Arcadis Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Arcadis Bundle
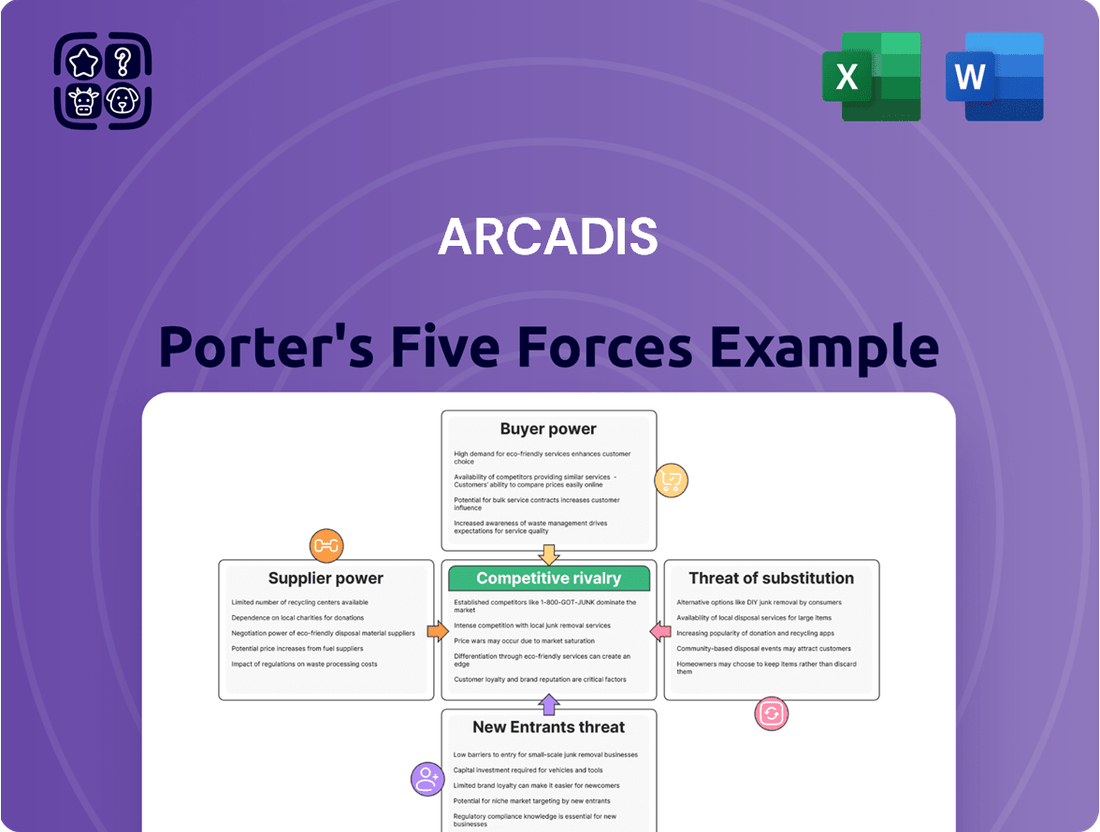
Arcadis operates within a complex industry landscape, shaped by the interplay of five key competitive forces. Understanding these dynamics—rivalry among existing competitors, the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, and the threat of substitute products—is crucial for Arcadis's strategic positioning.
The complete Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Arcadis offers a deep dive into each of these pressures, providing a data-driven framework to assess market attractiveness and identify strategic opportunities. Unlock actionable insights to navigate Arcadis’s competitive environment and drive informed decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Arcadis, a global leader in design, engineering, and consultancy, depends critically on its workforce. The availability of specialized talent, particularly in emerging fields, directly impacts its operational capacity and project execution. For instance, the demand for professionals skilled in advanced digital technologies, such as AI and data analytics in engineering, has surged. In 2024, the global shortage of AI specialists was estimated to be around 1.5 million, according to industry reports, a figure that directly translates to increased leverage for these individuals and their employers.
