Balaji Amines Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Balaji Amines Bundle
Balaji Amines faces moderate bargaining power from buyers due to specialized product offerings, yet intense competition from existing players and potential new entrants shapes its market. Understanding the nuances of supplier relationships and the threat of substitutes is crucial for navigating this landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Balaji Amines’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers for Balaji Amines is a significant factor, leaning towards moderate to high, especially concerning essential raw materials. This is largely driven by the concentration of suppliers for key inputs.
For example, methanol, a crucial component in Balaji Amines' production processes, is predominantly sourced through imports, with a substantial portion originating from the Middle East. This reliance on a concentrated group of international suppliers inherently grants them considerable influence over pricing and the reliability of supply chains for Balaji Amines.
Ammonia, methanol, and denatured ethyl alcohol are the bedrock of Balaji Amines' manufacturing process for aliphatic amines. Their uninterrupted availability is absolutely critical for keeping production lines running smoothly. In 2023, the cost of ammonia, a key feedstock, saw fluctuations driven by global energy prices, directly impacting Balaji Amines' cost structure.
Balaji Amines has experienced significant pressure from rising raw material costs. For instance, in the third quarter of fiscal year 2025, ammonia prices saw a notable increase of 20%, while methanol prices climbed by 10%.
These escalating input expenses, particularly for key materials like benzene, have directly impacted the company's profit margins, making it harder to maintain previous profitability levels.
Switching Costs for Balaji Amines
Switching suppliers for specialized chemical intermediates, like those Balaji Amines uses, can be quite costly. This involves a rigorous process of qualifying new suppliers, which includes extensive testing and validation to ensure the chemicals meet precise specifications. Furthermore, adapting existing production processes to accommodate new inputs can require significant investment in equipment recalibration and employee retraining.
These complexities create substantial switching costs for Balaji Amines' customers when they consider moving to a different supplier. The need to re-validate product quality and potentially re-engineer manufacturing steps can deter them from seeking alternatives, thereby enhancing the bargaining power of Balaji Amines' own suppliers. For instance, in the specialty chemicals sector, the lead time for qualifying a new supplier can extend for several months, impacting production schedules and potentially incurring substantial financial penalties.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Balaji Amines is influenced by these inherent switching costs, which can include:
- Supplier Qualification: The time and resources needed to vet and approve new chemical suppliers.
- Process Adaptation: Costs associated with modifying production lines and quality control measures for new raw materials.
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring consistent quality and performance of chemical intermediates from alternative sources.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting industry-specific regulations and certifications for new chemical inputs.
Backward Integration and Indigenous Technology
Balaji Amines' commitment to developing indigenous technology for amine production is a strategic move to control costs and potentially lessen dependence on external suppliers for specific manufacturing processes. This focus on self-sufficiency is crucial in an industry where technological advancements can significantly impact competitive positioning.
Despite Balaji Amines' efforts, the broader Indian chemical industry, as of recent reports, continues to exhibit a considerable reliance on imported raw materials. This dependency creates inherent vulnerabilities, as fluctuations in global supply chains or geopolitical events can directly impact input costs and availability for domestic manufacturers.
- Indigenous Technology Development: Balaji Amines aims to reduce reliance on external technology providers for amine manufacturing.
- Cost Reduction Strategy: Developing in-house technology is intended to lower production expenses.
- Industry-Wide Import Dependence: The Indian chemical sector, in general, still sources a significant portion of its raw materials from abroad.
- Strategic Vulnerability: This reliance on imports exposes the sector to global supply chain disruptions and price volatility.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Balaji Amines remains a key consideration, particularly for critical raw materials like methanol and ammonia. The company's reliance on imports for methanol, often sourced from the Middle East, grants suppliers significant leverage over pricing and supply stability. While Balaji Amines is investing in indigenous technology, the broader Indian chemical industry's dependence on imported feedstocks, as of early 2025, continues to expose manufacturers to global price volatility and supply chain risks.
