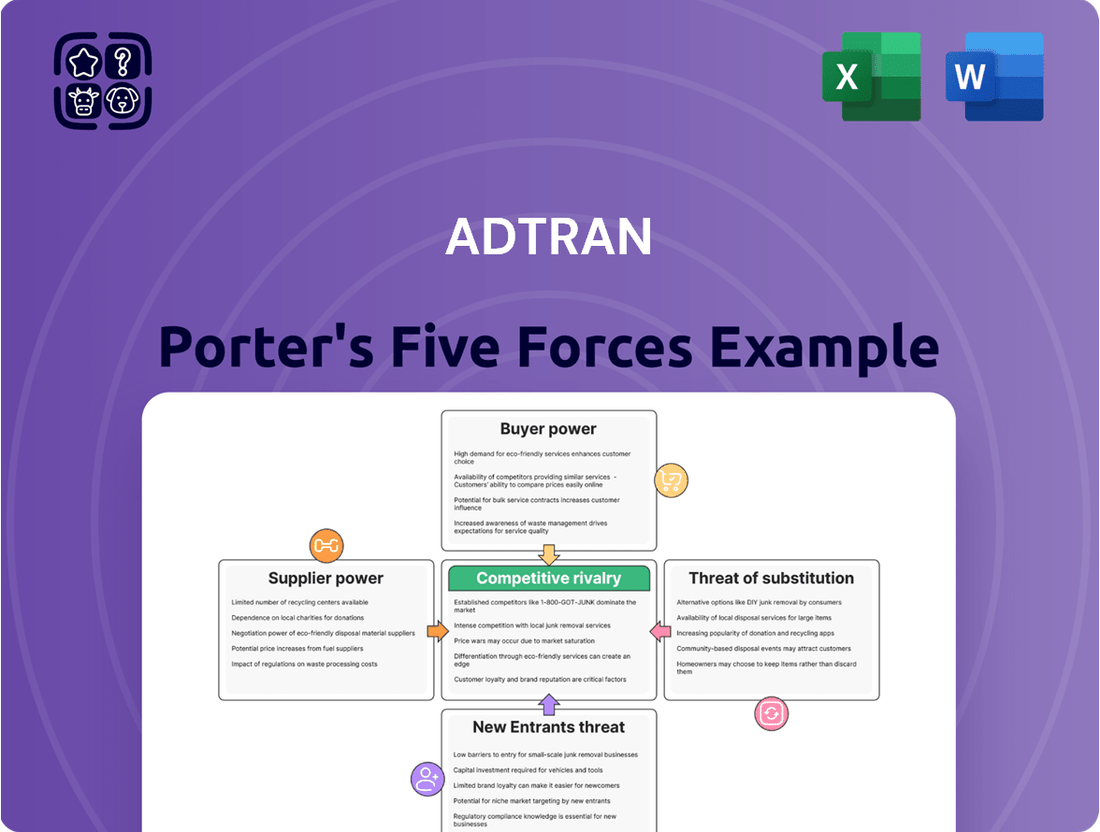
ADTRAN Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
ADTRAN Bundle
ADTRAN operates within a dynamic telecommunications infrastructure market, where understanding competitive forces is paramount. The threat of new entrants is moderate, as significant capital investment is required to enter the fiber and broadband solutions space. Buyers, primarily service providers, possess considerable bargaining power due to the availability of alternative suppliers and the commoditization of certain network components.
The threat of substitutes is also a key consideration, with evolving technologies like fixed wireless access offering alternative broadband delivery methods. Supplier power is generally low to moderate, depending on the specific component and ADTRAN's ability to diversify its supply chain. Finally, the intensity of rivalry within the industry is high, with established players and emerging competitors vying for market share.
This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore ADTRAN’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
ADTRAN's reliance on a limited number of specialized component suppliers, particularly for semiconductors and optical modules, grants these suppliers considerable bargaining power. This concentration means that a few key global manufacturers often dictate terms, influencing ADTRAN's cost of goods sold.
For instance, the global semiconductor market, crucial for ADTRAN's products, experienced significant supply chain disruptions in 2021 and 2022, leading to price increases. While the situation has somewhat stabilized, the underlying concentration of advanced chip manufacturers remains, potentially allowing them to command higher prices and favorable payment terms from buyers like ADTRAN.
