Allient Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Allient Bundle
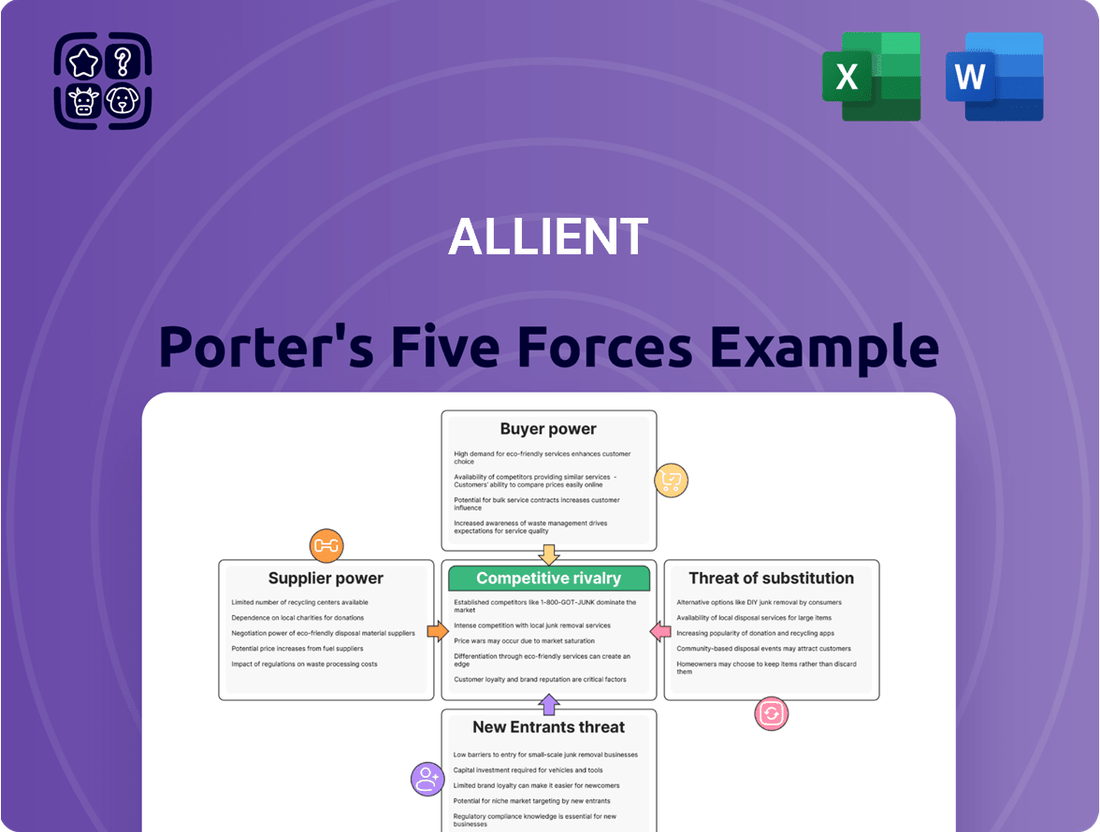
Allient's competitive landscape is shaped by powerful forces, from the bargaining power of its buyers to the constant threat of new entrants. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for navigating its market effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Allient’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Allient's reliance on specialized markets such as medical, life sciences, aerospace & defense, and industrial applications means it often needs unique components or materials. When there are few suppliers for these critical inputs, Allient's ability to negotiate favorable terms is diminished, giving suppliers greater leverage.
The company's acquisition of SNC Manufacturing Co., Inc. in January 2024, a maker of electrical transformers for defense and industrial uses, suggests a strategic move to reduce supplier dependence. By integrating such capabilities, Allient may be aiming to secure a more stable supply of essential components and bolster its own manufacturing expertise.
The intricate nature of precision motion, controls, and power systems for Allient likely translates to substantial switching costs. These expenses could encompass redesigning existing products, undergoing rigorous re-qualification processes for new components, or even retooling manufacturing lines. In 2024, companies across various sectors reported that the average cost to switch a critical component supplier could range from 10% to 25% of the annual component spend, impacting product performance and time-to-market.
Allient's commitment to high-performance, custom-engineered solutions suggests a reliance on suppliers offering specialized or proprietary components. If these suppliers possess unique or patented technologies critical to Allient's offerings, their bargaining power increases significantly.
