Banco Bradesco Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Banco Bradesco Bundle
Banco Bradesco navigates a dynamic Brazilian financial landscape, facing intense rivalry from established players and agile fintechs, while also contending with significant buyer power from a diverse customer base. The threat of substitutes, particularly digital alternatives, is ever-present, shaping the bank's strategic imperatives.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Banco Bradesco’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
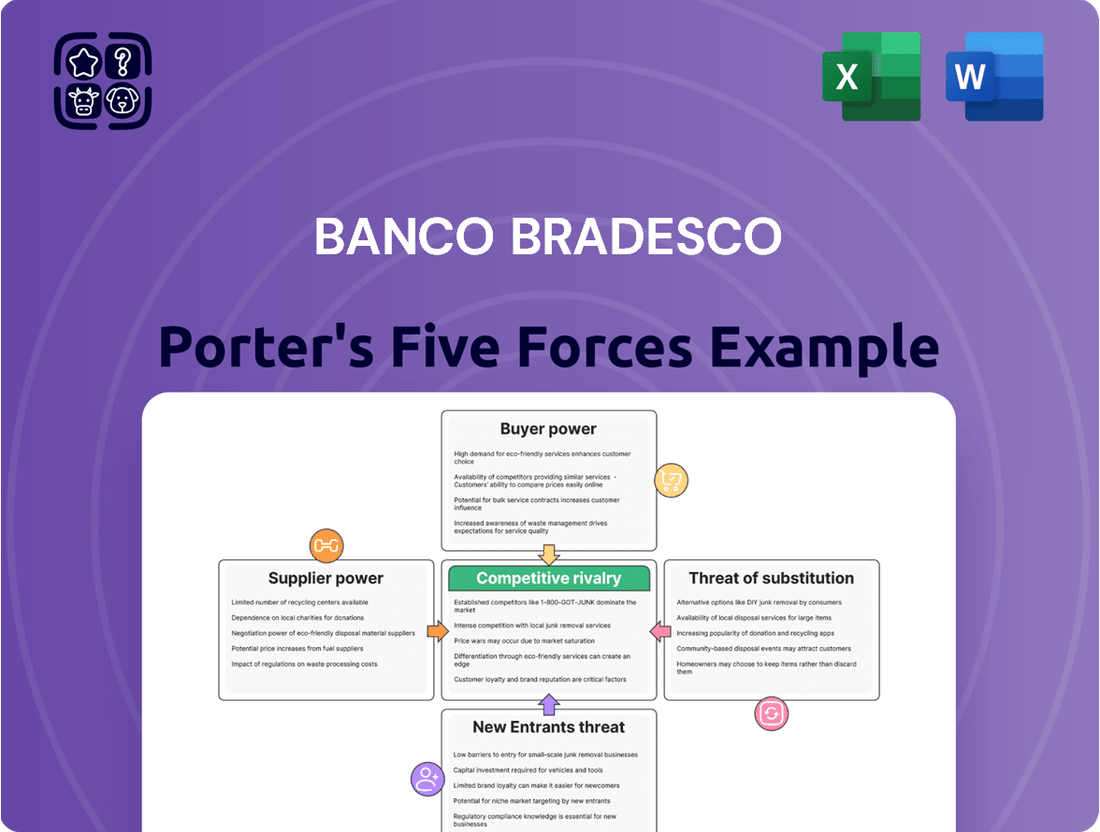
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Banco Bradesco's deep dive into digital transformation, particularly its significant investments in advanced technologies like AI, places considerable bargaining power in the hands of specialized software and IT infrastructure providers. The bank's commitment to cutting-edge solutions means these suppliers are crucial for its operational efficiency and competitive edge.
Bradesco's 2024 initiatives, including the adoption of agentic AI and agile methodologies, underscore a pronounced reliance on sophisticated technological partners. This dependency grants these providers leverage, as Bradesco requires their specialized expertise and infrastructure to maintain its forward-thinking strategy and service delivery.
