ASM Pacific Technology Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
ASM Pacific Technology Bundle
ASM Pacific Technology operates in a dynamic semiconductor equipment market, where intense rivalry and the threat of substitutes significantly shape its competitive landscape. Understanding the precise influence of each of Porter's Five Forces is crucial for navigating this complex environment.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping ASM Pacific Technology’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The bargaining power of suppliers to ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT) is significantly shaped by how concentrated and specialized the suppliers are. If only a few companies provide essential components or unique technologies for semiconductor manufacturing equipment, those suppliers gain considerable leverage.
For ASMPT, this means suppliers of highly specialized machinery parts, advanced materials, or proprietary software crucial for their production lines can command higher prices or dictate terms. For instance, if a particular type of high-precision optical lens or a unique chemical compound is only available from a single, specialized provider, ASMPT’s reliance on that supplier increases their bargaining power.
High switching costs for ASMPT significantly bolster the bargaining power of its suppliers. If ASMPT faces substantial expenses related to re-tooling manufacturing lines, undergoing rigorous qualification processes for new components, or redesigning its complex semiconductor equipment, it becomes more entrenched with its existing suppliers. This dependence limits ASMPT's ability to negotiate favorable terms or readily explore alternative sourcing options.
Suppliers offering unique or patented technologies, specialized materials, or highly customized components crucial for ASMPT's advanced packaging and SMT solutions wield significant bargaining power. This is especially evident in rapidly evolving fields like AI, where access to cutting-edge inputs is paramount.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
If suppliers possess a believable threat of moving into ASMPT's assembly and packaging equipment market themselves, their leverage would significantly grow. This scenario, while theoretically possible, is less probable given the substantial capital investment and specialized expertise required for manufacturing such sophisticated machinery.
The high barriers to entry in producing advanced semiconductor assembly and packaging equipment, characterized by complex engineering and significant R&D expenditure, generally deter suppliers from forward integration. For instance, the development of cutting-edge wire bonders or advanced packaging solutions demands years of innovation and substantial financial commitment, often exceeding the core competencies of component suppliers.
- Supplier Forward Integration Threat: Suppliers might consider producing their own assembly and packaging equipment if they perceive high profit margins and market share opportunities within ASMPT's customer base.
- Capital Intensity Barrier: The substantial capital required for R&D, manufacturing facilities, and skilled labor in the semiconductor equipment sector acts as a significant deterrent for most suppliers.
- Specialization and Expertise: Developing and manufacturing highly specialized equipment like ASMPT's wafer sorters or die attach machines requires deep technical knowledge and a proven track record, which component suppliers typically lack.
- ASMPT's Market Position: ASMPT's established reputation, extensive customer relationships, and continuous innovation in its product lines further strengthen its competitive moat against potential supplier encroachment.
Importance of ASMPT to Supplier's Business
The relative importance of ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT) as a customer significantly influences its suppliers' bargaining power. When ASMPT constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's overall revenue, that supplier is incentivized to maintain the relationship and offer more favorable terms to ASMPT.
For instance, if a key component supplier derives over 15% of its annual sales from ASMPT, ASMPT's ability to negotiate pricing and service levels increases. This reliance can diminish the supplier's leverage, making them more accommodating to ASMPT's demands.
- Supplier Dependence: If ASMPT represents a significant revenue stream for a supplier, their bargaining power over ASMPT is reduced.
- Revenue Contribution: For example, if ASMPT accounts for 20% of a key semiconductor equipment component supplier's revenue, that supplier is more likely to offer competitive pricing to retain ASMPT.
- Relationship Value: Suppliers who value ASMPT's business are less likely to exert strong bargaining power, potentially leading to more favorable terms for ASMPT.
- Market Share Impact: A supplier's dependence on ASMPT can also influence their own market position and willingness to compromise.
The bargaining power of suppliers to ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT) is influenced by the availability of substitutes for their products. If ASMPT can easily source comparable components or technologies from alternative suppliers, the leverage of existing suppliers diminishes significantly.
The threat of backward integration by ASMPT, where the company might consider producing its own critical components, also acts as a check on supplier power. However, given the specialized nature and capital intensity of semiconductor equipment manufacturing, this is often not a feasible or cost-effective strategy for ASMPT.
