Asplundh Tree Expert Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Asplundh Tree Expert Bundle
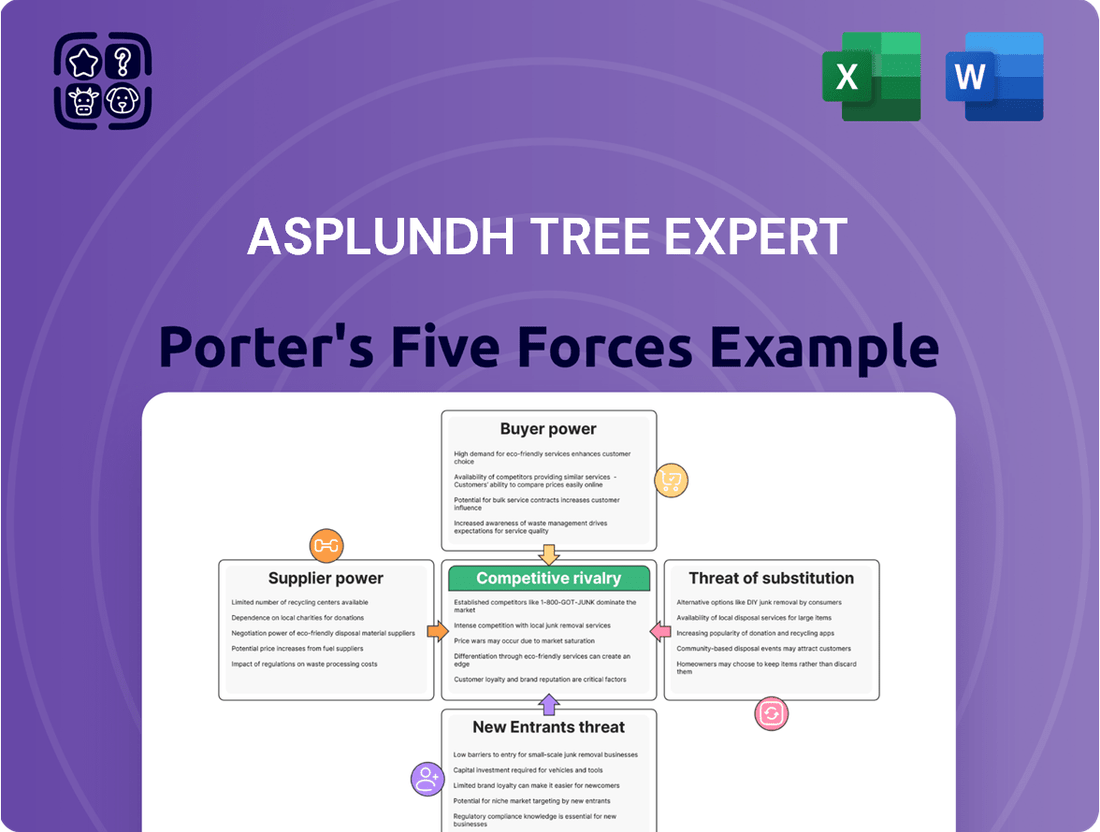
Asplundh Tree Expert navigates a landscape shaped by intense rivalry and significant buyer power, while the threat of new entrants and substitutes presents notable challenges. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for any stakeholder in the utility vegetation management sector.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Asplundh Tree Expert’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Asplundh Tree Expert relies heavily on specialized equipment, from heavy-duty trucks and aerial lifts to advanced cutting tools and potentially vegetation management software and drone technology. The bargaining power of suppliers for these highly specialized or proprietary items can be significant if there are few alternative providers.
The market for advanced vegetation management technology is expanding, with North America's equipment sector alone projected to exceed $2.3 billion by 2025. This growth in specialized technology, including AI and remote sensing, empowers suppliers in this niche, potentially increasing their leverage over buyers like Asplundh.
The bargaining power of skilled labor, particularly arborists and utility line personnel, is a significant factor for Asplundh. The demand for these specialized roles often outstrips supply, especially given the rigorous training and safety protocols required. In 2024, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projected continued demand for tree trimmers and pruners, highlighting a sector where skilled individuals can command better terms.
Labor shortages within the green industry and utility sectors directly empower these skilled workers. Companies like Asplundh must compete for talent, which can lead to increased wages and benefits. This dynamic gives experienced and certified professionals greater leverage in negotiating their employment conditions, impacting Asplundh's operational costs and efficiency.
