Baader Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Baader Bank Bundle
Baader Bank operates within a competitive financial landscape, where understanding the interplay of industry forces is crucial for strategic success. Our analysis reveals the significant impact of buyer bargaining power and the threat of substitutes on Baader Bank's profitability.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Baader Bank’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of key technology providers and software vendors significantly impacts Baader Bank's operational costs and flexibility. If only a handful of specialized financial technology firms supply essential trading platforms, data analytics tools, or back-office systems, these vendors gain considerable leverage. This can translate into higher licensing fees or less favorable contract terms for Baader Bank, directly affecting profitability and the ability to innovate.
Financial data providers hold considerable sway over Baader Bank. Services like real-time market data, research, and analytics are absolutely essential for Baader Bank's core operations, including market making, investment banking, and asset management. These providers' unique and often indispensable data offerings grant them significant bargaining power.
The bargaining power of suppliers is significantly influenced by the availability of highly specialized human capital within the financial sector. For Baader Bank, this is particularly evident in fields like quantitative analysis, cybersecurity, and regulatory compliance. A scarcity of professionals with deep expertise in these areas, exacerbated by high demand, can empower these individuals to command higher salaries and more favorable working conditions, directly impacting the bank's operational costs and talent acquisition strategies.
Supplier Power 4
Regulatory bodies and stock exchanges act as critical suppliers to Baader Bank, providing essential operating licenses, market access, and the fundamental rule frameworks. Their influence is substantial because compliance with these regulations is non-negotiable, and membership on exchanges is a prerequisite for Baader Bank's core market-making and trading activities.
The power of these suppliers is amplified by the high barriers to entry in financial markets and the stringent capital requirements imposed by regulators. For instance, in 2024, Baader Bank, like other financial institutions, must adhere to evolving capital adequacy ratios and conduct risk management practices dictated by bodies such as BaFin in Germany and the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA).
- High Barriers to Entry: The cost and complexity of obtaining and maintaining regulatory approvals create significant hurdles for new entrants, solidifying the power of existing regulatory frameworks.
- Mandatory Compliance: Baader Bank's ability to operate and generate revenue is directly contingent upon its adherence to the rules set forth by these suppliers.
- Exchange Dependencies: Access to liquidity and trading opportunities is solely dependent on maintaining memberships with key stock exchanges, giving these exchanges considerable leverage.
- Evolving Regulatory Landscape: Continuous updates to financial regulations, such as those concerning MiFID II or upcoming ESG reporting requirements, necessitate ongoing adaptation and investment by Baader Bank, underscoring supplier power.
Supplier Power 5
Baader Bank's reliance on liquidity providers and interbank lending markets significantly shapes its supplier power. The cost and availability of crucial capital, influenced by major financial institutions and central bank policies, directly affect Baader Bank's operational efficiency and profitability. For instance, in early 2024, the European Central Bank's (ECB) monetary policy decisions, including interest rate adjustments, had a notable impact on the cost of wholesale funding for banks like Baader Bank.
- Cost of Capital: Fluctuations in interbank lending rates, such as EURIBOR, directly influence Baader Bank's funding costs.
- Availability of Liquidity: Access to sufficient liquidity from larger financial institutions is essential for Baader Bank's trading and hedging activities.
- Central Bank Influence: Monetary policy decisions by entities like the ECB can alter the overall cost and availability of funds in the market.
- Market Conditions: Broader financial market stability or volatility can impact the willingness of suppliers to provide liquidity and the pricing of that liquidity.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Baader Bank is a critical factor in its cost structure and operational agility. Key suppliers include technology vendors, data providers, specialized talent, and regulatory bodies. The concentration of these suppliers, coupled with high switching costs and the essential nature of their services, grants them significant leverage.
