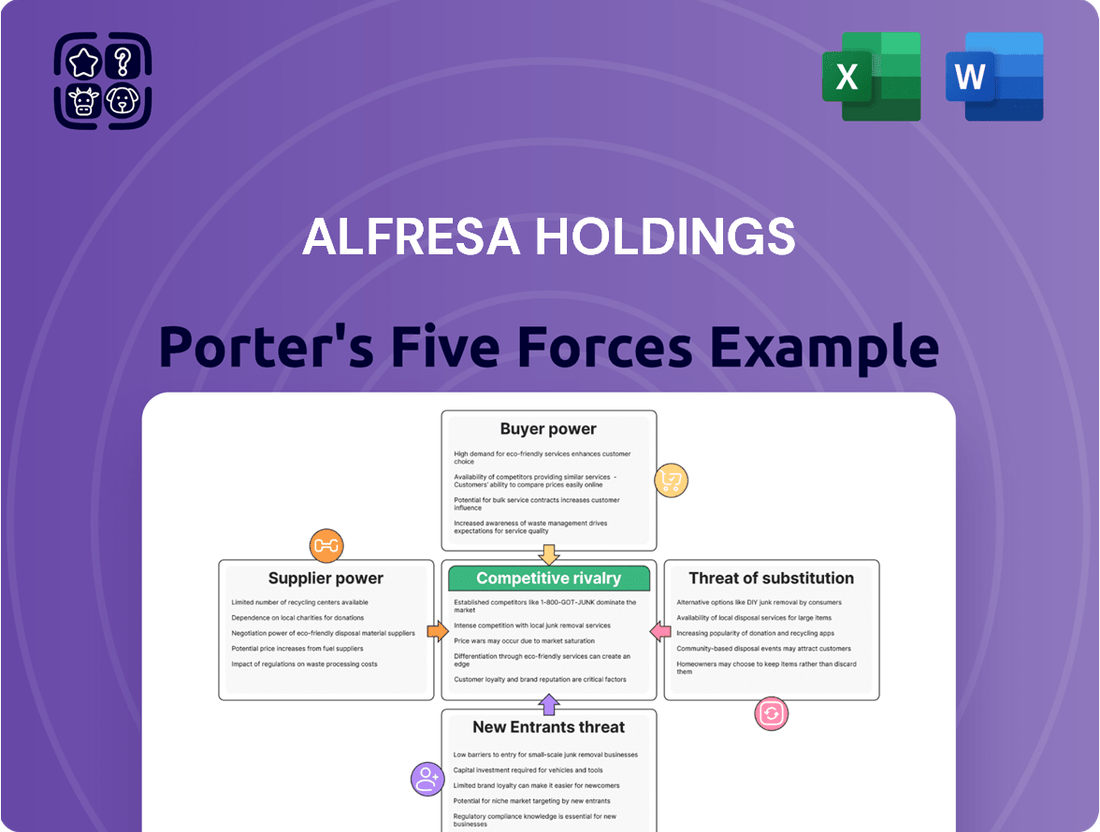
Alfresa Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Alfresa Holdings Bundle
Alfresa Holdings operates in a dynamic healthcare distribution landscape, where understanding competitive pressures is paramount. Our Porter's Five Forces analysis reveals the intricate interplay of buyer power, supplier leverage, the threat of new entrants, the intensity of rivalry, and the impact of substitutes on Alfresa's market position. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Alfresa Holdings’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The pharmaceutical and medical device sector in Japan, while strong, often features a limited number of suppliers for crucial specialized materials like active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) or advanced diagnostic reagents. This concentration means that if a few companies control the supply of essential components, they gain considerable leverage over companies like Alfresa Holdings.
Alfresa Holdings, a significant player in the wholesale pharmaceutical sector, depends heavily on its relationships with manufacturers and other suppliers. Maintaining these trust-based connections is crucial for securing a consistent and varied inventory. For instance, in fiscal year 2023, Alfresa Holdings reported total revenue of ¥2,341.3 billion, underscoring the sheer volume of products they manage, which directly ties into their supplier network's reliability.
