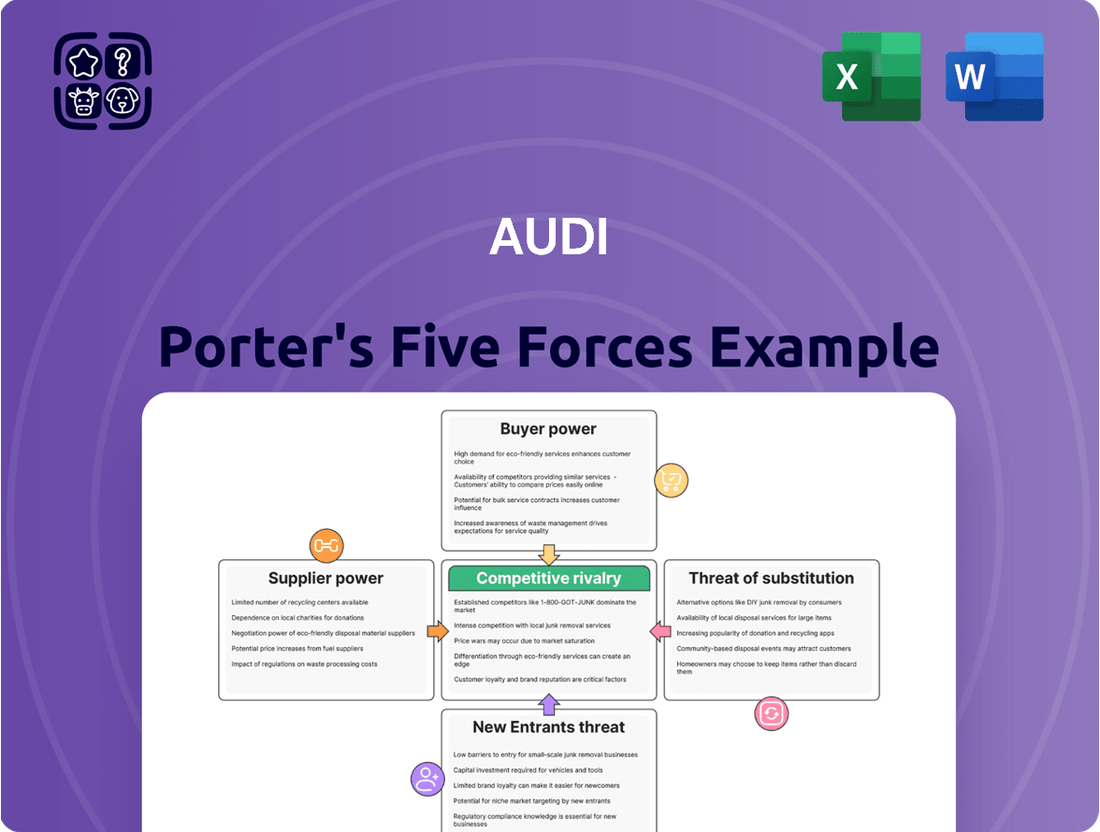
AUDI Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
AUDI Bundle
AUDI navigates a complex automotive landscape, where intense rivalry and the threat of new entrants significantly shape its market position. Understanding the bargaining power of both buyers and suppliers is crucial for AUDI's sustained profitability.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping AUDI’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The automotive sector, including manufacturers like Audi, often depends on a limited pool of specialized suppliers for crucial parts such as sophisticated electronics, electric vehicle batteries, and unique materials. This concentration means these suppliers can wield significant influence over automakers, particularly for components demanding substantial research and development investment or those with few substitute options.
High switching costs significantly bolster supplier bargaining power for Audi. The automotive sector, known for its intricate supply chains and demanding quality standards, means that changing suppliers involves substantial investments. For instance, re-tooling production lines, obtaining new certifications, and conducting rigorous compatibility tests can easily run into millions of euros and take months, even years, to complete. This makes Audi hesitant to switch, giving existing suppliers more leverage in price negotiations.
Suppliers providing highly specialized and proprietary technologies, such as advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) or sophisticated infotainment platforms, wield considerable bargaining power. Audi's commitment to innovation in these areas, including its investment in AI-driven vehicle features, makes it reliant on these specialized component providers.