Suppliers of critical, highly specialized components for ASMPT's advanced semiconductor manufacturing equipment, such as those for wafer processing or advanced packaging, hold considerable bargaining power. This is amplified when these components are not easily substitutable or when ASMPT faces high switching costs, estimated to be substantial given the integration complexity of their machinery.
| Factor | Impact on ASMPT | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High | A single supplier for a critical optical sensor for ASMPT's inspection equipment. |
| Switching Costs | High | Re-qualifying a new supplier for a complex motion control system could take months and incur significant engineering costs. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Low for highly specialized parts | Limited alternatives for proprietary software controlling advanced die-attach machines. |
| Supplier Importance to ASMPT | Varies; can reduce supplier power | If ASMPT represents over 10% of a supplier's revenue, that supplier is more accommodating. |
What is included in the product
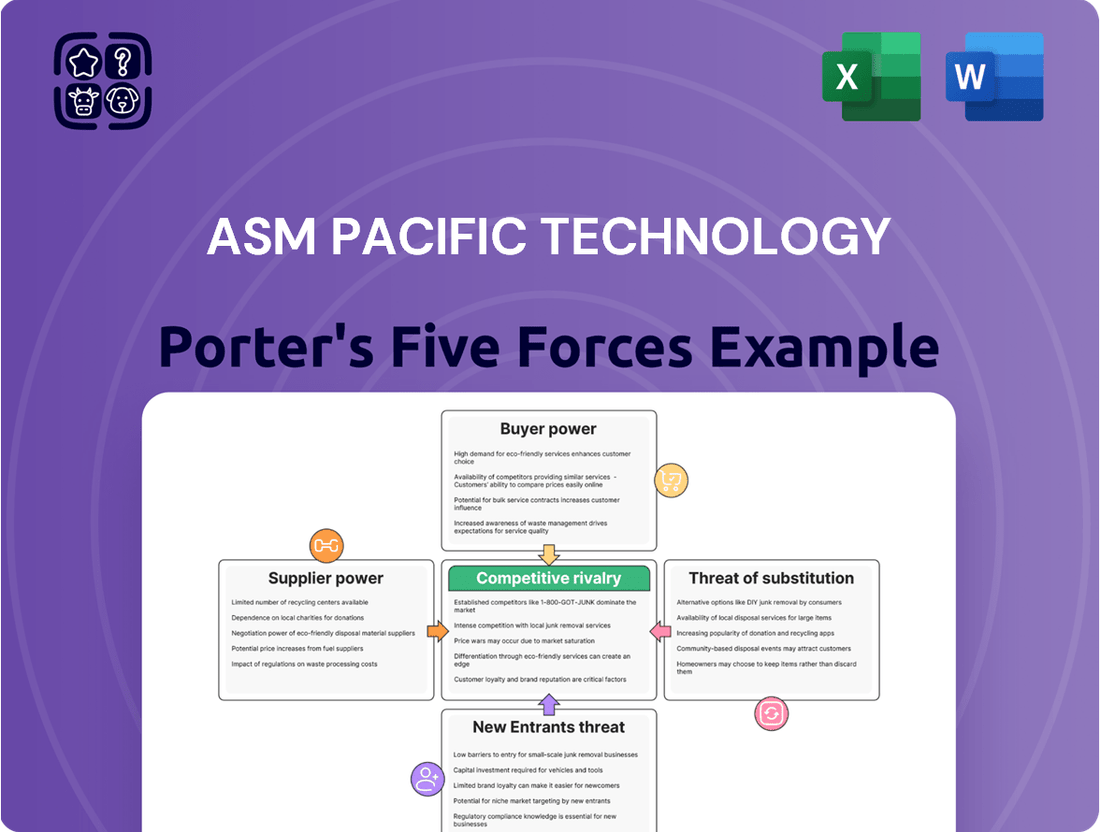
This analysis delves into the competitive forces impacting ASM Pacific Technology, examining the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the semiconductor equipment industry.
Instantly visualize the competitive landscape of the semiconductor industry with a dynamic, interactive Porter's Five Forces model for ASM Pacific Technology, simplifying complex strategic analysis.
