Bloom Energy Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Bloom Energy Bundle
Bloom Energy faces significant competitive forces, from the bargaining power of its customers to the threat of new entrants in the clean energy sector. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Bloom Energy’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Bloom Energy's reliance on specialized raw materials and components, like advanced ceramics and unique alloys for its solid oxide fuel cells, significantly impacts supplier bargaining power. The limited number of suppliers capable of producing these high-specification inputs, coupled with their proprietary nature, grants them considerable leverage. This dependence can translate into higher material costs and potential disruptions if supply chains are not carefully managed.
Switching suppliers for highly integrated or customized fuel cell components can involve substantial costs for Bloom Energy. These costs include re-engineering, re-tooling, and extensive testing to ensure system performance and reliability, which can significantly impact operational efficiency and product quality.
These high switching costs reduce Bloom Energy's flexibility and can reinforce the bargaining power of existing, entrenched suppliers who have already invested in the necessary integration and quality assurance processes. This situation can lead to less favorable pricing and contract terms for Bloom Energy.
The complexity of Bloom Energy's technology means that qualifying new suppliers is a time-consuming and resource-intensive process. This lengthy qualification period further entrenches existing suppliers and limits Bloom Energy's ability to readily diversify its supply base.
Bloom Energy's bargaining power of suppliers is significantly influenced by supplier concentration. If a few key suppliers control critical fuel cell components or specialized manufacturing processes, they hold considerable leverage. This is particularly true if these suppliers possess unique expertise or proprietary technology that Bloom Energy cannot easily substitute.
For instance, in 2024, the global market for rare earth metals, essential for certain high-performance magnets used in fuel cell components, saw significant price volatility due to the concentrated supply base, primarily in China. This concentration can force Bloom Energy to accept less favorable pricing and terms, impacting its cost of goods sold.
Impact of Raw Material Price Volatility
The prices of critical raw materials like nickel and rare earth elements, vital for Bloom Energy's fuel cell manufacturing, are susceptible to significant global market swings. This volatility allows suppliers to potentially increase prices, directly affecting Bloom Energy's cost of goods sold and overall profit margins. For instance, nickel prices saw considerable fluctuations in 2023 and early 2024, influenced by geopolitical events and supply chain disruptions.
Bloom Energy's capacity to manage these cost increases hinges on its own market leverage and the terms stipulated in its supply contracts. The company's ability to either absorb these higher material costs or pass them on to its customers is a key determinant of its financial resilience in the face of supplier power. In 2023, Bloom Energy reported that its cost of revenue increased by 15% compared to 2022, partly attributable to material cost pressures.
- Nickel Price Volatility: Nickel prices averaged around $16,000 per metric ton in early 2024, a notable increase from earlier periods, impacting manufacturers reliant on this material.
- Supply Chain Dependencies: Reliance on a limited number of suppliers for specialized components can amplify the bargaining power of those suppliers.
- Contractual Safeguards: The effectiveness of long-term supply agreements in mitigating price increases is crucial for Bloom Energy's cost management.
- Market Power Balance: Bloom Energy's ability to negotiate favorable terms is directly tied to its market position and the demand for its products.
Potential for Supplier Forward Integration
The potential for a supplier to integrate forward into Bloom Energy's fuel cell system manufacturing, while rare, represents a significant bargaining chip. If a key supplier possesses unique technology or controls a substantial portion of a critical component market, they could theoretically enter Bloom Energy's business. This threat, even if distant, grants suppliers leverage in pricing and terms negotiations.
Bloom Energy must carefully manage its supplier relationships, recognizing that this forward integration risk can influence contract discussions. For instance, in 2023, Bloom Energy reported its Cost of Revenue was $760.5 million, highlighting the importance of managing input costs effectively. A supplier's ability to disrupt this by becoming a competitor would directly impact Bloom Energy's profitability and market position.
- Supplier Leverage: The theoretical possibility of forward integration by specialized suppliers grants them inherent bargaining power.
