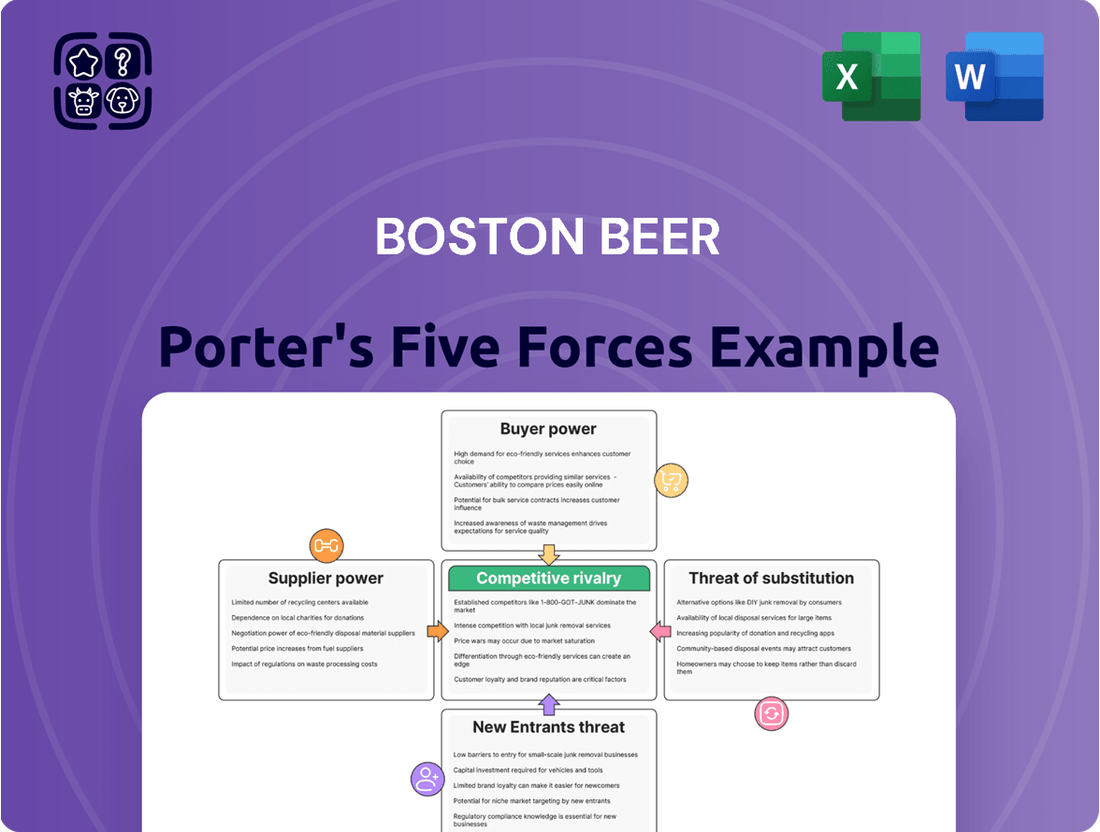
Boston Beer Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Boston Beer Bundle
Boston Beer faces moderate buyer power, as consumers have many craft beer options, but brand loyalty can mitigate this. The threat of new entrants is significant due to low barriers to entry in the craft beer market, while the threat of substitutes, like wine and spirits, remains a constant pressure. Supplier power is relatively low, as hops and malt are widely available commodities.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Boston Beer’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The Boston Beer Company's dependence on specific agricultural inputs, such as hops, malted barley, and unique yeast strains, directly influences supplier bargaining power. Fluctuations in the availability and cost of these ingredients, often tied to weather patterns and harvest yields, can substantially affect Boston Beer's manufacturing expenses and, consequently, its profitability.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Boston Beer can be significant when dealing with limited specialized suppliers. For instance, if a particular hop varietal or a unique brewing enzyme is critical to a flagship product like Samuel Adams Boston Lager, and only a few growers or manufacturers can produce it, those suppliers gain considerable leverage. This scarcity can translate into higher prices or less favorable payment terms for Boston Beer, impacting their cost of goods sold.