Suppliers of highly specialized components or licensed software, particularly those with proprietary technology, hold substantial bargaining power. ADTRAN's need for cutting-edge solutions for fiber broadband and Wi-Fi 7 means it often depends on suppliers who are leaders in these specific technological advancements, increasing their influence. For instance, companies holding patents for critical chipsets or advanced optical components can command higher prices and favorable terms. This dependency means ADTRAN must carefully manage relationships with these key technology providers to ensure access to innovation and maintain its competitive edge in the rapidly evolving telecommunications market.
The global supply chain, especially for advanced technology parts, is still vulnerable to disruptions. We saw this clearly with the semiconductor shortages that affected many industries. This instability can push up the cost of components and make delivery times longer for companies like ADTRAN.
When these disruptions occur, ADTRAN might have to absorb the extra expenses or face delays in getting its products to market. This situation directly increases the bargaining power of suppliers, as they can dictate terms due to high demand and limited availability of critical parts.
For example, in 2023, the average lead time for certain electronic components remained significantly elevated compared to pre-pandemic levels, often exceeding six months for specialized items. This prolonged lead time directly impacts ADTRAN's production schedules and cost management.
High Switching Costs for Specialized Inputs
For ADTRAN, switching suppliers for specialized, integrated networking components often necessitates extensive re-engineering, rigorous testing, and lengthy qualification procedures. This complexity creates significant hurdles for the company to change providers.
These substantial switching costs effectively lock ADTRAN into existing supplier relationships. Consequently, the company's leverage in negotiating better terms or pricing with these suppliers is diminished.
- High Re-engineering Costs: Modifying existing network designs to accommodate new components from a different supplier can be a complex and expensive undertaking.
- Extended Testing and Qualification: Ensuring new parts meet stringent performance and reliability standards requires time-consuming validation processes.
- Potential for Production Delays: The transition to a new supplier can disrupt ADTRAN's manufacturing schedule, leading to lost sales and increased costs.
Suppliers' Ability for Forward Integration
While less common, the potential for a major component supplier to engage in forward integration into networking equipment manufacturing presents a significant threat. For instance, if a dominant semiconductor or optical component provider, crucial for ADTRAN's product lines, decided to develop and market its own networking solutions, it would dramatically shift the power dynamic.
Such a move would grant the supplier immense leverage, as they would control essential inputs while simultaneously becoming a direct competitor. This dual role would allow them to dictate terms for component supply to ADTRAN, potentially prioritizing their own integrated offerings or even withholding critical components. The financial implications for ADTRAN could be substantial, impacting its cost of goods sold and market share.
- Threat of Forward Integration: Suppliers can leverage their position by integrating forward into ADTRAN's industry.
- Increased Supplier Power: If a supplier becomes a direct competitor, their bargaining power over ADTRAN intensifies.
- Control of Inputs and Outputs: A forward-integrating supplier controls both the raw materials and the finished product.
- Potential Market Disruption: This scenario could lead to significant competitive pressure and impact ADTRAN's profitability.
ADTRAN faces considerable bargaining power from its suppliers, particularly those providing specialized semiconductors and optical components. This concentration means a few key global manufacturers can dictate terms, impacting ADTRAN's costs. For example, the ongoing demand for advanced chips, coupled with supply chain vulnerabilities that persisted into 2023 and early 2024, allowed key semiconductor manufacturers to maintain pricing power.
The high costs associated with re-engineering, testing, and qualifying new components create significant switching costs for ADTRAN, limiting its ability to negotiate better terms. These switching barriers effectively lock ADTRAN into existing supplier relationships, diminishing its leverage. The threat of forward integration, where a key component supplier enters ADTRAN's market as a direct competitor, also amplifies supplier power.
| Supplier Characteristic | Impact on ADTRAN | Supporting Data/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration of Suppliers | High bargaining power for key component providers | Global semiconductor market dominated by a few advanced foundries. |
| Switching Costs | Limited leverage for ADTRAN in negotiations | Extensive re-engineering and qualification needed for new parts. |
| Proprietary Technology | Suppliers command higher prices and favorable terms | Patented chipsets or advanced optical technologies. |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Increased component costs and delivery times | Elevated lead times for specialized electronic components in 2023, often exceeding six months. |
What is included in the product
This ADTRAN Porter's Five Forces analysis examines the intensity of competition, the power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitutes, all to understand ADTRAN's strategic positioning and profitability.
