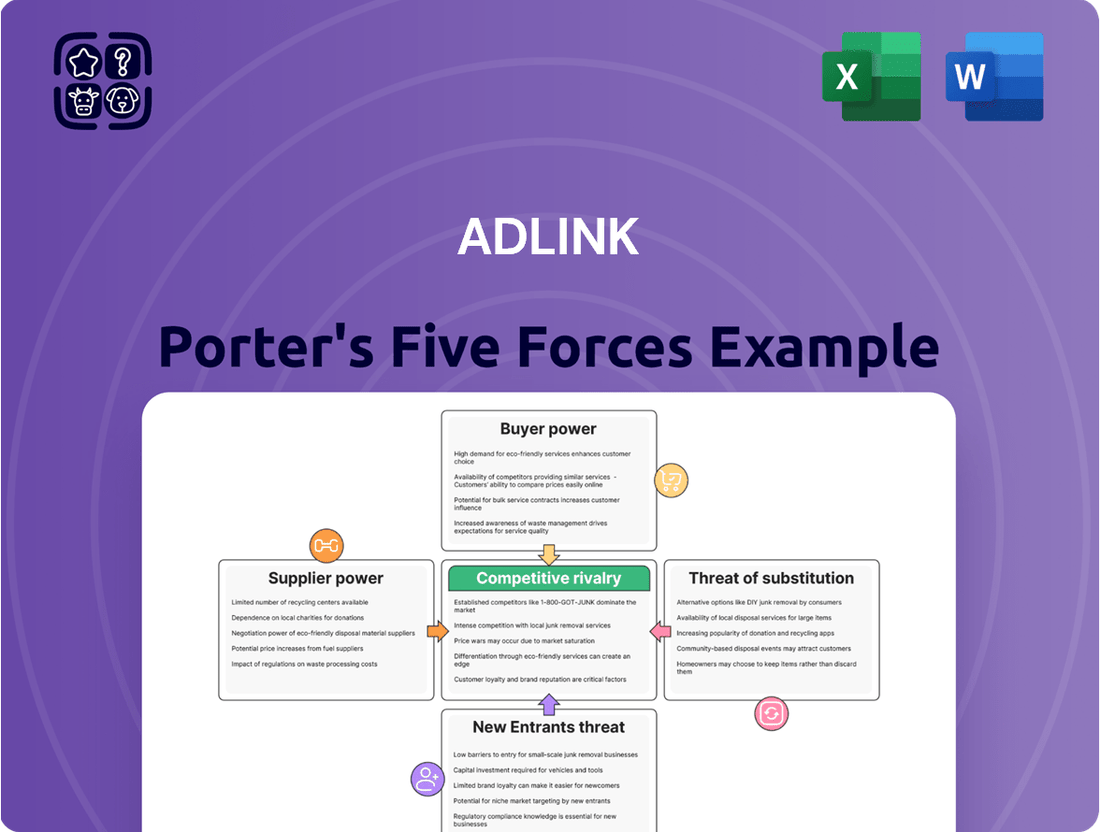
Adlink Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Adlink Bundle
Adlink operates within a dynamic landscape shaped by intense competition, powerful buyers, and the constant threat of new entrants and substitutes. Understanding these forces is crucial for navigating the market effectively.
The complete report reveals the real forces shaping Adlink’s industry—from supplier influence to threat of new entrants. Gain actionable insights to drive smarter decision-making.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Supplier concentration is a critical element impacting ADLINK's bargaining power with its suppliers. ADLINK depends heavily on a limited number of providers for specialized embedded computing components, such as processors from giants like Intel, NVIDIA, Arm, AMD, NXP, MediaTek, and Qualcomm.
When a market has few dominant suppliers for essential parts, these suppliers gain significant leverage. This concentration means ADLINK faces a higher risk of increased component costs or potential disruptions in its supply chain if these key suppliers decide to raise prices or face production issues.
For instance, the embedded computing sector often sees major chip manufacturers holding substantial market share, giving them considerable pricing power. This dynamic directly influences ADLINK's cost of goods sold and its ability to maintain competitive pricing for its own products.