Customers Bargaining Power
Customer concentration is a key factor in understanding the bargaining power of customers for ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT). ASMPT serves significant industries like automotive, communications, and consumer electronics. When a few major clients contribute a large chunk of revenue, they gain leverage to negotiate better pricing or demand tailored solutions.
In 2024, ASMPT's top five customers represented about 14% of its total revenue. This figure suggests a relatively diversified customer base, which generally means lower customer concentration risk and, consequently, less concentrated bargaining power among individual customers.
Switching costs for ASM Pacific Technology's (ASMPT) customers are a significant factor in their bargaining power. These costs can include the substantial expense and time involved in re-qualifying new equipment, integrating disparate software solutions, and retraining personnel to operate different systems. For instance, a semiconductor manufacturer investing heavily in ASMPT's advanced packaging equipment might face millions in costs and months of downtime to switch to a competitor's machinery.
High switching costs effectively lock customers into ASMPT's ecosystem, thereby diminishing their ability to negotiate lower prices or more favorable terms. This is because the disruption and financial outlay associated with transitioning to an alternative supplier are often prohibitive. In 2024, the semiconductor industry continued to see massive capital expenditures, underscoring the significant investment customers make in their production lines, making such switches even more daunting.
Customer price sensitivity significantly influences the bargaining power of buyers. In sectors like consumer electronics, where profit margins are often squeezed, customers, particularly large OEMs, can demand lower prices from ASMPT. For instance, in 2023, the global semiconductor market faced headwinds, leading to increased price negotiations across the supply chain.
However, this sensitivity can be mitigated when ASMPT offers highly specialized or critical solutions. For advanced packaging technologies essential for cutting-edge applications such as AI chips or high-performance computing, customers are often more willing to pay a premium for superior performance, reliability, and technological innovation, rather than solely focusing on cost reduction.
Customer's Ability to Integrate Backward
The bargaining power of customers integrating backward is generally low for ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT) because their assembly and packaging equipment is highly specialized and requires significant capital investment. This complexity makes it difficult for most customers to replicate ASMPT's technology in-house.
However, very large semiconductor manufacturers, those with substantial resources and specific strategic objectives, might explore developing some in-house capabilities. This is typically for niche applications or to gain a competitive edge in particular areas rather than a full-scale replacement of ASMPT's comprehensive solutions.
- High Capital Expenditure: The cost of developing and manufacturing advanced semiconductor assembly and packaging equipment is substantial, creating a barrier for backward integration.
- Technological Sophistication: ASMPT's products involve intricate engineering and proprietary technologies that are difficult and time-consuming to replicate.
- Economies of Scale: ASMPT benefits from economies of scale in production, which can lead to cost advantages that individual customers integrating backward would struggle to match.
- Focus on Core Competencies: Most semiconductor manufacturers prefer to focus on their core business of chip design and fabrication, outsourcing equipment needs to specialists like ASMPT.
Availability of Substitute Products/Services for Customers
The availability of substitute products and services significantly bolsters customer bargaining power against ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT). When customers can easily find comparable equipment or services from ASMPT's rivals, they gain considerable leverage. This is particularly true in the semiconductor equipment sector where multiple players offer solutions for assembly, packaging, and surface mount technology (SMT).
For instance, if a customer needs advanced packaging equipment, and several competitors offer machines with similar capabilities and performance metrics, they are less reliant on ASMPT. This competitive landscape allows customers to negotiate better pricing, demand more favorable terms, or switch suppliers if ASMPT's offerings are not perceived as superior or cost-effective. In 2023, the global semiconductor equipment market saw intense competition, with companies like KLA Corporation and Applied Materials also vying for market share, providing customers with a broad array of choices.
- Increased Customer Leverage: The presence of numerous alternative suppliers for semiconductor assembly and packaging equipment directly enhances customers' ability to negotiate favorable terms with ASMPT.
- Price Sensitivity: When substitutes are readily available, customers are more likely to be price-sensitive, pushing ASMPT to offer competitive pricing to retain business.
- Supplier Switching Costs: If switching costs are low, customers can more easily move to a competitor, further strengthening their bargaining position.
ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT) faces moderate bargaining power from its customers. While a diversified customer base in 2024, with top five clients representing only 14% of revenue, limits individual customer leverage, high switching costs for specialized semiconductor equipment do anchor clients. However, the availability of substitutes from competitors like KLA Corporation and Applied Materials, especially in a competitive 2023 market, allows customers to negotiate pricing and terms, particularly for less critical or standard solutions.
| Factor | ASMPT Impact | Customer Bargaining Power |
| Customer Concentration | Low (Top 5 customers ~14% of revenue in 2024) | Low to Moderate |
| Switching Costs | High (Equipment, integration, retraining) | Low |
| Price Sensitivity | Varies (High for standard, low for specialized tech) | Moderate |
| Backward Integration | Difficult for most customers | Low |
| Availability of Substitutes | High (Many competitors in semiconductor equipment) | Moderate to High |
What You See Is What You Get
ASM Pacific Technology Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete ASM Pacific Technology Porter's Five Forces Analysis, detailing the competitive landscape of the semiconductor equipment industry. You'll gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the sector. The document you see here is exactly what you’ll be able to download after payment, offering a comprehensive understanding of ASM Pacific Technology's strategic positioning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The semiconductor and electronics manufacturing equipment sector is populated by a number of significant global competitors. The competitive intensity is directly tied to the sheer volume of direct rivals and how their market share stacks up, particularly in crucial segments such as advanced packaging and Surface Mount Technology (SMT) solutions.
The global semiconductor manufacturing equipment market is projected to hit an impressive $125.5 billion by 2025. This substantial market size naturally attracts a diverse array of participants, all vying for a piece of the action.
The industry growth rate significantly influences competitive rivalry. In burgeoning segments like advanced packaging, particularly those fueled by AI and high-performance computing (HPC), competition might be less intense. This is because the market expansion is substantial enough to support the growth of multiple participants.
The advanced packaging market itself is a prime example, with projections indicating robust growth. It's expected to expand from an estimated USD 35.2 billion in 2025 to USD 70.7 billion by 2035. This represents a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.2%, suggesting ample opportunities for companies to gain market share without directly clashing for existing customers.
ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT) actively differentiates its offerings through substantial, ongoing investment in research and development. This commitment fuels the creation of advanced packaging technologies and sophisticated smart manufacturing solutions, setting them apart in a competitive landscape.
The company's strength in product differentiation, especially in critical areas like Thermo-Compression Bonding (TCB) and hybrid bonding, effectively mitigates direct price-based competition. This strategic focus on technological leadership helps ASMPT maintain a sustainable competitive advantage in the semiconductor equipment market.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers in the semiconductor equipment manufacturing industry, where ASM Pacific Technology operates, can significantly fuel competitive rivalry. When it's difficult or costly for companies to leave the market, they tend to stay and fight for market share, even when business conditions are less than ideal. This persistence can lead to prolonged periods of intense competition.
The specialized nature of the equipment ASM Pacific Technology produces, such as wafer processing and assembly equipment, implies substantial investments in unique machinery and intellectual property. These specialized assets make it challenging and expensive to repurpose or sell off, thereby creating high exit barriers. For instance, the development and manufacturing of advanced lithography or deposition equipment require highly specific engineering expertise and capital equipment that have limited resale value outside the industry.
Long-term contracts with major semiconductor manufacturers also contribute to exit barriers. These agreements often bind companies to supply chains and customer relationships for extended periods, making a swift departure impractical. Furthermore, high fixed costs associated with maintaining research and development facilities, manufacturing plants, and a skilled workforce mean that companies must continue operating to spread these costs, intensifying the competitive landscape.
- Specialized Assets: The semiconductor equipment sector involves highly specific machinery and intellectual property, making it difficult to exit or repurpose assets.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments with major clients in the semiconductor industry create dependencies that hinder quick exits.
- High Fixed Costs: Investments in R&D, manufacturing, and skilled labor necessitate continued operation to manage overheads, thereby increasing competitive pressure.
Strategic Stakes
The semiconductor and electronics manufacturing sectors are critical for national economic health and technological progress, fueling fierce competition among major players. Governments and large corporations are pouring significant capital into securing leadership and ensuring supply chain stability, a trend amplified by geopolitical investments in semiconductor infrastructure.
This intense rivalry is evident in the substantial R&D spending by industry leaders. For instance, in 2023, major semiconductor equipment manufacturers like ASML, Applied Materials, and Lam Research collectively invested tens of billions of dollars in innovation to maintain their competitive edge.
