Asseco Poland SA Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Asseco Poland SA Bundle
Asseco Poland SA navigates a dynamic IT sector shaped by moderate rivalry and significant buyer power, particularly from large enterprise clients. The threat of substitutes is present, but often mitigated by the specialized nature of its software solutions.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Asseco Poland SA’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Asseco Poland SA, a significant player in IT solutions, depends on a range of suppliers for essential elements like hardware, software, and specialized components. The leverage these suppliers hold is amplified when they provide unique technologies or operate in near-monopolistic markets, especially for niche software or critical hardware parts. For instance, in 2023, the global semiconductor shortage highlighted how dependent companies like Asseco can be on a few key chip manufacturers, demonstrating significant supplier power.
Asseco Poland SA faces significant supplier bargaining power due to high switching costs for critical components. These costs can involve substantial financial outlays and operational complexities when migrating from one specialized software provider or infrastructure partner to another, particularly for deeply integrated systems.
For instance, if Asseco relies on a proprietary embedded software solution from a single vendor, the expense and time required to re-engineer or replace that system could run into millions of euros, potentially impacting project timelines and client deliverables. This inherent dependency allows suppliers to negotiate more favorable terms, including price increases, as the cost and risk of switching are prohibitive.
The IT market is indeed extensive, but Asseco Poland SA's reliance on highly specialized software, such as core banking systems and sophisticated ERP solutions, significantly narrows the field of potential alternative suppliers. This specialization means that for critical components, the number of truly capable providers is limited, thereby increasing the bargaining power of those few suppliers.
However, for more commoditized IT needs, like standard office software or basic hardware infrastructure, Asseco can leverage a much broader supplier base. The presence of numerous vendors for these common inputs naturally dilutes individual supplier power, allowing Asseco to negotiate more favorable pricing and contract terms, a common strategy in competitive IT procurement.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers poses a significant concern for Asseco Poland. If a key IT component supplier were to develop the capability and strategic intent to offer their own integrated solutions, directly competing with Asseco's offerings, their bargaining power would escalate dramatically. This scenario could force Asseco to negotiate less favorable terms, such as higher prices or stricter contract conditions, simply to preserve the supply chain and mitigate the risk of facing a new, direct competitor in the market.
However, the practical execution of such forward integration in the complex IT solutions sector is often a formidable undertaking. Most suppliers would face substantial costs and considerable risks in attempting to replicate Asseco's established business model, which includes extensive R&D, sales networks, and customer support infrastructure. For instance, developing a comprehensive enterprise resource planning (ERP) system from scratch, a core offering for companies like Asseco, requires billions in investment and years of specialized expertise, making it an unlikely move for many component providers.
- Supplier Capability: The ability of a supplier to develop and market end-to-end IT solutions comparable to Asseco's.
- Strategic Interest: A supplier's motivation to move beyond component provision into direct market competition.
- Integration Costs: The significant financial investment required for a supplier to establish R&D, sales, and support for competing offerings.
- Market Risk: The inherent uncertainty and potential for failure associated with entering a highly competitive and complex market.
Talent Pool and Labor Costs
Asseco Poland SA, like many IT firms, views its highly skilled workforce as a crucial 'supplier.' Poland boasts a substantial and expanding pool of IT talent, with a significant number of graduates entering the market each year. This generally keeps the bargaining power of labor suppliers in check.
However, the European tech landscape is highly competitive for specialized IT professionals. This intense demand means that individual highly skilled workers or specialized IT consulting firms can still wield considerable bargaining power when it comes to negotiating salaries and employment terms.
- Talent Availability: Poland's IT sector is supported by a strong educational pipeline, with universities producing thousands of IT graduates annually.
- Competition: The high demand for specialized skills like AI, cybersecurity, and cloud computing can lead to bidding wars for top talent.
- Impact on Costs: While overall labor costs in Poland remain competitive compared to Western Europe, the scarcity of niche expertise can drive up compensation for those specific roles.
Asseco Poland SA’s bargaining power with suppliers is influenced by the concentration of providers for critical IT components. When suppliers offer unique or highly specialized products, such as advanced cybersecurity software or proprietary hardware, their leverage increases. For example, in 2024, the ongoing demand for specialized AI chips meant that manufacturers of these components held significant sway over pricing and delivery terms for IT firms. This situation is exacerbated when switching to an alternative supplier involves substantial costs and operational disruptions, making it difficult for Asseco to negotiate aggressively.