ADLINK faces significant switching costs when changing component suppliers. The effort and expense involved in redesigning products, re-validating systems, and potentially re-certifying solutions, particularly in demanding sectors like healthcare and transportation, can be substantial. These high switching costs can effectively lock ADLINK into existing supplier relationships, thereby increasing the bargaining power of those suppliers.
Suppliers who provide highly specialized or proprietary technologies, like advanced AI accelerators or unique industrial components, wield significant bargaining power. For ADLINK, if these critical inputs are not readily available from alternative sources, it creates a dependency that strengthens the supplier's hand in negotiations, potentially leading to less favorable terms for ADLINK.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers is a key consideration for ADLINK. If a supplier were to credibly threaten to enter the embedded computing market and compete directly, their bargaining power would escalate substantially. This would force ADLINK to potentially pay more for components or accept less favorable terms.
While it's less common for typical component suppliers to fully integrate into complex system manufacturing, the potential for them to offer more integrated solutions or even complete products is a growing concern. For instance, a semiconductor manufacturer might develop their own reference designs that closely resemble ADLINK's offerings, effectively becoming a competitor.
- Supplier Integration Threat: Suppliers moving into direct competition with ADLINK by offering integrated solutions or finished products.
- Increased Bargaining Power: If suppliers can credibly threaten to enter ADLINK's market, their leverage in negotiations rises.
- Market Entry Barriers: While challenging, some suppliers might possess the technical know-how and capital to attempt forward integration, especially in niche segments.
- Competitive Landscape Shift: Such integration would not only impact ADLINK's supplier relationships but also alter the competitive dynamics of the embedded computing industry.
Importance of ADLINK to Supplier
The bargaining power of suppliers is influenced by ADLINK's significance to them. If ADLINK constitutes a substantial portion of a supplier's annual revenue, that supplier will likely be more amenable to offering competitive pricing and favorable terms to secure ADLINK's continued patronage. For instance, if a key component supplier reported that ADLINK accounted for 15% of its total sales in 2024, this would give ADLINK considerable leverage.
Conversely, if ADLINK is a minor client for a large, diversified supplier, its individual importance is diluted. In such scenarios, ADLINK's ability to negotiate better terms is significantly reduced, as the supplier has many other customers to rely on. This asymmetry in dependence dictates the supplier's willingness to concede during negotiations.
- Customer Dependence: ADLINK's revenue contribution to its suppliers is a key determinant of supplier power.
- Supplier Diversification: Suppliers with a broad customer base are less influenced by any single client like ADLINK.
- Revenue Impact: A higher percentage of ADLINK's business with a supplier strengthens ADLINK's negotiating position.
- Market Share: Suppliers who view ADLINK as a critical customer for their own market share growth will be more accommodating.
ADLINK's bargaining power with its suppliers is significantly shaped by the concentration of suppliers in its key component markets. When few suppliers dominate the market for essential parts, like processors from Intel or NVIDIA, they gain considerable leverage, potentially leading to higher costs for ADLINK. This is compounded by substantial switching costs, as redesigning and re-validating systems for new components is resource-intensive, especially in regulated sectors.
The availability of substitute products also plays a role; if ADLINK can easily find alternative components, supplier power diminishes. However, for highly specialized or proprietary technologies, suppliers hold more sway due to ADLINK's dependency. Furthermore, the threat of suppliers integrating forward into ADLINK's market or ADLINK's own importance to a supplier's revenue stream directly impacts negotiation dynamics.
| Factor | ADLINK's Position | Supplier Bargaining Power |
| Supplier Concentration (e.g., Intel, NVIDIA) | High dependence on few key players | High |
| Switching Costs (Redesign, Re-validation) | Substantial, especially in regulated industries | High |
| Availability of Substitutes | Limited for specialized components | High |
| Supplier Forward Integration Threat | Potential for competitors to emerge | Moderate to High |
| ADLINK's Importance to Supplier Revenue | Varies; crucial for some, minor for others | Low to High |
What is included in the product
Adlink's Porter's Five Forces Analysis provides a comprehensive examination of the competitive landscape, detailing the intensity of rivalry, buyer and supplier power, threat of new entrants, and the impact of substitutes on Adlink's market position.
