Alten Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Alten Bundle
Alten's Porter's Five Forces Analysis reveals a dynamic competitive landscape, highlighting the intense rivalry among established players and the significant threat of new entrants. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the market effectively.
The complete report unlocks a comprehensive strategic breakdown of Alten’s market position, competitive intensity, and external threats—all in one powerful analysis. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making and secure your competitive edge.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The scarcity of specialized talent, particularly in fields like artificial intelligence and cybersecurity, significantly amplifies the bargaining power of suppliers for Alten. When highly skilled engineers and IT consultants are in short supply, these professionals and the firms that employ them gain considerable leverage. This can translate into increased compensation demands and higher recruitment expenses for Alten, impacting its operational costs.
Alten's substantial workforce of 57,700 employees, with a remarkable 88% being engineers, highlights the critical importance of managing this talent scarcity. The company's capacity to attract and retain these skilled individuals is paramount in mitigating the upward pressure on costs and ensuring a consistent supply of essential expertise, directly influencing its competitive position.
In a robust technology consulting and engineering market, the high demand for specialized talent significantly bolsters supplier bargaining power. This is particularly true for niche skill sets where shortages persist.
While the broader IT consulting market is expected to see growth, with a projected slight contraction in 2024 followed by an upswing in 2025, certain segments and regions experienced reduced activity. For instance, global IT services spending saw a modest increase in 2024, but this masked variations across different service lines and end-user industries.
Switching costs for Alten's suppliers, primarily its specialized consultants, are a key factor in their bargaining power. Replacing highly skilled consultants, especially those with niche industry expertise or long-term project involvement, can be a costly and time-consuming process for Alten. This includes expenses related to recruitment, extensive onboarding, and the potential for project delays, which can impact client satisfaction and revenue.
This inherent difficulty in replacing specialized talent creates a degree of dependence for Alten on its existing consultant pool. For instance, if a critical project requires a specific technical skill set that is scarce, Alten might face higher rates or less favorable terms from the consultant if they decide to leave. This dependence can be amplified for long-term engagements where the consultant has become deeply integrated into the client's operations.
Alten's strategic initiatives to bolster its HR structure and enhance manager mobility are designed to mitigate these switching costs. By fostering internal talent development and facilitating smoother transitions between projects and roles, Alten aims to reduce its reliance on external recruitment for specialized skills. This proactive approach can help to rebalance the bargaining power, making it less advantageous for individual consultants to demand significantly higher terms due to the threat of replacement.
Uniqueness of Skills
Suppliers who possess unique or highly specialized skills, particularly in niche technological areas relevant to Alten's core industries, can wield significant bargaining power. This is especially true when Alten seeks to establish itself as a leader in these specialized fields, as the availability of alternative suppliers with comparable expertise diminishes.
Alten's strategic focus on demanding sectors such as aerospace, automotive, defense, energy, finance, and telecommunications necessitates access to highly specific and often scarce skill sets. For instance, in 2024, the demand for specialized AI and cybersecurity engineers within the defense and aerospace sectors saw significant increases, driving up compensation and thus supplier leverage.
- Specialized Engineering Talent: Suppliers providing engineers with deep expertise in areas like advanced composite materials for aerospace or autonomous driving systems for automotive have a stronger position.
- Niche Software Development: Companies offering proprietary software solutions or specialized coding skills for regulated industries like finance or defense can command higher prices.
- Certification and Compliance Expertise: Suppliers demonstrating unique certifications or in-depth knowledge of complex regulatory frameworks in Alten's target markets enhance their bargaining power.
Threat of Forward Integration
The threat of forward integration by suppliers can impact Alten's bargaining power. Individual consultants or smaller, specialized firms might aim to offer their services directly to Alten's clients, effectively cutting out the intermediary. This could potentially siphon off business, especially for more niche or localized project components.
However, the scale and complexity of many projects Alten undertakes present a significant barrier to this type of forward integration. Clients often require the broad expertise, robust project management, and established global presence that larger firms like Alten provide. For instance, a multi-country digital transformation project demands a level of coordination and diverse skill sets that a single consultant or small firm typically cannot match.