The cost of key inputs directly impacts Balaji Amines' profitability. For example, during the third quarter of fiscal year 2025, ammonia prices increased by 20% and methanol by 10%, demonstrating the suppliers' ability to influence costs. These increases, coupled with rising benzene prices, have put pressure on the company's profit margins.
Switching suppliers for specialized chemical intermediates involves substantial costs for Balaji Amines, including rigorous qualification processes, potential production line adjustments, and quality assurance measures. These high switching costs for customers also indirectly bolster the power of Balaji Amines' own suppliers by limiting the company's flexibility.
| Raw Material | Q3 FY25 Price Change | Primary Source Region |
|---|---|---|
| Ammonia | +20% | Global |
| Methanol | +10% | Middle East (significant portion) |
| Benzene | Increasing costs | Global |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive intensity within the specialty chemicals sector, focusing on Balaji Amines' position regarding buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, substitutes, and rivalry.
Instantly assess competitive intensity with a visual breakdown of Balaji Amines' five forces, empowering swift strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Balaji Amines' diverse end-user industries, including pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and water treatment, significantly dilute the bargaining power of individual customers. This broad customer base means no single buyer or industry segment holds substantial leverage over pricing or terms.
For instance, the pharmaceutical sector, a key market for Balaji Amines, is characterized by stringent quality requirements and long-term supply agreements, which can sometimes lend customers more power. However, the company's presence in agrochemicals, which experienced robust growth in 2024 driven by increased agricultural output and demand for crop protection, balances this out.
The water treatment industry also provides a steady demand stream, further diversifying revenue and reducing reliance on any one sector. This wide market reach in 2024, encompassing multiple resilient and growing segments, effectively mitigates the risk of concentrated customer bargaining power.
The criticality of aliphatic amines and their derivatives to key industries significantly influences customer bargaining power. In 2024, these chemicals served as essential intermediates for pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, representing over 40% of total demand. This high dependency means customers often face limited viable alternatives for these vital inputs.
Consequently, customers' ability to negotiate lower prices or demand more favorable terms is somewhat constrained. Their reliance on these specific chemical intermediates for their own production processes reduces their leverage in price discussions with suppliers like Balaji Amines.
The hazardous nature and handling risks of aliphatic amines mean customers often stick with a few reliable local suppliers. This preference for established partners, like Balaji Amines, can significantly reduce their willingness to switch, thus diminishing their bargaining power.
For instance, in 2023, the global specialty chemicals market, which includes amines, saw continued demand driven by sectors prioritizing safety and consistent supply chains. Companies that demonstrate strong safety protocols and reliable delivery, such as Balaji Amines, build customer loyalty that dampens price sensitivity.
Market Demand Trends
The bargaining power of customers for Balaji Amines is influenced by market demand trends, particularly within its core sectors. The pharmaceutical and agrochemical industries, which are significant consumers of amines, are experiencing robust growth projections. For instance, the global pharmaceutical market is expected to reach approximately $2.4 trillion by 2027, indicating sustained demand for amine derivatives used in drug manufacturing. Similarly, the agrochemical sector, driven by increasing food demand and evolving agricultural practices, is also a strong contributor to amine consumption.
Resurgent domestic demand and positive international market trends are further shaping customer power. As India's economy expands, so does the need for chemicals in various industries, including pharmaceuticals and agriculture. International markets also present opportunities and challenges, with global supply chain dynamics and competitor pricing impacting customer leverage. Balaji Amines' ability to cater to these diverse and growing markets will be crucial in managing customer bargaining power.
- Pharmaceutical Industry Growth: Projected to reach around $2.4 trillion by 2027, fueling demand for amine-based intermediates.
- Agrochemical Sector Expansion: Driven by global food security needs, supporting consistent demand for agrochemical inputs.
- Domestic Demand Surge: India's economic growth translates to increased consumption across key industrial sectors.
- International Market Dynamics: Global trends and competition influence pricing and customer expectations.