Quickly identify and address competitive threats with a visual, easy-to-understand breakdown of all five forces.
Customers Bargaining Power
ADLINK's customer base spans critical industries like industrial automation, healthcare, and transportation. If a few major clients represent a substantial portion of sales within any of these sectors, they gain considerable leverage. This concentration allows these large customers to negotiate for lower prices, bespoke product configurations, or more favorable payment schedules, especially in scenarios involving significant project rollouts.
For ADLINK's customers, the process of switching embedded computing providers often comes with significant financial and operational hurdles. These can include the substantial expense of re-engineering existing systems to ensure compatibility, the cost of retraining personnel on new hardware and software platforms, and the potential for disruptions during the transition period. These substantial switching costs effectively anchor customers to their current providers, limiting their ability to leverage competitive offers.
Customer price sensitivity is a key factor in how much power buyers have. When customers are in markets with many choices or have limited funds, they tend to focus more on price, giving them more leverage. For example, in the semiconductor industry, where ADLINK operates, the availability of numerous suppliers can lead to increased price pressure if customers perceive products as largely interchangeable.
ADLINK can counter this by making its products stand out. By offering superior technology, dependable performance, or specialized customer service, ADLINK can reduce the likelihood that customers will solely base their purchasing decisions on price. This differentiation is crucial in markets where innovation and reliability are highly valued, as seen in the growing demand for edge computing solutions where performance is paramount.
Availability of Substitute Products for Customers
Customers wield significant bargaining power when a wide array of substitute embedded computing products and solutions are readily available. This abundance of alternatives allows them to switch providers with minimal cost or effort if they are dissatisfied with current offerings or pricing.
The burgeoning growth within the embedded computing sector, coupled with the rapid expansion of edge AI capabilities, is directly contributing to an increased number of viable options for customers. This market dynamic inherently shifts power towards the buyer.
- Market Growth: The global embedded systems market was valued at approximately $84.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach over $140 billion by 2028, indicating substantial new entrants and product diversification.
- Edge AI Proliferation: The demand for edge AI solutions is surging, with the edge AI market expected to grow from $11.7 billion in 2023 to over $40 billion by 2028, presenting numerous alternative solutions for embedded computing needs.
- Component Availability: The widespread availability of standardized components and open-source software further lowers the barrier to entry for new competitors, increasing the substitute product landscape.
- Customization vs. Off-the-Shelf: While custom solutions offer unique advantages, the increasing sophistication of off-the-shelf embedded computing platforms provides readily available substitutes for many common applications.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by ADLINK's customers can significantly amplify their bargaining power. If major clients, particularly those with substantial R&D budgets and a demand for bespoke embedded computing solutions, could realistically develop these capabilities internally, they would gain leverage. This scenario is more probable for large enterprises seeking highly specialized or proprietary systems that ADLINK currently provides.
For instance, a large automotive manufacturer, a key customer for ADLINK's edge computing hardware, might possess the engineering talent and capital to design its own in-vehicle computing modules. This would reduce their reliance on external suppliers like ADLINK, potentially leading to price concessions or more favorable contract terms. In 2024, the trend of vertical integration across various industries, driven by a desire for greater control over supply chains and intellectual property, makes this a pertinent consideration for ADLINK.
- Customer Capability: Large customers with strong internal R&D and engineering teams are more likely to pursue backward integration.
- Customization Needs: Clients requiring highly customized or proprietary embedded solutions face fewer switching costs and may consider in-house development.
- Industry Trends: The ongoing push for supply chain control and IP protection in 2024 increases the perceived viability of backward integration for major customers.