Allient's substantial investment in engineering and development, representing 7% of its sales in 2024, underscores a dedication to innovation. This focus likely necessitates close partnerships with specialized suppliers, potentially enhancing their leverage.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
If suppliers possess the capability and a strong incentive to integrate forward, meaning they could start producing the very components or systems that Allient currently manufactures, their bargaining power over Allient naturally grows. This scenario poses a significant threat, as it allows suppliers to capture more of the value chain.
While this threat might be less pronounced in highly specialized technical areas where Allient holds distinct integration and engineering expertise, it remains a potential concern. Suppliers might pursue forward integration if they identify opportunities to gain a larger share of profitability by moving up the value chain.
- Supplier Forward Integration Capability: Assesses if key suppliers have the technical and operational capacity to manufacture Allient's products.
- Supplier Incentive for Integration: Evaluates the potential profit margins and market share gains for suppliers by moving into Allient's business.
- Allient's Specialized Expertise: Quantifies the degree to which Allient's unique engineering and integration capabilities create a barrier to supplier forward integration.
- Industry Trends: Monitors for any industry-wide shifts or supplier strategies that indicate a growing trend towards forward integration in the relevant sectors.
Importance of Allient to Suppliers
Allient's considerable scale, evidenced by its 2024 revenue of $530 million, positions it as a potentially crucial client for its suppliers. This significant revenue stream can diminish a supplier's leverage, as they would likely prioritize retaining Allient as a customer.
Furthermore, Allient's extensive global footprint, encompassing operations in the United States, Canada, Mexico, Europe, and Asia-Pacific, suggests a broad and varied supplier base. This geographic diversity could also contribute to Allient's ability to negotiate favorable terms, as suppliers may compete more intensely for its business.
The importance of Allient to its suppliers is multifaceted:
- Significant Revenue Contribution: Allient's substantial revenue can make it a key client for many suppliers, reducing their inclination to exert excessive bargaining power.
- Global Client Base: A large and geographically dispersed client like Allient provides suppliers with a stable and broad market, potentially increasing their dependence on the relationship.
- Potential for Volume Discounts: Allient's scale might allow it to secure better pricing from suppliers due to the volume of goods or services purchased.
- Supplier Dependence: If Allient represents a significant portion of a supplier's overall business, the supplier's bargaining power is inherently weakened.
Allient's bargaining power with suppliers is somewhat limited due to its reliance on specialized markets requiring unique components. The high switching costs associated with critical components, estimated to be 10-25% of annual spend in 2024, further solidify supplier leverage. However, Allient's significant revenue of $530 million in 2024 and its global presence can mitigate this power by making it a crucial client for many suppliers.
| Factor | Impact on Allient's Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Specialization & Uniqueness | Decreases bargaining power | Allient operates in specialized markets (medical, aerospace) requiring unique inputs. |
| Switching Costs | Decreases bargaining power | Estimated 10-25% of annual spend in 2024 for critical component switches. |
| Allient's Scale & Revenue | Increases bargaining power | 2024 Revenue: $530 million, making it a key client for suppliers. |
| Supplier Forward Integration Capability | Potentially decreases bargaining power | Suppliers could move up the value chain if technically feasible and profitable. |
What is included in the product
This analysis unpacks the competitive forces impacting Allient, revealing the intensity of rivalry, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, and ultimately, Allient's strategic positioning.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats by visualizing the intensity of each Porter's Five Force with a dynamic, interactive dashboard.
Customers Bargaining Power
Allient's diverse market presence across medical, life sciences, aerospace & defense, and industrial sectors generally dilutes customer power. However, within specific segments, a few substantial clients could wield significant influence.
In 2023, Allient experienced notable customer concentration, with one customer accounting for 10% of total sales and another for 12%. This highlights a period where a small number of clients represented a considerable portion of revenue.
Encouragingly, by 2024, Allient reported that no single customer exceeded 10% of total sales. This shift indicates a successful effort to reduce customer concentration and, consequently, mitigate the bargaining power of individual large buyers.
Allient's focus on 'high-performance, custom-engineered solutions' means its products are likely deeply embedded within customer operations. This integration creates substantial switching costs for clients. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for a business to switch to a new enterprise resource planning (ERP) system, a comparable complex integration, can range from tens of thousands to millions of dollars, often involving significant downtime and retraining.