Switching suppliers for specialized pharmaceuticals and medical devices presents significant hurdles for Alfresa Holdings. These can include substantial costs associated with reconfiguring supply chains, implementing new quality assurance protocols, and the time-consuming process of negotiating fresh distribution contracts. For instance, a shift in a key pharmaceutical supplier might necessitate extensive validation of new manufacturing processes and product equivalency, adding months to the transition.
Forward Integration by Suppliers
Forward integration by suppliers, such as pharmaceutical manufacturers moving into distribution, can significantly alter the bargaining power landscape. This strategy aims to capture more of the value chain, potentially reducing reliance on existing wholesalers like Alfresa Holdings. For instance, a major drug producer might establish its own logistics network, directly serving pharmacies and hospitals.
This move directly challenges the established role of distributors. If successful, it could limit the pricing power of wholesalers by offering an alternative, more integrated channel. The threat of such integration influences how wholesalers negotiate terms with manufacturers.
- Potential for Manufacturers to Bypass Wholesalers: Pharmaceutical companies may invest in their own distribution infrastructure to gain greater control over product delivery and customer relationships.
- Impact on Wholesaler Margins: The success of forward integration by suppliers can compress margins for traditional distributors by introducing direct competition.
- Strategic Response by Wholesalers: Wholesalers like Alfresa Holdings may need to enhance their value-added services or explore backward integration to counter this threat.
Unique or Patented Inputs
Suppliers who possess unique or patented inputs, such as novel pharmaceuticals or specialized medical equipment, wield significant bargaining power over Alfresa Holdings. This is because the company would face limited viable alternatives for these critical components, forcing it to accept the suppliers' terms.
This situation is especially pronounced for cutting-edge drugs or therapies that are protected by strong intellectual property rights. For instance, if a key supplier holds a patent on a life-saving medication that Alfresa Holdings distributes, that supplier can dictate pricing and supply terms, as there are no direct substitutes available in the market.
- Suppliers with patented drugs: If a supplier has exclusive rights to a patented drug essential for patient care, Alfresa Holdings has few alternatives.
- Proprietary medical devices: Similarly, patents on advanced medical devices limit Alfresa's ability to source comparable technology elsewhere.
- Impact on cost of goods: This exclusivity can lead to higher procurement costs for Alfresa Holdings, directly impacting its profit margins.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Alfresa Holdings is substantial, particularly for specialized pharmaceuticals and medical devices where few alternatives exist. This power is amplified when suppliers hold patents on critical inputs, allowing them to dictate terms and pricing, which directly impacts Alfresa's cost of goods. For example, in fiscal year 2023, Alfresa Holdings' total revenue was ¥2,341.3 billion, highlighting the scale of their operations and their reliance on a stable supply chain.
| Factor | Impact on Alfresa Holdings | Example/Data Point (FY2023) |
|---|---|---|
| Supplier Concentration | High leverage for few suppliers of specialized inputs | Alfresa's ¥2,341.3 billion revenue indicates significant volume dependence on key suppliers. |
| Switching Costs | High due to reconfiguring supply chains, quality assurance, and contract negotiations | Time-consuming validation processes for new pharmaceutical suppliers can add months to transitions. |
| Supplier Forward Integration | Potential to bypass wholesalers, reducing distributor margins | Drug manufacturers establishing their own logistics networks directly challenge wholesale models. |
| Proprietary Inputs | Significant power for suppliers with patented drugs or unique devices | Exclusive rights to life-saving medications allow suppliers to set pricing and supply terms. |
What is included in the product
This Porter's Five Forces analysis for Alfresa Holdings identifies the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitutes within the Japanese healthcare and pharmaceutical distribution industry.