Impact of Global Economic Conditions on Customer Industries
While Balaji Amines' key customer industries, like pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, have shown robust demand, the broader global economic landscape presents challenges. Economic slowdowns or oversupply from competing regions can force producers to lower prices, thereby strengthening the bargaining power of customers who can then negotiate more favorable terms.
This dynamic is particularly relevant in 2024, where global supply chain adjustments and varying economic growth rates across regions are influencing raw material costs and finished product pricing. For instance, a slowdown in European automotive production, a significant end-user for some amine derivatives, could lead to decreased demand and increased price sensitivity from those buyers.
- Global Economic Headwinds: Persistent inflation and higher interest rates in major economies in early 2024 can dampen industrial output and consumer spending, indirectly impacting demand for chemicals.
- Regional Oversupply Impact: Increased production capacity for certain amines in countries with lower manufacturing costs can create pricing pressure for established players like Balaji Amines, giving customers more options.
- Customer Price Sensitivity: In a competitive market, customers are more inclined to switch suppliers or demand discounts if they perceive better value elsewhere, directly increasing their bargaining leverage.
Balaji Amines' diverse customer base across pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and water treatment significantly limits the bargaining power of any single buyer. The company's critical role in supplying essential intermediates, like aliphatic amines, which represented over 40% of demand in 2024 for key sectors, further constrains customer negotiation leverage due to limited viable alternatives.
The hazardous nature of these chemicals also encourages customers to stick with reliable suppliers like Balaji Amines, fostering loyalty and reducing price sensitivity. While robust demand in sectors like pharmaceuticals, projected to reach $2.4 trillion by 2027, supports pricing, global economic headwinds and potential regional oversupply in 2024 can introduce price pressures, thus increasing customer bargaining power.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Trend (2024 Focus) |
| Customer Diversification | Lowers power | Multiple end-user industries (pharma, agrochem, water treatment) |
| Product Criticality | Lowers power | Aliphatic amines essential intermediates (>40% demand in key sectors) |
| Supplier Switching Costs | Lowers power | Hazardous nature, handling risks favor established suppliers |
| End-Market Growth | Lowers power | Pharma market growth ($2.4T by 2027), agrochem expansion |
| Global Economic Conditions | Can increase power | Inflation, interest rates impacting industrial output; potential regional oversupply |
What You See Is What You Get
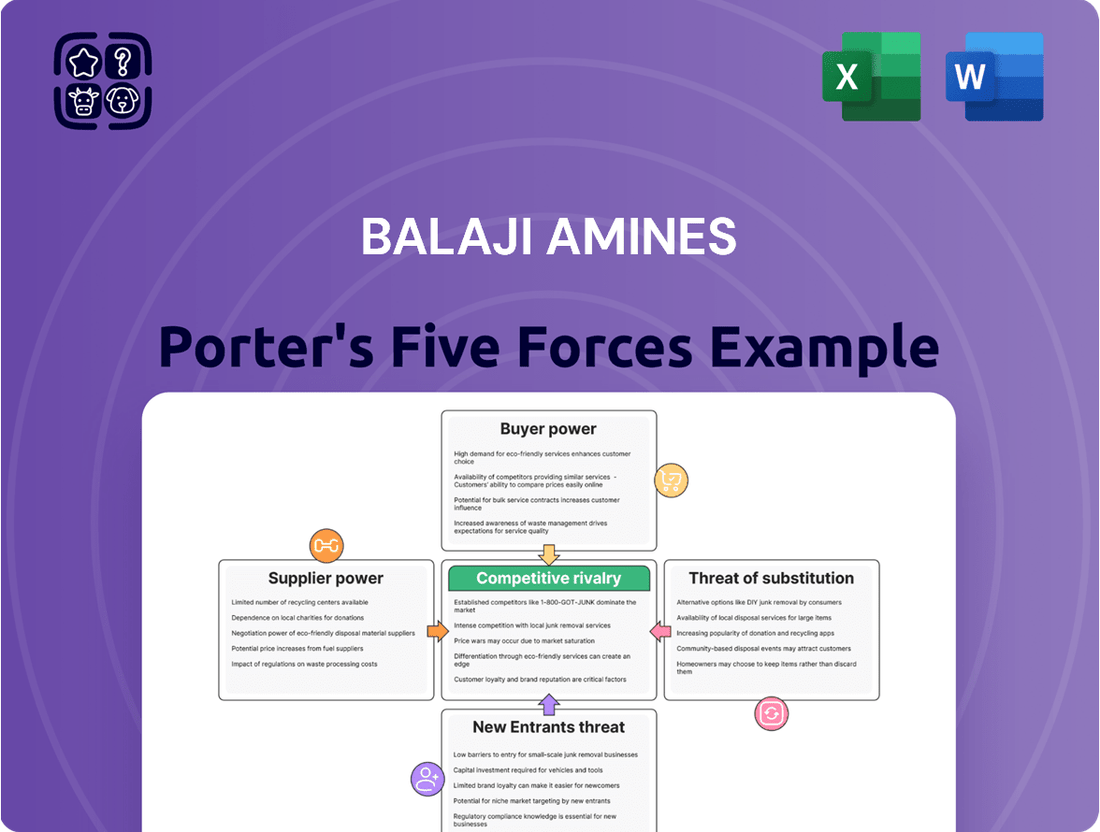