The complexity and potential disruption involved in replacing Allient's specialized motion, controls, and power systems are considerable. This is especially true for industries like aerospace and medical devices, where rigorous testing, certification, and validation processes are mandatory for any component change. The time and resources needed to re-qualify a new supplier's product in these sectors can easily extend over several years, making switching a less attractive option.
In sectors like medical, aerospace, and defense, where Allient operates, component performance and reliability often outweigh cost considerations. This criticality can significantly dampen customer price sensitivity, thereby lessening their bargaining power.
Allient's emphasis on providing high-performance, custom-engineered solutions for complex challenges indicates a customer base prioritizing value and specialized capabilities over mere price. For instance, in the aerospace sector, the cost of a faulty component can far exceed the initial purchase price due to potential safety risks and mission failure.
While customers always aim for good value, the specialized nature of Allient's offerings, particularly in critical applications, means that price might not be the primary decision-making factor. This dynamic supports Allient's position by reducing the leverage customers have based solely on price negotiations.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration for Allient's customers is generally low. This is because Allient offers specialized engineering, manufacturing, and testing services that require significant expertise and infrastructure.
Customers in sectors like aerospace, defense, and industrial automation typically lack the resources and focus to develop these capabilities in-house. For instance, the aerospace industry, a key market for Allient, demands highly specialized certifications and testing protocols that are costly to replicate.
While large clients might explore backward integration for very standardized or high-volume components, the complexity and capital investment involved in precision motion and control systems make this a rare occurrence. Allient's ability to provide integrated solutions reduces the incentive for customers to bring these functions in-house.
- Low threat of backward integration: Customers generally lack the specialized expertise for precision motion, controls, and power systems.
- High cost and inefficiency for customers: Developing in-house capabilities for Allient's services is typically uneconomical.
- Focus on core competencies: Customers in Allient's target industries prioritize their own specialized areas.
- Potential for large customers: Very large clients might consider integration for standardized, high-volume parts.
Availability of Substitute Products/Services for Customers
While Allient provides specialized power quality solutions, the availability of substitute products or services can influence customer bargaining power. Even if alternatives are not perfect matches, customers may consider them if they offer a comparable benefit at a lower cost or with less integration effort. This is particularly true if the underlying technology is widely understood and accessible.
For instance, if a customer can develop a similar solution internally using off-the-shelf components for mature technologies, or if another niche provider offers a slightly different but adequate solution, Allient faces pressure to maintain competitive pricing and demonstrate superior value. This leverage increases if switching costs for the customer are low.
Allient's recent performance in the power quality solutions market for HVAC and data centers, which saw growth amidst general industrial market softness, indicates that customers in these specific segments are actively seeking specialized solutions. This suggests that in certain areas, Allient is effectively meeting demand, potentially mitigating the impact of substitutes by offering unique or highly effective capabilities.
- Customer Leverage: The existence of alternative solutions, whether from competitors or internal development, grants customers bargaining power.
- Substitute Impact: Even imperfect substitutes can exert pressure on pricing and value proposition.
- Market Specifics: Allient's growth in HVAC/data center power quality solutions in 2024 highlights demand for specialized offerings, potentially reducing the immediate threat of substitutes in those niches.
Allient's bargaining power with customers is generally moderate, influenced by product specialization and switching costs. While a reduction in customer concentration by 2024, with no single customer exceeding 10% of sales, lessened individual client leverage, the high integration of Allient's custom solutions creates significant switching costs.
For example, in 2024, the cost to switch complex enterprise systems can range from tens of thousands to millions of dollars. This complexity, especially in regulated sectors like aerospace and medical, where recertification can take years, reduces customer price sensitivity and thus their bargaining power.
The threat of backward integration is low due to the specialized expertise required for Allient's precision systems. Customers in critical industries prioritize Allient's capabilities over the high cost and inefficiency of developing these in-house, reinforcing Allient's market position.
Same Document Delivered
Allient Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Allient Porter's Five Forces analysis, offering a comprehensive examination of competitive pressures within the industry. You're viewing the exact document that will be delivered instantly upon purchase, ensuring you receive a fully formatted and ready-to-use strategic tool. This detailed analysis will equip you with the insights needed to understand market dynamics and formulate effective business strategies.