ADLINK's customers can exert significant bargaining power when they represent a large portion of sales, especially if they can easily switch to competitors or develop similar solutions in-house. High switching costs and a wide availability of substitute products generally reduce this power, but a concentrated customer base or the potential for backward integration can shift leverage towards buyers.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | Supporting Data/Observation |
|---|---|---|
| Customer Concentration | High power if a few clients dominate sales. | Specific industry clients (e.g., automotive, industrial automation) may represent significant revenue streams for ADLINK. |
| Switching Costs | Low power if switching is costly. | Costs include re-engineering, retraining, and integration disruptions. |
| Availability of Substitutes | High power with many alternatives. | The embedded systems market saw a global valuation of $84.2 billion in 2023, indicating a competitive landscape with numerous providers. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | High power if customers can produce internally. | Large clients with R&D capabilities may consider in-house development for proprietary solutions, a trend noted in 2024 for supply chain control. |
What You See Is What You Get
Adlink Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview displays the complete Adlink Porter's Five Forces Analysis, offering a thorough examination of the competitive landscape. What you see here is the exact, professionally formatted document you will receive immediately after purchase, ensuring no discrepancies or missing information. This comprehensive analysis will equip you with actionable insights into the industry's dynamics, buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The embedded computing market is quite crowded, featuring a mix of specialized embedded solution providers and larger, more diversified technology firms. This means ADLINK faces competition from a significant number of companies.
Key rivals include established players such as Advantech, AAEON, Kontron, Flytech Technology Company, Axiomtek Company, and American Portwell Technology. These companies often have substantial resources and a broad market presence, directly impacting the intensity of competition.
In 2024, the embedded systems market is projected to reach approximately $130 billion, highlighting the substantial size of the arena ADLINK operates within. The sheer number of competitors, many of whom are well-funded and possess advanced technological capabilities, significantly amplifies the rivalry ADLINK experiences.
The embedded computing and edge AI markets are booming, with impressive growth forecasts. This rapid expansion, while offering opportunities for companies to grow by meeting new demand, also acts as a magnet for new competitors. The embedded computing sector is expected to climb from $42.39 billion in 2024 to $45.72 billion in 2025, a healthy 7.8% compound annual growth rate.
Furthermore, the industrial edge AI market is set for even more dramatic expansion. Valued at $3.7 billion in 2024, it's projected to surpass $11.9 billion by 2031, demonstrating a strong CAGR of 13.7%. This robust growth environment means that while existing players might find room to expand, the allure of these expanding markets will undoubtedly draw in new entrants, potentially intensifying rivalry in the long run.
ADLINK distinguishes itself by focusing on application-ready intelligent platforms and advanced edge AI solutions. This specialization allows them to offer embedded boards, systems, and modules with unique innovations, superior performance, and enhanced reliability. For instance, in 2024, ADLINK continued to emphasize its commitment to high-performance computing for demanding sectors like industrial automation, where precision and uptime are critical.
Switching Costs for Customers
High switching costs for customers can significantly dampen competitive rivalry. When it is costly or time-consuming for clients to switch from ADLINK to a competitor, it creates a natural barrier. This inertia makes it harder for rivals to gain market share by simply offering lower prices or new features, as the cost of changing outweighs the perceived benefit for many customers. For instance, if ADLINK's solutions involve deep integration into a client's existing systems, the effort and expense of migrating data, retraining staff, and reconfiguring infrastructure would be substantial.
Conversely, if switching costs are low, competitive rivalry intensifies considerably. Customers can readily move to alternatives if a competitor offers a slightly better deal or a more appealing product. This dynamic forces ADLINK to constantly innovate and remain competitive on price and features to retain its customer base. In the technology sector, where ADLINK operates, this can manifest as frequent price wars or a relentless pursuit of the next technological advancement to keep customers engaged.
- High switching costs deter customers from moving to competitors, reducing price pressure and fostering loyalty.
- Low switching costs empower customers to easily change providers, leading to increased price competition and a focus on customer retention.
- For ADLINK, the investment in robust customer support and integrated solutions can elevate switching costs, thereby mitigating direct competitive threats.
- In 2023, the average cost for businesses to switch cloud service providers, a comparable scenario, ranged from thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars depending on data volume and integration complexity, highlighting the impact of switching costs.
Exit Barriers
High exit barriers in the embedded computing sector, stemming from specialized assets and substantial R&D investments, can trap even unprofitable firms. This persistence contributes to market overcapacity.
For instance, companies heavily invested in proprietary hardware designs or advanced manufacturing processes face significant costs if they decide to exit. This difficulty in divesting specialized assets means these firms may continue operating, even at a loss.
