BMC Software Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
BMC Software Bundle
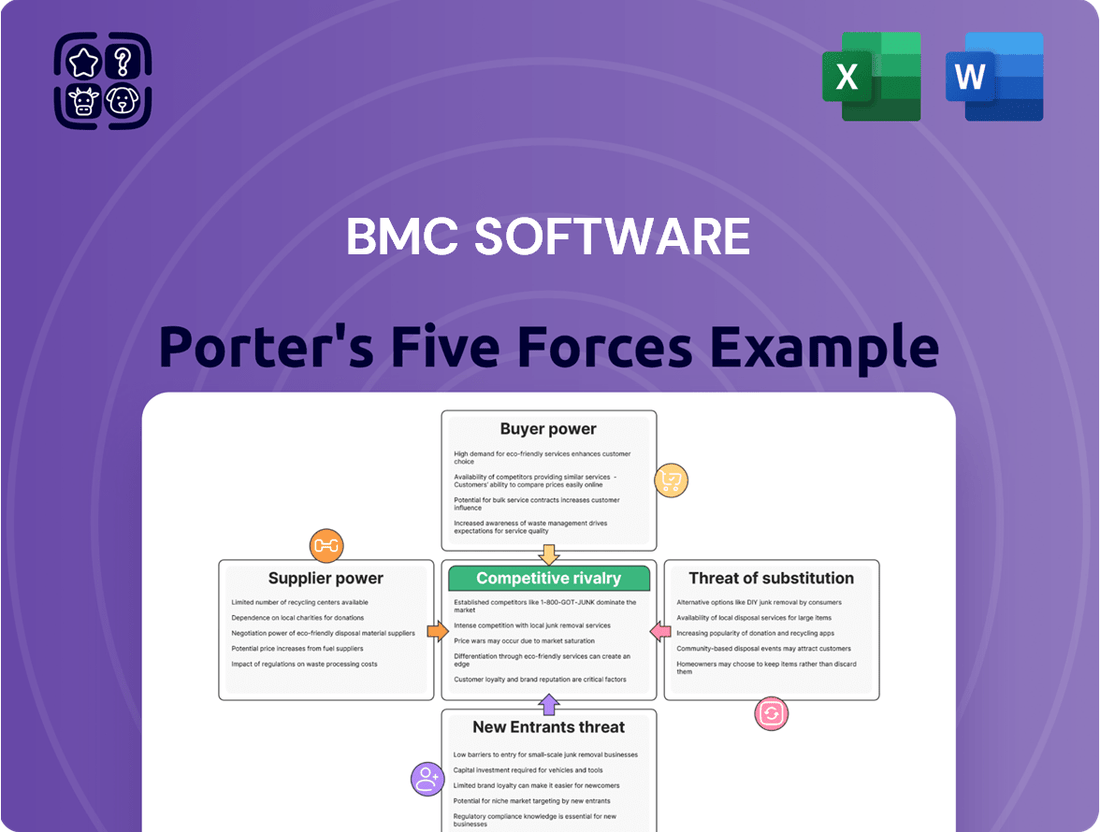
BMC Software operates in a dynamic IT management sector, facing significant competitive pressures. Understanding the interplay of these forces is crucial for strategic success. Our Porter's Five Forces analysis delves into the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes on BMC Software.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore BMC Software’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The specialized nature of IT management solutions, particularly those integrating AI, cloud computing, and cybersecurity, significantly amplifies the bargaining power of highly skilled professionals. Companies like BMC Software depend on a talent pool possessing deep expertise in these advanced domains, making talent acquisition and retention both critical and potentially expensive.
The robust demand for proficient IT professionals, especially in cloud computing, AI/ML, and cybersecurity, grants these individuals substantial leverage in the job market. For instance, in 2024, the average salary for a senior cloud engineer in the US could exceed $150,000 annually, reflecting this high demand and specialized skill requirement.
BMC Software's increasing reliance on major cloud infrastructure providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud significantly amplifies the bargaining power of these suppliers. These hyperscale providers hold a dominant market position, making their services critical for BMC's cloud-based offerings and hybrid/multi-cloud strategies. For instance, in 2024, AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud collectively controlled over 65% of the global cloud infrastructure market, highlighting their leverage.
