Air Methods Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Air Methods Bundle
Air Methods operates in a dynamic healthcare landscape, facing significant pressures from various market forces. Understanding these forces is crucial for anyone looking to grasp the company's competitive positioning.
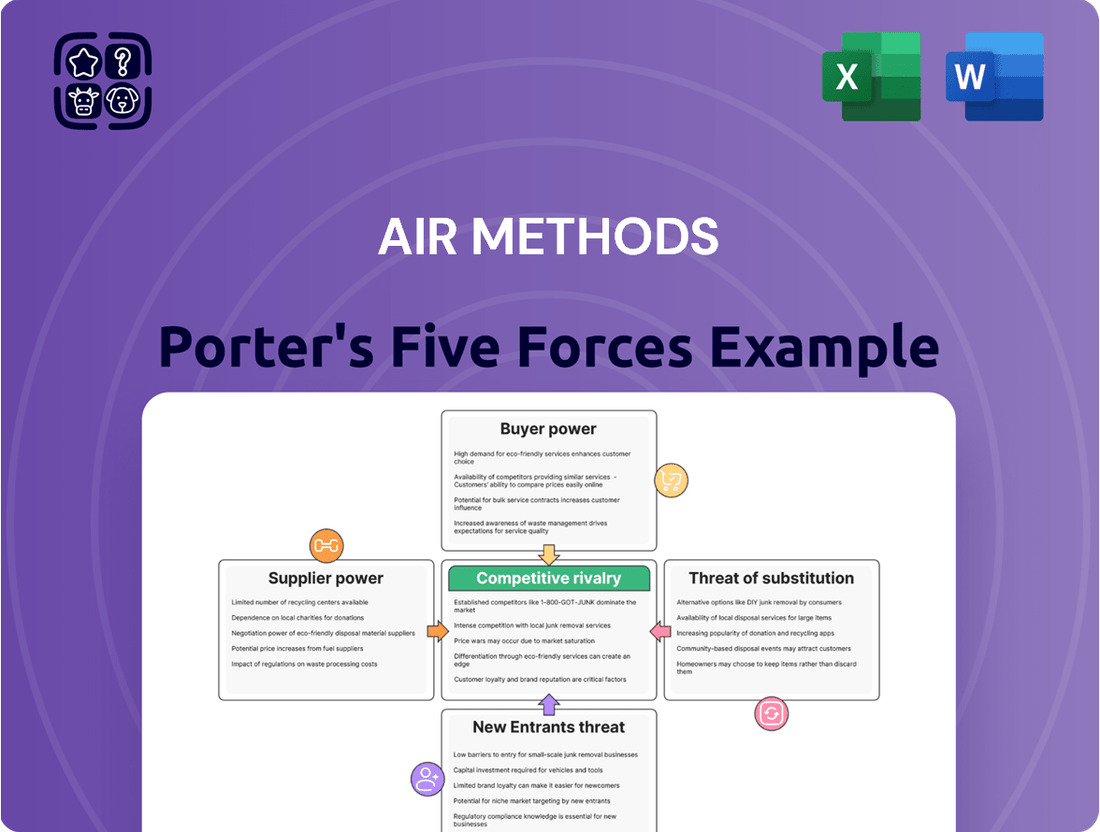
The threat of new entrants, for example, is a key consideration, as is the bargaining power of both buyers and suppliers within the air medical services sector.
Furthermore, the intensity of rivalry among existing players and the availability of substitute services significantly shape Air Methods's strategic environment.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Air Methods’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
The market for specialized medical transport aircraft, including helicopters and fixed-wing planes, is highly concentrated, with major manufacturers like Airbus Helicopters and Bell Textron dominating. This limited number of suppliers grants them significant bargaining power, enabling them to dictate pricing and contract terms. Air Methods' dependency is evident from its substantial investments, such as the March 2025 agreements for nearly 50 new aircraft, including models from both Airbus and Bell, vital for its fleet modernization. This situation ensures suppliers maintain strong leverage over Air Methods' operational costs and strategic planning.
