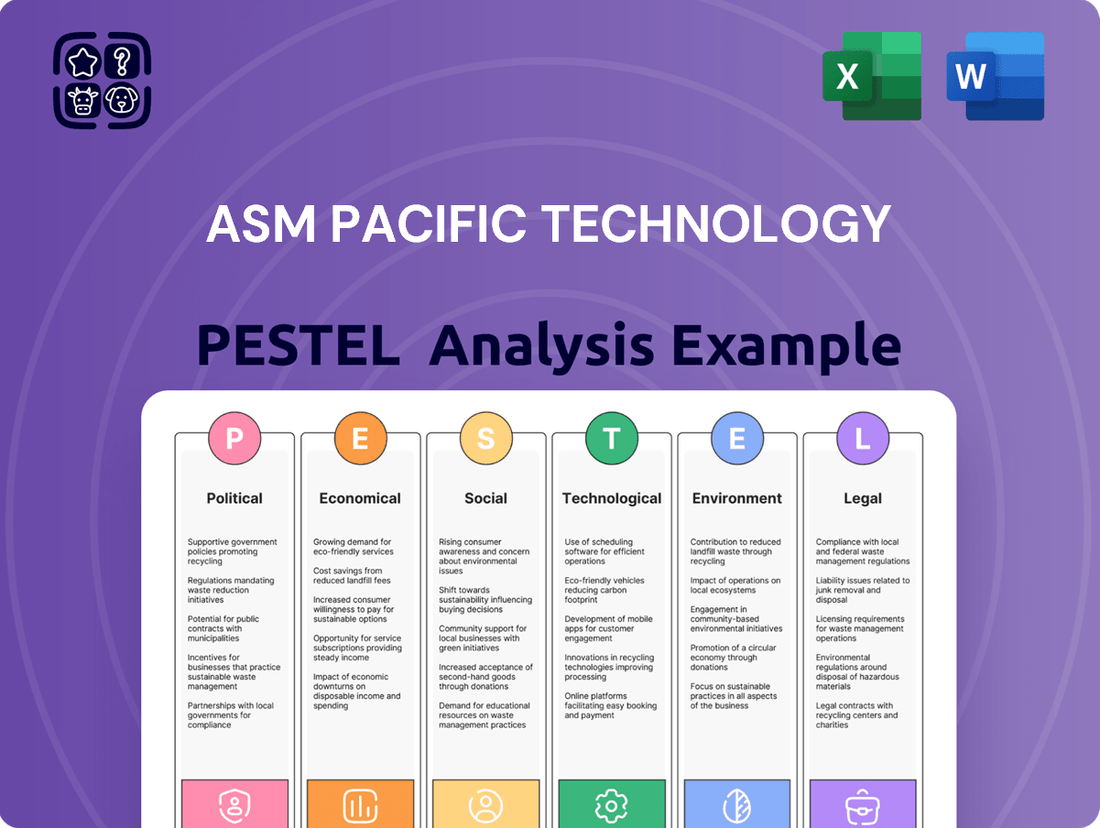
ASM Pacific Technology PESTLE Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
ASM Pacific Technology Bundle
Unlock critical insights into ASM Pacific Technology's operating environment with our comprehensive PESTLE analysis. Understand the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors influencing its strategic direction and market position. Equip yourself with the knowledge to anticipate challenges and capitalize on opportunities.
Gain a competitive edge by dissecting the external forces shaping ASM Pacific Technology's future. Our expertly crafted PESTLE analysis provides actionable intelligence for investors, strategists, and market analysts. Download the full version now to make informed decisions and drive sustainable growth.
Political factors
Geopolitical tensions, especially between the United States and China, continue to reshape the semiconductor landscape, directly affecting companies like ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT). These tensions have led to increased export controls and tariffs on advanced semiconductor technologies, creating significant disruptions in global supply chains and potentially limiting market access for ASMPT's equipment.
In response to these trade policies, there's a growing emphasis on building more regionalized semiconductor supply chains and fostering greater self-reliance in manufacturing capabilities. This shift could present both challenges and opportunities for ASMPT as it navigates evolving market dynamics and customer demands for localized production solutions.
Governments globally are actively promoting domestic semiconductor manufacturing through substantial subsidies and incentives, aiming to bolster national technological sovereignty. For ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT), this creates a dynamic environment. For instance, the US CHIPS and Science Act of 2022 allocated over $52 billion, while the EU Chips Act committed €43 billion to similar goals. These programs can encourage ASMPT to expand its presence in regions offering favorable financial support, potentially influencing its manufacturing footprint and R&D investment strategies.
Governments worldwide are increasingly recognizing semiconductors as critical national security assets, directly influencing defense capabilities and the advancement of military artificial intelligence. This strategic classification means heightened governmental oversight and stricter regulations are becoming the norm for the semiconductor industry.