Instantly understand strategic pressure from suppliers, buyers, new entrants, substitutes, and competitors with a powerful spider/radar chart for Alfresa Holdings.
Customers Bargaining Power
Alfresa Holdings' customer base, primarily composed of hospitals, clinics, and pharmacies throughout Japan, presents a nuanced picture regarding customer bargaining power. While there are many individual entities, the concentration of purchasing power within large hospital groups and national pharmacy chains can significantly influence negotiations.
These larger entities, due to their substantial procurement volumes, gain leverage to demand better pricing and terms from Alfresa. For instance, if a major hospital network decides to consolidate its pharmaceutical and medical supply purchasing, it can negotiate more aggressively, potentially impacting Alfresa's margins on those sales.
The bargaining power of customers for Alfresa Holdings is significantly shaped by Japan's universal National Health Insurance (NHI) system. This system, which mandates standardized pricing and encourages cost-efficiency, means healthcare providers are highly attuned to price, directly impacting Alfresa's revenue streams.
In 2024, the NHI system continues to exert pressure through regular drug price revisions. For instance, the annual price adjustment mechanism, which often leads to price cuts for pharmaceuticals, means that healthcare institutions procuring medicines and medical supplies are acutely price-sensitive. This sensitivity translates into a strong bargaining position for these customers, pushing Alfresa to maintain competitive pricing and manage its operational costs effectively to protect profit margins.
As a distributor, Alfresa Holdings' customers, particularly pharmacies and hospitals, have access to a wealth of product information. This allows them to readily compare prices and services offered by various pharmaceutical wholesalers. In 2023, the Japanese pharmaceutical market saw continued price competition, a trend that likely intensified customer scrutiny of distributor pricing.
The ability for these customers to switch distributors, while not always seamless, represents a significant lever in their bargaining power. This potential for customer churn encourages distributors like Alfresa to maintain competitive pricing and efficient service delivery to retain their client base.
Backward Integration by Customers
Backward integration by customers, such as large hospital groups or pharmacy chains, can significantly shift the bargaining power. These entities might explore direct procurement from manufacturers, bypassing traditional wholesalers like Alfresa Holdings for specific product categories. This potential bypass is a key lever in price negotiations.
While complete backward integration across the entire product spectrum is often impractical due to complexity and scale, the mere threat influences the power dynamic. For instance, a major hospital network in Japan, accounting for a substantial portion of pharmaceutical sales, could leverage its purchasing volume to demand lower prices from wholesalers if it perceives an opportunity to source directly.
- Customer Integration Threat: Large buyers like hospital groups can potentially integrate backward by sourcing directly from manufacturers, reducing reliance on intermediaries.
- Impact on Wholesalers: This threat pressures wholesalers to offer more competitive pricing and value-added services to retain business.
- Negotiating Leverage: The feasibility of direct sourcing, even for a limited range of products, grants customers significant negotiating power.
Importance of Reliable Supply and Services
Customers, particularly in the healthcare sector served by Alfresa Holdings, increasingly prioritize more than just the price of goods. Reliability in supply chains, efficient logistics, and a suite of comprehensive services are paramount. These services can include sophisticated inventory management solutions and robust post-marketing support, which directly influence customer loyalty and reduce their inclination to switch based on minor price differences.
Alfresa's strategic focus on delivering these value-added services acts as a significant differentiator. By excelling in areas like timely delivery and integrated supply chain management, Alfresa can solidify its relationships with customers. For instance, in 2024, the pharmaceutical distribution segment, a core area for Alfresa, continued to see demand for just-in-time delivery models, reducing the need for extensive customer warehousing and further embedding Alfresa's services into their operations.
- Reliable Supply: Ensuring consistent availability of critical medical supplies and pharmaceuticals.
- Efficient Logistics: Optimizing delivery routes and inventory management to meet customer needs promptly.
- Value-Added Services: Offering support such as inventory tracking, regulatory compliance assistance, and product lifecycle management.