The bargaining power of suppliers is moderately high for Asseco Poland SA, particularly concerning specialized software and hardware. While Poland has a robust IT talent pool, the scarcity of niche skills like advanced AI development or quantum computing expertise can empower individual professionals or specialized consulting firms. However, for more commoditized IT needs, Asseco benefits from a wide array of vendors, which dilutes supplier power and allows for more favorable terms.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers is a potential concern, though often limited by the high costs and complexity of entering Asseco's established market. For instance, a hardware component supplier would need billions in investment to develop comprehensive IT solutions comparable to Asseco's offerings, a prohibitive barrier for most.
| Supplier Type | Concentration | Switching Costs | Bargaining Power |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Software (e.g., Core Banking) | Low to Moderate | High | Moderate to High |
| Proprietary Hardware Components | Low to Moderate | High | Moderate to High |
| Commoditized IT Hardware | High | Low | Low |
| Standard Office Software | High | Low | Low |
| Highly Skilled IT Professionals | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate |
What is included in the product
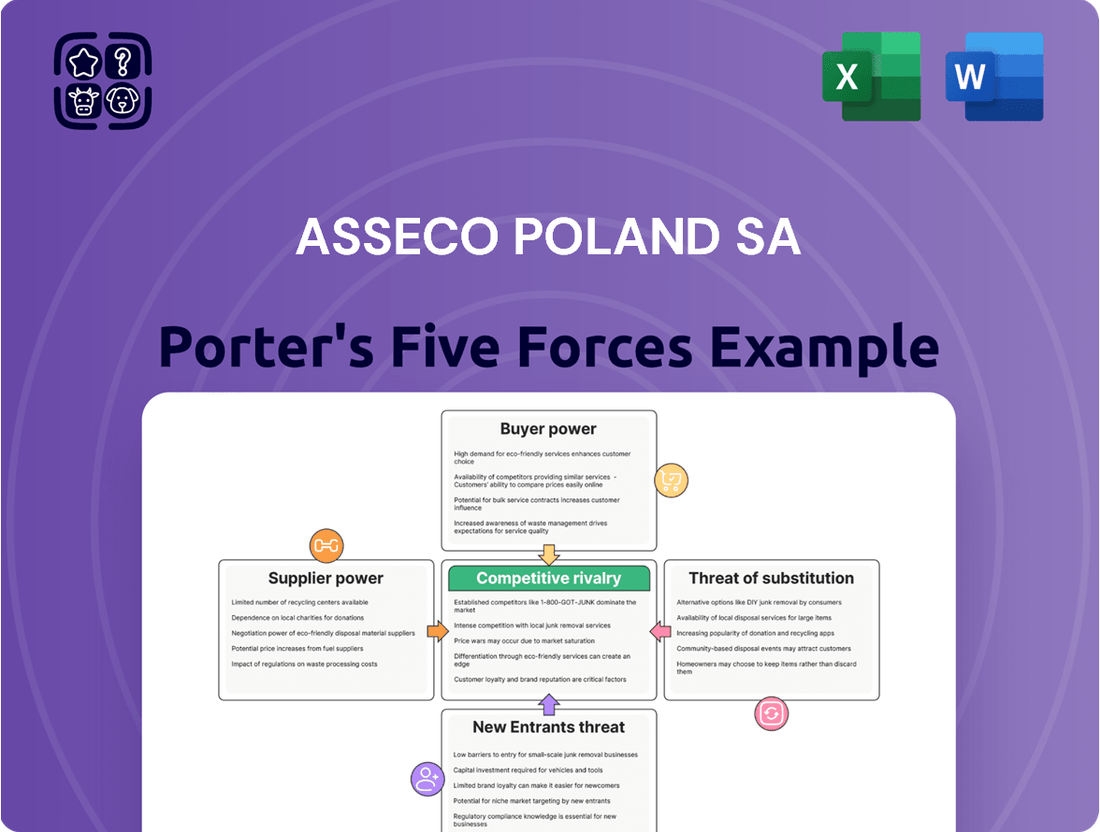
Tailored exclusively for Asseco Poland SA, analyzing its position within its competitive landscape by examining supplier and buyer power, threat of new entrants and substitutes, and competitive rivalry.