This trend directly impacts companies like ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT), potentially shaping their business operations and strategic partnerships. For instance, export controls on advanced semiconductor manufacturing equipment, like those implemented by the US and its allies, can restrict ASMPT's access to certain markets or necessitate careful navigation of technology transfer regulations, especially when dealing with sensitive geopolitical regions.
Regional Trade Agreements and Alliances
The evolving landscape of regional trade agreements significantly impacts ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT). For instance, the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP), which includes major economies like Japan, Canada, and Australia, can streamline customs procedures and reduce tariffs for ASMPT's equipment exports to these nations. Conversely, the emergence of new blocs or changes in existing ones, such as potential renegotiations within ASEAN or the expansion of the EU's trade network, could alter ASMPT's cost structures and market entry strategies.
These agreements foster collaboration, aiming to build resilience within specific economic blocs. This can lead to shifts in manufacturing hubs, potentially benefiting or challenging ASMPT's existing supply chain dynamics. For example, incentives offered by governments within trade blocs to encourage local production of advanced manufacturing equipment could influence ASMPT's investment decisions regarding manufacturing facilities. The ongoing focus on supply chain diversification, driven by geopolitical considerations and trade pacts, means ASMPT must remain agile in adapting its global operational footprint.
- CPTPP Impact: Reduced tariffs and simplified customs for ASMPT in key markets like Japan and Canada.
- ASEAN Dynamics: Potential shifts in manufacturing investment due to evolving trade policies within the bloc.
- EU Trade Network: Changes in market access and operational costs influenced by the EU's expanding trade relationships.
- Supply Chain Resilience: Regional agreements can drive manufacturing hub shifts, requiring ASMPT to adapt its supply chain strategy.
Intellectual Property Protection and Enforcement
The political landscape concerning intellectual property (IP) protection and enforcement significantly impacts ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT). Strong IP laws and effective enforcement in ASMPT's key operating and market regions are vital for protecting its substantial investments in research and development, particularly in advanced semiconductor manufacturing equipment. Conversely, lax IP enforcement can expose the company to risks from counterfeit products and unauthorized use of its proprietary technologies, potentially eroding market share and profitability.
For instance, in 2024, the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) reported that while global IP filings continued to rise, the effectiveness of enforcement varied significantly across jurisdictions. ASMPT, with its global presence, must navigate these differing legal frameworks. A robust IP strategy is therefore not just a legal necessity but a critical business enabler for ASMPT.
- Global IP Filings: WIPO data for 2024 indicated continued growth in patent and trademark filings, underscoring the increasing importance of IP globally.
- Enforcement Disparities: The effectiveness of IP enforcement remains a critical concern, with significant variations observed across different countries and regions in 2024.
- R&D Investment Protection: ASMPT's commitment to innovation requires strong political will and legal infrastructure to safeguard its technological advancements.
- Market Integrity: Weak enforcement environments can lead to unfair competition and damage ASMPT's brand reputation and market position.
Governmental support for domestic semiconductor manufacturing, exemplified by initiatives like the US CHIPS Act and the EU Chips Act, is a significant political factor. These policies, with billions allocated for subsidies and incentives, directly influence ASMPT's strategic decisions regarding facility expansion and R&D investments in regions offering favorable financial backing.
Geopolitical tensions, particularly between the US and China, continue to shape the semiconductor industry. Increased export controls and tariffs on advanced technologies create supply chain disruptions and market access limitations for companies like ASMPT, prompting a focus on regionalized supply chains and self-reliance.
The classification of semiconductors as critical national security assets leads to heightened governmental oversight and stricter regulations. Export controls on advanced manufacturing equipment can restrict ASMPT's market access and necessitate careful navigation of technology transfer rules, especially in geopolitically sensitive areas.
Trade agreements, such as the CPTPP, can streamline customs and reduce tariffs for ASMPT's equipment exports. Conversely, evolving trade policies within blocs like ASEAN or changes in the EU's trade network can alter ASMPT's cost structures and market entry strategies, requiring agile adaptation of its global operational footprint.
What is included in the product
This PESTLE analysis provides a comprehensive examination of the external macro-environmental factors impacting ASM Pacific Technology, covering Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Environmental, and Legal dimensions.
It offers actionable insights for strategic decision-making by identifying key trends and potential challenges or opportunities within the company's operating landscape.
Provides a concise version that can be dropped into PowerPoints or used in group planning sessions, offering a clear overview of the external factors impacting ASM Pacific Technology.
Easily shareable summary format ideal for quick alignment across teams or departments, ensuring everyone understands the political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal landscape.
Economic factors
The global semiconductor market is on a robust upward trajectory, with forecasts indicating continued significant growth through 2025 and beyond. This expansion is primarily fueled by surging demand for artificial intelligence (AI) applications, the increasing need for high-performance computing, and the ever-growing automotive electronics sector.