Asplundh Tree Expert relies heavily on fuel for its vast fleet, making it susceptible to price swings. In 2024, the industrial vegetation management sector saw herbicides represent a substantial portion of the North American market, a key input for Asplundh. While these are largely commodities, the sheer volume Asplundh purchases does grant suppliers a degree of leverage.
Acquired Companies and Niche Service Providers
Asplundh's strategic acquisitions of companies in related fields, like electrical testing and substation infrastructure, can temporarily shift bargaining power. Prior to full integration, these niche providers, such as the recently acquired Voltyx for apparatus testing and engineering, or Bobcat Power for electrical construction, may leverage their specialized skills and established client bases.
This initial leverage is often a result of unique expertise or proprietary technologies that Asplundh seeks to incorporate. For instance, Voltyx's specialized testing capabilities could have given it an edge in negotiations before becoming fully integrated into Asplundh's broader service offerings.
- Acquisition Strategy: Asplundh targets companies in adjacent sectors to expand its service portfolio.
- Niche Provider Leverage: Acquired niche firms may initially possess bargaining power due to specialized skills or client relationships.
- Recent Examples: Voltyx (apparatus testing) and Bobcat Power (electrical construction) are recent acquisitions illustrating this strategy.
Regulatory Compliance Solutions
The bargaining power of suppliers in the regulatory compliance solutions sector for Asplundh Tree Expert is significantly influenced by the growing complexity of environmental and safety regulations. Suppliers providing specialized software for vegetation management, data analytics, and compliance reporting are gaining leverage. For instance, utilities are facing increased pressure to adhere to standards like the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) Transmission Vegetation Management reliability standard, which was updated to enhance grid resilience. This necessitates advanced technological solutions that suppliers offer, making them more indispensable.
This trend is amplified by the potential for substantial penalties for non-compliance. Utilities are increasingly investing in integrated systems that streamline compliance processes and mitigate risks. Such systems often come from specialized vendors, consolidating their negotiating position. For example, the market for utility vegetation management software saw significant growth, with companies reporting increased demand for features that ensure adherence to evolving regulatory frameworks. This demand translates directly into stronger bargaining power for suppliers of these critical solutions.
- Increased Regulatory Scrutiny: Utilities must comply with evolving standards, such as NERC's Transmission Vegetation Management reliability standard, boosting the importance of compliance solution providers.
- Demand for Specialized Software: Solutions for data management, risk assessment, and real-time insights are crucial for utilities to avoid fines and disruptions.
- Strategic Importance of Vendors: Suppliers offering integrated compliance and vegetation management software gain leverage due to the critical nature of their offerings for utility operations.
- Financial Implications of Non-Compliance: The high cost of regulatory fines and service interruptions incentivizes utilities to invest in dependable compliance solutions, strengthening supplier positions.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Asplundh Tree Expert stems from specialized equipment, skilled labor, and essential inputs like fuel and herbicides. Suppliers of advanced vegetation management technology and regulatory compliance software hold significant leverage due to the niche nature of their products and the increasing complexity of utility regulations. The demand for skilled arborists and line personnel, often exceeding supply, further empowers labor as a supplier, forcing Asplundh to compete for talent. Even commodity suppliers like fuel providers can exert influence due to the sheer volume Asplundh purchases.
| Supplier Type | Key Inputs/Services | Impact on Asplundh | Example Data/Trend (2024) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Equipment Manufacturers | Aerial lifts, heavy-duty trucks, cutting tools, drones | High leverage if few alternatives exist for proprietary tech. | North American equipment sector projected to exceed $2.3 billion by 2025. |
| Skilled Labor (Arborists, Line Personnel) | Specialized vegetation management expertise | Strong bargaining power due to labor shortages and high demand. | U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projected continued high demand for tree trimmers. |
| Fuel Suppliers | Diesel, gasoline | Moderate leverage due to volume purchases and price volatility. | Industrial fuel costs remain a significant operational expense. |
| Herbicides & Chemicals | Vegetation control agents | Moderate leverage due to commodity nature but volume matters. | Herbicides represent a substantial portion of North American market costs. |
| Regulatory Software Vendors | Compliance tracking, data analytics | High leverage due to critical need for regulatory adherence. | Increased demand for software ensuring adherence to NERC standards. |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Asplundh Tree Expert, examining the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a clear, visual breakdown of Asplundh's industry landscape.
Customers Bargaining Power
Asplundh's main customers are large utility companies, municipalities, and government bodies. These clients wield considerable bargaining power because they purchase vast amounts of services and often engage in long-term contracts with vegetation management firms.
