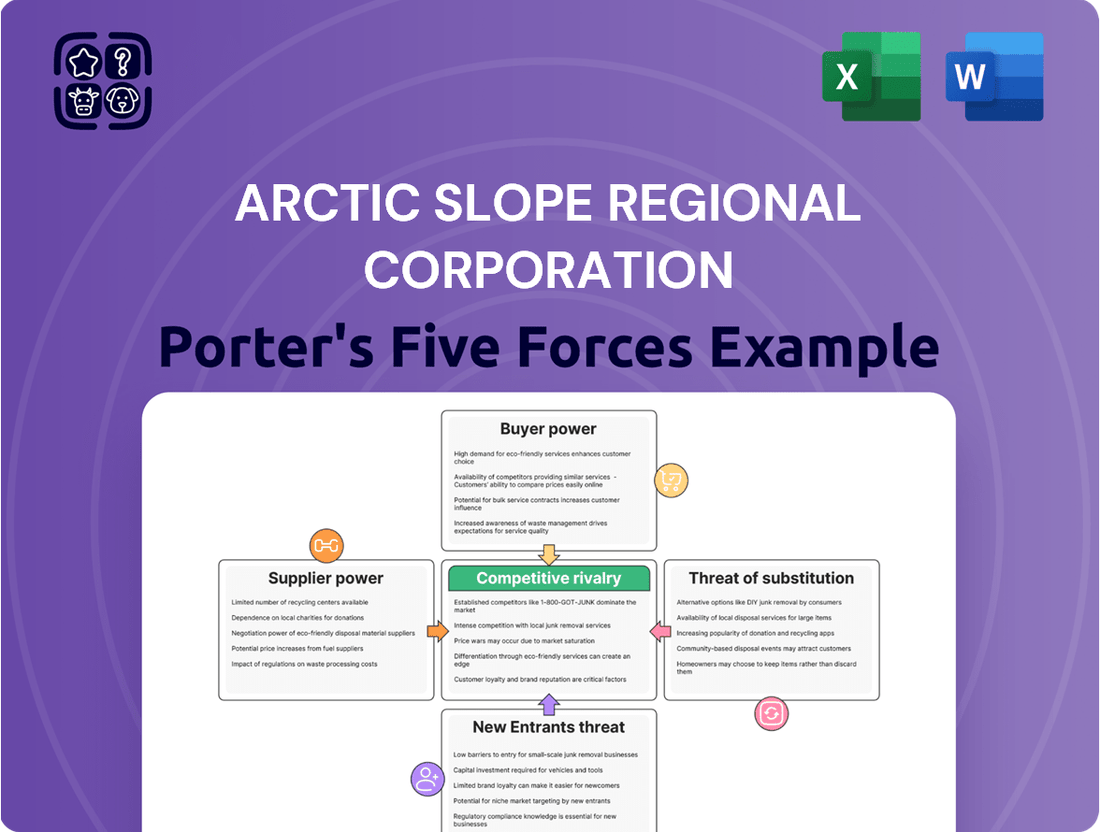
Arctic Slope Regional Corporation Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Arctic Slope Regional Corporation Bundle
Arctic Slope Regional Corporation navigates a unique landscape, facing moderate threats from new entrants and substitutes due to its specialized operational environment. Buyer power is somewhat limited by the essential nature of its services, while supplier power is influenced by the availability of specialized resources and skilled labor.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Arctic Slope Regional Corporation’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Arctic Slope Regional Corporation (ASRC) navigates industries like energy services and government contracting, often demanding highly specialized equipment and skilled labor. This reliance on niche resources grants suppliers significant leverage, particularly when ASRC faces high switching costs or limited alternative providers for these critical inputs.
The Arctic Slope Regional Corporation (ASRC) faces significant supplier bargaining power due to geographic constraints. Operating in the remote and challenging Arctic environment makes logistics and transportation exceptionally complex and expensive. This difficulty in accessing and moving goods means that suppliers capable of consistently delivering to these isolated areas, particularly those with existing Alaskan supply chains, gain considerable leverage because ASRC's choices for alternative providers are limited.