The financial sector, including institutions like Banco Bradesco, faces significant supplier power from human capital, especially in specialized areas. The demand for skilled professionals, particularly in technology and artificial intelligence, is exceptionally high. This intense competition for talent means that individuals with in-demand skills can negotiate better terms and compensation.
Banco Bradesco's own recruitment efforts highlight this trend. Since the beginning of 2024, the bank has actively hired over 2,100 technology professionals. This substantial influx of talent underscores the market's demand and the leverage skilled individuals possess, allowing them to influence employment conditions and potentially drive up labor costs for the bank.
While individual depositors generally hold minimal bargaining power, larger entities like institutional investors and the aggregated actions of the broader depositor base can exert influence on Bradesco's funding costs. For instance, in 2023, Brazil's benchmark Selic rate reached 11.75%, a significant increase from prior years, directly impacting the cost for banks to attract and retain deposits.
This competitive environment, especially with upward trending interest rates, can escalate the expense of securing and keeping deposits, thereby affecting Bradesco's overall profitability. The bank's ability to manage these funding costs is crucial, particularly as it navigates a market where depositors have more options and are more sensitive to yield differentials.
Interbank Market and Funding Sources
Banco Bradesco's reliance on the interbank market and other wholesale funding sources means supplier power is significant. The Central Bank of Brazil's monetary policy, including its benchmark Selic rate, directly influences the cost of these funds. For instance, the Selic rate stood at 10.50% as of May 2024, impacting Bradesco's borrowing costs.
- Interbank Market Dependence: Bradesco actively uses the interbank market for its liquidity needs, making it susceptible to the pricing power of other financial institutions.
- Wholesale Funding Costs: The bank's access to and cost of capital from wholesale markets are dictated by prevailing interest rates and market conditions, often tied to central bank policies.
- Selic Rate Impact: The Central Bank of Brazil's monetary policy, reflected in the Selic rate, directly influences the cost of funds for Bradesco, highlighting supplier leverage.
Regulatory Bodies and Compliance Services
The Central Bank of Brazil (BCB) and other regulatory bodies significantly influence Banco Bradesco's operations, acting as powerful suppliers of the essential legal and operational framework. Compliance with directives, such as those concerning capital adequacy ratios or new digital asset regulations, demands substantial investment in IT infrastructure and specialized consulting. For instance, in 2023, Brazilian banks collectively spent billions on compliance initiatives, reflecting the significant cost and resource allocation required to meet regulatory demands, thereby amplifying the bargaining power of these regulatory 'suppliers'.
- Regulatory Framework: The BCB dictates crucial operational parameters, including reserve requirements and lending standards.
- Compliance Costs: Adhering to evolving regulations, like those for open banking or anti-money laundering, necessitates significant financial and technological investment.
- Influence on Strategy: Changes in regulatory capital requirements or consumer protection laws directly impact Bradesco's strategic planning and product development.
- Service Providers: Specialized legal and IT firms that facilitate compliance also exert influence due to their expertise and the critical nature of their services.
Banco Bradesco's reliance on specialized technology providers, particularly those in AI and advanced software, grants these suppliers significant bargaining power. The bank's strategic focus on digital transformation, including its 2024 investments in agentic AI, means these partners are critical for maintaining its competitive edge and operational efficiency.
The demand for highly skilled IT professionals, a key component of Bradesco's operational strength, also empowers human capital suppliers. The bank's recruitment of over 2,100 technology professionals since early 2024 highlights this intense competition for talent, allowing skilled individuals to negotiate favorable terms.
Furthermore, Banco Bradesco's dependence on wholesale funding markets and the interbank market means that financial institutions and the Central Bank of Brazil exert considerable influence. The Selic rate, set by the Central Bank, directly impacts Bradesco's borrowing costs, with the rate at 10.50% as of May 2024, illustrating this supplier leverage.
