critical factor in evaluating new medical technologies.
If Boston Scientific's products fail to consistently exhibit strong clinical efficacy or offer clear economic advantages compared to competitors, these customers gain leverage. They can readily opt for alternatives that present more compelling, data-backed evidence of better performance and value. This trend towards data-driven purchasing amplifies the bargaining power of customers, as they can demand proof of superior outcomes before committing to a purchase.
- Clinical Efficacy: Demonstrating improved patient recovery times or reduced complication rates directly impacts purchasing decisions.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Evidence showing lower overall treatment costs or better long-term economic benefits strengthens customer negotiating power.
- Comparative Data: Availability of robust studies comparing Boston Scientific's products against alternatives, showcasing superior results, empowers customers.
- Real-World Evidence: Increasingly, healthcare systems demand real-world data from the field, not just controlled trial results, to validate product performance.
Customer Switching Costs Variability
The bargaining power of customers in the medical device sector, particularly for Boston Scientific, is significantly influenced by the variability in switching costs. For instance, while a complex surgical system might involve substantial costs for physician retraining and integration into hospital workflows, making switching difficult, simpler disposable products often present much lower barriers to entry for competitors. In 2023, Boston Scientific reported substantial revenue from its cardiovascular segment, where physician loyalty and established product lines can contribute to higher switching costs for hospitals and clinics.
Where switching is easier, customers, such as hospitals or even individual physicians, naturally gain more leverage. This increased power allows them to negotiate for better pricing or more favorable terms. For example, if a hospital can readily adopt a competitor's similar stent technology with minimal disruption, they can use this as a point of negotiation with Boston Scientific.
Boston Scientific actively works to mitigate this customer power by fostering sticky relationships. They achieve this through offering integrated solutions that combine multiple devices and services, creating a more comprehensive ecosystem. Furthermore, providing extensive training and ongoing support for their product lines helps to increase the cost and complexity for customers looking to switch to a rival, thereby solidifying their market position.
- High Switching Costs: Complex surgical systems, implanted devices requiring specific physician expertise, and integrated hospital IT solutions often present significant barriers to switching.
- Low Switching Costs: Disposable medical supplies, basic diagnostic tools, and products with widely available alternatives typically have lower switching costs.
- Customer Leverage: When switching costs are low, customers can more effectively negotiate prices and terms with manufacturers like Boston Scientific.
- Mitigation Strategies: Boston Scientific focuses on building customer loyalty through integrated product offerings, comprehensive training, and robust post-sale support.
Boston Scientific's customers, primarily large hospital systems and Group Purchasing Organizations (GPOs), wield significant bargaining power due to their purchasing volume and the availability of alternatives. In 2024, the emphasis on cost containment and value-based purchasing by healthcare providers intensified this pressure, forcing manufacturers to justify pricing through demonstrated clinical efficacy and cost-effectiveness. This environment allows well-informed buyers to negotiate aggressively for better terms.
The competitive landscape, with numerous comparable products from rivals like Medtronic and Abbott, further empowers customers. If Boston Scientific's offerings are perceived as less advantageous or more expensive, buyers can readily switch, leveraging this option to secure favorable pricing. This dynamic was particularly evident in 2023, where Boston Scientific's revenue growth occurred amidst intense competition, underscoring the need to constantly prove value.
Switching costs, while variable, generally favor customers when they are low, such as with disposable products. However, Boston Scientific mitigates this by offering integrated solutions and robust support, aiming to increase customer loyalty and the complexity of switching. For instance, their strong presence in the cardiovascular segment in 2023 benefited from established physician relationships, which can translate to higher switching costs for those specific product lines.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power Drivers | Impact on Boston Scientific |
|---|---|---|
| Major Hospital Systems | High volume purchasing, availability of substitutes, focus on cost containment | Downward pressure on pricing, demand for evidence-based value |
| Group Purchasing Organizations (GPOs) | Consolidated purchasing power, ability to negotiate large-scale contracts | Significant influence on pricing and contract terms across multiple product categories |
| Physicians/Clinicians | Preference for proven efficacy, ease of use, familiarity with existing technologies | Need for strong clinical data, training, and ongoing support to maintain adoption |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Boston Scientific Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. Our comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Boston Scientific delves into the competitive landscape, evaluating the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the medical device industry. This detailed examination provides actionable insights into Boston Scientific's strategic positioning and potential future challenges and opportunities.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The medical device sector, especially in interventional areas, is intensely competitive. Boston Scientific contends with major global entities like Medtronic, Johnson & Johnson, Abbott Laboratories, and Stryker, all possessing substantial research and development resources, broad product lines, and established distribution channels.
