Ascential Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Ascential Bundle
Ascential operates in a dynamic market shaped by intense competition, evolving customer demands, and the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its landscape.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Ascential’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Ascential's reliance on a concentrated supplier base, particularly for specialized technology platforms and data analytics tools, significantly amplifies supplier bargaining power. If only a handful of providers offer critical infrastructure or unique data sets, Ascential faces limited alternatives.
This concentration means switching providers could incur substantial costs and operational disruptions, potentially impacting Ascential's ability to deliver its services. For instance, if a key data provider, which might represent a significant portion of Ascential's data acquisition costs, were to increase prices, Ascential would have little recourse without impacting its core offerings.
Ascential's suppliers who offer proprietary data, unique software, or highly specialized expertise for its digital commerce, product design, or marketing solutions would wield significant bargaining power. The more unique and critical these inputs are, the more challenging it becomes for Ascential to identify viable alternatives, directly impacting Ascential's operational flexibility and cost structure.
Ascential faces significant supplier bargaining power due to high switching costs. For instance, if Ascential relies on specialized data analytics platforms or proprietary software from a particular vendor, the expense and complexity of migrating to a new system, including data integration and retraining personnel, would be substantial. This dependency makes it difficult for Ascential to negotiate better terms or switch providers, thereby strengthening the suppliers' position.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by Ascential's suppliers is a critical consideration. If key suppliers possess the capability and a strong incentive to enter Ascential's core markets directly, they could significantly disrupt Ascential's business model. This would not only diminish Ascential's dependence on these suppliers but could also transform them into formidable direct competitors.
Consider the data analytics sector where Ascential operates. Many data providers or technology enablers could potentially leverage their existing data sets and technical expertise to offer direct insights or platforms to Ascential's clients. For instance, a major data aggregation service might decide to build its own benchmarking tools or market intelligence platforms, directly competing with Ascential's offerings.
- Supplier Capability: Suppliers need the technical infrastructure, market knowledge, and financial resources to launch competing services.
- Supplier Incentive: High profit margins in Ascential's market or a desire to capture more of the value chain can drive this incentive.
- Market Dynamics: The increasing commoditization of certain data services could lower the barrier for suppliers to integrate forward.
- Ascential's Dependence: The greater Ascential's reliance on a specific supplier's unique data or technology, the higher the potential threat if that supplier chooses to integrate forward.
Supplier's Importance to Ascential's Business
The bargaining power of suppliers for Ascential is influenced by how critical their inputs are to Ascential's core operations, such as event delivery or data provision. If Ascential heavily depends on specialized technology or unique data sources from a supplier, and these are not easily substituted, that supplier gains significant leverage.
For instance, in 2024, Ascential's reliance on key data providers for its intelligence platforms, like those serving the retail and marketing sectors, could be substantial. If these data sources are proprietary or require extensive integration, suppliers of such data would possess considerable bargaining power. This is particularly true if Ascential's ability to offer competitive insights hinges on the quality and exclusivity of this data.
Ascential's strategic sourcing and supplier relationship management are therefore crucial. The company's ability to diversify its supplier base or develop in-house capabilities for critical inputs directly mitigates supplier bargaining power.
- Critical Inputs: Ascential's dependence on specialized data providers or event infrastructure suppliers for its core intelligence and event services.
- Supplier Leverage: High if inputs are unique, difficult to substitute, or essential for Ascential's competitive edge.
- Mitigation Strategies: Diversifying suppliers and developing internal capabilities can reduce supplier power.
Ascential's bargaining power with its suppliers is constrained by the criticality and uniqueness of the inputs provided. For example, if Ascential relies heavily on specialized data analytics platforms or proprietary data sets for its market intelligence services, suppliers of these inputs hold significant leverage. This is amplified if switching costs are high, making it difficult and expensive for Ascential to find alternative providers. In 2024, the demand for high-quality, granular data in sectors like retail and marketing means that providers of such unique data can command higher prices, directly impacting Ascential's cost structure.