Easily identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, streamlining strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
Asseco Poland SA's customer concentration and size are key factors in their bargaining power. The company serves large, critical sectors like banking, healthcare, and public administration, often engaging with major enterprise clients. This means that while Asseco has a broad customer portfolio, a few very large clients can wield considerable influence.
For instance, a significant contract with a major banking group or a large public administration entity represents a substantial portion of Asseco's revenue. Losing such a client, or even facing renegotiation demands from them, could lead to a noticeable impact on Asseco's financial performance. In 2023, Asseco Poland reported consolidated revenues of PLN 17.9 billion, highlighting the scale of business where individual large contracts are critical.
For clients deeply embedded with Asseco Poland SA's core banking systems or comprehensive ERP solutions, the hurdles to switching are substantial. These high switching costs stem from the intricate integration of Asseco's software into a client's existing IT infrastructure, the complex and often lengthy process of migrating vast amounts of data, and the significant investment required for retraining staff on new platforms. This 'lock-in' effect considerably diminishes the bargaining power of these customers, making them less likely to switch providers due to the sheer effort and expense involved.
However, the landscape shifts for Asseco's less integrated offerings or their newer cloud-based solutions. In these segments, the barriers to entry for competitors are generally lower, meaning customers can transition to alternative providers with greater ease and at a reduced cost. This increased flexibility in Asseco's more modular or cloud-native services empowers customers, giving them more leverage in negotiations and a greater ability to demand favorable terms or seek out competing solutions.
Customers considering Asseco Poland SA's offerings have a robust selection of alternatives. These range from other major European software providers like Comarch and global giants such as SAP and Oracle, to large consulting firms like Accenture and Deloitte, and even the option of in-house development. This broad competitive landscape significantly constrains Asseco's pricing power and its ability to unilaterally set contract terms.
The increasing shift towards Software as a Service (SaaS) models, particularly within the banking sector, further amplifies customer choice. These SaaS alternatives offer greater flexibility compared to traditional on-premise software installations, giving customers more leverage in their decision-making processes and potentially reducing their reliance on any single vendor.
Customer Price Sensitivity
Customer price sensitivity for Asseco Poland SA varies significantly across its diverse client base. In sectors such as public administration and healthcare, where budgets are often tightly controlled, customers tend to be more price-sensitive. This means that the cost of Asseco's solutions can be a major deciding factor in procurement processes. For example, in 2024, many public sector IT projects faced budget reviews, potentially increasing pressure on vendors like Asseco to offer competitive pricing.
Conversely, in the banking and finance sectors, the emphasis often shifts from price to the reliability and security of the IT systems. Customers in these industries understand that system failures or security breaches can have catastrophic financial and reputational consequences. Therefore, they are often willing to pay a premium for robust, dependable, and highly secure solutions that Asseco provides. This was evident in 2024 as financial institutions continued to invest heavily in cybersecurity and digital transformation, prioritizing function over minimal cost.
Asseco must therefore navigate this dual market dynamic. The company needs to strategically balance offering competitive pricing, especially in price-sensitive segments, with demonstrating the superior value, quality, and mission-critical nature of its offerings to clients in sectors where reliability is paramount. This requires a nuanced approach to pricing and value proposition communication.
- Public Administration & Healthcare: Higher price sensitivity due to budget constraints.
- Banking & Finance: Lower price sensitivity, prioritizing quality, security, and reliability.
- Asseco's Strategy: Balance competitive pricing with demonstrated value and mission-critical importance.
Customer's Ability to Demand Customization
Asseco Poland SA's customer base, particularly its large enterprise clients, possesses significant bargaining power when it comes to demanding customization. Given Asseco's focus on comprehensive software and system integration, these clients often require bespoke solutions tailored to their unique operational workflows. This ability to shape the product directly impacts Asseco's development process.
The demand for extensive customization by major clients can translate into a substantial increase in their bargaining leverage. They can dictate specific features and functionalities, effectively molding Asseco's offerings to their precise requirements. This dynamic can put considerable pressure on Asseco's resource allocation and impact project timelines, potentially affecting profitability if not managed efficiently.
- Customization Leverage: Large clients can negotiate terms based on their need for highly specific software adaptations.
- Project Complexity: Tailoring solutions for diverse client needs often results in more intricate and lengthy development cycles.