This fierce rivalry exerts constant pressure on Boston Scientific regarding pricing strategies, the pace of innovation, and maintaining its market share. For instance, in 2023, Medtronic reported revenues of approximately $31.2 billion, showcasing the scale of its operations and competitive capacity.
Boston Scientific, like many in the medtech industry, faces intense rivalry driven by high fixed costs. Developing a new medical device can cost hundreds of millions, with significant portions allocated to research, development, and rigorous clinical trials. For instance, bringing a complex cardiovascular device to market often involves over a decade of development and substantial regulatory hurdles, demanding massive upfront capital investment.
These substantial fixed costs create a powerful incentive for companies to achieve high sales volumes to recoup their investments. This pressure intensifies competition as firms aggressively pursue market share, often through product differentiation and aggressive pricing strategies. The sheer scale of investment required means only a limited number of players can realistically compete at the highest levels.
Furthermore, the medical device sector demands continuous innovation. Companies must consistently invest in R&D to stay ahead of technological advancements and evolving patient needs. In 2023, Boston Scientific reported R&D expenses of approximately $1.5 billion, highlighting the ongoing financial commitment necessary to maintain a competitive edge and develop next-generation products.
Boston Scientific operates in a market where product differentiation is a key battleground, often achieved through patented technologies and distinct device features. However, this advantage is constantly challenged as rivals aggressively innovate, striving to launch newer or enhanced medical devices. This dynamic fosters an ongoing innovation race, demanding significant R&D investments from companies like Boston Scientific to maintain their competitive edge and prevent their offerings from becoming commoditized.
The relentless pace of technological advancement in the medical device sector directly fuels this intense rivalry. Companies are continuously seeking to gain a competitive advantage by being the first to market with groundbreaking solutions or by significantly improving existing ones. For instance, in 2024, the cardiovascular segment saw numerous new stent and catheter technologies emerge, highlighting the pressure to innovate or risk losing market share.
Aggressive Marketing and Sales Strategies
Boston Scientific operates in a highly competitive landscape where rivals deploy aggressive marketing and sales tactics to win over healthcare professionals. These efforts are crucial for establishing preference and driving product adoption.
Direct sales forces are a primary battleground, with companies investing heavily in training and supporting their teams to build strong relationships with physicians. Clinical support and ongoing educational programs are also vital, as they demonstrate a commitment to patient care and physician development.
For instance, in 2024, the medical device industry saw significant spending on sales and marketing, with major players like Medtronic and Abbott Laboratories allocating substantial portions of their revenue to these areas to maintain market share. Boston Scientific itself reported strong growth in its sales force effectiveness initiatives.
- Aggressive Marketing: Competitors frequently launch targeted campaigns and promotional activities to highlight product benefits and differentiate themselves.
- Sales Force Engagement: Direct sales teams act as key conduits for product information, technical support, and relationship building with medical practitioners.
- Physician Education: Investment in symposia, workshops, and clinical trials aims to educate healthcare providers on the efficacy and advantages of their devices.
- Portfolio Breadth: Offering a comprehensive range of products can be a significant advantage in securing large hospital contracts and fostering long-term physician loyalty.
Global Market Expansion and Consolidation
The global medical device market, including areas where Boston Scientific operates, is characterized by intense rivalry driven by companies vying for market share in both developed and developing economies. For instance, in 2024, the global medical device market was projected to reach over $600 billion, with significant growth anticipated in emerging markets.
This pursuit of expansion fuels aggressive competition. Companies are constantly innovating and expanding their product portfolios to capture a larger piece of this growing pie. This creates a dynamic environment where staying ahead requires continuous investment in research and development and effective market penetration strategies.