In 2024, the global management consulting market was valued at an estimated $340 billion, with large, established firms capturing a significant portion due to their ability to handle complex, international engagements. This market dynamic reinforces that while smaller players may pose a threat for specific services, the overall demand for comprehensive solutions favors larger entities like Alten, mitigating the immediate impact of forward integration for core business.
This threat is less pronounced for Alten when considering the following:
- Client preference for established project management capabilities.
- Need for diverse, multi-disciplinary expertise in large-scale projects.
- Global reach and operational capacity required for international clients.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Alten is elevated due to the scarcity of specialized engineering talent, particularly in high-demand fields like AI and cybersecurity. This scarcity, evident in 2024 with increased demand in sectors like defense and aerospace, allows suppliers of these niche skills to command higher rates. Alten’s large workforce, with 88% engineers, underscores the critical need to manage this talent acquisition and retention effectively to control costs and maintain operational capacity.
Switching costs for Alten are also a significant factor. Replacing highly skilled consultants with niche expertise or long-term project involvement is costly and time-consuming, involving recruitment, onboarding, and potential project delays. This difficulty in replacement creates a dependence on existing talent. For instance, the global management consulting market, valued at approximately $340 billion in 2024, sees larger firms like Alten benefit from client preference for established project management and global reach, which can somewhat offset the threat of smaller suppliers integrating forward.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on Alten's Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Context (2024) |
|---|---|---|
| Scarcity of Specialized Talent (e.g., AI, Cybersecurity) | High | Increased demand in defense/aerospace sectors drove up compensation for specialized engineers. |
| High Switching Costs for Alten | High | Costly recruitment, onboarding, and potential project delays associated with replacing niche consultants. |
| Supplier Forward Integration Threat | Moderate | Client preference for large-scale project management and global reach of firms like Alten mitigates this for core business. |
| Supplier Uniqueness/Niche Expertise | High | Diminished availability of comparable expertise in specialized fields where Alten aims for leadership. |
What is included in the product
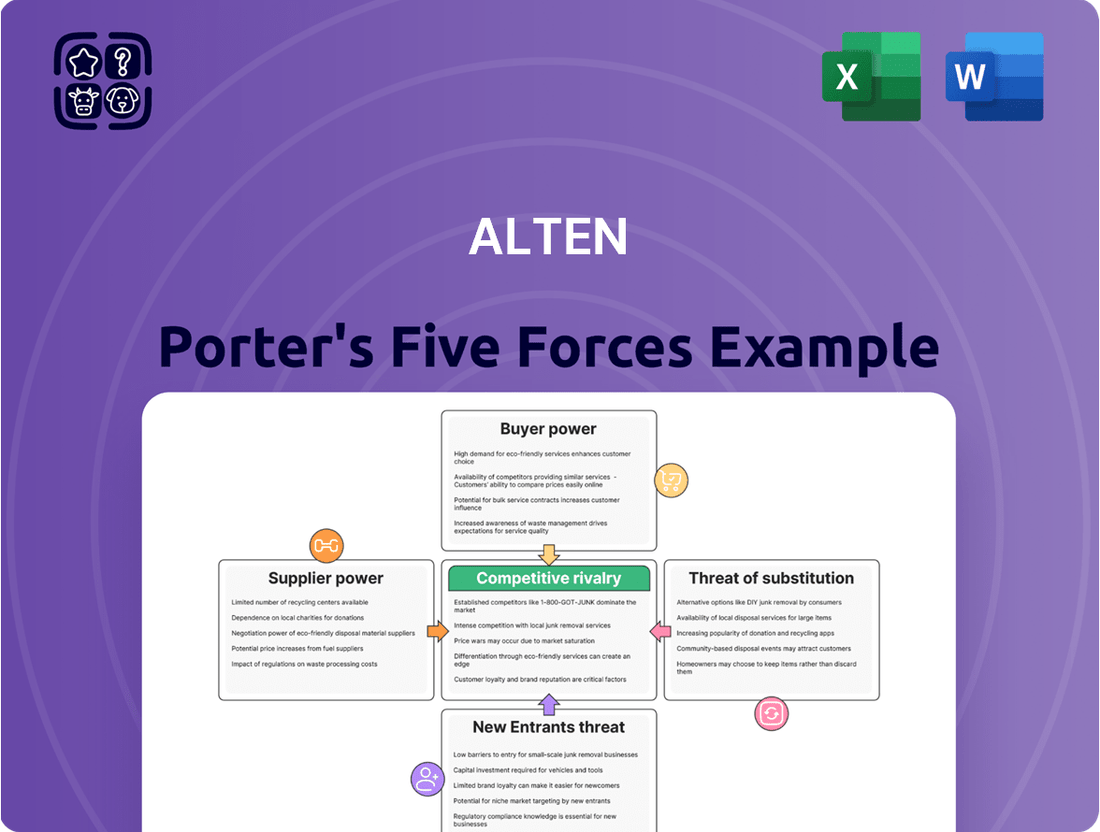
This analysis examines the five competitive forces impacting Alten, revealing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the availability of substitutes.