The sheer volume of services these entities require, coupled with the nature of their long-standing relationships, gives them significant leverage. For instance, utility companies are projected to invest a record $192 billion in infrastructure by 2025, creating substantial opportunities for companies like Asplundh but also highlighting the scale of these customer commitments.
The criticality of Asplundh's services significantly curtails customer bargaining power. Because reliable electricity delivery is essential, customers are unlikely to switch providers if faced with price increases. Vegetation management is a top priority for utility companies, as it's a major cause of power outages, with vegetation-related issues accounting for a substantial percentage of disruptions.
Asplundh frequently enters into long-term contracts with utility companies. These agreements create a predictable revenue stream and foster robust customer relationships, thereby diminishing the immediate bargaining power of these clients once the contract is established due to the costs and disruptions associated with switching providers. For instance, Asplundh secured several multi-year contracts with various state and local entities throughout 2024, solidifying these long-standing partnerships.
Vendor Consolidation and Integrated Solutions
Customers increasingly favor vendors offering integrated solutions, simplifying their procurement and management processes. This preference for a single point of contact can significantly reduce a customer's bargaining power, as they become more reliant on a provider capable of meeting diverse needs.
Asplundh's strategic acquisitions, like its expansion into electrical testing and substation services, directly address this customer demand. By broadening its service portfolio, Asplundh strengthens its position as a comprehensive solutions provider. This integration can lessen a customer's inclination to split their business among multiple vendors, thereby mitigating their ability to negotiate lower prices or more favorable terms based on vendor competition.
- Vendor Consolidation: Customers may consolidate their needs with fewer, more capable vendors.
- Integrated Solutions: A preference for vendors offering a wide range of services reduces the need for multiple suppliers.
- Asplundh's Strategy: Acquisitions in areas like electrical testing enhance Asplundh's integrated offering.
- Reduced Customer Leverage: Becoming a single-source provider diminishes customers' ability to play vendors against each other.
Internal Capabilities and Insourcing
While some major utility companies possess or could develop their own vegetation management teams, this is often not a complete solution. The highly specialized skills, extensive equipment, and rapid response needed for tasks like storm damage cleanup make full insourcing challenging and costly for many utilities. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for a utility to maintain a dedicated in-house vegetation management crew, including training, equipment, and overhead, can significantly exceed the cost of outsourcing to specialized firms.
The bargaining power of customers, particularly large utility companies, is somewhat tempered by the complexity and scale of vegetation management.
- Specialized Expertise: Utilities often lack the deep, specialized knowledge and experience Asplundh brings to vegetation management, especially concerning specific tree species and their impact on infrastructure.
- Scale and Scope: Managing vast networks of power lines requires a level of operational scale and geographic reach that is difficult and expensive for a single utility to replicate internally.
- Emergency Response: The critical need for immediate response during storms and other emergencies means utilities rely on contractors like Asplundh who are equipped and staffed for rapid mobilization.
The bargaining power of Asplundh's customers, primarily large utility companies, is substantial due to their significant purchasing volume and long-term contracts. However, this power is counterbalanced by the specialized nature and critical importance of vegetation management, which is essential for preventing power outages. The trend toward integrated solutions and Asplundh's strategic expansion into broader service offerings further consolidates its position, reducing customers' ability to leverage vendor competition.
| Customer Type | Bargaining Power Factors | Mitigating Factors for Asplundh |
|---|---|---|
| Large Utility Companies | High volume purchasing, long-term contracts | Criticality of services, specialized expertise, integrated solutions |
| Municipalities & Government Bodies | Potential for competitive bidding, budget constraints | Long-term relationships, specialized equipment, regulatory compliance needs |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Asplundh Tree Expert Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. It details Asplundh Tree Expert's competitive landscape through Porter's Five Forces, analyzing threats from new entrants, buyer and supplier power, and substitute products, alongside the intensity of rivalry within the industry. This comprehensive breakdown offers actionable insights for strategic decision-making.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The utility vegetation management sector is quite fragmented, featuring both large national operators and a multitude of smaller, local businesses. Asplundh, a significant entity, contends with substantial competitors such as BrightView Holdings, Lewis Tree Service, and The Davey Tree Expert Company, all vying for market share.
This competitive landscape is evolving, with a noticeable trend toward consolidation as major companies acquire smaller firms. These strategic moves aim to broaden service portfolios and extend operational territories across different regions.