Suppliers of crucial hardware, operating systems, and database technologies wield influence over BMC Software. While commodity components offer choice, specialized or proprietary tech suppliers can command greater leverage, impacting BMC's operational efficiency and product development timelines. For instance, reliance on a single major cloud provider for underlying infrastructure could grant that provider significant bargaining power.
AI/ML Model & Data Providers
The bargaining power of AI/ML model and data providers is escalating as businesses, including BMC, increasingly rely on artificial intelligence for enhanced IT management. Suppliers of sophisticated AI models, essential GPU compute power, and meticulously curated training datasets are becoming critical to the success of AI-driven enterprise solutions. For BMC, the quality and cost of these specialized AI components directly impact the performance and innovation of its AI-powered offerings.
The integration of AI into enterprise software is a major industry shift, elevating these AI/ML providers to the status of strategic partners rather than mere vendors. As of early 2024, the demand for AI-specific hardware, particularly GPUs, has seen significant price increases, with companies like NVIDIA reporting record revenues driven by AI demand, underscoring the leverage these suppliers hold. The market for high-quality, labeled datasets also continues to grow, with specialized providers commanding premium prices due to the effort and expertise involved in data preparation.
- Growing AI Integration: Over 60% of enterprises reported increased AI adoption in 2023, driving demand for specialized AI inputs.
- GPU Market Dynamics: The global GPU market is projected to reach over $100 billion by 2027, with AI workloads being a primary driver, indicating strong supplier pricing power.
- Data as a Differentiator: Companies are increasingly recognizing the strategic value of unique, high-quality datasets, leading to higher valuations for data providers.
- Strategic Partnerships: BMC's ability to secure cutting-edge AI models and data will depend on its capacity to forge strong relationships with key suppliers.
Strategic Partnership Leverage
BMC Software's strategic partnerships are a key element in its market strategy, allowing it to expand its reach and integrate its offerings. These alliances, which include resellers, system integrators, and technology partners, can wield significant influence. This is particularly true when partners control crucial market access or possess specialized skills for integrating BMC's complex solutions with other enterprise systems.
The bargaining power of these suppliers, or partners in this context, is amplified when they offer unique value propositions. For instance, a partner with exclusive distribution rights in a key geographic region or a proprietary integration methodology can command better terms. BMC's reliance on these partners for successful customer deployments means that the terms of these relationships are critical.
- Strategic Alliances: BMC cultivates relationships with a broad partner ecosystem, crucial for market penetration and solution delivery.
- Partner Influence: Partners with unique market access or specialized integration skills can exert considerable bargaining power.
- Customer Dependence: BMC's customer success often hinges on the capabilities and collaboration of its partners, increasing their leverage.
BMC Software's reliance on cloud infrastructure providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud gives these suppliers significant leverage. Their dominant market share, exceeding 65% globally in 2024, means BMC's cloud-based offerings are heavily dependent on their services. This dependence allows these hyperscale providers to influence pricing and terms, impacting BMC's operational costs and strategic flexibility.
The escalating integration of AI into enterprise solutions elevates the bargaining power of AI model and data providers. As of early 2024, the demand for specialized AI hardware, particularly GPUs, has driven significant price increases, with NVIDIA reporting record revenues. Similarly, the market for high-quality datasets is growing, with specialized providers commanding premium prices, directly affecting BMC's AI-powered product development and innovation.
BMC's strategic partnerships, including resellers and system integrators, can also exert considerable bargaining power, especially when they control crucial market access or possess unique integration skills. Customer success often depends on these partners, increasing their leverage in negotiations and impacting BMC's ability to deliver integrated solutions effectively.
| Supplier Type | 2024 Market Share/Data Point | Impact on BMC |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Infrastructure (AWS, Azure, Google) | >65% Global Market Share | High dependency, pricing influence |
| AI Hardware (e.g., GPUs) | Significant price increases, NVIDIA record revenues | Increased AI component costs, innovation dependency |
| Specialized Data Providers | Growing market, premium pricing for quality data | Higher AI development costs, data quality impact |
| Strategic Partners (Resellers, Integrators) | Crucial for market access and solution delivery | Leverage through unique skills and market control |
What is included in the product
BMC Software's Porter's Five Forces analysis dissects the competitive intensity within the enterprise IT management software market, examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the rivalry among existing competitors.
Instantly visualize competitive intensity across all five forces with a dynamic, interactive dashboard.