The continuation of struggling competitors due to these barriers can intensify price wars. By 2024, the embedded computing market, valued at approximately $30 billion, experienced heightened competition, partly due to firms being unable to easily exit.
- Specialized Assets: High costs associated with divesting unique manufacturing equipment or intellectual property.
- Long-Term Contracts: Obligations to customers can prevent immediate withdrawal from the market.
- R&D and Manufacturing Investments: Significant sunk costs in developing and producing specialized components.
- Brand Reputation: The desire to maintain brand presence, even in struggling segments, can delay exit decisions.
Competitive rivalry within the embedded computing market is intense, driven by a large number of established players and the sector's significant growth potential. Companies like Advantech and Kontron are major competitors, offering a wide range of embedded solutions. The embedded systems market is projected to reach around $130 billion in 2024, attracting numerous firms to this lucrative space.
ADLINK differentiates itself through specialized, application-ready intelligent platforms and edge AI solutions, focusing on high-performance computing for demanding industries. This strategy aims to create value beyond basic hardware, fostering customer loyalty. The embedded computing sector is expected to grow to $45.72 billion by 2025, while the industrial edge AI market, valued at $3.7 billion in 2024, is set to exceed $11.9 billion by 2031, indicating strong market expansion that fuels competition.
High switching costs, often incurred by customers integrating ADLINK's solutions deeply into their operations, serve as a deterrent to competitors. Conversely, low switching costs would intensify rivalry, forcing ADLINK to continuously innovate and compete on price and features. For example, the cost to switch cloud providers in 2023 could range from thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars, illustrating the impact of integration complexity on customer retention.
Exit barriers, such as specialized assets and substantial R&D investments, can keep even struggling companies in the market, potentially leading to overcapacity and price wars. By 2024, the embedded computing market experienced heightened competition partly due to these exit difficulties.
| Competitor | 2024 Market Presence | Key Offerings |
| Advantech | Major Player | Industrial PCs, IoT devices, embedded boards |
| AAEON | Significant Player | Embedded boards, industrial gateways, AI edge devices |
| Kontron | Established Competitor | Embedded computers, rugged solutions, network servers |
| Flytech Technology Company | Growing Presence | POS systems, industrial automation solutions |
| Axiomtek Company | Key Competitor | Industrial PCs, embedded systems, IoT solutions |
| American Portwell Technology | Notable Player | Industrial PCs, embedded computers, panel PCs |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for ADLINK's embedded computing solutions is primarily driven by their price-performance ratio compared to alternative technologies. General-purpose computing platforms and cloud-based AI services can often perform similar tasks, potentially at a lower initial cost or with greater flexibility.
However, ADLINK's embedded AI solutions offer critical advantages like real-time processing and offline operational capabilities, which are often superior to cloud-dependent alternatives. This inherent functionality in demanding environments significantly mitigates the threat of substitution for many of ADLINK's core markets.
Customer willingness to switch to alternatives hinges on how easily they can adopt those solutions, the perceived risks involved, and whether they have the right people to manage new technologies. For instance, a company might hesitate to switch to a new advertising platform if it requires extensive retraining of their marketing team or if data security concerns are high.
In sectors like manufacturing or healthcare, where systems need to be exceptionally reliable and perform very specific functions, customers are less likely to opt for substitutes that aren't as specialized. Consider a medical device company relying on Adlink's analytics for patient monitoring; they would likely find it difficult to substitute with a general-purpose analytics tool due to stringent regulatory requirements and the need for precise, real-time data.
Rapid advancements in alternative technologies, like enhanced cloud computing for remote data processing and integrated System-on-Chips (SoCs) combining multiple functions, pose a significant threat of substitutes. For instance, the increasing power and accessibility of cloud services mean businesses may opt out of on-premise hardware solutions, directly impacting hardware manufacturers.
The continuous evolution of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) further amplifies this threat. As AI capabilities become more sophisticated and IoT devices proliferate, they can offer functionalities that traditionally required specialized hardware or software, potentially displacing existing products and services.