Regulatory bodies like the Central Bank of Brazil act as powerful suppliers of the operational framework, imposing compliance requirements that necessitate significant investment. The substantial costs incurred by Brazilian banks in 2023 for compliance initiatives underscore the bargaining power of these regulatory entities and the service providers they necessitate.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Power Influence | Supporting Data/Fact (as of mid-2024 or latest available) |
|---|---|---|
| Technology & AI Providers | High | Bradesco's significant investments in AI and advanced IT infrastructure for digital transformation. |
| Skilled IT Professionals | High | Recruitment of over 2,100 tech professionals by Bradesco since early 2024, indicating high demand. |
| Wholesale Funding Markets / Interbank Lenders | High | Selic rate at 10.50% (May 2024) directly impacts Bradesco's borrowing costs. |
| Regulatory Bodies (e.g., Central Bank of Brazil) | High | Billions spent by Brazilian banks on compliance in 2023, driven by regulatory demands. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Banco Bradesco's position in the Brazilian financial sector.
Gain a strategic advantage by easily identifying and mitigating competitive threats within the banking sector.
Navigate the complex banking landscape with a clear, actionable framework for understanding and responding to market dynamics.
Customers Bargaining Power
The digital revolution in Brazil has dramatically expanded options for banking customers. With numerous fintechs and digital banks entering the market, consumers now have unprecedented ease in comparing services and switching providers. This heightened competition directly impacts established institutions like Banco Bradesco.
In 2023, Brazil saw a substantial surge in digital banking adoption, with estimates suggesting over 70% of banking transactions occurred digitally. This trend puts considerable pressure on traditional banks to not only match but exceed the user experience and pricing offered by agile fintech competitors, forcing Bradesco to innovate continuously.
The widespread adoption of PIX in Brazil has significantly shifted bargaining power towards customers. As of early 2024, PIX transactions consistently surpassed 20 million daily, offering a free and instant payment alternative that directly challenges traditional, often fee-based, bank transfer systems.
This accessibility reduces customer dependence on specific bank payment infrastructure, giving them more leverage to negotiate better terms or switch providers based on transaction costs and convenience. For instance, the sheer volume of PIX usage, which has become a primary payment method for many Brazilians, means banks must offer competitive services to retain these customers.
Brazil's Open Finance initiative, launched in phases starting in 2021 and progressing through 2024, significantly bolsters customer bargaining power. This regulatory push allows consumers to securely share their financial data with various institutions, promoting a more transparent and competitive market. For Banco Bradesco, this means customers can more easily compare offerings and switch providers, increasing pressure on Bradesco to offer attractive terms and services.
Price Sensitivity and Fee Pressure
Customers, especially retail clients, are more aware of pricing due to the clear fee structures offered by digital banks. This heightened price sensitivity puts pressure on Banco Bradesco to re-evaluate its fees and product terms.
For instance, in 2024, the growth of fintechs offering lower-cost alternatives for services like international transfers and digital payments intensified this fee pressure. Bradesco has responded by enhancing its digital offerings and reviewing its fee schedules to remain competitive.
- Retail segment price sensitivity is high.
- Digital banks offer transparent pricing, increasing competition.
- Bradesco faces pressure to reduce fees and improve product terms.
- 2024 saw increased competition from fintechs in payment services.
Demand for Integrated and Personalized Services
While many customers prioritize lower fees, a growing segment of Bradesco's clientele actively seeks integrated financial solutions, combining banking, insurance, and investment management. This demand for personalized, all-in-one services empowers these customers, giving them significant influence over Bradesco's product development and service quality, as the bank strives to meet these complex needs.
For instance, in 2024, Bradesco reported a notable increase in the uptake of its bundled financial products, indicating a clear customer preference for convenience and tailored offerings. This trend directly translates to customer bargaining power, as they can switch to competitors offering more comprehensive or better-integrated packages.
- Customer Demand for Integration: A significant portion of Bradesco's customer base seeks a unified experience across banking, insurance, and asset management.
- Influence on Product Development: This demand for tailored solutions gives customers leverage to influence Bradesco's innovation pipeline and service enhancements.
- 2024 Data Point: Bradesco observed a rise in customers utilizing its integrated product suites in 2024, underscoring the importance of this trend.