- Resource Strain: Meeting bespoke demands can stretch Asseco's development teams and financial resources.
Asseco Poland SA's bargaining power of customers is influenced by several factors, including switching costs, availability of substitutes, and price sensitivity. While high switching costs for core systems limit customer power, the availability of alternatives and varying price sensitivity across sectors create a mixed dynamic.
For instance, in 2024, public sector clients showed increased price sensitivity due to budget reviews, while financial institutions prioritized system reliability and security, demonstrating less price sensitivity. This dual market approach requires Asseco to tailor its value proposition and pricing strategies accordingly.
The ability of large clients to demand customization also significantly impacts their bargaining power, potentially influencing Asseco's development resources and project timelines.
| Factor | Impact on Asseco's Customer Bargaining Power | Example/Data Point (2024/2023) |
|---|---|---|
| Switching Costs | Lowers bargaining power for deeply integrated systems. | High integration costs for core banking systems create customer lock-in. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Increases bargaining power, especially for modular/cloud solutions. | Competition from SAP, Oracle, and consulting firms limits pricing power. |
| Price Sensitivity | Varies by sector; higher in public administration, lower in finance. | Public sector budget reviews in 2024 increased price pressure; financial sector prioritized security over cost. |
| Customization Demands | Increases bargaining power for large clients. | Bespoke feature requests can influence development timelines and resource allocation. |
Same Document Delivered
Asseco Poland SA Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Asseco Poland SA, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the IT sector. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted report you will receive immediately after purchase, providing actionable insights into industry attractiveness and competitive dynamics. You're looking at the final, ready-to-use analysis, ensuring you get precisely what you need without any placeholders or missing information.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The European software and IT services market is a crowded arena, featuring a multitude of local and international competitors. Asseco Poland navigates this landscape, contending with giants like Accenture, Deloitte, and IBM, alongside specialized firms such as FIS and Temenos in the critical core banking sector. This broad spectrum of rivals, from global powerhouses to niche regional players like Comarch, intensifies the competitive rivalry across all segments Asseco operates in.
The European enterprise software market is expected to see robust growth, with a projected compound annual growth rate of 11.7% between 2025 and 2030. This expansion signals a highly attractive market landscape.
While this growth offers opportunities for companies like Asseco Poland SA to expand, it also acts as a magnet for new entrants and intensifies competition among existing players vying for increased market share.
Asseco Poland SA's strong performance in Q1 2025, coupled with a significant order backlog, highlights its capacity to effectively capitalize on this expanding market and navigate the competitive environment.
Asseco Poland SA stands out by offering a suite of proprietary IT solutions coupled with specialized industry knowledge. This approach creates a significant barrier for competitors seeking to directly replicate their offerings, especially in core banking and enterprise resource planning (ERP) systems.
The complexity and integration required for these specialized systems translate into substantial switching costs for clients. For instance, migrating a core banking system can involve years of work and millions in expenditure, effectively locking in existing customers and lessening direct price competition among established players.
In 2024, Asseco continued to invest heavily in research and development, aiming to maintain its edge through ongoing innovation and enhanced integration capabilities. This focus on advanced features and seamless connectivity is vital for preserving product differentiation and reinforcing customer loyalty against potential rivals.
Mergers and Acquisitions Activity
The European IT sector is buzzing with mergers and acquisitions, a clear sign of intense competition. Companies are actively buying others to grow their market presence, snap up new technologies, and solidify their standing in the industry. This dynamic environment means that staying competitive often involves strategic acquisitions.
Asseco Poland SA is a prime example of a company leveraging M&A as a core competitive strategy. In 2024 alone, Asseco completed the acquisition of 14 companies, demonstrating a significant commitment to inorganic growth. This aggressive approach isn't new; since 2004, Asseco has acquired over 150 businesses.
- Asseco's 2024 M&A: Acquired 14 companies.
- Long-term M&A track record: Over 150 acquisitions since 2004.
- Industry trend: IT sector in Europe sees ongoing consolidation.
- Strategic driver: M&A is used to gain market share, technology, and scale.
Geographic and Sectoral Diversification
Asseco Poland's strategic geographic and sectoral diversification significantly tempers competitive rivalry. Operating in over 60 countries and across key sectors like banking, healthcare, public administration, and energy, the company is less vulnerable to intense competition within any single market or industry. This broad reach allows Asseco to offset pressures in one area by capitalizing on strengths or opportunities elsewhere, bolstering its overall business resilience.