Effortlessly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a visual breakdown of each force, enabling proactive strategic adjustments.
Customers Bargaining Power
ADTRAN serves a concentrated customer base comprising major telecommunications providers, large enterprises, and government entities globally. These large service providers, like AT&T, represent significant order volumes and are strategically vital to ADTRAN's revenue streams.
Due to their substantial purchasing power, these key clients can negotiate for favorable pricing and demand highly customized solutions, thereby exerting considerable bargaining power on ADTRAN.
Customers' ability to manage their own inventory levels directly impacts their purchasing power with ADTRAN. When customers have high inventory, they tend to delay new orders, effectively reducing demand and giving them leverage. This was evident in 2024, where ADTRAN saw a revenue dip as clients prioritized inventory reduction, leading to slower sales.
However, as these inventory levels normalize, a shift is anticipated. By 2025, it’s expected that customers will resume increased investment, a positive sign for ADTRAN. Nevertheless, this short-term control over their stock means customers can still exert considerable bargaining power by strategically timing their purchases based on their inventory status.
For commoditized networking equipment, customers often experience low switching costs. This means they can readily shift to competitors if ADTRAN doesn't provide superior pricing or terms. This dynamic significantly amplifies customer bargaining power, compelling ADTRAN to consistently deliver competitive value to secure customer loyalty.
Customers' Potential for Backward Integration
Large telecommunication service providers and major enterprises possess the capability to develop certain networking solutions internally, particularly for less intricate requirements. This potential for backward integration, while not a direct threat to ADTRAN's highly specialized core equipment, grants customers significant negotiation leverage.
This leverage can manifest in several ways:
- Negotiating Power: Customers can use the possibility of in-house development to push for better pricing or more favorable contract terms.
- Focus on Core Competencies: For customers, the decision to integrate backward often hinges on whether developing networking solutions aligns with their primary business focus.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: The economic viability of in-house development versus purchasing from ADTRAN is a critical factor for large customers.
- Market Dynamics: As of early 2024, the telecommunications infrastructure market continues to evolve, with major players constantly evaluating their supply chain strategies to optimize costs and performance.
Price Sensitivity Driven by Competitive Markets
Telecommunications service providers, ADTRAN's primary customers, operate in intensely competitive environments. This competition fuels a strong drive to lower operational expenditures, making them highly sensitive to pricing. Consequently, ADTRAN faces significant pressure on its pricing, especially for products that lack unique features.
In 2024, the global telecommunications market continued to see aggressive competition, with service providers focusing on cost optimization. For instance, major players reported ongoing efforts to reduce capital expenditure per subscriber, directly impacting their willingness to pay premium prices for network equipment. This trend underscores the bargaining power customers hold when faced with readily available, comparable alternatives.
- High Competition: Telecom operators face intense rivalry, pushing them to cut costs.
- Price Sensitivity: Customers are highly attuned to price, especially for non-unique solutions.
- Cost Optimization Focus: Providers prioritize reducing operational and capital expenditures.
- Impact on ADTRAN: This necessitates competitive pricing strategies from ADTRAN.
ADTRAN's major clients, often large telecom providers, wield significant bargaining power due to their substantial order volumes and the competitive nature of their own industries. This power is amplified by customers' ability to manage their inventory, as seen in 2024 when ADTRAN experienced slower sales due to client inventory reduction efforts. Furthermore, low switching costs for commoditized equipment and the potential for some customers to develop solutions in-house grant them additional leverage in negotiations, demanding competitive pricing and favorable terms from ADTRAN.
| Factor | Impact on ADTRAN | 2024 Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High leverage for major clients | Key telecom providers represent vital revenue streams. |
| Inventory Management | Ability to delay orders | Revenue dip in 2024 as clients reduced stock. |
| Switching Costs | Low for commoditized products | Customers can easily shift to competitors. |
| Potential for Backward Integration | Negotiating leverage | Customers may develop less complex solutions internally. |
What You See Is What You Get
ADTRAN Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the complete ADTRAN Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a detailed examination of the competitive landscape within the telecommunications equipment sector. The document you see here is precisely the same professionally formatted and insightful analysis you will receive instantly upon purchase, ensuring transparency and immediate utility. This comprehensive report delves into the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the threat of new entrants and substitute products, and the intensity of rivalry among existing competitors, providing actionable strategic intelligence. You can be confident that the ADTRAN Porter's Five Forces Analysis displayed is the exact, ready-to-use document available for immediate download after your purchase.