Quickly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each Porter's Five Forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
Client concentration is a critical factor in understanding a company's bargaining power with its customers. If a large chunk of Alten's income stems from just a handful of major clients, these clients gain significant leverage. They could push for reduced prices or more advantageous contract conditions, directly impacting Alten's profitability.
Alten's strategic move to globalize its sales force highlights the immense value placed on its top clients. These 120 key global customers are responsible for a substantial 78% of the company's total revenue. This concentration underscores the potential for these clients to wield considerable bargaining power.
The criticality of Alten's engineering and IT consulting services significantly curtails customer bargaining power. When clients rely on Alten for essential innovation, R&D, and digital transformation, their ability to impose unfavorable terms diminishes because these services are often indispensable to the client's core operations and future competitiveness.
The effort, time, and financial outlay required for clients to transition from Alten to a competitor significantly curtails their bargaining power. When clients are deeply entrenched, their ability to negotiate favorable terms with Alten is diminished.
High switching costs are often a byproduct of embedded systems, lengthy research and development collaborations, and the deep integration of Alten's solutions into a client's core operational processes. For instance, a client relying on Alten's proprietary embedded software for their product development faces substantial costs in re-engineering and testing alternative solutions.
In 2024, the average cost for an enterprise to switch IT service providers can range from tens of thousands to millions of dollars, depending on the complexity and scale of the integration, directly impacting how much leverage customers can exert.
Availability of Alternative Providers
The availability of numerous alternative technology consulting and engineering firms significantly enhances customer bargaining power. Global players such as Capgemini and Accenture, alongside a multitude of specialized regional providers, offer clients a wide array of choices. This competitive landscape means clients can readily switch providers if they are dissatisfied with pricing or service quality, putting pressure on Alten to remain competitive.
For instance, the global IT services market, which includes consulting and engineering, was valued at approximately $1.3 trillion in 2023 and is projected to grow. This vast market size directly translates to a high number of potential alternatives for any given client seeking technology consulting services. In 2024, clients are actively comparing offerings, making provider differentiation crucial.
- Increased Competition: A crowded market with many providers means clients have more leverage.
- Price Sensitivity: Clients can easily shop around for better rates, forcing firms to offer competitive pricing.
- Service Quality Demands: Customers expect high standards and can move to competitors if these are not met.
- Switching Costs: While switching can have costs, the availability of many alternatives can mitigate these for clients.
Clients' In-House Capabilities
Clients increasingly possess the capacity to develop or expand their in-house engineering and IT capabilities. This trend directly reduces their dependence on external consultants, especially for non-core or repetitive tasks. For instance, in 2024, many companies across sectors like automotive and aerospace have invested in upskilling their workforce in areas such as AI-driven design and cloud infrastructure management, aiming to bring more specialized functions in-house.
The growing internal capacity acts as a powerful bargaining tool for clients during negotiations with consulting firms. When clients can perform certain functions internally, they gain leverage to demand better pricing, service levels, or project scope from external providers. This is particularly evident in projects involving large-scale data analytics or software development, where companies are building internal centers of excellence.
- Increased In-House Skill Development: Companies are prioritizing training and hiring for specialized engineering and IT roles, building internal expertise.
