Bank of New York Mellon Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bank of New York Mellon Bundle
The Bank of New York Mellon operates within a complex financial landscape, where intense rivalry and the threat of new entrants significantly shape its competitive environment. Understanding the bargaining power of both buyers and suppliers is crucial for navigating this market effectively.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Bank of New York Mellon’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
BNY Mellon's reliance on specialized technology makes it vulnerable to concentrated key technology providers. If a few dominant vendors control essential software, data analytics, or cybersecurity, they gain significant leverage. This can lead to higher costs and slower innovation for BNY Mellon, as seen in the broader financial services sector where tech spending is projected to reach $70 billion by 2024.
The financial services sector, including investment management and digital assets, heavily relies on specialized expertise. A shortage of professionals skilled in areas like AI, blockchain, or intricate regulatory frameworks grants these individuals and niche consulting firms considerable leverage.
This scarcity directly impacts BNY Mellon by potentially driving up labor costs and creating hurdles in recruiting and retaining top talent. For instance, in 2024, the demand for cybersecurity professionals with financial sector experience saw salary increases of 15-20% compared to the previous year, highlighting the premium placed on specialized skills.
The Bank of New York Mellon (BNY Mellon) operates within a heavily regulated financial landscape, making regulatory and compliance service providers essential suppliers. These include specialized legal firms, expert compliance consultants, and innovative regulatory technology (RegTech) companies.
The intricate and constantly changing global financial regulations grant these niche providers significant bargaining power. This leverage can directly impact BNY Mellon's operational expenses and its ability to effectively manage risk, as demonstrated by the increasing investment in compliance technology, which saw a global market growth of approximately 15% in 2024.
Data and Information Providers
The bargaining power of data and information providers significantly impacts BNY Mellon. Access to accurate, timely financial data and market intelligence is crucial for BNY Mellon's investment management and analytical functions. Key data vendors, credit rating agencies, and financial news services hold considerable sway due to the proprietary and indispensable nature of their offerings.
This reliance on external data sources means that BNY Mellon's decision-making and ability to provide competitive investment insights can be directly influenced by the pricing and terms set by these providers. For instance, the cost of essential data feeds, which can run into millions of dollars annually for large financial institutions, directly impacts operational expenses.
- Data Dependency: BNY Mellon's core operations rely heavily on data from external sources, creating a dependence that suppliers can leverage.
- Proprietary Information: The unique and often exclusive nature of financial data and research gives providers significant pricing power.
- Market Intelligence Costs: In 2024, the market for financial data services saw continued growth, with major providers like Bloomberg and Refinitiv commanding substantial subscription fees, often in the tens of thousands of dollars per terminal annually.
- Impact on Competitiveness: The cost and availability of high-quality data directly affect BNY Mellon's capacity to generate alpha and offer differentiated services to clients.
Infrastructure and Utility Providers
BNY Mellon, like all major financial institutions, relies heavily on infrastructure and utility providers, such as telecommunications, cloud services, and data centers. While many of these services appear commoditized, a significant price hike or disruption from a key provider in a critical operational region could indeed impact BNY Mellon's ability to deliver services and maintain its extensive operations. For instance, the ongoing global expansion of cloud computing, a cornerstone of BNY Mellon's platform operating model, means that major cloud providers hold considerable sway.
The bargaining power of these infrastructure and utility suppliers is influenced by several factors. The concentration of providers in specific markets, the availability of alternative suppliers, and the switching costs for BNY Mellon all play a role. For example, while there are numerous telecommunications providers, the specialized needs for high-speed, secure data transmission for a global financial firm might limit the truly viable options.
- Cloud Provider Concentration: The global cloud computing market in 2024 is dominated by a few major players, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. This concentration can give these providers significant leverage in pricing and contract negotiations.
- Data Center Reliance: BNY Mellon's operations are underpinned by robust data center infrastructure. The availability and cost of specialized data center services, particularly those offering high levels of security and uptime, can be a point of negotiation.