Arctic Slope Regional Corporation (ASRC) faces significant supplier bargaining power when those suppliers possess specialized regulatory and environmental compliance expertise crucial for Alaskan operations. Given the rigorous environmental standards in Alaska, particularly for resource extraction and infrastructure projects, companies that can reliably manage permitting and compliance hold a distinct advantage. For instance, suppliers demonstrating a strong track record in navigating the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) or specific state-level environmental reviews can command higher prices or more favorable terms, as ASRC's ability to substitute them with less experienced providers is limited.
Limited Number of Qualified Suppliers
The Arctic Slope Regional Corporation (ASRC) might encounter a limited pool of qualified suppliers in highly specialized sectors crucial to its operations. This scarcity directly amplifies the bargaining power of these few suppliers. Finding alternative vendors who can meet ASRC's stringent technical, safety, and operational benchmarks becomes a significant hurdle, making it difficult to switch or negotiate favorable terms.
For instance, in the realm of advanced oil and gas extraction technologies or specialized environmental remediation services, the number of companies possessing the requisite expertise and certifications can be exceptionally low. This limited supply base means suppliers can often dictate terms, pricing, and delivery schedules, impacting ASRC's cost structure and project timelines. In 2023, the global market for specialized oilfield services saw price increases averaging 8-12% due to high demand and a constrained supply of skilled labor and advanced equipment.
- Limited Supplier Pool: In specialized industries, fewer than five qualified suppliers may exist capable of meeting ASRC's demanding specifications.
- Increased Supplier Leverage: This scarcity grants suppliers significant pricing power and control over contract terms.
- High Switching Costs: The difficulty in finding and vetting new suppliers with comparable capabilities raises the cost and time associated with changing vendors.
- Impact on ASRC: ASRC may face higher input costs and potential project delays if key suppliers exert their bargaining power.
Proprietary Technology or Services
When suppliers hold proprietary technology or unique service offerings vital to Arctic Slope Regional Corporation's (ASRC) operations, their bargaining power increases substantially. If ASRC cannot easily replicate or substitute these offerings, it faces potential disruptions and elevated costs.
For instance, if a key technology provider for ASRC's resource extraction or infrastructure development projects holds patents or exclusive licenses, they can command higher prices. This situation was evident in the energy sector in 2024, where specialized drilling equipment manufacturers with advanced, proprietary techniques saw increased leverage due to demand for efficient extraction methods.
- Proprietary Advantage: Suppliers with unique technological capabilities or exclusive service contracts gain a significant edge.
- High Switching Costs: ASRC would incur substantial expenses or operational delays if it tried to develop these capabilities in-house or find alternatives.
- Market Dynamics (2024 Example): In 2024, specialized technology providers in sectors relevant to ASRC, like advanced materials or data analytics for resource management, demonstrated increased pricing power due to their unique offerings.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Arctic Slope Regional Corporation (ASRC) is significantly influenced by the limited availability of specialized services and materials, particularly within the challenging Arctic environment. This scarcity, coupled with high switching costs for ASRC, allows suppliers to exert considerable leverage on pricing and terms.
Suppliers who possess unique technologies or proprietary processes, essential for ASRC's operations in sectors like energy or government contracting, hold a distinct advantage. For example, in 2024, companies offering advanced seismic data processing for oil exploration in remote regions could command premium pricing due to their specialized expertise and the difficulty ASRC faced in finding comparable alternatives.
| Factor | ASRC Impact | Supplier Leverage |
| Geographic Isolation | Increased logistics costs & limited alternatives | Higher pricing power for Arctic-capable suppliers |
| Specialized Expertise (e.g., environmental compliance) | Difficulty in finding qualified replacements | Ability to dictate terms and pricing |
| Proprietary Technology | High costs/delays for in-house development or substitution | Significant pricing control and favorable contract terms |
| Limited Supplier Pool (2024 Data) | Potential for fewer than 5 qualified vendors in niche areas | Amplified pricing power and negotiation control |
What is included in the product
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting the Arctic Slope Regional Corporation, revealing the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, and the barriers to entry within its operational sectors.