Customers Bargaining Power
BMC Software's customer base is heavily concentrated among large enterprises. This concentration means that a significant portion of BMC's revenue often comes from a relatively small number of major clients. These large organizations wield considerable purchasing power, allowing them to negotiate favorable pricing, service level agreements, and even demand customized features.
The substantial IT budgets and complex needs of these enterprise clients enable them to exert significant influence over vendors like BMC. For instance, a large enterprise might leverage its volume of business to secure discounts or require specific integrations that other vendors may not offer. In 2023, many large enterprises continued to consolidate their IT vendor relationships, further amplifying the bargaining power of those that remained key partners.
Customers in the enterprise IT management sector face a landscape brimming with choices, significantly amplifying their bargaining power. Major players like ServiceNow, IBM, Microsoft, and Atlassian offer robust alternatives, providing comparable IT automation, service management, operations, and security tools. This extensive selection empowers customers to readily switch providers if BMC Software’s offerings or pricing are not competitive, driving down BMC’s pricing power.
Switching IT management systems presents a dual challenge: significant upfront costs versus the frustration of underperforming legacy solutions. While migrating data, integrating new systems, and retraining staff can be expensive, customer dissatisfaction with slow performance, clunky interfaces, and poor usability in older platforms, including some BMC offerings, can make these costs more palatable. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that over 60% of IT decision-makers cited user experience as a primary driver for system upgrades, even with associated switching expenses.
Demand for ROI and Cost Efficiency
Customers, particularly large enterprises, are prioritizing a clear return on investment (ROI) and cost efficiency from their software purchases. This focus means they are more empowered to negotiate pricing and demand guarantees.
The pressure for demonstrable value means customers scrutinize IT spending, seeking solutions that directly enhance efficiency and reduce costs. For instance, in 2024, many businesses reported that IT cost optimization was a top priority, with a significant percentage looking to software vendors to contribute to these savings.
- Increased Scrutiny: Businesses are meticulously evaluating the financial benefits of software, demanding clear ROI metrics.
- Negotiating Power: The drive for cost savings grants customers leverage to negotiate pricing and favorable contract terms.
- Demand for Value: Vendors must prove how their solutions directly contribute to operational efficiency and cost reduction.
- Performance Guarantees: Customers are increasingly requesting performance-based guarantees tied to cost savings or efficiency gains.
Threat of In-house Development
Large enterprises often have the financial muscle and technical talent to build their own IT management tools, especially for core functions. This capability, or even the serious consideration of it, gives them significant bargaining power. For instance, a company like IBM, with its vast engineering resources, could theoretically develop proprietary solutions for its internal IT needs, reducing reliance on vendors like BMC Software.
This internal development capacity acts as a constant pressure point. Customers can leverage this threat to negotiate better terms or pricing from existing software providers. The credible threat of developing in-house means vendors must remain competitive and responsive to customer demands to retain business.
Furthermore, the growing availability and sophistication of open-source software provide another avenue for customers to reduce their dependence on commercial vendors. Organizations can adopt or adapt open-source solutions, which can be particularly appealing for less specialized or commodity IT management tasks.
- Internal Development Capability: Large enterprises can develop proprietary IT management solutions, reducing vendor dependency.
- Bargaining Leverage: The threat of in-house development empowers customers to negotiate better pricing and terms.
- Open-Source Alternatives: Viable open-source options offer customers a way to circumvent proprietary software for certain functions.
BMC Software's customers, particularly large enterprises, possess significant bargaining power due to market concentration and the availability of alternatives. This power is amplified by their substantial IT budgets and the potential for in-house development or open-source solutions, forcing BMC to offer competitive pricing and demonstrate clear ROI.