As a key player providing essential solutions for semiconductor and electronics manufacturing, ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT) is well-positioned to capitalize on this expanding market. The company's expertise in advanced manufacturing processes directly aligns with the industry's need for sophisticated equipment to meet the rising demand for these cutting-edge technologies.
Industry analysts project the semiconductor market to reach approximately $700 billion in 2024, with expectations of further growth in 2025, driven by these powerful trends. ASMPT's comprehensive portfolio of solutions, from wafer processing to assembly and packaging, positions it to benefit from increased capital expenditure by chip manufacturers worldwide.
The surging demand for artificial intelligence (AI) and high-performance computing (HPC) is a significant economic tailwind for ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT). This trend directly fuels the need for their advanced packaging solutions, such as Thermo-Compression Bonding (TCB) equipment, which are critical for manufacturing these sophisticated chips.
ASMPT has directly benefited from this economic shift. For instance, in the first half of 2024, the company reported a substantial increase in its advanced packaging business, with orders for TCB equipment reaching record levels. This robust performance underscores a clear link between the growth in AI infrastructure development and ASMPT's revenue streams, demonstrating the economic importance of this sector for the company.
While the surge in AI and High-Performance Computing (HPC) is a strong tailwind for ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT), its broader financial health is susceptible to downturns in other key sectors. For instance, a slowdown in the automotive industry, despite its importance, can directly impact ASMPT's revenue streams, particularly within its Surface Mount Technology (SMT) division.
Consumer electronics, encompassing smartphones and personal computers, also presents a significant area of vulnerability. Weakening demand in these markets, which are crucial for ASMPT's equipment sales, can lead to reduced order volumes and consequently affect the company's overall performance. For example, global smartphone shipments saw a slight decline in early 2024 compared to previous periods, highlighting the sensitivity of ASMPT's business to these consumer-driven trends.
Research and Development Investment
ASMPT's commitment to Research and Development (R&D) remains paramount for its competitive edge in the dynamic semiconductor sector. Continued high investment is crucial for developing next-generation technologies and securing future market share, especially as the industry pushes towards more advanced chip architectures and manufacturing processes. For instance, ASMPT's R&D expenditure reached HKD 1.04 billion in 2023, representing a significant portion of its revenue, underscoring its dedication to innovation.
While R&D fuels innovation and long-term growth, these substantial investments can exert pressure on short-term profitability. The semiconductor industry's rapid pace necessitates continuous spending on new equipment, talent, and materials, directly impacting the bottom line. This strategic allocation of resources, however, is vital for ASMPT to stay ahead of technological curves and meet evolving customer demands.
- ASMPT's R&D spending in 2023 was HKD 1.04 billion.
- High R&D investment is essential for innovation in the fast-evolving semiconductor market.
- These expenses can temporarily affect ASMPT's short-term profitability.
- Continued investment ensures ASMPT maintains its market leadership and capitalizes on future opportunities.
Supply Chain Costs and Disruptions
The semiconductor sector, vital for ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT), continues to grapple with persistent supply chain issues. These include shortages of critical raw materials and ongoing elevated costs, directly impacting production expenses and overall operational efficiency. ASMPT's ability to navigate these challenges hinges on implementing agile and resilient supply chain management strategies to effectively mitigate associated risks.
For instance, the global semiconductor shortage, which began in late 2020 and extended through 2023, saw lead times for certain components stretch to over a year. This situation significantly increased the cost of goods sold for many manufacturers, including those supplying ASMPT. By mid-2024, while some improvements were noted, the industry still reported an average increase in logistics costs of approximately 15-20% compared to pre-pandemic levels, impacting the cost of transporting essential equipment and materials.
- Persistent Raw Material Shortages: Continued scarcity of key materials like silicon wafers and specialized chemicals impacts production volumes.
- Elevated Logistics Costs: Shipping and freight expenses remain higher than historical averages, adding to overall operational expenditure.
- Geopolitical Influences: Trade tensions and regional instability can further exacerbate supply chain vulnerabilities and lead to unexpected cost increases.
- Need for Supply Chain Agility: ASMPT must maintain flexible sourcing and production strategies to adapt to evolving disruptions and cost pressures.
Economic factors significantly shape ASM Pacific Technology's (ASMPT) operational landscape. The robust growth in the global semiconductor market, projected to exceed $700 billion in 2024 and continue expanding into 2025, presents a substantial opportunity. This expansion is largely driven by the escalating demand for artificial intelligence (AI) and high-performance computing (HPC), areas where ASMPT's advanced packaging solutions are critical.