A clear, one-sheet summary of all five forces—perfect for quick decision-making regarding the Arctic Slope Regional Corporation's competitive landscape.
Instantly understand strategic pressure with a powerful spider/radar chart visualizing the Arctic Slope Regional Corporation's Porter's Five Forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Arctic Slope Regional Corporation (ASRC) operates within a landscape where government entities frequently act as significant customers. This dynamic grants these agencies considerable bargaining power, particularly given their substantial contract volumes and standardized procurement procedures. For instance, ASRC Federal, a subsidiary, has secured contracts with agencies like the Defense Logistics Agency (DLA).
The bargaining power of customers for Arctic Slope Regional Corporation (ASRC) can be significant in certain segments, particularly where a few major players dominate. For instance, in the energy services and resource development sectors on Alaska's North Slope, ASRC's client roster may include a limited number of large oil and gas companies or government entities. This concentration means these key customers can exert considerable influence during contract negotiations, potentially impacting pricing and terms.
While long-term contracts can offer stability for Arctic Slope Regional Corporation (ASRC), they can also empower customers. If these agreements include provisions for price adjustments or performance reviews, customers gain leverage, potentially impacting ASRC's profitability. For instance, if ASRC's operating costs rise unexpectedly, customers with such clauses could negotiate lower prices, diminishing ASRC's margins.
Customer's Ability to Self-Perform or Integrate Backward
For certain services, especially in sectors like construction or specialized industrial support, major clients of Arctic Slope Regional Corporation (ASRC) could explore developing their own internal capabilities or integrating backward into the supply chain. This possibility of self-performance acts as a significant lever for customer bargaining power.
ASRC must therefore consistently demonstrate superior cost-effectiveness and operational efficiency compared to any potential in-house alternative a large customer might consider. For instance, if a significant client in the oil and gas services sector, a key market for ASRC, were to evaluate the cost of bringing certain specialized maintenance or logistical services in-house, ASRC’s pricing and service delivery would be directly benchmarked against this internal cost. This pressure ensures ASRC remains competitive and responsive to client needs.
- Potential for In-House Development: Large industrial clients may possess the capital and technical expertise to develop their own service capabilities, reducing reliance on external providers like ASRC.
- Backward Integration Threat: Customers could acquire or develop the necessary assets and personnel to perform services currently offered by ASRC, thereby capturing that portion of the value chain.
- Cost Benchmarking: The threat of self-performance forces ASRC to maintain competitive pricing and operational efficiency, as clients will compare ASRC's costs against their potential internal costs.
- ASRC's Competitive Imperative: To counter this, ASRC must continually invest in technology, training, and process optimization to offer services that are demonstrably more efficient and cost-effective than in-house alternatives.
Price Sensitivity in Competitive Markets
In sectors where Arctic Slope Regional Corporation (ASRC) operates, particularly those with less product differentiation, customers can exhibit significant price sensitivity. This dynamic compels ASRC to engage in price-based competition, which inherently amplifies customer leverage.
For instance, in government contracting, a core ASRC business, bids are often heavily scrutinized for cost-effectiveness. A 2023 report highlighted that in federal IT services, price was a deciding factor in over 60% of contract awards where multiple vendors competed. This illustrates how customer focus on price can directly impact ASRC's profitability and market position.
- Price Sensitivity Impact: Customers' focus on lower prices can reduce profit margins for ASRC.
- Competitive Contracting: In bidding processes, cost often outweighs other factors, empowering buyers.
- Differentiation Challenge: Lack of unique product features makes customers more likely to switch based on price.