- Intensified Competition: Global expansion by players like Medtronic, Johnson & Johnson, and Abbott Laboratories directly challenges Boston Scientific's market position.
- Consolidation Impact: Major acquisitions, such as Medtronic's acquisition of Intuitive Surgical (though this did not happen, it exemplifies the trend), or smaller strategic tuck-in acquisitions by various players, create larger, more dominant entities.
- Portfolio Breadth: Companies with broader product offerings can leverage cross-selling opportunities and provide more comprehensive solutions to healthcare providers, increasing competitive pressure.
- Market Share Focus: The drive for global market share means companies are willing to invest heavily in marketing, sales, and product development, raising the stakes for all participants.
Competitive rivalry is a dominant force for Boston Scientific, stemming from a sector populated by well-established global giants like Medtronic and Johnson & Johnson, each with substantial R&D budgets and extensive product portfolios. This intense competition forces continuous innovation and aggressive pricing to maintain market share, as evidenced by Medtronic's 2023 revenue of approximately $31.2 billion, underscoring the scale of these rivals.
The high fixed costs associated with medical device development, often exceeding hundreds of millions for complex products, create immense pressure to achieve high sales volumes. Boston Scientific's own 2023 R&D expenditure of around $1.5 billion highlights the ongoing investment needed to stay competitive. This financial commitment means only a few can operate at the highest tier, intensifying the battle for market dominance.
Product differentiation through patented technology is crucial, yet this advantage is constantly challenged by rivals' rapid innovation cycles. The race to introduce new cardiovascular technologies in 2024 exemplifies this, demanding significant R&D to prevent commoditization. Furthermore, aggressive sales and marketing tactics, including substantial investments in direct sales forces and physician education by companies like Medtronic and Abbott, are key battlegrounds for securing physician preference and market share.
| Competitor | Approximate 2023 Revenue (USD Billions) | Key Competitive Factor |
| Medtronic | 31.2 | Scale, R&D, Broad Portfolio |
| Johnson & Johnson | (Medical Devices Segment) ~28.3 | Diversified Portfolio, Global Reach |
| Abbott Laboratories | (Medical Devices Segment) ~24.5 | Innovation in Diagnostics & Devices |
| Stryker | 23.9 | Orthopedics, Medical Technologies |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of pharmaceutical alternatives is a significant consideration for Boston Scientific. For certain conditions addressed by their medical devices, advancements in drug therapies could offer less invasive or more economical treatment options. For example, the development of novel cardiovascular drugs or improved pain management pharmaceuticals might diminish the demand for specific device-based interventions.
The ongoing progress in pharmaceutical research continuously poses a potential threat, as new or enhanced drug formulations could directly compete with Boston Scientific’s device solutions. This dynamic requires the company to closely monitor pharmacological developments that could impact the market share of its product lines, particularly in areas like cardiology and pain management where drug therapies are well-established.
The growing emphasis on preventative medicine and healthier lifestyles presents a significant threat of substitutes for medical device companies like Boston Scientific. Public health initiatives and individual choices to improve diet and exercise can lead to a reduction in the incidence or severity of diseases that typically require medical interventions.
For instance, increased adoption of plant-based diets and regular physical activity, as promoted by organizations like the World Health Organization, can mitigate the need for devices treating conditions such as cardiovascular disease or type 2 diabetes. While this trend unfolds gradually, a healthier population inherently shrinks the potential market for certain medical devices over the long term.
Advancements in medical science are a significant threat, potentially offering less invasive procedures or non-device alternatives that could replace Boston Scientific’s current offerings. For instance, the rise of regenerative medicine or advanced pharmaceutical interventions might diminish the need for certain implantable devices.
Digital health solutions, including remote monitoring and AI-powered diagnostics, pose another substitution threat. These technologies could reduce the reliance on some of Boston Scientific’s diagnostic or interventional devices, as seen in the growing adoption of telehealth, which saw a substantial increase in usage in 2023, with some reports indicating a 30% year-over-year rise in virtual consultations.
Alternative Medical Therapies
The rise of alternative medical therapies poses a potential threat of substitution for Boston Scientific's offerings. As gene therapies and regenerative medicine advance, they may offer non-device-based solutions for conditions currently addressed by Boston Scientific's implants and instruments.