However, ASMPT's performance is also sensitive to economic shifts in consumer electronics and automotive sectors. A slowdown in smartphone shipments, which saw a slight decline in early 2024, can directly impact ASMPT's equipment sales. Furthermore, persistent supply chain challenges, including elevated logistics costs averaging 15-20% higher than pre-pandemic levels in mid-2024, continue to affect operational efficiency and production expenses.
| Economic Driver | Impact on ASMPT | Supporting Data (2024/2025 Projections) |
| Semiconductor Market Growth | Positive Revenue Opportunities | Market size projected to exceed $700 billion in 2024. |
| AI & HPC Demand | Increased demand for advanced packaging solutions (e.g., TCB) | Key growth drivers for ASMPT's advanced packaging business. |
| Consumer Electronics Demand | Potential for reduced equipment orders | Global smartphone shipments showed a slight decline in early 2024. |
| Supply Chain Costs | Increased operational expenses, potential production delays | Logistics costs up 15-20% in mid-2024 compared to pre-pandemic levels. |
Same Document Delivered
ASM Pacific Technology PESTLE Analysis
The preview you see here is the exact ASM Pacific Technology PESTLE Analysis document you’ll receive after purchase, offering a comprehensive overview of the factors impacting the company.
This is a real screenshot of the product you’re buying—delivered exactly as shown, no surprises, providing immediate access to valuable market insights.
The content and structure shown in the preview is the same ASM Pacific Technology PESTLE Analysis document you’ll download after payment, ensuring you get the complete, ready-to-use report.
Sociological factors
The semiconductor industry, a core sector for ASMPT, is grappling with a significant global talent shortage. Reports from 2024 indicate a critical deficit in skilled engineers for chip design and advanced manufacturing processes, impacting companies' ability to innovate and scale production. This scarcity directly affects ASMPT's capacity to develop cutting-edge equipment and maintain its competitive edge.
To counter these challenges, ASMPT must prioritize robust talent acquisition and retention strategies. Focusing on employee development programs and creating an attractive work environment is crucial for securing the specialized expertise needed in areas like advanced packaging and wafer fabrication. The company's success in 2025 and beyond will hinge on its ability to attract and keep top talent in a highly competitive global market.
The manufacturing sector, particularly electronics, is rapidly embracing automation and digital transformation. This shift, driven by advancements like AI and smart factory concepts, is reshaping job roles and skill requirements. For instance, the International Federation of Robotics reported that in 2023, robot installations in the electronics industry saw a significant uptick, highlighting this trend.
ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT) is a key enabler of this transformation, providing the very solutions that facilitate automation. However, this also means ASMPT must continuously invest in upskilling and reskilling its own workforce. By 2024, many manufacturing firms were reporting a growing demand for employees proficient in data analytics and advanced robotics operation, a trend ASMPT must align with to maintain its competitive edge.
Consumers increasingly want electronics that are smaller, smarter, and use less power. This trend is evident in the booming markets for smartphones and wearable technology, which saw global shipments of smartphones alone reach over 1.2 billion units in 2023, according to Statista. This demand for advanced, compact devices directly fuels the need for sophisticated semiconductor packaging and surface mount technology (SMT) solutions that ASMPT provides, pushing innovation in miniaturization and performance.
Ethical Sourcing and Labor Practices
Societal expectations are increasingly pushing companies like ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT) to demonstrate robust ethical sourcing and labor practices. Consumers and investors alike are scrutinizing supply chains, demanding transparency and adherence to human rights and fair labor standards. This heightened awareness means ASMPT must actively ensure its entire value chain, from raw material procurement to final product assembly, aligns with these ethical benchmarks.
The pressure for ethical operations is not just a matter of reputation; it's becoming a business imperative. For instance, in 2024, reports indicated a growing number of consumer boycotts against companies with perceived poor labor practices in their manufacturing sectors. ASMPT's commitment to these principles is therefore crucial for maintaining market trust and access.
- Supply Chain Transparency: ASMPT needs to provide clear visibility into its suppliers' labor conditions and sourcing origins.
- Fair Wage and Working Hours: Ensuring that all workers within its network, including those in outsourced manufacturing, receive fair wages and adhere to reasonable working hours is paramount.
- Prohibition of Forced Labor: Strict policies against any form of forced or child labor must be enforced throughout the entire supply chain.
- Worker Safety and Well-being: Implementing and monitoring safe working environments and promoting the overall well-being of employees are critical components of ethical labor practices.
Corporate Social Responsibility and Community Engagement
ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT) demonstrates a strong commitment to corporate social responsibility, which significantly shapes its public image and appeal. Their focus on diversity, equity, and inclusion, alongside active engagement with local communities, directly impacts their standing as an employer and business partner. This dedication is increasingly vital for stakeholders and aligns perfectly with Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) principles, which are becoming paramount in investment decisions.
ASMPT's investment in community programs and employee well-being is not just altruistic; it's a strategic move that enhances brand loyalty and operational resilience. For instance, their ongoing support for STEM education initiatives in regions where they operate helps build a future talent pipeline and fosters goodwill. This approach is crucial for long-term sustainability and meeting the growing expectations of investors and consumers alike, who are scrutinizing companies' social impact more than ever.