- High R&D Investment: Companies in this space consistently allocate a significant portion of their revenue to research and development, often exceeding 15% for leading firms, to stay ahead in technological advancements.
- Geopolitical Influence: National security concerns and the desire for technological sovereignty are driving substantial government subsidies and investments in domestic semiconductor production, such as the CHIPS Act in the United States, which allocated over $52 billion.
- Consolidation and Partnerships: The high cost of advanced manufacturing and intense competition encourage strategic alliances and mergers, as seen with past significant acquisitions in the sector, aiming to achieve economies of scale and broaden technological portfolios.
Competitive rivalry within the semiconductor and electronics manufacturing equipment sector is characterized by a high degree of intensity, driven by the presence of numerous global players and significant R&D investments. ASM Pacific Technology differentiates itself through technological innovation in areas like advanced packaging, particularly Thermo-Compression Bonding (TCB) and hybrid bonding, which reduces direct price-based competition.
High exit barriers, stemming from specialized assets, long-term contracts, and substantial fixed costs, compel companies to remain and compete aggressively. Geopolitical factors and national interests in semiconductor supply chain security further fuel this competition, leading to significant government investments and corporate R&D spending, with major players investing billions annually.
| Key Competitor R&D Spending (Estimated Billions USD) | 2023 | 2024 (Projected) | 2025 (Projected) |
| ASML | ~5.0 | ~5.5 | ~6.0 |
| Applied Materials | ~2.5 | ~2.7 | ~2.9 |
| Lam Research | ~1.8 | ~2.0 | ~2.2 |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT) stems from alternative methods and technologies that can fulfill similar needs in semiconductor assembly, packaging, and electronics manufacturing. This could involve different packaging techniques or entirely novel manufacturing approaches that bypass traditional processes.
Advanced packaging technologies such as 2.5D/3D integration, hybrid bonding, and panel-level packaging are key examples of substitutes that offer enhanced performance and efficiency, potentially reducing reliance on ASMPT's current offerings. For instance, the growing adoption of chiplets and heterogeneous integration, enabled by these advanced packaging methods, presents a significant alternative pathway for achieving higher performance in semiconductor devices.
Customers closely scrutinize the price-performance ratio when considering substitute technologies for ASMPT's offerings. If an alternative provides similar or better functionality for less money, or a substantial performance upgrade at a reasonable premium, it directly challenges ASMPT's market position. For instance, the increasing adoption of organic interposers presents a cost-effective substitute to traditional silicon, though limitations in interconnect feature miniaturization remain a key differentiator.
Customer willingness to switch to alternative solutions for semiconductor manufacturing equipment is a key factor. This propensity is shaped by how easily new technologies can be adopted, the perceived risks involved, and how developed these alternative options are. For instance, if a competitor offers a significantly cheaper but less reliable alternative, the customer's decision will weigh these trade-offs.
Evolution of Semiconductor Design
The threat of substitutes in semiconductor design is significantly shaped by ongoing technological advancements. Innovations like chiplet technology and heterogeneous integration are altering the demand for specific packaging solutions. For instance, the increasing adoption of chiplets, which are smaller, specialized dies that can be combined to form a larger system-on-chip (SoC), directly impacts the requirements for advanced packaging techniques. This evolution means that while current packaging methods might be robust, the pace of design change could render them less competitive if they cannot adapt to these new architectures.
These design shifts present a dual-edged sword for companies like ASM Pacific Technology. On one hand, they open doors for advanced packaging solutions that enable higher performance and integration. On the other, they introduce a constant need for innovation to keep pace with emerging design paradigms. Consider the projected growth in advanced packaging, with some market analyses indicating it could reach over $70 billion by 2027, highlighting the potential but also the dynamic nature of this segment. Failure to align with these evolving design trends could lead to existing solutions becoming substitutes themselves, replaced by more suitable alternatives.
- Chiplet Technology: Enables modular design, potentially reducing reliance on monolithic SoC packaging.
- Heterogeneous Integration: Combines different types of semiconductor components, requiring versatile packaging.
- Market Adaptability: Companies must continually innovate packaging to match evolving semiconductor architectures.
- Investment in R&D: Crucial for staying ahead of design-driven shifts in packaging demand.