Fluctuations in commodity prices for key inputs like barley, hops, aluminum for cans, and glass for bottles significantly impact Boston Beer Company's cost of goods sold. For instance, in 2023, the price of aluminum, a critical component for beverage cans, saw considerable volatility, influenced by global supply chain dynamics and energy costs. This directly affects the company's margins.
Suppliers of these essential raw materials wield considerable bargaining power, particularly during periods of scarcity or heightened demand. When supply tightens, such as during adverse weather affecting hop harvests or disruptions in grain production, suppliers can dictate higher prices. Boston Beer, like other brewers, faces the difficult choice of absorbing these increased costs, which erodes profitability, or passing them on to consumers through higher prices, potentially impacting sales volume.
Logistics and transportation costs
Logistics and transportation providers are crucial suppliers for Boston Beer, impacting the cost of delivering packaging and ingredients. Fluctuations in fuel prices directly affect these costs. For instance, the average price of diesel fuel in the US saw significant increases in early 2024, reaching levels that would undoubtedly put pressure on transportation expenses for national distribution.
Disruptions within the supply chain, whether due to weather events, labor shortages, or geopolitical factors, can further empower logistics suppliers. When the availability of transportation services is limited, these suppliers can command higher rates, directly impacting Boston Beer's operational costs and potentially its profit margins. This heightened bargaining power for logistics companies means they can negotiate more favorable terms, especially for a company with a nationwide reach like Boston Beer.
- Increased Fuel Costs: Rising diesel prices directly inflate transportation expenses for raw material delivery.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Disruptions in logistics networks enhance the leverage of transportation providers.
- National Distribution Impact: Boston Beer's broad market presence makes it particularly susceptible to transportation cost increases.
- Negotiating Power: Logistics suppliers can leverage these factors to negotiate higher rates, impacting Boston Beer's bottom line.
Supplier concentration in specific segments
While Boston Beer Company sources many common ingredients from a broad supplier base, specific niche inputs like certain premium hop varieties or unique flavorings for its hard seltzer portfolio can originate from a more concentrated group of suppliers. This concentration means that if Boston Beer becomes heavily reliant on these specialized suppliers, it can face increased pricing power from them, potentially leading to higher costs or less favorable contract terms.
For instance, in 2024, the demand for specific aroma hops, crucial for craft beer profiles, saw significant increases in pricing due to limited harvest yields and growing global demand. This situation directly impacts brewers like Boston Beer, who depend on these specialized hops to differentiate their products.
- Supplier Concentration: Niche ingredients for hard seltzers and craft beers may come from a limited number of suppliers.
- Pricing Power: Concentrated suppliers can command higher prices or dictate less favorable terms.
- Impact on Boston Beer: Reliance on these niche suppliers can increase input costs and reduce bargaining leverage.
- Market Trends: Limited availability and high demand for specific hops in 2024 exemplify this supplier power.
Boston Beer's reliance on key ingredients like hops and malted barley, often subject to weather-driven supply fluctuations, significantly influences supplier bargaining power. In 2024, for instance, specific aroma hop prices saw increases due to limited harvests and robust global demand, directly impacting brewers.
The concentration of suppliers for niche ingredients, such as specialized hops for craft beers or unique flavorings for hard seltzers, can grant those suppliers considerable leverage. This is particularly true when Boston Beer becomes dependent on a few select producers, leading to potential price hikes or less favorable contract terms.
Transportation and logistics providers also hold significant sway, especially with rising fuel costs impacting national distribution. Disruptions in the supply chain further amplify the bargaining power of these logistics suppliers, allowing them to negotiate higher rates and affecting Boston Beer's operational expenses.
| Input Category | Key Factors Influencing Supplier Power | Impact on Boston Beer | 2024 Data/Trend Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural Inputs (Hops, Malt) | Weather patterns, harvest yields, global demand | Cost of Goods Sold, Profitability | Increased pricing for specific aroma hops due to limited harvests and high demand. |
| Packaging Materials (Aluminum, Glass) | Commodity price volatility, energy costs | Manufacturing Expenses, Margins | Aluminum prices experienced volatility in 2023 due to global supply chain dynamics. |
| Logistics & Transportation | Fuel prices, supply chain disruptions, labor availability | Distribution Costs, Operational Expenses | Rising diesel prices in early 2024 directly increased transportation expenses for national distribution. |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Boston Beer examines the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitutes within the craft beer industry.
