Shanghai Wanye Enterprises Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
Shanghai Wanye Enterprises Bundle
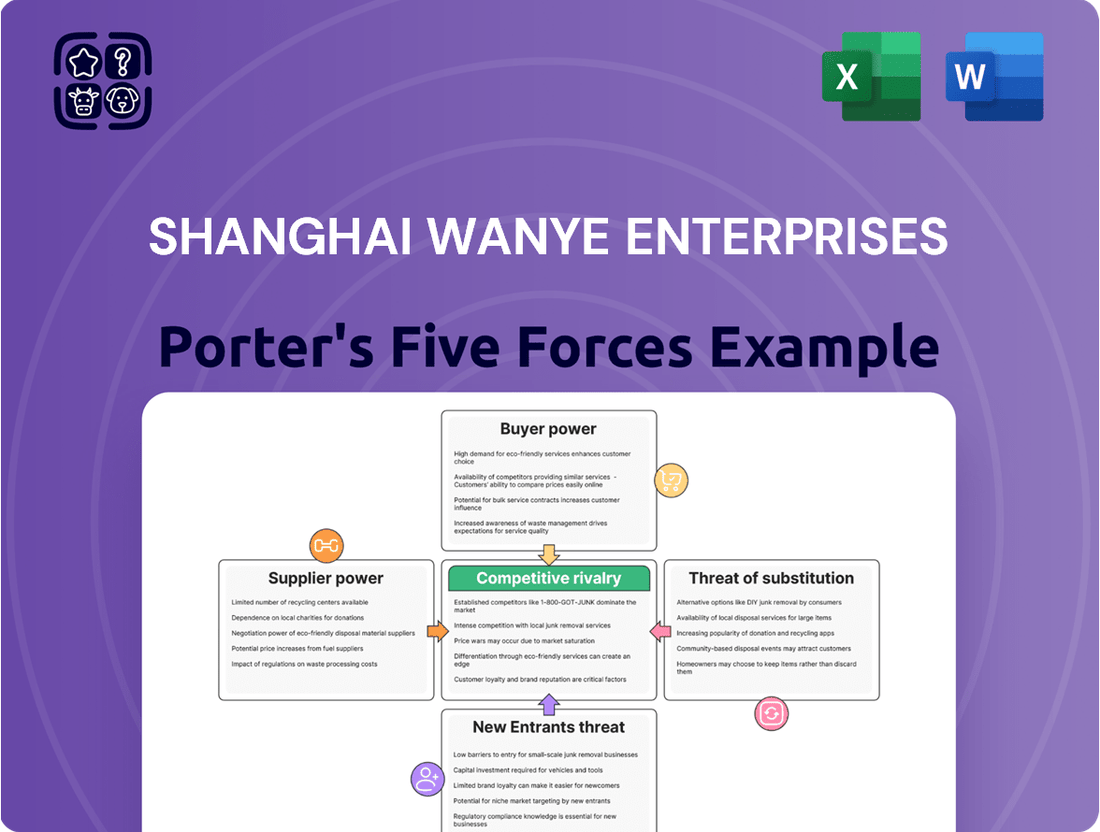
Shanghai Wanye Enterprises operates within a dynamic market, facing moderate threats from new entrants and intense rivalry among existing players. Understanding the bargaining power of both buyers and suppliers is crucial for navigating its competitive landscape. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore Shanghai Wanye Enterprises’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
Shanghai Wanye Enterprises, operating within the semiconductor equipment sector, faces a significant challenge from supplier concentration. This industry often depends on a select group of highly specialized providers for essential components and advanced technologies, such as those for lithography. In 2024, the semiconductor equipment market saw continued consolidation among key material and component suppliers, meaning fewer options for manufacturers like Shanghai Wanye.
The bargaining power of suppliers is significantly influenced by the uniqueness of their inputs. For instance, in the semiconductor manufacturing equipment sector, suppliers of advanced optical components or high-precision robotics possess considerable leverage. These specialized inputs are often difficult to substitute and may be protected by robust intellectual property rights, allowing suppliers to command premium pricing.
