TÜV Rheinland AG Porter's Five Forces Analysis
Fully Editable
Tailor To Your Needs In Excel Or Sheets
Professional Design
Trusted, Industry-Standard Templates
Pre-Built
For Quick And Efficient Use
No Expertise Is Needed
Easy To Follow
TÜV Rheinland AG Bundle
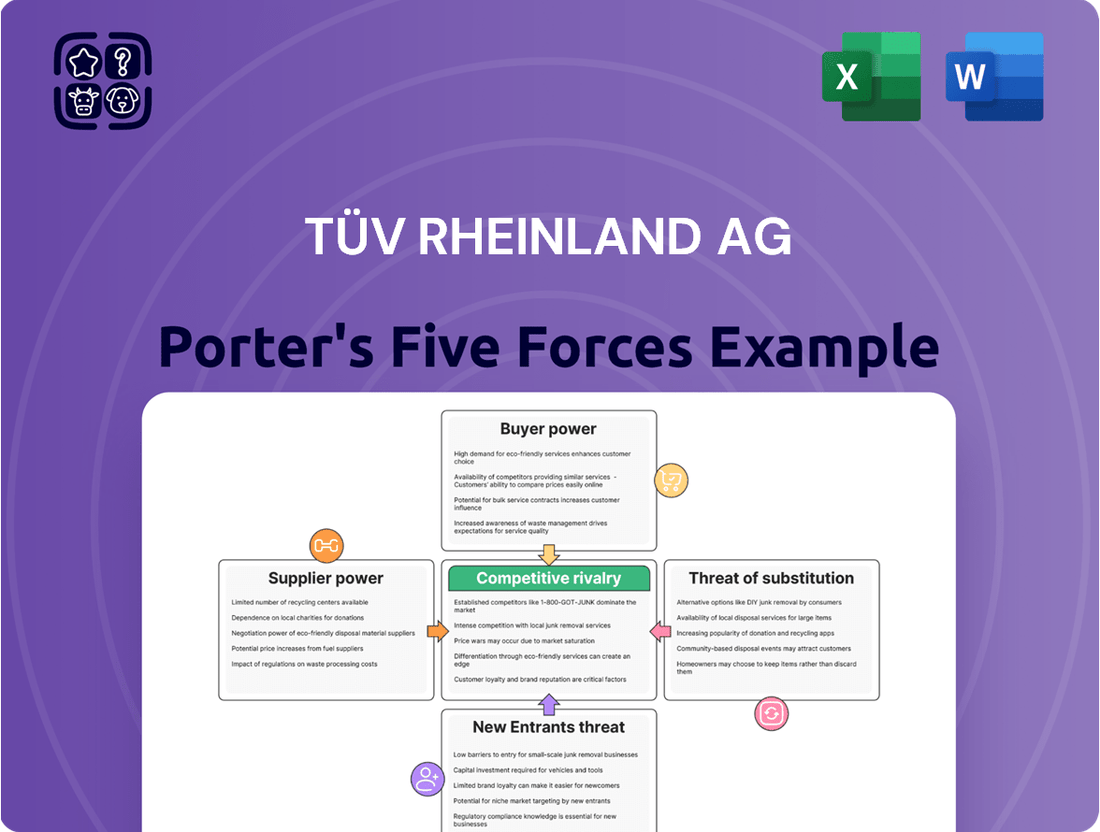
TÜV Rheinland AG operates in a complex landscape shaped by several powerful forces. Understanding the intensity of buyer power and the threat of substitutes is crucial for navigating this market. The bargaining power of suppliers and the threat of new entrants also present significant challenges and opportunities.
The competitive rivalry within the testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) sector is particularly noteworthy, influencing pricing and service innovation. This brief snapshot only scratches the surface. Unlock the full Porter's Five Forces Analysis to explore TÜV Rheinland AG’s competitive dynamics, market pressures, and strategic advantages in detail.
Suppliers Bargaining Power
TÜV Rheinland AG's reliance on highly skilled engineers and accredited professionals in specialized fields like cybersecurity and renewable energy significantly bolsters the bargaining power of these experts. The scarcity of such talent means that individuals with these niche skills can command higher wages and dictate terms, impacting TÜV Rheinland's operational costs and service expansion plans. For instance, the global shortage of cybersecurity talent, estimated to have over 3.5 million unfilled positions in 2024 according to Cybersecurity Ventures, directly translates to increased recruitment costs and potential delays in project delivery for TÜV Rheinland's testing and certification services in this domain.