For example, in 2024, the cost of specialized financial data feeds, crucial for Baader Bank's trading operations, remained high due to limited providers. Similarly, the scarcity of cybersecurity experts in the financial sector in 2024 allowed these professionals to command premium salaries, impacting Baader Bank's human capital costs.
| Supplier Category | Impact on Baader Bank | Example (2024 Context) |
|---|---|---|
| Technology Vendors | Higher licensing fees, potential for less favorable contract terms impacting innovation. | Limited competition for specialized trading platforms can lead to increased costs. |
| Financial Data Providers | Indispensable data offerings grant significant bargaining power, affecting operational costs. | Real-time market data subscriptions are essential but costly. |
| Specialized Human Capital | High demand and scarcity of expertise (e.g., quantitative analysts) drive up salary costs. | Cybersecurity and AI specialists command high compensation packages. |
| Regulatory Bodies & Exchanges | Mandatory compliance and exchange memberships dictate operational costs and strategy. | Adherence to evolving capital adequacy ratios (e.g., Basel IV implications) and trading fees. |
| Liquidity Providers | Influence cost of capital and availability of funds, impacting profitability. | Reliance on interbank lending and central bank policies (e.g., ECB rates). |
What is included in the product
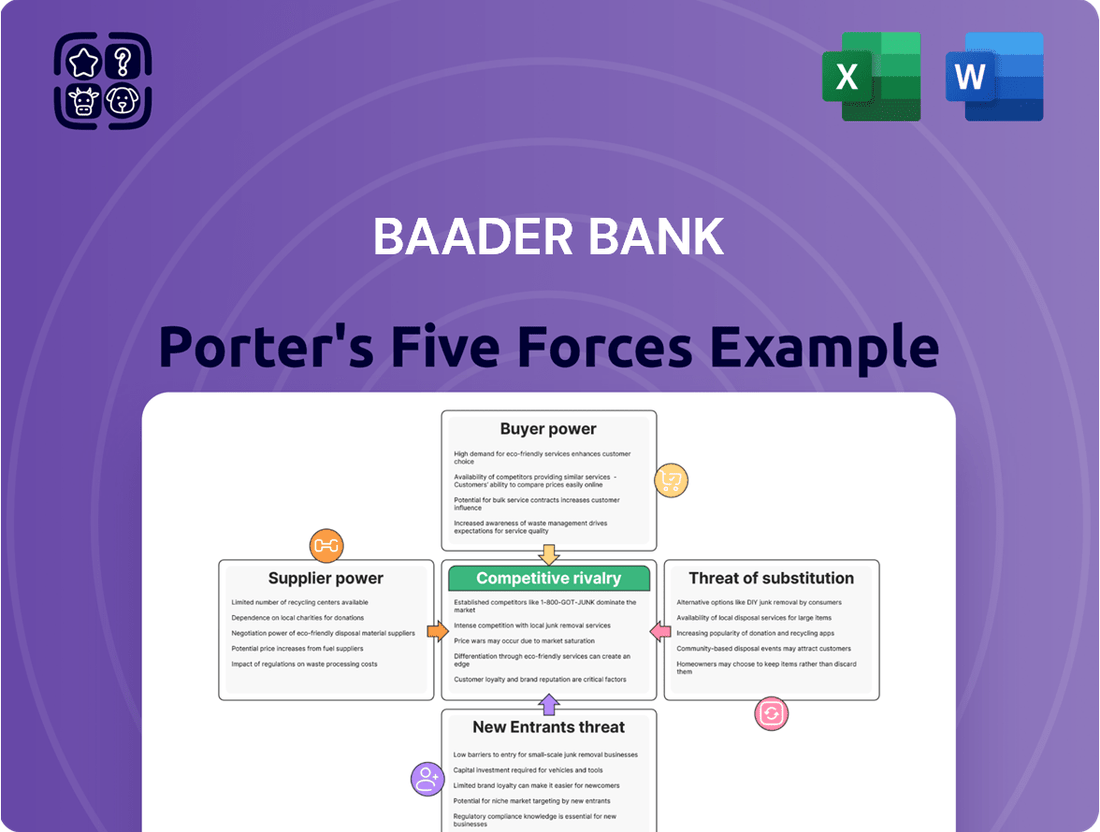
Analyzes the competitive intensity and profitability potential for Baader Bank by examining industry rivals, buyer and supplier power, new entrants, and substitute products.
Instantly visualize competitive pressures and identify strategic vulnerabilities with a dynamic, interactive five forces model.
Customers Bargaining Power
Baader Bank's client base is notably diverse, encompassing institutional investors, corporate clients, and private individuals. This fragmentation means that no single customer or small group of customers holds significant sway over the bank's pricing or service terms. For instance, while Baader Bank serves a broad range of institutional clients, their relatively small individual contribution to the bank's overall revenue limits their collective bargaining power.