Shanghai Wanye faces significant switching costs when changing suppliers. These costs can include the expense and time involved in re-qualifying new components to meet their stringent quality standards, as well as re-tooling production lines to accommodate different supplier specifications. For instance, in 2024, the average cost for a manufacturing company to switch a critical component supplier was estimated to be upwards of $50,000, factoring in engineering and testing.
These substantial upfront investments make it economically challenging for Shanghai Wanye to easily switch suppliers, even if a competitor offers a slightly lower price. The potential for production disruptions and the need for extensive validation processes further solidify the bargaining power of their existing suppliers, particularly for specialized or proprietary parts.
Threat of Forward Integration by Suppliers
The threat of forward integration by suppliers represents a significant concern for Shanghai Wanye Enterprises. If suppliers possess the capability and the motivation to begin manufacturing semiconductor equipment themselves, they could directly compete with Shanghai Wanye. This potential competition can compel Shanghai Wanye to agree to less favorable terms, such as higher prices or stricter contract conditions, simply to deter their suppliers from entering the market as rivals.
For instance, a key supplier of specialized components for semiconductor manufacturing equipment might leverage its deep understanding of the production process and existing manufacturing infrastructure to produce finished equipment. This could be particularly potent if the supplier has established strong relationships with end-users in the semiconductor industry.
- Supplier Capability: Suppliers with existing manufacturing expertise and access to capital are better positioned for forward integration.
- Market Incentives: High profit margins in the semiconductor equipment market can strongly incentivize suppliers to integrate forward.
- Competitive Pressure: The threat of a supplier becoming a competitor can weaken Shanghai Wanye's negotiating position.
Importance of Shanghai Wanye to Suppliers
The bargaining power of suppliers to Shanghai Wanye is significantly shaped by Shanghai Wanye's importance as a customer. If Shanghai Wanye constitutes a minor fraction of a supplier's total sales, that supplier likely holds greater leverage.
Conversely, when Shanghai Wanye represents a substantial portion of a supplier's revenue, the company gains more influence in negotiations. For instance, if a key component supplier derives over 15% of its annual income from Shanghai Wanye, it might be less inclined to risk that relationship through aggressive pricing demands.
- Supplier Dependence: If Shanghai Wanye is a critical client, suppliers are more accommodating to its pricing and terms.
- Customer Concentration: A high degree of customer concentration for a supplier amplifies Shanghai Wanye's bargaining position.
- Revenue Impact: The percentage of a supplier's revenue generated by Shanghai Wanye directly correlates with the company's negotiation strength.
The bargaining power of suppliers for Shanghai Wanye Enterprises is amplified by industry consolidation and the specialized nature of their offerings. In 2024, the semiconductor equipment sector continued to see fewer, more dominant suppliers for critical components, limiting Shanghai Wanye's options and increasing supplier leverage. High switching costs, often exceeding $50,000 per component change in 2024, further entrench suppliers, making it difficult for Shanghai Wanye to explore alternatives even with potential price advantages.
The threat of forward integration by these specialized suppliers also weighs heavily on Shanghai Wanye's negotiation position. If suppliers can leverage their expertise and infrastructure to enter the equipment manufacturing market, they could become direct competitors, forcing Shanghai Wanye into less favorable terms. Furthermore, Shanghai Wanye's own customer concentration with key suppliers can either bolster or diminish its bargaining power; if Shanghai Wanye represents a significant portion of a supplier's revenue, it gains more negotiating strength.
| Factor | Impact on Shanghai Wanye | 2024 Data/Context |
| Supplier Concentration | Increases supplier power | Continued consolidation in specialized component supply. |
| Uniqueness of Inputs | Increases supplier power | Proprietary optical and robotic components command premium pricing. |
| Switching Costs | Increases supplier power | Estimated $50,000+ for critical component supplier changes. |
| Threat of Forward Integration | Increases supplier power | Suppliers with manufacturing capability and market access pose a competitive threat. |
| Shanghai Wanye's Customer Importance | Decreases supplier power (if high) | Suppliers with >15% revenue from Shanghai Wanye are more accommodating. |
What is included in the product
Uncovers key drivers of competition, customer influence, and market entry risks tailored to Shanghai Wanye Enterprises' unique position in the market.
Instantly grasp the competitive landscape of Shanghai Wanye Enterprises with a dynamic, interactive analysis that highlights key pressures and opportunities.