The scarcity of expertise in niche areas like computational fluid dynamics for complex infrastructure projects or advanced materials science for sustainable construction further amplifies supplier power. Firms that can attract and retain these highly sought-after professionals, or the specialized consultancies that provide them, gain a significant advantage. This can lead to higher labor costs and longer lead times for critical projects, as Arcadis navigates a competitive talent landscape where specialized skills command a premium.
Suppliers of advanced software, like Building Information Modeling (BIM) platforms and AI-driven analytics, wield considerable influence. Arcadis's growing dependence on these tools for operational improvements and new developments allows these specialized software providers to dictate terms and pricing more effectively. For instance, a major BIM software provider might see its annual recurring revenue grow by 15-20% in 2024, reflecting strong demand and limited alternatives for sophisticated project management.
For large, intricate projects, Arcadis frequently collaborates with specialized subcontractors and niche consultants. When these partners hold exclusive knowledge, critical certifications, or a well-established name in a particular field, such as advanced geotechnical analysis or specific regulatory compliance, their ability to negotiate terms with Arcadis is significantly enhanced.
Material and Equipment Providers for Project Implementation
Arcadis, as a consultancy, often specifies materials and equipment for client projects. Suppliers of specialized or sustainable materials, particularly those with few alternatives, hold significant bargaining power. This is amplified by the increasing global emphasis on green building and infrastructure, driving demand for eco-friendly options.
For instance, the global market for green building materials was valued at approximately $272.7 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $496.2 billion by 2028, growing at a compound annual growth rate of 12.8%. This robust growth indicates a strong supplier position for those offering certified sustainable products.
- Specialized Equipment: Suppliers of proprietary or highly technical equipment essential for project execution can command higher prices due to limited substitutes.
- Sustainable Materials: Providers of certified green or circular economy materials benefit from increased client demand and regulatory push, enhancing their negotiation leverage.
- Limited Supplier Base: When only a few suppliers can meet Arcadis's project requirements for specific inputs, their bargaining power is considerably strengthened.
- Supplier Concentration: A fragmented market with many small suppliers generally results in less supplier power, while a concentrated market with a few dominant players increases it.
Global Excellence Centers and Outsourcing Partners
Arcadis leverages Global Excellence Centers (GECs) and outsourcing partners to boost efficiency and expertise. The bargaining power of these suppliers hinges on factors like the availability of specialized talent in their respective regions and how crucial their contributions are to Arcadis's project execution. For instance, the availability of highly skilled engineering talent in regions like India or Eastern Europe, where Arcadis has a significant presence, can moderate supplier power.
The criticality of services provided by these GECs and outsourcing partners is a key determinant of their bargaining power. If these centers provide highly specialized or proprietary services that are difficult to replicate, their leverage increases. Conversely, if their services are more commoditized and easily sourced from multiple providers, Arcadis can exert more downward pressure on costs.
- Supplier Concentration: The number of qualified GECs and outsourcing partners available globally influences their bargaining power. A limited pool of highly specialized providers grants them greater leverage.
- Switching Costs: The expense and effort required for Arcadis to transition to a different GEC or outsourcing partner impact supplier power. High switching costs empower existing suppliers.
- Labor Market Dynamics: The cost and availability of skilled labor in the regions where GECs operate directly affect their pricing and bargaining position. For example, competitive salaries in 2024 for specialized engineering roles in key GEC locations can influence Arcadis's operational costs.
- Service Differentiation: The uniqueness and value-added services offered by GECs and outsourcing partners can significantly enhance their bargaining power, making them less susceptible to price competition.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Arcadis is significant, particularly for specialized talent and advanced software. For instance, the global shortage of AI specialists in 2024, estimated at 1.5 million, grants these individuals and their employers considerable leverage, driving up labor costs for Arcadis. Similarly, providers of essential BIM software can dictate terms due to strong demand and limited alternatives, with some major platforms seeing 15-20% annual recurring revenue growth in 2024.