- Risk Mitigation: Bloom Energy needs strategies to counter this potential competitive threat while fostering essential supplier partnerships.
- Cost Management: With 2023 Cost of Revenue at $760.5 million, controlling supplier costs is paramount, making this threat particularly relevant.
Bloom Energy faces significant supplier bargaining power due to its reliance on specialized, high-specification components with limited suppliers. This concentration, coupled with high switching costs and lengthy supplier qualification processes, grants existing suppliers considerable leverage, potentially leading to higher material costs and supply chain vulnerabilities. For example, the price of nickel, a key material, saw significant fluctuations in early 2024, impacting manufacturers like Bloom Energy.
| Factor | Impact on Bloom Energy | 2024 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High leverage for limited suppliers of specialized components. | Concentrated supply of rare earth metals for magnets impacted pricing in early 2024. |
| Switching Costs | Substantial costs (re-engineering, re-tooling) limit flexibility. | High costs reinforce existing supplier relationships and terms. |
| Material Price Volatility | Susceptibility to global market swings affects cost of goods sold. | Nickel prices averaged around $16,000/ton in early 2024, showing notable increases. |
| Cost of Revenue Impact | Supplier cost increases directly affect profit margins. | Bloom Energy's 2023 Cost of Revenue was $760.5 million, highlighting the importance of managing input costs. |
What is included in the product
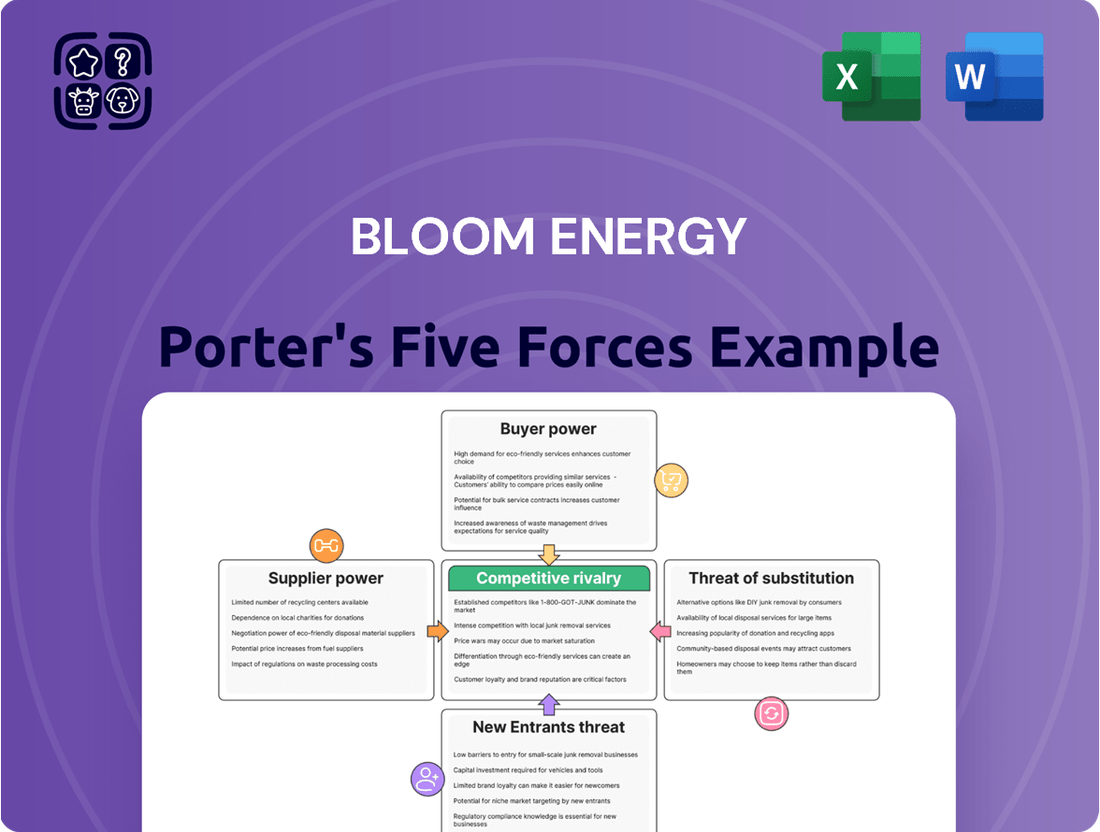
This analysis of Bloom Energy's competitive landscape examines the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes, providing strategic insights into its market position.