Customers Bargaining Power
Shanghai Wanye Enterprises' primary customers are integrated circuit manufacturers and semiconductor fabrication plants. The bargaining power of these customers is significantly influenced by their concentration. If a few large customers account for a substantial percentage of Shanghai Wanye's revenue, they can leverage this position to negotiate lower prices or more favorable terms.
Shanghai Wanye Enterprises faces significant customer bargaining power due to the availability of substitutes in the semiconductor equipment market. Customers can source similar equipment from numerous domestic and international suppliers, a situation exacerbated by China's drive for technological self-sufficiency. This globalized market means buyers have ample choices, strengthening their negotiating position.
Customers' price sensitivity is a key driver of their bargaining power. When customers face high cost structures or operate in intensely competitive markets, they are more likely to push for lower prices. For instance, in the semiconductor industry, where profit margins can be tight, equipment buyers will actively seek the most economical solutions, directly impacting suppliers like Shanghai Wanye Enterprises.
Threat of Backward Integration by Customers
The threat of backward integration by customers is a significant concern for Shanghai Wanye Enterprises. If its major clients, particularly those in the semiconductor manufacturing sector, possess the financial resources and technical expertise to develop their own semiconductor equipment, they could choose to produce it in-house. This capability directly pressures Shanghai Wanye to offer more competitive pricing and favorable contract terms to retain these crucial customer relationships.
For instance, major semiconductor foundries often invest heavily in research and development, and by 2024, many were exploring in-house solutions for specialized equipment needs to gain greater control over their supply chains and reduce costs. This strategic shift by powerful customers directly impacts Shanghai Wanye's pricing power and market share.
- Customer Capability: Major semiconductor manufacturers often have substantial R&D budgets, exceeding billions of dollars annually, enabling them to explore in-house equipment development.
- Cost Reduction Incentive: By producing equipment internally, large customers could potentially reduce their capital expenditure by an estimated 10-15% compared to purchasing from external suppliers.
- Supply Chain Control: The desire for greater control over critical equipment and reduced reliance on external vendors drives the consideration of backward integration.
- Competitive Pressure: As competitors explore in-house solutions, Shanghai Wanye faces increased pressure to maintain its value proposition through innovation and cost-effectiveness.
Volume of Purchases by Customers
The volume of equipment purchased by customers significantly influences their bargaining power with Shanghai Wanye Enterprises. Larger customers, by virtue of their substantial orders, can command better pricing and more favorable contract terms.
For instance, in 2024, major construction firms or large real estate developers who are consistent, high-volume buyers of Shanghai Wanye's equipment are likely to leverage their purchasing scale. This allows them to negotiate discounts that smaller, infrequent buyers cannot access.
- High-volume buyers can negotiate lower unit prices.
- Significant order sizes grant customers more leverage on delivery schedules and payment terms.
- The collective purchasing power of a large customer base can exert downward pressure on prices.
Shanghai Wanye Enterprises' customers, primarily integrated circuit manufacturers, possess considerable bargaining power. This power stems from the availability of numerous global suppliers, China's push for technological independence, and customers' sensitivity to price, especially in a competitive semiconductor market.
The threat of backward integration is a significant factor, as large clients with substantial R&D budgets, potentially billions annually, might develop their own equipment to reduce costs by an estimated 10-15% and gain supply chain control.
Furthermore, the volume of purchases directly impacts negotiations; high-volume buyers in 2024, such as major construction firms, can secure better pricing and terms than smaller clients.
| Factor | Impact on Bargaining Power | Example/Data Point (2024) |
| Customer Concentration | High if few large customers | Major foundries represent a significant portion of revenue for specialized equipment suppliers. |
| Availability of Substitutes | High due to global suppliers | China's semiconductor industry aims for 70% self-sufficiency by 2025, increasing local and international equipment options. |
| Price Sensitivity | High in competitive markets | Semiconductor manufacturers often operate on tight margins, driving demand for cost-effective solutions. |
| Threat of Backward Integration | Moderate to High | Large foundries invest heavily in R&D, exploring in-house solutions to reduce capital expenditure by 10-15%. |
| Purchasing Volume | High for large-scale buyers | Consistent, high-volume orders from major developers allow for negotiated discounts. |
Same Document Delivered
Shanghai Wanye Enterprises Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview showcases the comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for Shanghai Wanye Enterprises, detailing the competitive landscape and strategic implications. The document displayed here is the part of the full version you’ll get—ready for download and use the moment you buy, providing an in-depth examination of industry rivalry, buyer power, supplier power, threat of new entrants, and threat of substitutes. You're looking at the actual document; once you complete your purchase, you’ll get instant access to this exact file, enabling immediate strategic planning.