Air Methods heavily relies on suppliers for highly specialized and certified medical equipment to outfit its 'flying intensive care units'. The niche nature of this equipment, such as advanced patient monitoring systems and ventilators, coupled with stringent FAA and medical certification requirements, significantly limits the number of available suppliers. This specialization gives these few suppliers considerable power over pricing and innovation, impacting Air Methods' operational costs, which remain a key focus for profitability in 2024. The demand for cutting-edge medical technology further empowers these vendors.
Pilots, mechanics, and medical professionals like nurses and paramedics are critical to Air Methods' air ambulance operations, requiring extensive specialized training. A persistent shortage of these trained aero-medical professionals, combined with the unionized nature of some groups, significantly elevates their bargaining power for higher wages and improved working conditions. This dynamic was a notable factor contributing to the financial pressures that ultimately led to the company's bankruptcy in 2023, reflecting ongoing challenges for the sector in 2024.
Fuel Price Volatility
Fuel price volatility grants significant power to aviation fuel suppliers, as it directly and substantially impacts Air Methods' operating costs. For air medical transport, fuel is a critical and highly unpredictable expense, making the company highly susceptible to global oil market fluctuations. In 2024, crude oil prices have shown continued volatility, with Brent crude generally trading around $80-90 per barrel, influencing jet fuel prices significantly.
- Jet fuel costs can represent 20-30% of an airline's total operating expenses.
- Global events in 2024, like geopolitical tensions, directly affect oil supply and prices.
- Air Methods' reliance on specialized aviation fuel limits substitution options.
- Hedging strategies are often employed to mitigate this supplier power, though not eliminating it.
Proprietary Technology and Parts
Aircraft manufacturers wield significant power by controlling proprietary replacement parts and technology crucial for Air Methods' fleet. This creates high switching costs, as the company is largely locked into specific suppliers for essential components, impacting operational efficiency and maintenance budgets. Despite Air Methods' United Rotorcraft division designing aeromedical technology, it does not eliminate the fundamental reliance on original equipment manufacturer (OEM) parts for the aircraft themselves, which continues into 2024. This dependency means Air Methods must often accept supplier terms for critical repairs and upgrades.
- OEM parts often command premium pricing, affecting Air Methods' 2024 cost of operations.
- Switching aircraft models to avoid proprietary parts involves substantial capital expenditure and training.
- Supply chain stability for specialized parts remains a key concern for air medical operators.
- United Rotorcraft's focus is on internal medical integrations, not core aircraft components.
Suppliers exert substantial bargaining power over Air Methods due to the concentrated market for specialized aircraft, proprietary parts, and niche medical equipment. The scarcity of highly-trained aero-medical professionals and volatile fuel prices further amplify this leverage, critically impacting Air Methods' operating costs and strategic flexibility in 2024. This collective power forces Air Methods to accept supplier terms, affecting profitability.
| Supplier Type | Bargaining Lever | 2024 Impact | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aircraft OEMs | Limited Manufacturers | High Capital Costs | Proprietary Parts | Maintenance Dependency |
| Medical Equipment | Niche Certification | High Unit Costs | Specialized Tech | Operational Necessity |
| Skilled Labor | Staff Shortages | Rising Wages | Training Investment | Service Continuity |
| Fuel Providers | Price Volatility | Unpredictable Expenses | Global Events | Operational Burden |
What is included in the product
Explores the intensity of rivalry, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants, and the threat of substitutes specifically for Air Methods.
Visually map competitive pressures with a dynamic, interactive dashboard—effortlessly identify and address strategic threats.
Streamline competitive assessment with pre-built templates, allowing instant analysis of industry dynamics and strategic positioning.