Niche consultants and subcontractors with proprietary knowledge or critical certifications also hold strong bargaining power, influencing contract terms. Furthermore, suppliers of sustainable materials are gaining leverage, evidenced by the green building materials market's projected growth to $496.2 billion by 2028. This scenario highlights how Arcadis must navigate a landscape where specialized inputs and expertise are increasingly valuable.
| Supplier Type | Key Leverage Factors | Impact on Arcadis | Example Data (2024/2025) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized Talent (e.g., AI Engineers) | Scarcity, high demand | Increased labor costs, project delays | Global AI specialist shortage: ~1.5 million |
| Advanced Software (e.g., BIM) | Limited alternatives, critical functionality | Pricing power, potential for contract lock-in | Major BIM software ARR growth: 15-20% |
| Niche Consultants/Subcontractors | Proprietary knowledge, certifications | Negotiation advantage on terms and pricing | N/A (highly project-specific) |
| Sustainable Materials | Growing client/regulatory demand | Higher material costs, potential supply chain constraints | Green building materials market projected to reach $496.2B by 2028 |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Arcadis, evaluating the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of substitutes, and the intensity of rivalry within the industry.
Effortlessly visualize competitive intensity with a dynamic, interactive dashboard that highlights key pressure points.
Customers Bargaining Power
Arcadis's significant involvement in large-scale infrastructure and government projects means a few major clients can hold considerable sway. These clients, often national or regional governments, represent substantial contract values, giving them leverage in negotiations. For instance, a single €500 million infrastructure project can represent a significant portion of a division's annual revenue, making Arcadis highly responsive to the client's demands.
Arcadis's 'Key Client Program' is designed to cultivate deeper relationships with its most significant customers. This focus, while beneficial for securing substantial, recurring revenue streams, inherently grants these key clients greater bargaining power. Their strategic importance to Arcadis means these clients can exert more influence over pricing and contract terms, especially given the potential for significant future business.
For highly complex, multi-year projects, clients might find their bargaining power diminishes once the engagement is underway. This is due to significant switching costs and the deep integration of Arcadis's specialized expertise, making it difficult and expensive to change providers mid-project. For example, a major infrastructure project could involve years of planning and execution, locking in the client.
However, the initial stages of negotiating these long-term, complex contracts remain a critical juncture where clients can exert considerable influence. They can leverage this period to secure favorable terms and conditions before Arcadis commits substantial resources. In 2024, the demand for large-scale engineering and consulting services remained robust, giving clients some leverage in initial contract negotiations.
Client Demand for Sustainable and Digital Solutions
Clients are increasingly demanding sustainable and digitally integrated solutions. This shift in preference empowers them, as they can choose providers that best meet these evolving criteria. Arcadis's strategic focus on a 'Planet Positive Future' and digital innovation directly addresses this, aiming to differentiate its offerings and thereby reduce the leverage customers hold by showcasing unique, high-value capabilities.
Arcadis's commitment to sustainability is evident in its 2024 performance, where it reported a 15% increase in revenue from sustainable projects. Furthermore, the company's digital services segment saw a 22% growth in the same year, reflecting a strong market response to its digitally driven solutions. This ability to deliver on client priorities for both sustainability and digital transformation is crucial in managing customer bargaining power.
- Client Demand: Growing preference for sustainability and digital solutions strengthens client negotiating power.
- Arcadis's Strategy: Focus on 'Accelerating a Planet Positive Future' and digital services directly counters this by offering specialized value.
- 2024 Data: 15% revenue growth from sustainable projects and 22% growth in digital services highlight market alignment.
- Mitigation: Arcadis can reduce customer power by demonstrating unique value through its aligned strategic offerings.
Price Sensitivity and Budget Constraints
Customers' bargaining power significantly impacts Arcadis, especially when price sensitivity is high. This is particularly evident in sectors like public infrastructure, where government entities often operate under strict budget constraints. For instance, in 2024, many public tenders saw increased competition, driving down initial bid prices and putting pressure on profit margins for engineering and consulting firms like Arcadis.