Instantly visualize Bloom Energy's competitive landscape with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces analysis, highlighting key pressures and opportunities for strategic advantage.
Customers Bargaining Power
Bloom Energy's large commercial and industrial customer base significantly influences its bargaining power. These clients, often major corporations with substantial energy requirements, possess considerable leverage due to the scale of their potential contracts.
These sophisticated buyers frequently participate in competitive bidding, driving down prices and demanding tailored solutions. For instance, in 2023, Bloom Energy reported that its revenue was heavily concentrated among a few large customers, highlighting their ability to negotiate favorable terms and service level agreements.
The availability of diverse energy alternatives significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. Customers can easily switch to or compare Bloom Energy's fuel cell solutions with traditional grid power, rooftop solar with battery storage, or even other forms of distributed generation. This broad marketplace means Bloom Energy must consistently prove its value proposition against a wide range of competitors.
The significant initial capital expenditure for Bloom Energy's fuel cell systems places considerable bargaining power in the hands of its customers. These upfront costs can be a major hurdle, forcing potential buyers to meticulously evaluate the total cost of ownership and the projected return on investment. This financial scrutiny empowers customers to negotiate aggressively on pricing, financing options, and contract terms, as the substantial initial outlay makes them highly sensitive to favorable deal structures.
Customer Focus on Reliability and Resilience
Bloom Energy's core value proposition hinges on delivering reliable and resilient energy solutions, a critical factor for its commercial and industrial clientele. This emphasis on dependability means customers expect near-perfect system uptime and performance. For instance, in 2023, Bloom Energy reported a 97% customer retention rate, indicating high satisfaction with their reliability, but any deviation from this standard can amplify customer leverage.
Customers' focus on uninterrupted operations means any perceived failure in Bloom Energy's fuel cell systems can translate into significant financial losses for them. This high stake amplifies their bargaining power, as they may demand price concessions or seek alternative, more dependable suppliers if reliability falters. The critical nature of energy supply for businesses like data centers or manufacturing plants underscores this dynamic.
- High Expectations: Customers prioritize consistent energy delivery, placing significant pressure on Bloom Energy to maintain exceptional uptime.
- Financial Impact: Unreliable energy can lead to substantial financial losses for customers, increasing their willingness to negotiate or switch providers.
- Demand for Performance Guarantees: Customers may leverage their need for resilience to negotiate for stronger performance guarantees and service level agreements.
Long-Term Service and Maintenance Contracts
Bloom Energy's reliance on long-term service and maintenance contracts, often spanning 15-20 years, inherently grants customers significant bargaining power. These agreements are crucial for ensuring system uptime and performance, making customers reliant on Bloom's expertise. For instance, in 2023, Bloom Energy reported that approximately 97% of its installed generation capacity was covered by its service agreements, highlighting the critical nature of these contracts for both parties.
Customers can effectively leverage the negotiation of these long-term service agreements to secure favorable terms. This includes negotiating specific service guarantees, uptime commitments, and performance metrics that align with their operational needs. The ongoing necessity for maintenance and support throughout the system's lifecycle ensures that customers retain a degree of influence, particularly when renewal periods approach or when seeking to expand their Bloom Energy installations.
- Customer Retention: Long-term service contracts foster customer loyalty but also create a dependency that customers can use during negotiations.
- Performance Guarantees: Customers can negotiate strict performance guarantees, linking payment or penalties to uptime and energy output.