Accreditation bodies and regulatory authorities hold significant sway over TÜV Rheinland AG, as their certifications are essential for market access and operational legitimacy. For instance, the American Association for Laboratory Accreditation (A2LA) and national bodies like Korea's NIST RRA are critical for TÜV Rheinland's testing and certification services across various industries. Failure to maintain these accreditations would directly impede TÜV Rheinland's ability to operate, giving these bodies considerable bargaining power.
Suppliers of highly specialized and expensive testing equipment, laboratory instruments, and proprietary software hold significant bargaining power over TÜV Rheinland AG. The limited number of vendors offering cutting-edge technology, especially for rapidly evolving sectors such as AI-driven inspection or sophisticated battery performance analysis, grants these suppliers considerable leverage. This leverage translates into their ability to dictate pricing and terms for critical components and systems essential for TÜV Rheinland's advanced testing services.
Proprietary Methodologies and Standards
When developers create proprietary testing methodologies or industry standards that become widely adopted or even mandated, they gain significant influence. While TÜV Rheinland actively participates in developing and applying standards, a strong reliance on dominant, externally created methods can shift bargaining power to those original creators, impacting licensing and implementation terms.
This influence is particularly evident in rapidly evolving sectors. For instance, advancements in areas like AI model validation or quantum computing testing may see early movers who establish rigorous, proprietary benchmarks gain leverage. Companies that develop and successfully promote these foundational methodologies can dictate terms for their use, effectively controlling access to critical testing protocols.
- Influence of Dominant Standards: Suppliers who develop widely adopted proprietary testing methodologies can dictate terms for their use.
- Licensing Power: Creators of essential industry standards may hold leverage in licensing agreements for their methodologies.
- Market Entry Barriers: Exclusive or patented testing processes can act as barriers for competitors, strengthening supplier power.
- Evolving Sectors: In emerging fields like AI or quantum computing, early adopters of proprietary validation methods can gain significant bargaining power.
Infrastructure and IT Service Providers
Infrastructure and IT service providers, like those offering cloud solutions such as Microsoft Azure, wield considerable bargaining power over TÜV Rheinland AG. This is particularly true as TÜV Rheinland continues its digital transformation, heavily relying on these specialized IT solutions for data management and operational efficiency. The critical nature of these services means that disruptions or price increases from these suppliers can significantly impact TÜV Rheinland's business continuity and strategic execution.
The dependence on a few key players in the cloud computing market, for instance, concentrates power in their hands. For example, in 2024, the global public cloud market was projected to reach over $600 billion, with a few dominant providers holding a substantial share. This market concentration allows these providers to dictate terms and pricing, as switching costs for comprehensive IT infrastructure can be prohibitively high for a company like TÜV Rheinland.
- High Switching Costs: Migrating complex IT systems and vast datasets from one cloud provider to another involves significant time, resources, and potential operational disruption, giving existing providers leverage.
- Concentrated Market: The IT infrastructure and cloud services market is dominated by a few major global players, limiting the number of viable alternatives for TÜV Rheinland.
- Essential Services: Reliable and secure IT infrastructure, including cloud services, is fundamental to TÜV Rheinland's digital operations and data handling, making these suppliers indispensable.
- Supplier Innovation: Leading IT service providers continuously invest in R&D, offering advanced solutions that TÜV Rheinland needs to remain competitive, further solidifying their supplier power.
The bargaining power of suppliers for TÜV Rheinland AG is significantly influenced by the specialized nature of inputs and the concentration of providers. Suppliers of highly specialized testing equipment and proprietary software, particularly for emerging fields like AI or advanced battery analysis, hold considerable leverage due to the limited vendor pool and the critical need for cutting-edge technology.