The utility vegetation management sector is booming, with significant growth anticipated. This expansion is fueled by increased infrastructure spending, rising electricity needs, and a stronger emphasis on grid reliability and wildfire mitigation. For instance, the global market was valued at $29.06 billion in 2025 and is projected to reach $46.97 billion by 2034, demonstrating a compound annual growth rate of 5.48%.
This robust growth inherently intensifies competition. As the market expands, more companies are drawn to it, leading to a more crowded landscape. Consequently, existing players and new entrants alike will aggressively compete for a larger piece of this expanding market, potentially driving down prices and increasing marketing efforts.
While many vegetation management firms offer similar core services, differentiation is key. Companies can stand out by specializing in niche areas, embracing advanced technology like drone-based surveying, maintaining impeccable safety records, and demonstrating robust emergency response capabilities. Asplundh's strategic acquisitions, such as its expansion into electrical testing and engineering, bolster its ability to offer integrated infrastructure solutions, a significant differentiator against competitors with more limited service portfolios.
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Standards
The utility vegetation management industry operates under a strict regulatory framework, emphasizing safety and compliance. Companies adept at navigating these rules and consistently meeting high standards, like Asplundh, develop a significant competitive edge. In 2023, the industry saw continued focus on environmental regulations and worker safety protocols, with significant investments made by leading firms in training and equipment to meet these evolving demands.
Non-compliance carries severe financial and reputational risks. For instance, Asplundh entered into a settlement in 2023 with the U.S. Department of Labor concerning wage and hour practices, highlighting the potential costs associated with regulatory oversight. Such incidents underscore the importance of robust compliance programs for maintaining market position and avoiding costly penalties.
- Stringent Safety Protocols: Adherence to OSHA and EPA regulations is paramount, impacting operational costs and efficiency.
- Environmental Compliance: Managing vegetation impacts on ecosystems requires compliance with various environmental protection laws, influencing project planning and execution.
- Labor Law Adherence: Compliance with wage and hour laws, as seen in past settlements, is critical for avoiding significant financial penalties and reputational damage.
- Industry-Specific Certifications: Obtaining and maintaining certifications can signal a company's commitment to quality and compliance, differentiating it from competitors.
Labor Availability and Expertise
The availability of a skilled and trained workforce is a significant competitive differentiator in the tree care industry. Companies that excel in developing comprehensive training programs, fostering employee loyalty, and attracting qualified individuals gain a distinct edge. This is particularly true amidst ongoing labor shortages within the green industry, impacting operational efficiency and safety standards.
For Asplundh Tree Expert, this translates into a need to continuously invest in its workforce. For instance, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics projected a 7% growth in employment for tree trimmers and pruners from 2022 to 2032, indicating a competitive hiring landscape. Companies with strong safety records and career development opportunities are better positioned to attract and retain talent.
- Skilled Workforce Advantage: Companies with robust training and high retention rates can deliver services more efficiently and safely, a crucial factor in a labor-scarce environment.
- Impact of Labor Shortages: Persistent labor shortages in the green industry intensify competition for qualified personnel, directly affecting service delivery capabilities.
- Asplundh's Position: Asplundh's ability to attract and retain skilled arborists and ground workers is a key determinant of its competitive strength and operational capacity.
Competitive rivalry within the utility vegetation management sector is intense due to its fragmented nature and the presence of major players like BrightView Holdings and The Davey Tree Expert Company. This rivalry is amplified by industry consolidation, where larger firms acquire smaller ones to expand service offerings and geographic reach.
The market's robust growth, projected to reach $46.97 billion by 2034, attracts new entrants, further intensifying competition and potentially leading to price pressures. Companies differentiate themselves through specialized services, technological adoption like drone surveying, and strong safety and emergency response capabilities.
Asplundh's strategic acquisitions, such as its move into electrical testing, enhance its ability to offer integrated solutions, a key differentiator. The industry's stringent regulatory environment, focusing on safety and compliance, also shapes competition, with firms like Asplundh leveraging their adherence to standards as a competitive advantage.
The scarcity of skilled labor further fuels competition, making workforce development and retention critical. Asplundh's success hinges on its ability to attract and retain qualified arborists, especially given the projected 7% employment growth for tree trimmers and pruners between 2022 and 2032.
SSubstitutes Threaten
While Asplundh excels in traditional tree trimming, alternative vegetation management methods pose a threat. Chemical treatments, such as herbicides, are a significant substitute, holding a notable share of the North American industrial vegetation management market in 2024.
