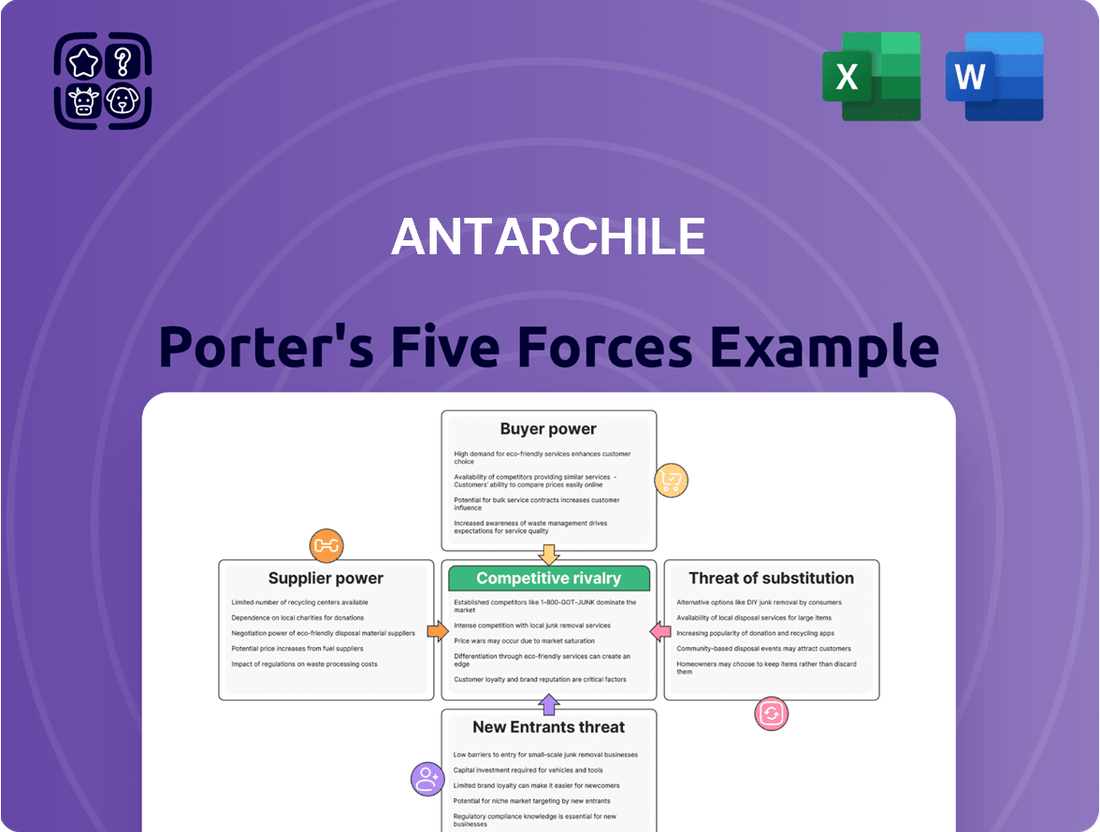
AntarChile Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
AntarChile Bundle
AntarChile operates within a complex competitive landscape, shaped by the bargaining power of its buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the intensity of rivalry. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating its market effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping AntarChile’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The concentration of suppliers is a key factor in AntarChile's bargaining power. For instance, in its forestry operations, if a limited number of companies supply specialized wood processing chemicals, those suppliers hold considerable sway. In 2023, the Chilean forestry sector, a significant area for AntarChile, saw a concentration where the top three timber exporters accounted for over 60% of total export volume, indicating potential supplier leverage.
The uniqueness of inputs significantly bolsters supplier bargaining power for AntarChile. If suppliers provide highly specialized or proprietary technologies, such as advanced drilling equipment or unique mineral processing chemicals, and these inputs are critical with limited substitutes, their ability to influence pricing and terms increases substantially. For instance, in 2024, the mining sector saw a surge in demand for specialized rare earth processing technologies, where a few key suppliers held considerable leverage due to the niche nature of their offerings.
The costs and complexities AntarChile faces when switching suppliers directly influence supplier bargaining power. High switching costs, such as the need for new equipment or specialized training for employees, would make it more difficult and expensive for AntarChile to change suppliers. This increased dependence on current suppliers grants them greater leverage in negotiations.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of suppliers integrating forward into AntarChile's core businesses, such as a timber supplier moving into pulp production, represents a significant escalation of supplier bargaining power. This potential shift could transform former partners into direct competitors, putting AntarChile in a precarious position.