- Customer Retention: Building strong partnerships through superior service delivery, thereby mitigating price-based competition.
Alfresa Holdings' customers, primarily hospitals and pharmacies in Japan, possess considerable bargaining power. This is amplified by the nation's universal healthcare system, which emphasizes cost efficiency and standardized pricing, making customers highly sensitive to price fluctuations. The 2024 drug price revisions, a recurring event in Japan, often lead to pharmaceutical price cuts, further strengthening the negotiating position of healthcare providers who procure these goods from distributors like Alfresa.
The ability of customers to compare prices and services from various wholesalers, coupled with the potential threat of backward integration or switching distributors, grants them significant leverage. While Alfresa aims to mitigate this through value-added services like reliable supply chains and efficient logistics, the underlying price sensitivity and market transparency remain key drivers of customer bargaining power.
| Factor | Impact on Alfresa | 2024 Context |
|---|---|---|
| Price Sensitivity (NHI System) | Pushes for competitive pricing, impacting margins | Continued pressure due to annual drug price revisions |
| Information Availability | Facilitates easy price comparison | Intensified customer scrutiny of distributor pricing |
| Switching Potential | Encourages competitive pricing and service | Customer retention remains critical for market share |
| Backward Integration Threat | Leveraged in price negotiations | Potential for direct sourcing influences wholesaler terms |
Preview the Actual Deliverable
Alfresa Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete Alfresa Holdings Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of industry competitiveness. The document you see is precisely what you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring transparency and no hidden content. You can confidently expect this professionally formatted analysis, ready for immediate application to your strategic planning needs.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The Japanese pharmaceutical and medical product wholesale market is a mature landscape dominated by a handful of significant, well-established companies, with Alfresa Holdings being a prominent example. This concentration of large players naturally fuels a high degree of competitive rivalry as each entity vies for market share and customer loyalty.
In 2023, the Japanese pharmaceutical wholesale market saw Alfresa Holdings report net sales of ¥2,464 billion, highlighting its substantial presence. Competitors like Medipal Holdings, with ¥2,294 billion in net sales for the same period, and Toho Pharmaceutical, which also operates within this concentrated market, further intensify the competitive environment.
The Japanese pharmaceutical and medical device markets are indeed seeing growth, largely driven by an aging population and ongoing technological innovation. However, within this landscape, the wholesale distribution segment may face more moderate expansion. This dynamic can lead to intensified competition as companies vie for a larger piece of the existing market pie.
In the wholesale pharmaceutical distribution sector, product differentiation for Alfresa Holdings is inherently limited due to the standardized nature of many drugs. Competition primarily hinges on operational excellence rather than unique product features.
Alfresa Holdings, like its peers, differentiates through superior logistics, ensuring timely and reliable delivery across Japan. Their extensive product catalog and commitment to supply chain integrity are key competitive advantages.
Value-added services, such as advanced inventory management systems and digital ordering platforms, further distinguish Alfresa. These offerings enhance customer efficiency and build stronger, more integrated relationships within the healthcare ecosystem.
High Fixed Costs and Capacity
The wholesale distribution sector, particularly for pharmaceuticals like Alfresa Holdings operates within, demands substantial capital for logistics, warehousing, and sophisticated IT systems. This creates a high barrier to entry due to significant fixed costs.
These high fixed costs incentivize companies to maximize their operational capacity. When the industry experiences overcapacity, it often triggers aggressive pricing competition as firms strive to cover their overheads, impacting profitability across the board.
- High Capital Investment: Establishing a robust pharmaceutical wholesale distribution network involves considerable upfront investment in temperature-controlled warehouses, a fleet of delivery vehicles, and advanced inventory management software.
- Capacity Utilization Pressure: For instance, in 2024, the pharmaceutical wholesale market in Japan, where Alfresa Holdings is a major player, faced pressures from an aging population and evolving healthcare policies, potentially leading to periods where capacity outstripped immediate demand.