For instance, in 2024, Asseco Poland continued its expansion in the public administration sector, securing new contracts that offset slower growth in other segments. This diversification strategy is crucial for navigating the highly competitive IT landscape, where rapid technological shifts and new entrants can quickly alter market dynamics. By spreading its operations, Asseco can absorb the impact of aggressive pricing or innovation from competitors in, say, the banking sector, by drawing on its established position in healthcare IT.
- Geographic Reach: Operations in over 60 countries, reducing reliance on any single market.
- Sectoral Breadth: Presence in banking, healthcare, public administration, and energy, among others.
- Risk Mitigation: Diversification buffers against intense rivalry in specific sectors or regions.
- Resilience Enhancement: Ability to leverage strengths in one area to counter competitive pressures in another.
Competitive rivalry in the European IT market is intense, with Asseco Poland facing global giants and specialized niche players. The market's projected 11.7% CAGR from 2025-2030 fuels this competition, attracting new entrants and intensifying existing rivalries.
Asseco differentiates itself through proprietary solutions and deep industry expertise, particularly in core banking and ERP, creating high switching costs for clients. This, combined with significant R&D investment in 2024 and a strategic acquisition spree, including 14 companies that year, reinforces its competitive standing. Asseco's diversification across over 60 countries and multiple sectors further mitigates the impact of rivalry in any single market.
| Metric | Asseco Poland SA | European IT Market (2025-2030 Projection) |
|---|---|---|
| Key Competitors | Accenture, Deloitte, IBM, FIS, Temenos, Comarch | Broad spectrum including global and niche players |
| Asseco's 2024 M&A Activity | 14 companies acquired | Industry trend of consolidation |
| Geographic Presence | Over 60 countries | N/A |
| Sectoral Diversification | Banking, Healthcare, Public Admin, Energy, etc. | N/A |
SSubstitutes Threaten
For large organizations, especially in banking and public administration, building IT solutions internally presents a significant substitute threat to Asseco Poland SA's offerings. This internal development route offers enhanced control and bespoke customization, though it frequently entails elevated expenses and extended project timelines. For instance, in 2023, many large European banks continued to invest heavily in their internal IT capabilities, with some reporting IT spending in the billions of euros, underscoring the scale of potential in-house projects.
Asseco's competitive strategy must therefore consistently highlight its advantages in efficiency, specialized knowledge, and overall cost-effectiveness when contrasted with the resources and time commitment required for in-house IT teams. The company's ability to deliver faster time-to-market and leverage economies of scale in software development and maintenance is crucial in countering this substitute threat.
The rise of generic cloud platforms like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, alongside powerful open-source solutions, presents a significant threat of substitution for Asseco Poland SA. These platforms offer scalable and often more budget-friendly alternatives for various IT infrastructure and software needs, particularly for non-critical business functions.
For instance, many companies are migrating their data storage and processing to cloud providers, reducing their reliance on on-premise solutions that Asseco might traditionally offer. The global cloud computing market was projected to reach over $1.3 trillion by the end of 2024, highlighting the massive scale of these substitute offerings.
The rise of Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) and Banking-as-a-Service (BaaS) presents a substantial threat to Asseco Poland SA's traditional software sales. These subscription-based models offer flexibility and lower initial costs, making them attractive alternatives to upfront licensing. For instance, the global BaaS market was projected to reach over $2.5 billion by 2024, highlighting the growing customer preference for these agile solutions.
Disruptive Technologies (e.g., AI, Blockchain)
Rapid advancements in disruptive technologies like AI and blockchain present a significant threat of substitution for Asseco Poland SA. These innovations can spawn entirely new solutions that render existing offerings obsolete. For instance, AI-powered analytics platforms could substitute traditional business intelligence tools that Asseco currently provides. The market for IT services is dynamic, with global IT spending projected to reach $5.06 trillion in 2024, according to Gartner, highlighting the constant evolution and potential for disruption.
While Asseco actively integrates cutting-edge technologies, a nimble competitor could introduce a breakthrough that rapidly marginalizes Asseco's legacy systems. This necessitates continuous innovation to maintain market relevance and competitive advantage. The pace of change means that even established solutions can face obsolescence quickly if not updated or replaced.