- Telecommunications Costs: Global financial institutions incur substantial costs for high-bandwidth, low-latency network connectivity. While competition exists, the need for reliable, secure global networks can limit the bargaining power of BNY Mellon with major telecommunications carriers.
BNY Mellon's dependence on specialized technology providers, particularly in areas like cloud computing and cybersecurity, grants these vendors significant bargaining power. The concentration of major cloud providers, such as AWS and Microsoft Azure, in the 2024 market means they can dictate terms, impacting BNY Mellon's infrastructure costs.
The financial services industry's reliance on specialized expertise, especially in emerging fields like AI and blockchain, elevates the bargaining power of skilled professionals and niche consulting firms. This scarcity, evidenced by 15-20% salary increases for cybersecurity experts in 2024, drives up labor costs for BNY Mellon.
Providers of essential financial data and market intelligence, like Bloomberg and Refinitiv, wield considerable influence due to the proprietary and indispensable nature of their services. The substantial annual subscription fees for these data feeds, often tens of thousands of dollars per terminal in 2024, directly impact BNY Mellon's operational expenses and competitive edge.
Regulatory and compliance service providers, including specialized legal firms and RegTech companies, possess strong bargaining power due to the complex and evolving regulatory landscape. BNY Mellon's increased investment in compliance technology, a market that grew by approximately 15% globally in 2024, highlights the essential nature and associated costs of these services.
| Supplier Type | Key Factors Influencing Bargaining Power | Examples for BNY Mellon | 2024 Market Insight | Impact on BNY Mellon |
| Technology Providers | Concentration, specialization | Cloud services (AWS, Azure), Cybersecurity software | Cloud market dominated by few major players | Higher infrastructure costs, potential vendor lock-in |
| Specialized Expertise | Scarcity of skills, demand | AI specialists, Blockchain developers, Compliance consultants | 15-20% salary increase for cybersecurity pros | Increased labor costs, talent acquisition challenges |
| Data & Information Providers | Proprietary nature, indispensability | Financial data terminals (Bloomberg), Credit rating agencies | High annual subscription fees for data feeds | Significant operational expenses, impacts decision-making |
| Regulatory & Compliance Services | Regulatory complexity, specialization | Legal firms, RegTech solutions | 15% global market growth for RegTech in 2024 | Increased compliance costs, risk management expenses |
What is included in the product
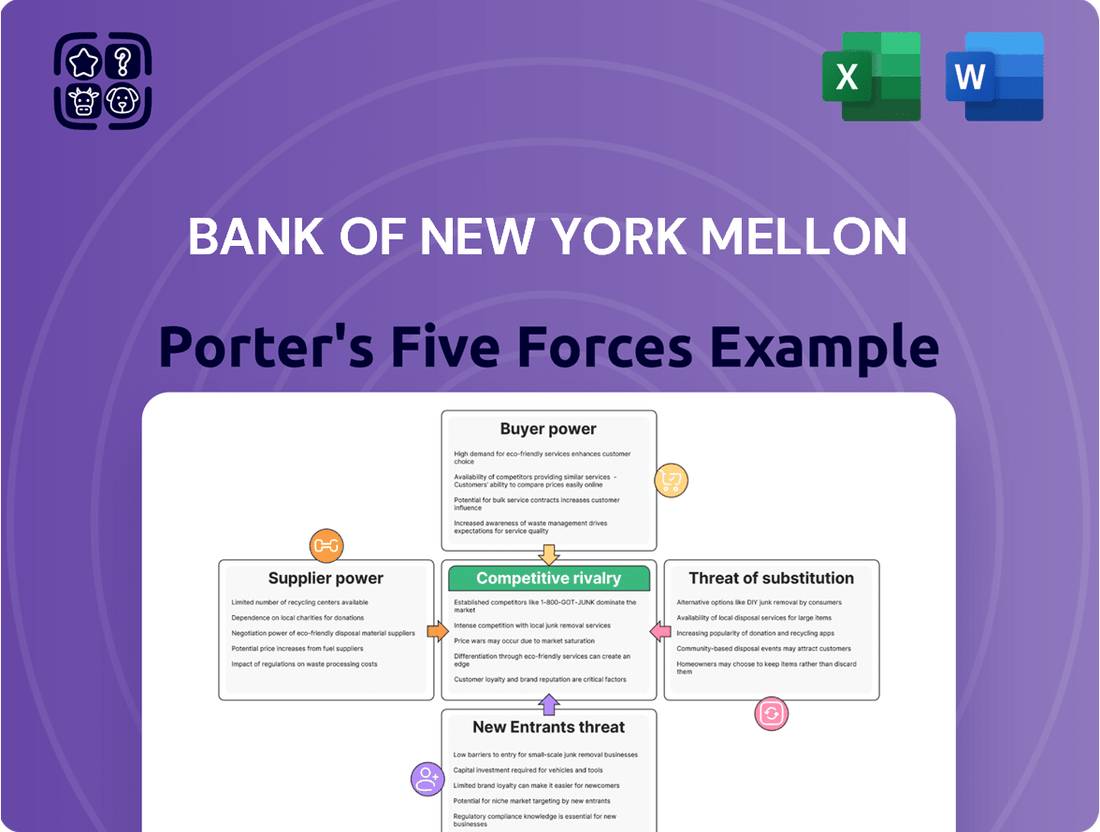