- Lifecycle Leverage: The extended operational life of Bloom Energy's systems means customers have repeated opportunities to renegotiate terms, maintaining their bargaining power.
Bloom Energy's customers, particularly large industrial and commercial entities, wield significant bargaining power due to the substantial scale of their energy needs and the high upfront costs associated with fuel cell installations. This financial commitment makes customers highly sensitive to pricing and contract terms, allowing them to negotiate aggressively for favorable deals and performance guarantees. For example, in 2023, Bloom Energy's revenue concentration among a few major clients underscored their ability to influence terms.
The availability of numerous energy alternatives further strengthens customer leverage. Clients can readily compare Bloom Energy's offerings against traditional grid power, solar, or other distributed generation solutions, compelling Bloom to consistently demonstrate its value proposition. This competitive landscape means Bloom must offer compelling pricing and performance to retain its customer base.
| Factor | Customer Bargaining Power Impact | Bloom Energy's 2023 Data/Context |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Scale | High | Revenue concentration among large clients |
| Upfront Costs | High | Significant capital expenditure for fuel cells |
| Alternative Energy Sources | High | Availability of grid power, solar, etc. |
| Service Contracts | Moderate to High | 97% of generation capacity covered by service agreements |
What You See Is What You Get
Bloom Energy Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Bloom Energy Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive examination of competitive forces. You'll gain insights into the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors, and the threat of substitute products or services. This detailed analysis is professionally formatted and ready for your immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The distributed energy market is incredibly varied, with Bloom Energy competing against companies offering a wide array of technologies. Beyond fuel cells, this includes microturbines, reciprocating engines, combined heat and power (CHP) systems, and increasingly, advanced battery storage. This broad technological spectrum means Bloom Energy isn't just up against other fuel cell providers; it's contending with a much larger group of energy solution companies.
This diverse competitive environment naturally fuels intense rivalry. Companies are constantly innovating and seeking market share in a sector that’s rapidly changing. For instance, the global distributed generation market was valued at approximately $220 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, presenting a large but contested opportunity for all players.
Bloom Energy faces competition from both well-established energy giants with extensive resources and a history in the sector, as well as nimble, innovative startups that are quick to adopt new technologies. This dynamic means Bloom Energy must continuously adapt and differentiate its offerings to stand out in a crowded and evolving marketplace.
Bloom Energy operates in an industry characterized by substantial fixed costs, primarily stemming from the research, development, and manufacturing of its advanced fuel cell technology. These significant upfront investments necessitate a strong focus on achieving high sales volumes to effectively amortize these costs and reach profitability.
This high fixed cost structure inherently pressures companies like Bloom Energy to pursue aggressive sales strategies. For instance, securing large-scale projects is crucial. In 2023, Bloom Energy announced several significant projects, including a 20-megawatt (MW) fuel cell installation for a major data center in California, demonstrating the drive for volume.
The need to cover these high overheads intensifies competition. Companies are often compelled to offer competitive pricing to win contracts and gain market share, leading to a dynamic where price becomes a key differentiator, further fueling rivalry among players in the clean energy sector.
Competitive rivalry in the fuel cell energy sector is intense, fueled by a relentless pursuit of innovation. Companies are locked in a race to improve efficiency, expand fuel options, lower costs, and seamlessly integrate their systems into existing infrastructure. This drive for differentiation means constant technological advancement, better performance data, and more attractive service packages are key battlegrounds.
Bloom Energy, for instance, has focused on its solid oxide fuel cell technology, emphasizing its ability to run on various fuels, including natural gas and hydrogen. In 2023, the company reported a revenue of $1.16 billion, showcasing its market presence. To stay ahead, maintaining a technological lead and quickly responding to changing customer demands are absolutely critical for Bloom Energy's success against its rivals.
Market Growth and Strategic Partnerships
The distributed generation market, a key area for Bloom Energy, is indeed growing. This expansion is fueled by the global push for energy transition and the increasing need for resilient power solutions. However, this growth also means more companies are vying for a piece of the pie, making competition quite intense.