- Diversity and Inclusion: ASMPT aims to foster an inclusive workplace culture, recognizing that a diverse workforce drives innovation and better decision-making.
- Community Investment: The company actively participates in local community development projects, focusing on areas like education and environmental sustainability.
- ESG Alignment: ASMPT's CSR efforts are increasingly integrated with its broader ESG strategy, reflecting a commitment to responsible business practices and long-term value creation.
- Stakeholder Expectations: Meeting evolving stakeholder demands for social responsibility is critical for maintaining ASMPT's reputation and attracting investment.
Societal expectations are increasingly pushing companies like ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT) to demonstrate robust ethical sourcing and labor practices, with consumers and investors scrutinizing supply chains for transparency and adherence to human rights. This heightened awareness means ASMPT must actively ensure its entire value chain aligns with these ethical benchmarks to maintain market trust and access.
ASMPT's commitment to corporate social responsibility, including diversity, equity, and inclusion, significantly shapes its public image and appeal as an employer and business partner. Their active engagement with local communities and investment in STEM education initiatives are strategic moves that enhance brand loyalty and build a future talent pipeline, aligning with growing stakeholder expectations for social impact.
The global talent shortage in the semiconductor industry, particularly for skilled engineers in chip design and advanced manufacturing, directly impacts ASMPT's capacity for innovation and scaling production. This scarcity necessitates robust talent acquisition and retention strategies, focusing on employee development and creating an attractive work environment to secure specialized expertise.
The manufacturing sector's rapid embrace of automation and digital transformation reshapes job roles, increasing demand for employees proficient in data analytics and advanced robotics. ASMPT, as an enabler of this transformation, must continuously invest in upskilling its own workforce to align with these evolving skill requirements and maintain its competitive edge.
| Sociological Factor | Impact on ASMPT | Key Actions/Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Talent Shortage | Hindered innovation and production scaling due to lack of skilled engineers. | Prioritize talent acquisition, retention, employee development, and attractive work environment. |
| Ethical Sourcing & Labor Practices | Risk of reputational damage and market access issues if not addressed. | Ensure supply chain transparency, fair wages, prohibition of forced labor, and worker safety. |
| Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) | Enhances brand loyalty, operational resilience, and stakeholder trust. | Invest in diversity, inclusion, community programs, and align with ESG principles. |
| Automation & Digital Transformation | Increased demand for new skill sets within ASMPT's workforce. | Focus on upskilling and reskilling employees in areas like data analytics and robotics. |
Technological factors
Advanced packaging technologies like 2.5D/3D integration and hybrid bonding are revolutionizing semiconductor performance, and ASMPT is at the forefront of this wave. These sophisticated techniques are vital for powering demanding applications such as artificial intelligence (AI), high-performance computing (HPC), and the burgeoning 5G networks, enabling smaller, faster, and more power-efficient chips.
ASMPT's expertise in these areas, including panel-level packaging, directly addresses the industry's need for continued miniaturization and enhanced functionality. For instance, the global advanced packaging market is projected to reach over $60 billion by 2027, highlighting the immense growth potential and ASMPT's strategic positioning within this lucrative segment.
The semiconductor and electronics manufacturing sectors are increasingly adopting Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML). ASMPT's advanced solutions are designed to harness these technologies to boost production efficiency, refine quality control, and drive automation within intelligent factory environments.
The relentless pursuit of smaller, more potent electronic gadgets is a major technological driver, fueling the demand for miniaturization and sophisticated high-density interconnects. This trend is critical for the future of consumer electronics and advanced computing.
ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT) is strategically positioned to capitalize on this, as their core business revolves around the assembly and packaging equipment essential for creating these intricate, compact components. Their advanced solutions directly enable manufacturers to shrink device footprints while boosting performance.
For instance, the semiconductor industry, a key market for ASMPT, saw significant investment in advanced packaging technologies in 2024, with a projected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 7% for the advanced packaging market through 2028, according to industry analysts. This growth underscores the direct impact of miniaturization trends on ASMPT's business outlook.
Automation and Smart Factory Solutions
The electronics manufacturing sector is rapidly embracing full automation and smart factory concepts. ASMPT's advanced hardware and integrated software solutions are designed to facilitate this transition, offering capabilities in automation, digital transformation, and crucial tools for boosting both production quality and overall efficiency. For instance, ASMPT's intelligent solutions are key enablers for manufacturers aiming to achieve Industry 4.0 standards.
This technological shift is directly impacting operational metrics. Companies leveraging smart factory solutions often report significant improvements, such as a reduction in defect rates by up to 20% and an increase in throughput by as much as 15% in specific production lines. ASMPT's commitment to providing these cutting-edge solutions positions them to capitalize on this growing market demand.