The threat of forward integration by suppliers also plays a role. If a supplier has the capability and incentive to offer services directly to Ascential's customers, they can exert greater pressure. Imagine a key data provider developing its own market analysis tools; this could turn a supplier into a direct competitor. Ascential's strategy to mitigate this involves diversifying its supplier base and building internal capabilities for essential functions, thereby reducing its dependence on any single entity.
| Factor | Impact on Ascential | Example Scenario |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High bargaining power for suppliers | Few providers of critical event technology platforms |
| Uniqueness of Input | High bargaining power for suppliers | Proprietary data sets essential for market intelligence |
| Switching Costs | High bargaining power for suppliers | Significant expenses and disruption to change data analytics vendors |
| Forward Integration Threat | High bargaining power for suppliers | Data providers developing direct client-facing analysis tools |
What is included in the product
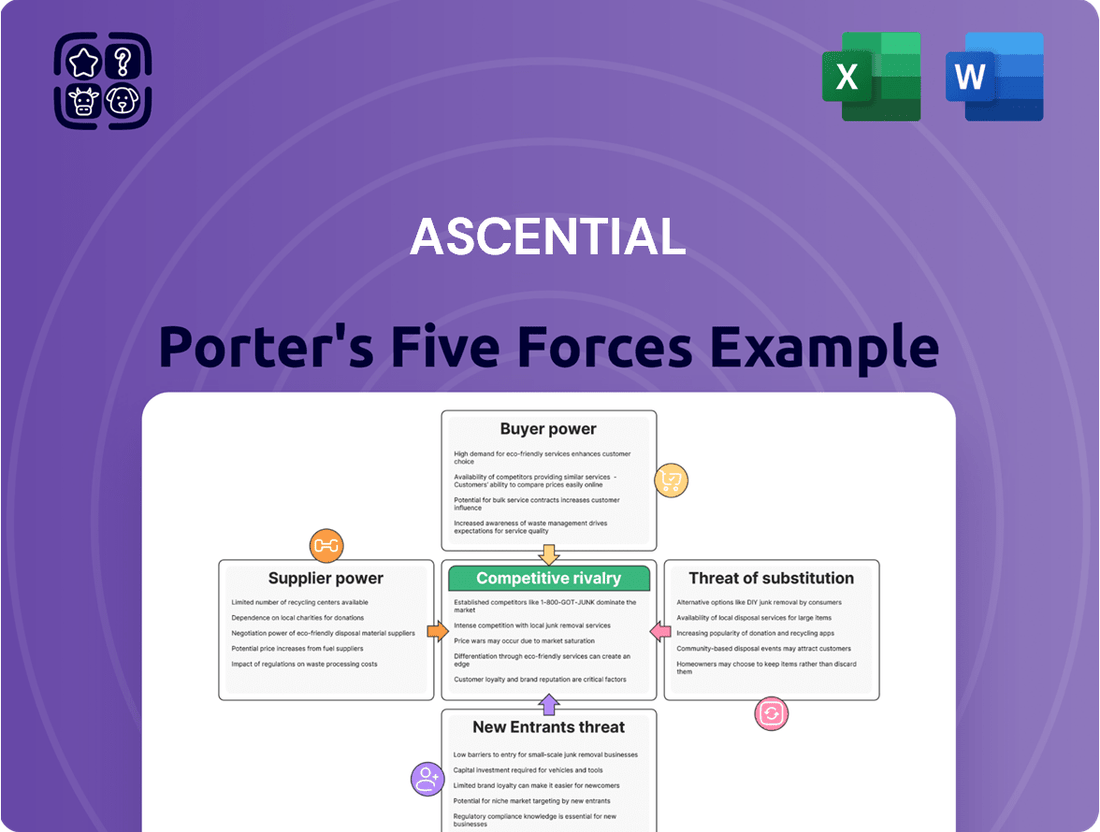
This analysis dissects the competitive forces impacting Ascential, evaluating the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within its markets.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each of Porter's Five Forces with a dynamic, interactive dashboard.
Customers Bargaining Power
If Ascential's revenue is heavily reliant on a small number of major clients, these customers wield significant influence. For instance, if the top 5 clients represent over 40% of Ascential's total sales, they could leverage this concentration to negotiate more favorable pricing or service agreements. This substantial reliance means these key customers can effectively dictate terms, potentially impacting Ascential's profitability and operational flexibility.
If Ascential's customers find it simple to switch to other information, data, and analytics providers without incurring substantial costs or facing major operational hurdles, their ability to negotiate effectively grows. This scenario compels Ascential to maintain competitive pricing and superior service standards to retain its client base.
Customer price sensitivity significantly impacts Ascential's bargaining power of customers. If clients perceive Ascential's data and insights as easily replaceable or commoditized, they will naturally push for lower prices, directly affecting Ascential's revenue streams.