The bargaining power of customers for Baader Bank is influenced by switching costs, which vary significantly across client segments. For institutional and corporate clients, these costs can be substantial, stemming from the integration of Baader Bank's services into their existing financial infrastructure, the value of long-standing relationships, and the complexity of customized service agreements. This often translates to lower customer power.
Conversely, private clients, particularly those utilizing online brokerage services, often face lower switching costs. The ease with which they can transfer assets and the availability of numerous alternative platforms mean they can exert greater influence by demanding better terms or services, or by simply moving their business elsewhere.
In 2024, the digital transformation in financial services has further amplified this trend. The proliferation of user-friendly, low-cost online platforms means that for retail investors, the perceived effort and expense to switch providers have diminished considerably, thereby increasing their collective bargaining power.
Baader Bank's clients, particularly those utilizing more standardized services like basic securities trading, exhibit significant price sensitivity. This is evident as clients can easily switch to competitors offering similar execution services, leading to increased pressure on fees, commissions, and bid-ask spreads.
In 2024, the German banking sector, where Baader Bank operates, saw continued pressure on net interest margins due to a competitive landscape. For instance, while specific client data for Baader Bank isn't publicly detailed for this specific force, the broader market trend indicates that for commoditized brokerage services, clients actively seek out the lowest transaction costs. This can be seen in the ongoing competition among online brokers, where even small differences in fees can sway client decisions.
Buyer Power 4
Baader Bank's clients face a highly competitive financial services landscape, significantly amplifying buyer power. The German and international markets boast a multitude of alternative service providers, ranging from established investment banks and online brokers to innovative fintech platforms.
This abundance of choice empowers clients, giving them considerable leverage to negotiate terms or readily switch to providers offering better pricing, services, or technology. For instance, the German online brokerage market alone has seen substantial growth, with platforms like Trade Republic attracting millions of users by offering commission-free trading, directly challenging traditional players.
- High client mobility: The ease with which clients can switch between financial service providers due to digital platforms and regulatory changes (like PSD2 in Europe) increases their bargaining power.
- Price sensitivity: In many segments, particularly retail brokerage, clients are highly price-sensitive, leading providers to compete aggressively on fees and commissions.
- Availability of substitutes: The proliferation of fintech solutions and neobanks offers clients alternatives for various banking and investment needs, eroding the switching costs for traditional institutions.
- Information asymmetry reduction: Clients now have access to more information about market conditions and competitor offerings, enabling them to make more informed decisions and demand better terms.
Buyer Power 5
Customers in the financial sector, including those interacting with Baader Bank, possess significant bargaining power due to their enhanced access to information. The proliferation of online comparison platforms and readily available market data allows clients to easily scrutinize services, pricing structures, and the performance of various financial institutions. This transparency directly empowers them to negotiate more favorable terms or switch providers if unsatisfied.
For instance, in 2024, the digital transformation of financial services has made it simpler than ever for retail and institutional investors to compare trading fees, research quality, and execution speeds across a multitude of banks and brokers. This ease of comparison, coupled with the increasing availability of independent reviews and ratings, shifts the leverage towards the customer. They can readily identify the most competitive offerings, putting pressure on Baader Bank to maintain attractive pricing and superior service levels to retain its client base.
- Informed Decision-Making: Clients can access detailed performance reports and fee schedules from multiple providers, enabling direct comparison.
- Price Sensitivity: Increased transparency on fees and commissions means customers can easily identify and opt for lower-cost alternatives.
- Switching Costs: While historically a barrier, digital platforms have reduced the friction and cost associated with changing financial service providers.
Baader Bank's customers, particularly in the retail segment, wield considerable bargaining power due to the low switching costs and high price sensitivity prevalent in 2024. The ease of accessing and comparing services across numerous digital platforms means clients can readily shift their business for even minor fee advantages. This competitive environment forces Baader Bank to continuously offer competitive pricing and superior service to retain its diverse client base.