Consider the semiconductor industry: the rise of specialized AI accelerators, like Google's TPUs or NVIDIA's GPUs, offers powerful alternatives to general-purpose CPUs for specific workloads. In 2024, the AI chip market is projected to reach over $200 billion, demonstrating the substantial shift towards these specialized, and potentially substitutive, technologies.
Indirect Substitutes (e.g., Software-only solutions)
The threat of indirect substitutes for ADLINK's offerings is growing, particularly from software-only solutions. These can run on more generic hardware, making them a viable alternative for applications that don't demand ADLINK's specialized, high-performance integrated platforms. This trend is amplified by the increasing adoption of open-source embedded software, which lowers the barrier to entry for software-centric competitors.
For instance, in the industrial automation sector, while ADLINK excels in providing robust edge computing hardware, pure software platforms running on standard industrial PCs or even cloud infrastructure can perform many control and data processing tasks. This shift means that a company might opt for a powerful server with specialized software rather than ADLINK's purpose-built embedded system for certain use cases. The cost savings associated with generic hardware and open-source software can be a significant draw for customers. As of early 2024, the market for industrial software solutions continues to expand, with many vendors offering scalable platforms that can be adapted to a wide range of hardware, thereby increasing the substitute threat.
- Software-only solutions: Increasingly capable of handling tasks previously requiring specialized hardware.
- Generic hardware: Lower cost and wider availability make it an attractive alternative for less demanding applications.
- Open-source embedded software: Reduces development costs and accelerates the creation of software-centric alternatives.
- Market trends: Growth in industrial software platforms indicates a rising competitive pressure from indirect substitutes.
Regulatory or Industry Standard Shifts
Changes in industry standards or regulations can significantly boost the threat of substitutes. For instance, a new mandate in 2024 requiring all new vehicles to meet specific emissions standards could make electric vehicles a more attractive substitute for traditional gasoline-powered cars. This shift, driven by regulatory pressure, directly impacts the competitive landscape by elevating the viability of alternative solutions.
Consider how evolving environmental regulations are pushing industries toward more sustainable practices. For example, the European Union's continued push for circular economy principles, reinforced in 2024 directives, encourages the adoption of reusable materials and product-as-a-service models, thereby increasing the threat from companies offering these alternative business approaches over traditional product sales.
- Regulatory Shifts Favoring Alternatives: New mandates can directly increase the attractiveness of substitute products or services.
- Industry Standard Evolution: Changes in what is considered the norm can open doors for different technologies or business models.
- Example: Energy Efficiency Mandates: Requirements for higher energy efficiency in 2024 might push consumers towards more efficient appliances, a substitute for less efficient older models.
- Example: Open Architecture Requirements: Mandates for open architectures in software or hardware can favor interoperable solutions over proprietary ones.
The threat of substitutes for ADLINK's specialized embedded computing solutions is substantial, driven by advancements in general-purpose computing, cloud services, and increasingly capable software-only platforms. While ADLINK's offerings provide critical advantages like real-time processing and offline functionality, the rising power and accessibility of alternatives, coupled with cost considerations and ease of adoption, present a significant challenge. The market for AI chips, projected to exceed $200 billion in 2024, highlights the rapid growth of specialized technologies that can serve as substitutes for traditional embedded systems.
| Substitute Category | Key Characteristics | Impact on ADLINK | 2024 Market Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| General-Purpose Computing | Lower initial cost, broader availability | Potential displacement for less demanding applications | Continued growth in x86 and ARM architectures for edge |
| Cloud-Based AI Services | Scalability, flexibility, reduced on-premise hardware needs | Threatens demand for localized processing power | AI cloud market robust, with significant investment in 2024 |
| Software-Only Solutions | Runs on generic hardware, lower development costs (open-source) | Can perform similar tasks, especially with evolving industrial software platforms | Industrial software market expanding, offering adaptable solutions |
| Specialized AI Accelerators (e.g., GPUs, TPUs) | High performance for specific AI workloads | Direct competition for compute-intensive tasks | AI chip market projected over $200 billion in 2024 |
Entrants Threaten
Entering the embedded computing market, particularly for industrial and specialized applications like those ADLINK targets, demands significant capital. Consider the costs for research and development of advanced edge AI solutions, building or retrofitting manufacturing facilities, and establishing robust supply chains. For instance, in 2024, the global edge AI hardware market was projected to reach over $12 billion, indicating the scale of investment needed to compete.