The bargaining power of customers for Arctic Slope Regional Corporation (ASRC) is notably strong in segments where a few large entities, such as government agencies or major energy companies, represent a significant portion of its client base. These substantial clients can leverage their purchasing volume and the potential for self-sufficiency to negotiate favorable terms. For example, ASRC Federal's contracts with the Defense Logistics Agency (DLA) highlight the influence government entities wield due to their procurement scale.
| Customer Segment | Key Leverage Points | Impact on ASRC |
|---|---|---|
| Government Agencies (e.g., DLA) | Large contract volumes, standardized procurement, potential for insourcing | Price pressure, stringent contract terms, need for competitive bidding |
| Major Oil & Gas Companies (North Slope) | Concentrated market, potential for backward integration, price sensitivity | Negotiating power on service pricing and contract duration, margin compression |
| Industrial Services Clients | Threat of developing in-house capabilities, cost benchmarking | Constant pressure to improve efficiency and cost-effectiveness, risk of losing business to insourcing |
What You See Is What You Get
Arctic Slope Regional Corporation Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces analysis of the Arctic Slope Regional Corporation, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic positioning within its industry. The document you see here is precisely what you will receive upon purchase, offering an in-depth examination of buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, threat of substitutes, and industry rivalry. This exact, professionally formatted analysis is ready for immediate download and use, ensuring you get the full, uncompromised insights you need.
Rivalry Among Competitors
ASRC's broad business scope, encompassing energy services, government contracting, construction, and resource development, naturally places it in a position of facing diverse competitive pressures. This means the intensity of rivalry varies significantly depending on the specific industry segment. For instance, in the energy services sector, ASRC might compete with established global oilfield service providers, while its government contracting arm contends with specialized defense and technology firms.
This diversification, while a strength in risk management, also necessitates ASRC navigating multiple competitive arenas simultaneously. For example, in 2024, the energy services market saw significant consolidation, increasing rivalry among remaining players. Simultaneously, the government contracting landscape continues to be highly competitive, with a strong emphasis on technological innovation and cost-efficiency, areas where ASRC must consistently prove its mettle against a wide array of specialized competitors.
Arctic Slope Regional Corporation (ASRC) faces significant competition from other Alaska Native Corporations (ANCs). These ANCs, much like ASRC, leverage specific preferences within federal contracting, particularly through the Small Business Administration's (SBA) 8(a) program. This creates a concentrated competitive landscape within Alaska, where ANCs frequently compete for the same government contracts and natural resource development projects.
For instance, in 2023, ANCs collectively secured a substantial portion of federal contracts designated for small and disadvantaged businesses, highlighting the intensity of this rivalry. ASRC's ability to secure these opportunities is directly influenced by the success and strategic positioning of other ANCs vying for similar government work and land use agreements.
The government contracting arena is intensely competitive. Arctic Slope Regional Corporation's subsidiary, ASRC Federal, faces a crowded field of both large, established players and agile small businesses all pursuing the same federal contracts. This dynamic is evident in the bidding processes for significant awards, such as those from the Defense Logistics Agency (DLA).
For instance, in fiscal year 2023, the DLA awarded billions in contracts, with many of these opportunities being highly contested. ASRC Federal’s success in securing a portion of these contracts, like the recent $300 million IT support services contract from the DLA, underscores the need for continuous competitive positioning against numerous other bidders.
Challenges in Arctic Construction and Resource Development
Competitive rivalry in Arctic construction and resource development is fierce, driven by the extreme operational hurdles. High material costs, a scarcity of skilled labor, and intricate logistical networks significantly narrow the field of capable companies, thus amplifying the competition among those that can operate effectively. ASRC Construction, for instance, navigates this demanding landscape, vying for critical projects such as infrastructure repairs following natural disasters.
The limited number of companies equipped to handle the unique demands of Arctic operations means that competition for contracts is often intense. These firms must contend with factors like permafrost instability and extreme weather, which drive up project costs and complexity. For example, in 2023, the average cost for Arctic infrastructure projects saw a notable increase compared to similar projects in more temperate regions, reflecting these inherent challenges.
- High Operational Costs: Arctic projects face elevated expenses due to transportation, specialized equipment, and extreme weather adaptation.
- Limited Pool of Competitors: The stringent requirements for operating in the Arctic restrict the number of firms capable of undertaking major construction and resource development.
- Project Scarcity and Demand: Competition intensifies for the limited number of available projects, particularly those involving essential infrastructure upgrades or resource extraction.
Market Growth and Economic Conditions in Alaska
The economic landscape of Alaska significantly shapes the competitive intensity within its industries. While federal infrastructure investments and the vital oil and gas sector present growth avenues, a constrained labor pool and volatile energy prices intensify the struggle for resources and talent among businesses.