The abundance of alternative financial service providers, including agile fintechs and established online brokers, significantly amplifies customer leverage. For instance, in 2024, the German market saw platforms like Trade Republic offering commission-free trading, directly challenging traditional players and empowering retail investors with cost-effective options. This competitive pressure means clients can easily switch to providers offering better terms, forcing Baader Bank to remain competitive on pricing and service quality.
| Customer Segment | Switching Costs | Price Sensitivity | Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|---|
| Institutional/Corporate | High | Moderate | Low to Moderate |
| Private/Retail (Online Brokerage) | Low | High | High |
Full Version Awaits
Baader Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact Baader Bank Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape, including the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry. This detailed report is ready for your immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Baader Bank operates in a competitive landscape populated by numerous specialized German investment banks, large universal banks with substantial investment banking arms, and dedicated market-making firms. This environment is characterized by intense rivalry as these entities vie for market share and client business.
The strength and aggressiveness of these competitors directly influence the level of competitive rivalry. For instance, in 2023, the German banking sector saw continued consolidation and strategic repositioning, with many universal banks enhancing their investment banking services to capture a broader range of financial needs, thereby increasing pressure on specialized players like Baader Bank.
The competitive rivalry within Baader Bank's operating environment, particularly in German and European investment banking, trading, and asset management, is notably high. This intensity is amplified by slower market growth rates, forcing established players to vie more aggressively for existing market share.
In 2024, the German financial services sector, while showing resilience, experienced moderate growth. For instance, the German banking sector's net interest income saw a modest increase, but fee and commission income, crucial for investment banking and asset management, faced pressure from increased competition and evolving client demands. This environment means companies like Baader Bank must constantly innovate and differentiate to capture and retain business.
Baader Bank distinguishes itself through its specialized focus on institutional clients and its comprehensive range of services, including prime brokerage, capital markets, and research. This specialization, particularly in areas like exchange-traded products and structured products, creates a degree of differentiation that mitigates direct price competition compared to banks offering more commoditized retail trading services. For instance, Baader Bank's expertise in niche markets allows them to command higher fees for their specialized advisory and execution services, reducing the pressure to compete solely on transaction costs.
Competitive Rivalry 4
Competitive rivalry in the investment banking and market making sector is intensified by significant exit barriers. Firms face substantial investments in technology, regulatory compliance, and specialized talent, making it costly to withdraw from the market. This can lead to prolonged competition, even when industry profitability declines.
High fixed costs are a key driver of this intense rivalry. For instance, maintaining cutting-edge trading platforms and robust cybersecurity systems requires continuous capital expenditure. In 2024, major investment banks continued to allocate billions to technology upgrades, a trend expected to persist.
- High Fixed Costs: Significant upfront and ongoing investments in technology infrastructure and regulatory adherence create substantial hurdles for firms looking to exit.
- Specialized Human Capital: The need for highly skilled traders, analysts, and compliance officers means that workforce costs are a major component, making it difficult to divest or downsize without significant severance expenses.
- Regulatory Burden: Stringent capital requirements and compliance protocols, such as those mandated by Basel III and its subsequent revisions, tie up capital and increase operational complexity, further deterring exits.
Competitive Rivalry 5
Baader Bank faces intense competition from a diverse set of players, each with distinct strategic aims. Many rivals are aggressively pursuing market share through competitive pricing and expanded service offerings, particularly in the digital banking and wealth management sectors. For instance, established universal banks continue to leverage their broad customer bases and extensive branch networks, while fintech disruptors are rapidly gaining traction with innovative, user-friendly platforms and lower fee structures.
The competitive landscape is characterized by a mix of strategic objectives. Some competitors are focused on achieving economies of scale through consolidation, aiming to become dominant players in specific European markets. Others are carving out niche specializations, concentrating on particular client segments like high-net-worth individuals or institutional investors, offering highly tailored services. Technological innovation is a key battleground, with many banks and fintechs investing heavily in AI, blockchain, and personalized digital experiences to attract and retain customers.
Baader Bank's rivals are employing various competitive tactics. This includes aggressive marketing campaigns, strategic partnerships, and significant investments in technology to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency. For 2024, many European banks reported increased IT spending, with a focus on digital transformation and cybersecurity. For example, some major German banks have allocated billions of euros towards modernizing their IT infrastructure and developing new digital products, directly impacting the competitive intensity for Baader Bank.
- Market Share Focus: Rivals are actively seeking to expand their customer base, often through aggressive pricing and promotional offers, particularly in online brokerage and wealth management.
- Niche Specialization: Some competitors are concentrating on specific client segments, offering specialized services in areas like sustainable investing or private banking.