The bargaining power of customers for Banco Bradesco is significantly amplified by the digital banking landscape in Brazil. Increased competition from fintechs and digital banks, coupled with the widespread adoption of PIX and the progress of Open Finance, has empowered consumers with more choices and greater leverage. This forces Bradesco to focus on competitive pricing, enhanced user experiences, and integrated financial solutions to retain its customer base.
| Factor | Impact on Bradesco | Customer Leverage |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Banking Competition | Pressure to innovate and lower fees | Easy comparison and switching |
| PIX Adoption | Reduced reliance on traditional transfers | Free, instant payment option |
| Open Finance | Increased transparency and data sharing | Ability to compare and switch easily |
| Price Sensitivity | Need for competitive fee structures | Demand for lower transaction costs |
| Demand for Integrated Solutions | Opportunity for bundled offerings | Preference for convenience and personalization |
Full Version Awaits
Banco Bradesco Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact, comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of Banco Bradesco you'll receive immediately after purchase, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications for this major Brazilian financial institution. You'll gain a deep understanding of the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the banking sector. This document is ready for your immediate use, offering valuable insights for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Bradesco faces intense rivalry from established giants like Itaú Unibanco, Banco do Brasil, and Santander Brasil, all vying for dominance in Brazil's banking sector. These institutions actively compete by introducing new products and services, aiming to capture and retain customers across retail, corporate, and investment banking. For instance, in the first quarter of 2024, the Brazilian banking sector saw continued growth, with major banks reporting robust earnings, underscoring the ongoing battle for market share.
Digital banks and fintechs like Nubank, C6 Bank, and Banco Inter are intensifying competition. These agile players frequently undercut traditional banks on fees and provide slicker digital interfaces, drawing in younger customers and those prioritizing convenience. For instance, Nubank reported over 100 million customers globally by early 2024, showcasing the rapid adoption of these digital-first models.
The widespread adoption of PIX, Brazil's instant payment system, has significantly reshaped the competitive landscape for banks like Banco Bradesco. By standardizing real-time transfers and drastically reducing transaction costs, PIX has intensified rivalry. This has directly impacted traditional revenue streams, such as fees from TED and DOC transfers, forcing established players to re-evaluate their strategies.
In 2023, PIX transactions in Brazil reached an astonishing 42 billion, a substantial increase from 11.7 billion in 2022, highlighting its rapid integration into the financial ecosystem. This surge in PIX usage means that banks are now under immense pressure to innovate and offer more value-added services beyond basic payment processing to maintain profitability and customer loyalty.
Diversification of Service Offerings
Banco Bradesco and its competitors are actively diversifying their service portfolios to stay ahead. This means moving beyond standard banking services into areas such as insurance, wealth management, and specialized loans for sectors like agribusiness. This strategic shift broadens the competitive landscape considerably.
This diversification necessitates ongoing investment in developing new products and strengthening capabilities for cross-selling services to existing and new customers. For instance, in 2024, Bradesco reported significant growth in its insurance and asset management segments, demonstrating this trend.
- Diversification into Insurance: Bradesco Seguros, a subsidiary, plays a crucial role in the group's diversified strategy.
- Asset Management Growth: Bradesco Asset Management is a key player in managing investment funds for a wide range of clients.
- Agribusiness Focus: The bank has been increasing its exposure to agribusiness loans, recognizing the sector's economic importance.
- Cross-selling Initiatives: The bank actively promotes bundled products, combining banking, insurance, and investment services.
Regulatory Push for Increased Competition
The Central Bank of Brazil is actively fostering a more competitive financial landscape. Initiatives like Open Banking and PIX are designed to break down the traditional oligopoly, encouraging new players and pushing established institutions to enhance their services and efficiency.
This regulatory push directly impacts competitive rivalry by lowering barriers to entry and increasing customer choice. For instance, PIX, launched in November 2020, has seen rapid adoption, with over 165 million users and 34.4 billion transactions processed by the end of 2023, demonstrating a significant shift in payment behaviors and potentially reducing reliance on traditional banking services.
- Open Banking: Mandated data sharing to enable new service providers and foster innovation.
- PIX Instant Payments: Facilitated a surge in peer-to-peer and business transactions, increasing competition in payment processing.