Balaji Amines Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis for Balaji Amines, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning within the chemical industry. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact, professionally formatted file, ready for your immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global amine industry operates as an oligopoly, meaning a handful of large companies hold significant market share. This concentration means that competition is primarily among these few key players, influencing pricing and innovation strategies.
In 2024, the top six global amine producers collectively controlled around 50% of the total production capacity. This high degree of market concentration suggests that actions taken by one major player, such as price adjustments or capacity expansions, are likely to have a substantial impact on the entire industry.
In India, Alkyl Amines Chemicals Ltd. stands as a formidable competitor to Balaji Amines. Despite Balaji Amines often leading in key financial metrics like revenue, revenue growth, profitability, and return ratios, the competitive landscape remains highly contested, pushing both companies to continually innovate and optimize operations.
Competitive rivalry within the amine industry is intensifying, significantly impacted by persistent oversupply from China. This influx of products has driven down prices, creating a challenging environment for companies like Balaji Amines. In FY2025, this pressure contributed to a noticeable dip in the company's revenue and squeezed profit margins.
High Fixed Costs and Capacity Utilization
The chemical manufacturing industry, including the production of amines, is characterized by significant capital investment. This means companies like Balaji Amines face substantial fixed costs related to plant and machinery. Achieving optimal capacity utilization is therefore paramount for these businesses to spread these costs and ensure profitability.
Fluctuations in market demand can create challenges in maintaining high capacity utilization. Companies must skillfully manage production levels to avoid idle capacity, which directly impacts their profit margins. This balancing act is a constant pressure point within the competitive landscape.
- High Capital Intensity: The chemical sector requires extensive investment in plant, equipment, and technology, leading to substantial fixed costs.
- Capacity Utilization is Key: For companies like Balaji Amines, running plants at or near full capacity is essential to cover these fixed costs and achieve economies of scale.
- Profitability Link: Inefficient capacity utilization can severely erode profit margins due to the high proportion of fixed costs.
- Demand Sensitivity: The need for efficient capacity management makes companies vulnerable to demand cycles and market downturns.
Strategic Expansion and Product Diversification
Balaji Amines is intensifying its competitive rivalry through significant strategic expansion and product diversification. The company is actively increasing its manufacturing capacity and introducing new products such as Electronic Grade DMC, Dimethyl Ether (DME), N-Methyl Morpholine (NMM), and Isopropylamine. This proactive approach is designed to solidify its market standing and create distinct offerings compared to rivals.