This analysis delves into the competitive forces shaping the financial services industry for Bank of New York Mellon, examining threats from new entrants, the power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry, and the impact of substitutes.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures across all five forces, enabling swift identification of strategic vulnerabilities and opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of customers is a significant factor for Bank of New York Mellon (BNY Mellon), particularly when dealing with its large institutional clients. These clients, which include major pension funds, sovereign wealth funds, and global corporations, represent a substantial portion of BNY Mellon's business. For instance, BNY Mellon reported $45.4 trillion in assets under custody and administration as of the first quarter of 2024, with a significant portion attributable to these large entities.
Due to the sheer volume of assets they entrust to BNY Mellon, these institutional clients wield considerable leverage. They can negotiate for more competitive pricing on services like custody, fund administration, and securities lending. Furthermore, their size allows them to demand highly customized solutions and elevated service levels, directly impacting BNY Mellon's operational costs and profit margins.
BNY Mellon's clients often seek a broad spectrum of interconnected services, such as asset servicing, corporate trust, and treasury services. This complexity allows large, sophisticated clients to wield considerable bargaining power by consolidating their needs and negotiating better pricing across BNY Mellon's diverse offerings.
Switching custodians or asset servicers presents significant hurdles for large financial institutions. The complexity of integrating new systems and migrating vast amounts of data can be both time-consuming and expensive, effectively locking in many clients. This inherent difficulty in switching directly impacts the bargaining power of customers, as the perceived effort and cost of changing providers can be substantial.
BNY Mellon actively works to mitigate this customer power by investing in its service offerings. Initiatives like Pershing X and the Eliza AI platform are designed to create a more integrated and user-friendly experience. By offering advanced technological solutions and streamlining operational processes, BNY Mellon aims to increase client loyalty and make the prospect of switching to a competitor less appealing.
Price Sensitivity and Fee Pressure
Institutional clients in financial services are keenly aware of costs, particularly for standardized offerings. This price sensitivity directly impacts BNY Mellon, forcing it to keep its fees competitive to avoid losing business, which can affect its overall fee income. For example, in 2024, the competition for custody services, a core BNY Mellon offering, intensified, leading to potential margin compression for providers.
BNY Mellon’s strategic initiatives, including investments in operational efficiency and the integration of artificial intelligence, are designed to mitigate these fee pressures. By streamlining processes and leveraging technology, the company aims to control its cost base, thereby protecting its profitability even when faced with demanding client pricing expectations. This focus on efficiency is crucial for maintaining margins in a market where price is a significant differentiator.