| Factor | Impact on BMC Software | Supporting Data/Trend (2023-2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High bargaining power for key accounts | Many large enterprises continued IT vendor consolidation in 2023, increasing the leverage of their chosen partners. |
| Availability of Alternatives | Pressure on pricing and features | Competitors like ServiceNow and IBM offer comparable solutions, enabling customers to switch easily if BMC is not competitive. |
| Switching Costs vs. Dissatisfaction | Can drive upgrades despite costs | A 2024 survey found over 60% of IT decision-makers cited user experience as a primary driver for system upgrades, even with switching expenses. |
| Focus on ROI and Cost Efficiency | Demand for value and negotiation leverage | In 2024, IT cost optimization was a top priority for many businesses, with a significant portion expecting software vendors to contribute to savings. |
| Internal Development/Open Source | Threat of reduced vendor reliance | The credible threat of in-house development or adoption of open-source alternatives compels vendors to remain competitive. |
Preview Before You Purchase
BMC Software Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete BMC Software Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of competitive forces within the enterprise software market. The document you are currently viewing is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring full transparency and immediate access to actionable insights.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The enterprise IT management software market is a crowded space brimming with established companies. BMC Software faces significant rivalry from giants like ServiceNow, IBM, and Microsoft, alongside strong contenders such as Atlassian, Broadcom, and Ivanti, all offering overlapping solutions in IT automation, service management, operations, and security. This intense competition means companies are constantly vying for market share.
Competitive rivalry in the software sector, especially for BMC Software, is intensely driven by the relentless pace of innovation, particularly concerning Artificial Intelligence (AI) and automation. Companies are locked in a race to embed cutting-edge AI features into their offerings, focusing on areas like predictive analytics, automated IT operations, and robust cybersecurity solutions. This continuous push for advancement necessitates substantial investment in research and development to maintain market relevance.
The integration of generative AI has emerged as a pivotal trend, with competitors actively deploying new AI-powered functionalities to differentiate themselves. For instance, in 2024, many enterprise software providers, including those in IT service management and automation, have showcased generative AI capabilities aimed at simplifying complex tasks and improving user experience. This arms race in AI development means that failing to keep pace can quickly lead to a loss of competitive edge.
The markets BMC Software serves, such as digital transformation, cybersecurity, and IT automation, are experiencing robust growth. For instance, the global IT services market was projected to reach $1.3 trillion in 2024, a substantial increase that allows many companies, including BMC, to expand without solely relying on market share gains from competitors.
This high market growth is a significant factor. It means that even with many vendors competing, there's enough demand for everyone to potentially grow their revenue. Think of it like a rapidly expanding pie; more slices can be created, reducing the intensity of direct competition for existing slices.
The increasing IT spending globally, driven by digital adoption, creates a larger opportunity. In 2023, worldwide IT spending was estimated at $4.7 trillion, and this trend is expected to continue. This larger market size can temper the aggressive rivalry that often characterizes more mature or stagnant industries.
Focus on User Experience and Cost Efficiency
Competitive rivalry in the enterprise software space, particularly for solutions like those BMC offers, is increasingly defined by a dual focus on user experience and cost efficiency. Competitors are actively differentiating by providing modern, intuitive interfaces, directly addressing customer frustrations with complex legacy systems. This emphasis on ease of use, coupled with a strong value proposition or lower total cost of ownership (TCO), intensifies the competitive landscape as firms vie to capture market share by offering more accessible and economically beneficial solutions.
BMC itself is strategically addressing these market dynamics. The company has been investing in enhancing its product suite to deliver superior user experiences and greater cost efficiencies. A significant move in this direction includes its business segmentation, which aims to allow for more focused development and go-to-market strategies tailored to specific customer needs and market demands. This restructuring is intended to bolster BMC's competitive standing by better aligning its offerings with the evolving expectations around usability and economic value.
The drive for better user experience and cost efficiency is a significant factor shaping the competitive intensity. For instance, many customers are seeking to reduce their IT operational expenses. In 2024, many enterprises reported that optimizing IT spend and improving the productivity of their IT staff through user-friendly tools were key priorities. Companies that can demonstrate a clear path to cost savings and a streamlined user journey are gaining a distinct advantage.
- User Interface Modernization: Competitors are investing heavily in redesigning their platforms for intuitive navigation and ease of use, aiming to reduce training time and increase end-user adoption.
- Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Emphasis: Beyond initial licensing, vendors are highlighting long-term savings through factors like reduced maintenance, lower support costs, and optimized resource utilization.
- Addressing Legacy System Pain Points: A key competitive lever is offering solutions that simplify migration from or integration with older, more cumbersome systems, thereby reducing technical debt and operational complexity for customers.
- BMC's Strategic Adjustments: BMC's business segmentation strategy is designed to sharpen its focus on delivering improved user experiences and demonstrable cost efficiencies within its core product areas.