For instance, if a key raw material supplier for AntarChile's forestry operations were to establish its own pulp and paper facilities, it would directly challenge AntarChile's market share. Such a move would necessitate a strategic re-evaluation of supplier relationships, potentially forcing concessions to maintain supply stability and avoid direct market conflict.
- Forward Integration Risk: Suppliers entering AntarChile's value chain (e.g., fuel suppliers into distribution) directly increases their leverage.
- Competitive Threat: This integration turns suppliers into potential rivals, impacting AntarChile's market position.
- Strategic Response: AntarChile may need to offer favorable terms or explore alternative sourcing to mitigate this risk.
Importance of AntarChile to Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers is a key consideration in AntarChile's Porter's Five Forces analysis. The relative importance of AntarChile as a customer significantly influences this dynamic. If AntarChile constitutes a large chunk of a supplier's sales, the supplier is likely more amenable to negotiating favorable terms, potentially lowering AntarChile's input costs.
Conversely, if AntarChile is a minor client for its suppliers, the suppliers would possess greater leverage. This means they might be less inclined to offer concessions, potentially driving up AntarChile's operational expenses. For instance, in 2024, companies heavily reliant on a few key suppliers for specialized components, like certain mining equipment for AntarChile's operations, might face higher input prices if those suppliers have a diverse customer base.
- Supplier Dependency: The extent to which suppliers depend on AntarChile for revenue directly impacts their bargaining power.
- Market Concentration: If the supplier market is concentrated with few players, their ability to dictate terms increases.
- Input Differentiation: Highly differentiated or unique inputs give suppliers more leverage than standardized ones.
- Switching Costs: High costs for AntarChile to switch to alternative suppliers bolster supplier power.
The bargaining power of suppliers for AntarChile is influenced by several factors, including the concentration of suppliers, the uniqueness of their offerings, and the costs associated with switching. For example, in 2024, the Chilean energy sector, a key area for AntarChile, experienced supply chain pressures for specialized turbine components, giving those few manufacturers significant leverage.
The ability of suppliers to integrate forward into AntarChile's business operations also amplifies their bargaining power. If a supplier of raw materials, for instance, were to move into processing or distribution, they could become direct competitors, forcing AntarChile to negotiate from a weaker position. In 2023, several raw material providers in Latin America were observed exploring vertical integration into downstream markets, signaling a potential shift in supplier leverage.
AntarChile's importance as a customer also plays a crucial role. If AntarChile represents a substantial portion of a supplier's revenue, the supplier is more likely to offer favorable terms. However, if AntarChile is a small client, suppliers hold more power, potentially leading to higher input costs. For example, in 2024, a mining company like AntarChile relying on niche equipment suppliers might face higher prices if those suppliers serve a broad, diverse client base.
| Factor | Impact on AntarChile | 2024 Data/Trend Example |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High concentration increases supplier power. | Limited suppliers for specialized mining explosives in Chile, giving them strong pricing control. |
| Uniqueness of Inputs | Unique inputs grant suppliers significant leverage. | Proprietary software for port logistics, essential for AntarChile's operations, held by few providers. |
| Switching Costs | High switching costs empower existing suppliers. | Significant investment required for new machinery if changing equipment suppliers in the forestry sector. |
| Forward Integration Threat | Suppliers becoming competitors reduces AntarChile's power. | Potential for a key logistics partner to expand into direct shipping services, challenging AntarChile. |
| Customer Importance | AntarChile's revenue share impacts supplier negotiation. | If AntarChile is a small client for a large supplier, supplier terms are less flexible. |
What is included in the product
This analysis provides a comprehensive examination of the competitive forces impacting AntarChile, detailing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes.
AntarChile Porter's Five Forces Analysis offers a streamlined, visual representation of competitive pressures, simplifying complex market dynamics for faster, more informed strategic planning.
Customers Bargaining Power
The concentration of AntarChile's customer base varies across its diverse segments. In energy distribution, a large number of residential and commercial customers generally limits the bargaining power of any single entity. However, significant industrial consumers within this segment could exert more influence if they represent a substantial portion of energy sales.