Furthermore, the increasing reliance on cloud infrastructure and IT services, dominated by a few major global players, grants these providers substantial bargaining power. High switching costs associated with migrating complex IT systems amplify this influence, making TÜV Rheinland susceptible to price increases and dictated terms from these essential technology partners.
| Supplier Type | Source of Power | Impact on TÜV Rheinland | Example Data (2024/2025) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specialized IT/Cloud Services | Market concentration, high switching costs | Increased operational costs, potential service disruption | Global public cloud market projected over $600 billion in 2024. |
| Skilled Professionals (e.g., Cybersecurity) | Talent scarcity, specialized skills | Higher recruitment costs, project delays | Global cybersecurity talent shortage estimated at over 3.5 million unfilled positions in 2024. |
| Accreditation Bodies | Essential for market access and legitimacy | Risk of operational impediments if accreditations are revoked | N/A (Regulatory reliance, not a transactional supplier in the same vein) |
| Proprietary Testing Methodologies | Industry adoption, potential mandates | Licensing costs, reliance on external standards | N/A (Industry standard development, not direct supplier costs) |
What is included in the product
Uncovers the competitive intensity within TÜV Rheinland AG's diverse service sectors, detailing the threat of new entrants, buyer and supplier power, and the impact of substitutes on its market position.
Instantly identify and mitigate competitive threats with a dynamic Porter's Five Forces analysis, allowing TÜV Rheinland AG to proactively address market pressures.
Customers Bargaining Power
TÜV Rheinland's bargaining power of customers is significantly influenced by regulatory mandates for its services. Many of TÜV Rheinland's offerings, such as automotive inspections, medical device certifications, and renewable energy testing, are legally required for market access and safety compliance. This regulatory necessity means that customers cannot easily bypass these services, as non-compliance can lead to substantial fines, product recalls, or complete market exclusion.
For example, the European Union's General Product Safety Regulation mandates that products placed on the market must be safe. TÜV Rheinland's role in conformity assessment and certification for many product categories directly addresses these requirements. In 2024, the global market for product testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) services was valued at over $200 billion, with regulatory compliance being a primary driver for a significant portion of this market.
This regulatory backdrop limits the ability of customers to negotiate prices or terms for these essential services. The penalties for failing to meet these standards, which can include millions in fines and reputational damage, far outweigh any potential savings from challenging TÜV Rheinland's service costs. Consequently, customers have very little leverage to demand lower prices for services that are non-negotiable for their business operations.
Companies certified by TÜV Rheinland often face substantial costs if they decide to switch to a different certification body. These costs can include new audits, re-testing of products or systems, and potential disruptions to ongoing operations or market access. For instance, in the automotive sector, a manufacturer holding TÜV Rheinland certifications for key components would likely incur significant expenses to re-validate those components with a new agency, potentially delaying new model launches.
The investment in understanding and complying with TÜV Rheinland's specific auditing and testing protocols also creates a barrier. Once a company has invested time and resources to meet these standards, the perceived value of that established relationship and familiarity discourages switching. This is particularly true for complex certifications, such as those in the aerospace or medical device industries, where the compliance framework is intricate and deeply integrated into a company's quality management systems.
In 2024, the global market for product certification and testing services, a key area for TÜV Rheinland, was projected to reach over $200 billion, reflecting the significant value placed on these services. Companies within this market often prioritize long-term partnerships due to the cumulative switching costs, thereby strengthening TÜV Rheinland's position against potential new entrants or smaller competitors seeking to lure away established clients.
TÜV Rheinland AG caters to a broad spectrum of clients, ranging from global enterprises to smaller enterprises. While large clients may leverage their purchasing volume for price negotiations, the fundamental need for safety, quality assurance, and robust risk management across all sectors, especially in high-risk industries, often mitigates their price leverage. For instance, in 2024, industries like automotive and renewable energy, where safety failures can have catastrophic consequences, saw continued strong demand for TÜV Rheinland's certification and inspection services, underscoring the criticality of their offerings.
Brand Reputation and Trust in TIC Services
Customers increasingly seek TÜV Rheinland, a globally recognized Testing, Inspection, and Certification (TIC) provider, to bolster their own brand reputation and ensure their products gain market acceptance. This strong preference for established names like TÜV Rheinland, which has cultivated deep trust and brand equity over many decades, significantly diminishes customers' inclination to opt for less reputable or more economical alternatives.
For instance, in 2023, TÜV Rheinland reported revenue of €3.1 billion, underscoring its substantial market presence and the trust placed in its services by a vast customer base seeking to validate product quality and safety.