- Price Sensitivity: Institutional clients often prioritize cost savings, especially for services that are perceived as commodities.
- Fee Pressure: This client behavior translates into direct pressure on BNY Mellon to offer competitive pricing, potentially impacting revenue from fees.
- Operational Efficiency: BNY Mellon's investment in operational improvements and AI is a direct response to manage costs and sustain profitability amidst fee pressure.
- Competitive Landscape: The financial services sector is highly competitive, amplifying the bargaining power of clients who can readily switch providers for better rates.
Access to Alternative Solutions
Customers increasingly have access to alternative solutions, whether through developing in-house capabilities or engaging specialized fintech providers for niche services. This trend directly impacts the bargaining power of BNY Mellon's clientele.
The burgeoning digital asset custody services and the emergence of tokenized assets present clients with novel choices that can bypass traditional banking infrastructure. This diversification of options empowers customers to seek out more tailored or cost-effective solutions.
BNY Mellon's strategic moves, such as its expansion into digital asset custody and collaborations like the one with Goldman Sachs for tokenized money market funds, highlight its awareness of these shifting client demands and market dynamics. These initiatives are crucial for maintaining competitiveness.
- Increased Fintech Competition: The financial services landscape is increasingly populated by agile fintech firms offering specialized solutions, potentially fragmenting BNY Mellon's client base.
- Digital Asset Adoption: The growing acceptance and development of digital assets and tokenization offer clients new avenues for custody and transaction services outside of traditional providers.
- In-house Capabilities: Larger institutional clients may develop internal capabilities for certain services, reducing their reliance on external providers like BNY Mellon.
- Partnership Strategies: BNY Mellon's partnerships, such as with Goldman Sachs for tokenized money market funds, are a direct response to client demand for innovative digital solutions, aiming to retain and attract business in this evolving market.
The bargaining power of customers for BNY Mellon is substantial, primarily driven by its large institutional client base. These clients, managing vast sums of assets, can negotiate for better pricing and customized services, directly impacting BNY Mellon's profitability. For instance, BNY Mellon reported $45.4 trillion in assets under custody and administration as of Q1 2024. The complexity of switching custodians also creates a degree of client stickiness, though the rise of fintech alternatives and digital assets is introducing new competitive pressures.
| Factor | Impact on BNY Mellon | Client Action |
|---|---|---|
| Client Size & Asset Volume | High leverage for negotiation | Demand lower fees, customized solutions |
| Service Interdependence | Clients can bundle services for better terms | Consolidate needs across BNY Mellon's offerings |
| Switching Costs | Creates client retention | Less incentive to switch despite price differences |
| Price Sensitivity | Pressure on fee income | Seek competitive pricing, potentially impacting margins |
| Alternative Solutions | Increased competition | Explore fintech, in-house capabilities, digital assets |
Preview Before You Purchase
Bank of New York Mellon Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of The Bank of New York Mellon, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, offering an in-depth examination of industry rivalry, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of substitute products. You can trust that this is the exact, fully formatted analysis ready for your immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
BNY Mellon faces formidable competition from global financial titans like State Street Corporation, JPMorgan Chase & Co., Citigroup Inc., and Northern Trust Corporation. These established players offer a broad spectrum of similar investment management and asset servicing solutions, intensifying the battle for market dominance.
This intense rivalry particularly impacts BNY Mellon's core custody and asset servicing business, where market share is fiercely contested. For instance, as of the first quarter of 2024, the total assets under custody and administration for the top five custody banks, including BNY Mellon, collectively reached trillions of dollars, highlighting the sheer scale of competition.
The financial services industry is experiencing intense rivalry fueled by rapid technological innovation, especially in areas like artificial intelligence and blockchain. Companies are pouring billions into these advancements to boost efficiency, enhance customer interactions, and introduce novel offerings. For instance, in 2023, the global financial services sector saw significant investment in AI, with projections indicating continued substantial growth.