Within the forestry sector, AntarChile's customers might include large pulp and paper manufacturers or international timber buyers. If a few of these clients purchase a significant volume of timber or wood products, they would possess considerable bargaining power, potentially negotiating for lower prices or more favorable payment terms.
The fishing segment's customer concentration is also a key factor. If AntarChile sells a large proportion of its catch to a limited number of processing plants or international distributors, these major buyers could demand better pricing. For example, in 2023, the global seafood market saw fluctuations driven by demand from large retail chains, indicating the leverage such entities can hold.
Similarly, in mining, AntarChile's customers are typically large industrial operations or international commodity traders. The presence of a few dominant buyers in the mining supply chain would grant them significant leverage, enabling them to negotiate prices and contract conditions that reflect their substantial purchasing volume.
Customer switching costs significantly influence AntarChile's bargaining power. If customers can easily switch to competing fuel distributors or pulp suppliers with minimal effort or expense, their ability to demand lower prices increases. For instance, in 2024, the Chilean energy market saw increased competition, with new entrants offering competitive pricing, potentially lowering switching costs for some industrial energy consumers.
Conversely, if AntarChile provides specialized products or highly integrated services that are difficult for customers to replicate with other providers, switching costs become a barrier. This would diminish the bargaining power of those particular customer segments. For example, long-term contracts for customized logistics solutions or proprietary technology integration could lock in customers, reducing their leverage.
AntarChile's customers exhibit varying degrees of price sensitivity, directly impacting their bargaining power. In markets for basic forestry products, for instance, where offerings are largely commoditized, customers are highly attuned to price, readily switching suppliers for even minor cost advantages. This sensitivity grants them significant leverage.
Conversely, for AntarChile's more specialized offerings, where factors like product quality, consistent supply, and reliable service are critical, customer price sensitivity tends to be lower. In these segments, customers are more willing to pay a premium, thereby diminishing their bargaining power and allowing AntarChile greater pricing flexibility.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by AntarChile's customers significantly amplifies their bargaining power. If customers, such as large industrial consumers or paper manufacturers, possess the capability and inclination to produce the goods or services AntarChile provides internally, they can exert considerable pressure on pricing and terms. For instance, a major client might consider acquiring its own power generation facilities if AntarChile's energy prices become uncompetitive, or a large buyer of raw materials could invest in upstream operations like forestry.
This potential for self-sufficiency means customers can credibly threaten to bypass AntarChile, forcing the company to remain highly competitive. In 2024, the trend of vertical integration across various industries, driven by a desire for greater control over supply chains and cost management, suggests this threat is a relevant consideration for companies like AntarChile. For example, reports from late 2023 indicated a rise in M&A activity where large consumers acquired suppliers to secure critical inputs.
- Customer Control: Customers can leverage the threat of backward integration to demand better pricing and service from AntarChile.
- Industry Trends: The ongoing push for supply chain resilience and cost efficiency in 2024 makes backward integration a more attractive option for many of AntarChile's clients.
- Competitive Pressure: AntarChile must continually offer compelling value propositions to deter customers from bringing production in-house.
Availability of Substitute Products for Customers
The availability of substitute products significantly erodes AntarChile's bargaining power. When customers have readily accessible alternatives, they are less reliant on AntarChile's specific offerings. For instance, the growing adoption of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power directly competes with traditional fuel markets, offering consumers a viable alternative and increasing their leverage.
Similarly, in the construction and materials sector, the proliferation of alternative building materials such as composite lumber or recycled plastics can diminish demand for traditional wood products. This substitution threat forces AntarChile to remain competitive on price and quality to retain its customer base, thereby amplifying customer power.
- Substitution Threat: Customers can switch to renewable energy sources like solar and wind power, reducing reliance on traditional fuels.
- Material Alternatives: In construction, materials like composite lumber or recycled plastics offer alternatives to wood products.
- Increased Customer Leverage: The presence of substitutes empowers customers to demand lower prices or better terms from AntarChile.
- Market Dynamics: By 2024, the global renewable energy market is projected to reach trillions, highlighting the growing impact of substitutes across various industries.
AntarChile's customers possess significant bargaining power when they are concentrated or when switching costs are low. For example, large industrial clients in the energy or mining sectors can negotiate better terms due to their substantial purchasing volumes. The Chilean energy market in 2024, with increased competition, has seen lower switching costs for some consumers, enhancing their leverage.