- Price Competition: This environment naturally fosters intense price competition, as companies aim to fill their distribution capacity and maintain market share, even if it means accepting lower margins.
Mergers and Acquisitions Activity
Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) activity is a significant factor in the Japanese wholesale pharmaceutical market, influencing competitive rivalry. Consolidation through M&A can lead to fewer, but larger, players. For instance, in 2023, the Japanese pharmaceutical wholesale market saw continued consolidation trends as companies sought economies of scale and expanded their reach. This strategic maneuvering can reshape market dynamics, potentially increasing the market power of surviving entities.
These consolidation efforts, including strategic alliances, directly impact the competitive landscape for companies like Alfresa Holdings. When major players merge or form alliances, the number of direct competitors can shrink, but the market power of the remaining larger entities often grows. This can lead to more intense competition among these dominant firms, impacting pricing and service offerings.
The trend towards M&A in the Japanese wholesale sector is driven by several factors, including the need to optimize supply chains, enhance technological capabilities, and navigate an increasingly complex regulatory environment. For example, companies are investing in digital transformation to improve efficiency, and M&A can accelerate this process by acquiring firms with established technological infrastructure or expertise.
- Consolidation Impact: M&A activity in Japan's wholesale pharmaceutical market leads to fewer competitors but stronger market positions for remaining players.
- Market Power Shift: Strategic alliances and mergers can significantly increase the market power of larger entities, altering competitive dynamics.
- Efficiency Drivers: The pursuit of economies of scale and optimized supply chains are key motivators for M&A in this sector.
Competitive rivalry within the Japanese pharmaceutical wholesale market is intense, driven by the presence of large, established players like Alfresa Holdings. With significant capital investment required for operations, companies are incentivized to maximize capacity, which can lead to price wars when demand fluctuates. Mergers and acquisitions further consolidate the market, creating fewer but more powerful competitors who then engage in heightened competition on operational efficiency and value-added services.
| Company | 2023 Net Sales (JPY Billion) | Key Competitors |
|---|---|---|
| Alfresa Holdings | 2,464 | Medipal Holdings, Toho Pharmaceutical |
| Medipal Holdings | 2,294 | Alfresa Holdings, Toho Pharmaceutical |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Hospitals and large clinic chains may explore direct procurement from pharmaceutical manufacturers, especially for high-volume or specialized medical supplies. This bypasses the traditional wholesaler model, presenting a significant substitute threat to companies like Alfresa Holdings. For instance, in 2024, major hospital systems have been actively negotiating directly with drug makers for certain patented medications, aiming to reduce costs.
Large pharmacy chains, by developing or expanding their own distribution networks, can significantly reduce their dependence on external wholesalers like Alfresa. This internal capability acts as a direct substitute for Alfresa's core distribution services within the retail pharmacy sector.
For example, major drugstore chains in Japan, which is Alfresa's primary market, have been increasingly exploring direct sourcing and optimized logistics to control costs and improve efficiency. This trend intensifies the threat of substitutes, as these chains possess the scale to make such investments viable.
The increasing adoption of telemedicine and home healthcare services in Japan, a trend amplified by the nation's rapidly aging demographic, presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional medical supply chain models. These evolving healthcare delivery methods, particularly those catering to Japan's substantial elderly population, could necessitate shifts in how medical products reach consumers. For instance, by 2023, Japan's population aged 65 and over represented approximately 29.9% of its total population, highlighting the market demand for home-based care solutions.
While these services still rely on the physical delivery of medical supplies, they may favor alternative distribution channels or direct-to-patient models for specific product categories. This could potentially bypass traditional intermediaries, impacting established supply chain structures. The growth in digital health platforms, with numerous startups emerging in this space, indicates a growing competitive landscape that could offer alternative ways for patients to access necessary medical goods and services.