BNY Mellon's strategic investments, such as its 'Eliza' AI platform, underscore the critical role of technology in maintaining a competitive advantage. This focus on digital transformation and platform operating models allows firms to differentiate themselves and capture market share. The drive for technological superiority is a key battleground, influencing how services are delivered and how clients engage with financial institutions.
Competitors in the financial services sector often face a strategic choice: specialize in a narrow niche or offer a broad spectrum of services. BNY Mellon, for instance, has built its business model around providing a comprehensive suite of solutions, encompassing asset servicing, corporate trust, and treasury services. This broad approach means the bank is not just competing with other large, diversified financial institutions but also with more specialized players within each of its service areas.
The intensity of this competitive rivalry is significant, whether a competitor focuses on a specific product like custody services or aims to provide an integrated offering similar to BNY Mellon. For example, in the asset servicing market, BNY Mellon competes with firms like State Street and Northern Trust, both of which also offer extensive services. This necessitates continuous innovation and a clear demonstration of value across BNY Mellon's diverse portfolio to maintain its market position.
Pricing Pressure and Margin Compression
The banking sector, especially for services like traditional custody, is intensely competitive. This often translates into significant pricing pressure, forcing institutions to lower fees to attract and retain clients. For BNY Mellon, this means that margin compression is a constant challenge, impacting overall profitability.
BNY Mellon's success in navigating this environment hinges on its operational efficiency and robust cost control initiatives. By streamlining processes and managing expenses effectively, the company can better absorb the impact of lower pricing. Furthermore, a strategic shift towards higher-margin, fee-based services provides a crucial counterbalance to the pressure on more commoditized offerings.
- Intense Competition: High competition, particularly in commoditized areas like traditional custody, drives down prices.
- Margin Compression: This pricing pressure directly leads to reduced profit margins for all participants in these segments.
- BNY Mellon's Strategy: Profitability is maintained through operational efficiency, cost management, and a focus on higher-margin fee-based services.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance Costs
The financial services industry operates under a dense and constantly shifting regulatory framework, significantly intensifying competitive rivalry. Firms like BNY Mellon face substantial compliance costs, which can be a barrier to entry for smaller competitors and tend to favor larger institutions with the financial capacity to absorb these expenses. For instance, in 2024, the global financial industry continued to grapple with increased regulatory scrutiny following past crises, leading to significant investments in compliance technology and personnel across the sector.
These regulatory mandates, while costly, also serve to level the playing field by imposing uniform standards. However, the dynamic nature of these regulations means that companies must remain exceptionally agile. For example, the ongoing evolution of data privacy regulations and anti-money laundering (AML) requirements in 2024 demanded continuous adaptation, creating opportunities for those who could efficiently integrate new compliance measures and challenges for those who lagged behind.
- Increased Compliance Burden: Financial institutions globally, including BNY Mellon, must invest heavily in meeting evolving regulatory requirements, such as those related to capital adequacy, consumer protection, and cybersecurity.
- Cost Advantage for Larger Players: Substantial compliance costs can disproportionately affect smaller firms, allowing larger, well-resourced entities to absorb these expenses more readily and potentially gain a competitive edge.
- Regulatory Arbitrage and Adaptation: While regulations can create barriers, they also present opportunities for firms that can effectively navigate and adapt to new rules, potentially outmaneuvering less agile competitors.
- Impact of Global Regulations: In 2024, BNY Mellon, like its peers, had to manage a complex web of international regulations, such as those stemming from Basel III finalization and evolving digital asset frameworks, impacting operational costs and strategic planning.
BNY Mellon faces intense rivalry from global financial giants like State Street and Northern Trust, particularly in its core custody and asset servicing business. This competition drives pricing pressure, leading to margin compression, which BNY Mellon counters through operational efficiency and a strategic shift towards higher-margin services.
The financial services landscape is also shaped by rapid technological advancements, with firms investing heavily in AI and blockchain to enhance services and efficiency. BNY Mellon's own investments, such as its 'Eliza' AI platform, highlight the critical role of technology in differentiating offerings and capturing market share in this dynamic environment.