Customers Bargaining Power
Air Methods' primary customer base, including hospitals, healthcare systems, and government agencies, holds substantial bargaining power. These large entities often negotiate long-term contracts for air medical services, leveraging their scale to secure favorable terms. In 2024, as healthcare systems continue to consolidate, their ability to demand specific service levels and competitive pricing structures intensifies. This power is particularly pronounced in regions with multiple air medical transport providers, leading to increased pressure on service fees and contract conditions for companies like Air Methods.
Insurance companies, as the primary payers for air ambulance services, wield substantial bargaining power over providers like Air Methods, dictating reimbursement rates. The implementation of the No Surprises Act, effective January 1, 2022, significantly bolstered insurers' positions by restricting out-of-network balance billing. This legislation means Air Methods cannot bill patients for the difference between its charges and what the insurer pays for out-of-network services. In 2024, this continues to pressure Air Methods' revenue, as a 2024 Government Accountability Office (GAO) report highlights the continued impact of the Act on air ambulance billing practices.
In emergency air medical situations, individual patient choice is severely limited, as first responders or hospital staff typically select the air ambulance provider. This dynamic significantly reduces the bargaining power of the patient or their family during critical moments. While non-emergency patient transfers offer slightly more choice, this segment represents a smaller portion of Air Methods' overall market. Consequently, the power shifts to the entities dispatching emergency services, not the direct consumer, influencing service procurement in 2024.
Rise of Subscription-Based Models
The emergence of subscription-based models directly impacts the bargaining power of customers, as these programs reduce patients' out-of-pocket expenses and foster loyalty. While still evolving, these models allow consumers to pre-select provider networks, shifting some power to them by offering predictable costs for air medical transport services. Air Methods faces pressure to compete with providers that offer such membership plans, which can influence pricing strategies. In 2024, an increasing number of air medical service providers are exploring or implementing membership programs to secure patient bases.
- Membership models can reduce patient out-of-pocket costs, enhancing customer loyalty.
- These programs empower consumers by allowing pre-selection of air medical transport providers.
- Air Methods must adapt its strategy to compete with providers offering subscription plans.
- The prevalence of such models continues to grow in the air medical industry as of 2024.
Consolidation of Payers
The healthcare landscape has seen significant consolidation among insurance providers, creating larger and more powerful negotiating entities. These major payers, such as UnitedHealthcare and Elevance Health, now possess greater leverage to demand lower rates and more favorable contract terms from air medical service providers like Air Methods.
This trend intensifies the pressure on profitability for air ambulance operators, as a substantial portion of their revenue depends on these negotiated rates. For example, in 2024, the continued dominance of a few large insurers means that air medical services face constrained reimbursement, directly impacting their financial health.
- Major insurers like UnitedHealthcare and Elevance Health control a large share of the market.
- Their increased bargaining power leads to lower reimbursement rates for air medical transport.
- Air Methods' profitability is directly impacted by these negotiated contract terms.
- The trend of payer consolidation continues to exert downward pressure on service fees in 2024.
Customers, primarily hospitals and large consolidated insurers, wield significant bargaining power over Air Methods, dictating contract terms and reimbursement rates. The No Surprises Act, effective since 2022, empowers insurers by limiting out-of-network balance billing, directly impacting Air Methods' revenue streams. While individual patient choice is limited in emergencies, the growing adoption of membership models offers consumers more cost predictability. This collective customer leverage, intensified by market consolidation in 2024, pressures Air Methods' pricing and profitability.