Biological controls, like using grazing animals, and non-chemical mechanical methods also offer alternatives. The viability of these substitutes hinges on their effectiveness, environmental footprint, and regulatory approval, creating a dynamic competitive landscape for Asplundh.
Technological advancements like AI and remote sensing, including drones and satellites, are indeed changing how utilities monitor vegetation. For instance, the global drone services market was projected to reach $4.47 billion in 2024, with vegetation management being a key application. These tools allow for more precise identification of encroachment and prediction of growth.
However, these innovations primarily enhance the efficiency and targeting of vegetation management services. They don't eliminate the fundamental need for physical clearing and maintenance work. Companies like Asplundh, which specialize in these hands-on services, remain essential for the actual execution of vegetation control, even with improved monitoring capabilities.
Undergrounding utility lines, while a direct substitute for overhead vegetation management, presents a limited threat to Asplundh. This method effectively removes the need for tree trimming in those areas. However, the immense cost and time involved in such infrastructure projects make it a high-capital, long-term solution rather than an immediate, widespread replacement for Asplundh's core services.
Utility Self-Performance
The threat of substitutes for Asplundh's vegetation management services, particularly from utility self-performance, is present but often constrained. While a utility might consider bringing vegetation management in-house, the substantial upfront capital required for specialized equipment and training, coupled with the unpredictable nature of storm-related work, typically makes outsourcing to experienced providers like Asplundh more economically viable and operationally flexible. For instance, the cost of a single high-reach tree trimming bucket truck can exceed $500,000, and maintaining a fleet along with skilled personnel for fluctuating demand presents a significant financial hurdle for many utilities.
Utilities face considerable challenges in establishing and maintaining their own robust vegetation management capabilities. The investment in specialized machinery, ongoing training for arborists and equipment operators, and the need for a flexible workforce to handle peak demand, especially during storm events, are substantial. This complexity often leads utilities to rely on external experts, which can be more cost-effective than absorbing the full operational and capital expenditure of an in-house program.
- Capital Expenditure: Utility self-performance requires significant investment in specialized equipment, with costs for advanced tree trimming vehicles potentially running into hundreds of thousands of dollars each.
- Operational Complexity: Managing a dedicated vegetation management workforce, including recruitment, training, and ensuring safety compliance, adds considerable operational overhead for utilities.
- Demand Fluctuation: The variable demand for vegetation management, particularly the surge during storm restoration, makes it difficult for in-house teams to scale efficiently, often leading to underutilization or capacity shortages.
- Cost-Effectiveness: For many utilities, outsourcing to specialized firms like Asplundh offers a more predictable and often lower overall cost structure compared to the fixed and variable expenses of maintaining an in-house operation.
Reduced Vegetation Growth
While a widespread reduction in vegetation growth due to natural processes is improbable, extreme environmental conditions like prolonged droughts could theoretically decrease the overall need for vegetation management services. For instance, if significant portions of a service area experienced multi-year droughts, the growth rate of trees and brush might slow, potentially impacting demand for routine trimming.
However, the broader impact of climate change presents a counteracting force. The increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events, such as severe storms and hurricanes, directly boost the demand for Asplundh's services. These events necessitate rapid storm restoration efforts and proactive vegetation management to prevent future damage, creating a net increase in business opportunities even amidst localized environmental stresses.
- Climate Change Impact: Increased frequency of extreme weather events drives demand for storm restoration.
- Drought Scenario: Prolonged droughts could theoretically slow vegetation growth, reducing routine maintenance needs.
- Net Effect: The demand for vegetation management is more likely to be driven up by storm-related work than down by reduced growth.
While chemical herbicides are a significant substitute, holding a notable share of the North American industrial vegetation management market in 2024, their effectiveness can be limited by environmental regulations and public perception. Biological controls and non-chemical mechanical methods also present alternatives, but their scalability and cost-effectiveness for large-scale utility operations remain a consideration.
Technological advancements like AI and drone-based monitoring, with the drone services market projected at $4.47 billion in 2024, enhance efficiency but do not replace the need for physical clearing. Undergrounding utility lines is a substitute for overhead vegetation management, but its high capital cost makes it a long-term, limited threat.
Utilities bringing vegetation management in-house face substantial capital expenditure, with specialized vehicles costing upwards of $500,000 each. The operational complexity of managing a dedicated workforce and the demand fluctuations, especially during storms, often make outsourcing to specialists like Asplundh more cost-effective and flexible.
While prolonged droughts could theoretically slow vegetation growth, the increasing frequency of extreme weather events, driven by climate change, significantly boosts demand for storm restoration and proactive vegetation management, creating a net increase in business opportunities.