Rivalry Among Competitors
The competitive landscape for Shanghai Wanye Enterprises is shaped by a dynamic semiconductor equipment market in China, which is seeing rapid expansion and a growing number of both local and international contenders. This robust growth fuels intense rivalry as companies vie for market share.
Despite China's drive for domestic semiconductor production, established global giants such as Applied Materials, ASML, and Tokyo Electron continue to dominate, particularly in the high-end, technologically advanced equipment segment. Their continued presence intensifies the competitive pressure on all players.
In 2023, China's domestic semiconductor equipment manufacturers saw notable growth, with some reporting revenue increases exceeding 30%, signaling their increasing competitiveness. However, the market's reliance on imported advanced lithography and etching tools remains substantial, highlighting the entrenched position of foreign leaders.
The global semiconductor equipment market is expected to see robust growth through 2025, fueled by the insatiable demand from AI and other cutting-edge technologies. This expansion, however, is a double-edged sword for competitive rivalry.
As the market balloons, companies like Shanghai Wanye Enterprises will likely face intensified competition. The allure of a growing pie means more players will enter or expand their efforts, leading to a fiercer battle for market share and technological dominance.
The degree to which Shanghai Wanye's integrated circuit core equipment and services are differentiated significantly impacts competitive rivalry. Unique features, such as proprietary process technologies or advanced automation capabilities, can create a moat, reducing direct price wars. For instance, if Shanghai Wanye offers a lithography system with demonstrably higher resolution than competitors, this differentiation can command premium pricing and customer loyalty.
Exit Barriers
The semiconductor equipment industry, where Shanghai Wanye Enterprises operates, is characterized by substantial exit barriers. These include the immense cost of specialized manufacturing assets, often running into hundreds of millions of dollars, and the continuous, significant R&D investments required to stay competitive. For instance, leading players like ASML invest billions annually in R&D to maintain their technological edge.
These high exit barriers mean that even companies experiencing financial difficulties may find it challenging to cease operations. The specialized nature of their machinery and intellectual property makes liquidation or repurposing difficult and often unprofitable. This can lead to prolonged market presence for underperforming firms, intensifying rivalry as they strive to recover costs.
Furthermore, long-standing relationships with major chip manufacturers are a critical factor. Once a supplier establishes deep integration with a customer's production processes, switching to a new vendor incurs significant costs and risks for the customer. This lock-in effect further discourages companies from exiting, as they may hold onto market share even when unprofitable due to these entrenched ties.
- Specialized Assets: Semiconductor manufacturing equipment is highly specific and costly, with few alternative uses, making divestment difficult.
- R&D Investment: Continuous, high-volume R&D spending creates a significant financial commitment that can be hard to abandon.
- Customer Relationships: Deeply integrated supply chains and long-term contracts create switching costs for customers, deterring suppliers from exiting.
Strategic Stakes
The semiconductor industry is a cornerstone of China's ambition for technological independence, making domestic players like Shanghai Wanye crucial. This national focus translates into significant government backing, creating an environment where success is not just desired but mandated.
This high-stakes environment fuels intense competition among Chinese semiconductor firms. Companies are pushed to invest heavily and innovate rapidly to meet national objectives, a dynamic that can lead to aggressive market strategies and a constant drive for market share.
- Government Support: China's "Made in China 2025" initiative, for example, has allocated billions towards boosting domestic semiconductor production and R&D.
- Aggressive Investment: Major Chinese chipmakers saw their capital expenditures increase significantly in 2023, with some planning further substantial investments for 2024 to expand capacity and technological capabilities.
- Talent Acquisition: The competition extends to securing top engineering talent, with companies offering highly competitive packages to attract skilled professionals in the field.