Furthermore, the complex and evolving regulatory framework adds another layer of competition. While compliance costs can be a barrier for smaller players, they also necessitate agility and investment, with BNY Mellon, like its peers, navigating global regulations such as Basel III finalization and digital asset frameworks throughout 2024.
| Competitor | Key Services | 2024 Estimated Assets Under Custody/Administration (USD Trillions) |
|---|---|---|
| State Street Corporation | Asset Servicing, Investment Management | ~40-45 |
| JPMorgan Chase & Co. | Custody, Asset Servicing, Investment Banking | ~25-30 |
| Northern Trust Corporation | Asset Servicing, Wealth Management | ~15-20 |
| Citigroup Inc. | Custody, Securities Services | ~10-15 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For extremely large institutional clients, managing and servicing their assets internally instead of using a third-party provider like BNY Mellon presents a potential substitute. This is especially relevant for sophisticated entities possessing the required infrastructure, expertise, and operational scale.
However, the significant complexity, substantial costs, and demanding regulatory landscape often render a complete in-house solution less appealing for the majority of institutions. For instance, managing global custody and securities lending operations in-house requires massive investment in technology and compliance, which most firms find prohibitive compared to outsourcing.
Direct investment platforms and robo-advisors present a growing threat of substitution for certain wealth management services offered by institutions like BNY Mellon, especially for affluent individuals. These digital solutions provide automated, cost-effective investment advice and portfolio management, potentially drawing clients away from traditional wealth managers.
For instance, the global robo-advisory market was valued at approximately $5.3 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $32 billion by 2030, indicating a significant shift towards these digital alternatives. This trend suggests that BNY Mellon, while focused on institutional clients, must consider how these accessible platforms might impact its broader wealth management offerings.
Emerging blockchain and decentralized finance (DeFi) solutions pose a significant threat by offering alternative methods for asset management and transfer, potentially replacing traditional custody and settlement services. Tokenized assets are a prime example, promising quicker and more transparent transactions than conventional systems.
BNY Mellon is proactively addressing this by investing in digital asset custody and launching tokenized money market funds. This strategic engagement acknowledges the disruptive potential of these technologies, viewing them as both a competitive challenge and a pathway for innovation.
Specialized Fintech Solutions
The rise of specialized fintech firms presents a significant threat of substitutes for Bank of New York Mellon (BNY Mellon). These agile companies are unbundling traditional banking services, offering highly focused solutions in areas like payments, data analytics, and regulatory compliance. For example, companies like Stripe have captured a substantial share of the online payment processing market, directly competing with BNY Mellon's transaction services. Similarly, data analytics platforms are increasingly sophisticated, potentially replacing some of the insights BNY Mellon provides through its custody and asset servicing divisions.
This trend forces BNY Mellon to constantly innovate and demonstrate the added value of its integrated, comprehensive offerings. The competitive pressure from these niche players necessitates continuous investment in technology and service enhancement to retain clients who might otherwise opt for specialized, potentially more cost-effective, fintech alternatives. In 2023, the global fintech market was valued at over $1.1 trillion, highlighting the scale of this disruptive force.
- Niche Payment Solutions: Fintechs like Square (now Block) and PayPal offer streamlined payment gateways, challenging BNY Mellon's traditional transaction volumes.
- Data Analytics Tools: Specialized platforms provide advanced financial data analysis, potentially substituting BNY Mellon's data reporting and insights services.
- Automated Compliance: Regtech firms offer automated solutions for regulatory adherence, a service BNY Mellon also provides, creating direct substitution opportunities.
- Market Growth: The fintech sector's rapid expansion, with projections indicating continued double-digit annual growth, underscores the persistent threat of substitutes.
Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) and Passive Investing
The rise of Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) and passive investing presents a significant threat of substitution for BNY Mellon's actively managed fund offerings. Investors are increasingly drawn to ETFs due to their typically lower expense ratios and the broad market exposure they provide. For instance, global ETF assets under management reached an estimated $10.9 trillion by the end of 2023, a substantial increase from previous years, indicating a strong shift in investor preference.
These low-cost alternatives, often managed by index providers or other asset managers, can divert substantial assets away from traditional active management strategies. This trend directly impacts BNY Mellon's investment management segment, as clients may opt for passive solutions to reduce fees and achieve market-like returns. The accessibility and transparency of ETFs make them a compelling substitute, especially for retail investors.
Key aspects of this threat include:
- Lower Fees: ETFs generally charge lower management fees compared to actively managed funds, making them a more cost-effective choice for investors seeking long-term growth.
- Market Accessibility: ETFs offer diversified exposure to various asset classes and markets with a single transaction, simplifying investment for a broad range of investors.
- Growth in Passive Assets: The proportion of assets invested passively continues to grow, with passive strategies managing a significant and increasing share of the overall investment market.
The threat of substitutes for BNY Mellon is multifaceted, encompassing in-house capabilities, digital platforms, and innovative financial technologies. While direct in-house management by large institutions is often cost-prohibitive, the growing accessibility of robo-advisors and direct investment platforms challenges BNY Mellon's wealth management services, particularly for affluent individuals. The global robo-advisory market's projected growth from $5.3 billion in 2023 to over $32 billion by 2030 highlights this shift.
Emerging blockchain and DeFi solutions, such as tokenized assets, offer alternative methods for asset management and transfer, potentially replacing traditional custody and settlement services. BNY Mellon's investment in digital asset custody demonstrates an awareness of this disruptive potential. Furthermore, specialized fintech firms are unbundling traditional banking services, with companies like Stripe capturing significant market share in payment processing, a sector where BNY Mellon operates. The global fintech market's valuation exceeding $1.1 trillion in 2023 underscores the competitive pressure from these niche players.
The increasing popularity of ETFs and passive investing presents another significant substitute for BNY Mellon's actively managed funds. Global ETF assets under management reached approximately $10.9 trillion by the end of 2023, reflecting a strong investor preference for lower fees and broad market exposure. This trend directly impacts BNY Mellon's investment management segment, as clients increasingly opt for cost-effective passive solutions.
| Substitute Category | Examples | Impact on BNY Mellon | Market Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-house Management | Large institutions managing assets internally | Feasible for highly sophisticated clients, but costly and complex. | High infrastructure and compliance costs make it prohibitive for most. |
| Digital Investment Platforms | Robo-advisors, direct investment platforms | Challenges wealth management services, especially for affluent individuals. | Global robo-advisory market projected to grow from $5.3B (2023) to $32B+ (2030). |
| Blockchain & DeFi | Tokenized assets, decentralized finance | Offers alternative custody and settlement, potentially replacing traditional services. | BNY Mellon is investing in digital asset custody to address this. |
| Fintech Firms | Specialized payment processors, data analytics, regtech | Unbundling services, competing in niche areas like payments and data insights. | Global fintech market valued over $1.1T (2023); Stripe example in payments. |
| Passive Investing (ETFs) | Exchange-Traded Funds | Attracts assets away from actively managed funds due to lower fees and accessibility. | Global ETF AUM reached ~$10.9T by end of 2023. |
Entrants Threaten
The financial services sector, particularly for global players like Bank of New York Mellon managing trillions in assets, is characterized by exceptionally high capital requirements and rigorous regulatory oversight. New entrants must navigate substantial barriers to entry, including securing necessary licenses, adhering to complex international regulations, and building robust financial infrastructure. For instance, in 2024, capital adequacy ratios for major banks remain a significant hurdle, often requiring billions in initial investment, thereby strongly discouraging new competition.
BNY Mellon's formidable brand reputation, cultivated since its founding in 1784, presents a significant barrier to new entrants. Its established trust and perceived reliability in managing vast global assets are not easily replicated. For instance, as of Q1 2024, BNY Mellon held over $47 trillion in assets under custody and administration, a testament to decades of client confidence.