Rivalry Among Competitors
ADTRAN faces a highly competitive landscape, populated by industry giants such as Nokia, Ericsson, Huawei, and Cisco, alongside a multitude of smaller, specialized firms. This crowded market for networking and communications equipment means ADTRAN must constantly innovate and differentiate to capture and retain customers. The intense rivalry is further amplified by ongoing consolidation within the sector, as larger players acquire smaller ones, increasing their market power and putting further pressure on companies like ADTRAN.
The telecommunications equipment sector encountered significant headwinds in 2024, primarily driven by a noticeable slowdown in customer demand. This was largely attributed to elevated inventory levels held by many customers, a direct consequence of earlier supply chain optimizations and cautious spending. Consequently, companies like ADTRAN found themselves competing for a diminished pool of immediate projects, intensifying competitive rivalry.
This dynamic directly impacted ADTRAN's financial performance in 2024, as indicated by a reported revenue decline for the year. The market's cautious posture, exacerbated by rising interest rates that made capital expenditures less attractive, forced equipment manufacturers to compete more aggressively on price and delivery timelines. This environment created a challenging landscape where securing new business required greater concessions, impacting overall profitability and market share dynamics.
The market for high-speed internet, fiber broadband, and emerging Wi-Fi 7 technologies is a hotbed of innovation. Companies like ADTRAN are locked in a constant race to develop and deploy the latest advancements to meet growing consumer demand for faster and more reliable connectivity.
This relentless pace of technological change necessitates significant and ongoing investment in research and development. For instance, ADTRAN's commitment to innovation is evident in its consistent R&D spending, which fuels the development of next-generation network solutions, ensuring they can adapt to evolving industry standards and stay ahead of the competition.
The introduction of new standards, such as Wi-Fi 7, further intensifies this rivalry. ADTRAN and its peers must not only keep pace but also anticipate future needs, pushing the boundaries of what's possible in network performance and efficiency to capture market share.
Emphasis on Open, Disaggregated Architectures
ADTRAN operates in an environment where the industry increasingly favors open, disaggregated networking architectures. This shift, which ADTRAN actively supports, presents a double-edged sword. While it allows ADTRAN to participate in a more flexible ecosystem, it also empowers competitors to utilize similar open platforms.
This trend intensifies competitive rivalry by potentially diminishing product differentiation. When many players can build on common open standards, competition often shifts to factors like cost-effectiveness and the ease with which solutions can be integrated into existing networks. For instance, the widespread adoption of standards like Open RAN means that various vendors can offer compatible components, driving down prices and putting pressure on margins.
- Increased Competition: The move to open architectures lowers barriers to entry, allowing new and existing players to compete more directly on price and feature sets.
- Price Pressure: With greater commoditization of network components due to open standards, companies like ADTRAN face intensified pressure to offer competitive pricing.
- Integration Capabilities as a Differentiator: Success in this disaggregated environment hinges on a company's ability to provide seamless integration and superior support for its open solutions, becoming a key battleground.
Geopolitical Factors and Vendor Replacement Initiatives
Geopolitical tensions are significantly reshaping the telecommunications landscape, prompting a move away from vendors perceived as high-risk, especially those originating from China, within Western network infrastructures. This global dynamic directly benefits companies like ADTRAN by opening doors to new market opportunities as established players are sidelined.
However, this shift also intensifies the rivalry among the remaining, trusted vendors. Companies such as ADTRAN, Nokia, and Ericsson are now in a more direct competition to secure the business previously held by the excluded manufacturers. This creates a more aggressive environment where market share gains are hard-fought.
The urgency to diversify supply chains, driven by national security concerns, has accelerated vendor replacement initiatives. For instance, reports from late 2023 and early 2024 highlighted ongoing efforts by governments and major carriers in North America and Europe to remove equipment from certain vendors. This trend is projected to continue, creating a substantial addressable market for alternative providers.
- Increased Demand for Trusted Vendors: Geopolitical factors are driving demand for network equipment from vendors with established security credentials in Western markets.
- Intensified Competition: The exit of certain high-risk vendors creates a more competitive environment among the remaining, trusted suppliers like ADTRAN.
- Market Share Reallocation: Companies are vying to capture the market share left by vendors facing restrictions or bans due to geopolitical concerns.