Instantly understand competitive pressures with a visual Porter's Five Forces analysis, providing clarity on market dynamics for Boston Beer.
Customers Bargaining Power
Major national and regional retail chains, like Kroger and Walmart, wield considerable influence over Boston Beer Company's sales channels. These large retailers account for substantial sales volumes, enabling them to negotiate favorable pricing and promotional terms.
The bargaining power of these retail giants stems from their ability to influence product placement and demand promotional allowances, directly impacting Boston Beer's profitability and market access.
Independent wholesalers wield significant bargaining power within Boston Beer's three-tier distribution system. Their consolidation and territorial control mean Boston Beer Company must negotiate terms for pricing, marketing, and shelf space, as these wholesalers are essential conduits to retailers.
In 2024, the craft beer market saw continued consolidation among distributors. For instance, Reyes Beer Division, a major player, expanded its footprint, potentially increasing its leverage over brewers like Boston Beer by controlling access to a larger portion of the market.
Consumers in the alcoholic beverage market, including those who enjoy Boston Beer Company's products, can be quite sensitive to price. This is particularly true in crowded categories like hard seltzers, where numerous options are available. For instance, while Boston Beer has strong brands like Samuel Adams and Truly, the sheer volume of competing hard seltzers means consumers can easily opt for a cheaper alternative if prices rise too much.
This price sensitivity directly impacts Boston Beer's bargaining power. If they were to significantly increase prices on their popular brands, consumers might simply switch to a less expensive craft beer, a different seltzer brand, or even other alcoholic beverages altogether. This limits the company's ability to pass on increased costs without risking a noticeable drop in sales volume.
Shifting consumer preferences
Consumer preferences are changing at a dizzying pace, and this gives buyers a significant amount of leverage. We saw this clearly with the explosive growth of hard seltzers, which then saw a plateau or even a decline. Similarly, the sustained demand for non-alcoholic beverages highlights another shift. Boston Beer Company, to stay competitive, has to keep coming up with new products and adjusting its offerings to match what consumers want, otherwise, they risk becoming less popular and seeing sales drop.
This dynamic means Boston Beer Company needs to be incredibly agile. For instance, in 2023, the company continued to navigate the challenging craft beer market, with shipments for its Samuel Adams brand facing declines, underscoring the need to respond to evolving tastes. Their strategy often involves investing in innovation and marketing to capture emerging trends.
- Evolving Beverage Trends: The rise of hard seltzers, followed by a cooling in demand, and the persistent growth in non-alcoholic options demonstrate how quickly consumer tastes can shift, granting buyers greater influence.
- Innovation Imperative: Boston Beer Company must continually adapt its product portfolio, investing in research and development to align with these changing preferences, or face potential market share erosion.
- Market Responsiveness: The company's ability to quickly pivot and capitalize on new trends, such as the burgeoning non-alcoholic beer segment, is crucial for maintaining relevance and driving future sales.
Availability of diverse product choices
The sheer volume of beverage options available to consumers significantly amplifies their bargaining power. From a vast spectrum of craft beers to the surging popularity of hard seltzers, ciders, wines, and spirits, customers are spoiled for choice. This extensive variety makes it challenging for Boston Beer Company to rely solely on product differentiation, necessitating a robust brand presence to capture consumer loyalty.
In 2024, the alcoholic beverage market continued to diversify, with craft beer sales, a core segment for Boston Beer, facing increased competition from ready-to-drink (RTD) cocktails and non-alcoholic options. For instance, the RTD cocktail segment saw substantial growth, with some reports indicating double-digit percentage increases in sales volume year-over-year, directly presenting an alternative to Boston Beer's traditional offerings.
- Consumers can easily switch between a wide array of beer styles, seltzers, and other alcoholic beverages.
- The proliferation of craft breweries and the expansion of spirits and wine portfolios provide numerous substitutes.
- Boston Beer Company must invest in strong branding and marketing to maintain customer preference amidst this diverse landscape.