- Global Recognition: TÜV Rheinland's worldwide network and accreditations provide assurance to customers aiming for international market access.
- Brand Equity: The long-standing reputation and trust associated with TÜV Rheinland reduce customer search costs and risk perception.
- Reduced Switching Incentives: The significant investment in building and maintaining their own brand credibility through reliable TIC services makes customers less likely to switch to unproven providers.
Increasing Demand for Integrated Solutions
The increasing complexity of global supply chains, coupled with the drive towards digitalization and sustainability, is pushing customers to demand more comprehensive, integrated Testing, Inspection, and Certification (TIC) solutions. This trend significantly shifts bargaining power towards customers who can more easily consolidate their needs with providers offering a one-stop shop.
TÜV Rheinland AG, by offering a broad spectrum of services across diverse industries and embracing emerging fields like Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) and Artificial Intelligence (AI), is well-positioned to meet this evolving customer demand. This ability to provide holistic solutions enhances customer loyalty and diminishes their leverage to deconstruct and source individual services from multiple, less integrated providers.
- Growing Demand for Integrated TIC: Customers are increasingly seeking consolidated service offerings due to supply chain complexity and digitalization.
- TÜV Rheinland's Broad Service Portfolio: The company's ability to offer services across various sectors, including ESG and AI, addresses this integrated demand.
- Reduced Customer Bargaining Power: By providing comprehensive solutions, TÜV Rheinland strengthens customer relationships and limits their ability to unbundle services.
While customers generally have some leverage, TÜV Rheinland's essential, often mandated services, combined with high switching costs and the value of its brand, significantly temper customer bargaining power. The critical nature of safety and compliance means customers cannot easily forgo these services, thereby limiting their ability to negotiate on price or terms.
The need for regulatory compliance, as seen in the over $200 billion global TIC market in 2024, means customers must engage with accredited bodies like TÜV Rheinland, reducing their power to seek alternatives. Furthermore, the substantial costs and operational disruptions associated with switching certification providers create strong customer inertia.
The company's broad service portfolio, addressing complex needs like ESG and AI, also strengthens its position. By offering integrated solutions, TÜV Rheinland reduces the incentive for customers to unbundle services, further solidifying its relationships and limiting individual customer leverage.
| Factor | Impact on Customer Bargaining Power | TÜV Rheinland's Position |
| Regulatory Mandates | Lowers customer power; services are essential for market access. | Enables strong demand due to non-discretionary nature of services. |
| Switching Costs | Lowers customer power; high costs deter switching. | Creates customer loyalty and reduces churn. |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Lowers customer power; customers prefer established, trusted providers. | Attracts and retains clients seeking credibility. |
| Integrated Service Demand | Shifts power towards providers offering consolidated solutions. | Leverages broad portfolio to meet complex customer needs. |
Preview Before You Purchase
TÜV Rheinland AG Porter's Five Forces Analysis
This preview shows the exact document you'll receive immediately after purchase—no surprises, no placeholders. The comprehensive Porter's Five Forces Analysis for TÜV Rheinland AG delves into the competitive landscape, scrutinizing the threat of new entrants, the bargaining power of buyers and suppliers, the intensity of rivalry among existing firms, and the threat of substitute products or services. This in-depth analysis provides strategic insights into TÜV Rheinland AG's market position and potential challenges.
Rivalry Among Competitors
TÜV Rheinland AG operates within a highly competitive landscape, facing significant rivalry from other large global players in the Testing, Inspection, and Certification (TIC) sector. Companies like SGS, Bureau Veritas, Intertek, DEKRA, and TÜV SÜD are formidable competitors, each boasting extensive international networks and comprehensive service offerings that directly challenge TÜV Rheinland's market position.
These major TIC providers possess established global footprints and a broad spectrum of services, mirroring TÜV Rheinland's own capabilities. This parity in resources and reach intensifies competition, particularly for securing large-scale contracts and expanding market share across diverse industries and geographies. For instance, SGS, often cited as the largest TIC company by revenue, reported revenues of approximately CHF 6.4 billion for the fiscal year 2023, highlighting the substantial scale of these global rivals.