| Customer Segment | Bargaining Power | 2024 Impact | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hospitals/Healthcare Systems | High | Consolidation drives leverage for lower contract rates. | ||
| Insurance Companies | Very High | No Surprises Act limits billing; large payers demand lower rates. | ||
| Individual Patients | Low (Emergency), Moderate (Membership) | Limited choice in emergencies; membership models offer cost control. |
Preview Before You Purchase
Air Methods Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. The comprehensive Air Methods Porter's Five Forces Analysis presented here meticulously examines the competitive landscape of the air medical services industry, scrutinizing the bargaining power of buyers, the threat of new entrants, the power of suppliers, the intensity of rivalry among existing firms, and the threat of substitute services. Each force is thoroughly analyzed to provide actionable insights into Air Methods' strategic positioning and potential challenges within this dynamic sector. You'll gain a deep understanding of the external factors influencing Air Methods' profitability and growth opportunities.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The air ambulance market is moderately concentrated but highly competitive, featuring key players such as Air Methods, Global Medical Response, and PHI. Alongside these large entities, numerous smaller, regional operators contribute to intense competition. This dynamic creates a fierce struggle for market share, hospital contracts, and skilled personnel across the sector. Air Methods, despite being a dominant force, faces significant rivalry, with competitive pressures continuing to shape its strategic decisions in 2024.
Competition in air medical transport is intense, primarily driven by critical factors like rapid response times, the quality of medical care provided, and impeccable safety records. Operators such as Air Methods constantly upgrade their fleets, with new aircraft models entering service in 2024, to enhance speed and reliability, directly impacting patient outcomes. The ability to reach patients quickly and deliver high-quality care, often within minutes of a call, is a primary differentiator in this life-saving sector. Geographic coverage also plays a crucial role, with companies vying for optimal base locations to minimize transit times.
Air medical transport providers face intense price competition, particularly when negotiating with large customers like hospitals and insurance companies for service contracts. Pressure on reimbursement rates, notably from government payers such as Medicare and the ongoing implications of the No Surprises Act, further exacerbates price-based rivalry. The No Surprises Act, effective January 2022, limited out-of-network billing, impacting revenue streams for providers like Air Methods. This competitive pricing environment and declining reimbursement rates were significant factors contributing to Air Methods' financial restructuring and Chapter 11 bankruptcy filing in 2024. The company emerged from bankruptcy in May 2024, having reduced its debt by over $1.7 billion.
Strategic Expansion and Base Locations
Companies strategically place their operational bases to ensure rapid response times and secure market presence in specific geographic areas, intensifying competitive rivalry. Air Methods' strategy includes opening new greenfield bases and optimizing field operations to better serve communities and compete with rivals. For instance, the air ambulance market saw continued expansion in 2024, with operators like Air Methods focusing on optimizing existing hubs and establishing new locations to enhance coverage. This strategic footprint directly impacts their ability to capture critical transport contracts and maintain a leading position in the highly competitive air medical services sector.
- Air Methods operates over 300 bases across 48 states as of 2024, emphasizing broad geographic coverage.
- Strategic base placement reduces response times, a critical factor in emergency medical services.
- New greenfield bases expand market reach into underserved or high-demand areas.
- Optimizing field operations enhances efficiency and service delivery, directly impacting competitive advantage.
Fleet Modernization and Technology
Competitive rivalry in air medical transport is significantly fueled by ongoing investments in new aircraft and cutting-edge medical technology. Air Methods is actively enhancing its capabilities, exemplified by its planned fleet modernization. For instance, in 2024, Air Methods continued to integrate advanced avionics and medical equipment into its existing fleet, preparing for future expansions. This strategic move, including significant orders for Airbus and Bell helicopters scheduled for delivery through 2025, directly aims to bolster service offerings and maintain its leading market position.
- Air Methods operates over 400 aircraft, a key competitive scale advantage.
- The air medical transport market size in 2024 continues to see significant investment in technology.
- New helicopter models offer enhanced speed, range, and patient care features.
- Competitors like PHI Air Medical are also upgrading their fleets, intensifying rivalry.