In-house Manufacturing Capabilities of Customers
A significant threat to ASMPT's business comes from the potential for customers, particularly large integrated device manufacturers (IDMs) and original equipment manufacturers (OEMs), to develop or enhance their own in-house assembly and packaging capabilities. This internal expansion directly substitutes for the services ASMPT provides.
For instance, major players in the semiconductor industry might invest heavily in their own advanced packaging lines. This strategic move allows them to gain greater control over their supply chain, potentially reduce costs, and accelerate innovation cycles. By bringing these processes in-house, they lessen their dependence on third-party equipment suppliers like ASMPT.
Consider the trend in advanced packaging technologies, such as wafer-level packaging and chiplet integration. As these become more critical for performance, leading IDMs may find it strategically advantageous to build proprietary expertise and infrastructure. For example, in 2023, Intel announced significant investments in its own advanced packaging technologies, demonstrating this in-house capability development.
- Customer Vertical Integration: Large semiconductor firms may choose to integrate assembly and packaging operations to capture more value and ensure intellectual property protection.
- Technological Self-Sufficiency: Developing in-house expertise in advanced packaging allows customers to tailor solutions precisely to their product roadmaps, reducing reliance on external equipment vendors.
- Cost Control and Efficiency: For high-volume production, customers might find it more economical to manage their own manufacturing processes, thereby substituting ASMPT's offerings.
The threat of substitutes for ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT) is significant, driven by evolving semiconductor design and manufacturing paradigms. Advanced packaging technologies like chiplets and heterogeneous integration offer alternative ways to achieve high performance, potentially reducing demand for ASMPT's current equipment. For instance, the increasing adoption of chiplets allows for modular system design, bypassing traditional monolithic approaches.
Customers evaluate substitutes based on their price-performance ratio. If an alternative offers comparable or superior functionality at a lower cost, or a substantial performance gain for a reasonable premium, it directly challenges ASMPT. For example, organic interposers are emerging as a more cost-effective substitute to silicon interposers, despite some limitations in feature density.
The willingness of customers to switch to alternatives depends on ease of adoption, perceived risks, and the maturity of these substitute technologies. Companies like ASMPT must continuously innovate their packaging solutions to align with emerging semiconductor architectures, such as the growing demand for advanced packaging solutions, which is projected to exceed $70 billion by 2027.
Furthermore, the threat is amplified by the increasing trend of major semiconductor players developing or enhancing their in-house assembly and packaging capabilities. This vertical integration allows them to control their supply chains and accelerate innovation, reducing their reliance on external equipment vendors. Intel's significant investments in its own advanced packaging technologies in 2023 exemplify this strategic shift towards self-sufficiency.
| Substitute Technology | Key Advantage | Potential Impact on ASMPT |
|---|---|---|
| Chiplet Technology | Modular design, performance flexibility | Reduces reliance on monolithic packaging equipment |
| Heterogeneous Integration | Integration of diverse components | Requires adaptable and advanced packaging solutions |
| Organic Interposers | Cost-effectiveness | Challenges silicon interposer market share |
| In-house Customer Capabilities | Supply chain control, IP protection | Directly substitutes external equipment supply |
Entrants Threaten
The semiconductor and electronics manufacturing equipment sector is incredibly capital-intensive. Companies need massive upfront investments for research and development, state-of-the-art manufacturing plants, and highly specialized machinery. This financial hurdle significantly deters new players from entering the market.
These substantial capital requirements create a formidable barrier for potential new entrants. For context, the global semiconductor manufacturing equipment market is projected to hit an all-time high of $125.5 billion in sales by 2025, underscoring the immense financial commitment needed to compete.
Established players like ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT) hold a significant advantage due to their extensive intellectual property and patents in advanced packaging and SMT solutions. This deep well of proprietary technology acts as a formidable barrier, requiring new entrants to invest heavily in developing or licensing comparable innovations, a process that is both time-consuming and capital-intensive.
ASMPT's commitment to research and development, evidenced by its consistent investment in innovation, allows it to continuously introduce industry-shaping solutions. For instance, in 2023, the company reported R&D expenses of HK$1,310 million, underscoring its dedication to maintaining a technological edge that deters potential new competitors.