Digital Platforms and E-commerce
The increasing digitalization of healthcare presents a significant threat of substitutes for traditional wholesale distribution models. E-commerce platforms are emerging that can facilitate direct transactions between pharmaceutical manufacturers, healthcare providers, and even patients, bypassing intermediaries like Alfresa Holdings.
These digital platforms can offer greater convenience, potentially lower costs through reduced overhead, and faster delivery times. For instance, in 2024, the global e-commerce market for pharmaceuticals was projected to reach substantial figures, indicating a growing acceptance of online channels for healthcare product procurement.
- Direct-to-Provider/Patient Models: Online portals allow manufacturers to sell directly, reducing reliance on wholesalers.
- Cost Efficiency: Digital platforms can often operate with lower margins than traditional distribution networks.
- Market Growth: The digital health market continues its rapid expansion, with e-pharmacy sales showing consistent year-over-year growth.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in logistics and supply chain management are further enabling these digital substitutes.
Alternative Therapies or Preventative Measures
The threat of substitutes for Alfresa Holdings' distribution services is influenced by evolving healthcare paradigms. While not directly replacing distribution itself, advancements in alternative therapies, such as cell and gene therapies, could alter the demand for traditional pharmaceuticals. Similarly, a greater emphasis on preventative medicine might reduce the overall volume of certain treatments requiring distribution.
For instance, the global market for cell and gene therapy is projected to reach significant figures, with some estimates suggesting it could exceed $30 billion by 2026, indicating a growing segment that may have different distribution needs than conventional drugs. This shift necessitates adaptability in logistics and supply chain management for distributors like Alfresa Holdings.
- Growing Cell and Gene Therapy Market: This sector's expansion presents a potential shift in product types handled by distributors.
- Preventative Medicine Trends: Increased focus on wellness and early intervention could decrease reliance on certain pharmaceutical treatments.
- Logistical Adaptability: Distributors must be prepared for specialized handling and storage requirements for novel therapies.
- Impact on Traditional Volumes: Changes in treatment modalities may affect the overall volume of traditional pharmaceuticals distributed.
The threat of substitutes for Alfresa Holdings' services stems from evolving healthcare models that can bypass traditional distribution channels. Direct procurement by large hospitals and the expansion of proprietary logistics by major pharmacy chains represent significant challenges. Furthermore, the rise of telemedicine and digital health platforms offers alternative pathways for medical product access, potentially reducing reliance on established wholesalers.
| Substitute Type | Description | 2024/2025 Relevance |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Procurement by Hospitals | Hospitals buying directly from manufacturers. | Major hospital systems actively negotiating for high-volume/specialized drugs in 2024. |
| In-house Pharmacy Logistics | Large pharmacy chains managing their own distribution. | Japanese drugstore chains exploring direct sourcing and optimized logistics. |
| Telemedicine & Home Healthcare | Delivery models favoring direct-to-patient or alternative channels. | Japan's elderly population (approx. 29.9% in 2023) drives demand for home-based care solutions. |
| Digital Health Platforms/E-commerce | Online platforms facilitating direct transactions. | Global pharmaceutical e-commerce market showing significant growth and acceptance in 2024. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the pharmaceutical and medical product wholesale distribution sector in Japan, where Alfresa Holdings operates, demands substantial upfront capital. New players must invest heavily in establishing large, compliant warehouses, sophisticated logistics networks, specialized temperature-controlled transportation, and advanced IT systems for inventory management and regulatory compliance. This high capital requirement acts as a significant barrier, deterring potential new entrants.
The healthcare sector in Japan presents substantial barriers to entry due to its highly regulated nature. New companies must navigate a complex web of stringent licensing requirements, permits, and adherence to rigorous quality and safety standards for both pharmaceutical and medical device distribution. For instance, obtaining approval for new drug distribution can involve lengthy processes and significant investment in demonstrating compliance with the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) guidelines.