To navigate this competitive environment, companies are actively forming strategic partnerships. These can take the form of joint ventures, alliances, or even acquisitions. For instance, in 2023, Bloom Energy announced a collaboration with Baker Hughes to develop hydrogen-powered solutions, highlighting the trend of integrating new technologies through strategic ties.
- Market Growth Drivers: The distributed generation market is benefiting from increased demand for energy security and the ongoing shift towards cleaner energy sources.
- Competitive Intensity: Fierce competition exists among established players and new entrants seeking to capitalize on market expansion.
- Strategic Alliances: Companies are actively pursuing partnerships, mergers, and acquisitions to enhance their market standing and technological capabilities.
- Impact of Collaborations: These strategic moves are actively reshaping the competitive dynamics within the sector.
Customer Switching Costs and Brand Loyalty
For customers, integrating Bloom Energy's fuel cell technology involves substantial upfront capital expenditure and complex operational alignment, making it costly and time-consuming to switch to an alternative provider once a system is operational. This inherent stickiness in the customer relationship, however, is established during a highly competitive initial sales cycle where Bloom Energy and its rivals vie for market share. For instance, in 2023, Bloom Energy reported that its average selling price per kilowatt for its fuel cell systems was around $4,000, highlighting the significant investment required by customers.
Bloom Energy actively cultivates brand loyalty by emphasizing the proven reliability and consistent performance of its distributed energy solutions, alongside robust customer support and maintenance services. This focus on long-term value and operational excellence aims to secure repeat business and positive word-of-mouth referrals. The company's commitment to innovation and its track record of delivering clean, reliable power are key differentiators that foster customer retention.
- High Initial Investment: Customers face significant capital outlay for Bloom Energy's systems, creating a barrier to switching.
- Operational Integration: The complexity of integrating distributed energy systems makes switching providers difficult.
- Brand Loyalty Drivers: Reliability, performance, and customer service are crucial for retaining customers.
- Competitive Sales Cycle: The initial decision to adopt Bloom Energy's technology is made in a highly competitive market landscape.
Competitive rivalry within the distributed energy sector is fierce, with Bloom Energy facing a broad range of competitors offering diverse technologies like microturbines, engines, and battery storage. This intense competition is driven by the market's rapid evolution and the significant growth potential, with the global distributed generation market valued at approximately $220 billion in 2023.
Companies like Bloom Energy are compelled to innovate continuously and secure large contracts to offset substantial fixed costs associated with R&D and manufacturing. For instance, Bloom Energy's 2023 revenue of $1.16 billion reflects its efforts to gain market share amidst this pressure, often leading to competitive pricing strategies.
Strategic alliances are becoming increasingly common as companies seek to enhance their market position and technological capabilities. Bloom Energy's 2023 collaboration with Baker Hughes exemplifies this trend, highlighting how partnerships are reshaping the competitive landscape as players vie for dominance in the clean energy transition.
| Competitor Type | Key Differentiators | Market Share Focus | Bloom Energy's Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| Established Energy Giants | Extensive resources, existing infrastructure | Broad energy solutions, grid integration | Technological leadership, specialized solutions |
| Innovative Startups | Agility, emerging technologies | Niche markets, disruptive pricing | Continuous R&D, strategic partnerships |
| Other Fuel Cell Providers | Specific fuel cell chemistries, cost reduction | Targeted applications, efficiency improvements | Solid oxide technology, fuel flexibility |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The most significant substitute for Bloom Energy's on-site power solutions is the traditional centralized electricity grid. For many businesses, grid power is a readily available and often cost-effective choice, particularly in regions with robust and reliable infrastructure.
Bloom Energy faces the challenge of consistently proving its value proposition over grid reliance. This means highlighting superior energy resilience, potential cost savings, especially during peak demand periods, and the sustainability benefits of their fuel-flexible solid oxide fuel cells to encourage customers to switch.