For instance, in 2023, the global market for business intelligence software, a sector Ascential operates within, saw intense competition with many providers offering similar functionalities. This competitive landscape means that if Ascential fails to clearly articulate the unique value proposition of its offerings, customers will likely gravitate towards more cost-effective alternatives, thereby increasing their bargaining power.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The bargaining power of Ascential's customers is significantly influenced by the threat of backward integration. If Ascential's clients, particularly large enterprises in the retail and consumer goods sectors, possess the capability and financial resources to develop their own internal solutions for critical functions like digital commerce analytics, product data management, or marketing intelligence, they can diminish their dependence on Ascential's services.
This potential for in-house development grants customers considerable leverage during price and contract negotiations. For instance, a major e-commerce platform might assess the cost and feasibility of building its own competitive intelligence tools rather than continuing to subscribe to Ascential's data. In 2024, many large corporations are investing heavily in AI and data science teams, making the prospect of internal development more realistic.
The threat of backward integration can manifest in several ways:
- Development of proprietary analytics platforms: Customers might build their own systems to track competitor pricing and product launches.
- In-house data management solutions: Large retailers could centralize their product information management internally, reducing the need for external data providers.
- Acquisition of smaller technology firms: Customers might buy companies that offer capabilities Ascential provides, effectively bringing those services in-house.
- Increased negotiation power for favorable terms: The mere possibility of integration allows customers to demand better pricing and service level agreements from Ascential.
Availability of Alternative Solutions
The availability of numerous alternative solutions significantly impacts Ascential's bargaining power with its customers. With many providers offering similar data, analytics, and consulting services, customers gain leverage. This abundance of choice allows them to easily compare offerings and negotiate for more favorable terms, thereby diminishing Ascential's ability to dictate prices.
For instance, in the digital advertising intelligence sector, where Ascential operates, the market is quite fragmented. Companies can often find comparable data and insights from various sources, including specialized analytics firms and even broader market research providers. This competitive landscape means Ascential must remain competitive on pricing and value proposition to retain its customer base.
- Fragmented Market: The presence of numerous competitors offering similar data and analytics services creates a buyer's market.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers can readily switch to lower-cost alternatives if Ascential's pricing is perceived as too high.
- Negotiating Power: The ease of finding substitutes empowers customers to demand better pricing and service conditions.
- Reduced Switching Costs: Low barriers to switching between providers further enhance customer bargaining power.
Ascential customers possess considerable bargaining power, particularly when they can easily switch to competitors or develop in-house solutions. For example, the global business intelligence market, where Ascential competes, is highly fragmented, with many providers offering similar functionalities. This intense competition means customers can readily compare prices and features, pushing Ascential to maintain competitive pricing and demonstrate unique value. In 2023, the market saw numerous players vying for market share, increasing customer options.
The threat of backward integration further amplifies customer leverage. Large enterprises, especially in retail and consumer goods, are increasingly investing in AI and data science teams, making internal development of analytics tools more feasible. For instance, a major e-commerce player might evaluate building its own competitive intelligence tools instead of relying on Ascential. This potential for self-sufficiency grants customers significant power to negotiate better terms and pricing from Ascential.
| Factor | Impact on Ascential | 2024 Trend Example |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High reliance on few clients increases their power. | If top 5 clients exceed 40% of revenue, they can negotiate better terms. |
| Switching Costs | Low costs empower customers to switch easily. | Ease of migration to alternative data providers forces Ascential to offer competitive pricing. |
| Price Sensitivity | Commoditized data leads to price pressure. | If Ascential's offerings are seen as easily replaceable, customers will demand lower prices. |
| Backward Integration | Capability to build in-house solutions reduces dependence. | Increased corporate investment in AI/data science teams makes internal development more viable. |
| Availability of Substitutes | Numerous alternatives give customers choice. | Fragmented markets allow customers to easily compare and negotiate for better deals. |
Same Document Delivered
Ascential Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Ascential Porter's Five Forces Analysis you will receive immediately after purchase, offering an in-depth examination of the competitive landscape. You are viewing the exact, professionally formatted document, ensuring no surprises or placeholders disrupt your strategic planning. This detailed analysis is ready for your immediate use, providing actionable insights into Ascential's market position and potential threats.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The information, data, and analytics market is characterized by a substantial number of competitors, spanning large, established information conglomerates and specialized niche analytics firms. This sheer volume and diversity of players significantly amplify competitive rivalry, as each entity strives to capture a larger share of the market.