Strategic Partnerships and Market Specialization
Strategic partnerships and market specialization are key drivers of competitive rivalry in the software industry. Companies are increasingly forming alliances and honing their focus on specific market segments or technologies to outmaneuver competitors. This trend is exemplified by BMC's strategic decision to split into two distinct entities. BMC Helix, for instance, is designed to accelerate innovation by concentrating on digital services and AI, while the other entity focuses on mainframe and automation solutions. This strategic segmentation allows for a more concentrated deployment of resources and expertise, directly intensifying the competitive landscape.
This specialization allows companies to build deeper expertise and offer more tailored solutions, creating a more fragmented yet intensely competitive market. For example, in 2024, the cloud computing market, a key area for BMC, saw intense competition with major players like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud investing heavily in specialized services and forming strategic partnerships to capture market share. This drive for specialization means that even within broad software categories, niche players can emerge and challenge established giants by offering superior, focused solutions.
- Market Specialization: Companies are narrowing their focus to specific technologies or customer needs to build competitive advantages.
- Strategic Alliances: Partnerships are being formed to share resources, expand market reach, and jointly develop innovative solutions.
- Resource Concentration: Specialization allows for a more efficient allocation of R&D and marketing budgets towards core competencies.
- Intensified Rivalry: These strategies lead to a more dynamic competitive environment where specialized offerings can disrupt established market positions.
Competitive rivalry in the enterprise IT management software market is fierce, driven by innovation and market growth. BMC Software faces strong competition from established players and emerging specialists, with a significant emphasis on AI and user experience.
The market's expansion, with global IT spending projected to continue its upward trend, allows multiple vendors to grow. However, the race to integrate advanced AI, particularly generative AI, and to offer cost-efficient, user-friendly solutions intensifies competition. Strategic partnerships and market specialization are also key differentiators.
BMC's strategic segmentation into BMC Helix and a mainframe/automation focused entity reflects the industry trend towards specialization to enhance competitive positioning.
| Key Competitor | Primary Offerings | 2024 Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| ServiceNow | IT Service Management (ITSM), Workflow Automation | AI-powered automation, enhanced user experience |
| IBM | Hybrid Cloud, AI, Automation | AI integration, cloud modernization services |
| Microsoft | Azure Cloud, Dynamics 365, Microsoft 365 | AI-driven productivity, cloud security |
| Broadcom | Mainframe Software, Cybersecurity | Mainframe modernization, security solutions |
| Atlassian | Team Collaboration, Project Management | DevOps automation, AI-assisted workflows |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large enterprises, BMC's core clientele, frequently possess robust in-house IT departments capable of developing bespoke software solutions. This internal capacity directly substitutes for BMC's offerings, particularly when customer needs are highly specialized or when control over IT infrastructure is paramount. For instance, a 2024 survey indicated that 65% of Fortune 500 companies have dedicated teams for custom software development, highlighting the significant threat of in-house IT capabilities.
The rise of robust open-source software presents a significant threat to BMC Software. Solutions like Ansible, Kubernetes, and Prometheus offer powerful IT management and automation capabilities, often at a fraction of the cost of proprietary alternatives. This maturity means that organizations with in-house technical skills can effectively deploy and manage these open-source tools, bypassing the need for expensive licenses.
Managed Service Providers (MSPs) and IT outsourcing present a significant threat of substitutes for BMC Software. Businesses can choose to outsource their entire IT infrastructure and management to MSPs, bypassing the need to directly purchase, implement, and maintain complex software solutions like those offered by BMC. This approach effectively outsources the IT operational burden and associated capital expenditure, acting as a direct substitute for in-house software deployment and management.
Cloud-Native Services and Platforms
Public cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offer robust, integrated suites of services that can directly replace many of BMC's traditional offerings. For instance, AWS CloudWatch and Azure Monitor provide comprehensive monitoring and logging capabilities, while services like Azure Automation and AWS Systems Manager handle IT process automation, often negating the need for separate BMC solutions.
The growing adoption of cloud-first strategies means enterprises are increasingly inclined to utilize these native cloud tools, especially for workloads residing within their cloud environments. This preference for integrated solutions is driven by perceived cost efficiencies and simplified management. By 2024, a significant portion of IT spending is allocated to cloud services, with estimates suggesting that cloud infrastructure services revenue alone is projected to reach over $300 billion globally.