The automotive industry, particularly for premium brands like Audi, sees suppliers with unique technological capabilities in areas like electric vehicle powertrains or autonomous driving software as having significant leverage. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that the global market for automotive ADAS is projected to reach over $70 billion, highlighting the value and specialization of these suppliers.
Forward Integration Potential
The potential for a key supplier to integrate forward into vehicle manufacturing represents a theoretical, albeit less common, avenue to increase their bargaining power against Audi. This means a supplier could potentially start building cars themselves, thereby competing directly with Audi. While this is a significant shift, the immense capital investment required for automotive production makes it a less immediate threat for Audi compared to industries with lower entry barriers.
For instance, the sheer scale of setting up a car manufacturing plant, including research and development, assembly lines, and distribution networks, runs into billions of dollars. In 2023, the average cost to develop a new car model was estimated to be over $1 billion, highlighting the deterrent for suppliers considering such a move. Therefore, while the possibility exists, it remains a distant concern for Audi in the current automotive landscape.
- Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers could theoretically enter vehicle manufacturing, increasing their leverage.
- Capital Intensity Barrier: The extremely high cost of car production acts as a significant deterrent for suppliers.
- Theoretical vs. Practical: While a concept, it's not an immediate or widespread concern for Audi due to these costs.
- Industry Comparison: This threat is less pronounced for Audi than in industries with lower capital requirements for market entry.
Raw Material and Labor Costs
Suppliers to the automotive industry, including those providing raw materials and labor, are experiencing significant cost increases. These rising expenses, driven by factors like inflation and increased demand, can be passed on to manufacturers such as Audi. For instance, the average hourly wage for manufacturing workers in Germany, where Audi has a strong presence, saw a notable increase in 2024, contributing to higher labor costs for component suppliers.
Global supply chain volatility, a persistent issue through 2024 and into early 2025, further empowers suppliers. Disruptions stemming from geopolitical events and natural disasters can limit the availability of key components and raw materials, allowing suppliers to command higher prices. This pressure directly impacts Audi's cost of goods sold and can squeeze profit margins if these increases cannot be effectively mitigated.
- Rising Material Costs: Prices for key automotive metals like aluminum and steel have shown upward trends in 2024, impacting the cost of vehicle production.
- Labor Cost Inflation: Increased wage demands and labor shortages in manufacturing sectors globally are driving up the cost of skilled labor for component suppliers.
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities: Geopolitical tensions and logistical challenges continue to create uncertainty and cost premiums for many essential automotive inputs.
Suppliers to Audi possess considerable bargaining power due to the concentrated nature of the automotive supply chain, especially for specialized components like advanced electronics and EV batteries. High switching costs, involving re-tooling and certifications, further solidify this power, making it difficult and expensive for Audi to change providers. For instance, the global automotive ADAS market was projected to exceed $70 billion in 2024, underscoring the value and specialization of these suppliers.
Rising material and labor costs, exacerbated by global inflation and supply chain volatility through 2024 and early 2025, allow suppliers to pass on increased expenses to automakers like Audi. This directly impacts Audi's production costs and profit margins, as seen with upward trends in raw material prices and increased wage demands for skilled manufacturing labor.
| Factor | Impact on Suppliers' Bargaining Power | Supporting Data (2024/Early 2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Components | High | Automotive ADAS market projected over $70 billion |
| Switching Costs | High | Millions of euros and months/years for re-tooling and certification |
| Rising Material Costs | High | Upward trends in aluminum and steel prices |
| Labor Cost Inflation | High | Notable increase in German manufacturing wages; labor shortages |
| Supply Chain Volatility | High | Geopolitical tensions and logistical challenges create cost premiums |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting AUDI, examining the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the automotive industry.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces for Audi.
Gain a strategic advantage by pinpointing where Audi faces the most pressure, enabling targeted action to alleviate pain points.
Customers Bargaining Power
The substantial financial outlay required for luxury vehicles like Audi significantly empowers customers. When a purchase represents a major investment, buyers naturally become more analytical, seeking the best possible value, which can translate into demands for discounts or added features. This high price point inherently grants individual consumers a degree of leverage in their negotiations with dealerships.