- Strategic Outsourcing Decisions: Clients are more selective, outsourcing only highly specialized or temporary needs, while handling routine tasks internally.
- Negotiating Leverage: The availability of internal resources allows clients to negotiate more favorable terms and pricing with external service providers.
- Cost Efficiency Focus: Bringing capabilities in-house is often driven by a desire for greater cost control and efficiency in the long run.
When customers have significant leverage, they can demand lower prices or better terms, impacting a company's profitability. Alten's reliance on its top 120 global clients, who contribute 78% of its revenue, means these clients hold considerable sway. However, the indispensable nature of Alten's engineering and IT services, coupled with high switching costs for clients, helps to mitigate this customer power.
The availability of numerous competitors in the global IT services market, valued at approximately $1.3 trillion in 2023, gives clients many options. This abundance of alternatives, including major players like Capgemini and Accenture, allows clients to easily switch providers if dissatisfied, pressuring Alten to maintain competitive pricing and quality. Furthermore, clients are increasingly building in-house capabilities, which enhances their negotiating position by reducing reliance on external consultants.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Alten's Situation |
| Client Concentration | High | Significant (120 clients = 78% revenue) |
| Criticality of Services | Low | Low (essential for client innovation) |
| Switching Costs | Low | High (embedded systems, R&D collaborations) |
| Availability of Alternatives | High | High (large global IT services market) |
| In-house Capabilities | High | Increasing (clients building internal expertise) |
Full Version Awaits
Alten Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. You'll gain a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape through our detailed Porter's Five Forces analysis, covering threats of new entrants, bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, threat of substitute products or services, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors. This analysis is professionally formatted and ready for your immediate use.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The technology consulting and engineering sector is quite crowded. It's a market with many players, from massive global companies to smaller, specialized outfits, all vying for business. This fragmentation naturally fuels strong rivalry.
Alten finds itself in direct competition with giants like Capgemini and Accenture, who have extensive reach and broad service offerings. However, the landscape also includes a vast number of regional and niche firms, each focusing on specific industries or technological expertise, intensifying the competitive pressure across the board.
For instance, in 2023, the global IT services market was valued at approximately $1.3 trillion, with consulting being a significant segment. This massive market size attracts a wide array of competitors, from large, diversified consultancies to highly specialized boutique firms, all contributing to the high level of competitive rivalry that Alten navigates.
In a slower-growing market, competition intensifies as firms fight for market share. While the technology consulting market is generally growing, a slowdown in activity, particularly in Europe and specific sectors like Automotive and Life Sciences in 2024, has heightened competitive pressures. This means companies are more aggressively vying for the available projects, leading to tighter margins and a greater need for differentiation.
Alten distinguishes itself in a competitive landscape by focusing on specialized expertise and innovative service offerings. For instance, their strategic partnership with Mistral AI, a leading generative AI company, allows them to offer cutting-edge AI integration solutions. This differentiation through advanced technology and deep domain knowledge helps them stand out from rivals who may offer more commoditized services, thereby reducing the intensity of direct competition.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers can intensify competitive rivalry by trapping firms in an industry even when they are not profitable. This often leads to price wars and a more aggressive market landscape. For instance, if a consulting firm has invested heavily in highly specialized software or has long-term client contracts, exiting the market becomes costly and difficult, forcing them to continue operating and competing, potentially at lower margins.
While specific exit barrier data for Alten is not publicly available, the nature of engineering and IT consulting suggests potential barriers. These can include the significant investment in specialized human capital, where highly skilled engineers and IT professionals are not easily transferable to other industries. Furthermore, ongoing project commitments and the need to maintain client relationships can act as significant deterrents to a swift exit.
- Specialized Assets: High upfront investment in proprietary technology or unique infrastructure can make selling or repurposing assets difficult.
- Long-Term Contracts: Commitments to clients for ongoing projects can legally and operationally bind firms to the industry.
- Human Capital: The specialized skills and knowledge of employees are often industry-specific, making redeployment challenging.
- Emotional Factors: The pride and identity associated with a long-standing business can also contribute to reluctance to exit.