This diversification strategy directly impacts competitive rivalry by broadening Balaji Amines' market reach and reducing reliance on existing product lines. For instance, the introduction of Electronic Grade DMC targets the high-growth electronics sector, a segment where differentiation can command premium pricing and market share. The company's ongoing capital expenditure, with significant investments planned for these new projects, signals its commitment to outmaneuvering competitors through innovation and capacity building.
- Strategic Expansion: Balaji Amines is investing heavily in new projects like Electronic Grade DMC and Dimethyl Ether (DME).
- Product Diversification: The company is adding N-Methyl Morpholine (NMM) and Isopropylamine to its portfolio.
- Market Position: These moves aim to strengthen its competitive edge and differentiate from existing players.
- Capacity Growth: The expansion efforts are supported by substantial capital expenditure plans, indicating aggressive growth.
Competitive rivalry in the amine sector is fierce, with Balaji Amines facing strong competition from domestic players like Alkyl Amines Chemicals Ltd. This rivalry is further intensified by global oversupply, particularly from China, which has pressured pricing and profit margins. For example, in FY2025, this competitive pressure contributed to a noticeable dip in Balaji Amines' revenue and squeezed its profit margins.
Balaji Amines is actively countering this by expanding its product portfolio and manufacturing capacity. The company is investing in new products such as Electronic Grade DMC and Dimethyl Ether (DME), alongside N-Methyl Morpholine (NMM) and Isopropylamine. These strategic moves aim to enhance its market position and differentiate its offerings.
The high capital intensity of the chemical industry means that efficient capacity utilization is crucial for profitability. Balaji Amines' focus on expansion and diversification is a direct response to the need to maintain high utilization rates and mitigate the impact of intense competition and fluctuating demand.
| Key Competitor | Balaji Amines' FY2024 Revenue (approx.) | Balaji Amines' FY2024 Profit Margin (approx.) | Key Competitive Factor |
| Alkyl Amines Chemicals Ltd. | INR 2,700 Crore | 18% | Domestic Market Share |
| Global Producers (China) | N/A (Vast Capacity) | Lower Pricing | Price Pressure & Oversupply |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Balaji Amines' focus on aliphatic amines, highly specialized chemical intermediates, presents a low threat of substitutes. These compounds, crucial for pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and water treatment, possess unique properties that make finding direct replacements difficult. For instance, in the pharmaceutical sector, specific amine derivatives are essential for the synthesis of active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs), where minor structural changes can render a compound ineffective or toxic.
The threat of substitutes for amines, particularly in complex formulations, is relatively low. Amines are fundamental building blocks in the synthesis of a vast array of pharmaceuticals, including critical drugs and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs). Their unique chemical properties make them indispensable for creating precise and effective compounds.
Furthermore, amines play a crucial role in the agricultural sector, forming the basis for many pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers. The demand for highly specific and potent agrochemicals, driven by the need for efficient crop protection and yield enhancement, means that simple or less effective substitutes are not viable alternatives for these essential applications.
For end-users in critical sectors like pharmaceuticals, the cost and complexity of switching from Balaji Amines' established chemical intermediates are substantial. This involves extensive re-validation, new regulatory filings, and potential reformulation, creating significant barriers to adopting alternatives.
These high switching costs effectively lock in existing customers, making it less appealing for them to explore substitute products or processes. This customer retention is a key factor in maintaining Balaji Amines' market position, as evidenced by their consistent revenue growth, which reached INR 3,025 crore in FY23.
Limited Cost-Effective Alternatives
While theoretical substitutes might exist for certain niche applications of amines, their practical adoption is severely hampered by cost-effectiveness and performance parity. For instance, while some bio-based chemicals could theoretically replace certain amines, their current production costs are significantly higher than those associated with traditional petrochemical routes. Balaji Amines benefits from an established, highly efficient, and scaled production infrastructure, allowing them to maintain a competitive cost structure that makes it challenging for alternatives to gain market share purely on price alone.
The established efficiency and cost structure of amine production by companies like Balaji Amines make it difficult for alternatives to compete solely on price.