Competitive rivalry within Shanghai Wanye Enterprises' market is fierce, driven by both established global leaders and a rapidly growing cohort of domestic Chinese firms. The push for technological self-sufficiency in China, supported by substantial government investment, intensifies this competition, forcing companies to innovate rapidly and aggressively pursue market share.
The semiconductor equipment sector is characterized by high exit barriers, including massive capital investments in specialized assets and continuous R&D spending, which keeps even struggling firms in the market. This, coupled with deep customer relationships and integration, further entrenches existing players and heightens the competitive struggle for new entrants and existing rivals alike.
Anticipated market growth through 2025, fueled by AI and advanced technologies, will likely attract even more players, intensifying the battle for dominance. Companies like Shanghai Wanye must focus on differentiation through unique technologies or advanced capabilities to carve out their niche and mitigate direct price competition.
| Metric | 2023 (Approximate) | 2024 Projections | Key Trend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Domestic Chinese Semiconductor Equipment Revenue Growth | >30% | Continued strong growth | Increasing competitiveness of local players |
| Global Semiconductor Equipment Market Growth | Strong | Robust growth through 2025 | Demand driven by AI and advanced technologies |
| R&D Investment by Leading Players (e.g., ASML) | Billions USD annually | Continued high investment | Essential for maintaining technological edge |
SSubstitutes Threaten
The threat of substitutes for Shanghai Wanye's integrated circuit (IC) core equipment is primarily driven by emerging alternative manufacturing technologies or processes that could diminish the necessity of their current offerings. While direct substitutes for the highly specialized core equipment are scarce, significant shifts in chip design or the adoption of entirely new computing paradigms, such as quantum computing or advanced neuromorphic chips, could reduce the overall demand for traditional IC manufacturing equipment. For instance, the projected growth of specialized AI accelerators, which might employ novel fabrication techniques, could divert investment away from general-purpose IC manufacturing lines.
Shanghai Wanye Enterprises faces a threat from customers shifting to alternative solutions that lessen their need for specialized manufacturing equipment. For instance, a move towards more standardized or modular chip designs could diminish the demand for highly advanced, bespoke machinery, impacting Wanye's core offerings.
The threat of substitutes for Shanghai Wanye Enterprises in integrated circuit production is moderate. While direct equipment replacements are limited, alternative approaches like advanced materials or novel fabrication methods could emerge. For instance, the development of new semiconductor materials that require less complex or costly manufacturing processes could offer a more cost-effective path to achieving similar performance outcomes.
Performance-Price Trade-off
Customers continually assess the performance-price balance of Shanghai Wanye's offerings against available substitutes. If competing products deliver comparable functionality at a lower price point, or superior features for a similar cost, the threat of substitution intensifies. For instance, in 2024, the real estate development sector, where Shanghai Wanye operates, saw a notable increase in modular construction techniques, offering faster build times and potentially lower upfront costs for certain types of properties, directly impacting the perceived value of traditional construction methods.
This evaluation directly influences customer loyalty and purchasing decisions. A significant shift in the market towards more cost-effective or technologically advanced alternatives could erode Shanghai Wanye's market share if its value proposition becomes less competitive. For example, advancements in sustainable building materials in 2024 provided developers with options that, while potentially carrying a higher initial cost, offered long-term operational savings, forcing a re-evaluation of the performance-price trade-off.
- Performance-Price Evaluation: Buyers compare Shanghai Wanye's equipment value against substitute options.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Substitutes offering lower cost for similar performance or better performance for similar cost pose a threat.
- Market Dynamics (2024): Increased adoption of modular construction and sustainable materials presented new performance-price considerations in real estate development.
- Impact on Market Share: Failure to maintain a competitive performance-price ratio can lead to reduced customer demand and market share erosion.
Technological Disruption
Technological disruption poses a significant threat to companies like Shanghai Wanye Enterprises, particularly those involved in manufacturing. For instance, advancements in quantum computing could eventually render current semiconductor fabrication methods obsolete, impacting the demand for specialized manufacturing equipment. The semiconductor industry, a key area for Wanye, saw global capital expenditures reach approximately $180 billion in 2023, highlighting the substantial investment in existing technologies that could be disrupted.
Emerging materials science could also present substitutes for traditional silicon-based integrated circuits. Innovations in areas like graphene or organic semiconductors might offer alternative solutions for electronic components, potentially reducing reliance on established manufacturing processes. This shift could diminish the market share for companies heavily invested in current technologies.