The acquisition of Ascential plc by Informa in October 2024 is a pivotal event that is expected to significantly alter the competitive dynamics within this sector. Informa, a global academic publisher and events organizer, now integrates Ascential's data and analytics capabilities, potentially creating a more concentrated and formidable competitor.
In industries with slower growth, companies often find themselves locked in more aggressive competition. This is because they are essentially vying for a bigger slice of a pie that isn't expanding much. In contrast, a booming market can offer opportunities for companies to grow by simply capturing new customers, which can ease competitive pressures.
Considering the location analytics market in North America, a sector relevant to Ascential's business, it's expected to see robust expansion. Projections indicate this market will grow substantially between 2025 and 2033, suggesting a dynamic environment where growth opportunities might temper direct rivalry for existing market share.
Ascential's competitive rivalry is significantly influenced by its product differentiation. If Ascential's digital commerce, product design, and marketing insights services are perceived as unique and valuable, it can reduce direct competition. For instance, their focus on providing actionable, data-driven insights in niche areas like retail intelligence can set them apart.
However, if competitors offer similar services, Ascential could face intensified rivalry, potentially leading to price wars. In 2024, the market for data and insights is crowded, with many players offering analytics and consulting. Ascential's ability to consistently deliver specialized, high-value services that competitors struggle to replicate is crucial for mitigating this pressure.
High Fixed Costs and Exit Barriers
High fixed costs, such as those in the semiconductor manufacturing sector, often force companies to maintain high production volumes to spread these costs. For instance, a new semiconductor fabrication plant can cost billions of dollars, making underutilization extremely detrimental. This pressure to operate at capacity intensifies competition, as firms may engage in price cutting to secure sales and cover their substantial overheads, leading to lower profitability for all players.
Significant exit barriers also contribute to fierce rivalry. These barriers can include specialized assets that are difficult to sell, high severance costs for employees, or long-term contracts. In the airline industry, for example, the enormous investment in aircraft and the complexity of regulatory approvals make exiting the market a daunting prospect. Consequently, airlines often continue to fly even when unprofitable, exacerbating competitive pressures and leading to sustained price wars.
- High fixed costs pressure firms to maximize capacity utilization.
- Exit barriers discourage companies from leaving the market, intensifying competition.
- Industries like semiconductor manufacturing and airlines exemplify this dynamic.
- This often results in price wars and reduced profitability across the sector.
Strategic Stakes
When competitors have significant strategic stakes in a market, meaning they are highly motivated to achieve market leadership or defend their current position, the competitive rivalry intensifies considerably. This drive often translates into heightened investment in research and development for new products and more aggressive marketing campaigns to capture or retain market share.
For instance, in the fiercely competitive e-commerce analytics sector, where Ascential operates, companies like Similarweb and Semrush are heavily invested in expanding their global reach and feature sets. In 2024, the digital advertising market, a key area for Ascential's data services, saw continued intense competition, with major players like Google and Meta reinvesting heavily in their platforms and data analysis capabilities to maintain dominance. This strategic imperative fuels a dynamic environment where innovation and market penetration are paramount.
- High Strategic Stakes: Competitors are driven to gain market leadership or protect existing market share, leading to more aggressive rivalry.
- Increased Investment: This ambition fuels greater spending on innovation, such as new data analytics tools and platform enhancements.
- Marketing Aggression: Companies deploy more robust marketing strategies to win or retain customers in a competitive landscape.
- Market Dynamics: In 2024, the digital analytics and e-commerce intelligence sectors demonstrated this, with companies like Similarweb and Semrush actively expanding their offerings and global presence.
The competitive rivalry within the information and analytics market is intense, fueled by a large number of diverse players. Ascential's acquisition by Informa in October 2024 is a significant development, potentially consolidating market power. While growth in sectors like location analytics offers opportunities, differentiation remains key to mitigating direct competition, especially in a crowded 2024 market.
| Factor | Impact on Ascential | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Competitors | High rivalry due to many specialized and large players. | Crowded market with diverse offerings. |
| Product Differentiation | Crucial for reducing direct competition; niche services offer an advantage. | Ascential's specialized insights in retail intelligence are a differentiator. |
| Market Growth Rate | Slower growth can intensify rivalry; robust growth can temper it. | Location analytics market projected for substantial growth, potentially easing direct competition. |
| Strategic Stakes | High motivation for market leadership drives aggressive competition. | Digital advertising market sees heavy investment from major players like Google and Meta. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Ascential's services is significant, as customers can often find alternative ways to achieve their data and analytics goals. This includes building in-house data analysis capabilities or leveraging readily available, albeit less specialized, free online resources. The increasing democratization of data analytics skills means more companies are equipped to handle some of these needs internally.