- Integrated Cloud-Native Tools: AWS, Azure, and GCP offer built-in monitoring, automation, and security services that can substitute for BMC's standalone products.
- Enterprise Cloud Adoption: As more companies adopt cloud-first strategies, they are more likely to opt for native cloud tools for their cloud-based workloads.
- Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud Trends: The prevalence of multi-cloud and hybrid environments further complicates substitution, as organizations seek unified management across diverse platforms.
- Market Shift: Gartner predicted that by 2025, over 80% of enterprises will be operating in a hybrid or multi-cloud environment, underscoring the shift towards integrated cloud solutions.
Manual Processes and General-Purpose Tools
While not a direct competitor for enterprise-level IT management, manual processes and general-purpose tools like spreadsheets can serve as a substitute for some smaller businesses or specific departments. These alternatives are often chosen when the cost or complexity of dedicated software is perceived as too high. For instance, a small team might manage IT support tickets using a shared spreadsheet, a practice that, while less efficient, offers a low-barrier entry point.
These basic methods represent a threat because they fulfill a fundamental need, albeit at a much lower level of sophistication. In 2024, many small businesses still leverage Microsoft Excel for inventory management and basic CRM functions, avoiding the subscription costs of specialized software. This can limit the market penetration of advanced IT management solutions in certain segments, particularly those prioritizing immediate cost savings over long-term scalability and efficiency.
- Manual Processes: Organizations might use spreadsheets for tracking IT assets, managing user requests, or monitoring system performance.
- General-Purpose Tools: Basic ticketing systems or project management software not specifically designed for IT management can be adapted.
- Cost Sensitivity: Smaller businesses or departments with limited budgets may opt for these less expensive, though less capable, alternatives.
- Perceived Complexity: The perceived difficulty of implementing and managing sophisticated IT management software can drive adoption of simpler tools.
The threat of substitutes for BMC Software is significant, stemming from various alternatives that can fulfill similar IT management and automation needs. These substitutes range from in-house development and open-source solutions to managed service providers and public cloud offerings. The increasing maturity and accessibility of these alternatives mean businesses have more choices, often at lower costs or with greater flexibility, directly impacting BMC's market position.
Integrated cloud-native tools from major providers like AWS, Azure, and GCP offer a compelling substitute, especially as enterprises increasingly adopt cloud-first strategies. These platforms provide built-in monitoring, automation, and security functionalities, reducing the need for BMC's specialized software. By 2024, global cloud infrastructure services revenue was projected to exceed $300 billion, highlighting the scale of this shift.
Open-source software presents another powerful substitute, with solutions like Kubernetes and Ansible offering advanced IT management capabilities at minimal cost. For organizations with skilled IT teams, these tools can effectively replace proprietary software. Similarly, Managed Service Providers (MSPs) allow businesses to outsource their IT operations entirely, acting as a direct substitute for purchasing and managing complex software suites.
Even simpler, manual processes and general-purpose tools like spreadsheets can serve as substitutes for specific functions, particularly for smaller businesses prioritizing immediate cost savings. While less sophisticated, these low-barrier alternatives address basic IT needs, potentially limiting BMC's penetration in certain market segments.
| Substitute Category | Examples | Key Advantages | Threat Level |
| In-house Development | Custom-built IT solutions | Tailored functionality, full control | Moderate to High |
| Open-Source Software | Kubernetes, Ansible, Prometheus | Low cost, flexibility, community support | High |
| Managed Service Providers (MSPs) | Outsourced IT management | Reduced operational burden, predictable costs | High |
| Public Cloud Native Tools | AWS CloudWatch, Azure Monitor, GCP Operations Suite | Integration, scalability, often bundled pricing | Very High |
| Manual Processes/General Tools | Spreadsheets, basic ticketing systems | Low cost, ease of use for simple tasks | Low to Moderate |
Entrants Threaten
The enterprise IT management software market demands massive upfront capital for research and development. Building robust solutions for automation, service management, operations, and security requires significant financial backing and specialized talent, creating a formidable entry barrier.
For instance, companies like BMC Software invest heavily in R&D, with their 2023 annual report highlighting substantial expenditures aimed at enhancing their AI and automation capabilities. This continuous need for innovation, particularly in areas like generative AI for IT operations, further escalates the cost and complexity for potential new entrants, making it difficult to compete with established players.