This heightened price sensitivity can manifest in more rigorous bidding processes, where clients meticulously compare proposals not just on technical merit but also on cost. Arcadis, like its competitors, must navigate these scenarios by demonstrating value beyond the lowest price. For example, a client might prioritize a slightly higher upfront cost if it guarantees long-term operational savings or reduced lifecycle maintenance, a factor Arcadis can leverage.
- Price Sensitivity in Public Sector: Public sector clients in 2024 frequently exhibited high price sensitivity due to ongoing fiscal pressures, impacting tender outcomes.
- Margin Pressure: Intense bidding processes in 2024 led to increased pressure on Arcadis's profit margins.
- Value-Based Selling: Arcadis needs to emphasize long-term value and cost savings to counter pure price competition.
Arcadis faces significant customer bargaining power, particularly from large government clients and its key accounts. These clients can leverage their substantial contract values and strategic importance to influence pricing and terms. While deep project integration can reduce power mid-contract, initial negotiations remain critical for clients to secure favorable conditions.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Arcadis | 2024 Relevance |
| Client Size | Large government and infrastructure projects | High leverage due to contract value | Major projects represent significant revenue shares |
| Key Client Program | Cultivating relationships with top customers | Increased influence for strategic clients | Securing recurring revenue streams |
| Switching Costs | Deep expertise and multi-year engagements | Diminished client power mid-project | Lock-in on complex, long-term projects |
| Demand for Sustainability & Digital | Client preference for eco-friendly and tech-driven solutions | Empowers clients to choose specialized providers | Arcadis's 15% revenue growth in sustainable projects and 22% in digital services in 2024 shows alignment, mitigating this power. |
| Price Sensitivity | Budget constraints, especially in public sector | Leads to intense bidding and margin pressure | Increased competition in 2024 public tenders drove down initial bid prices. |
Full Version Awaits
Arcadis Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Arcadis Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of competitive forces within the industry. The document you see here is the exact, professionally formatted analysis you will receive instantly upon purchase, ensuring you gain immediate access to valuable strategic insights without any alterations or missing sections.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The global design, engineering, and consultancy sector is notably fragmented, featuring a vast number of regional and international firms vying for projects. This wide competitive spread means Arcadis faces rivalry from a diverse array of companies, from specialized boutique firms to large, multi-disciplinary organizations. For instance, in 2023, the global engineering services market was valued at approximately $1.5 trillion, underscoring the sheer volume of participants and the intense competition for market share.
Competitive rivalry in the consulting sector, including for Arcadis, is increasingly shaped by a firm's capacity for differentiation. This often hinges on specialized expertise, such as in climate adaptation strategies or the complex demands of the energy transition, alongside a commitment to digital innovation. Companies are vying to stand out by mastering cutting-edge tools like artificial intelligence, digital twins, and advanced data analytics.
Arcadis's strategic investments in these differentiating capabilities are therefore paramount for maintaining and enhancing its competitive edge. For instance, their focus on digital solutions, including the use of AI in project management and data analysis, positions them to offer more efficient and insightful services compared to competitors with less advanced digital offerings.
Competition for skilled talent, particularly in rapidly evolving fields like artificial intelligence and sustainability, is a major driver of rivalry. Companies that excel at building a strong employer brand and offering compelling career progression pathways are better positioned to attract and keep top performers.
In 2024, the demand for AI specialists remained exceptionally high, with average salaries for experienced AI engineers often exceeding $150,000 annually in major tech hubs. Similarly, the push for net-zero initiatives has intensified the competition for sustainability consultants and engineers, with firms actively investing in recruitment and retention bonuses to secure this expertise.
Strategic Partnerships and Acquisitions
Competitors in the consulting and engineering sector actively pursue strategic partnerships and acquisitions to broaden their service portfolios, extend their global footprint, and bolster their core competencies. This consolidation trend significantly intensifies rivalry.
Arcadis has strategically engaged in acquisitions to strengthen its market position. For instance, in 2023, Arcadis completed the acquisition of IBI Group, a global architecture, engineering, and technology firm, for approximately $1.1 billion. This move aimed to enhance Arcadis's digital capabilities and urban development expertise.
- Arcadis's acquisition of IBI Group in 2023 for around $1.1 billion significantly expanded its digital and urban planning services.