Established relationships and trust are significant barriers for new entrants in the pharmaceutical distribution sector, impacting Alfresa Holdings. These deep-seated connections with suppliers and healthcare providers are built over years, fostering loyalty and preferential treatment that new companies struggle to replicate. For instance, in 2023, Alfresa Corporation reported a strong network of over 20,000 customer sites, highlighting the extensive reach and established trust it commands.
Economies of Scale and Scope
The threat of new entrants for Alfresa Holdings is significantly mitigated by the substantial economies of scale and scope enjoyed by established players in the pharmaceutical wholesale and distribution sector. Large, incumbent wholesalers like Alfresa benefit from considerable cost advantages in purchasing, allowing them to negotiate better terms with manufacturers. For instance, in 2024, major pharmaceutical distributors continued to leverage their vast distribution networks, optimizing logistics and warehousing to achieve lower per-unit costs.
New entrants would find it exceptionally challenging to replicate these efficiencies. They would struggle to achieve similar purchasing power or build a comparable distribution infrastructure without incurring prohibitive upfront costs. This cost disadvantage makes it difficult for newcomers to compete effectively on price against established entities, thereby limiting the threat of new market participants.
Key factors contributing to this barrier include:
- Purchasing Power: Large volume purchases by established wholesalers lead to lower acquisition costs for pharmaceuticals.
- Logistical Efficiency: Extensive and optimized distribution networks reduce transportation and warehousing expenses per unit.
- Operational Scale: High operational volumes allow for greater absorption of fixed costs, leading to lower overall per-unit operational expenses.
Brand Recognition and Reputation
Alfresa Holdings benefits significantly from its established brand recognition and a deeply ingrained reputation for reliability within Japan's critical healthcare supply chain. This isn't just about a name; it's about trust built over years of consistent service and quality. For any new company looking to enter this sector, overcoming this established goodwill presents a considerable hurdle.
New entrants would require substantial investment in marketing and a considerable amount of time to cultivate a similar level of trust and brand loyalty among healthcare providers and consumers. For instance, building a comparable reputation might take a new player five to ten years, during which Alfresa can further solidify its market position. In 2024, the healthcare distribution market in Japan is highly competitive, but established players like Alfresa have a distinct advantage due to these intangible assets.
- Strong Brand Recognition: Alfresa Holdings is a well-known and respected name in the Japanese healthcare sector.
- Reputation for Reliability: The company is trusted for its consistent and dependable supply chain operations.
- High Entry Barrier: New competitors face a significant challenge in building a comparable reputation and customer confidence.
- Time and Investment: Establishing a similar level of market trust requires substantial marketing spend and years of dedicated effort.
The threat of new entrants for Alfresa Holdings is low due to significant capital requirements, stringent regulatory hurdles, and the need for established relationships. New companies must invest heavily in infrastructure and navigate complex licensing, a process that can take years and considerable financial resources.
Economies of scale and scope further deter new players, as established firms like Alfresa benefit from lower per-unit costs through bulk purchasing and efficient logistics. For example, in 2024, major pharmaceutical distributors continued to leverage vast networks to optimize costs.
Brand recognition and a reputation for reliability, built over decades, create a substantial intangible barrier. New entrants would need extensive time and investment to build comparable trust among healthcare providers, making direct competition challenging.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High investment needed for warehouses, logistics, and IT systems. | Significant deterrent due to substantial upfront costs. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating stringent licensing, permits, and PMDA guidelines. | Lengthy and costly processes requiring extensive expertise. |
| Established Relationships | Deep-seated trust and loyalty with suppliers and providers. | Difficult for newcomers to replicate, limiting market access. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantages from large-volume purchasing and distribution. | New entrants face higher per-unit costs, hindering price competitiveness. |
| Brand Reputation | Strong recognition and trust built over years of reliable service. | Requires significant time and marketing investment to achieve comparable standing. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Alfresa Holdings is built upon a foundation of publicly available data, including the company's annual reports, investor relations materials, and relevant industry publications. We also incorporate insights from market research reports and government data to provide a comprehensive view of the competitive landscape.