- Reduced Oligopoly: Regulatory efforts aim to decentralize market power from a few large banks.
- Innovation Pressure: Existing banks must innovate to retain customers and compete with fintechs.
Banco Bradesco operates in a fiercely competitive Brazilian banking market, facing pressure from both traditional rivals and agile fintechs. The intense rivalry is driven by innovation in products and digital services, with major banks like Itaú Unibanco and Santander Brasil actively competing for market share. This dynamic is further amplified by the rapid adoption of PIX, Brazil's instant payment system, which has lowered transaction costs and intensified competition in payment processing.
| Competitor | Market Share (approx.) | Key Competitive Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Itaú Unibanco | ~20-25% | Digital transformation, credit expansion, fee reduction |
| Santander Brasil | ~10-15% | Focus on digital channels, agribusiness lending, customer acquisition |
| Nubank | Rapidly growing, significant digital presence | Low fees, superior UX, credit card dominance, expansion into investments |
| Banco do Brasil | ~15-20% | Government partnerships, agribusiness focus, digital service enhancement |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of fintech payment systems like PIX presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional banking services. PIX, launched by the Central Bank of Brazil, has seen explosive growth, processing over 10 billion transactions in 2023 alone, demonstrating its rapid adoption as a primary payment method. This instant, fee-free alternative directly competes with bank transfers and card payments, eroding a key revenue stream for institutions like Banco Bradesco.
Non-bank lending platforms, such as peer-to-peer lenders and specialized fintech companies, present a significant threat of substitution for traditional banks like Banco Bradesco. These alternatives often cater to specific market segments, like SMEs and individuals, offering faster approval times and more customized loan products than conventional banking services.
In 2024, the fintech lending sector continued its robust growth, with transaction volumes on major platforms showing double-digit increases year-over-year. For instance, some leading P2P platforms reported facilitating billions in new loans, capturing market share from traditional credit providers by leveraging technology for streamlined underwriting and customer onboarding.
The threat of substitutes for Banco Bradesco's investment and asset management platforms is significant. Customers have a growing array of options outside of traditional banking institutions to manage and grow their wealth. For instance, independent brokerage firms, specialized robo-advisors, and user-friendly online investment platforms offer alternative avenues for investment, often with competitive fee structures and a wider selection of investment products.
This shift is reflected in the market. In 2024, the global robo-advisory market was projected to reach over $2.5 trillion in assets under management, demonstrating a clear preference for digital, often lower-cost, investment solutions. These platforms can provide similar diversification and portfolio management services as a bank, but without the broader service bundle, allowing them to focus on competitive pricing and user experience, thus posing a direct substitute to Bradesco's offerings.
Cryptocurrencies and Central Bank Digital Currencies (Drex)
The growing adoption of cryptocurrencies and the impending launch of Brazil's digital currency, Drex, pose a significant threat of substitution for traditional banking services. As of early 2024, the global cryptocurrency market capitalization has fluctuated, but its increasing mainstream acceptance and the development of clearer regulatory frameworks, particularly in Brazil with Drex's pilot programs, suggest a potential shift in how value is stored and transferred. This could impact demand for conventional deposit and transaction services offered by institutions like Banco Bradesco.
Drex, specifically, aims to modernize Brazil's financial system by offering a digital version of the Real, potentially streamlining payments and financial operations. This initiative, alongside the broader trend of digital asset adoption, could reduce reliance on traditional banking intermediaries for certain financial activities.
- Cryptocurrency Market Cap: While volatile, the global cryptocurrency market capitalization has seen significant growth, reaching trillions of dollars at various points, indicating substantial value stored in digital assets.
- Drex Pilot Programs: Brazil's Central Bank has been actively conducting pilot programs for Drex throughout 2023 and into 2024, testing its functionalities and preparing for broader implementation.
- Digital Transactions: The increasing volume of digital transactions globally, including those facilitated by cryptocurrencies, suggests a growing comfort level with non-traditional payment methods.