For instance, in 2024, Alaska's unemployment rate hovered around 3.5%, a figure that, while low, signifies a competitive environment for attracting and retaining skilled workers. This scarcity can force companies to offer more attractive compensation and benefits, thereby increasing operating costs and potentially leading to more aggressive bidding on contracts.
- Federal Infrastructure Spending: Alaska is slated to receive substantial federal funding for infrastructure projects, creating opportunities but also drawing in a broader range of competitors.
- Oil and Gas Activity: Fluctuations in global energy prices directly impact the profitability and investment in Alaska's oil and gas sector, influencing the pace of development and the intensity of competition for exploration and production rights.
- Labor Market Constraints: A persistently tight labor market in Alaska means companies often face heightened competition for qualified personnel, impacting project timelines and operational efficiency.
- Resource Competition: The limited availability of certain resources, coupled with increased demand from various sectors, can escalate competition among firms vying for access and supply.
ASRC faces intense rivalry across its diverse business segments, particularly in government contracting and Arctic construction. The federal contracting space sees ASRC Federal competing with a broad array of large and small businesses for significant awards, as evidenced by the billions in contracts awarded by agencies like the DLA in 2023. In Arctic construction, the high operational costs and limited pool of qualified firms amplify competition for essential infrastructure projects.
The competitive landscape is further shaped by other Alaska Native Corporations, which frequently vie for the same federal contracts and resource development opportunities. This internal competition among ANCs was highlighted in 2023 when they collectively secured a substantial share of small and disadvantaged business federal contracts. Alaska's tight labor market, with an unemployment rate around 3.5% in 2024, also intensifies rivalry for skilled personnel, impacting project costs and efficiency.
| Industry Segment | Key Competitors | Competitive Dynamics | 2023/2024 Data Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| Government Contracting | Large established firms, agile small businesses, other ANCs | High competition for federal awards, emphasis on innovation and cost-efficiency | DLA awarded billions in contracts in FY23; ANCs secured substantial share of SBA 8(a) contracts in 2023. |
| Arctic Construction | Specialized engineering and construction firms | Intense rivalry due to high operational costs, limited skilled labor, and project scarcity | Average cost for Arctic infrastructure projects increased in 2023 due to inherent challenges. |
| Energy Services | Global oilfield service providers | Consolidation in 2024 increased rivalry among remaining players | Market saw significant consolidation in 2024. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Arctic Slope Regional Corporation (ASRC), with its significant stake in energy services and resource development, faces a growing threat from alternative energy sources. The global momentum towards renewables like solar and wind power, driven by climate concerns and technological advancements, could gradually erode the long-term demand for traditional fossil fuel extraction and related services, impacting ASRC's core business segments.
Despite Alaska's continued reliance on oil and gas, as evidenced by oil production remaining a key component of the state's revenue, the worldwide transition to cleaner energy is undeniable. For instance, global renewable energy capacity additions reached record levels in 2023, with solar photovoltaic alone accounting for a substantial portion, signaling a potential shift away from fossil fuel dependency that could affect industries like ASRC's.
Customers, especially large entities like government agencies or major corporations, might choose to build their own internal teams for services ASRC offers, such as facility management or specialized construction. This trend directly impacts ASRC by potentially decreasing the need for its outsourced expertise.
For instance, a significant government contract for base operations could be brought in-house if the agency deems it more cost-effective or strategically advantageous, thereby eliminating a revenue stream for ASRC.
Technological advancements pose a significant threat of substitution for Arctic Slope Regional Corporation (ASRC). Emerging technologies in areas like remote sensing, drone-based surveying, and advanced materials could offer more efficient and cost-effective alternatives to traditional methods ASRC employs, especially in the demanding Arctic climate. For example, innovations in autonomous drilling or renewable energy solutions might reduce reliance on services ASRC currently provides.
Non-Traditional Construction Methods
The rise of non-traditional construction methods presents a significant threat of substitutes for ASRC Construction. Innovations like modular construction and off-site prefabrication can offer faster build times and potentially lower labor costs compared to traditional on-site building. For instance, the global modular construction market was valued at approximately $100 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow substantially, indicating a strong shift towards these alternatives.