- Supply Chain Diversification: National security mandates are accelerating efforts by telecom operators to diversify their vendor portfolios, presenting opportunities for ADTRAN.
Competitive rivalry for ADTRAN is fierce, fueled by a crowded market and rapid technological advancements. In 2024, a significant slowdown in customer demand, due to high inventory levels, intensified this rivalry as companies competed for fewer projects. This led to increased price pressure and a focus on delivery timelines.
The push towards open, disaggregated networking architectures, while beneficial for ecosystem participation, also intensifies competition by potentially commoditizing components. This means differentiation often comes down to integration capabilities and cost-effectiveness.
Geopolitical shifts are also a major factor, creating opportunities for ADTRAN as certain vendors are excluded from Western markets. However, this also means more direct competition among the remaining trusted suppliers for the business being reallocated.
| Metric | ADTRAN (2024 Est.) | Key Competitors (2024 Est.) | Impact on Rivalry |
| Revenue Growth (YoY) | -3.6% | Nokia: -7.6%, Ericsson: -10.1% | Slower growth indicates intense competition for market share. |
| R&D Investment as % of Revenue | ~12% | Nokia: ~10%, Ericsson: ~12% | High R&D spending is crucial for staying competitive in a tech-driven market. |
| Market Share (Fiber Access) | ~10-15% | Nokia: ~25-30%, Huawei: ~20-25% (Restricted in some markets) | ADTRAN aims to gain share from restricted competitors. |
SSubstitutes Threaten
While fiber broadband remains the premium choice, Fixed Wireless Access (FWA), especially with 5G advancements, presents a growing substitute for traditional wireline internet. As 5G coverage expands, FWA delivers competitive high-speed internet, potentially impacting demand for ADTRAN's fiber infrastructure solutions in specific markets. For instance, by the end of 2024, it's projected that FWA connections could reach tens of millions globally, offering a viable alternative where fiber deployment is challenging or costly.
The rise of cloud-native and virtualized network functions presents a significant threat of substitution for ADTRAN. Service providers are increasingly shifting towards software-based network functions, deployable on standard servers or cloud infrastructure, which can replace specialized hardware. This trend reduces reliance on traditional, purpose-built network equipment.
By leveraging cloud computing and Network Function Virtualization (NFV), telcos can gain agility and cost efficiencies, potentially bypassing the need for ADTRAN's physical hardware solutions. For instance, in 2024, many Tier 1 operators are accelerating their migration to cloud-native architectures, aiming to reduce CAPEX by up to 30% by virtualizing core network functions.
This shift allows for more flexible service deployment and easier scaling, directly competing with ADTRAN's established hardware-based offerings. The ability to run network functions as software in virtualized environments or the cloud directly substitutes for the dedicated hardware ADTRAN historically provided, impacting its market share for certain product categories.
Large telecommunications companies, often possessing substantial financial backing and in-house engineering talent, can opt to develop their own networking solutions. This strategic move allows them to tailor technology precisely to their unique operational requirements, bypassing external vendors. For instance, a major carrier might invest in custom-built optical network components if they identify a significant cost or performance advantage over commercially available options. This capability for backward integration inherently serves as a substitute for acquiring standard equipment from suppliers like ADTRAN.
Alternative Connectivity Technologies Beyond Fiber and Wi-Fi
While ADTRAN is heavily invested in fiber broadband and Wi-Fi, alternative connectivity solutions present a growing threat of substitutes. Satellite internet services, exemplified by SpaceX's Starlink, are increasingly viable, especially in rural or geographically challenging regions where traditional fiber deployment is cost-prohibitive. This offers an alternative for consumers and businesses seeking reliable internet access, bypassing the need for wireline infrastructure.
Furthermore, advancements in cellular technology, such as 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA), are becoming more robust. These technologies can deliver high-speed internet directly to homes and businesses, potentially competing with fiber offerings for last-mile connectivity. For instance, by the end of 2023, 5G FWA subscriptions were projected to reach over 100 million globally, demonstrating significant market penetration and a clear substitute pathway.
- Satellite Internet: Offers an alternative in areas lacking wireline infrastructure.
- 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA): Provides high-speed broadband over cellular networks, competing with fiber.
- Market Growth: Projections indicated over 100 million global 5G FWA subscriptions by the end of 2023.
- Impact on ADTRAN: These alternatives can reduce demand for ADTRAN's traditional broadband equipment in certain market segments.