Audi enjoys significant brand loyalty, a key factor in mitigating customer bargaining power. However, the automotive landscape in 2024 shows a trend of increasing brand defection. For instance, studies indicate that a notable percentage of new car buyers are actively considering multiple brands, diminishing the absolute hold of any single manufacturer.
This willingness to switch means customers can exert more pressure on pricing and features. If Audi's offerings don't align with evolving customer desires or competitive value propositions, buyers are more likely to explore alternatives, thereby increasing their bargaining leverage.
Customers today wield significant power due to the widespread availability of information. Online platforms allow them to easily compare Audi's pricing, features, and competitor offerings, making informed decisions more accessible than ever before. For instance, in 2024, a significant portion of car buyers extensively researched vehicles online, often spending weeks comparing options before visiting a dealership.
The growing desire for personalization also amplifies customer bargaining power. Audi faces pressure to offer a high degree of customization, from interior finishes to advanced technological features, allowing customers to tailor vehicles to their specific needs and preferences. This trend means customers are less likely to accept standardized offerings and are willing to seek out brands that provide greater flexibility.
Increasing Competition in the Luxury Segment
The luxury automotive sector is experiencing a significant surge in competition, directly impacting customer bargaining power. Established titans like BMW and Mercedes-Benz are facing increased pressure not only from each other but also from emerging luxury brands and the rapidly expanding electric vehicle (EV) market. This proliferation of high-end choices empowers consumers, giving them a wider array of options to consider when making a purchase.
This heightened competition translates into greater leverage for customers. For instance, in 2024, the luxury EV segment alone saw numerous new model launches from both established automakers and dedicated EV manufacturers, offering consumers advanced technology and performance at various price points. This abundance of choice means customers can more readily demand better features, pricing, or customization options.
- Intensified Competition: The luxury car market is crowded with established brands like BMW and Mercedes-Benz, plus new entrants and a growing EV segment.
- Increased Consumer Choice: This competitive landscape provides buyers with a broader selection of vehicles, enhancing their ability to negotiate.
- EV Market Impact: The rapid growth of luxury electric vehicles in 2024, with many new models, has further diversified options and strengthened customer power.
- Demand for Value: With more choices available, customers are better positioned to seek premium features and competitive pricing.
Shifting Consumer Preferences (EVs, Hybrids)
Consumer preferences are indeed evolving, with a notable shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrids. This trend grants customers greater bargaining power as they have more choices available to them. For instance, in 2023, global EV sales surpassed 13 million units, a significant increase from previous years, indicating growing consumer interest.
While Audi is making substantial investments in EV and hybrid technology, the pace of adoption varies by market. Some regions show strong enthusiasm for battery-electric vehicles, but others exhibit a more cautious approach. This uneven demand means that customers in less receptive markets can leverage their choices, potentially influencing pricing and feature offerings.
- Growing Demand for EVs: Global EV sales saw a substantial jump, reaching over 13 million units in 2023, highlighting a significant shift in consumer interest.
- Hybrid Vehicle Popularity: The increasing interest in hybrid vehicles provides customers with an additional alternative, further diversifying their options and enhancing their bargaining position.
- Market Variability: Uneven adoption rates for battery-electric vehicles across different regions mean that consumer influence can be more pronounced in markets with slower EV uptake.
- Audi's Investment: Audi's significant investment in electric and hybrid powertrains aims to meet these changing demands, but the diverse market reception still empowers customers with choice.
Audi's customers possess considerable bargaining power, amplified by the sheer volume of available information and the increasing ease with which they can compare offerings. In 2024, a vast majority of luxury car buyers extensively utilize online resources to research pricing, features, and competitor vehicles, often before even visiting a dealership. This transparency means customers are well-informed and can readily identify opportunities for better deals or added value.
The luxury automotive market's heightened competition further strengthens customer leverage. With numerous established brands and a burgeoning electric vehicle (EV) segment, consumers have a wider array of choices than ever before. For example, the luxury EV market alone saw numerous new model introductions in 2024, offering advanced technology and performance across various price points, empowering buyers to negotiate more effectively.