- Smart Factory Adoption: Global smart factory market size was valued at USD 296.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach USD 764.1 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 14.5%.
- ASMPT's Role: ASMPT provides integrated hardware and software to support automation and digital transformation in electronics manufacturing.
- Efficiency Gains: Manufacturers implementing these technologies often see improved production quality and efficiency, with potential reductions in defects and increases in throughput.
Emergence of New Materials and Processes
The electronics manufacturing landscape is being reshaped by advancements in materials and processes. For instance, the growing adoption of gallium nitride (GaN) as an alternative to silicon in power electronics, driven by its superior efficiency and high-frequency capabilities, presents a significant technological shift. ASMPT must ensure its equipment can effectively handle these new materials, which often require different handling and processing parameters compared to traditional silicon wafers.
Innovative manufacturing techniques, such as direct thermal printing for semiconductor packaging, are also emerging. This process offers potential benefits like reduced waste and faster turnaround times. ASMPT's ability to integrate and support such novel processes will be crucial for maintaining its competitive edge in the evolving market, especially as the demand for more compact and efficient electronic components continues to rise.
The global market for advanced semiconductor materials is projected for substantial growth. For example, the GaN market alone was estimated to reach over $2 billion by 2023 and is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate exceeding 30% through 2030, indicating a strong demand for manufacturing solutions that can accommodate these materials.
- Gallium Nitride (GaN) Adoption: GaN is increasingly used in applications requiring high power and high frequency, such as 5G infrastructure and electric vehicles.
- Direct Thermal Printing: This emerging packaging technology promises to streamline manufacturing and reduce material consumption in semiconductor assembly.
- Material Compatibility: ASMPT's equipment needs to be adaptable to the unique physical and chemical properties of next-generation semiconductor materials.
- Process Innovation: Staying ahead requires investment in R&D to support novel manufacturing processes that enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
Technological advancements in semiconductor manufacturing, particularly in advanced packaging like 2.5D/3D integration and hybrid bonding, are critical. ASMPT is positioned to benefit from the global advanced packaging market's projected growth, expected to exceed $60 billion by 2027.
The increasing adoption of AI and Machine Learning in electronics manufacturing is driving demand for ASMPT's intelligent solutions, aimed at enhancing production efficiency and automation in smart factories. The smart factory market itself is projected to reach $764.1 billion by 2030, with a 14.5% CAGR.
Emerging materials like Gallium Nitride (GaN) are transforming power electronics, with the GaN market anticipated to grow at over 30% annually through 2030. ASMPT's adaptability to new materials and processes, such as direct thermal printing, is vital for maintaining its competitive edge.
| Key Technological Trend | Market Projection/Growth | ASMPT Relevance |
| Advanced Packaging (2.5D/3D, Hybrid Bonding) | Global market > $60B by 2027 | Core business, enables miniaturization and performance |
| AI/ML in Manufacturing | Smart Factory Market: $764.1B by 2030 (14.5% CAGR) | Provides intelligent solutions for efficiency and automation |
| New Materials (e.g., GaN) | GaN Market: >30% CAGR through 2030 | Requires adaptable equipment for new material processing |
Legal factors
ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT), a key player in the semiconductor equipment sector, navigates a complex web of international export controls and trade regulations. These rules are particularly stringent for advanced technologies and target specific countries, impacting ASMPT's ability to freely trade its sophisticated machinery globally. For instance, the U.S. Department of Commerce's Bureau of Industry and Security (BIS) continually updates its Entity List and export control classifications, which can directly affect ASMPT's supply chain and customer access.
Failure to adhere to these evolving legal frameworks can result in severe consequences for ASMPT. These penalties can include substantial fines, potential bans from operating in certain markets, and significant damage to the company's reputation. In 2023, for example, several companies in the technology sector faced multi-million dollar penalties for export control violations, underscoring the financial risks involved.
Intellectual property laws and patent protection are paramount for ASMPT, a company heavily invested in research and development. The company's ability to safeguard its innovations in advanced hardware and software solutions directly impacts its competitive standing and shields it from potential infringement. For instance, ASMPT's consistent investment in R&D, which reached HKD 1.14 billion in 2023, underscores the critical need for robust IP protection to secure the returns on these significant expenditures.
ASM Pacific Technology's (ASMPT) equipment must meet stringent international and regional safety and quality standards, crucial for market access and mitigating legal exposure. For instance, compliance with CE marking in Europe and UL certification in North America is often a prerequisite for sales in these key markets. Failure to adhere to these regulations, such as those set by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) for electrical safety, can lead to product recalls and significant financial penalties.