- Cost Disadvantage: Emerging substitutes often face higher production costs due to less mature manufacturing processes and economies of scale.
- Performance Parity: Many potential substitutes do not yet match the performance characteristics of established amines in critical industrial applications.
- Switching Costs: Industries relying on amines have invested in specific equipment and processes, creating significant switching costs for alternative materials.
- Market Dominance: Balaji Amines' strong market position and long-term customer relationships further solidify the difficulty for substitutes to penetrate the market.
Emerging Product Lines as Internal Substitutes/Enhancements
Balaji Amines' development of new product lines, such as Dimethyl Ether (DME), presents a unique situation within the threat of substitutes. DME can serve as a substitute for Liquefied Petroleum Gas (LPG) in specific industrial uses, but this is an internal innovation rather than an external threat.
This strategic move allows Balaji Amines to proactively capture new market segments and potentially enhance its overall product portfolio. For instance, the company has been investing in its specialty chemicals segment, which includes products like DME. This focus on diversification demonstrates a strategy to mitigate external substitute threats by creating its own market opportunities.
- Internal Innovation: Development of products like DME acts as an internal substitute or enhancement, not an external threat.
- Market Capture: This strategy allows Balaji Amines to enter new markets and reduce reliance on existing product lines.
- Strategic Diversification: Investments in specialty chemicals, including DME, showcase a proactive approach to managing competitive landscapes.
- Mitigating External Threats: By innovating, the company aims to stay ahead of potential substitute products offered by competitors.
The threat of substitutes for Balaji Amines' core products, aliphatic amines, remains low due to their specialized nature and critical applications. In sectors like pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals, the unique chemical properties of these amines make direct replacements difficult and often impractical. For example, the stringent purity and performance requirements in API synthesis mean that even minor deviations from established amine intermediates can lead to significant formulation failures.
Switching costs for end-users are a substantial barrier, involving extensive re-validation, regulatory approvals, and potential reformulation processes. This inertia, coupled with Balaji Amines' established market position and efficient production, makes it challenging for potential substitutes to gain traction. The company's revenue growth, reaching INR 3,025 crore in FY23, underscores its ability to retain customers despite the theoretical existence of alternatives.
While some bio-based alternatives might emerge, their current higher production costs compared to Balaji Amines' scaled petrochemical routes limit their competitiveness. The company’s strategic development of products like Dimethyl Ether (DME) serves as an internal diversification rather than an external threat, allowing them to capture new market segments and proactively manage competitive pressures.
| Factor | Impact on Balaji Amines | Supporting Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Applications | Low Threat | Amines are critical for pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals with unique performance needs. |
| Switching Costs | Low Threat | High costs for reformulation, re-validation, and regulatory approvals for end-users. |
| Cost-Effectiveness of Substitutes | Low Threat | Emerging bio-based alternatives often have higher production costs than established amine production. |
| Internal Innovation (e.g., DME) | Mitigates External Threat | Allows Balaji Amines to enter new markets and diversify, reducing reliance on traditional product lines. |
Entrants Threaten
The aliphatic amines and specialty chemicals sector demands significant upfront capital for plant construction, machinery, and regulatory compliance. For instance, establishing a new, state-of-the-art chemical manufacturing facility can easily run into hundreds of millions of dollars, creating a formidable financial hurdle.
High fixed costs associated with skilled labor, ongoing research and development, and stringent environmental safety measures further deter potential new entrants. These ongoing expenses necessitate a substantial and sustained revenue stream from the outset, which is difficult for newcomers to achieve.
Balaji Amines' proprietary, indigenous technology for amine manufacturing creates a significant barrier to entry. This developed expertise offers a distinct cost advantage, making it difficult for new companies to match their production efficiency and pricing. For instance, in 2023, Balaji Amines reported a revenue of ₹3,500 crores, showcasing their established market presence built on these technological strengths.