For instance, the global regenerative medicine market was valued at approximately $13.4 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating increasing adoption of these therapies. While often used adjunctively, some of these cutting-edge treatments could eventually become direct competitors, impacting demand for traditional medical devices.
- Growing Acceptance: Alternative therapies are gaining traction, potentially diverting patients from device-dependent treatments.
- Direct Competition: Advanced gene and regenerative therapies could offer alternative solutions for specific medical conditions.
- Market Growth: The regenerative medicine market's expansion signals a shift in healthcare preferences.
- Innovation Landscape: The broad scope of medical innovation means new substitutes can emerge rapidly.
Evolution of Surgical Techniques
The relentless advancement in surgical techniques, such as the increasing adoption of robotic surgery and minimally invasive procedures, presents a significant threat of substitution for Boston Scientific. These evolving methods can reduce the need for certain traditional devices, potentially making them obsolete. For instance, the global robotic surgery market was valued at approximately $5.9 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a shift in procedural preferences.
Boston Scientific must actively innovate and adapt its product portfolio to align with these new surgical paradigms. Failure to do so could lead to a decline in demand for its existing offerings as newer, more effective, or less invasive alternatives emerge. The company's strategic focus on developing solutions for these advanced procedures is crucial for maintaining market relevance.
- Robotic Surgery Growth: The robotic surgery market is expanding rapidly, with projections indicating continued strong growth through 2030.
- Minimally Invasive Trend: An increasing preference for minimally invasive techniques necessitates devices designed for these approaches.
- Innovation Imperative: Boston Scientific's ability to develop and integrate new technologies is vital to counter the threat of substitute surgical methods.
The threat of substitutes for Boston Scientific is multifaceted, encompassing advancements in pharmaceuticals, regenerative medicine, and evolving surgical techniques. For instance, the global regenerative medicine market was valued at approximately $13.4 billion in 2023, signaling a growing preference for non-device alternatives. Similarly, the robotic surgery market reached roughly $5.9 billion in 2023, highlighting a shift towards less invasive procedures that may reduce reliance on certain traditional Boston Scientific devices.
Digital health solutions, including telehealth, also present a substitution threat. Telehealth usage saw a significant increase in 2023, with some reports indicating a 30% year-over-year rise in virtual consultations, potentially impacting the demand for some diagnostic or interventional devices. This dynamic necessitates continuous innovation from Boston Scientific to adapt its product portfolio to these emerging trends and maintain market relevance.
| Substitute Area | 2023 Market Value (Approx.) | Trend/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Regenerative Medicine | $13.4 billion | Growing adoption, potential direct competition for devices. |
| Robotic Surgery | $5.9 billion | Increasing preference for minimally invasive procedures. |
| Telehealth/Digital Health | Significant growth (e.g., 30% YoY increase in virtual consultations in 2023) | Reduced reliance on some diagnostic/interventional devices. |
Entrants Threaten
The medical device sector, including companies like Boston Scientific, requires massive upfront investment. Developing a new device involves extensive research and development, rigorous clinical trials, and establishing sophisticated manufacturing capabilities, with costs often running into hundreds of millions of dollars. For instance, bringing a new cardiovascular device to market can easily exceed $100 million when factoring in all regulatory and testing phases.
Stringent regulatory hurdles, like the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) clearance or European CE marking, present a formidable barrier to entry in the medical device sector where Boston Scientific operates. New companies must invest substantial resources, often millions of dollars and several years, into generating robust clinical evidence and ensuring strict compliance before any product can reach the market.
Boston Scientific benefits from a formidable brand reputation cultivated over decades, fostering deep-seated trust among physicians and healthcare institutions. This established credibility, hard-earned through consistent product performance and innovation, presents a significant hurdle for any new competitor seeking market entry. For instance, in 2024, Boston Scientific's extensive portfolio, spanning cardiology, endoscopy, and neuromodulation, continues to be a cornerstone in many hospital supply chains, reflecting the strength of these physician relationships.