These alternative methods can bypass some of the logistical challenges and weather dependencies inherent in Arctic construction, a key operating environment for ASRC. The increasing adoption of these techniques across various project types, from residential to commercial, means clients might opt for these more efficient or cost-effective solutions, thereby impacting demand for ASRC's conventional construction services.
- Modular Construction: Offers faster project completion and reduced on-site labor requirements.
- Off-Site Fabrication: Enhances quality control and minimizes weather-related delays, a critical factor in Arctic environments.
- 3D Printing in Construction: Emerging technologies promise further cost reductions and design flexibility, posing a long-term threat.
- Pre-engineered Building Systems: Provide standardized, efficient solutions that can compete on cost and speed.
Shifts in Government Spending Priorities
A significant portion of Arctic Slope Regional Corporation's (ASRC) revenue is derived from government contracts. Shifts in federal or state spending priorities could introduce substitutes for ASRC's current service offerings. For example, if government funding moves away from infrastructure development or resource management, areas where ASRC has strong contract bases, it could impact their revenue streams.
This redirection of funds might favor different types of contractors or entirely new programs that don't align with ASRC's core competencies. In 2023, federal spending on defense and infrastructure remained robust, but projections for 2024 indicate potential adjustments based on evolving geopolitical landscapes and domestic policy goals.
- Government Contract Dependence: ASRC's reliance on government contracts makes it vulnerable to changes in public spending.
- Shifting Priorities: A move in government focus away from ASRC's service areas creates substitute opportunities for other entities.
- 2024 Budgetary Considerations: Anticipated changes in federal budgets for 2024 could directly affect contract availability in ASRC's sectors.
The threat of substitutes for Arctic Slope Regional Corporation (ASRC) is multifaceted, encompassing alternative energy sources, evolving construction methods, and shifts in government spending priorities. The global push towards renewable energy, with record capacity additions in 2023, directly challenges ASRC's reliance on fossil fuel-related services. Simultaneously, advancements in modular construction, a market valued around $100 billion in 2023, offer clients more efficient alternatives to traditional building practices, particularly relevant in ASRC's Arctic operating environment.
| Threat of Substitute | Impact on ASRC | Supporting Data/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy Sources | Reduces demand for fossil fuel extraction and services. | Global renewable capacity additions hit record levels in 2023. |
| Modular & Off-site Construction | Competes with traditional construction services on speed and cost. | Global modular construction market valued at $100 billion in 2023. |
| In-house Service Provision | Decreases need for outsourced expertise. | Potential for government agencies to internalize operations. |
| Technological Advancements | Offers more efficient alternatives to current methods. | Innovations in autonomous drilling and remote sensing. |
Entrants Threaten
The threat of new entrants for Arctic Slope Regional Corporation (ASRC) is significantly mitigated by high capital requirements. Industries where ASRC is active, such as energy services, large-scale construction, and resource development, demand massive upfront investments in specialized equipment, infrastructure, and advanced technology. For instance, the oil and gas sector, a key area for ASRC, often sees exploration and production projects costing billions of dollars. This financial barrier effectively deters many potential new competitors from entering the market.
Operating in Alaska's North Slope, a region rich in natural resources and ecologically sensitive, presents significant regulatory challenges for new entrants. These include navigating complex environmental laws and securing numerous permits, which can be both time-consuming and costly.
For instance, the permitting process for oil and gas exploration in Alaska, a key industry on the North Slope, can take years and involve multiple federal, state, and local agencies. This extensive oversight, designed to protect the unique Arctic environment, acts as a substantial barrier to entry.
The Arctic Slope Regional Corporation (ASRC) operates in an environment where specialized labor is a significant barrier to new entrants. The extreme conditions of the Arctic demand a workforce possessing unique skills in cold-weather operations, remote logistics, and specialized technical fields relevant to industries like oil and gas or resource extraction. Finding individuals with this precise combination of experience is challenging.