- AI-driven automation can replace manual processes in areas like customer service and data entry, impacting traditional software solutions.
- Blockchain technology offers decentralized alternatives for secure data management and transactions, potentially substituting centralized databases and payment systems.
- Cloud-native architectures enable faster deployment and scalability, potentially making on-premise or less agile solutions less attractive.
- The global AI market is expected to grow significantly, with some projections indicating it could reach over $1.3 trillion by 2030, underscoring the transformative potential of this technology.
Process Re-engineering or Manual Alternatives
While Asseco Poland SA's core enterprise systems are generally insulated from direct substitution, less complex or peripheral software solutions could face threats. Customers might re-engineer their processes to eliminate the need for certain software, or in some niche cases, revert to manual alternatives. This is particularly relevant for standalone tools rather than integrated platforms.
For Asseco, this means their offerings must demonstrably deliver significant efficiency gains and a clear competitive edge. The value proposition needs to be strong enough to outweigh the perceived cost or complexity of adopting new software, especially when simpler, albeit less automated, methods exist. For instance, a company might choose to streamline its workflow to avoid implementing a new project management module if the existing manual tracking is deemed sufficient for a specific team.
- Process Simplification: Businesses can redesign workflows to bypass the need for specific software functionalities.
- Manual Workarounds: In less critical areas, a return to manual data entry or tracking may be considered.
- Value Justification: Asseco's solutions must offer clear ROI and competitive advantages to deter substitution.
- Focus on Core Strengths: The threat is more pronounced for non-essential software modules than for core ERP or banking systems.
The threat of substitutes for Asseco Poland SA is multifaceted, encompassing internal IT development, generic cloud platforms, SaaS/BaaS models, and disruptive technologies like AI. While core enterprise systems are more resilient, peripheral solutions face direct substitution. For example, the global cloud computing market's projected growth to over $1.3 trillion by the end of 2024 underscores the scale of these alternatives.
Asseco must continually emphasize its efficiency, expertise, and cost-effectiveness compared to in-house development or simpler workarounds. The company's ability to provide faster time-to-market and economies of scale is vital. The increasing adoption of BaaS, with a projected market of over $2.5 billion by 2024, highlights a customer shift towards more agile, subscription-based models.
Disruptive technologies like AI, with market projections reaching over $1.3 trillion by 2030, pose a significant threat by potentially rendering existing solutions obsolete. Asseco's strategy must involve continuous innovation to integrate these advancements and maintain market relevance against agile competitors and evolving customer preferences.
| Substitute Category | Description | Impact on Asseco | Example Data Point (2024 Projections/Estimates) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Internal IT Development | Large organizations building solutions in-house | Reduces demand for external software providers | Large banks' IT spending in billions of euros (2023) |
| Generic Cloud Platforms & Open Source | AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, open-source software | Offers scalable, cost-effective alternatives | Global cloud computing market > $1.3 trillion |
| SaaS & BaaS Models | Subscription-based software delivery | Challenges traditional software licensing | Global BaaS market > $2.5 billion |
| Disruptive Technologies (AI, Blockchain) | New technologies creating novel solutions | Potential to make existing offerings obsolete | Global IT spending > $5.06 trillion; AI market growth |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the specialized enterprise software market, particularly for critical sectors like banking and healthcare, demands significant upfront capital. This includes substantial investment in research and development, robust IT infrastructure, and attracting highly skilled personnel. For instance, developing sophisticated core banking systems, a key area for Asseco Poland SA, is inherently capital-intensive, posing a considerable hurdle for newcomers.
Asseco Poland SA's ongoing commitment to investing in its proprietary software solutions further solidifies this barrier to entry. This continuous development and enhancement of their product portfolio require substantial financial resources, making it challenging for potential competitors to match the depth and breadth of their offerings. In 2023, Asseco Poland reported consolidated revenue of PLN 17.4 billion, showcasing the scale of operations and investment required in this sector.
The software industry serving sectors like banking, finance, healthcare, and public administration is characterized by substantial regulatory hurdles. New entrants must invest heavily in understanding and complying with complex frameworks, such as GDPR for data privacy or specific financial regulations like PSD2 in Europe. This compliance burden, including obtaining certifications and undergoing audits, acts as a significant barrier, making it difficult and costly for newcomers to enter these markets. For instance, Asseco Poland SA's extensive experience and established compliance protocols in these sensitive areas provide a considerable advantage over potential new competitors.