BNY Mellon benefits significantly from economies of scale, managing $52.1 trillion in assets under custody and administration as of December 31, 2024. This massive scale allows for substantial cost efficiencies across its wide array of financial services.
New entrants face a daunting challenge replicating BNY Mellon's operational leverage and integrated service offerings. Achieving comparable cost advantages and a similar breadth of solutions would require immense initial capital and considerable time to build trust and market presence.
Technological Complexity and Investment
The threat of new entrants into the financial services sector, particularly for a firm like BNY Mellon, is significantly shaped by the immense technological complexity and the capital required to establish a competitive presence. Developing and maintaining the sophisticated technological platforms essential for global asset servicing, investment management, and treasury services necessitates ongoing, substantial investment. This includes robust IT infrastructure, advanced cybersecurity measures, and a commitment to innovation, such as integrating artificial intelligence and blockchain technologies.
New players entering this arena would need to commit massive and sustained capital expenditures to match the technological capabilities of established institutions. For instance, the global IT spending in the financial services sector was projected to reach over $300 billion in 2024, highlighting the scale of investment required.
- High Capital Outlay: New entrants must allocate billions of dollars for technology development and maintenance to achieve parity with incumbents.
- Cybersecurity Demands: Significant investment in state-of-the-art cybersecurity is non-negotiable to protect sensitive client data and maintain trust.
- Innovation Pace: Keeping pace with rapid technological advancements, like AI-driven analytics and distributed ledger technology, requires continuous R&D funding.
- Regulatory Compliance Tech: Implementing and updating technology to meet evolving global financial regulations adds another layer of cost and complexity.
Access to Distribution Channels and Client Relationships
New entrants face significant hurdles in replicating BNY Mellon's deeply entrenched client relationships and extensive distribution networks. These relationships, cultivated over many years, are crucial for accessing and serving a diverse global client base, creating a substantial barrier to entry that new firms struggle to overcome quickly.
BNY Mellon's ability to leverage its established channels means new competitors must invest heavily and patiently to build comparable reach and trust. For instance, as of Q1 2024, BNY Mellon reported assets under custody and administration of $45.2 trillion, a testament to the scale and depth of its client engagement.
- Client Retention: BNY Mellon's long-standing relationships foster high client retention, making it difficult for new entrants to gain market share.
- Distribution Reach: The company's vast network of distribution channels provides unparalleled access to capital markets.
- Trust and Reputation: Decades of reliable service have built a strong reputation, a critical factor in attracting and retaining clients in the financial services industry.
The threat of new entrants for BNY Mellon is considerably low due to the immense capital requirements and stringent regulatory landscape inherent in global financial services. New players must overcome substantial initial investments in technology, compliance, and infrastructure, alongside building a trusted brand reputation, making market entry exceptionally challenging.
BNY Mellon's significant economies of scale, managing $52.1 trillion in assets under custody and administration as of December 31, 2024, create cost advantages that new entrants cannot easily match. This scale directly translates into lower per-unit operating costs, a critical competitive edge.
The established client relationships and extensive distribution networks of BNY Mellon, evidenced by $45.2 trillion in assets under custody and administration in Q1 2024, pose a formidable barrier. Replicating this level of client trust and market access requires years of dedicated effort and substantial resources.
| Barrier Type | BNY Mellon's Strength | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | Billions required for infrastructure and licensing | Extremely High |
| Technology Investment | Ongoing significant spend on advanced platforms | Very High |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Founded 1784, trillions in assets managed | Very High |
| Economies of Scale | $52.1 trillion AUA (Dec 2024) | High |
| Client Relationships | $45.2 trillion AUA (Q1 2024) | High |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Bank of New York Mellon leverages data from SEC filings, financial reports, and industry analysis from reputable firms like S&P Global Market Intelligence and IBISWorld. We also incorporate insights from macroeconomic indicators and regulatory updates to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