Customers with high price sensitivity, particularly in commoditized markets like basic forestry products, can exert considerable influence. The threat of backward integration also empowers customers; a large paper manufacturer, for instance, might consider its own timber sourcing if AntarChile's prices rise. This potential for self-sufficiency forces AntarChile to remain competitive.
The availability of substitutes further strengthens customer bargaining power. In the energy sector, the rise of renewable alternatives like solar and wind power in 2024 directly challenges traditional fuel providers. Similarly, alternative building materials can reduce demand for wood products, compelling AntarChile to offer more attractive pricing and terms.
| Factor | Impact on AntarChile's Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Trend (as of 2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High for large industrial buyers, Low for dispersed residential customers | Significant industrial consumers in energy and mining can negotiate volume discounts. |
| Switching Costs | Low in competitive markets, High for specialized integrated services | Increased competition in Chile's energy sector in 2024 lowered switching costs for some clients. |
| Price Sensitivity | High for commoditized products, Low for specialized offerings | Basic forestry products see high price sensitivity; specialized logistics services command premiums. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Significant for capable, large customers | Vertical integration trends in 2024 make self-sufficiency a viable customer strategy. |
| Availability of Substitutes | High, especially in energy and materials | Renewable energy market growth and alternative building materials increase customer options. |
Full Version Awaits
AntarChile Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact AntarChile Porter's Five Forces Analysis you'll receive immediately after purchase, offering a comprehensive breakdown of competitive forces within its industry. You'll gain insights into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This detailed analysis is professionally formatted and ready for your immediate use, ensuring no surprises or placeholders.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The intensity of competitive rivalry within AntarChile's diverse business segments is directly tied to the number and market share of its competitors. For instance, in Chile's energy distribution sector, a concentrated market with a few dominant players might see less aggressive rivalry compared to a fragmented market with many smaller firms vying for customers, potentially leading to price wars.
In 2024, the Chilean energy distribution landscape features major players like Enel Chile and CGE, whose market positions and strategic decisions significantly shape competitive dynamics. Similarly, the forestry sector, a key area for AntarChile, is characterized by a mix of large, established companies and smaller regional players. The relative size and number of these entities directly impact pricing power and market share battles.
AntarChile's operations in fishing and mining also face varying competitive pressures. In fishing, the number of concessions and the size of individual fishing fleets can determine the level of competition. Mining, a capital-intensive industry, often sees rivalry among a smaller number of large global corporations, but the presence of junior miners can also add competitive intensity. These factors collectively influence AntarChile's profitability and strategic maneuvering.
The growth rate of the industries AntarChile operates within significantly shapes competitive rivalry. In sectors experiencing robust expansion, such as the projected recovery in Chile's mining and commodity export sectors, companies can often grow by capturing new demand rather than aggressively battling for existing market share. This dynamic can temper price wars and reduce the intensity of marketing battles.
Conversely, slower-growing or mature industries typically see heightened competition. Companies in these environments are more prone to engage in price reductions and intensified promotional activities to secure or maintain their positions. For instance, if AntarChile has significant exposure to a mature segment of the Chilean market, it might face more aggressive tactics from competitors vying for a limited pool of customers.
Chile's economic outlook for 2024 suggests a moderate growth trajectory, with key sectors like mining showing signs of recovery. This recovery is crucial as it can provide AntarChile with opportunities for expansion within its operational areas, potentially easing the pressure of direct rivalry by increasing the overall market pie.
AntarChile operates in sectors where product differentiation can significantly impact competitive rivalry. For instance, in the energy sector, while basic fuels are largely commoditized, advanced biofuels or specialized lubricants can offer differentiation. In 2024, the global market for sustainable aviation fuel, a differentiated product, saw significant growth, indicating a shift in competitive focus beyond just price.
Switching costs for customers in AntarChile’s diverse portfolio vary. For basic commodities like raw minerals, switching costs are typically low, leading to intense price-based competition. Conversely, in sectors like telecommunications or specialized industrial services, customers may face higher costs to switch providers due to integration with existing systems or contractual obligations, thereby moderating rivalry.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers within the industries where AntarChile operates can significantly fuel competitive rivalry. When companies find it difficult or costly to leave a market, they may continue to operate even when facing losses. This persistence can stem from specialized assets that have little alternative use, substantial fixed costs that must be absorbed, or even strong emotional ties to the business. In 2024, this dynamic could lead to persistent overcapacity across various sectors, putting continuous downward pressure on prices as firms fight for market share.