Asseco Poland has cultivated a robust brand reputation and fostered enduring customer loyalty, especially within Poland and across the European continent. This established trust acts as a significant deterrent for nascent competitors seeking to penetrate the market.
Clients relying on mission-critical IT infrastructure often gravitate towards established and proven vendors, making it challenging for new, unproven entities to gain traction. Asseco's substantial order backlog, which stood at PLN 15.4 billion at the end of Q1 2024, underscores this deep customer confidence and the predictable nature of its revenue streams.
Access to Distribution Channels and Expertise
New companies entering the IT solutions market, particularly those targeting sectors like banking, energy, and public administration, would find it difficult to establish the extensive distribution networks that Asseco Poland SA already possesses. This established reach is a significant barrier, as replicating such a widespread presence requires substantial time and investment.
Furthermore, the specialized expertise needed to cater to the complex and often highly regulated demands of these industries is not easily acquired. Asseco's deep understanding and long-standing relationships within these sectors provide a competitive edge that new entrants would struggle to match in the short to medium term. For instance, Asseco's 2023 revenue reached PLN 17.4 billion, showcasing its scale and market penetration.
- Distribution Network Challenges: New entrants face hurdles in building comparable distribution channels to Asseco's established international presence.
- Expertise Gap: Acquiring the deep sectoral knowledge required for banking, energy, and public administration is a significant barrier.
- Replication Difficulty: Asseco's wide international footprint and sector-specific expertise are hard for new competitors to replicate quickly.
- Market Penetration: Asseco's 2023 revenue of PLN 17.4 billion demonstrates its substantial market share and established client base.
Talent Acquisition and Retention
The intense competition for skilled IT professionals in Poland, a significant talent hub, presents a considerable threat to new entrants. Companies like Asseco Poland SA benefit from established recruitment channels and a strong employer brand, making it easier to attract and retain top talent. The increasing demand for specialized tech skills across Europe, particularly in areas like cloud computing and cybersecurity, further exacerbates this challenge, potentially hindering the rapid scaling of new businesses.
In 2024, the European IT talent market continued to see wage inflation, with average salaries for experienced software developers in Poland rising by an estimated 8-12% year-on-year. This upward pressure on compensation makes it more costly for new entrants to build competitive teams. Furthermore, Asseco's long-standing presence and reputation in the Polish IT sector mean they often have access to a wider pool of experienced candidates and can offer more attractive long-term career development opportunities, acting as a deterrent for emerging competitors.
- High Demand for Niche Skills: New entrants struggle to find professionals with specialized expertise, such as AI/ML engineers or blockchain developers, which are crucial for modern IT solutions.
- Established Employer Branding: Asseco's brand recognition allows them to attract a larger volume of applicants, including those seeking stability and career progression.
- Retention Challenges: The high mobility of IT talent means new companies face difficulties retaining their workforce against the allure of established firms offering better benefits and project diversity.
- Rising Labor Costs: Increased competition for talent drives up salary expectations, making it more expensive for new entrants to build and scale their IT teams effectively.
The threat of new entrants for Asseco Poland SA is generally low due to substantial capital requirements for R&D and infrastructure, coupled with significant regulatory compliance burdens in sectors like banking and healthcare. Asseco's established brand reputation, deep customer loyalty, and extensive distribution networks further solidify these barriers. The intense competition for skilled IT professionals also makes it challenging for newcomers to build and retain competitive teams, especially with rising labor costs observed in 2024.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Asseco Poland SA's Advantage |
| Capital Requirements | High investment in R&D, infrastructure, and talent. | Significant hurdle for new players. | Established financial capacity and operational scale. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Complex frameworks in banking, healthcare, etc. | Costly and time-consuming to navigate. | Proven compliance expertise and established protocols. |
| Brand Reputation & Loyalty | Trust built over years with clients. | Difficult for new entities to gain market acceptance. | Strong market presence and long-term client relationships. |
| Talent Acquisition & Retention | Competition for specialized IT skills. | Challenges in building and scaling teams. | Strong employer brand and access to experienced professionals. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Asseco Poland SA is built upon a foundation of publicly available financial statements, annual reports, and investor relations materials. We also leverage industry-specific market research reports and competitor analysis from reputable sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