Solar photovoltaic (PV) systems and wind turbines, often coupled with advanced battery storage, are becoming potent substitutes for traditional on-site power generation. By 2024, the levelized cost of energy (LCOE) for utility-scale solar PV has fallen significantly, making it a more attractive option for many businesses. This trend directly challenges Bloom Energy's value proposition if it cannot effectively communicate its advantages.
The decreasing costs of these intermittent renewable sources and storage technologies mean businesses can increasingly find competitive alternatives for cleaner, decentralized power. For instance, the global renewable energy capacity additions in 2023 were projected to reach record levels, indicating a strong market shift. Bloom Energy needs to emphasize its unique benefits, such as providing reliable baseload power, a smaller physical footprint compared to some renewable installations, and its future-proofing with hydrogen readiness, to differentiate itself.
Beyond Bloom Energy's fuel cells, a range of other on-site distributed generation technologies compete for customer needs. These include established options like natural gas-fired reciprocating engines, microturbines, and combined heat and power (CHP) systems. These alternatives present varying operational profiles, fuel adaptability, and cost considerations, forcing Bloom Energy to continually prove its economic and environmental advantages.
Energy Efficiency and Demand-Side Management
Customers are increasingly adopting energy efficiency measures, which can significantly reduce their reliance on new power generation, including Bloom Energy's fuel cells. For instance, in 2024, the International Energy Agency reported that energy efficiency improvements saved the equivalent of 2.5 billion tons of oil globally, demonstrating a substantial reduction in overall energy demand.
Optimizing building management systems and participating in demand response programs further diminish the need for constant, high-output power generation. These strategies effectively act as indirect substitutes by lowering energy consumption. As of early 2025, many utilities are expanding their demand response programs, offering incentives that can reduce peak electricity demand by 5-15% for participating customers.
Bloom Energy's value proposition must therefore align with a customer's comprehensive energy management strategy, not just the provision of on-site generation. This integration is crucial as customers seek holistic solutions to manage energy costs and carbon footprints.
The threat of substitutes is amplified by:
- Growing adoption of smart grid technologies and IoT devices enabling real-time energy monitoring and optimization, leading to reduced consumption.
- Increasing availability and decreasing cost of energy storage solutions, which can shift energy usage to off-peak hours, lessening the need for continuous generation.
- Government incentives and regulations promoting energy conservation and efficiency, making these alternatives more financially attractive to businesses and consumers.
Emerging Energy Technologies and Hybrid Systems
The energy landscape is constantly evolving, with new technologies frequently appearing. Innovations like small modular reactors (SMRs) and advanced geothermal systems, though not yet widespread, could become viable alternatives to Bloom Energy’s fuel cell technology. For instance, by the end of 2024, several countries are expected to have made significant progress in demonstrating SMR prototypes, potentially impacting the long-term viability of current energy solutions.
Bloom Energy needs to stay vigilant regarding these emerging energy sources and hybrid systems. The development of advanced energy storage, such as improved battery chemistries or hydrogen storage, also presents a potential threat. As of mid-2024, global investment in energy storage solutions has reached record highs, indicating a strong market push for these alternatives.
- Emerging Technologies: SMRs, advanced geothermal, and novel energy storage are developing rapidly.
- Market Dynamics: Significant global investment in energy storage by mid-2024 signals growing demand for alternatives.
- Strategic Imperative: Bloom Energy must monitor these trends and consider integration or strategic adaptation to maintain competitiveness.
The threat of substitutes for Bloom Energy's fuel cell technology is substantial, encompassing the traditional grid, renewable energy sources with storage, and other on-site generation methods. As of 2024, the declining costs of solar PV and wind power, coupled with advancements in battery storage, present increasingly competitive alternatives for businesses seeking decentralized and cleaner energy solutions. For instance, global renewable energy capacity additions in 2023 saw record growth, highlighting a significant market shift towards these substitutes.