Pricing Pressure
Intense competition within the IT services sector frequently translates into significant pricing pressure, directly affecting the profitability of companies like Alten. Clients are increasingly focused on optimizing their IT expenditures and enhancing productivity, especially in the current economic climate of 2024. This heightened demand for cost-efficiency makes clients more sensitive to pricing, pushing service providers to offer more competitive rates.
This pricing pressure is evident in market trends. For instance, reports from early 2024 indicated that many businesses were scrutinizing their vendor contracts, seeking to renegotiate terms or switch providers for better value. This environment forces companies to differentiate beyond price, focusing on specialized skills, service quality, and innovation to maintain margins.
- Market Dynamics: Fierce competition among IT service providers intensifies pricing pressure as clients prioritize cost optimization.
- Client Behavior: In 2024, businesses actively sought IT cost reductions and productivity improvements, leading to greater price sensitivity.
- Margin Impact: The need to remain competitive often forces companies to accept lower profit margins on projects.
- Strategic Response: Companies must leverage unique value propositions, such as specialized expertise or superior service delivery, to counter price-based competition.
Competitive rivalry in the technology consulting and engineering sector is significant due to the market's fragmentation and the presence of numerous global and niche players. This intense competition forces companies to differentiate themselves through specialized expertise and innovation to maintain profitability.
The sheer size of the global IT services market, valued at around $1.3 trillion in 2023, attracts a wide array of competitors, from large consultancies to smaller, specialized firms. This dynamic intensifies rivalry, particularly when market growth slows, as seen with specific sectors in 2024 experiencing tighter margins due to increased competition for projects.
| Competitor | Market Presence | Differentiation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Alten | Global, specialized focus | AI integration (e.g., Mistral AI partnership), deep domain knowledge |
| Accenture | Global, broad service offerings | Scale, extensive client relationships, digital transformation services |
| Capgemini | Global, diverse portfolio | Cloud services, data analytics, digital engineering |
| Niche/Regional Firms | Specific industries/geographies | Highly specialized technical skills, tailored solutions |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Clients increasingly possess the capability to develop or enhance their internal engineering and research and development teams. This growing in-house expertise serves as a significant substitute for external consulting services, particularly for ongoing projects or when safeguarding proprietary intellectual property is paramount. For instance, a large automotive manufacturer might decide to invest in its own advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) development team rather than outsourcing to a firm like Alten, especially if the technology is core to its future competitive advantage.
The rise of sophisticated off-the-shelf software and cloud platforms presents a significant threat of substitution for custom development. For instance, the global cloud computing market was projected to reach $1.3 trillion by 2024, indicating a massive shift towards readily available solutions.
These pre-built options, covering everything from CRM to project management, can often meet a significant portion of business needs at a lower cost and with faster deployment times. This directly impacts companies offering bespoke software solutions, as clients may opt for these accessible alternatives.
However, the threat isn't absolute. Complex systems integration and the need for tailored functionalities still create a demand for expert consulting services. Many businesses find that while off-the-shelf solutions provide a base, adapting them to unique operational workflows and integrating them with existing infrastructure still requires specialized knowledge, mitigating the full impact of substitution.
The increasing sophistication of automation and AI tools presents a significant threat of substitutes for consulting services. These technologies can now perform tasks like data analysis, report generation, and even some strategic planning, directly competing with human consultants. For instance, AI-powered platforms can analyze vast datasets far quicker than traditional methods, potentially reducing the need for human analysts in certain project phases.
Alten recognizes this evolving landscape and is proactively addressing it. The company's strategic investments in AI and its integration into their service delivery model are crucial for maintaining competitiveness. By leveraging AI, Alten aims to not only offset the threat of substitutes but also to enhance the value and efficiency of its own consulting offerings, ensuring clients receive cutting-edge solutions.
Freelance Platforms/Gig Economy
The rise of freelance platforms and the gig economy presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional consulting firms. Clients can easily find individual experts for specific tasks, often at a lower cost than engaging a full-service firm. For instance, by mid-2024, platforms like Upwork and Fiverr reported millions of active freelancers, demonstrating a vast pool of readily available talent.