The Testing, Inspection, and Certification (TIC) market is experiencing robust growth, with projections indicating a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) between 3.4% and 5.3% through 2035, fueling intense competition.
This expanding market naturally attracts more players and encourages existing ones to aggressively pursue market share, leading to heightened rivalry.
TÜV Rheinland AG's own strategic acquisitions during 2023 and 2024 are a clear indicator of a broader industry trend towards consolidation.
Larger, well-capitalized companies like TÜV Rheinland are actively acquiring smaller or specialized TIC providers to expand their service portfolios and geographic reach.
This consolidation intensifies competition among the remaining major players as they battle for dominance in an increasingly concentrated market.
Competitors in the testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) market, including TÜV Rheinland, actively differentiate through deep specialization across various sectors such as automotive, aerospace, and renewable energy. This focus allows them to build unique expertise and offer tailored solutions that command premium pricing and foster customer loyalty.
The drive for competitive advantage is fueled by significant investments in research and development (R&D) and digital transformation. For instance, in 2024, TÜV Rheinland continued to allocate substantial resources towards developing advanced testing methodologies for emerging technologies like artificial intelligence and cybersecurity, ensuring they remain at the forefront of industry needs.
Innovation in testing processes, such as the adoption of AI-driven analytics and virtual testing environments, provides a critical edge. Companies that can demonstrate superior technical capabilities and faster turnaround times, often enabled by digital platforms, are better positioned to capture market share and deter new entrants.
Global Reach and Local Presence
TÜV Rheinland's competitive rivalry is intensified by the need for both a broad global reach and intimate local market understanding. While the company's extensive international operations, with over half of its 2024 revenue generated outside Germany, provide a significant advantage, rivals are equally adept at utilizing their worldwide networks and securing crucial local accreditations to vie for market share across diverse geographical landscapes.
This dual requirement means that competitors can effectively challenge TÜV Rheinland by demonstrating strong capabilities in specific regions, even if their overall global footprint is smaller. The ability to navigate local regulatory environments and build trust within specific communities is as vital as a widespread international presence.
- Global Network Strength: Many competitors, like SGS and Bureau Veritas, also boast substantial global operations, allowing them to offer services across numerous countries.
- Local Accreditation Importance: Securing and maintaining accreditations from national and regional bodies is critical for market access and credibility, a factor all major players must manage.
- Regional Specialization: Some competitors may focus on specific regions or industries, developing deep expertise that allows them to compete effectively against TÜV Rheinland's broader offerings.
- Service Portability: The ability for clients to receive consistent, high-quality services across different geographies is a key differentiator, pushing all players to standardize while adapting locally.
Regulatory Landscape and Compliance Expertise
Competitive rivalry within the testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) sector, including for TÜV Rheinland AG, is significantly shaped by the ability to master and adapt to intricate, ever-changing international regulatory frameworks. Companies vie for dominance not just on technical prowess but on their deep understanding and application of these complex rules.
This means compliance expertise itself becomes a crucial battleground. For instance, the emergence of stringent regulations, such as those concerning per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) or new cybersecurity mandates, requires substantial investment in specialized knowledge and resources. TÜV Rheinland, like its peers, actively cultivates this expertise to offer reliable guidance and certification services.
The financial implications are substantial; companies that can efficiently navigate these regulatory shifts gain a distinct advantage. For example, in 2024, sectors like electronics and automotive faced increased scrutiny and new compliance requirements, directly impacting the demand for TIC services. TÜV Rheinland's ability to offer timely and accurate certifications for these evolving standards directly influences its market position.
- Navigating Global Standards: Competition intensifies as companies must demonstrate proficiency in diverse international regulations, from EU directives to national standards.
- Investment in Expertise: Significant R&D and personnel investment is channeled into understanding and interpreting new regulations, such as those impacting PFAS or digital security.
- Compliance as a Differentiator: The ability to provide seamless and authoritative compliance certification is a key factor in winning contracts and building client trust.
- Market Responsiveness: Companies that can quickly adapt their services to emerging regulatory demands, like those concerning AI governance in 2024, gain a competitive edge.