The inherent complexity and hazardous nature of chemical processes involved in amine production also deter potential new entrants. Significant capital investment in specialized equipment, safety protocols, and skilled personnel is required, alongside navigating stringent regulatory approvals. This technical and safety hurdle, coupled with Balaji Amines' established operational excellence, makes replicating their capabilities a formidable challenge.
The chemical sector, including companies like Balaji Amines, faces significant regulatory burdens. Obtaining environmental clearances and adhering to stringent safety standards are crucial, especially for processes involving hazardous materials. For instance, in 2024, the Indian government continued to emphasize stricter compliance with environmental protection laws, impacting manufacturing operations.
These extensive regulatory requirements act as a formidable barrier for potential new entrants. The process of securing necessary permits and approvals can be lengthy and capital-intensive, demanding specialized expertise and substantial investment in compliance infrastructure. This complexity deters many from entering the market.
Established Market Leadership and Capacity Expansion
Balaji Amines' established market leadership, particularly as India's largest aliphatic amines manufacturer and a sole producer of specific specialty chemicals, presents a significant barrier to entry. This dominance, reinforced by substantial ongoing capacity expansions across its product portfolio, effectively saturates the market, making it exceedingly challenging for new entrants to secure meaningful market share.
The company's strategic investments in expanding production capacity are a direct deterrent to potential competitors. For instance, Balaji Amines' planned capacity expansions for products like Ethylamines and Dimethylformamide are designed to further solidify its market position and absorb anticipated demand growth, leaving less room for new players to establish a foothold.
- Market Dominance: Balaji Amines is the largest manufacturer of aliphatic amines in India.
- Sole Producer: Holds exclusive manufacturing rights for certain specialty chemicals.
- Capacity Expansion: Ongoing large-scale expansions across multiple product lines.
- Market Saturation: Expansions aim to absorb demand, limiting entry opportunities.
Government Support and Industry Growth
The Indian chemical industry is on a strong growth trajectory, with projections indicating it will reach $300 billion by 2025. This expansion, particularly within the specialty chemicals segment, presents an attractive landscape for potential new players. Government support, such as the exploration of production-linked incentive (PLI) schemes, is designed to bolster domestic manufacturing capabilities.
These initiatives, while aimed at strengthening the overall industry, could inadvertently lower barriers to entry for new companies by providing financial and operational advantages. Such government backing might encourage new entrants to establish a foothold in a rapidly growing market.
- Projected Indian Chemical Industry Growth: Expected to reach $300 billion by 2025.
- Specialty Chemicals Sector Expansion: This segment is also experiencing significant growth.
- Government Initiatives: Potential for Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes to support domestic manufacturing.
- Impact on New Entrants: Government support could potentially encourage new companies to enter the market.
The threat of new entrants for Balaji Amines is moderate, primarily due to high capital requirements and established technological expertise. However, government initiatives and market growth could attract new players.
The significant upfront investment needed for chemical manufacturing facilities, coupled with the complexity and regulatory hurdles, acts as a substantial deterrent. Balaji Amines' proprietary technology and market dominance further solidify these barriers.
Despite these challenges, the projected growth of the Indian chemical industry, expected to reach $300 billion by 2025, and potential government support through PLI schemes could lower entry barriers for new companies.
Balaji Amines' ongoing capacity expansions, such as for Ethylamines and Dimethylformamide, are designed to capture market share and deter new entrants by creating a more saturated market landscape.
| Factor | Impact on New Entrants | Balaji Amines' Position |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | High barrier | Established infrastructure |
| Technology & Expertise | Significant barrier | Proprietary processes, operational excellence |
| Regulatory Compliance | Lengthy and costly | Experienced in navigating regulations |
| Market Dominance | Difficult to gain share | Largest aliphatic amines producer in India |
| Industry Growth & Support | Potential opportunity | Prepares for increased demand |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Balaji Amines Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial statements, annual reports, and investor presentations. We supplement this with data from industry-specific market research reports and chemical industry trade publications to capture a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