This accessibility allows businesses to bypass established consulting models for smaller, more defined projects. The flexibility and cost-effectiveness offered by these platforms make them an attractive alternative, especially for companies seeking specialized skills without the overhead of a long-term contract or a large firm's fees. The global freelance platform market size was projected to reach over $9 billion in 2024, highlighting the scale of this substitute.
- Increased Accessibility: Online platforms connect clients directly with individual consultants, democratizing access to expertise.
- Cost Efficiency: Freelancers often charge less than consulting firms, making specialized services more affordable.
- Project-Specific Solutions: Clients can hire for niche tasks, avoiding the broader scope and cost of traditional engagements.
- Market Growth: The gig economy continues to expand, with millions of professionals offering services across various industries.
Direct Outsourcing to Lower-Cost Regions
Clients may bypass high-value consulting firms by directly outsourcing engineering and IT tasks to regions with lower labor costs. This bypasses the need for the oversight and project management typically provided by firms like Alten. For example, in 2024, the global IT outsourcing market was valued at over $400 billion, with significant growth in offshore delivery centers.
Alten addresses this threat by bolstering its own offshore capabilities. Their investment in offshore delivery centers, particularly in India, allows them to offer competitive pricing for certain services. This strategy aims to retain clients who might otherwise seek direct offshore solutions.
Key aspects of Alten's response include:
- Strengthening Offshore Delivery Centers: Expanding capacity and expertise in locations like India to offer cost-effective solutions.
- Integrated Service Offerings: Providing end-to-end solutions that combine offshore execution with high-value onshore expertise, making direct outsourcing less appealing for complex projects.
- Focus on Value-Added Services: Emphasizing specialized skills, innovation, and strategic guidance that are difficult for clients to replicate through direct outsourcing.
The threat of substitutes for engineering and IT consulting services is amplified by the increasing capability of clients to develop solutions internally. Furthermore, the proliferation of sophisticated off-the-shelf software and cloud platforms offers readily available alternatives to custom development, as seen in the projected $1.3 trillion global cloud computing market for 2024. The rise of automation and AI tools also directly competes by performing tasks previously handled by consultants, while the gig economy provides access to individual experts, often at lower costs, evidenced by millions of active freelancers on platforms like Upwork and Fiverr by mid-2024.
Entrants Threaten
The technology consulting sector, while not burdened by extensive physical infrastructure, demands substantial capital for global expansion, crucial research and development, strategic acquisitions, and securing elite talent. Alten's aggressive acquisition strategy in 2024, including the notable purchase of Worldgrid, underscores the significant capital investment required to fuel growth and maintain competitiveness in this dynamic market.
The ability to attract, recruit, and retain a deep pool of highly skilled engineers and IT professionals across various industries and locations presents a significant hurdle for newcomers. Established companies often possess robust employer branding and extensive recruitment networks, advantages that nascent competitors struggle to replicate.
In 2024, the global demand for specialized tech talent continued to outstrip supply, with reports indicating a shortage of over 4 million cybersecurity professionals alone. This scarcity directly translates to higher recruitment costs and longer onboarding times for new entrants attempting to build a competitive workforce.
In the tech consulting sphere, established client relationships are a formidable barrier for newcomers. Firms like Accenture and Deloitte have cultivated decades-long partnerships, making it difficult for new entrants to even get a foot in the door. For instance, a 2024 report indicated that over 70% of major enterprise IT projects in North America are awarded to incumbent consulting firms, underscoring the power of existing trust.
Economies of Scale/Scope
Economies of scale are a significant barrier to entry for new competitors in the IT services sector, particularly for established players like Alten. These large firms benefit from their global delivery models, enabling them to spread fixed costs across a wider operational base. For instance, Alten's ability to leverage shared resources, such as global development centers and standardized processes, significantly reduces the per-unit cost of delivering services. This cost advantage makes it difficult for smaller, newer firms to compete on price.
Furthermore, Alten's extensive experience in undertaking large, multi-disciplinary projects allows them to refine their operational efficiencies and project management capabilities. This accumulated expertise translates into lower project execution costs and higher profit margins, further deterring potential entrants who lack this proven track record and scale. In 2023, the global IT services market was valued at over $1.3 trillion, with large providers capturing a substantial share due to these scale advantages.