Rivalry Among Competitors
Allient competes in a landscape populated by both highly specialized niche players and larger, more diversified industrial corporations. The exact number of direct competitors varies significantly across its specialized market segments, but the presence of numerous smaller, focused firms alongside broad-based conglomerates with relevant business units naturally heightens competitive intensity.
While specific figures for Allient's direct competitors aren't publicly detailed, industry analysis indicates that in many of its operational areas, such as advanced manufacturing solutions or specialized engineering services, there are dozens of smaller, agile firms. For instance, in the industrial automation sector, where Allient has offerings, reports from 2024 suggest over 50 significant players globally, many focusing on specific technological niches.
Allient's strategy of a unified 'One-Team approach' and its global operational footprint are designed to navigate this complex competitive environment. This approach aims to leverage its diverse capabilities to effectively challenge competitors, whether they are smaller, specialized entities or larger, established industrial giants across its various market segments.
Allient operates in diverse markets, each with its own growth trajectory. The aerospace and defense sector, for instance, demonstrated robust expansion, with Allient reporting a significant 25% revenue increase in this segment during Q1 2025. Similarly, power quality solutions for critical infrastructure like HVAC and data centers continued to show strong demand.
However, the broader industrial and vehicle markets faced headwinds. These segments experienced a noticeable softness in demand throughout 2024 and into the first quarter of 2025. When certain market segments grow more slowly, it can naturally lead to heightened competitive rivalry as companies vie more aggressively for the available business.
Allient stands out by offering high-performance, custom-engineered solutions alongside a full suite of engineering, manufacturing, and testing services. This specialized approach creates unique value, sidestepping direct price wars with competitors.
The company's commitment to differentiation is further underscored by its 'Simplify to Accelerate NOW' initiative, designed to boost efficiency and customer responsiveness. This focus on tailored, high-value offerings directly combats intense rivalry by building strong customer loyalty.
Switching Costs for Customers
The custom-engineered nature of Allient's solutions significantly raises switching costs for its clients. This means that once a customer integrates Allient's technology, the expense and complexity involved in migrating to a different provider become substantial deterrents to changing suppliers. This inherent stickiness in customer relationships directly dampens the intensity of competitive rivalry within the industry.
Allient's commitment to delivering robust, reliable, and high-value products is a key driver of these elevated switching costs. For instance, in 2023, Allient reported that its top 10 customers had been with the company for an average of over 15 years, a testament to the deep integration and perceived value of their offerings. This long-term customer retention suggests that the cost and disruption of switching outweigh the potential benefits of competitor solutions.
- High Integration Costs: Customers face significant expenses related to re-engineering, testing, and deploying new systems if they switch from Allient.
- Loss of Customization Benefits: Switching would mean losing the tailored functionalities and optimizations that Allient's custom-engineered products provide.
- Operational Disruption: A change in technology providers can lead to temporary, but impactful, disruptions in a customer's ongoing operations.
- Supplier Relationship Value: Long-standing relationships with Allient often include specialized support and understanding of the client's unique operational needs, which are difficult to replicate.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers can trap companies in a market, intensifying competition. These barriers include specialized assets, long-term commitments, and substantial employee severance costs, all of which make leaving a market difficult and costly. This can lead to prolonged periods of low profitability as companies are unable to exit.
For Allient, the precision manufacturing and engineering sectors likely involve specialized assets. While specific figures for Allient's asset specialization are not publicly detailed, such investments typically represent significant capital outlays that are not easily redeployed. This inherent nature of its operations suggests a potential for moderate exit barriers.
Allient's strategic focus, exemplified by the December 2024 launch of its Defense Solutions Business Unit, underscores a commitment to growth and market presence rather than divestment. Such strategic initiatives often involve new investments and long-term planning, further reinforcing the idea that exit is not a primary consideration for the company in its current operational landscape.
- Specialized Assets: High capital investment in unique machinery and technology can make exiting costly.
- Long-Term Contracts: Existing agreements with customers or suppliers can obligate continued operation.
- Employee Severance: Significant costs associated with laying off a specialized workforce can deter exit.