- Such M&A activity by rivals creates larger, more integrated competitors, increasing pressure on smaller players.
- The pursuit of scale through partnerships and acquisitions allows firms to offer more comprehensive solutions, thereby raising the bar for competitive offerings.
Emphasis on Sustainability and ESG Credentials
Competitive rivalry in the consulting sector is intensifying as firms increasingly differentiate themselves through robust sustainability and Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) credentials. Companies are actively vying to demonstrate their commitment to planet-positive solutions, making these factors a significant competitive battleground.
- Arcadis's ESG Leadership: Arcadis has consistently highlighted its dedication to sustainability, aiming to integrate ESG principles across its operations and client projects.
- Market Demand for Sustainable Solutions: In 2024, there's a palpable shift in client demand, with a greater emphasis on consultants who can offer verifiable sustainable outcomes and navigate complex ESG regulations.
- Competitive Differentiation: Firms with strong ESG track records, such as Arcadis's reported progress in reducing its Scope 1 and 2 emissions, are better positioned to win business from environmentally conscious clients.
- Impact on Project Bidding: A firm's sustainability performance is becoming a critical factor in bid evaluations, directly influencing competitive positioning and project acquisition.
The intense competition within the design, engineering, and consultancy sector means Arcadis faces pressure from numerous firms, ranging from specialized niche players to large multinational corporations. This rivalry is amplified by a constant drive for differentiation through specialized expertise in areas like climate adaptation and digital innovation, with firms leveraging AI and digital twins to gain an edge.
The battle for top talent, particularly in high-demand fields like AI and sustainability, is a significant factor in competitive rivalry. For example, in 2024, the demand for AI specialists remained exceptionally high, with experienced professionals commanding salaries often exceeding $150,000 annually in major tech hubs, reflecting the premium placed on these skills.
Strategic mergers and acquisitions are also reshaping the competitive landscape, as firms like Arcadis acquire others to expand their service offerings and global reach. Arcadis's 2023 acquisition of IBI Group for approximately $1.1 billion exemplifies this trend, aiming to bolster its digital and urban development capabilities and creating a more formidable competitor.
| Metric | Arcadis & Competitors | 2024 Trend/Data |
|---|---|---|
| Market Fragmentation | Highly fragmented global market | Continued presence of numerous regional and international firms |
| Key Differentiators | Specialized expertise, digital innovation (AI, digital twins) | Increasing investment in AI talent and digital solutions |
| Talent Competition | High demand for AI and sustainability experts | Average AI engineer salaries >$150k in major hubs; intense competition for sustainability consultants |
| M&A Activity | Strategic acquisitions to expand capabilities | Arcadis acquired IBI Group for ~$1.1B in 2023, enhancing digital and urban planning services |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large organizations, particularly government entities and major corporations, are increasingly building out their internal capabilities in design, engineering, and consulting. This trend directly impacts firms like Arcadis as these clients may opt to handle certain projects in-house, diminishing their need for external expertise. For instance, a significant infrastructure project might see a national government agency expanding its own planning and oversight teams.
For less complex projects, the growing availability and advancement of standardized design software and project management tools present a threat. These tools empower clients to handle certain tasks internally, potentially reducing the need for external consultants. For instance, in 2024, the global market for project management software was projected to reach over $10 billion, indicating a significant increase in accessible solutions.
Clients increasingly bypass traditional consultants by directly engaging contractors offering design-build services. This trend allows for streamlined project delivery and potentially lower costs, as the contractor manages both design and construction phases. For example, in 2024, the global design-build market was projected to reach over $230 billion, indicating a significant shift towards integrated service models.
Furthermore, the rise of specialized technology vendors presents another substitute. These companies offer sophisticated, integrated smart solutions for infrastructure and building management, directly addressing client needs without the need for intermediary consultancy. This direct access to advanced technology can reduce reliance on traditional advisory services, particularly for clients seeking specific digital enhancements or operational efficiencies.