The growing demand for personalization in vehicles also plays a significant role. Customers expect greater customization options, from interior finishes to advanced technological features, pushing Audi to offer more tailored solutions. This trend means buyers are less inclined to accept standardized models and are more likely to seek out brands that provide flexibility, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
| Factor | Impact on Audi's Customer Bargaining Power | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Information Availability | High | Majority of buyers research extensively online before purchase. |
| Competition Intensity | High | Numerous luxury brands and a rapidly expanding EV segment offer diverse choices. |
| Product Differentiation | Moderate | Increasing demand for personalization requires tailored offerings. |
| Switching Costs | Moderate | Brand loyalty exists, but increased model variety and EV adoption offer alternatives. |
Full Version Awaits
AUDI Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete AUDI Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of the competitive landscape. The document you see is precisely what you'll receive immediately after purchase, providing ready-to-use insights into industry rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitute products. No placeholders or mockups, just the fully formatted, professionally written analysis ready for your strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Audi faces fierce competition within the luxury automotive sector. Established players like BMW, Mercedes-Benz, and Lexus offer comparable product ranges, cutting-edge technology, and appeal to the same affluent demographic, intensifying the battle for market dominance. For instance, in 2023, BMW Group reported a global sales volume of over 2.5 million vehicles, while Mercedes-Benz Group delivered approximately 2.03 million vehicles, showcasing the sheer scale of these rivals.
Audi's competitive rivalry is intensified by its aggressive product portfolio renewal. In 2024 and 2025, the company is set to launch more than 20 new models, with half of them being fully electric. This ambitious plan aims to ensure Audi boasts the youngest model lineup in the automotive industry, directly confronting rivals who are also rapidly updating their offerings.
The automotive industry's shift towards electrification has dramatically heightened competitive rivalry. Tesla's early lead and innovative approach, coupled with the aggressive market entry of Chinese EV makers like BYD, which saw its 2023 sales surpass 3 million vehicles, are forcing established players like Audi to accelerate their EV strategies significantly.
Audi is investing billions, with plans to allocate approximately €37 billion to electrification and digitalization through 2028, aiming to launch more than 20 new electric models by the same year. However, this intense competition is met with challenges like volatile consumer demand for EVs and the substantial capital expenditure required for battery technology, charging infrastructure, and software development.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
The automotive industry's competitive rivalry is intensely fueled by rapid technological advancements, particularly in autonomous driving, connected car features, and the emerging concept of software-defined vehicles. Audi's long-standing 'Vorsprung durch Technik' slogan underscores its dedication to being at the forefront of innovation. However, this commitment is mirrored by its competitors, who are also making substantial investments in these critical areas, leading to a fierce technology arms race.
This constant push for innovation means that companies like Audi must continuously invest in research and development to maintain their competitive edge. For instance, in 2024, the global automotive R&D spending is projected to reach significant figures, with a substantial portion allocated to electrification and autonomous driving technologies. This ongoing investment cycle intensifies rivalry as companies vie to capture market share through superior technological offerings.
- Autonomous Driving: Significant investments are being made by major automakers and tech companies, with projections indicating a substantial market growth for ADAS (Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems) and autonomous driving solutions in the coming years.
- Connected Car Technologies: The integration of 5G and advanced infotainment systems is becoming standard, with companies focusing on seamless connectivity and data-driven services to enhance the user experience.
- Software-Defined Vehicles: The industry is shifting towards vehicles where software plays a central role in functionality and updates, creating new competitive battlegrounds for over-the-air updates and digital services.
- R&D Investment: Major automotive players are earmarking billions of dollars annually for R&D, with a significant portion dedicated to future mobility solutions, indicating the high stakes involved in technological leadership.
Geopolitical and Economic Headwinds
The automotive sector is navigating significant global economic shifts, with inflation and interest rate hikes impacting consumer demand and production costs. This challenging backdrop intensifies competition as manufacturers fight to maintain market share and profitability.
International competition is particularly fierce, exacerbated by geopolitical tensions and trade policies, such as the US imposing tariffs on imported vehicles and auto parts. These factors create an uneven playing field and force companies to adapt their strategies rapidly to mitigate risks and capitalize on opportunities.