- Strategic Investments: Initiatives like Allient's Defense Solutions Business Unit signal a long-term commitment, reducing the likelihood of a near-term exit.
Allient faces a competitive landscape with numerous specialized firms and larger, diversified corporations, intensifying rivalry. While specific competitor numbers aren't public, the industrial automation sector alone had over 50 significant global players in 2024, many with niche focuses. Allient's strategy of custom-engineered solutions and strong customer relationships, evidenced by its top 10 customers averaging over 15 years of partnership as of 2023, helps mitigate direct price competition and raises switching costs.
The company's commitment to high-value offerings and initiatives like 'Simplify to Accelerate NOW' further differentiate it, fostering customer loyalty and reducing the impact of rivals. While some segments like aerospace and defense showed strong growth (Allient's 25% Q1 2025 revenue increase), slower markets in 2024 and early 2025 can spur more aggressive competition for market share.
Allient's custom solutions create significant switching costs for clients, including re-engineering expenses and potential operational disruptions, making it harder for competitors to poach customers. The company's focus on long-term customer retention and strategic investments, such as the December 2024 launch of its Defense Solutions Business Unit, indicates a strategy built on sustained value rather than market exit, suggesting moderate exit barriers.
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Allient hinges on whether alternative solutions can match its high-performance, custom-engineered offerings in terms of price and capability. For instance, if a competitor can deliver comparable reliability and precision for medical or aerospace applications at a significantly lower cost, it would directly impact Allient's market position.
While generic or off-the-shelf alternatives might struggle to meet the demanding specifications of Allient's core markets, rapid technological advancements could introduce viable substitutes. For example, innovations in additive manufacturing or novel materials might enable lower-cost, yet sufficiently performant, components that were previously only achievable through Allient's specialized engineering.
Allient's management is acutely aware of external factors that could bolster the threat of substitutes. Evolving trade dynamics, particularly concerning rare earth minerals critical for certain high-tech applications, could escalate the cost of Allient's custom solutions, making price-sensitive substitutes more attractive to customers. In 2024, global supply chain disruptions continued to highlight the volatility of raw material costs, a key consideration when evaluating the price-performance ratio of potential substitutes.
Customers in Allient's core markets, such as aerospace and defense, place a premium on unwavering reliability and exact specifications. This means their likelihood of switching to alternative solutions is typically low, particularly when the applications are mission-critical, as any failure can lead to significant financial or operational repercussions. For instance, in the aerospace sector, the cost of a component failure can run into millions of dollars, making proven custom solutions highly valued.
Indirect substitutes can emerge from completely different technological paths that address the same customer need. For instance, innovations in software-driven automation or novel material science could present alternatives to Allient's traditional hardware-based motion and power control systems. Allient's commitment to research and development, which saw its R&D expenses reach $238.2 million in fiscal year 2024, is vital for preempting these potential market shifts.
Innovation and Technological Advancements in Other Industries
Rapid innovation in industries beyond traditional competitors can introduce unforeseen substitutes for Allient's offerings. For example, advancements in energy storage, like solid-state batteries, could offer alternative power solutions that bypass conventional methods Allient currently serves. Similarly, breakthroughs in additive manufacturing could disrupt the demand for precision-machined components, impacting Allient's established supply chains.
Allient is actively mitigating this threat by broadening its technological base and market reach. The acquisition of SNC Manufacturing in 2023, for instance, bolstered its presence in clean power and industrial automation, areas ripe for innovation. This strategic move helps Allient adapt to evolving market demands and potential substitute technologies by integrating new capabilities directly into its portfolio.
- Emergence of New Energy Storage: Advances in battery technology could offer alternatives to traditional power generation and distribution systems that Allient supports.
- Additive Manufacturing Disruption: Innovations in 3D printing could reduce reliance on conventionally manufactured precision components.
- Allient's Strategic Response: Acquisitions like SNC Manufacturing (2023) expand Allient's footprint in innovative sectors like clean power and automation.
- Diversification as a Buffer: By investing in and acquiring companies in adjacent, technologically advancing fields, Allient aims to stay ahead of potential substitute threats.
Regulatory or Standard Changes
Changes in industry regulations, safety standards, or environmental mandates can significantly increase the threat of substitutes. For instance, new emissions standards could make existing combustion engine vehicles less attractive compared to electric alternatives, a shift Allient must monitor closely within its diverse market segments.