Furthermore, energy efficiency measures and demand response programs act as indirect substitutes by reducing overall energy consumption, thereby lessening the need for new power generation. By early 2025, utilities are expanding demand response programs, offering incentives that can reduce peak electricity demand by 5-15%, further diminishing the reliance on continuous generation. Bloom Energy must therefore continuously demonstrate its unique value proposition, including reliable baseload power and hydrogen readiness, to differentiate itself in this dynamic market.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | 2024/2025 Market Trend/Data | Impact on Bloom Energy |
| Centralized Grid | Availability, established infrastructure, cost-effectiveness in some regions | Reliability remains high in developed regions, but grid instability in others creates opportunities. | Direct competitor, requires Bloom to prove cost and resilience advantages. |
| Renewables (Solar PV/Wind) + Storage | Decreasing LCOE, sustainability, decentralization | Utility-scale solar PV LCOE has fallen significantly; global renewable capacity additions reached record levels in 2023. | Growing competitiveness, necessitates highlighting baseload power and smaller footprint advantages. |
| Other On-Site Generation (e.g., Gas Engines, Microturbines) | Established technologies, varying fuel flexibility and cost profiles | Continued deployment, especially for combined heat and power (CHP) applications. | Requires continuous demonstration of economic and environmental superiority. |
| Energy Efficiency & Demand Response | Reduced energy consumption, optimized usage | IEA reported 2.5 billion tons of oil equivalent saved globally by efficiency in 2024; utilities expanding demand response programs by 5-15% peak reduction. | Indirectly reduces demand for any new generation, requiring Bloom to be part of a holistic energy strategy. |
Entrants Threaten
The advanced fuel cell manufacturing and distributed energy sector demands immense capital for cutting-edge R&D and state-of-the-art production facilities. For instance, establishing a new fuel cell manufacturing plant can easily cost hundreds of millions of dollars, a figure that deters many potential entrants.
The intricate nature of Bloom Energy's solid oxide fuel cell technology presents a substantial hurdle for potential new entrants. This complexity spans materials science, electrochemistry, and sophisticated system engineering, demanding highly specialized knowledge and significant research and development investment.
Bloom Energy's robust intellectual property, including a substantial patent portfolio and accumulated proprietary know-how, acts as a powerful deterrent. Developing comparable, competitive technology while navigating existing patents would be an exceptionally time-consuming and costly endeavor for any newcomer.
The threat of new entrants in the on-site power solutions market, particularly for Bloom Energy, is significantly influenced by substantial regulatory hurdles. These include intricate permitting processes, stringent environmental compliance mandates, and complex grid interconnection standards that differ greatly across various geographical regions.
New companies entering this space must dedicate considerable financial resources and time to meticulously understand and adhere to these diverse regulations. This creates a significant operational barrier, demanding expertise in navigating bureaucratic systems that Bloom Energy has already established.
For instance, in 2024, the average time to obtain necessary permits for energy projects in the US can extend from several months to over a year, depending on the project's scale and location, highlighting the time investment required for new players.
Need for Established Distribution Channels and Customer Trust
The need for established distribution channels and customer trust presents a significant barrier for new entrants looking to compete with Bloom Energy. Developing robust sales and distribution networks, along with fostering strong relationships with commercial and industrial clients, demands substantial time, effort, and financial investment.
Newcomers would find it challenging to immediately match Bloom Energy's existing market presence, brand recognition, and established customer base. In this industry, trust and demonstrated reliability are paramount, making it difficult for new players to gain traction.
- Distribution Network Investment: Building a nationwide or global distribution and service network is a capital-intensive undertaking, often requiring years to establish.
- Customer Acquisition Cost: Acquiring large commercial and industrial clients typically involves lengthy sales cycles and high upfront costs, which new entrants may struggle to absorb.