TÜV Rheinland AG faces intense competition from global TIC giants like SGS, Bureau Veritas, and Intertek, all offering comparable services and possessing vast international networks. This rivalry is fueled by a growing TIC market, projected to expand significantly in the coming years, driving consolidation and aggressive market share pursuits. For instance, SGS reported revenues around CHF 6.4 billion in 2023, showcasing the scale of these major competitors. TÜV Rheinland's strategic acquisitions in 2023-2024 mirror this industry trend, aiming to bolster its service portfolio and reach amidst fierce competition.
| Competitor | Approximate 2023 Revenue (CHF Billion) | Key Service Areas |
|---|---|---|
| SGS | 6.4 | TIC, Supply Chain Services, Digitalization |
| Bureau Veritas | 6.0 | TIC, Certification, ESG Services |
| Intertek | 4.8 | TIC, Assurance, Testing, Inspection, Certification |
| DEKRA | 4.0 | Automotive, Safety, TIC |
SSubstitutes Threaten
Large corporations might establish internal testing and compliance departments, aiming to decrease their dependence on external Testing, Inspection, and Certification (TIC) providers. This can offer cost savings and greater control over the testing process.
However, these in-house capabilities often lack the independent verification and the universally recognized accreditations that third-party organizations like TÜV Rheinland possess. This is particularly crucial for navigating complex international regulations and ensuring market access.
For instance, a company developing a new medical device might find its internal testing results insufficient for FDA or CE marking approval without an independent assessment from a recognized body. TÜV Rheinland, a global leader, provides such crucial third-party validation, a service difficult and costly to replicate internally with the same level of credibility.
The availability of self-certification or supplier declarations can act as a substitute for independent verification services like those offered by TÜV Rheinland. In sectors with less stringent regulatory oversight, companies might opt for these internal assurances to cut costs. However, this approach inherently lacks independent validation, potentially limiting market acceptance and exposing businesses to greater liability risks if conformity claims are inaccurate. For instance, in certain component manufacturing segments in 2024, a shift towards self-declarations became more prevalent, but this also led to increased scrutiny from downstream buyers concerned about product quality and compliance.
Emerging technologies, such as AI-powered quality inspections or IoT sensors for real-time monitoring, are more often integrated by Testing, Inspection, and Certification (TIC) companies to bolster their existing services. For instance, TÜV Rheinland is actively investing in digital solutions to improve efficiency and data analysis. These advancements augment the core value proposition of TIC, which relies on expert judgment and impartial assessment, rather than directly replacing the need for certification and inspection services.
Shift in Regulatory Frameworks
A notable threat to TÜV Rheinland AG's business model arises from potential shifts in regulatory frameworks. For instance, a significant deregulation in key markets could lessen the mandatory requirement for certain tests, inspections, and certifications (TIC). While core safety and quality standards are unlikely to be entirely abandoned, any reduction in mandated external TIC services could theoretically impact demand for TÜV Rheinland's offerings.
Consider the impact of potential government policies that favor self-certification or reduce the scope of third-party oversight. For example, if a major market like the European Union were to significantly streamline its product certification processes, it could diminish the need for independent bodies like TÜV Rheinland in specific sectors. This could be driven by a desire to foster innovation or reduce business costs.
The threat of substitutes in this context also includes the development of new technologies or industry standards that bypass traditional TIC processes. If innovative testing methodologies emerge that are more efficient or cost-effective and are accepted by regulatory bodies, they could serve as substitutes for TÜV Rheinland’s established services.
- Potential Deregulation: A relaxation of mandatory testing requirements in key sectors, such as automotive or electronics, could reduce demand for independent TIC services.
- Technological Advancements: New testing methodologies or digital solutions that offer faster, cheaper, or more integrated compliance could emerge as substitutes.
- Industry Self-Regulation: Increased reliance on industry-led quality assurance programs or self-certification schemes could bypass the need for external TIC providers.
- Geopolitical Shifts: Changes in international trade agreements or regulatory alignment between countries might alter the landscape of required certifications.
Consulting Firms Offering Compliance Advice
Management or specialized consulting firms can indeed offer valuable advice on compliance and quality management systems. This can sometimes lessen a company's immediate need for extensive external testing during the initial planning or advisory stages. For instance, many consulting engagements focus on process improvement and regulatory interpretation.
However, these consulting services are fundamentally different from the accredited, independent testing and certification that TÜV Rheinland provides. Consultants advise on how to meet standards, while TÜV Rheinland validates that a product or system actually meets those standards through rigorous, objective evaluation.