Competitive rivalry for Air Methods is intense, driven by key players like Global Medical Response and PHI, alongside numerous regional operators vying for market share. Competition hinges on rapid response times, quality of care, and strategic base placement, with Air Methods operating over 300 bases across 48 states as of 2024. Intense price pressures, exacerbated by the No Surprises Act, led to Air Methods' 2024 financial restructuring and emergence from bankruptcy in May 2024, having reduced debt by over $1.7 billion. Ongoing investments in fleet modernization, with Air Methods operating over 400 aircraft, further fuel this high-stakes competition.
| Metric | Air Methods (2024) | Industry Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Bases Operated | Over 300 (48 states) | Geographic coverage, response times |
| Aircraft in Fleet | Over 400 | Scale, service capability |
| Debt Reduction (Post-Bankruptcy) | Over $1.7 Billion | Financial stability, competitive positioning |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The primary substitute for air medical transport is the ground ambulance. For shorter distances, particularly in areas with robust road infrastructure, ground transport remains a more cost-effective and readily available alternative in 2024. For instance, a ground ambulance ride can often be a fraction of the cost of air medical transport, which can exceed tens of thousands of dollars. However, for time-critical emergencies like severe trauma or stroke, or in remote locations where road access is limited, air transport maintains a significant advantage in speed and accessibility.
For stable patients needing transport, especially over longer distances, Non-Emergency Medical Transport (NEMT) on commercial flights with a medical escort presents a significantly cheaper substitute. This service, while distinct from emergency transport, effectively replaces inter-facility transfers for stable patients. The NEMT market is expanding rapidly, with projections indicating a global market size exceeding $10 billion by 2024, providing a compelling lower-cost alternative to traditional air ambulance services for non-critical cases. This growth underscores a clear shift towards more economical patient transport solutions where speed is not the primary factor.
Advances in telemedicine and improved on-site medical care present a notable substitute threat. For example, remote diagnostics and immediate stabilization at the scene can reduce the urgent need for rapid air transport, shifting patient care models. While not directly replacing air ambulance services, enhanced ground-level care, which saw investments grow significantly in 2024, can stabilize patients, enabling less urgent and often more cost-effective transport options. This evolution impacts the demand for immediate high-acuity air medical services.
Emerging eVTOL Technology
Emerging electric vertical take-off and landing (eVTOL) aircraft pose a growing threat as a substitute, especially for urban medical transport missions. These quieter, more environmentally friendly vehicles, with companies like Joby Aviation and Archer Aviation making strides, could disrupt traditional helicopter services in the long term. While still in development, the global eVTOL market is projected to reach significant valuations, indicating a future shift in air mobility.
- eVTOLs offer reduced noise pollution compared to conventional helicopters.
- They promise lower operational costs and zero direct emissions.
- Several companies anticipate commercial eVTOL operations by 2025-2026.
- The air medical transport sector could see gradual adoption for specific routes.
Patient Refusal or Alternative Transport
The threat of substitutes for Air Methods is significant, particularly from patient refusal or alternative transport methods. The high cost of air ambulance services, often averaging over $30,000 per flight in 2024, can deter patients who might opt for ground transport, even against medical advice. This financial burden makes less optimal transport methods a chosen substitute, particularly for non-critical transfers or in areas with robust ground EMS. Patients may also arrange private transportation if their condition permits, further reducing demand for costly air services.
- Ground ambulance services: A primary substitute, especially for non-life-threatening or shorter-distance transports.
- Private vehicle transport: Utilized by patients capable of self-transport or arranging personal rides.
- Patient refusal of service: Direct rejection of air transport due to cost concerns or perceived necessity.
- Telemedicine/remote consultation: Reduces the need for immediate physical transport in some cases.
The threat of substitutes for Air Methods is substantial, primarily from ground ambulances and non-emergency medical transport, which offer significantly lower costs for non-critical cases. Patient refusal due to the high average flight cost, exceeding $30,000 in 2024, also diverts demand. Emerging technologies like telemedicine and future eVTOLs further expand these alternatives, impacting the need for high-acuity air services.
| Substitute | Key Advantage | 2024 Data Point |
|---|---|---|
| Ground Ambulance | Lower Cost | Fraction of air transport cost |
| NEMT (Commercial) | Significant Cost Savings | Global market > $10B |
| Patient Refusal | Cost Avoidance | Air flight > $30,000 avg. |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the air medical transport sector demands exceptionally high capital investment, creating a significant barrier for potential new entrants. A new company would need to acquire or lease a substantial fleet of specialized, medically equipped aircraft, which represents a massive financial outlay. For instance, Air Methods continued significant capital expenditures in 2024, allocating funds for fleet modernization and new aircraft acquisitions. This substantial upfront cost deters many potential competitors, limiting the threat of new entrants due to the immense financial resources required.