The rapid pace of innovation in consumer electronics, for example, means that new device architectures or functionalities could emerge that bypass the need for certain types of integrated circuits. This could lead to a decline in demand for the specific components and manufacturing capabilities that Shanghai Wanye Enterprises currently offers. The global semiconductor market itself is projected to grow, but the nature of that growth is subject to rapid technological shifts.
- Technological Disruption: Rapid advancements in computing, such as quantum computing, could make current semiconductor manufacturing equipment redundant.
- Materials Science: Innovations in materials like graphene could offer alternative solutions to silicon-based integrated circuits.
- Consumer Electronics: New device architectures might reduce the demand for specific types of integrated circuits and manufacturing processes.
- Industry Investment: The $180 billion global semiconductor capital expenditure in 2023 underscores the risk of investing in technologies that could be rapidly superseded.
The threat of substitutes for Shanghai Wanye Enterprises is moderate, primarily stemming from evolving technologies and materials that could reduce the need for its core integrated circuit (IC) equipment. While direct substitutes are scarce, shifts in chip design or the adoption of new computing paradigms like quantum computing could impact demand. For instance, the rise of specialized AI accelerators might divert investment from traditional IC manufacturing lines.
Customers continually evaluate the performance-price ratio of Wanye's offerings against alternatives. In 2024, the real estate sector, where Wanye also operates, saw increased adoption of modular construction, offering faster, potentially lower-cost building solutions. This highlights how alternative methods can alter the perceived value of established processes, a dynamic that could affect Wanye if its value proposition weakens.
Technological advancements, such as new materials science innovations like graphene, could offer alternatives to silicon-based ICs, potentially reducing reliance on current manufacturing processes. The semiconductor industry's substantial investment, with global capital expenditures reaching approximately $180 billion in 2023, underscores the risk of rapid technological obsolescence.
| Threat of Substitutes | Description | Example/Data Point |
| Technological Shifts | Emerging computing paradigms (e.g., quantum computing) could reduce demand for traditional IC manufacturing equipment. | Growth of specialized AI accelerators potentially diverting investment. |
| Materials Science | Innovations in materials like graphene could offer alternatives to silicon-based ICs. | New materials requiring less complex or costly manufacturing processes. |
| Customer Value Perception | Customers assess performance-price balance against substitutes. | Modular construction in real estate in 2024 offered faster build times and potentially lower costs. |
| Industry Investment Risk | Significant capital expenditure in current technologies faces disruption risk. | Global semiconductor capital expenditures reached ~$180 billion in 2023. |
Entrants Threaten
The semiconductor equipment industry is characterized by formidable capital requirements, acting as a significant barrier to entry. Companies venturing into this space must be prepared for immense upfront investments in cutting-edge research and development, sophisticated manufacturing plants, and highly specialized machinery. For instance, establishing a new semiconductor fabrication facility, a crucial component for equipment manufacturers, can easily cost billions of dollars, with estimates often exceeding $10 billion for advanced nodes.
Shanghai Wanye Enterprises, like many established players in its sector, possesses a robust portfolio of intellectual property and patents. This IP creates a significant hurdle for potential new entrants, as developing comparable technologies or securing licenses for existing ones requires substantial investment and time. For instance, in the competitive landscape of advanced materials, companies with patented manufacturing processes can command higher margins and market share, making it difficult for newcomers without similar protections to compete on price or performance.
Established players in Shanghai's real estate market, like Shanghai Wanye Enterprises, often leverage significant economies of scale. For instance, in 2024, large developers could negotiate bulk discounts on construction materials, potentially reducing per-unit costs by 5-10% compared to smaller, new entrants. This cost advantage makes it difficult for newcomers to compete on price.
Furthermore, the experience curve plays a crucial role. Decades of navigating Shanghai's complex zoning laws, construction regulations, and supply chain management have honed the operational efficiency of established firms. This accumulated expertise, difficult to replicate quickly, allows them to anticipate and mitigate risks more effectively than a new entrant, creating a substantial barrier.