While consulting firms might help prepare documentation or internal processes, they do not possess the accredited laboratories or the legal standing to issue certifications. This distinction is crucial; TÜV Rheinland's value proposition lies in its impartiality and its ability to provide a universally recognized mark of quality and safety, which consultants cannot replicate.
For example, in 2024, the global management consulting market was estimated to be worth over $300 billion, indicating a significant demand for advisory services. Nevertheless, TÜV Rheinland's specialized testing and certification services address a distinct market need for verifiable compliance and assurance, a segment where consultants typically do not compete directly.
The threat of substitutes for TÜV Rheinland AG's services primarily stems from internal capabilities and a shift towards self-regulation. While some large corporations may develop in-house testing, these often lack the crucial independent verification and universal accreditation that TÜV Rheinland offers. For instance, regulatory bodies like the FDA or CE marking require independent assessments, a service difficult and costly for companies to replicate with the same credibility.
The rise of self-certification or supplier declarations presents another substitute, particularly in sectors with less stringent oversight. While this can reduce costs, it sacrifices independent validation, potentially limiting market acceptance and increasing liability. In 2024, some component manufacturing segments saw an increase in self-declarations, leading to greater scrutiny from buyers concerned about quality and compliance.
Emerging technologies, such as AI-powered inspections, are more likely to be integrated into existing TIC services rather than replacing them. TÜV Rheinland itself is investing in digital solutions to enhance its core value proposition of expert judgment and impartial assessment.
Potential deregulation and shifts in regulatory frameworks pose a significant threat. A reduction in mandated third-party oversight, for example, could decrease demand for TÜV Rheinland’s services. Similarly, new, more efficient testing methodologies accepted by regulatory bodies could act as substitutes for established TIC processes.
Entrants Threaten
Establishing a Testing, Inspection, and Certification (TIC) business, particularly one with global reach like TÜV Rheinland, demands substantial financial commitment. This includes significant investment in cutting-edge laboratories, sophisticated testing apparatus, and the development of a robust international operational network. For example, setting up advanced automotive testing facilities alone can run into tens of millions of euros. This considerable initial outlay serves as a formidable hurdle for potential new competitors seeking to enter the market.
TÜV Rheinland AG, like many players in the testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) industry, faces a significant barrier to entry due to extensive accreditation and regulatory compliance requirements. Navigating the labyrinth of national and international accreditations, such as ISO standards and specific governmental approvals, is a costly and lengthy undertaking, often taking years and substantial investment to achieve. This complex web of certifications is not merely bureaucratic; it is fundamental to market access and establishing credibility across diverse sectors like automotive, medical devices, and renewable energy.
For instance, obtaining a single ISO 17025 accreditation, a benchmark for testing and calibration laboratories, can involve meticulous process documentation, rigorous internal audits, and successful external assessments. In 2024, the average time for a laboratory to achieve initial ISO 17025 accreditation was reported to be between 12 to 18 months. Beyond general standards, TÜV Rheinland must also secure approvals from myriad national regulatory bodies, each with its own unique set of demands and testing protocols. This geographical and industry-specific compliance burden acts as a formidable deterrent for new entrants who lack the established infrastructure, expertise, and financial resources to replicate such a comprehensive compliance framework.
The testing, inspection, and certification (TIC) sector demands a deep bench of specialized expertise. Companies like TÜV Rheinland, with its workforce of 25,900 employees, highlight the significant investment required to cultivate and retain this talent. This specialized knowledge, spanning various technical fields and regulatory landscapes, acts as a substantial barrier to entry for potential new competitors.
Established Brand Reputation and Trust
The threat of new entrants is significantly mitigated by the established brand reputation and deep-seated trust that companies like TÜV Rheinland AG have cultivated over many years within the Testing, Inspection, and Certification (TIC) sector. In an industry where independent verification of safety, quality, and compliance is critical, customers place immense value on the credibility of the certifying body. Newcomers struggle to replicate the decades of consistent performance and proven reliability that underpin the trust customers place in established players.