Established players like ADLINK leverage significant economies of scale in manufacturing and procurement, reducing per-unit costs. For instance, in 2024, ADLINK’s extensive supply chain network likely allowed for more favorable pricing on components compared to a new entrant.
Furthermore, years of experience in developing and deploying solutions across various industrial sectors have equipped ADLINK with invaluable technical expertise and market knowledge. Replicating this depth of experience and customer trust presents a substantial hurdle for any new competitor attempting to enter the market.
ADLINK's strong reputation for dependable, high-performance embedded solutions, particularly in sectors like industrial automation, healthcare, and transportation, fosters significant brand loyalty. This established trust makes it challenging for newcomers to gain traction. For instance, ADLINK's commitment to quality has historically translated into strong customer retention rates, a key factor in deterring new entrants.
Access to Distribution Channels
New entrants face significant hurdles in establishing the necessary distribution channels to effectively reach ADLINK's varied customer segments, which span industrial automation, healthcare, and transportation. Building a comparable network to ADLINK's, which benefits from established relationships with distributors such as Rutronik, requires substantial investment and time.
Consider the following points regarding access to distribution channels as a threat:
- Established Networks: ADLINK's existing partnerships with key distributors provide immediate access to a broad customer base, a significant barrier for newcomers.
- Channel Costs: Developing and maintaining effective distribution channels can incur substantial upfront and ongoing costs, impacting profitability for new entrants.
- Customer Relationships: New entrants must invest heavily in building trust and relationships with customers who are already served by established players like ADLINK.
Regulatory Barriers and Intellectual Property
The threat of new entrants for ADLINK is significantly influenced by regulatory hurdles and intellectual property. Sectors ADLINK operates in, such as industrial automation and transportation, often demand rigorous certifications and compliance with evolving standards. For instance, in the automotive sector, meeting ISO 26262 functional safety standards is a substantial undertaking for any new player.
Furthermore, ADLINK's established position is bolstered by its portfolio of patents and proprietary technologies. These intellectual property rights create a formidable barrier, making it challenging and costly for new companies to replicate ADLINK's product offerings and market presence. As of early 2024, the semiconductor and embedded systems industries continue to see significant investment in R&D, with companies actively seeking to protect their innovations through patents.
- Regulatory Compliance: Sectors like healthcare technology and public transportation require extensive approvals, increasing new entrant costs.
- Intellectual Property: ADLINK's patent portfolio protects its core technologies, making market entry more difficult for competitors.
- R&D Investment: High R&D spending by existing players, including ADLINK, creates a technological moat that new entrants struggle to overcome.
The threat of new entrants for ADLINK is moderate, primarily due to high capital requirements for R&D and manufacturing, coupled with significant economies of scale enjoyed by established players. While the embedded computing market is growing, with the global edge AI hardware market projected to exceed $12 billion in 2024, the specialized nature of ADLINK's industrial applications demands substantial upfront investment. This includes the cost of developing advanced solutions and securing robust supply chains, creating a considerable barrier for newcomers.
| Barrier to Entry | Impact on New Entrants | ADLINK's Position |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High costs for R&D, manufacturing, and supply chain development. | Leverages existing infrastructure and R&D investments. |
| Economies of Scale | New entrants lack cost advantages in procurement and production. | Benefits from lower per-unit costs due to high-volume production. |
| Brand Loyalty & Reputation | Difficult to overcome established customer trust and brand recognition. | Strong reputation for reliability in industrial sectors. |
| Distribution Channels | Challenging and costly to build comparable networks. | Established partnerships with distributors like Rutronik. |
| Intellectual Property & Regulations | Navigating patents and industry-specific certifications is complex. | Protects core technologies through patents and adheres to industry standards. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis is built upon a foundation of robust data, including company annual reports, financial statements, and industry-specific market research from leading providers like IBISWorld and Statista. We also incorporate insights from regulatory filings and macroeconomic data to ensure a comprehensive understanding of the competitive landscape.