Entrants Threaten
The utility vegetation management sector demands a significant upfront financial commitment. New companies entering this space must acquire specialized machinery, a large fleet of vehicles, and advanced technology to compete effectively. For instance, Asplundh’s operational scale is underscored by its ownership of over 20,000 vehicles, highlighting the substantial asset base necessary for widespread service delivery.
Asplundh's core services, like utility line clearance and specialized arboriculture, require deep technical knowledge and a proven track record of safety. New companies entering this field must invest heavily in training and equipment to meet industry standards, a significant hurdle.
Asplundh's deep-rooted relationships and multi-year contracts with major utility companies and government bodies present a formidable barrier to new entrants. These long-standing partnerships, built on trust and proven performance, are crucial for critical infrastructure maintenance, making it difficult for newcomers to displace established providers. Asplundh's unwavering focus on line clearance for the utility sector since 1928 underscores their enduring commitment and expertise, further solidifying their position.
Regulatory and Compliance Hurdles
The utility vegetation management sector, where Asplundh Tree Expert operates, is characterized by significant regulatory and compliance hurdles that act as a substantial barrier to new entrants. Navigating the intricate web of federal and state regulations, including those mandated by bodies like the North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC), demands considerable expertise and investment. For instance, compliance with NERC reliability standards, which govern the bulk electric system, requires rigorous operational protocols and reporting, a complex undertaking for any new player.
New entrants would face substantial upfront costs and ongoing expenses to ensure adherence to these evolving compliance standards. This includes meeting stringent environmental protection laws, such as those related to herbicide application and waste disposal, as well as labor laws governing worker safety and training. In 2024, the emphasis on environmental stewardship and worker safety continues to intensify, adding layers of complexity and cost for companies operating in this space.
- Significant investment required for regulatory compliance and certification.
- Complex and evolving federal and state environmental and labor laws.
- NERC reliability standards necessitate advanced operational protocols and reporting.
- High costs associated with obtaining permits and licenses in multiple jurisdictions.
Economies of Scale and Scope
Asplundh's significant advantage lies in its massive economies of scale. This allows them to negotiate better prices on equipment like specialized tree trimming machinery and vehicles, and to spread the high costs of training a large workforce across many projects. For example, in 2023, Asplundh reported revenues exceeding $5 billion, indicative of their operational breadth.
Newcomers face a steep uphill battle to replicate Asplundh's purchasing power and operational efficiency. The sheer volume of business Asplundh handles enables cost reductions per unit that are simply unattainable for smaller, less established firms. This scale is particularly vital for winning large, multi-year contracts with major utility companies, which often require a proven track record and extensive resources.
- Economies of Scale: Asplundh's extensive operational footprint and diverse service offerings (vegetation management, infrastructure services, storm restoration) allow for significant cost advantages in equipment procurement and training.
- Procurement Power: Their large-scale purchasing of specialized equipment and materials translates into lower per-unit costs compared to smaller competitors.
- Operational Efficiency: A vast network of crews and resources enables Asplundh to achieve greater efficiency and faster response times, crucial for securing and retaining large utility contracts.
- Barriers to Entry: The capital investment required to match Asplundh's scale of operations and service breadth presents a substantial barrier for potential new entrants.
The threat of new entrants in the utility vegetation management sector is significantly mitigated by the immense capital requirements and established relationships Asplundh possesses. New companies must overcome substantial financial hurdles, including acquiring a vast fleet of specialized vehicles and equipment, akin to Asplundh's over 20,000-vehicle fleet. Furthermore, securing long-term contracts with major utility providers, built on years of trust and demonstrated safety and expertise, presents a formidable barrier that newcomers struggle to breach.
| Factor | Asplundh's Advantage | Implication for New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | Vast fleet (20,000+ vehicles), specialized machinery, advanced technology. | Requires substantial upfront capital, difficult to match scale. |
| Technical Expertise & Safety Record | Decades of experience in utility line clearance, proven safety protocols. | High investment in training and certification needed to meet industry standards. |
| Customer Relationships | Long-standing, multi-year contracts with major utilities and government bodies. | Difficult to displace established providers without a proven track record. |
| Economies of Scale | Over $5 billion in revenue (2023), enabling significant procurement power and cost efficiencies. | New entrants lack purchasing power, leading to higher per-unit costs. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Asplundh Tree Expert Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings, and insights from trade associations to capture the competitive landscape.