Existing players in the semiconductor equipment manufacturing industry, like ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT), benefit immensely from significant economies of scale. This allows them to achieve lower per-unit costs in manufacturing, R&D, and procurement. For instance, ASMPT's substantial global footprint and market share in 2024 suggest considerable purchasing power and optimized production processes.
The experience curve further solidifies this advantage. Companies with a longer operational history have refined their processes, leading to greater efficiency and cost-effectiveness. This accumulated knowledge makes it challenging for newcomers to match the cost structure and operational smoothness that established firms like ASMPT have cultivated over years of operation.
Customer Loyalty and Switching Costs
Building strong customer relationships and trust within the semiconductor equipment sector is a lengthy process. ASMPT's strategy of fostering close partnerships with its clients underscores this. For instance, in 2023, ASMPT reported that a significant portion of its revenue came from repeat customers, demonstrating the value placed on these established relationships.
The semiconductor industry also presents substantial switching costs for existing customers. This is largely due to the intricate integration and rigorous qualification processes required for new equipment. Consequently, new entrants face a considerable hurdle in persuading customers to transition from proven, integrated solutions provided by established players like ASMPT.
- Customer Loyalty: ASMPT’s focus on long-term partnerships cultivates deep customer loyalty, making it difficult for new entrants to gain traction.
- High Switching Costs: The significant investment in integrating and qualifying new semiconductor manufacturing equipment creates a barrier for customers considering alternatives.
- Established Trust: Years of reliable performance and support from incumbent suppliers like ASMPT build a level of trust that new entrants struggle to replicate quickly.
Regulatory Hurdles and Industry Standards
The semiconductor sector, where ASM Pacific Technology operates, is heavily regulated. Companies must adhere to rigorous quality, safety, and environmental standards, often requiring significant upfront investment and ongoing compliance efforts. For instance, the U.S. Export Administration Regulations (EAR) and similar international controls can impact the transfer of advanced technology, adding complexity for new players.
Navigating these intricate regulatory landscapes and industry-specific standards presents a substantial barrier to entry. New entrants face considerable costs and time commitments to achieve compliance, which can delay market penetration and erode initial profitability. This environment favors established companies with existing infrastructure and expertise in managing these requirements.
- Stringent Quality Control: Semiconductor manufacturing demands near-perfect defect rates, often measured in parts per billion, necessitating advanced process control and metrology systems.
- Safety Regulations: Handling of hazardous materials and high-energy processes requires strict adherence to workplace safety protocols, such as those mandated by OSHA in the U.S.
- Environmental Compliance: Manufacturing processes often involve chemicals and water usage, subject to environmental protection laws like the Clean Air Act and Clean Water Act.
- Industry Standards: Adherence to standards like SEMI (Semiconductor Equipment and Materials International) is crucial for interoperability and market acceptance.
The threat of new entrants for ASM Pacific Technology (ASMPT) remains relatively low due to significant barriers. The capital-intensive nature of semiconductor equipment manufacturing, coupled with extensive R&D requirements and established intellectual property, makes it extremely difficult for newcomers to compete effectively. For example, ASMPT's 2023 R&D investment of HK$1,310 million highlights the ongoing need for substantial financial commitment to innovation.
Furthermore, the economies of scale enjoyed by established players like ASMPT, along with strong customer loyalty and high switching costs, create a formidable moat. Building trust and navigating the complex regulatory landscape also present considerable challenges for any potential new entrants seeking to enter the market.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example for ASMPT |
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment for R&D and manufacturing facilities. | Global semiconductor equipment market projected to reach $125.5 billion by 2025. |
| Intellectual Property | Proprietary technology and patents in advanced packaging and SMT. | ASMPT's continuous innovation in advanced solutions. |
| Economies of Scale | Lower per-unit costs due to high production volumes and purchasing power. | ASMPT's substantial global market share in 2024. |
| Customer Loyalty & Switching Costs | Long-term relationships and integration complexities deter customers from switching. | Significant portion of ASMPT's 2023 revenue from repeat customers. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Adherence to stringent quality, safety, and environmental standards. | Navigating SEMI standards and export control regulations. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for ASM Pacific Technology leverages data from company annual reports, investor presentations, and industry-specific market research reports. We also incorporate insights from financial news outlets and competitor filings to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