Allient operates in markets where regulatory landscapes are dynamic. Compliance with evolving standards is a constant factor influencing product development and the need for differentiation. This means that technologies that meet new, stricter requirements could emerge as stronger substitutes.
The company's December 2024 sustainability report underscores its focus on environmental stewardship and compliance. This proactive approach is crucial, as it positions Allient to potentially mitigate the threat of substitutes driven by environmental regulations.
- Regulatory Shifts: Evolving government regulations and safety standards can quickly make current technologies obsolete, opening the door for new substitute products or services.
- Environmental Mandates: Increasingly stringent environmental regulations, particularly concerning emissions and resource usage, are a key driver for the adoption of greener alternatives across many industries Allient serves.
- Compliance Costs: The cost and complexity of complying with new regulations can make it more attractive for customers to switch to simpler or already compliant substitute solutions.
- Technological Adaptation: The pace at which Allient and its competitors can adapt their offerings to meet new regulatory requirements will directly impact the threat posed by substitutes.
The threat of substitutes for Allient is moderate, primarily due to the highly specialized nature of its custom-engineered solutions in demanding sectors like aerospace and defense. However, rapid technological advancements and potential shifts in raw material costs or regulatory environments could introduce more viable alternatives, especially if they offer a compelling price-performance ratio.
Allient's significant investment in research and development, evidenced by its $238.2 million R&D expenditure in fiscal year 2024, is a key strategy to preempt and neutralize substitute threats. By continuously innovating and expanding its technological capabilities, such as through acquisitions like SNC Manufacturing in 2023, Allient aims to maintain its competitive edge and adapt to evolving market needs.
While customers in Allient's core markets prioritize reliability and exact specifications, making them less prone to switching, indirect substitutes from entirely different technological paths could emerge. For example, advancements in additive manufacturing or new energy storage solutions might offer alternative ways to meet customer needs, underscoring the importance of Allient's diversification and technological foresight.
Regulatory changes and environmental mandates can also amplify the threat of substitutes by making existing technologies less attractive. Allient's focus on sustainability and compliance, as highlighted in its December 2024 report, is crucial for navigating these shifts and ensuring its offerings remain competitive against potentially greener or more compliant alternatives.
| Factor | Impact on Allient | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Specialized Customization | High barrier to substitution in core markets | Maintain premium quality and performance |
| Technological Advancements | Potential for new, lower-cost substitutes | Invest heavily in R&D ($238.2M in FY24) |
| Raw Material Volatility | Can make substitutes more price-competitive | Diversify supply chains, explore alternative materials |
| Regulatory Changes | Can favor new, compliant technologies | Proactive compliance and sustainability focus |
| Acquisitions (e.g., SNC Mfg. 2023) | Expands capabilities, counters new tech | Strategic growth into adjacent markets |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the precision motion, controls, and power systems market, particularly for custom-engineered solutions, demands substantial capital. This includes significant outlays for research and development, specialized manufacturing facilities, and sophisticated testing equipment. These upfront costs create a formidable barrier for potential new competitors.
Allient itself demonstrates this need, with capital expenditures of $9.7 million in 2024. Projections for 2025 indicate continued investment, with planned capital expenditures between $10 million and $12 million. This consistent reinvestment highlights the capital-intensive nature of the industry and the ongoing financial commitment required to remain competitive.
Allient benefits from significant economies of scale due to its extensive global manufacturing presence and its service to a wide array of diverse markets. This broad reach allows for more efficient production and distribution, lowering per-unit costs.
Furthermore, Allient leverages economies of scope by providing a comprehensive suite of engineering, manufacturing, and testing services. This integrated approach offers customers a one-stop solution, creating value beyond individual services.
New entrants face a considerable hurdle in matching Allient's cost efficiencies and the breadth of its integrated offerings. Achieving similar economies would necessitate massive upfront investment and considerable time, making it challenging to compete effectively on price or through bundled solutions.
Allient's ongoing 'Simplify to Accelerate NOW' program is designed to further optimize its operational efficiency, potentially widening this competitive gap and increasing the barriers for potential new market participants.