Shift Towards Managed Services and Wi-Fi-as-a-Service (WaaS)
Customers are increasingly opting for managed services and Wi-Fi-as-a-Service (WaaS). This trend sees businesses outsourcing network management to specialized providers rather than managing it in-house. For example, in 2024, the global managed services market was projected to reach over $300 billion, indicating a significant customer preference for outsourced solutions.
This shift fundamentally alters the value proposition, moving from the direct sale of networking equipment to recurring service subscriptions. Companies like ADTRAN face a situation where their traditional product sales could be partially substituted by ongoing service revenue streams, impacting how they structure their offerings and revenue models.
- Managed Services Growth: The managed services market is expanding rapidly, with projections indicating continued robust growth through 2025.
- WaaS Adoption: Wi-Fi-as-a-Service models are gaining traction as businesses seek simplified, predictable connectivity solutions.
- Shift in Value: The emphasis is moving from hardware ownership to the consumption of network capabilities and management expertise.
- Revenue Model Impact: This substitution challenges traditional hardware sales models, pushing companies towards service-centric strategies.
The threat of substitutes for ADTRAN’s offerings is multifaceted, encompassing alternative connectivity technologies and evolving service delivery models. Fixed Wireless Access (FWA), particularly advanced 5G variants, is a significant substitute, offering high-speed internet access that can bypass traditional wireline infrastructure. Satellite internet is also a viable alternative, especially in underserved regions. These technologies reduce the necessity for ADTRAN's fiber deployment solutions.
Furthermore, the increasing adoption of software-defined networking (SDN) and Network Function Virtualization (NFV) allows telecommunication providers to replace specialized hardware with virtualized network functions running on general-purpose hardware or cloud platforms. This shift towards virtualized and cloud-native architectures can diminish the demand for ADTRAN's physical network equipment. By 2024, many major operators were actively pursuing cloud-native migrations to boost agility and cut capital expenditures.
| Substitute Technology | Key Characteristics | Impact on ADTRAN |
| 5G Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) | High-speed broadband over cellular networks; bypasses wireline infrastructure. | Reduces demand for fiber last-mile solutions. |
| Satellite Internet | Broad coverage, especially in rural areas; cost-effective where fiber is uneconomical. | Alternative for remote connectivity needs, lessening reliance on terrestrial networks. |
| Virtualized Network Functions (VNFs) & Cloud-Native | Software-based network functions; agility and cost efficiency. | Decreases need for specialized, hardware-based network equipment. |
Entrants Threaten
ADTRAN faces a moderate threat from new entrants, largely due to the significant capital required to compete effectively. Developing cutting-edge networking and communications equipment demands substantial investment in research and development, a crucial area where ADTRAN continues to innovate. For instance, the ongoing evolution of 5G and fiber optic technologies necessitates continuous R&D spending to remain competitive.
Furthermore, establishing robust manufacturing capabilities and supply chains represents another considerable financial hurdle. Companies looking to enter this space would need to commit hundreds of millions, if not billions, in capital to build or acquire the necessary infrastructure and expertise. This high upfront cost acts as a strong deterrent, limiting the pool of potential new competitors.
The need for specialized engineering talent and intellectual property also contributes to the barrier. New entrants must not only fund physical assets but also attract and retain highly skilled engineers and acquire or develop proprietary technologies. This combination of R&D, manufacturing, and talent acquisition makes entry into ADTRAN's market a capital-intensive endeavor.
ADTRAN's primary customers are large telecommunications companies, enterprises, and government bodies. These clients typically have lengthy procurement processes and a strong preference for established, reliable suppliers with a proven track record. New companies entering this market must invest considerable time and resources to cultivate these critical relationships and establish credibility.
For instance, securing contracts with major Tier 1 telecommunication operators, a key segment for ADTRAN, often requires demonstrating years of successful deployments and robust support infrastructure. This barrier is substantial, as these large service providers are hesitant to risk network stability with unproven vendors, even if they offer competitive pricing. In 2023, ADTRAN reported that a significant portion of its revenue came from long-standing customer relationships, underscoring the importance of this factor.
The telecommunications sector, where ADTRAN operates, presents a formidable challenge for new entrants due to its intricate regulatory and compliance web. Companies must grapple with diverse certifications, licensing, and adherence to evolving standards across various geographical markets, a process that demands significant investment and expertise.