Alternative Advisory Services
Clients may opt for specialized advisory services from firms focusing solely on management or IT consulting, particularly for strategic planning or digital transformation initiatives. This can divert business from Arcadis's integrated offerings.
For instance, in 2024, the global management consulting market was valued at approximately $270 billion, with a significant portion dedicated to strategy and digital transformation services, highlighting the competitive landscape.
Arcadis counters this by emphasizing its unique ability to blend digital solutions with deep industry expertise, providing a more holistic approach than standalone consultancies.
- Diversification of Advisory Providers: Clients can choose from pure-play management consultancies, IT firms, or niche digital transformation specialists.
- Strategic Planning and Digital Transformation Focus: These specific service areas are particularly susceptible to substitution by specialized firms.
- Arcadis's Integrated Approach: Combining digital and advisory services aims to create a stickier client relationship and a more comprehensive value proposition.
- Market Dynamics: The substantial size of the management consulting sector, especially in digital and strategy, underscores the threat of specialized alternatives.
Shifting Project Delivery Models
The rise of evolving project delivery models, such as integrated project delivery (IPD) and public-private partnerships (PPPs), presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional design and engineering consultants like Arcadis. These new models can fundamentally alter the consultant's role, potentially disintermediating them or shifting value to other entities within the project lifecycle. For instance, IPD brings together key stakeholders early on, fostering collaboration that might reduce reliance on a standalone design firm.
The increasing adoption of these alternative delivery methods means that clients may find value in solutions that bypass or significantly alter the traditional consultant-client relationship. Public-private partnerships, in particular, often bundle design, construction, and operation services, creating a comprehensive offering that substitutes for fragmented, consultant-led approaches. Arcadis's ability to adapt and integrate into these evolving structures is therefore crucial for its continued relevance and competitive positioning.
For example, the global PPP market saw significant activity in 2024, with numerous infrastructure projects across sectors like transportation and energy being awarded under these frameworks. This trend underscores the growing preference for integrated solutions that may offer a substitute for traditional consulting services. Arcadis's strategic focus on embracing and leading within these new delivery models is essential to mitigate the threat of substitutes and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
- Integrated Project Delivery (IPD): This collaborative approach brings together owners, designers, and contractors early in the process, potentially reducing the distinct role of a traditional design consultant.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): These models often bundle design, construction, and financing, offering a comprehensive solution that can substitute for standalone engineering and design services.
- Shifting Client Needs: Clients increasingly seek end-to-end solutions, pushing consultants to adapt their service offerings to remain competitive against integrated alternatives.
- Market Adaptability: Arcadis's success hinges on its capacity to evolve its business model to participate effectively in or lead these alternative project delivery methods.
Clients increasingly handle projects internally, especially large organizations and governments, reducing reliance on external firms like Arcadis. The growth of project management software, exceeding $10 billion globally in 2024, further empowers clients to manage tasks independently. Additionally, design-build services and specialized technology vendors offer integrated solutions, directly competing with traditional consultancy models.
| Substitute Type | Description | 2024 Market Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Capabilities | Clients managing projects in-house. | Significant trend for large organizations. |
| Project Management Software | Tools enabling self-management of projects. | Global market projected over $10 billion. |
| Design-Build Services | Integrated design and construction. | Global market projected over $230 billion. |
| Specialized Tech Vendors | Direct providers of smart solutions. | Growing threat for specific digital needs. |
Entrants Threaten
While a basic consultancy might have low startup costs, truly competing with a global leader like Arcadis demands substantial investment. This includes building a broad spectrum of specialized technical expertise, acquiring cutting-edge digital platforms, and establishing a worldwide operational footprint.
For Arcadis, a significant barrier to new entrants lies in the critical importance of reputation, brand recognition, and a proven track record. Building trust and demonstrating expertise in delivering complex, large-scale design and engineering projects takes years, if not decades, of consistent performance. New companies simply do not possess this established credibility, making it difficult to attract clients who prioritize reliability and proven success, especially for high-stakes infrastructure and building projects.