For instance, the global business analytics market was valued at approximately $37.9 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly, indicating a competitive landscape where specialized services like Ascential's face pressure from broader, more accessible solutions. Companies might opt for general consulting firms or invest in self-service analytics platforms that reduce reliance on external specialists.
The threat of substitutes is amplified when alternative solutions provide a similar or better performance at a lower price point. Ascential's clients will weigh the cost of its specialized data and analytics against more generalized or cost-effective substitutes available in the market. For instance, if a competitor offers a broad market research report for a fraction of Ascential's subscription fee, and it meets a significant portion of the client's needs, the substitute becomes a compelling option.
Customers are increasingly sensitive to the price-performance trade-off. If substitute offerings, such as readily available open-source data tools or less specialized consulting firms, can deliver comparable insights for less investment, they represent a significant challenge. In 2024, the market for data analytics and market intelligence saw continued growth, with many new entrants offering niche or more affordable solutions, intensifying this pressure on established players like Ascential.
Customer willingness to switch to alternatives hinges on their comfort with new technologies, perceived risks, and the ease of transitioning. For instance, in the streaming service market, a customer's openness to trying a new platform like Disney+ over Netflix in 2024, driven by exclusive content or lower pricing, directly increases the threat of substitution.
Technological Advancements Enabling Substitutes
Rapid advancements in artificial intelligence and data analytics tools present a significant threat of substitutes for Ascential's core offerings. Companies and even individuals can leverage these technologies to perform tasks previously requiring specialized expertise, potentially reducing reliance on Ascential's consulting and data services. For instance, the proliferation of user-friendly AI-powered analytics platforms might diminish the demand for expert consulting in market research and strategy formulation.
The accessibility and decreasing cost of these substitute technologies are key drivers. For example, many AI tools are now available on a subscription basis, making them more affordable than traditional consulting engagements. In 2024, the global AI market was valued at approximately $200 billion, with significant growth projected in areas directly impacting business intelligence and analytics.
- AI-powered analytics platforms offer self-service data analysis, bypassing the need for external consultants.
- Automation tools can handle routine data collection and processing, reducing Ascential's role in these areas.
- Open-source data science libraries empower in-house teams to develop custom analytical solutions.
- The growing availability of specialized AI models for tasks like sentiment analysis or trend prediction directly competes with Ascential's insights.
Regulatory Changes or Industry Shifts
Changes in regulations can significantly alter the attractiveness of substitutes. For example, if new data privacy laws, like strengthened GDPR enforcement in 2024, impose stricter compliance burdens on third-party data aggregators, companies might find in-house data management solutions more appealing and cost-effective. This shift makes simpler, internally managed alternatives a more viable threat.
Broader industry shifts also play a critical role. A move towards open-source software or a greater emphasis on data localization, driven by geopolitical considerations in 2024, could encourage businesses to develop or adopt alternative platforms that bypass traditional proprietary solutions. This trend amplifies the threat from substitutes by making them more accessible and aligned with evolving business needs.
Consider the impact of evolving technological standards. The widespread adoption of new interoperability protocols by mid-2025 could make it easier for alternative service providers to integrate with existing business systems, thereby lowering switching costs and increasing the competitive pressure from substitutes. This development directly challenges established players who rely on proprietary ecosystems.
- Regulatory Impact: Stricter data privacy laws can boost demand for in-house solutions, making them a stronger substitute.
- Industry Trends: The rise of open-source and data localization policies favors alternative, non-traditional offerings.
- Technological Shifts: New interoperability standards in 2024-2025 reduce barriers for substitute providers.
The threat of substitutes for Ascential's services is substantial, as customers can often find alternative methods to achieve their data and analytics objectives. This includes developing in-house data analysis capabilities or utilizing readily available, though less specialized, free online resources. The increasing accessibility of data analytics skills means more companies are equipped to handle some of these needs internally.