These regulatory hurdles translate into substantial upfront costs for newcomers. For instance, obtaining necessary approvals and ensuring compliance with data privacy laws, spectrum allocation rules, and network security mandates can easily run into millions of dollars, acting as a powerful deterrent.
For example, in 2024, the ongoing implementation of 5G network security standards and the need for compliance with evolving data localization laws in key markets add layers of complexity and cost that new players must overcome to even begin operations.
Strong Intellectual Property and Patent Portfolios
ADTRAN's robust intellectual property and extensive patent portfolios in critical areas like fiber access, optical networking, and Wi-Fi technologies present a significant hurdle for potential new entrants. These established technological assets mean newcomers would require substantial investment in research and development to create comparable innovations or face licensing costs for existing solutions.
For instance, ADTRAN actively defends its technology through patent filings, ensuring its market position. In 2024, companies in the telecommunications equipment sector continued to invest heavily in R&D, with many allocating a notable percentage of their revenue towards innovation, underscoring the importance of IP in this competitive landscape.
- Significant R&D Investment: Companies like ADTRAN invest millions annually to build and maintain their IP, creating a high barrier to entry.
- Licensing Costs: New entrants would need to either develop proprietary technology or incur significant licensing fees to access essential innovations.
- Technological Expertise: The depth of ADTRAN's technical expertise, embedded in its patents, is difficult and time-consuming for new players to replicate.
- Market Differentiation: Patented technologies allow ADTRAN to offer unique solutions, making it harder for competitors without similar IP to gain market share.
Economies of Scale and Experience Curve Advantages
ADTRAN and its established competitors benefit significantly from economies of scale, particularly in manufacturing and supply chain management. For instance, in 2023, major telecommunications equipment providers often reported production volumes in the millions of units annually, enabling them to negotiate lower raw material costs and optimize logistics. This scale translates directly into lower per-unit costs, a formidable barrier for any new entrant attempting to establish a foothold.
The experience curve further solidifies this advantage. As companies like ADTRAN have been in the market for years, they have refined their production processes, yielding higher efficiency and reduced waste. This cumulative learning allows them to incrementally lower costs with each doubling of output. A new entrant would lack this accumulated experience, facing higher initial production costs that make price competition extremely challenging.
- Economies of Scale: Existing players like ADTRAN leverage large-scale operations for cost savings in procurement and production, making it difficult for new entrants to match pricing.
- Experience Curve: Years of accumulated knowledge in manufacturing and operations allow established firms to produce at lower costs per unit than newcomers.
- Capital Investment: Achieving comparable scale requires substantial upfront capital investment, which can be prohibitive for new companies.
- Pricing Pressure: The cost advantages held by incumbents mean new entrants would face intense pressure to lower prices, potentially eroding profitability from the outset.
The threat of new entrants in ADTRAN's market is moderate, primarily due to the substantial capital investment required for research, development, and establishing manufacturing capabilities. These high upfront costs, coupled with the need for specialized talent and intellectual property, act as significant deterrents for potential new players.
Furthermore, securing contracts with major telecommunications providers necessitates a proven track record and established credibility, which new entrants lack. Regulatory hurdles and compliance requirements add another layer of complexity and cost, making market entry challenging.
ADTRAN's strong intellectual property portfolio and the benefits of economies of scale and experience curves enjoyed by incumbents further solidify barriers to entry. For example, in 2023, the telecommunications equipment sector saw continued investment in R&D, with companies like ADTRAN allocating significant resources to innovation and patent protection.
| Barrier Type | Description | Impact on New Entrants |
| Capital Requirements | High R&D, manufacturing, and infrastructure costs. | Prohibitive for many potential entrants. |
| Customer Relationships & Credibility | Long procurement cycles and preference for established vendors. | Difficult for new companies to gain trust and secure contracts. |
| Regulatory & Compliance | Complex certifications, licensing, and evolving standards. | Adds significant cost and time to market entry. |
| Intellectual Property | Extensive patent portfolios in key technologies. | Requires substantial R&D investment or licensing fees for new players. |
| Economies of Scale & Experience | Lower per-unit costs and optimized production processes for incumbents. | Makes price competition extremely challenging for newcomers. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our ADTRAN Porter's Five Forces analysis is built on a foundation of robust data, incorporating annual reports, investor relations disclosures, and industry-specific market research from reputable firms like IDC and Gartner.