- Brand Reputation and Reliability: Bloom Energy's track record and established reputation for reliable fuel cell technology are significant assets that new competitors would need considerable time and proven performance to replicate.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve Effects
Bloom Energy's established position grants it significant economies of scale in manufacturing and procurement. For instance, in 2023, Bloom Energy reported generating $1.16 billion in revenue, indicating substantial operational volume that allows for more efficient resource utilization compared to potential newcomers. This scale translates directly into lower per-unit production costs, creating a substantial barrier for new entrants aiming to compete on price.
New entrants would struggle to match Bloom Energy's cost structure due to the absence of these scale advantages. They would need considerable upfront investment to build out production capacity and establish supply chains, a process that inherently involves higher initial per-unit costs. Until a new entrant achieves a similar level of operational scale and navigates the learning curve, it will likely face a significant cost disadvantage.
- Economies of Scale: Bloom Energy leverages its substantial revenue base to negotiate better terms with suppliers and optimize its manufacturing processes, leading to reduced per-unit costs.
- Experience Curve: Years of operation have allowed Bloom Energy to refine its production techniques and improve efficiency, further lowering costs as output increases.
- Cost Disadvantage for New Entrants: Start-ups would initially incur higher production costs due to smaller volumes and less optimized processes, making it difficult to compete on price with Bloom Energy.
- Investment Barrier: Achieving comparable scale and efficiency requires significant capital investment, acting as a deterrent for potential new competitors.
The threat of new entrants in Bloom Energy's market is considerably low due to several significant barriers. The immense capital required for research, development, and state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities, often running into hundreds of millions of dollars, acts as a primary deterrent. Furthermore, Bloom Energy's proprietary solid oxide fuel cell technology, with its inherent complexity in materials science and engineering, demands highly specialized knowledge and substantial R&D investment that new players would struggle to replicate quickly.
Bloom Energy's extensive patent portfolio and accumulated know-how create a formidable intellectual property barrier, making it exceptionally costly and time-consuming for newcomers to develop competitive technologies. Regulatory hurdles, including complex permitting, environmental compliance, and grid interconnection standards, add another layer of difficulty, with new projects in 2024 facing permit acquisition times that can range from several months to over a year.
The need for established distribution channels and customer trust also presents a significant challenge, as building robust sales networks and fostering client relationships requires years of effort and financial commitment. Bloom Energy's established market presence, brand recognition, and proven reliability are assets that new entrants would find difficult to match in the short to medium term.
Economies of scale, driven by Bloom Energy's substantial revenue, such as its $1.16 billion in revenue in 2023, allow for more efficient resource utilization and lower per-unit production costs. New entrants would face a significant cost disadvantage until they achieve similar operational scale and navigate the learning curve, requiring considerable upfront investment to build production capacity and establish supply chains.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Bloom Energy's Advantage | Illustrative Data/Fact |
| Capital Requirements | High cost of R&D and manufacturing facilities | Deters entry due to immense upfront investment | Established infrastructure and financial backing | Hundreds of millions for a new plant |
| Technology Complexity | Intricate fuel cell technology requiring specialized knowledge | Requires significant R&D and expertise | Proprietary technology and accumulated know-how | Demands expertise in materials science, electrochemistry |
| Intellectual Property | Extensive patent portfolio and proprietary knowledge | Costly and time-consuming to develop comparable tech | Strong patent protection and trade secrets | Navigating existing patents is a major hurdle |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex permitting, environmental, and grid standards | Time-consuming and costly compliance | Established relationships and expertise in navigating regulations | Permit acquisition can take 6-12+ months (2024) |
| Distribution & Customer Trust | Need for established sales networks and client relationships | Difficult to gain market traction without proven reliability | Existing distribution channels and strong brand reputation | Lengthy sales cycles and high acquisition costs |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high production volume | Incurs higher initial production costs | Efficient resource utilization and lower per-unit costs | $1.16 billion revenue (2023) enables scale advantages |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Bloom Energy Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of comprehensive data, including Bloom Energy's SEC filings, investor presentations, and annual reports. We also incorporate industry-specific market research from firms like Wood Mackenzie and BloombergNEF, alongside macroeconomic data from government agencies and reputable financial news outlets.