- Global Economic Volatility: The IMF projected a global growth of 3.2% for 2024, a slight slowdown from 2023, indicating a cautious economic environment that pressures automotive sales.
- Trade Tensions: Ongoing trade disputes and the potential for new tariffs directly impact the cost of components and finished vehicles, forcing strategic adjustments in supply chains and pricing.
- Intensified Rivalry: With market growth slowing in many regions, established automakers and new entrants are locked in a battle for customers, pushing innovation and efficiency to the forefront.
Audi operates in a highly competitive luxury automotive market, facing strong pressure from established rivals like BMW and Mercedes-Benz, as well as emerging EV players. The rapid pace of technological advancement, particularly in electrification and autonomous driving, necessitates continuous, substantial R&D investment, creating a demanding environment for market share and profitability.
| Competitor | 2023 Global Sales (approx.) | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| BMW Group | 2.5 million+ vehicles | Electrification, Digitalization, Performance |
| Mercedes-Benz Group | 2.03 million vehicles | Luxury EVs, Software, Autonomous Systems |
| Tesla | 1.81 million vehicles | EV Innovation, Software-Defined Vehicles, Charging Infrastructure |
| BYD | 3 million+ vehicles (overall) | EVs, Battery Technology, Global Expansion |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Public transportation and ride-sharing services, like Uber and Lyft, present a viable substitute for car ownership, particularly in densely populated urban environments. While Audi's core customer base might not entirely forgo personal vehicle ownership, these alternatives can diminish the necessity for multiple cars within a household or influence the decision to purchase a secondary vehicle, impacting overall market demand.
The increasing adoption of Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) platforms presents a significant threat to traditional automotive manufacturers like Audi. These services, which allow users to access transportation on demand, are particularly resonating with younger consumers. For instance, by 2023, ride-sharing services and car-sharing platforms have seen substantial growth in urban areas, indicating a shift in preference away from personal vehicle ownership.
This shift directly impacts the demand for new vehicle sales, including the premium segment where Audi operates. As more individuals opt for subscription-based or pay-per-use transportation solutions, the necessity and desire for owning a personal car, especially a luxury one, may diminish. This trend could lead to a long-term erosion of Audi's core market if they do not adapt their business model.
The rise of e-bikes and electric scooters presents a subtle but growing threat to traditional car manufacturers like Audi. While not a direct replacement for a luxury vehicle, these micromobility options are increasingly attractive for short urban trips, potentially decreasing the demand for a secondary car or even a primary vehicle for some city dwellers.
In 2024, the global e-bike market is projected to reach over $40 billion, with significant growth in urban areas. This trend suggests a shift in personal transportation preferences, particularly among younger demographics and those prioritizing convenience and environmental impact for shorter journeys, thereby indirectly impacting the perceived need for a premium car in certain use cases.
Used Car Market
The robust used luxury car market presents a significant threat of substitutes for new Audi vehicles. Consumers seeking the prestige and features of a luxury brand can often find well-maintained pre-owned models at a considerably lower price point. This affordability can divert potential buyers away from purchasing new models, directly impacting Audi's sales volume and revenue streams.
For instance, in 2024, the average depreciation for luxury vehicles can be substantial in the first few years, making certified pre-owned options highly attractive. This trend means that a consumer looking for an Audi A4 might find a lightly used, higher-trim model from a previous year for the price of a new, base-model competitor, or even a new Audi in a lower segment.
- Affordability: Used luxury cars offer access to premium features and brand cachet at a reduced cost, making them a compelling alternative to new vehicles.
- Depreciation Advantage: The steepest depreciation often occurs in the first few years of ownership, making pre-owned luxury cars a financially savvy choice for many buyers.
- Market Size: The certified pre-owned (CPO) market for luxury brands, including Audi, is substantial and growing, providing a wide selection of vehicles.
- Feature Access: Buyers can often acquire higher specification or more feature-rich used models for the same budget as a new, entry-level luxury car.