AntarChile's diversified investment portfolio, spanning sectors like construction, infrastructure, and energy, suggests a complex web of potentially high exit barriers. For instance, exiting a large-scale infrastructure project often involves substantial unrecoverable costs and contractual obligations. Similarly, specialized equipment used in construction or energy generation might have limited resale value, trapping capital. This situation forces companies to remain engaged, potentially intensifying competition among existing players.
- Specialized Assets: Industries like infrastructure often require unique, non-transferable equipment, making divestment challenging.
- High Fixed Costs: Significant upfront investments in plant, property, and equipment in sectors like energy can make exiting prohibitively expensive.
- Contractual Obligations: Long-term contracts in areas like concessions or project management can bind companies to industries even when profitability wanes.
- Emotional Attachment: For some businesses, particularly those with a long history or strong brand identity, the emotional cost of exiting can be a barrier.
Diversity of Competitors
The competitive landscape for AntarChile is characterized by a significant diversity among its rivals. Companies operating in similar sectors often hail from different national origins, possess varied strategic objectives, and maintain distinct cost structures. This heterogeneity can amplify rivalry, as competitors with differing goals may engage in aggressive tactics to gain market share, making their actions less predictable for AntarChile.
For instance, in the Chilean market, AntarChile faces competition from both large multinational corporations and smaller, locally focused businesses. Multinational players might leverage economies of scale and global brand recognition, while local firms could benefit from deep understanding of the domestic market and established relationships. This mix means AntarChile must contend with a broad spectrum of competitive strategies.
- Diverse Strategic Objectives: Competitors may prioritize rapid growth, market penetration, or long-term profitability, leading to varied pricing and investment strategies.
- Varied Cost Structures: Differences in operational efficiency, access to capital, and labor costs can create significant cost advantages for some rivals, influencing their pricing power.
- National Ownership Impact: State-owned enterprises or companies with strong national backing might operate with different risk appetites or strategic mandates compared to privately held firms.
- Unpredictable Competitive Behavior: When competitors have disparate origins and aims, their responses to market shifts or AntarChile's actions can be more erratic, escalating competitive intensity.
Competitive rivalry within AntarChile's varied business segments is shaped by the number, size, and strategic objectives of its competitors. In 2024, sectors like energy distribution in Chile, dominated by players such as Enel Chile and CGE, exhibit concentrated competition. Conversely, the fishing and mining sectors present a mix of large global corporations and smaller regional entities, each contributing to the competitive intensity through differing strategies and cost structures. This heterogeneity among rivals, from multinationals leveraging scale to local firms with market intimacy, creates a dynamic and often unpredictable competitive environment for AntarChile.
| Sector | Key Competitors (2024) | Rivalry Intensity Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Distribution (Chile) | Enel Chile, CGE | Concentrated market, few dominant players, pricing strategies |
| Forestry | Large established firms, regional players | Market share battles, pricing power |
| Fishing | Various concession holders, fleet sizes | Number of concessions, fleet capacity |
| Mining | Global corporations, junior miners | Capital intensity, commodity price volatility |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for AntarChile is substantial, particularly in its core sectors of energy and forestry. In energy, the accelerating global shift towards renewable sources like solar and wind directly challenges traditional fossil fuel operations. By the end of 2023, renewable energy capacity globally saw a record increase, adding approximately 510 gigawatts, a nearly 50% jump from the previous year, according to the International Energy Agency. This rapid expansion makes cleaner alternatives increasingly viable and cost-competitive, directly impacting demand for conventional energy sources that AntarChile may rely on.
Similarly, in the forestry sector, AntarChile faces substitutes for its wood products. Advances in materials science are leading to the development of innovative alternatives for construction and packaging. For instance, engineered wood products and advanced composite materials offer comparable or even superior performance characteristics in certain applications. Furthermore, the growing emphasis on sustainability and circular economy principles can favor recycled materials or bio-based alternatives over virgin timber, presenting a persistent challenge to traditional wood product markets.
The attractiveness of substitutes for AntarChile hinges significantly on their price-performance trade-off. If alternatives can deliver similar or better results for less money, AntarChile faces a heightened threat.