Allient's commitment to precision and specialty solutions means they likely possess proprietary technologies and patents. This intellectual property creates a significant hurdle for new companies looking to enter the market. Developing comparable technologies or securing licenses for existing ones requires substantial investment in research and development, along with considerable time, making it a costly endeavor for potential competitors.
Access to Distribution Channels
New companies face significant hurdles in accessing established distribution channels, particularly in specialized sectors like medical, aerospace, and defense where Allient operates. These industries demand proven reliability and performance, making it difficult for newcomers to displace incumbent suppliers. Allient's established relationships and reputation are key advantages, as evidenced by its strategic move to launch a dedicated Defense Solutions Business Unit in December 2024, reinforcing its access to this critical market.
Gaining entry into Allient's existing distribution networks requires substantial investment and time. New entrants must build trust and demonstrate consistent quality to secure partnerships. Allient's focus on high-stakes markets means that distribution partners are carefully vetted, creating a barrier for less experienced competitors.
- Established Relationships: Allient benefits from long-standing ties with key distributors and end-users, making it difficult for new entrants to replicate this network.
- Industry Reputation: The company's proven track record in demanding sectors like aerospace and medical provides a significant competitive edge in distribution access.
- Strategic Market Focus: The creation of a Defense Solutions Business Unit in late 2024 highlights Allient's commitment to solidifying and expanding its reach within critical, high-barrier-to-entry markets.
Brand Identity and Customer Loyalty
Allient's established brand identity and deep-rooted customer loyalty present a formidable barrier to new entrants. In industries where the performance of motion control solutions directly impacts critical operations, trust built over years of reliable service is invaluable. New competitors would struggle to replicate the confidence customers place in Allient's proven track record, especially given the company's strategic shift towards providing comprehensive, solutions-oriented offerings. This evolution, underscored by its rebrand from Allied Motion to Allient in August 2024, solidifies its market position and makes it harder for newcomers to gain traction.
The threat of new entrants is significantly mitigated by the high switching costs associated with Allient's customer base. Organizations relying on Allient's specialized motion control systems often have integrated these solutions deeply into their operational workflows. Replacing these systems would necessitate substantial investment in new hardware, software, and employee retraining, making a shift to an unproven competitor financially and operationally burdensome. For instance, many of Allient's clients operate in sectors like aerospace and defense, where system validation and certification processes are lengthy and costly, further cementing customer loyalty.
- Brand Recognition: Allient's long-standing reputation for quality and reliability in motion control solutions.
- Customer Loyalty: High retention rates due to the critical nature of its products and integrated solutions.
- Switching Costs: Significant financial and operational hurdles for customers looking to adopt new providers.
- Strategic Rebranding: The August 2024 rebrand to Allient reinforces its commitment to comprehensive solutions, enhancing its market differentiation.
The threat of new entrants into Allient's precision motion, controls, and power systems market is considerably low. High capital requirements for R&D and specialized manufacturing, as evidenced by Allient's 2024 capital expenditures of $9.7 million and planned 2025 investments of $10-12 million, create a significant barrier. Proprietary technologies, established distribution channels, and strong customer loyalty further deter new competition.
New entrants would struggle to match Allient's economies of scale and scope, which are bolstered by its global manufacturing footprint and integrated service offerings. The company's 'Simplify to Accelerate NOW' program aims to enhance this efficiency gap. Furthermore, the August 2024 rebranding to Allient underscores a strategic focus on comprehensive solutions, making it harder for newcomers to gain market traction.
| Barrier to Entry | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | High costs for R&D, specialized manufacturing, and testing equipment. | Significant financial hurdle. |
| Economies of Scale & Scope | Allient's global presence and integrated services lower costs and increase value. | Difficult for new entrants to compete on price or offering breadth. |
| Proprietary Technology & Patents | Exclusive technologies developed by Allient. | Requires substantial investment in R&D or licensing for competitors. |
| Distribution Channels & Relationships | Established networks and trust in high-stakes sectors like aerospace and defense. | Challenging for new entrants to gain access and displace incumbents. |
| Customer Loyalty & Switching Costs | Deep integration of solutions and high costs associated with system changes. | Makes it financially and operationally burdensome for customers to switch. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a robust foundation of data, drawing from industry-specific market research reports, company annual filings, and expert interviews to capture the nuances of competitive dynamics.