Technological Obsolescence and Rapid Innovation
The threat of substitutes for Audi is significantly amplified by technological obsolescence and the relentless pace of innovation. Emerging technologies in electric vehicle (EV) powertrains and autonomous driving capabilities are rapidly redefining consumer expectations, potentially rendering existing internal combustion engine (ICE) models less appealing. For instance, by the end of 2023, global EV sales had surpassed 13 million units, a figure expected to grow substantially, indicating a strong consumer shift towards newer technologies that might be offered by competing brands as substitutes.
This rapid evolution means Audi's current vehicle lineup could quickly appear outdated, prompting consumers to delay purchases or seek out alternatives that offer the latest advancements. The increasing availability of highly advanced EVs from both established automakers and new entrants presents a direct substitute threat. For example, by mid-2024, many competitors were showcasing next-generation battery technology promising longer ranges and faster charging, directly challenging the perceived value of Audi's existing offerings.
- Technological Obsolescence: Rapid advancements in EV and autonomous driving tech can make current Audi models seem outdated quickly.
- Consumer Behavior Shift: Buyers may delay purchases or choose competitors offering newer, more advanced substitutes.
- Market Trend: Global EV sales exceeding 13 million units by end-2023 highlight a strong consumer move towards newer technologies.
- Competitive Landscape: Competitors are rapidly introducing next-generation battery tech, increasing the threat of substitution.
The threat of substitutes for Audi is multifaceted, encompassing alternative transportation methods and the pre-owned vehicle market. Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) platforms and micromobility options like e-bikes are gaining traction, particularly in urban settings, potentially reducing the need for personal car ownership. Furthermore, the robust used luxury car market offers a compelling value proposition, allowing consumers to access premium brands at a lower cost, directly diverting sales from new Audi vehicles.
| Substitute Type | Impact on Audi | 2024 Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| MaaS & Ride-Sharing | Reduces demand for new car purchases, especially secondary vehicles. | Continued growth in urban adoption, impacting car ownership models. |
| Micromobility (E-bikes, Scooters) | Decreases demand for short urban trips, potentially affecting secondary car needs. | Global e-bike market projected to exceed $40 billion in 2024. |
| Used Luxury Cars | Offers premium features at lower prices, diverting new car buyers. | Significant depreciation in early years makes CPO options highly attractive. |
Entrants Threaten
The automotive industry, particularly the luxury segment where Audi operates, demands substantial capital for research and development, sophisticated manufacturing plants, and broad distribution networks. For instance, developing a new electric vehicle platform can cost billions of dollars, a figure that deters many potential entrants. This high initial investment creates a significant barrier, protecting established players like Audi from widespread new competition.
Audi's established brand equity and deep-rooted customer loyalty represent a significant barrier to new entrants. Years of consistent delivery on luxury, performance, and cutting-edge technology have fostered a strong emotional connection and trust with consumers.
New competitors find it exceptionally difficult to match Audi's decades-long cultivation of prestige and reliability, which translates into a substantial competitive advantage and a deterrent for potential market entrants seeking to quickly gain market share.
The automotive sector is burdened by exceptionally rigorous regulatory and safety standards across the globe. These requirements necessitate substantial capital outlays for compliance, extensive testing procedures, and ongoing adaptation to evolving mandates, presenting a significant hurdle for any potential new entrant aiming to establish a foothold in the market.
For instance, in 2024, new vehicle emissions standards, such as those being implemented or tightened in the European Union and various US states, demand advanced engineering and costly manufacturing processes. Companies must invest heavily in research and development for cleaner technologies, and rigorous crash testing protocols, like those mandated by NHTSA in the US, add further layers of complexity and expense, effectively deterring less-capitalized newcomers.
Technological Expertise and Supply Chain Integration
The threat of new entrants for Audi is significantly shaped by the immense technological expertise and intricate supply chain integration required in the luxury automotive sector. Developing and manufacturing high-end vehicles necessitates deep knowledge in areas like advanced powertrain engineering, sophisticated infotainment systems, and cutting-edge autonomous driving software. For instance, in 2024, the automotive industry continued to see substantial investment in R&D for electric vehicle (EV) technology and software-defined vehicles, with major players committing billions of dollars, making it a high barrier for newcomers to match this level of innovation.