Established players like BMC Software have cultivated decades of brand reputation and customer trust, presenting a formidable barrier for newcomers. Enterprises often prioritize stability and proven reliability for their critical IT infrastructure, favoring vendors with a solid history of support and performance. Building this level of trust and a strong brand identity requires substantial time and investment, making it difficult for new entrants to quickly establish credibility.
Customer switching costs are a significant hurdle for new entrants in the IT management software market. Migrating complex data, retraining staff, and re-integrating systems with existing infrastructure represent substantial investments for businesses. For instance, a study in late 2023 indicated that the average cost for an enterprise to switch IT service management platforms can range from $50,000 to over $500,000, depending on the scale and complexity of the existing setup.
These high switching costs mean that even if a new entrant offers a more advanced or cost-effective solution, convincing established customers to make the leap is challenging. This "stickiness" of existing customer bases provides a protective moat for incumbent players like BMC Software, making it difficult for newcomers to gain market share rapidly.
Complex Sales and Distribution Channels
The threat of new entrants in the enterprise software market, particularly for companies like BMC, is significantly tempered by the intricate nature of sales and distribution channels. Establishing the necessary infrastructure to effectively reach and serve large enterprise clients is a substantial hurdle.
Selling complex, high-value software solutions demands specialized sales forces with deep technical understanding and industry-specific knowledge, alongside extensive professional services for implementation and ongoing support. Newcomers must invest heavily in building these capabilities, a process that is both time-consuming and capital-intensive.
Furthermore, a robust network of strategic partners and system integrators is often crucial for market penetration and customer adoption. BMC, for instance, relies on a well-established partner ecosystem that provides reach and credibility, making it difficult for new players to replicate this advantage quickly.
- High Barrier to Entry: Building specialized enterprise sales teams and professional services organizations requires significant upfront investment and proven track records.
- Partner Ecosystem Reliance: New entrants must cultivate relationships with key channel partners and integrators to gain market access, a process that can take years.
- Customer Trust and Relationships: Enterprise clients often prefer established vendors with a history of reliability and strong existing relationships, which new entrants lack.
Rapid Technological Evolution and AI Expertise
The rapid evolution of technology, especially in areas like AI and cloud computing, presents a significant hurdle for new companies entering the software market. To compete effectively, newcomers need substantial investment and deep technical knowledge to develop and integrate advanced AI capabilities, a challenge underscored by the fact that AI spending by enterprises is projected to reach $200 billion by 2026, according to IDC.
Incumbent software vendors, like BMC, already possess sophisticated AI-driven features and extensive data sets, creating a high bar for differentiation. This constant demand for innovation means that new entrants must not only match existing functionalities but also invest heavily in research and development to offer truly novel solutions, making it difficult to gain market traction.
- High R&D Investment: New entrants require significant capital to develop and integrate cutting-edge AI and machine learning capabilities, mirroring the substantial investments already made by established players.
- Talent Acquisition: Access to specialized AI and cloud computing talent is crucial, and competition for these skilled professionals remains intense, driving up labor costs for emerging companies.
- Integration Complexity: Successfully integrating new AI features into existing IT infrastructures, a common requirement for enterprise software, demands specialized expertise that new entrants may lack.
The threat of new entrants into the enterprise IT management software market is considerably low due to several formidable barriers. These include the immense capital required for research and development, the need for established brand reputation and customer trust, and the high switching costs for existing clients. Furthermore, the complexity of sales channels and the rapid pace of technological advancement, particularly in AI, demand significant investment and expertise that new players often struggle to match.
| Barrier | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | High R&D costs for advanced features like AI and automation. | Requires substantial upfront funding, limiting the number of potential entrants. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Decades of proven reliability and customer relationships. | New entrants lack the credibility and trust enterprises demand for critical IT infrastructure. |
| Switching Costs | Significant expense and complexity in migrating data and retraining staff. | Makes it difficult for new vendors to attract established customers, even with superior offerings. |
| Sales & Distribution Channels | Need for specialized sales forces and extensive partner ecosystems. | Replicating established networks and expertise is time-consuming and costly. |
| Technological Advancements | Constant need for innovation in AI and cloud computing. | New entrants must invest heavily to match or surpass incumbent capabilities. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for BMC Software is built upon a foundation of robust data, including BMC's own annual reports and investor presentations, alongside industry-specific market research from Gartner and IDC. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