For instance, consider the renewable energy sector. In 2024, the levelized cost of electricity (LCOE) for utility-scale solar photovoltaic (PV) projects in the United States averaged around $28 per megawatt-hour (MWh), a substantial decrease from previous years. This makes solar a more compelling substitute for traditional energy sources that AntarChile might be involved with, especially if it offers comparable or improved energy output per dollar invested.
Customer willingness to switch to alternatives significantly impacts AntarChile's market position. For instance, in the Chilean telecommunications sector, a key market for AntarChile, a 2023 study indicated that over 40% of mobile subscribers had switched providers in the preceding two years, driven by competitive pricing and bundled service offerings. This high propensity to substitute suggests that AntarChile must continuously innovate and offer compelling value propositions to retain its customer base.
Factors like customer awareness of available alternatives, the perceived risks associated with switching, and ingrained brand loyalty play crucial roles. If customers are well-informed about competing services and face minimal barriers or perceived risks in transitioning, their propensity to substitute increases. AntarChile must actively monitor customer sentiment and competitor strategies to gauge this propensity and proactively address any potential erosion of loyalty.
Technological Advancements Enabling Substitutes
Rapid technological advancements are a significant driver in the emergence and improvement of substitutes, thereby intensifying their threat. Innovations in areas like renewable energy storage, for example, could directly challenge the market share of traditional fossil fuels. By mid-2024, global investment in clean energy technologies, including battery storage, reached record highs, indicating a strong push towards alternatives.
The development of new materials also presents a constant challenge to established industries. Consider the potential for advanced composites or bio-based materials to replace wood and pulp products in construction and packaging. In 2024, the market for sustainable packaging materials saw substantial growth, with companies actively exploring and adopting alternatives to traditional paper-based solutions.
- Technological disruption is a key factor in substitute threat: Innovations can quickly render existing products or services less attractive.
- Energy sector example: Advancements in electric vehicles and battery technology directly impact the demand for gasoline and diesel fuels. Global EV sales in 2024 are projected to exceed 15 million units, a significant increase from previous years.
- Materials science impact: New materials, such as advanced polymers or recycled composites, can substitute for traditional materials like wood or metals in various applications. The global market for advanced materials is expected to continue its upward trajectory in 2024.
- Economic viability of substitutes: As new technologies mature, their cost-effectiveness often improves, making them more competitive against established offerings.
Regulatory and Environmental Pressures Favoring Substitutes
Increasing regulatory and environmental pressures are significantly favoring the adoption of substitutes for AntarChile's traditional offerings. For instance, in 2024, many nations intensified their commitments to decarbonization, often translating into stricter emissions standards for industries reliant on fossil fuels, which are core to some of AntarChile's operations.
Government incentives, such as tax credits for renewable energy installations or subsidies for electric vehicles, directly encourage consumers and businesses to switch away from conventional energy sources and transportation. This trend is evident globally, with projections indicating continued growth in renewable energy capacity.
- Government incentives for renewable energy sources are projected to grow significantly in 2024-2025.
- Stricter environmental regulations are being implemented across various sectors, impacting traditional industries.
- Consumer demand for sustainable products is a growing driver for the adoption of alternatives.
The threat of substitutes for AntarChile remains a significant concern, particularly as cleaner and more cost-effective alternatives emerge across its key sectors. In 2024, the global push towards sustainability and technological advancements continues to accelerate the adoption of these substitutes, directly impacting traditional industries.
| Industry Sector | Substitute Example | 2024 Impact/Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Energy | Renewable energy (solar, wind) | Global renewable capacity additions in 2024 projected to continue strong growth, making them increasingly competitive with fossil fuels. Levelized cost of solar PV in the US averaged around $28/MWh in 2024. |
| Forestry/Materials | Advanced composites, bio-based materials | Growing demand for sustainable packaging and construction materials. Market for advanced materials expected to see continued growth in 2024, offering performance advantages. |
| Telecommunications | Alternative service providers, new technologies (e.g., satellite internet) | High customer churn rates persist, with over 40% of mobile subscribers in Chile switching providers in the two years prior to 2023, driven by competitive pricing. |
Entrants Threaten
AntarChile's deep-seated economies of scale and scope across its energy, forestry, fishing, and mining sectors present a formidable barrier for new competitors. Achieving comparable cost efficiencies would be a significant hurdle for any new player trying to enter these markets.