This trust is not easily earned or quickly acquired, creating a substantial barrier for potential new entrants. TÜV Rheinland, for instance, has built its reputation on a foundation of impartiality and technical expertise, making it a go-to partner for businesses requiring assurance in their products and processes. The market recognizes the significant investment in time and resources required to build such a strong and reliable brand image.
- Decades of operation: TÜV Rheinland has been operating for over 150 years, a testament to its enduring reputation and ability to adapt and maintain trust.
- Global recognition: Its brand is recognized and respected worldwide, a significant advantage over any new entrant lacking international visibility.
- Customer loyalty: The sector relies on repeat business and long-term partnerships, which are fostered by established trust and proven service quality.
Economies of Scale and Scope
TÜV Rheinland AG, as a major player in the Testing, Inspection, and Certification (TIC) industry, benefits significantly from economies of scale and scope. These advantages create a substantial barrier for new entrants. Large, established companies can spread their fixed costs over a much larger volume of business, leading to lower per-unit costs. For example, in 2024, major TIC providers continued to invest heavily in global laboratory networks and certification infrastructure, costs that are difficult for a new, smaller entity to replicate. This scale allows them to offer competitive pricing that is challenging for newcomers to match.
Economies of scope further strengthen this position. TÜV Rheinland’s diversified service portfolio, covering everything from product safety to cybersecurity and sustainability, allows them to leverage existing customer relationships and operational expertise across different service lines. This means they can offer bundled services or cross-sell solutions more efficiently than a new entrant focused on a narrow niche. In 2024, the trend of integrated service offerings in the TIC sector continued, with companies like TÜV Rheinland expanding their capabilities to provide holistic solutions, a breadth of service that is a significant hurdle for any new competitor to overcome.
- Economies of Scale: Large TIC firms like TÜV Rheinland can achieve lower per-unit costs due to high-volume operations, making it difficult for new entrants to compete on price.
- Economies of Scope: TÜV Rheinland's broad range of services allows for cost synergies and enhanced customer value propositions, which are hard for specialized new firms to replicate.
- Capital Investment: The substantial capital required for global infrastructure, accreditations, and skilled personnel in the TIC sector acts as a significant deterrent to new market entrants.
- Brand Reputation and Trust: Established players have built decades of trust and recognition, a critical factor in a service industry where reliability and impartiality are paramount, posing a challenge for new, unproven entities.
The threat of new entrants for TÜV Rheinland AG is considerably low due to the immense capital requirements for establishing a global Testing, Inspection, and Certification (TIC) operation. Setting up advanced testing facilities alone can cost tens of millions of euros, a prohibitive expense for most new players. Additionally, the complex and costly process of obtaining numerous national and international accreditations, such as ISO standards, acts as a significant deterrent, often taking 12 to 18 months to achieve for a single accreditation in 2024.
Furthermore, the need for specialized expertise, exemplified by TÜV Rheinland's workforce of 25,900 employees, presents another substantial barrier. New entrants must invest heavily in recruiting and retaining highly skilled personnel across diverse technical fields. This, coupled with the decades required to build a strong brand reputation and the trust associated with it, makes it exceedingly difficult for newcomers to compete effectively. The established scale and scope of operations, leading to economies of scale and scope, further solidify TÜV Rheinland's competitive advantage by enabling lower per-unit costs and diversified service offerings, which are challenging for smaller, newer firms to replicate.
| Barrier to Entry | Impact on New Entrants | TÜV Rheinland's Advantage |
| Capital Requirements | High initial investment for facilities and infrastructure | Established global network and advanced laboratories |
| Accreditations & Compliance | Lengthy and costly process for multiple certifications | Extensive portfolio of accreditations and regulatory approvals |
| Specialized Expertise | Need to hire and retain highly skilled personnel | Large, experienced workforce with deep technical knowledge |
| Brand Reputation & Trust | Difficult to build credibility and customer loyalty | Over 150 years of operation, global recognition, and proven reliability |
| Economies of Scale & Scope | Inability to match pricing and breadth of services | Lower per-unit costs and comprehensive, integrated service offerings |
Porter's Five Forces Analysis Data Sources
Our Porter's Five Forces analysis for TÜV Rheinland AG is built upon comprehensive data from their annual reports, investor relations materials, and relevant industry association publications. We also incorporate insights from reputable market research firms and economic databases to provide a robust understanding of the competitive landscape.