Economies of scope also play a crucial role. Alten's broad portfolio of services, spanning areas like digital transformation, cloud computing, cybersecurity, and data analytics, allows them to serve a diverse range of industries. This diversification means they can cross-sell services to existing clients and achieve greater operational synergy by sharing knowledge and resources across different service lines. For example, a client engaging Alten for cloud migration might also utilize their cybersecurity expertise, increasing the overall value and stickiness of the relationship.
- Global Delivery Models: Alten's worldwide presence allows for cost optimization through offshore and nearshore talent pools, reducing labor expenses compared to domestic-only operations.
- Resource Sharing: Centralized functions like R&D, sales, and marketing are leveraged across multiple projects and geographies, spreading costs and increasing efficiency.
- Large Project Expertise: Proven success in managing complex, large-scale projects builds operational muscle and cost-control mechanisms that are hard for newcomers to replicate quickly.
- Service Diversification: Offering a comprehensive suite of services across various industries enables Alten to achieve economies of scope, leading to integrated solutions and cross-selling opportunities.
Regulatory Hurdles/Industry Certifications
Operating in sectors like aerospace, defense, energy, and life sciences demands extensive certifications and a deep understanding of complex compliance frameworks. For instance, companies in the pharmaceutical industry must navigate rigorous FDA approval processes, which can take years and cost millions. This extensive regulatory landscape significantly deters new players who may lack the capital or expertise to meet these demanding standards.
These stringent requirements act as substantial barriers to entry, effectively limiting the number of new companies that can realistically compete. In 2024, the average cost for bringing a new drug to market, including regulatory approval, was estimated to be over $2 billion. This financial and temporal commitment makes it incredibly difficult for startups to challenge established firms.
- Aerospace: FAA certification for aircraft manufacturing is a multi-year, multi-million dollar process.
- Life Sciences: FDA approval for new drugs can take 7-10 years and cost upwards of $2.6 billion.
- Energy: Navigating environmental permits and safety regulations for power generation facilities involves significant compliance costs.
The threat of new entrants in the technology consulting sector is generally low, primarily due to the substantial capital required for global expansion, R&D, and talent acquisition. For example, Alten's 2024 acquisition of Worldgrid highlights the significant investment needed to compete. Furthermore, established client relationships, a deep pool of specialized talent, and significant economies of scale, as seen in Alten's global delivery models and service diversification, create formidable barriers.
The high cost of talent acquisition, exacerbated by a global shortage of IT professionals in 2024, makes it difficult for newcomers to build a competitive workforce. Established firms also benefit from strong employer branding and extensive recruitment networks, advantages that new entrants struggle to replicate. This talent gap means higher recruitment costs and longer onboarding times for new players.
Moreover, the need for extensive certifications and deep understanding of complex compliance frameworks in sectors like aerospace and life sciences presents a significant hurdle. For instance, the multi-year, multi-million dollar process for FDA drug approval, estimated to cost over $2 billion by 2024, deters new entrants lacking the necessary capital or expertise.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants | Example (2024 Data) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | Investment in global expansion, R&D, and talent. | High barrier, requiring significant funding. | Worldgrid acquisition by Alten underscores high investment needs. |
| Talent Acquisition | Securing skilled engineers and IT professionals. | Challenging due to talent shortages and high recruitment costs. | Shortage of over 4 million cybersecurity professionals globally. |
| Client Relationships | Existing trust and long-term partnerships. | Difficult for newcomers to penetrate established markets. | Over 70% of major enterprise IT projects awarded to incumbents. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantages from large-scale operations. | New entrants struggle to match pricing and efficiency. | Global IT services market valued over $1.3 trillion in 2023. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meeting industry-specific certifications and legal standards. | Demands significant capital, expertise, and time. | New drug market entry costs exceeding $2 billion, including FDA approval. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from company annual reports, industry-specific market research, and publicly available financial filings. This ensures a comprehensive understanding of competitive intensity and market dynamics.