The scarcity of such highly skilled labor within Alaska itself presents a considerable hurdle for any new company aiming to compete. For instance, as of early 2024, Alaska's overall labor force participation rate hovered around 63%, and the availability of workers with proven Arctic operational expertise is even more constrained, making recruitment a costly and time-intensive process for newcomers.
Established Relationships and Local Knowledge
ASRC's deep historical presence and extensive local knowledge in the Arctic Slope region present a significant barrier to new entrants. This embeddedness, cultivated over decades, grants ASRC an unparalleled understanding of the unique operational, environmental, and cultural nuances of the area. For instance, ASRC's subsidiaries like ASRC Energy Services have been instrumental in major North Slope energy projects, leveraging this local expertise.
New companies would struggle to replicate ASRC's established relationships with local Inupiat communities and government bodies. These relationships are crucial for navigating regulatory landscapes, securing permits, and fostering community support, all vital for successful operations in this sensitive environment. ASRC's commitment to local hiring and development, a cornerstone of its operations, further solidifies these ties.
- Deep Local Expertise: ASRC's decades of experience on the North Slope provide an intimate understanding of the region's challenges and opportunities, a critical advantage over newcomers.
- Community and Government Relations: Strong, long-standing relationships with local communities and regulatory agencies are difficult and time-consuming for new entrants to build.
- Operational Integration: ASRC's integrated approach to resource development, often involving multiple subsidiaries, creates efficiencies that are hard for standalone new entrants to match.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve
Existing players like Arctic Slope Regional Corporation (ASRC) leverage significant economies of scale across their diverse business segments, from energy and construction to natural resources. For instance, ASRC's substantial presence in the oil and gas sector allows for bulk purchasing and optimized operational logistics, driving down per-unit costs. This scale translates into a competitive edge that is difficult for newcomers to replicate.
Furthermore, ASRC benefits from an established experience curve, meaning they have honed their processes and developed deep operational expertise over years of activity. This accumulated knowledge allows for greater efficiency, better risk management, and quicker adaptation to market changes. New entrants would face substantial hurdles in matching this level of operational proficiency and cost-effectiveness, requiring considerable time and capital investment to bridge the gap.
- Economies of Scale: ASRC's large operational footprint enables cost advantages through bulk purchasing and optimized resource allocation.
- Experience Curve: Years of operation have endowed ASRC with refined processes and deep industry knowledge, enhancing efficiency.
- Barriers to Entry: New entrants would need substantial capital and time to achieve comparable cost efficiencies and operational expertise.
- Competitive Disadvantage: Without these established advantages, new companies would operate at a significant cost disadvantage compared to ASRC.
The threat of new entrants for Arctic Slope Regional Corporation (ASRC) is substantially low due to immense capital requirements in its core industries, such as energy services and resource development. For example, initiating an oil and gas exploration project in Alaska can easily cost billions of dollars, a prohibitive sum for most potential competitors. This financial barrier, coupled with stringent regulatory hurdles and the need for specialized Arctic operational expertise, significantly limits the influx of new companies into ASRC's operating environment.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example for ASRC |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment needed for infrastructure, equipment, and technology. | Oil and gas exploration projects costing billions. |
| Regulatory Hurdles | Complex environmental laws, permitting processes, and compliance requirements. | Years-long permitting for Arctic oil exploration, requiring multiple agency approvals. |
| Specialized Labor | Scarcity of skilled workers with experience in extreme cold-weather operations and remote logistics. | Alaska's limited labor pool with proven Arctic operational expertise, making recruitment costly. |
| Established Relationships | Deeply ingrained ties with local communities and government bodies. | ASRC's long-standing partnerships critical for navigating regulations and securing permits. |
| Economies of Scale & Experience Curve | Cost advantages from large-scale operations and honed processes from years of experience. | ASRC's bulk purchasing power and optimized logistics in the energy sector. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Arctic Slope Regional Corporation is built upon a foundation of diverse data sources, including the corporation's own annual reports and investor relations materials, alongside industry-specific publications and government economic data relevant to the Arctic region.
We supplement these primary sources with insights from market research databases and reports from entities tracking the energy and resource sectors, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape and potential threats.