For instance, in its energy division, AntarChile benefits from integrated generation and distribution networks, allowing for lower per-unit production costs. Similarly, its extensive forestry operations leverage efficient supply chains from planting to processing, a scale that is difficult for newcomers to replicate quickly.
In 2024, AntarChile's diversified portfolio generated substantial revenue, with its energy segment alone contributing significantly to its overall financial strength. This broad operational base allows for cross-subsidization and shared infrastructure, further solidifying its cost advantage and deterring potential entrants who lack this established foundation.
AntarChile operates in sectors like mining and energy distribution, which demand substantial initial investments. For instance, establishing a new energy distribution network or a significant mining operation can easily run into billions of dollars for infrastructure, equipment, and regulatory compliance.
These high capital requirements act as a significant deterrent for potential new competitors. Companies looking to enter AntarChile's core markets in 2024 would need to secure extensive financing, making it a challenging proposition compared to industries with lower entry barriers.
AntarChile's deeply entrenched distribution networks for fuels, along with its integrated supply chains in forestry and fishing, present a formidable barrier to new competitors. For instance, in 2024, the company's extensive network of service stations across Chile provided unparalleled reach for its fuel products, a critical advantage that new entrants would struggle to replicate quickly or affordably.
Establishing comparable distribution channels or securing access to existing ones requires substantial investment and time, making it a significant deterrent. The sheer scale and efficiency of AntarChile's operations in 2024, particularly in logistics and warehousing for its various business segments, mean that newcomers face considerable upfront costs and operational complexities to even begin competing.
Government Policy and Regulation
Government policy and regulation significantly shape the threat of new entrants for AntarChile. In 2024, Chile's regulatory landscape, encompassing licensing, environmental permits, and sector-specific rules, continues to present substantial hurdles. For instance, stringent fishing quotas and evolving environmental standards for aquaculture, a key sector for AntarChile, can deter new players by increasing initial investment and compliance costs.
These regulatory frameworks act as a powerful barrier, effectively limiting the ease with which new companies can establish themselves in AntarChile's operating environments.
- Licensing Requirements: Obtaining necessary permits for operations, particularly in sensitive sectors like fishing and energy, can be a lengthy and costly process.
- Environmental Regulations: Strict adherence to environmental protection laws, including impact assessments and waste management, adds to the operational burden for new entrants.
- Industry-Specific Rules: Regulations tailored to specific industries, such as those governing salmon farming or renewable energy projects, can create specialized knowledge and capital barriers.
- Policy Changes: Anticipating and adapting to shifts in government policy, like potential changes to fishing laws or energy subsidies, introduces uncertainty and risk for potential new competitors.
Brand Identity and Customer Loyalty
AntarChile, through its significant holdings in companies like Empresas Copec, benefits from a deeply ingrained brand identity and a loyal customer base. This established trust acts as a substantial barrier to entry for potential new competitors.
Newcomers would face the daunting task of not only matching the product or service quality but also investing heavily in marketing and customer relationship management to even begin chipping away at the loyalty AntarChile commands. For instance, Empresas Copec's extensive network of service stations and its diverse portfolio across sectors like forestry, energy, and fishing have cultivated strong customer relationships over decades.
- Brand Recognition: AntarChile's associated brands are household names in Chile and beyond, making it difficult for new entrants to gain visibility.
- Customer Loyalty Programs: Established loyalty programs and customer satisfaction initiatives further solidify existing customer relationships, increasing the cost and effort required for new entrants to acquire customers.
- Switching Costs: For many of AntarChile's offerings, switching costs, whether financial or psychological, can deter customers from moving to a new provider, even if prices are competitive.
The threat of new entrants for AntarChile is significantly mitigated by substantial capital requirements and established distribution networks. Sectors like energy and mining demand billions in initial investment, a hurdle that deters many potential competitors. For example, in 2024, AntarChile's energy division's integrated generation and distribution infrastructure represents a massive upfront cost for any newcomer. Furthermore, its extensive fuel station network provides unparalleled market reach, making it difficult and expensive for new players to establish a comparable presence.
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our AntarChile Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, drawing from AntarChile's official annual reports and investor presentations, alongside industry-specific market research from reputable firms. We also incorporate data from Chilean regulatory bodies and macroeconomic indicators to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