- The growing non-alcoholic beverage sector also presents an indirect competitive threat, broadening consumer choices beyond alcoholic drinks.
The bargaining power of customers is a significant factor for Boston Beer Company, influenced by evolving beverage trends and a vast array of choices. Consumers can easily switch between different craft beers, hard seltzers, and increasingly, non-alcoholic options or ready-to-drink (RTD) cocktails.
This wide selection means Boston Beer must constantly innovate and market effectively to retain customer loyalty. For example, the company's Samuel Adams brand has faced shipment declines, highlighting the need to adapt to changing tastes. In 2024, the RTD cocktail segment continued its strong growth, presenting a direct alternative to Boston Beer's core products.
Consumer price sensitivity is another key element, especially in crowded categories like hard seltzers, where cheaper alternatives are readily available. This limits Boston Beer's ability to pass on cost increases without risking sales volume.
| Beverage Category | Growth Trend (2024 Estimate) | Impact on Boston Beer |
|---|---|---|
| Craft Beer | Moderate Growth / Stagnation | Requires continued brand strength and innovation |
| Hard Seltzers | Slowing Growth / Decline | Intensified price competition, need for product differentiation |
| RTD Cocktails | Strong Growth (Double-digit %) | Direct competition, potential market share diversion |
| Non-Alcoholic Beverages | Consistent Growth | Broadens consumer choice, indirect competition |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Boston Beer Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Boston Beer, detailing the competitive landscape, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and substitutes. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, offering an in-depth strategic overview without any alterations or missing sections.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The alcoholic beverage market is a battlefield dominated by global giants like Anheuser-Busch InBev and Molson Coors. These behemoths wield immense power with their massive marketing budgets, sprawling distribution networks, and significant pricing leverage, making it challenging for smaller players to compete effectively.
Boston Beer Company finds itself in direct contention not only with these established giants but also with their increasingly craft-like brand extensions and their aggressive entries into the booming seltzer market. This intense rivalry underscores the critical need for Boston Beer to continually innovate and differentiate its product offerings to stand out.
For instance, Anheuser-Busch InBev's net sales reached approximately $54.4 billion in 2023, showcasing their sheer scale. Molson Coors also reported strong performance, with net sales of $12.1 billion in 2023. Boston Beer Company, while a significant player in its niche, operates on a much smaller scale, highlighting the competitive pressure from these larger entities.
The craft beer market has seen an explosion in the number of independent breweries. In 2023, the U.S. boasted over 9,000 craft breweries, a significant increase that intensifies competition. This proliferation means Boston Beer Company faces a highly fragmented market where numerous regional and local players are constantly emerging.
These smaller breweries often differentiate themselves by offering unique, niche, or locally sourced products. They directly challenge Boston Beer's established brand by appealing to consumers looking for novel experiences and supporting local businesses. This competition for consumer attention, taproom space, and retail shelf placement is a constant pressure.
The hard seltzer market, a significant growth engine for Boston Beer's Truly brand, is now incredibly crowded. We're seeing a flood of new competitors, from big beverage companies to smaller, agile startups, all vying for consumer attention.
This intense rivalry means pricing is becoming a major battleground, with companies resorting to more promotions to grab market share. This increased spending directly impacts the profitability of the hard seltzer segment.
For instance, in 2023, the hard seltzer category experienced a notable slowdown in growth compared to its explosive earlier years, with some reports indicating a decline in overall volume for certain major brands as consumer preferences diversified.
Innovation race and brand differentiation
The alcoholic beverage market is a hotbed of innovation, with companies constantly vying to capture consumer interest through new flavors and product lines. This intense competition means Boston Beer Company, like its rivals, must continuously invest in research and development and robust marketing strategies to stay ahead. For instance, in 2023, the craft beer segment, a key area for Boston Beer, saw numerous new product introductions, reflecting this ongoing innovation race.
Brand differentiation is equally crucial. Boston Beer's success with Samuel Adams, for example, highlights the power of a strong, recognizable brand in a crowded marketplace. However, the rise of numerous smaller craft breweries and the increasing popularity of hard seltzers and ready-to-drink (RTD) cocktails mean that maintaining brand distinctiveness requires ongoing effort and significant marketing spend. The market share shifts observed in 2024, with established brands facing pressure from newer entrants, underscore this point.