For instance, the global business analytics market was valued at approximately $37.9 billion in 2023 and is projected for significant growth, indicating a competitive landscape where specialized services like Ascential's face pressure from broader, more accessible solutions. Companies might opt for general consulting firms or invest in self-service analytics platforms that reduce reliance on external specialists.
The threat of substitutes is amplified when alternative solutions offer similar or better performance at a lower price point. Ascential's clients will weigh the cost of its specialized data and analytics against more generalized or cost-effective substitutes available in the market. For example, if a competitor offers a broad market research report for a fraction of Ascential's subscription fee, and it meets a significant portion of the client's needs, the substitute becomes a compelling option.
Customer willingness to switch to alternatives hinges on their comfort with new technologies, perceived risks, and ease of transition. For example, in the streaming service market, a customer's openness to trying a new platform like Disney+ over Netflix in 2024, driven by exclusive content or lower pricing, directly increases the threat of substitution.
Rapid advancements in artificial intelligence and data analytics tools present a significant threat of substitutes for Ascential's core offerings. Companies and even individuals can leverage these technologies to perform tasks previously requiring specialized expertise, potentially reducing reliance on Ascential's consulting and data services. For example, the proliferation of user-friendly AI-powered analytics platforms might diminish the demand for expert consulting in market research and strategy formulation.
The accessibility and decreasing cost of these substitute technologies are key drivers. For example, many AI tools are now available on a subscription basis, making them more affordable than traditional consulting engagements. In 2024, the global AI market was valued at approximately $200 billion, with significant growth projected in areas directly impacting business intelligence and analytics.
- AI-powered analytics platforms offer self-service data analysis, bypassing the need for external consultants.
- Automation tools can handle routine data collection and processing, reducing Ascential's role in these areas.
- Open-source data science libraries empower in-house teams to develop custom analytical solutions.
- The growing availability of specialized AI models for tasks like sentiment analysis or trend prediction directly competes with Ascential's insights.
Changes in regulations can significantly alter the attractiveness of substitutes. For example, if new data privacy laws, like strengthened GDPR enforcement in 2024, impose stricter compliance burdens on third-party data aggregators, companies might find in-house data management solutions more appealing and cost-effective. This shift makes simpler, internally managed alternatives a more viable threat.
Broader industry shifts also play a critical role. A move towards open-source software or a greater emphasis on data localization, driven by geopolitical considerations in 2024, could encourage businesses to develop or adopt alternative platforms that bypass traditional proprietary solutions. This trend amplifies the threat from substitutes by making them more accessible and aligned with evolving business needs.
Consider the impact of evolving technological standards. The widespread adoption of new interoperability protocols by mid-2025 could make it easier for alternative service providers to integrate with existing business systems, thereby lowering switching costs and increasing the competitive pressure from substitutes. This development directly challenges established players who rely on proprietary ecosystems.
- Regulatory Impact: Stricter data privacy laws can boost demand for in-house solutions, making them a stronger substitute.
- Industry Trends: The rise of open-source and data localization policies favors alternative, non-traditional offerings.
- Technological Shifts: New interoperability standards in 2024-2025 reduce barriers for substitute providers.
The threat of substitutes for Ascential is heightened by the increasing availability of cost-effective, user-friendly technologies. For instance, AI-powered analytics platforms allow businesses to conduct their own data analysis, diminishing the need for external expertise. In 2024, the global AI market's significant growth, estimated around $200 billion, underscores the competitive pressure from these emerging alternatives.
Furthermore, shifts towards open-source solutions and data localization policies, observed in 2024, favor alternative platforms that bypass traditional proprietary models. Coupled with evolving interoperability standards by mid-2025, these trends reduce switching costs for customers, making substitutes more attractive and directly challenging established players like Ascential.
| Key Substitute Drivers | Description | Impact on Ascential | 2024/2025 Data Point |
| AI & Analytics Platforms | User-friendly tools for self-service data analysis. | Reduces reliance on specialized consulting. | Global AI market valued at ~$200 billion in 2024. |
| Open-Source & Data Localization | Shift towards accessible, often free, software and localized data management. | Favors alternative, non-proprietary solutions. | Growing trend driven by geopolitical considerations in 2024. |
| Interoperability Standards | New protocols easing integration with existing business systems. | Lowers switching costs for customers, increasing substitute viability. | Expected widespread adoption by mid-2025. |
| Cost-Performance Trade-off | Customer preference for solutions offering comparable insights at lower prices. | Increases pressure from generalized or niche providers. | Customer sensitivity to price-performance is a key factor. |
Entrants Threaten
The significant capital needed to establish robust data platforms, global event infrastructure, and proprietary analytics tools presents a major hurdle for new competitors looking to enter Ascential's market. For instance, building a comprehensive data analytics suite comparable to Ascential's capabilities often requires millions of dollars in upfront investment for technology, talent, and data acquisition. This financial barrier makes it challenging for emerging companies to challenge established players with existing, scaled operations.