Embedded Finance Solutions
The rise of embedded finance presents a significant threat by integrating financial services directly into non-financial customer journeys, potentially bypassing traditional banking channels. For instance, e-commerce platforms offering instant credit at checkout or ride-sharing apps facilitating in-app payments and loans reduce the need for customers to engage with banks directly for these services.
This trend allows consumers to access financial products precisely when and where they need them, diminishing the perceived value of standalone banking relationships. By 2024, the global embedded finance market is projected to reach substantial figures, indicating a growing adoption and a direct challenge to incumbent banks' customer acquisition and retention strategies.
- Embedded Finance Growth: Projections indicate the embedded finance market could reach trillions globally by 2027, with significant growth already observed in 2024.
- Disintermediation Risk: Non-financial companies integrating financial services can capture customer relationships and transaction data, weakening banks’ direct customer touchpoints.
- Consumer Convenience: The seamless integration of financial solutions into everyday platforms offers unparalleled convenience, making it harder for traditional banks to compete on user experience alone.
- New Revenue Streams: For non-financial entities, offering embedded finance creates new revenue opportunities and strengthens customer loyalty, further incentivizing the shift away from traditional banking.
The increasing availability of alternative payment methods, such as digital wallets and direct peer-to-peer transfers, significantly challenges traditional banking transaction fees. PIX, Brazil's instant payment system, processed over 10 billion transactions in 2023, demonstrating a massive shift towards fee-free alternatives that directly impact banks' revenue from interbank transfers and card processing.
Fintech lending platforms offer faster, more tailored loan products, capturing market share from traditional banks. In 2024, these platforms saw continued double-digit growth in transaction volumes, with some facilitating billions in new loans by leveraging technology for streamlined underwriting, directly competing with Banco Bradesco's credit offerings.
The rise of robo-advisors and independent investment platforms presents a substitute for wealth management services. The global robo-advisory market was projected to exceed $2.5 trillion in assets under management in 2024, highlighting customer preference for lower-cost, digital investment solutions over traditional bank offerings.
The development of digital currencies like Drex and the growing adoption of cryptocurrencies offer alternative stores of value and transaction mechanisms. Drex pilot programs are underway in Brazil, and the global cryptocurrency market capitalization, while volatile, represents trillions of dollars, potentially reducing reliance on traditional banking for certain financial activities.
Embedded finance, where financial services are integrated into non-financial platforms, bypasses traditional banking channels. By 2024, the global embedded finance market is projected for substantial growth, enabling consumers to access credit and payments at point-of-need, diminishing the necessity of direct engagement with banks.
| Substitute | Impact on Banco Bradesco | 2023/2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| PIX Payments | Erosion of transaction fee revenue | 10+ billion transactions processed in 2023 |
| Fintech Lending Platforms | Loss of loan market share | Double-digit annual growth in transaction volumes |
| Robo-Advisors | Reduced demand for traditional wealth management | Projected $2.5+ trillion in AUM by 2024 |
| Digital Currencies (Drex, Crypto) | Potential decline in deposit and transaction service usage | Trillions in global crypto market cap; Drex pilot programs ongoing |
| Embedded Finance | Disintermediation of customer relationships | Significant projected market growth by 2024 |
Entrants Threaten
While Brazil's banking sector is known for its intricate regulatory landscape, which naturally deters new entrants, the Central Bank of Brazil has been making efforts to streamline licensing procedures, particularly for fintechs and specialized financial institutions. For instance, in 2023, the Central Bank continued to refine regulations around open banking and digital account opening, making it easier for new, technology-driven firms to enter the market. This ongoing simplification, however, does not eliminate the need for significant capital and compliance expertise, meaning the barrier remains substantial for traditional banking models.
Establishing a full-service bank akin to Banco Bradesco demands immense capital, a robust infrastructure, and a widespread network, creating a significant hurdle for prospective competitors. For instance, in 2023, Bradesco reported total assets exceeding R$1.9 trillion, illustrating the scale of investment required.
Further complicating entry, regulatory bodies like the Central Bank of Brazil are continuously evaluating minimum capital requirements. Such reviews, potentially increasing the threshold for new entrants, act as a substantial deterrent, safeguarding incumbent institutions.