- Technological Innovation: A significant driver of competition involves investment in digital platforms, AI-driven advisory services, and streamlined customer onboarding processes.
- Profitability vs. Growth: The strategic objectives vary, with some players prioritizing rapid growth and market penetration, while others focus on maintaining profitability through cost efficiency and premium service offerings.
Baader Bank faces intense competition from a diverse range of financial institutions, including specialized German investment banks, large universal banks, and dedicated market makers. This rivalry is amplified by slower market growth, forcing players to aggressively pursue existing market share. For instance, in 2023, universal banks in Germany enhanced their investment banking services, increasing pressure on specialized firms.
The competitive intensity is further driven by high fixed costs associated with technology and regulatory compliance, making market exit difficult. In 2024, major banks continued significant IT spending, with billions allocated to upgrades, a trend that directly impacts Baader Bank’s operational environment.
Rivals are actively employing tactics such as competitive pricing, expanded digital services, and strategic partnerships to gain market share. Many European banks increased IT spending in 2024, focusing on digital transformation and cybersecurity to enhance customer experience and operational efficiency, thereby intensifying competition for Baader Bank.
| Competitor Type | Key Competitive Tactics | Impact on Baader Bank |
| Universal Banks | Leveraging broad customer bases, extensive branch networks, enhanced investment banking services | Increased pressure on market share, need for differentiation in specialized services |
| Fintech Disruptors | Innovative platforms, lower fee structures, user-friendly digital experiences | Challenging traditional service models, demanding digital innovation |
| Niche Specialists | Highly tailored services for specific client segments (e.g., HNWIs, institutional investors) | Requires Baader Bank to maintain and enhance its own niche expertise and service quality |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The rise of direct market access (DMA) platforms and advanced automated trading systems presents a significant threat. These technologies empower institutional clients to bypass traditional intermediaries like Baader Bank, directly accessing liquidity for execution services. This disintermediation allows for potentially lower costs and faster execution, directly challenging the value proposition of full-service brokers.
The rise of robo-advisors and digital wealth management platforms presents a significant threat of substitution for Baader Bank's traditional private client asset management. These automated services offer investment advice and portfolio management, often at considerably lower fees and with increased accessibility compared to human-managed portfolios.
For instance, the global robo-advisory market was valued at approximately USD 2.5 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong shift towards digital solutions. This trend means clients may opt for these cost-effective and convenient alternatives, reducing demand for Baader Bank's personalized, higher-fee services.
Corporate clients are increasingly exploring financing avenues beyond traditional investment banking services. This includes direct lending from private equity firms and venture capital, as well as innovative options like crowdfunding platforms. For instance, the global private debt market reached an estimated $1.5 trillion in 2023, demonstrating a significant shift away from conventional capital markets.
Threat of Substitution 4
The rise of blockchain and decentralized finance (DeFi) presents a significant threat of substitution to traditional financial intermediaries like Baader Bank. These emerging technologies offer alternative avenues for issuing, trading, and managing financial assets, potentially disintermediating established market structures.
DeFi platforms are gaining traction, with total value locked (TVL) in DeFi protocols reaching hundreds of billions of dollars in recent years, demonstrating a growing user base and transaction volume. For instance, by early 2024, the DeFi ecosystem saw substantial growth in lending, borrowing, and trading activities conducted on-chain, bypassing traditional banking systems.
- Blockchain-based platforms allow for peer-to-peer transactions, reducing reliance on central authorities.
- DeFi solutions offer automated market makers and smart contracts for trading and lending, increasing efficiency.
- Growing TVL in DeFi indicates a shift in capital allocation away from traditional finance.
Threat of Substitution 5
Large technology companies, often referred to as Big Tech, pose a significant threat of substitution for traditional banks like Baader Bank. These tech giants possess immense user bases, sophisticated data analytics, and powerful brand loyalty, enabling them to directly offer financial services. For instance, in 2024, companies like Apple Pay and Google Pay continued to expand their payment processing capabilities, directly competing with bank-offered payment solutions.
Their ability to integrate financial services seamlessly into existing ecosystems, such as e-commerce platforms or social media, creates a compelling alternative for consumers. This integration can lead to a more convenient and personalized user experience, potentially drawing customers away from established banking channels. By leveraging their vast data, Big Tech firms can also offer highly targeted lending or investment products, directly substituting for offerings from Baader Bank.