Ascential benefits from robust brand loyalty, exemplified by its flagship events like Cannes Lions and Money20/20. These established platforms, coupled with a reputation for delivering valuable, actionable insights, foster deep trust among their B2B audiences. Newcomers face a significant hurdle in replicating this established credibility and recognition, particularly within Ascential's niche, high-value market segments.
Ascential's proprietary data and advanced analytics platforms, especially in digital commerce and marketing, create a significant barrier. Developing comparable technology and cultivating specialized expertise requires substantial upfront investment, deterring many potential new entrants.
Access to Distribution Channels and Customer Relationships
New players entering the information and events sector face a substantial barrier when trying to establish and maintain widespread distribution networks and strong customer ties. Ascential, for instance, has cultivated relationships with customers in over 100 countries, a global reach that is difficult for newcomers to replicate quickly.
The challenge lies in gaining access to these established channels and winning over existing customer loyalty, which often requires significant investment and time. Without these, new entrants struggle to effectively reach their target audience and build a solid customer base.
- Established Distribution Networks: Ascential's global presence, serving customers in over 100 countries, highlights the difficulty new entrants face in building comparable distribution capabilities.
- Customer Loyalty and Relationships: Deep-seated customer relationships are hard-won and represent a significant barrier, as existing players have already invested in trust and satisfaction.
- Cost of Market Penetration: Acquiring customers and securing distribution access typically demands substantial marketing expenditure and strategic partnerships, which can be prohibitive for new entrants.
Regulatory Barriers and Compliance Costs
The information and data analytics sector faces significant regulatory hurdles, particularly concerning data privacy and security. New players must grapple with intricate compliance frameworks, such as GDPR or CCPA, which demand substantial investments in legal counsel, technology, and ongoing monitoring. For instance, in 2024, companies operating in the EU saw compliance costs for data protection measures average around 1.3% of their annual revenue, a figure that can be prohibitive for startups.
These compliance costs act as a powerful deterrent to new entrants. Navigating a labyrinth of regulations, including those related to data handling, cybersecurity standards, and anti-trust laws, requires specialized expertise and financial resources that established firms have already absorbed. The sheer complexity and expense associated with meeting these requirements can effectively raise the barrier to entry, protecting incumbent businesses.
- Data Privacy Regulations: Compliance with laws like GDPR and CCPA necessitates significant investment in data protection infrastructure and legal expertise.
- Cybersecurity Standards: Meeting stringent cybersecurity mandates requires advanced technological solutions and continuous updates, adding to operational expenses.
- Antitrust and Competition Laws: Potential entrants must also consider regulations designed to prevent monopolistic practices, which can involve costly legal reviews and potential divestitures.
- Industry-Specific Compliance: Depending on the niche within data analytics, sector-specific regulations (e.g., HIPAA for healthcare data) further increase the compliance burden.
The threat of new entrants for Ascential is moderate, primarily due to high capital requirements and established brand loyalty. Significant investment is needed for data platforms and event infrastructure, making it difficult for newcomers to compete. Ascential's strong brand recognition, particularly with flagship events like Cannes Lions, further deters new players by demanding substantial effort to replicate its credibility.
| Barrier to Entry | Ascential's Advantage | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Millions invested in data, analytics, and global event infrastructure. | High initial cost deters many potential competitors. |
| Brand Loyalty & Reputation | Strong recognition for events like Cannes Lions and Money20/20. | Difficult for new entrants to build comparable trust and market presence. |
| Proprietary Data & Analytics | Advanced platforms in digital commerce and marketing. | Requires substantial investment in technology and expertise for replication. |
| Distribution Networks & Customer Ties | Global reach serving over 100 countries. | Challenging for new players to establish similar broad market access and relationships. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating data privacy (GDPR, CCPA) and cybersecurity. | Significant costs (e.g., ~1.3% of revenue for EU data protection in 2024) and expertise needed. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, including company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and regulatory filings. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of competitive dynamics.