Intellectual Property and Patent Landscape
The medical device industry, including companies like Boston Scientific, is characterized by a robust intellectual property and patent landscape. Established players possess extensive patent portfolios that protect their core technologies and product designs. For instance, in 2024, the medical device sector continued to see significant patent filings, with major companies investing heavily in R&D to secure new innovations. This dense web of intellectual property acts as a substantial barrier to entry, as new entrants must navigate existing patents to avoid infringement, which can lead to costly legal battles or require expensive licensing agreements.
The threat of new entrants is significantly mitigated by this IP protection. Developing a truly novel medical device often requires years of research and development, and even then, the risk of infringing on existing patents held by incumbents like Boston Scientific is high. In 2023, patent litigation in the medical device space remained a significant concern, with settlements often running into millions of dollars, further deterring smaller or less-resourced new companies.
- High R&D Investment: Companies like Boston Scientific invest billions annually in research and development, generating a continuous stream of patentable innovations.
- Patent Portfolio Strength: The sheer volume and breadth of patents held by established medical device manufacturers create a formidable defensive moat.
- Enforcement Costs: The high cost and complexity of patent litigation discourage new entrants from challenging existing IP.
- Licensing Barriers: Accessing essential patented technologies often requires costly licensing, impacting the profitability of new ventures.
Economies of Scale in Manufacturing and Distribution
Boston Scientific, like many medical device manufacturers, faces a significant threat from new entrants due to the substantial economies of scale enjoyed by established players. Large incumbents benefit from lower per-unit costs in manufacturing, bulk purchasing of raw materials, and the efficiency of established global distribution networks. For instance, in 2023, major medical device companies reported operating margins that often exceed 20%, a testament to their scale efficiencies.
New entrants, by contrast, must build their operations from the ground up. This means they often operate at a much smaller scale, leading to higher per-unit production costs. Establishing efficient supply chains and achieving widespread market penetration comparable to Boston Scientific's reach is incredibly capital-intensive and time-consuming.
This inherent cost disadvantage makes it exceptionally difficult for newcomers to compete effectively, particularly on price or by matching the distribution speed and breadth of established firms. For example, the average cost to bring a new medical device to market can range from tens of millions to hundreds of millions of dollars, a barrier that deters many potential entrants.
- Economies of Scale: Incumbents like Boston Scientific leverage scale in manufacturing, procurement, and distribution, leading to lower per-unit costs.
- Cost Disadvantage for New Entrants: Smaller-scale operations for new companies result in higher production costs and less efficient supply chains.
- Market Reach Challenges: New entrants struggle to establish the widespread distribution networks that established players already possess.
- Competitive Barrier: The cost and logistical hurdles created by economies of scale make it difficult for new companies to compete on price or service.
The threat of new entrants for Boston Scientific is considerably low due to the immense capital required for research, development, and regulatory approval in the medical device industry. For instance, the average cost to bring a new medical device to market can range from tens of millions to hundreds of millions of dollars, a substantial deterrent for any aspiring competitor.
Furthermore, established players like Boston Scientific benefit from significant economies of scale, leading to lower per-unit production costs and more efficient supply chains. New entrants often face a considerable cost disadvantage, making it difficult to compete on price or match the market reach of incumbents.
The robust intellectual property landscape, coupled with stringent regulatory requirements, also acts as a powerful barrier. Navigating existing patents and obtaining necessary approvals can be a lengthy and expensive process, further limiting the appeal and feasibility for new companies to enter this market.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High R&D, clinical trials, and manufacturing setup costs (often >$100M for specialized devices). | Significant financial hurdle, limiting the pool of potential entrants. |
| Intellectual Property | Extensive patent portfolios protecting core technologies. | Risk of infringement litigation and costly licensing agreements. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Strict FDA/CE marking processes requiring extensive clinical evidence and compliance. | Time-consuming and expensive, delaying market entry and increasing upfront investment. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs for established players in manufacturing, procurement, and distribution. | New entrants face higher operating costs, impacting price competitiveness. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Boston Scientific leverages data from annual reports, SEC filings, and industry-specific market research reports to understand competitive dynamics.
We also incorporate insights from financial news outlets, competitor press releases, and healthcare industry trade publications to provide a comprehensive view of the forces at play.