Arcadis, like many in the engineering and consulting sector, faces significant barriers to entry due to stringent regulatory frameworks. Obtaining necessary certifications, such as those for environmental compliance, health and safety standards, and quality management systems, requires substantial investment in time and resources. For instance, many infrastructure projects necessitate adherence to ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 standards, which can take new firms years to achieve and prove their worthiness.
Access to Key Talent and Global Networks
The threat of new entrants is significantly influenced by access to key talent and global networks. Attracting and retaining highly skilled engineers, designers, and consultants, particularly those with specialized niche expertise, presents a substantial hurdle for newcomers. Established firms like Arcadis have cultivated deep talent pools over decades, making it difficult for new players to compete for top-tier professionals.
New entrants often find it challenging to replicate the extensive global networks and established talent ecosystems that incumbent firms have painstakingly built. For instance, Arcadis's presence in over 30 countries and its workforce of approximately 30,000 employees as of early 2024, signifies a vast network of expertise and client relationships that is hard to match quickly.
- Talent Acquisition Costs: New entrants face higher recruitment costs to attract skilled professionals away from established companies.
- Network Effects: Established firms benefit from network effects where their existing global presence and client relationships attract more talent and business.
- Niche Expertise Gap: The scarcity of engineers and consultants with highly specialized skills, such as in advanced digital engineering or sustainable infrastructure, creates a barrier for new entrants needing immediate access to such capabilities.
- Brand Reputation: A strong brand reputation, built over years, aids established firms in attracting talent, a factor new entrants must work to build.
Economies of Scale and Scope in Large Projects
Arcadis, as a major player, leverages significant economies of scale and scope. This allows the company to efficiently undertake and manage large, complex, multi-disciplinary projects that require substantial resources and expertise. For instance, in 2024, the global construction market was valued at over $10 trillion, with a significant portion attributed to mega-projects often awarded to established firms capable of handling their scale and intricacies.
New entrants face a considerable hurdle in matching this capability. Without substantial upfront investment in technology, personnel, and established supply chains, it is challenging for them to compete effectively on bids for these large-scale projects. The upfront capital required to even bid on such projects can be prohibitive, creating a significant barrier to entry.
- Economies of Scale: Larger firms can spread fixed costs over a greater output, leading to lower per-unit costs.
- Economies of Scope: Arcadis can utilize existing resources and expertise across a range of services, reducing costs for new project types.
- Capital Intensity: Mega-projects demand massive capital outlays for equipment, materials, and labor, which new entrants often lack.
- Risk Management: Established firms have proven track records and risk management frameworks essential for large, high-stakes projects.
The threat of new entrants for Arcadis is relatively low due to substantial capital requirements and the need for specialized expertise. Building a global presence and a strong reputation in the engineering and consulting sector demands significant upfront investment in talent, technology, and operational infrastructure, making it difficult for newcomers to compete effectively.
Established firms like Arcadis benefit from strong brand recognition and a proven track record, which are crucial for securing large-scale projects. New entrants lack this credibility, making it challenging to win over clients who prioritize reliability and past performance in high-stakes endeavors.
Regulatory hurdles and the necessity of obtaining certifications further elevate the barriers to entry. Adhering to stringent standards for environmental compliance, safety, and quality management requires considerable time and financial resources, which new firms often cannot readily access.
| Barrier Type | Arcadis Advantage | New Entrant Challenge |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Investment | Leverages existing scale for large projects. | High upfront costs for global operations and technology. |
| Reputation & Track Record | Decades of proven success and client trust. | Lack of established credibility and project history. |
| Talent & Networks | Extensive global talent pool and established relationships. | Difficulty attracting top-tier specialists and building networks. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Established systems for certifications and standards. | Time and cost to achieve necessary accreditations. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Arcadis Porter's Five Forces analysis leverages a robust combination of data sources, including Arcadis's internal project data, market intelligence reports, and public financial disclosures from relevant companies to provide a comprehensive view of competitive dynamics.
We integrate insights from industry-specific research, economic forecasts, and stakeholder interviews to ensure a nuanced understanding of the forces shaping the competitive landscape for Arcadis.