Incumbent banks like Banco Bradesco have cultivated strong brand recognition over many years, fostering deep customer trust that new entrants find challenging to quickly match. For instance, in 2024, Bradesco continued to be a leading financial institution in Brazil, with millions of active customers relying on its established reputation for security and reliability in managing their finances.
This established trust is a significant barrier. Customers are often hesitant to entrust their sensitive financial data and significant assets to unfamiliar institutions, especially when considering long-term financial planning or critical transactions where perceived security is paramount.
Technological Investment and Digital Maturity
While fintechs are known for their technological agility, established banks like Banco Bradesco are aggressively investing in their own digital transformation. For instance, in 2023, Bradesco announced plans to invest R$10 billion in technology and innovation through 2027, focusing on areas like artificial intelligence and cybersecurity. This substantial investment raises the technological bar significantly for potential new entrants.
Newcomers must not only develop innovative financial solutions but also possess the capital and expertise to build and maintain secure, robust digital infrastructures comparable to those of incumbents. This includes meeting stringent regulatory requirements and ensuring data privacy, which can be a substantial hurdle.
- High Capital Requirements: Significant upfront investment is needed for advanced technology, cybersecurity, and regulatory compliance.
- Technological Sophistication: New entrants must match or exceed the digital maturity and AI capabilities of established players.
- Security and Trust: Building customer trust requires demonstrating advanced cybersecurity measures, a costly undertaking.
Open Banking and PIX as Enablers for Niche Entrants
Open Banking and PIX are paradoxically lowering entry barriers for niche players in Brazil's financial sector. These initiatives enable new entrants to access customer data with consent and utilize PIX's established payment infrastructure, reducing the need for significant upfront investment in data management and payment processing.
This shift allows specialized fintechs to concentrate on innovative service offerings rather than foundational infrastructure. For instance, by leveraging Open Banking APIs, a new wealth management app can access a user's transaction history from Bradesco (with permission) and integrate seamlessly with PIX for fund transfers, bypassing the need to build these capabilities internally.
- Open Banking Growth: By the end of 2023, over 30 million Brazilians had shared their financial data through Open Banking, indicating a significant user base now open to third-party financial services.
- PIX Transaction Volume: PIX processed an average of 100 million transactions daily in early 2024, highlighting its dominance and accessibility as a payment rail for new entrants.
- Fintech Funding: In 2023, Brazilian fintechs raised over $2 billion in funding, demonstrating investor confidence in new players leveraging these technological advancements.
The threat of new entrants for Banco Bradesco remains moderate, primarily due to high capital requirements and established brand loyalty. However, regulatory shifts and technological advancements are creating avenues for specialized fintechs.
While the Brazilian banking sector requires substantial capital, as evidenced by Bradesco's total assets exceeding R$1.9 trillion in 2023, regulatory streamlining for fintechs is ongoing. New entrants must overcome significant hurdles like matching Bradesco's R$10 billion technology investment announced in 2023 and building customer trust, a challenge compounded by Bradesco's strong reputation in 2024.
Conversely, initiatives like Open Banking, with over 30 million users by the end of 2023, and the ubiquity of PIX, processing around 100 million daily transactions in early 2024, lower entry barriers for niche players. These advancements allow new firms to leverage existing infrastructure, though they still need to attract customers and secure funding, with Brazilian fintechs raising over $2 billion in 2023.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Bradesco's Position |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High barrier, but evolving for fintechs | Very High (R$1.9T+ assets in 2023) |
| Brand Trust & Loyalty | Significant hurdle to overcome | Very High (millions of customers in 2024) |
| Technology Investment | Requires matching incumbents' spend | High (R$10B planned through 2027) |
| Regulatory Environment | Streamlining for fintechs, but complex overall | Established compliance framework |
| Open Banking/PIX | Lowers barriers for niche services | Adapting to leverage these platforms |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Banco Bradesco is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial statements, annual reports, and regulatory filings. We also incorporate insights from reputable financial news outlets, industry analysis reports, and macroeconomic data from sources like the Central Bank of Brazil.