- Innovation is key: Competitors are consistently releasing new products, requiring significant R&D investment from Boston Beer.
- Brand building is vital: Effective marketing is essential to differentiate Boston Beer's offerings in a saturated market.
- Market dynamics: The craft beer segment and the growing RTD category present ongoing challenges and opportunities for brand differentiation and innovation.
Consolidation and strategic alliances
The beer industry, including the craft segment where Boston Beer Company operates, has experienced significant consolidation. Larger breweries frequently acquire or form alliances with smaller craft operations to expand their market share and product offerings. For instance, in 2023, Constellation Brands, a major player, continued to expand its craft portfolio through strategic investments and acquisitions, aiming to capture a larger slice of the premium beer market.
These consolidation trends create formidable competitors for independent brewers. Companies that can achieve greater scale through mergers and acquisitions often benefit from enhanced distribution networks, increased marketing budgets, and greater purchasing power. This dynamic can put smaller, independent breweries at a disadvantage if they lack the resources to compete on a similar level, potentially impacting their market presence and profitability.
Boston Beer Company itself has navigated this landscape, engaging in strategic partnerships. However, the ongoing consolidation means that the competitive intensity remains high. In 2024, the trend shows no signs of slowing, with major beverage companies actively seeking to bolster their craft and specialty beer offerings.
- Ongoing Consolidation: Major beverage corporations are actively acquiring craft breweries to broaden their portfolios.
- Strategic Alliances: Partnerships and joint ventures are common strategies to gain market access and distribution.
- Impact on Independents: Smaller brewers face challenges in matching the scale and market reach of consolidated entities.
- Competitive Pressure: Consolidation increases the competitive rivalry, demanding greater innovation and efficiency from all players.
Competitive rivalry is fierce for Boston Beer Company, facing giants like Anheuser-Busch InBev and Molson Coors, whose 2023 net sales were $54.4 billion and $12.1 billion respectively. The proliferation of over 9,000 craft breweries in the U.S. by 2023 further fragments the market, intensifying competition for shelf space and consumer attention, especially with the hard seltzer market seeing increased entrants and pricing pressures impacting profitability.
| Competitor | 2023 Net Sales (Approx.) | Key Competitive Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Anheuser-Busch InBev | $54.4 billion | Scale, Marketing Budget, Distribution |
| Molson Coors | $12.1 billion | Brand Portfolio, Market Reach |
| Independent Craft Breweries | Varies (Thousands of players) | Niche Products, Local Appeal, Innovation |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The increasing consumer focus on health and wellness is a significant driver for the growth of non-alcoholic beverage options. This trend directly impacts Boston Beer Company as consumers increasingly opt for alternatives like non-alcoholic beers, sparkling waters, and functional beverages, which can replace traditional alcoholic drink consumption occasions.
In 2024, the non-alcoholic beverage market, particularly non-alcoholic beer, has seen substantial expansion. For instance, the U.S. non-alcoholic beer market alone was projected to reach over $3 billion by 2025, indicating a strong and growing preference for these substitutes.
The appeal of wine and spirits, including ready-to-drink (RTD) cocktails, is a significant competitive force for Boston Beer Company. These categories are not only mature but also experiencing growth, directly vying for consumer dollars allocated to alcoholic beverages.
Shifting consumer preferences towards premium spirits or the convenience of RTDs can pull customers away from Boston Beer's traditional beer and hard seltzer products. For instance, the spirits market saw substantial growth, with the global spirits market valued at approximately USD 1.3 trillion in 2023 and projected to grow. This demonstrates the strong consumer demand and the potential for these substitutes to capture market share.
The increasing legalization of cannabis is paving the way for cannabis-infused beverages, presenting a novel substitute for traditional alcoholic drinks, especially in the recreational market. As of 2024, the global legal cannabis market was valued at approximately $130 billion, with beverage segments showing significant growth potential.
While still in its early stages, this emerging category could draw consumers looking for alternative ways to socialize or relax, potentially affecting the long-term demand for Boston Beer’s core products. For instance, the U.S. cannabis beverage market alone is projected to reach several billion dollars in the coming years, indicating a tangible threat to established beverage categories.