- Big Tech's User Base Advantage: Companies like Meta and Amazon have billions of active users, providing an immediate customer pool for financial services.
- Data Analytics for Personalization: Advanced AI and machine learning allow Big Tech to offer tailored financial products, enhancing customer engagement.
- Brand Trust and Recognition: Established tech brands often enjoy higher consumer trust than traditional financial institutions, facilitating adoption of new financial offerings.
- Cross-Selling Opportunities: Tech companies can bundle financial services with their core products, creating a sticky ecosystem that is difficult for banks to replicate.
The threat of substitutes for Baader Bank is multifaceted, stemming from technological advancements and evolving client preferences. Direct market access platforms and automated trading systems allow institutional clients to bypass intermediaries, potentially lowering costs. Robo-advisors and digital wealth management platforms offer competitive, lower-fee alternatives for private clients, with the global robo-advisory market projected for substantial growth. Furthermore, corporate clients are increasingly turning to private equity, venture capital, and crowdfunding for financing, diverting business from traditional investment banking channels. The burgeoning DeFi sector, with its peer-to-peer transactions and automated market makers, also presents a significant disintermediation risk.
| Substitute Area | Key Characteristics | Impact on Baader Bank | Example Data Point (2023/2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Market Access (DMA) | Bypasses intermediaries, lower costs, faster execution | Reduced demand for execution services from traditional brokers | N/A (Specific DMA platform data not publicly available for direct comparison) |
| Robo-Advisors/Digital Wealth Management | Automated advice, lower fees, increased accessibility | Substitution for traditional private client asset management | Global robo-advisory market valued at ~USD 2.5 billion (2023) |
| Alternative Financing (Private Debt, Crowdfunding) | Direct lending, innovative capital raising | Reduced corporate client reliance on investment banking services | Global private debt market reached ~USD 1.5 trillion (2023) |
| Decentralized Finance (DeFi) | Peer-to-peer, automated smart contracts, disintermediation | Potential to bypass traditional financial intermediaries for asset issuance and trading | Total Value Locked (TVL) in DeFi reaching hundreds of billions of dollars |
| Big Tech Financial Services | Integrated ecosystems, data analytics, brand loyalty | Direct competition in payment processing, lending, and investment products | Expansion of payment capabilities by Apple Pay and Google Pay (2024) |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants for Baader Bank is significantly mitigated by the rigorous regulatory landscape in Germany and the broader European Union. Financial authorities like BaFin in Germany and the European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA) impose stringent licensing requirements and compliance protocols. These hurdles are not only complex but also financially demanding, requiring substantial capital and expertise to navigate successfully.
Operating as a market maker and investment bank, such as Baader Bank, demands significant capital investment. This includes meeting stringent capital adequacy ratios, maintaining substantial liquidity buffers, and establishing robust operational reserves. For instance, as of early 2024, European banks are subject to Basel III regulations, which mandate specific minimum capital requirements, often in the high single digits as a percentage of risk-weighted assets, alongside additional liquidity coverage ratios.
These substantial financial barriers effectively deter many aspiring firms from entering the market. The sheer scale of capital needed to establish the necessary infrastructure, technology, and regulatory compliance makes it incredibly challenging for new players to compete with established institutions like Baader Bank, which already possess these resources and a proven track record.
In the financial services sector, particularly for established players like Baader Bank, the threat of new entrants is significantly mitigated by the immense value of brand reputation and deep-seated client trust. Building this level of credibility in an industry where financial security and reliability are paramount takes years, if not decades. Newcomers find it exceptionally difficult to replicate the long-standing relationships that incumbents have cultivated, creating a substantial barrier to entry.
Consider the German banking sector, where Baader Bank operates. As of early 2024, customer loyalty remains a critical factor. A study by Kantar in late 2023 revealed that over 60% of German consumers prioritize trust and established relationships when choosing a financial institution. This deep client trust, nurtured over many years, provides Baader Bank with a robust competitive advantage, making it challenging for nascent firms to quickly gain market share or attract a significant customer base.
Threat of New Entrants 4
The threat of new entrants for Baader Bank is significantly moderated by the substantial economies of scale and scope already established by existing players. These advantages are particularly pronounced in areas like technology infrastructure, where substantial investment is required for trading platforms and data management. For instance, in 2023, the German banking sector saw IT spending increase, reflecting the ongoing need for technological advancement to remain competitive.