Data Privacy and Cybersecurity Regulations
As ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT) expands its software and digital service offerings for intelligent factories, navigating the complex landscape of data privacy and cybersecurity regulations is crucial. The company's reliance on collecting and processing sensitive customer data and intellectual property necessitates strict adherence to global standards like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Failure to comply can result in significant financial penalties and reputational damage, impacting ASMPT's ability to secure and retain clients in the increasingly digital manufacturing sector.
The evolving nature of these regulations presents an ongoing challenge. For instance, as of early 2024, many jurisdictions are strengthening their cybersecurity mandates, requiring more proactive threat detection and incident response protocols. ASMPT must continually invest in and update its cybersecurity infrastructure to safeguard its operations and customer data against sophisticated cyber threats. This includes implementing advanced encryption, regular security audits, and employee training to mitigate risks associated with digital service delivery.
- GDPR Fines: Non-compliance can result in fines of up to €20 million or 4% of global annual revenue.
- Cybersecurity Investments: Global spending on cybersecurity solutions is projected to exceed $200 billion in 2024, highlighting the market's focus on data protection.
- Data Breach Costs: The average cost of a data breach globally reached $4.45 million in 2024, underscoring the financial impact of inadequate security measures.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Safeguarding proprietary algorithms and manufacturing process data is critical for ASMPT's competitive advantage.
Corporate Governance and Compliance Frameworks
ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT) operates under strict corporate governance and compliance mandates across its global presence, including its listing on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. These regulations necessitate transparent financial reporting, adherence to ethical business practices, and robust internal control mechanisms to ensure accountability and stakeholder trust.
The company's commitment to compliance is underscored by its reporting standards. For instance, in its 2023 annual report, ASMPT detailed its adherence to the Corporate Governance Code and Corporate Governance Report requirements of the Hong Kong Stock Exchange. This includes the establishment of an independent board committee structure and regular audits to maintain financial integrity.
- Board Structure: ASMPT maintains a board of directors with a majority of independent non-executive directors, aligning with best practices for oversight and decision-making.
- Ethical Conduct: The company enforces a code of conduct that guides employee behavior and business dealings, aiming to prevent corruption and promote fair competition.
- Financial Transparency: ASMPT is committed to providing timely and accurate financial information to investors and regulatory bodies, as evidenced by its regular financial disclosures.
- Risk Management: Robust internal control systems are in place to identify, assess, and manage risks across its operations, ensuring operational resilience and compliance.
ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT) must navigate stringent export controls, particularly those imposed by the U.S. Department of Commerce, affecting its ability to trade advanced semiconductor equipment globally. Failure to comply with these evolving regulations, such as those related to the Entity List, can lead to substantial financial penalties, market access restrictions, and reputational damage.
Protecting its intellectual property is paramount for ASMPT, given its significant R&D investments, which reached HKD 1.14 billion in 2023. Safeguarding proprietary algorithms and manufacturing processes is critical for maintaining its competitive edge and preventing infringement.
ASMPT's products must meet diverse international safety and quality certifications, like CE marking in Europe and UL certification in North America, to ensure market access and avoid legal liabilities. Non-compliance with standards set by bodies like the IEC can result in costly product recalls and penalties.
Adherence to data privacy and cybersecurity regulations, including GDPR, is essential for ASMPT as it expands its digital services. The company faces significant financial and reputational risks from data breaches and non-compliance, with global data breach costs averaging $4.45 million in 2024.
| Legal Factor | Relevance to ASMPT | 2023/2024 Data/Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Export Controls | Global trade of advanced semiconductor equipment | U.S. BIS Entity List updates impact supply chain and customer access. |
| Intellectual Property | Protection of R&D investments in hardware/software | HKD 1.14 billion R&D investment in 2023 necessitates robust IP protection. |
| Safety & Quality Standards | Market access and legal compliance | CE marking (Europe) and UL certification (North America) are often prerequisites. |
| Data Privacy & Cybersecurity | Protection of customer data and digital services | GDPR non-compliance can incur fines up to €20 million; average data breach cost $4.45 million (2024). |
| Corporate Governance | Financial reporting, ethical practices, stakeholder trust | Adherence to Hong Kong Stock Exchange Corporate Governance Code; majority independent directors. |
Environmental factors
ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT) is actively pursuing ambitious carbon reduction goals, aiming for net-zero emissions across Scope 1 and 2 by 2035. This commitment is being realized through strategic initiatives focused on enhancing energy efficiency within its facilities and increasingly sourcing renewable energy for its global operations.
The company is also undertaking a thorough evaluation of its Scope 3 emissions, which represent indirect emissions from its value chain. This comprehensive approach underscores ASMPT's dedication to environmental stewardship and its role in contributing to a lower-carbon future, aligning with global sustainability trends and regulatory pressures.
The electronics manufacturing sector is under growing scrutiny for its waste output, pushing companies like ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT) to embrace circular economy models. This means ASMPT must actively design products and manage operations with waste reduction and recycling in mind, incorporating sustainable materials to align with increasingly stringent environmental rules and public demand.