Shift towards health-conscious choices
The growing consumer focus on health and wellness presents a significant threat of substitutes for Boston Beer Company. Individuals are increasingly scrutinizing calorie counts, sugar levels, and alcohol by volume (ABV) in their beverage choices. This trend directly impacts the demand for traditional beers and hard seltzers, pushing consumers towards alternatives that better align with their health objectives.
This shift is evident in the beverage market's evolving landscape. For instance, the non-alcoholic beverage sector experienced substantial growth, with sales of non-alcoholic beers and spirits reaching an estimated $2.7 billion in the US by the end of 2023. Furthermore, a 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of consumers are actively seeking beverages with lower sugar content. This indicates a strong preference for options that support healthier lifestyles, potentially diverting consumers away from Boston Beer's core products.
- Health-Conscious Consumer Behavior: A rising tide of consumers are prioritizing wellness, leading them to re-evaluate their beverage consumption habits.
- Alternative Beverage Categories: Lighter beers, low-ABV options, and non-alcoholic drinks are gaining traction as viable substitutes.
- Market Data Support: The non-alcoholic beverage market's growth and consumer surveys highlighting sugar reduction preferences underscore this threat.
- Impact on Boston Beer: These trends challenge Boston Beer's traditional product portfolio, necessitating adaptation to meet evolving consumer demands.
Cost-effectiveness of other recreational activities
The cost-effectiveness of alternative recreational activities presents a significant threat to Boston Beer. Consumers often have a broad spectrum of leisure pursuits competing for their disposable income, many of which do not involve alcoholic beverages. For example, in 2024, spending on experiences like travel and entertainment saw robust growth, potentially diverting funds that might otherwise be spent on craft beer.
This competition extends beyond direct beverage substitutes. Consider the rising popularity of home-based entertainment, streaming services, and outdoor activities like hiking or cycling. These options can be perceived as more cost-effective or offer different value propositions compared to purchasing craft beer, especially for frequent consumption occasions.
- Alternative Leisure Spending: In 2024, US consumer spending on entertainment and recreation services grew by an estimated 7.5%, highlighting a strong demand for non-alcoholic experiences.
- Cost Perception: A significant portion of consumers, particularly younger demographics, increasingly prioritize value for money, making budget-friendly activities a more attractive option.
- Occasion Substitution: Social gatherings or relaxation periods traditionally associated with beer consumption can now be fulfilled by activities like attending live music events (often with non-alcoholic beverage options) or engaging in fitness classes, which may be perceived as healthier and more cost-efficient overall.
The threat of substitutes for Boston Beer is substantial, driven by evolving consumer preferences and a widening array of beverage choices. Health-conscious consumers are increasingly turning to non-alcoholic options, while the growing popularity of spirits and ready-to-drink cocktails directly competes for market share. Furthermore, emerging categories like cannabis-infused beverages present a novel, albeit nascent, challenge.
In 2024, the non-alcoholic beer market alone was a significant force, projected to exceed $3 billion in the U.S. by 2025. This growth, coupled with a consumer survey in 2024 revealing over 60% actively seeking lower sugar content, underscores the shift away from traditional alcoholic beverages. The global spirits market, valued at approximately $1.3 trillion in 2023, also demonstrates the strong appeal of alternative alcoholic options.
Beyond beverages, alternative leisure activities also pose a threat. In 2024, U.S. consumer spending on entertainment and recreation services saw an estimated 7.5% growth, indicating a diversion of disposable income from alcoholic beverages to experiences. This broadens the competitive landscape, as consumers may opt for cost-effective or health-oriented activities over beer consumption.
| Substitute Category | 2024 Market Insight/Trend | Impact on Boston Beer |
| Non-Alcoholic Beverages | U.S. market projected over $3 billion by 2025; 60%+ consumers seek lower sugar (2024 survey). | Direct competition for occasions previously filled by beer/seltzer. |
| Spirits & RTDs | Global spirits market ~ $1.3 trillion (2023); RTDs offer convenience. | Captures consumer spending allocated to alcoholic drinks. |
| Cannabis-Infused Beverages | Emerging market with significant growth potential (U.S. market projected billions). | Potential long-term diversion from traditional alcohol consumption. |
| Alternative Leisure Activities | U.S. entertainment/recreation spending grew 7.5% (2024). | Diverts disposable income and consumer time from beverage purchases. |
Entrants Threaten
The craft beer market, a significant segment for Boston Beer Company, presents a notable threat due to its relatively low barriers to entry for small-scale brewing operations. This accessibility allows a proliferation of microbreweries and brewpubs to establish themselves, directly impacting market fragmentation.