Government Policy and Support
Government policy in China significantly shapes the threat of new entrants in sectors like semiconductors, which is relevant to Shanghai Wanye Enterprises. While China actively promotes domestic semiconductor development, its support often targets existing national champions or specific strategic initiatives. This can create a less equitable environment for entirely new, independent companies seeking to enter the market.
Furthermore, evolving export controls, particularly concerning advanced technologies, introduce substantial complexities for new players that rely on global supply chains and international collaboration. For instance, in 2024, continued restrictions on the export of advanced chipmaking equipment to China by countries like the United States directly impact the ability of new domestic firms to acquire state-of-the-art manufacturing capabilities.
- Government Support Bias: Chinese government subsidies and incentives, while substantial, often prioritize established national semiconductor companies, potentially disadvantaging nascent independent entrants.
- Export Control Impact: International export controls, particularly on advanced manufacturing equipment and intellectual property, create significant hurdles for new companies needing access to cutting-edge technology in 2024.
- Regulatory Landscape: Navigating China's complex and evolving regulatory environment, including licensing and compliance, can be a substantial barrier for new domestic and foreign entrants alike.
Access to Distribution Channels and Customer Relationships
New entrants into Shanghai Wanye Enterprises' market would struggle to establish effective distribution channels and cultivate deep relationships with integrated circuit manufacturers. These manufacturers often rely on established, long-term partnerships with existing equipment suppliers, viewing the machinery as critical to their operations and unwilling to risk disruption with unproven vendors.
The integrated circuit industry, particularly in advanced manufacturing, demands a high degree of trust and proven reliability in equipment suppliers. Building these connections takes significant time and investment, creating a substantial barrier for new players seeking to displace incumbent suppliers to major players like Shanghai Wanye Enterprises.
- Distribution Channel Barriers: Established suppliers have secured distribution networks, making it difficult for new entrants to reach target customers efficiently.
- Customer Relationship Loyalty: Integrated circuit manufacturers prioritize stable, long-term relationships with trusted equipment providers, presenting a hurdle for newcomers.
- Switching Costs: The high cost and operational disruption associated with changing critical manufacturing equipment deter customers from adopting new suppliers.
The threat of new entrants for Shanghai Wanye Enterprises is significantly mitigated by the immense capital requirements and established intellectual property within its operating sectors, particularly semiconductors and real estate.
For instance, the cost of building a new semiconductor fabrication plant can exceed $10 billion, a prohibitive sum for most newcomers. Furthermore, decades of navigating complex regulations and building supplier relationships create an experience curve advantage for incumbents, making it difficult for new firms to compete effectively on price or operational efficiency.
Government policies in China, while promoting domestic growth, often favor existing national champions, and international export controls on advanced technologies further complicate market entry for new players. Established distribution channels and strong customer loyalty within the integrated circuit industry also present substantial barriers, as manufacturers are reluctant to risk disruption by switching to unproven suppliers.
| Barrier Type | Description | Example Impact (Approximate) |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Requirements | High upfront investment in R&D, manufacturing, and machinery. | Semiconductor fab costs >$10 billion. |
| Intellectual Property | Patented technologies and proprietary processes. | Difficult for new entrants to replicate or license, impacting competitive pricing. |
| Economies of Scale | Cost advantages from bulk purchasing and efficient operations. | 2024 bulk material discounts for large developers: 5-10% cost reduction. |
| Experience Curve | Accumulated expertise in regulations, supply chains, and risk management. | Faster, more efficient operations for established firms. |
| Government Policy | Targeted support for national champions, less for independent entrants. | Creates an uneven playing field for new domestic companies. |
| Export Controls | Restrictions on advanced technology and equipment access. | Impacts new firms needing state-of-the-art capabilities in 2024. |
| Distribution Channels | Secured networks and established relationships with customers. | Difficult for new entrants to gain market access. |
| Customer Relationships | Prioritization of trusted, long-term supplier partnerships. | Newcomers face challenges displacing incumbents. |
| Switching Costs | High costs and operational disruption associated with changing suppliers. | Deters customers from adopting new equipment providers. |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for Shanghai Wanye Enterprises is built upon a robust foundation of data, including the company's official annual reports, filings with the Shanghai Stock Exchange, and industry-specific market research reports from reputable firms. We also leverage macroeconomic data from official Chinese statistical bureaus to understand the broader economic context influencing the industry.