Newcomers face considerable hurdles in replicating the cost efficiencies that Baader Bank and its peers achieve through their existing scale. This includes the operational costs associated with robust compliance departments and sophisticated risk management systems, which are essential for navigating complex financial regulations. Building these capabilities from scratch demands significant capital and expertise, making it difficult for new entrants to match the cost per transaction of established institutions.
Furthermore, Baader Bank benefits from extensive distribution networks and established client relationships, which are difficult and time-consuming to build. In 2024, customer acquisition costs remain a significant factor in the financial services industry. New entrants would need to invest heavily in marketing and sales to gain market share, further increasing their initial cost base.
- Economies of Scale: Baader Bank leverages its size for cost advantages in technology, compliance, and risk management.
- High Initial Investment: New entrants require substantial capital for infrastructure and regulatory compliance.
- Distribution Networks: Established players possess broad client reach, a difficult barrier for newcomers.
- Regulatory Burden: The complex regulatory environment in Germany adds significant operational costs for new financial institutions.
Threat of New Entrants 5
The threat of new entrants in the banking sector, particularly for a firm like Baader Bank, is significantly influenced by the difficulty of attracting and retaining specialized talent. Established institutions often boast comprehensive compensation packages, extensive training programs, and clear career progression paths that are challenging for newcomers to replicate. This creates a substantial barrier, as a strong team of skilled professionals is crucial for navigating complex financial markets and delivering competitive services.
In 2024, the competition for top financial talent remained fierce. For instance, investment banking roles, which require deep expertise in areas like M&A, capital markets, and quantitative analysis, saw average compensation packages rise by an estimated 8-12% year-over-year in major financial hubs. Startups or new entrants struggle to match these established salary benchmarks and the allure of long-term career stability offered by larger, well-capitalized banks.
Furthermore, the regulatory landscape in banking demands a high level of compliance expertise. New entrants must invest heavily in building teams with specialized knowledge of evolving financial regulations, such as those related to capital adequacy, anti-money laundering, and data privacy. This is a costly and time-consuming endeavor, often favoring established players who already have these capabilities embedded within their operations.
- Talent Acquisition Costs: New entrants face higher recruitment costs, often needing to offer premium salaries and signing bonuses to lure experienced professionals away from established firms.
- Retention Challenges: Retaining specialized talent is difficult for new players due to the superior benefits, career advancement opportunities, and established reputation of incumbent banks.
- Regulatory Expertise Gap: Building a team with the necessary regulatory compliance knowledge is a significant hurdle, requiring substantial investment in specialized legal and compliance personnel.
- Brand Recognition: Established banks benefit from strong brand recognition, which aids in attracting talent by offering a sense of prestige and stability.
The threat of new entrants for Baader Bank is significantly low due to substantial barriers like high capital requirements, stringent regulatory compliance, and the need for established brand reputation and client trust. These factors make it exceptionally difficult for new firms to enter and compete effectively in the German financial services market.
Economies of scale further solidify Baader Bank's position, allowing for cost efficiencies in technology and operations that newcomers would struggle to match. The existing distribution networks and deep client relationships built over time also present a considerable hurdle for any aspiring competitor.
The intense competition for specialized financial talent and the significant investment required to build regulatory expertise also deter potential new entrants. Established players like Baader Bank possess inherent advantages in attracting and retaining skilled professionals and navigating complex compliance landscapes.
| Barrier | Impact on New Entrants | Relevance to Baader Bank |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Very High - Significant investment needed for licensing and operations. | Established, mitigating factor. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Very High - Complex and costly to navigate. | Established, mitigating factor. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | High - Difficult to build quickly. | Strong, mitigating factor. |
| Economies of Scale | High - Cost disadvantages for smaller operations. | Significant, mitigating factor. |
| Talent Acquisition & Retention | High - Competition for skilled professionals is intense. | Advantageous, mitigating factor. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Baader Bank leverages a comprehensive suite of data sources, including Baader Bank's own annual reports and investor presentations, alongside industry-specific research from financial analysts and market intelligence firms. This blend ensures a robust understanding of competitive dynamics within the banking sector.