While these smaller players may not possess the national distribution or brand recognition of Boston Beer, their local appeal and ability to cater to niche consumer preferences can chip away at market share. For instance, the number of craft breweries in the U.S. has steadily increased, reaching over 9,000 by the end of 2023, indicating a highly competitive landscape where new entrants can readily emerge.
While it might seem easy for a small brewery to pop up, truly competing with a company like Boston Beer on a national level demands a massive amount of money. Think about building or acquiring large-scale brewing operations, running extensive marketing campaigns to get your name out there, and setting up a distribution system that can reach customers all over the country. These significant upfront costs create a pretty steep hurdle for anyone looking to enter the market at that scale.
The threat of new entrants for Boston Beer Company is significantly mitigated by the strong brand recognition and loyalty it has cultivated. Brands like Samuel Adams and Truly have built substantial equity over years, making it difficult for newcomers to gain traction. For instance, in 2024, Boston Beer continued to leverage these established names in its marketing efforts, aiming to solidify its market position against emerging craft and hard seltzer brands.
Complex regulatory environment
The alcoholic beverage industry is a minefield of federal, state, and local regulations. These rules dictate everything from obtaining licenses and producing beverages to how they're distributed and marketed. For instance, the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) oversees federal oversight, while individual states have their own unique requirements.
Navigating this intricate web, especially the established three-tier system (producer, distributor, retailer), acts as a substantial barrier. New entrants face significant costs and complexities in securing the necessary permits and establishing compliant distribution channels, making market entry a costly endeavor.
- Federal Regulations: TTB requires permits for production and labeling approval.
- State Licensing: Each state has unique licensing requirements for manufacturers, wholesalers, and retailers.
- Three-Tier System: This structure mandates separate licenses for production, distribution, and retail, adding layers of compliance and cost.
- Marketing Restrictions: Regulations often limit how alcoholic beverages can be advertised and promoted, impacting market entry strategies.
Access to distribution channels
Gaining access to established distribution channels presents a significant hurdle for new entrants in the craft beer market. The three-tier system, with its independent wholesalers, requires new brewers to build relationships and secure shelf space against established brands. Boston Beer Company, with its extensive history and volume, naturally commands more favorable terms with these distributors.
New entrants often find it difficult to negotiate the same advantageous agreements as incumbents like Boston Beer. These established players leverage their long-standing relationships and greater sales volume to secure prime placement and efficient delivery networks. For instance, in 2024, the craft beer market continued to be dominated by a few large players who benefit from existing distribution power.
- Distribution Barrier: New entrants face significant challenges in securing access to established distribution networks, particularly the independent wholesalers crucial for market penetration.
- Established Relationships: Boston Beer Company benefits from long-standing relationships with distributors, giving it leverage over newer competitors.
- Volume Leverage: Higher sales volumes allow established players like Boston Beer to negotiate more favorable distribution terms and gain preferential shelf space.
While the sheer number of craft breweries might suggest a low threat, the capital required for national distribution and brand building is substantial, acting as a significant deterrent. Furthermore, Boston Beer's strong brand loyalty, exemplified by continued marketing of Samuel Adams and Truly in 2024, creates a formidable barrier for newcomers seeking to gain market share.
The complex regulatory environment and the entrenched three-tier distribution system also pose considerable challenges for new entrants. These factors, combined with the leverage Boston Beer holds with established distributors due to its sales volume, effectively limit the threat of new companies significantly impacting its market position.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for The Boston Beer Company is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research from reputable firms. We also incorporate data from trade publications and news archives to capture current market trends and competitive actions.