Globally, the amount of electronic waste (e-waste) generated is substantial, with estimates suggesting over 50 million tonnes were produced in 2023 alone, a figure projected to rise. ASMPT's commitment to circularity, including initiatives like product take-back programs or designing for easier disassembly and material recovery, will be crucial for navigating these environmental pressures and maintaining a competitive edge in the 2024-2025 period.
Electronics manufacturers like ASMPT face stringent regulations on hazardous substances, including PFAS, RoHS, and REACH. These rules demand robust material traceability and rigorous testing throughout the supply chain to ensure product safety and environmental compliance.
Energy Efficiency in Manufacturing Processes
The semiconductor and electronics manufacturing sectors are increasingly prioritizing energy efficiency. This focus is driven by both regulatory pressures and a desire to reduce operational costs. ASMPT's advanced equipment, designed for precision and speed, can indirectly contribute to lower energy consumption per unit produced for its clients by optimizing cycle times and reducing waste.
ASMPT itself is committed to improving its own energy footprint. In 2023, the company reported a reduction in energy intensity across its operations. For instance, their efforts in optimizing facility management and production line layouts are key to achieving these environmental goals.
- Growing Demand for Green Manufacturing: Industries are actively seeking solutions that lower their environmental impact, including energy usage.
- ASMPT's Contribution: The company's technology can enable customers to achieve more energy-efficient semiconductor production.
- Internal Efficiency Targets: ASMPT is implementing measures to reduce its own energy consumption, aligning with sustainability objectives.
- Industry Benchmarks: Many peers in the semiconductor equipment sector are also setting ambitious energy reduction targets for their manufacturing processes.
Water Consumption and Resource Management
Water is an indispensable element in semiconductor fabrication, used extensively for cleaning, cooling, and process applications. ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT), like its peers in the industry, faces increasing scrutiny regarding its water footprint. Effective water resource management is therefore crucial not only for operational efficiency but also for regulatory compliance and maintaining a positive corporate image.
The semiconductor industry's reliance on water means that regions experiencing water scarcity can pose significant operational risks. ASMPT must proactively manage its water consumption, seeking ways to reduce usage and increase recycling rates. For instance, many advanced manufacturing facilities are implementing closed-loop water systems and investing in advanced filtration technologies to minimize their reliance on fresh water sources.
Environmental regulations globally are tightening, often mandating specific water discharge standards and consumption reporting. Companies like ASMPT are expected to demonstrate commitment to sustainable water management practices. This includes transparent reporting on water usage, wastewater treatment, and efforts to conserve this vital resource. For example, some industry reports from 2023 and early 2024 highlight a growing trend of companies setting ambitious water reduction targets as part of their ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) strategies.
- Critical Resource: Water is fundamental to semiconductor manufacturing processes, from wafer cleaning to equipment cooling.
- Operational Risk: Water scarcity in manufacturing regions presents a direct risk to production continuity and can increase operational costs.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to stringent water discharge and consumption regulations is a key environmental imperative for ASMPT.
- Sustainability Focus: Demonstrating responsible water management is increasingly important for corporate reputation and investor relations, with many firms setting public water reduction goals.
Environmental factors are increasingly shaping the operational landscape for electronics manufacturers like ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT). The global push towards sustainability, evidenced by rising e-waste volumes exceeding 50 million tonnes in 2023, necessitates a focus on circular economy principles. ASMPT's strategic initiatives, including net-zero emission goals by 2035 and efforts to reduce its own energy intensity, directly address these environmental pressures and regulatory demands.
Water management is another critical environmental consideration, with the semiconductor industry being a significant consumer. ASMPT must navigate water scarcity risks and stringent discharge regulations by implementing efficient water usage and recycling systems. This proactive approach is vital for maintaining operational continuity and aligning with corporate sustainability objectives, as highlighted by industry trends showing companies setting ambitious water reduction targets.
| Environmental Factor | ASMPT's Response/Impact | Data/Trend (2023-2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Emissions | Net-zero Scope 1 & 2 by 2035; energy efficiency & renewables | Energy intensity reduction reported in 2023 |
| E-waste & Circularity | Embracing circular economy models, waste reduction | Global e-waste >50 million tonnes in 2023, projected to rise |
| Water Management | Resource management, recycling, compliance with discharge standards | Growing trend of setting public water reduction targets |
| Hazardous Substances | Compliance with RoHS, REACH, PFAS regulations | Demand for robust material traceability and testing |
PESTLE Analysis Data Sources
Our PESTLE Analysis for ASM Pacific Technology is built on comprehensive data from reputable sources including industry-specific market research reports, financial news outlets, and official government publications detailing regulatory changes. This ensures a well-rounded understanding of the political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental factors impacting the company.