The air medical transport sector is heavily regulated, imposing significant barriers to new entrants. Companies must navigate extensive certifications from aviation authorities like the FAA and health departments for aircraft, personnel, and operations. These complex and costly regulatory requirements, including the need for accreditation from bodies such as CAMTS, demand substantial upfront investment and ongoing compliance efforts, making market entry challenging for any new entity seeking to establish services in 2024.
New entrants into the air medical transport sector would face significant hurdles in establishing crucial relationships. Building trust with hospitals, emergency services, and a vast network of insurance providers demands a proven track record of safety and operational reliability. As of 2024, securing long-term contracts with major healthcare systems, which often span multiple years, takes extensive negotiation and demonstrated capability. This intricate web of relationships, built over decades, gives established players like Air Methods a powerful competitive advantage, making market penetration incredibly difficult for newcomers without substantial investment and time.
Economies of Scale
Large, established air medical transport providers like Air Methods benefit significantly from economies of scale, making new entry challenging. Air Methods, with its extensive fleet and operational footprint across 48 states as of 2024, secures advantageous pricing on aircraft procurement and maintenance contracts. New entrants face substantial cost disadvantages in areas such as bulk fuel purchasing agreements and administrative overhead.
For instance, a new competitor would struggle to match the per-unit cost savings Air Methods achieves through its large-volume operations, potentially facing 15-20% higher operational costs per flight hour initially. This inherent cost structure makes it exceptionally difficult for a new firm to compete on price with incumbent market leaders.
- Air Methods operates over 300 bases, offering significant purchasing power for helicopters and parts.
- Bulk fuel contracts provide cost efficiencies, often yielding savings of 10-15% compared to smaller volume purchases.
- Centralized maintenance facilities and staff reduce per-aircraft maintenance expenses substantially.
- Established administrative infrastructure lowers per-patient billing and operational management costs.
Shortage of Specialized Talent
The air medical sector faces a significant threat from new entrants due to a severe shortage of specialized talent. There is a limited pool of highly skilled pilots, mechanics, and critical care medical professionals with the specific training required for air ambulance operations. New companies entering the market would directly compete with established players like Air Methods for this scarce workforce, inevitably driving up labor costs. This talent scarcity makes it incredibly challenging for new entrants to fully staff their operations efficiently.
- Pilot shortages persist, with the U.S. facing a deficit of over 18,000 pilots in 2024, impacting all aviation sectors.
- Specialized medical crew, including flight paramedics and nurses, require extensive critical care and flight training, limiting availability.
- The competition for maintenance technicians remains fierce, as the industry struggles to attract and retain certified aviation mechanics.
- Increased demand for air medical services further intensifies the competition for these essential, highly trained personnel.
The air medical transport sector faces a low threat from new entrants, primarily due to immense capital requirements for specialized aircraft and a highly regulated operational environment. New firms struggle to establish crucial hospital and insurance relationships while competing with established players like Air Methods, who benefit from significant economies of scale. Furthermore, the severe shortage of specialized pilots and medical personnel in 2024 makes staffing incredibly challenging for any new market participant.
| Barrier | 2024 Impact | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Costs | High | New H135 helicopter: $6-8 million. |
| Regulation | Complex | FAA Part 135 certification: 12-24 months. |
| Talent Scarcity | Severe | U.S. pilot deficit: over 18,000. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Air Methods is built on a foundation of industry-specific market research reports, comprehensive financial filings from Air Methods and its competitors, and insights from aviation industry trade publications.