Establishing and managing a complex, global supply chain is another formidable hurdle. Audi, like other premium automakers, relies on a vast network of specialized suppliers for components ranging from high-strength steel and advanced battery cells to intricate electronic modules and luxury interior materials. This integration ensures quality and efficiency but requires significant upfront investment and long-term relationship building. By 2024, the automotive supply chain remained subject to geopolitical tensions and material shortages, further complicating the entry for new players who would need to secure reliable and cost-effective sourcing.
- High R&D Investment: The automotive industry's R&D spending, particularly in EV and autonomous technology, reached hundreds of billions globally by 2024, creating a substantial financial barrier.
- Complex Global Supply Chains: Securing reliable access to specialized components, from advanced batteries to luxury interior materials, requires extensive networks and significant capital.
- Technological Sophistication: Expertise in areas like advanced electronics, software integration, and AI for driver assistance systems is crucial and difficult to replicate quickly.
- Brand Reputation and Loyalty: Established luxury brands like Audi benefit from decades of building trust and customer loyalty, which new entrants must overcome with superior offerings.
Intense Competition and Market Saturation
The luxury automotive market, where Audi operates, is already a crowded space with formidable, established global brands. This high level of existing competition makes it incredibly difficult for any new player to carve out a significant market share. For instance, in 2023, the global luxury car market saw sales of over 10 million units, dominated by established names like Mercedes-Benz, BMW, and Audi itself.
New entrants would face substantial barriers, including the immense capital required for research, development, manufacturing, and establishing a global distribution and service network. Building brand loyalty and trust in the luxury segment, which is crucial for sustained success, takes years and significant marketing investment.
- High Capital Requirements: Establishing a luxury automotive brand requires billions in investment for R&D, manufacturing facilities, and global supply chains.
- Brand Loyalty and Reputation: Existing players benefit from decades of brand building and customer trust, making it hard for newcomers to attract discerning luxury buyers.
- Economies of Scale: Established manufacturers leverage large production volumes to reduce per-unit costs, a significant advantage over smaller, new entrants.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Meeting stringent safety and emissions standards globally adds another layer of complexity and cost for any new automotive manufacturer.
The threat of new entrants in the luxury automotive sector, where Audi competes, is generally low due to extremely high barriers. These include the massive capital investment needed for R&D, manufacturing, and global distribution networks, which can easily run into billions of dollars. For example, developing a new electric vehicle platform alone can cost upwards of $10 billion. Furthermore, established brands like Audi benefit from decades of cultivating brand loyalty and trust, making it incredibly difficult for newcomers to gain traction in a market that values heritage and proven quality.
Regulatory hurdles, such as stringent emissions and safety standards, also pose a significant challenge. In 2024, evolving mandates for electric vehicles and autonomous driving technology require continuous, substantial investment in research and development, a cost that deters many potential entrants. The complexity of global supply chains, essential for sourcing specialized components from advanced battery cells to luxury interior materials, further solidifies the position of established players who have long-standing relationships with key suppliers.
The automotive industry's technological sophistication, particularly in areas like AI-driven driver assistance and advanced infotainment systems, demands deep expertise that is hard for new entrants to replicate quickly. By 2024, significant global R&D spending in EV and autonomous technology, totaling hundreds of billions, underscores this point. The sheer scale of operations for existing manufacturers also allows them to achieve economies of scale, reducing per-unit costs and creating a competitive pricing advantage that new entrants struggle to match.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | Billions required for R&D, manufacturing, and distribution. | Very High Barrier |
| Brand Loyalty & Reputation | Decades of trust and prestige in the luxury segment. | Very High Barrier |
| Technological Sophistication | Expertise in EV, autonomous driving, and software integration. | High Barrier |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meeting global safety and emissions standards. | High Barrier |
| Economies of Scale | Established players benefit from large production volumes. | Moderate Barrier |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Audi Porter's Five Forces analysis is built on a foundation of comprehensive data, including Audi's annual and sustainability reports, industry-specific market research from firms like IHS Markit and PwC, and regulatory filings from automotive authorities worldwide.
We leverage publicly available financial data from Audi's investor relations, competitor financial statements, and automotive industry trade publications to assess competitive intensity, supplier and buyer power, and the threat of new entrants and substitutes.
